Cyclophilin A as a Pro-Inflammatory Factor Exhibits Embryotoxic and Teratogenic Effects during Fetal Organogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Fetal mCypA Overexpression Impaired the Antenatal Development of Transgenic Embryos
2.2. The High Dose of rhCypA Injected into Pregnant Females during Fetal Organogenesis Provoked External Anatomical Anomalies in Mouse Embryos
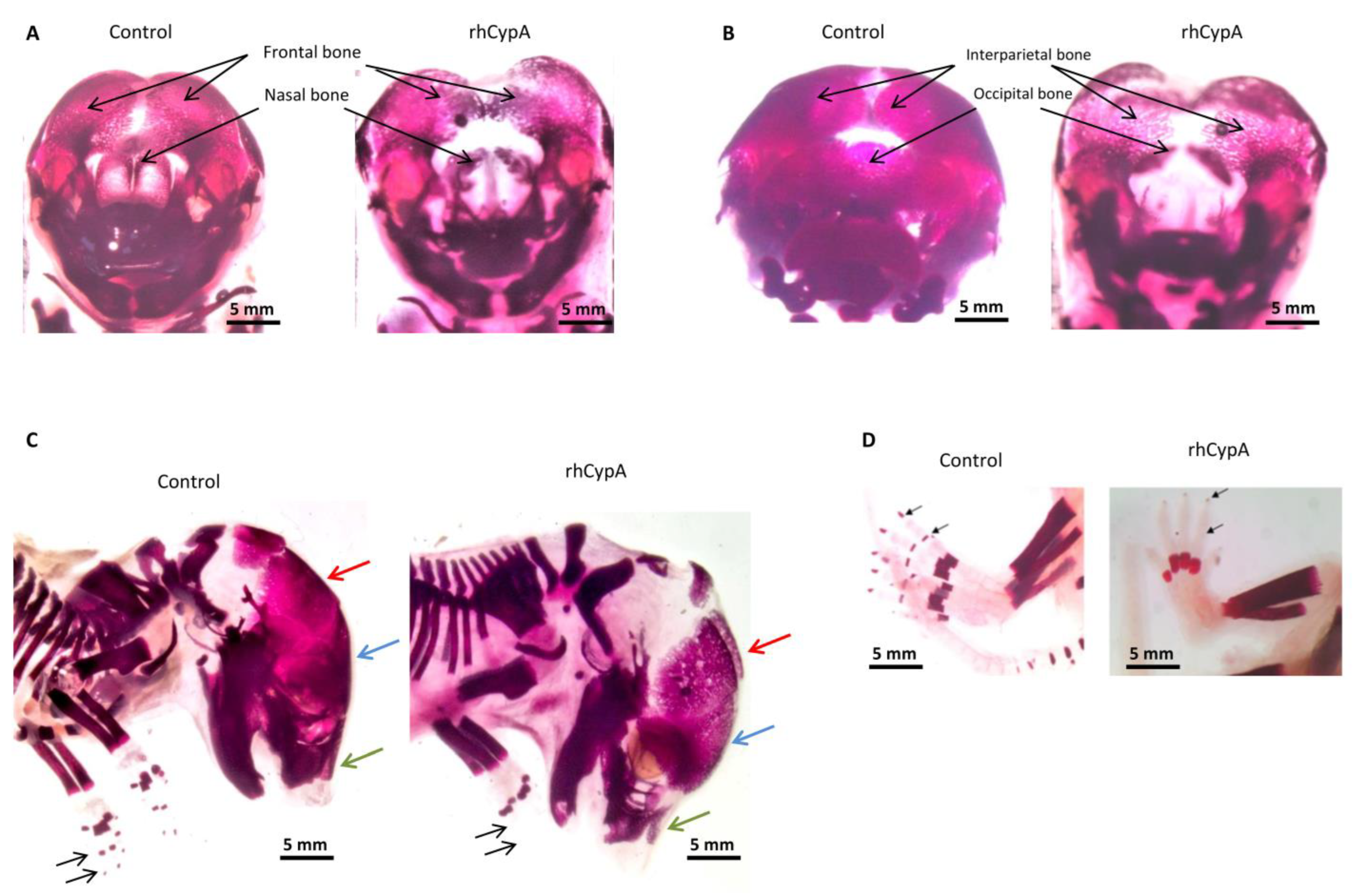
2.3. The High Level of Maternal CypA during Organogenesis Induced Skeletal Defects in Mouse Embryos
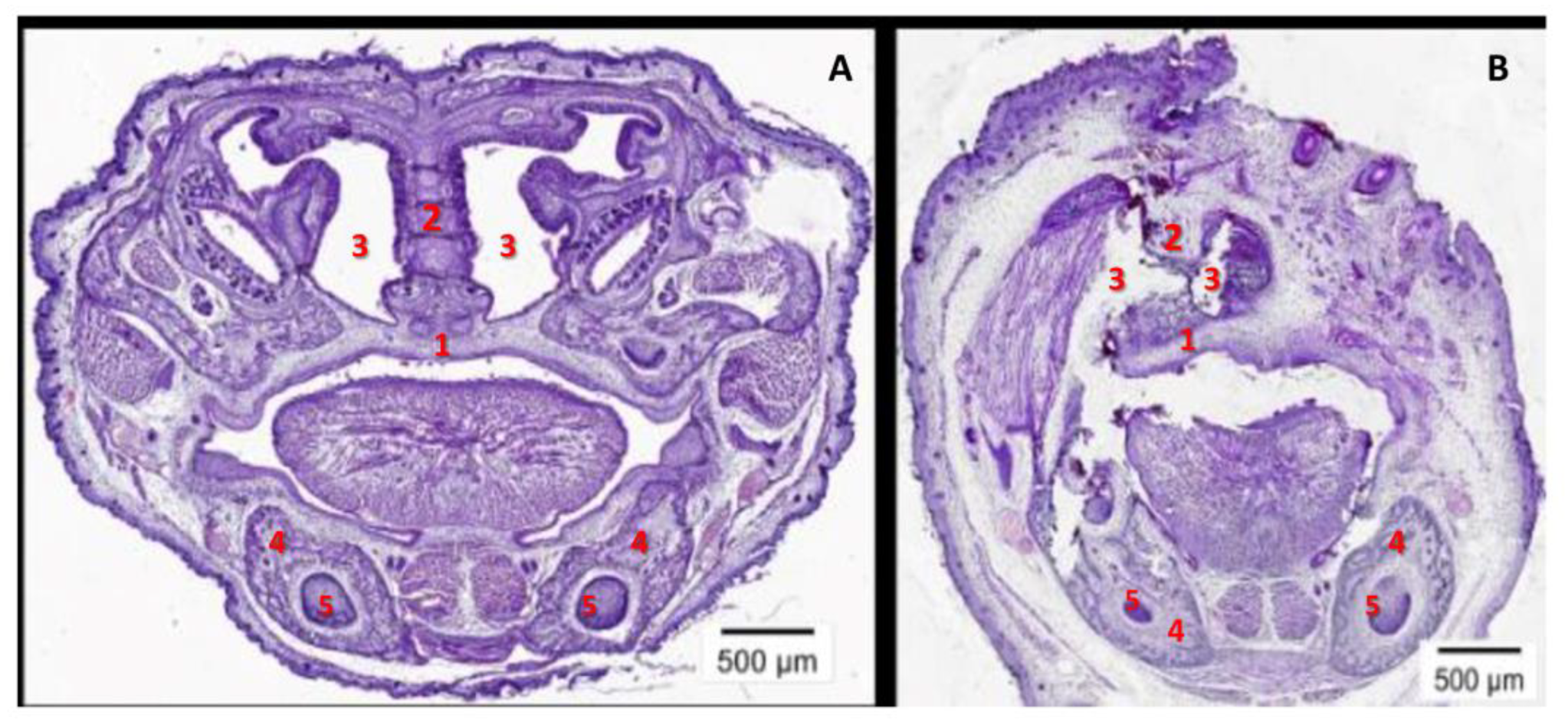
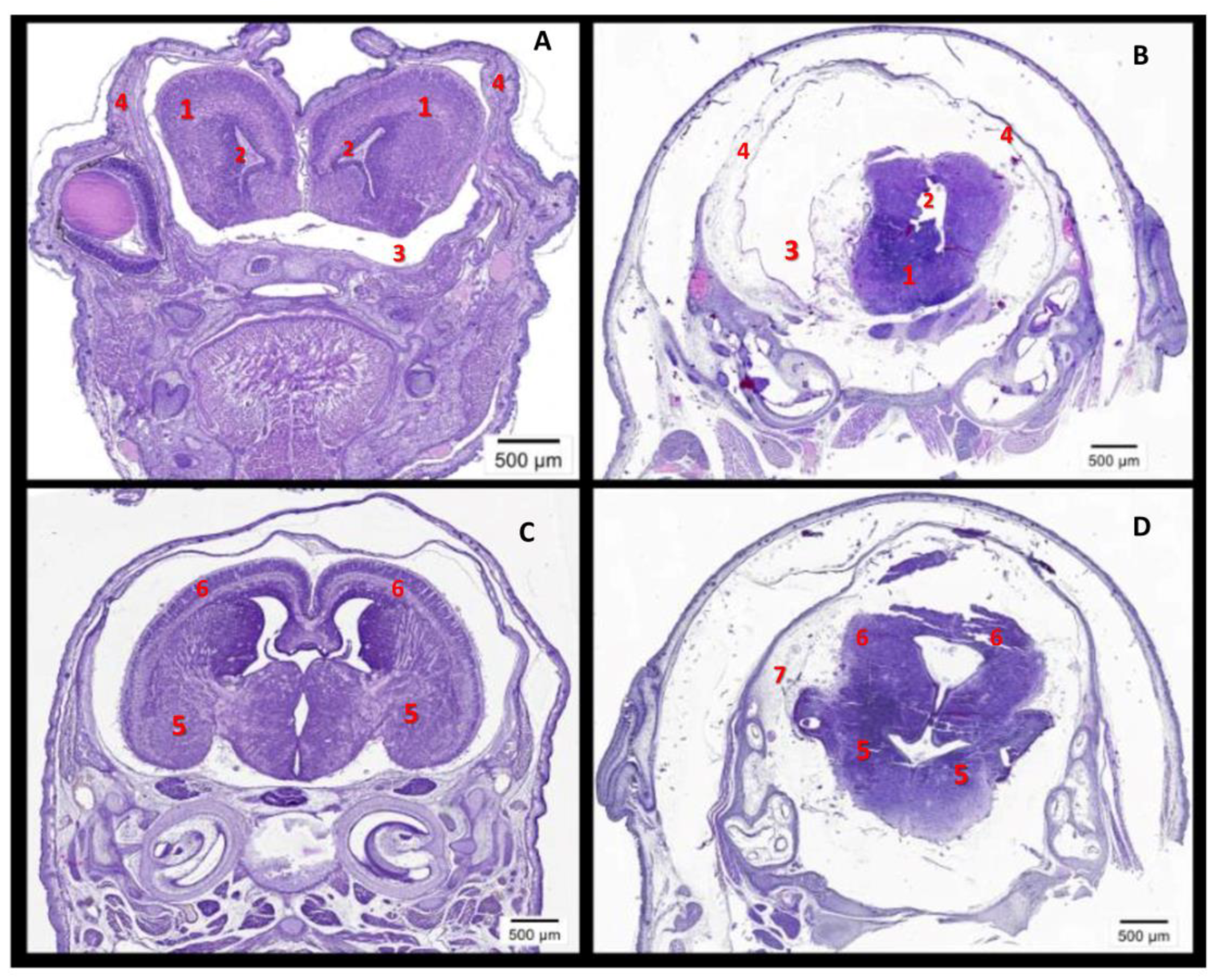
2.4. The High Level of Maternal CypA during Organogenesis Damaged the Fetal Brain’s Development
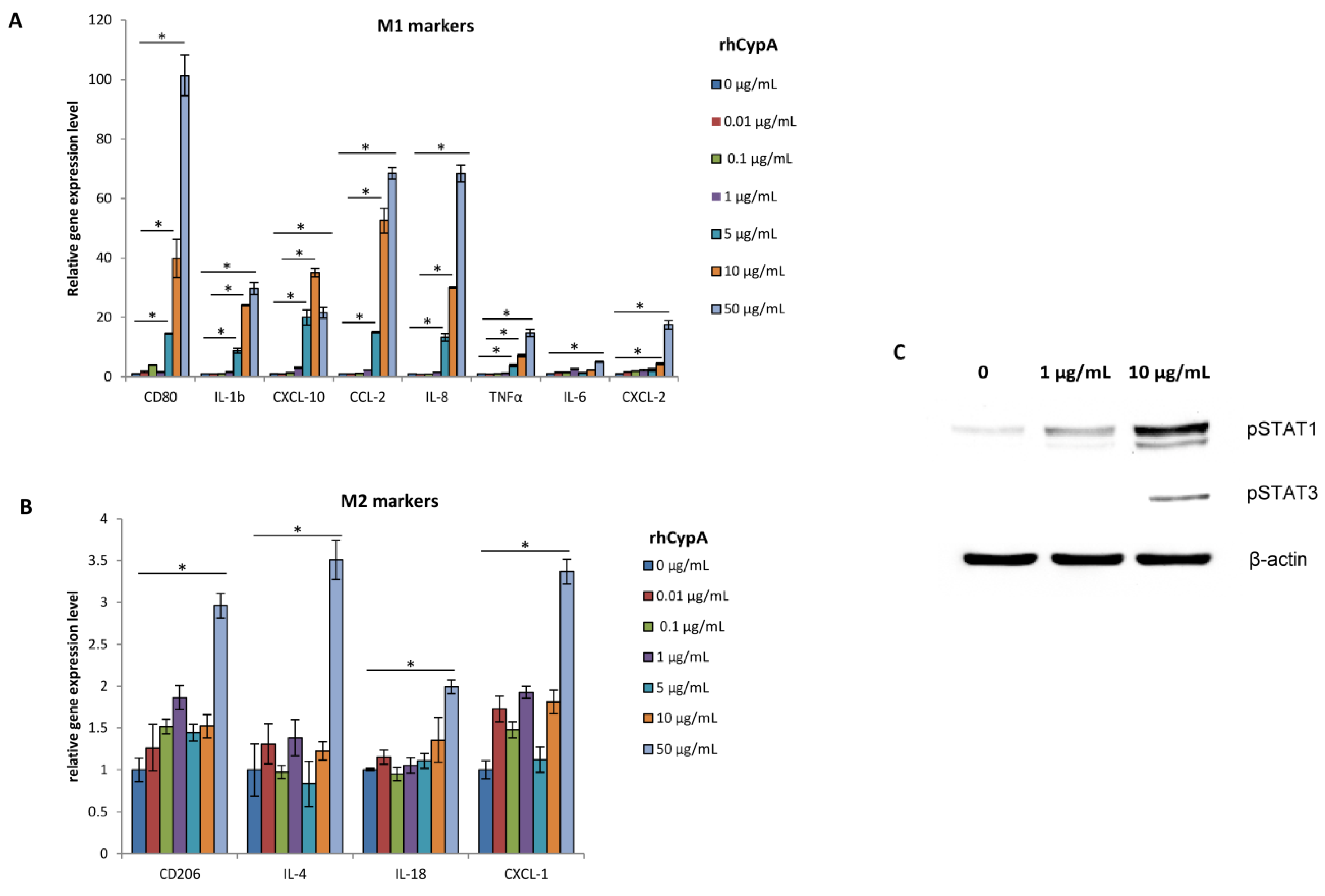
2.5. RhCypA Induced Macrophage M1 Polarization In Vitro via Activation of STAT1 and STAT3 Signaling Pathways
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Orsi, N.M. Cytokine networks in the establishment and maintenance of pregnancy. Hum. Fertil. 2008, 11, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, S.; Nakashima, A.; Shima, T.; Ito, M. Th1/Th2/Th17 and regulatory T-cell paradigm in pregnancy. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 63, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekel, N.; Gnainsky, Y.; Granot, I.; Mor, G. Inflammation and implantation. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 63, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor, G. Inflammation and pregnancy: The role of toll-like receptors in trophoblast-immune interaction. Ann. N. Y Acad. Sci. 2008, 1127, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challis, J.R.; Lockwood, C.J.; Myatt, L.; Norman, J.E.; Strauss, J.F., 3rd; Petraglia, F. Inflammation and pregnancy. Reprod. Sci. 2009, 16, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, J.A.; Haimovici, F.; Anderson, D.J. Products of activated lymphocytes and macrophages inhibit mouse embryo development in vitro. J. Immunol. 1987, 139, 2250–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pampfer, S.; Moulaert, B.; Vanderheyden, I.; Wuu, Y.D.; De Hertogh, R. Effect of tumour necrosis factor alpha on rat blastocyst growth and glucose metabolism. J. Reprod. Fertil. 1994, 101, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.K.; Heeley, J.M.; Wyman, A.H.; Schlichting, E.L.; Moley, K.H. TRAIL and KILLER are expressed and induce apoptosis in the murine preimplantation embryo. Biol. Reprod. 2004, 71, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak-Kim, J.; Bao, S.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, J.W.; Gilman-Sachs, A. Immunological modes of pregnancy loss: Inflammation, immune effectors, and stress. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2014, 72, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Khalil, R.A. Matrix Metalloproteinases in Normal Pregnancy and Preeclampsia. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 148, 87–165. [Google Scholar]
- Colgan, J.; Asmal, M.; Neagu, M.; Yu, B.; Schneidkraut, J.; Lee, Y.; Sokolskaja, E.; Andreotti, A.; Luban, J. Cyclophilin A regulates TCR signal strength in CD4+ T cells via a proline-directed conformational switch in Itk. Immunity 2004, 21, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigro, P.; Pompilio, G.; Capogrossi, M.C. Cyclophilin A: A key player for human disease. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Heitman, J. The cyclophilins. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Jiang, M.; Zhao, X.; Gu, M.; Wang, Z.; Xu, S.; Yue, W. Cyclophilin A promotes non-small cell lung cancer metastasis via p38 MAPK. Thorac. Cancer. 2018, 9, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khromykh, L.M.; Kulikova, N.L.; Anfalova, T.V.; Muranova, T.A.; Abramov, V.M.; Vasiliev, A.M.; Khlebnikov, V.S.; Kazansky, D.B. Cyclophilin A produced by thymocytes regulates the migration of murine bone marrow cells. Cell Immunol. 2007, 249, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, K.; Gwinn, W.M.; Bower, M.A.; Watson, A.; Okwumabua, I.; MacDonald, H.R.; Bukrinsky, M.I.; Constant, S.L. Extracellular cyclophilins contribute to the regulation of inflammatory responses. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawar, F.U.; Wu, J.; Zhao, L.; Khattak, M.N.K.; Mei, J.; Lin, L. Updates in understanding the role of cyclophilin A in leukocyte chemotaxis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, U.; Zhang, R.; Yang, H.; Li, M.; Doan, L.X.; Chen, C.; Yao, Q. Effects of cyclophilin A on myeloblastic cell line KG-1 derived dendritic like cells (DLC) through p38 MAP kinase activation. J. Surg. Res. 2005, 127, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, W.J.; Jeon, S.T.; Koh, E.M.; Cha, H.S.; Ahn, K.S.; Lee, W.H. Cyclophilin A may contribute to the inflammatory processes in rheumatoid arthritis through induction of matrix degrading enzymes and inflammatory cytokines from macrophages. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, C.-L.; Lin, C.-H.; Lin, T.-H.; Wena, F.-C.; Su, C.-W.; Fan, S.-S.; Hsieh, M. Secreted cyclophilin A induction during embryo implantation in a model of human trophoblast–endometrial epithelium interaction. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2012, 164, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Lin, S.; Xu, R.; Du, T.X.; Li, Y.; Gao, H.; Diao, H.L.; Zhang, X.H. Cyclophilin A plays an important role in embryo implantation through activating Stat3. Reproduction 2020, 160, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanga, Z.-H.; Suna, S.-Y.; Chenb, Q.-N.; Lia, Y.-Y.; Caia, X.-H. The first-trimester maternal serum cyclophilin A concentrations in women with complicated pregnancy as preeeclampsia. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 484, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shi, Y.; Regan, J.; Karuppaiah, K.; Ornitz, D.M.; Long, F. Osx-Cre targets multiple cell types besides osteoblast lineage. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theile, K. The House Mouse: Atlas of Embryonic Development; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Clouthier, D.; Bueno, M.; Tavares, A.; Lyonnet, S.; Amiel, J.; Gordon, C. Understanding the Basis of Auriculocondylar Syndrome: Insights From Human and Mouse Genetic Studies. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2013, 163, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcucio, R.; Hallgrimsson, B.; Young, N.M. Facial Morphogenesis: Physical and Molecular Interactions Between the Brain and the Face. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2015, 115, 299–320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sakai, D.; Trainor, P. Face off against ROS: Tcof1/Treacle safeguards neuroepithelial cells and progenitor neural crest cells from oxidative stress during craniofacial development. Dev. Growth Differ. 2016, 58, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Xu, X.H.; Jin, L. Macrophage Polarization in Physiological and Pathological Pregnancy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, K.C.; Jena, M.K.; Pradhan, B.S.; Nayak, N.; Das, S.; Hsu, C.D.; Wheeler, D.S.; Chen, K.; Nayak, N.R. VEGF may contribute to macrophage recruitment and M2 polarization in the decidua. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, S.; Venugopal, A.; Kutty, V.A.; Chitrasree, V.A.; Mullassari, A.; Pratapchandran, N.S.; Santosh, K.R.; Pillai, M.R.; Kartha, C.C. Plasma level of cyclophilin A is increased in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and suggests presence of vascular disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalajzic, I.; Kalajzica, Z.; Kaliterna, M.; Gronowicz, G.; Clark, S.H.; Lichtler, A.C.; Rowe, D. Use of type I collagen green fluorescent protein transgenes to identify subpopulations of cells at different stages of the osteoblast lineage. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2002, 1, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasi, M.G.; Riminucci, M.; De Angelis, L.; Borello, U.; Berarducci, B.; Innocenzi, A.; Caprioli, A.; Sirabella, D.; Baiocchi, M.; De Maria, R.; et al. The mesoangioblast: A multipotent, self-renewing cell that originates from the dorsal aorta and differentiates into most mesodermal tissues. Development 2002, 129, 2773–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, S.C.; Robin, C.; Dzierzak, E. Mesenchymal progenitor cells localize within hematopoietic sites throughout ontogeny. Development 2005, 132, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, E.; van Beek, L.; Piersma, A.H. Osteoblast differentiation of murine embryonic stem cells as a model to study the embryotoxic effect of compounds. Toxicol. In Vitro 2012, 26, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Smith, G.N.; Croy, B.A. Natural killer cell-triggered vascular transformation: Maternal care before birth? Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinina, A.; Zamkova, M.; Antoshina, E.; Trukhanova, L.; Gorkova, T.; Kazansky, D.; Khromykh, L. Analyses of the Toxic Properties of Recombinant Human Cyclophilin A in Mice. J. Immunotoxicol. 2019, 16, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, S.; Borbely, A.; Fernandes, I.; Campa, A. Serum Amyloid A in the Placenta and Its Role in Trophoblast Invasion. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.I.; Ramy, A.R.; Abdelhamid, A.S.; Ellaithy, M.I.; Omar, A.; Harara, R.M.; Fathy, H.; Abolouz, A.S. Maternal serum amyloid A level as a novel marker of primary unexplained recurrent early pregnancy loss. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2017, 136, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, Y.; Matsui, N.; Kamihigashi, S.; Narahara, H.; Miyakawa, I. Effects of interferon-gamma on secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor by endometrial stromal cells. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2000, 43, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lash, G.E.; Otun, H.A.; Innes, B.A.; Kirkley, M.; De Oliveira, L.; Searle, R.F.; Robson, S.C.; Bulmer, J.N. Interferon-gamma inhibits extravillous trophoblast cell invasion by a mechanism that involves both changes in apoptosis and protease levels. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 2512–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, D.A.; Chaouat, G.; Arck, P.C.; Mittruecker, H.W.; Levy, G.A. Cytokine-dependent abortion in CBA x DBA/2 mice is mediated by the procoagulant fgl2 prothrombinase. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Knöfler, M. Human tumour necrosis factor: Physiological and pathological roles in placenta and endometrium. Placenta 2009, 30, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denney, J.M.; Nelson, E.L.; Wadhwa, P.D.; Waters, T.P.; Mathew, L.; Chung, E.K.; Goldenberg, R.L.; Culhane, J.F. Longitudinal modulation of immune system cytokine profile during pregnancy. Cytokine 2011, 53, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen-Bouterse, S.A.; Romero, R.; Tarca, A.L.; Kusanovic, J.P.; Espinoza, J.; Kim, C.J.; Kim, J.S.; Edwin, S.S.; Gomez, R.; Draghici, S. The transcriptome of the fetal inflammatory response syndrome. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 63, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegorzewska, M.; Nijagal, A.; Wong, C.M.; Le, T.; Lescano, N.; Tang, Q.; MacKenzie, T.C. Fetal intervention increases maternal T cell awareness of the foreign conceptus and can lead to immune-mediated fetal demise. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 1938–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, E.; Romero, R.; Yeo, L.; Diaz-Primera, R.; Marin-Concha, J.; Para, R.; Lopez, A.M.; Pacora, P.; Gomez-Lopez, N.; Yoon, B.H.; et al. The fetal inflammatory response syndrome: The origins of a concept, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and obstetrical implications. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020, 25, 101146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.P.; Tayade, C.; Ashkar, A.A.; Hatta, K.; Zhang, J.; Croy, B.A. Interferon gamma in successful pregnancies. Biol. Reprod. 2009, 80, 848–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Torre, E.; Mulla, M.J.; Yu, A.G.; Lee, S.-J.; Kavathas, P.B.; Abrahams, V.M. Chlamydia trachomatis infection modulates trophoblast cytokine/chemokine production. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 3735–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.-H.; Dong, L.; Du, M.-R.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Li, D.-J. Cyclosporin A improves murine pregnancy outcome in abortion-prone matings: Involvement of CD80/86 and CD28/CTLA-4. Reproduction 2008, 135, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.-R.; Dong, L.; Zhou, W.-H.; Yan, F.-T.; Li, D.-J. Cyclosporin A improves pregnancy outcome by promoting functions of trophoblasts and inducing maternal tolerance to the allogeneic fetus in abortion-prone matings in the mouse. Biol. Reprod. 2007, 76, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, M.; Papa, I.; Venturi, V.; Lazzarotto, T.; Faldella, G.; Gabrielli, L.; Guerra, B.; Landini, M.P.; Salvioli, G.P. Congenital infection with human herpesvirus 6 variant B associated with neonatal seizures and poor neurological outcome. J. Med. Virol. 2003, 70, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashdown, H.; Dumont, Y.; Ng, M.; Poole, S.; Boksa, P.; Luheshi, G.N. The role of cytokines in mediating effects of prenatal infection on the fetus: Implications for schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2006, 11, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlgren, J.; Samuelsson, A.-M.; Jansson, T.; Holmäng, A. Interleukin-6 in the maternal circulation reaches the rat fetus in mid-gestation. Pediatr. Res. 2006, 60, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.E.; Li, J.; Garbett, K.; Mirnics, K.; Patterson, P.H. Maternal immune activation alters fetal brain development through interleukin-6. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 10695–10702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnayake, U.; Quinn, T.; Walker, D.; Dickinson, H. Cytokines and the neurodevelopmental basis of mental illness. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keffer, J.; Probert, L.; Caziaris, H.; Georgopoulos, S.; Kaslaris, E.; Kioussis, D.; Kollias, G. Transgenic mice expressing human tumour necrosis factor: A predictive genetic model of arthritis. EMBO J. 1991, 13, 4025–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldring, S.R.; Goldring, M.B. Cytokines and skeletal physiology. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1996, 324, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lader, C.S.; Flanagan, A.M. Prostaglandin E2, Interleukin 1α, and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Increase Human Osteoclast Formation and Bone Resorption In Vitro. Endocrinology 1998, 7, 3157–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, M.C. The Role of Cytokines in Bone Remodeling. J. Clin. Densitom. 1998, 2, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, J. The Effects of Immune Cell Products (Cytokines and Hematopoietic Cell Growth Factors) on Bone Cells. In Osteoimmunology, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Diao, L.; Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Kwak-Kim, J.Y.H. The role of decidual immune cells on human pregnancy. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2017, 124, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schonkeren, D.; van der Hoorn, M.L.; Khedoe, P.; Swings, G.; van Beelen, E.; Claas, F.; van Kooten, C.; de Heer, E.; Scherjon, S. Differential distribution and phenotype of decidual macrophages in preeclamptic versus control pregnancies. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.; Chen, J.; Xu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, J.; Zeng, H.; Jiang, J.; Chen, T.; Qin, Z.; Li, H.; et al. STAT1 and CXCL10 involve in M1 macrophage polarization that may affect osteolysis and bone remodeling in extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Gene 2022, 809, 146040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Zhang, M.; Lei, W.; Yang, R.; Fu, S.; Fan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, T. Advances in the role of STAT3 in macrophage polarization. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1160719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marten, H.; Hofker, J.V.D.; Deursen, J.V. Transgenic Mouse: Methods and Protocols; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 209. [Google Scholar]
- Silaeva, Y.Y.; Kalinina, A.A.; Vagida, M.S.; Khromykh, L.M.; Deikin, A.V.; Ermolkevich, T.G.; Sadchikova, E.R.; Goldman, I.L.; Kazansky, D.B. Decrease in pool of T lymphocytes with surface phenotypes of effector and central memory cells under influence of TCR transgenic β-chain expression. Biochemistry 2013, 78, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silaeva, Y.Y.; Kirikovich, Y.K.; Skuratovskaya, L.N.; Deikin, A.V. Optimal Number of Embryos for Transplantation in Obtaining Genetic-Modified Mice and Goats. Russ. J. Dev. Biol. 2018, 49, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, I.; Canaff, L.; Rafeh, J.; Angrula, A.; Li, J.; Riddle, R.; Boraschi-Diaz, I.; Komarova, S.; Clemens, T.; Murshed, M.; et al. Osteoblast menin regulates bone mass in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 3910–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dacic, S.; Kalajzic, I.; Visnjic, D.; Lichtler, A.C.; Rowe, D.W. Col1a1-driven transgenic markers of osteoblast lineage progression. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2001, 16, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinina, A.A.; Kolesnikov, A.V.; Kozyr, A.V.; Kulikova, N.L.; Zamkova, M.A.; Kazansky, D.B.; Khromykh, L.M. Preparative Production and Purification of Recombinant Human Cyclophilin A. Biochemistry 2022, 87, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.W. Alizarin Red S and Toluidine Blue for Differentiating Adult or Embryonic Bone and Cartilage. Stain Technol. 1941, 16, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Control (PBS) | rhCypA 2.0 mg/mouse | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5–5.5 dpc (Pre-Implantation Period) | 6.5–11.5 dpc (Organogenesis) | 12.5–17.5 dpc (Fetogenesis) | |||
| Analysis of anatomical anomalies | |||||
| Total number of fetuses studied | 49 | 55 | 69 | 56 | |
| with anatomical anomalies (%) | 2 (4.1) | 2 (3.6) | 16 (23.0) | 1 (1.8) | |
| Analysis of skeletal anomalies | |||||
| Total number of fetuses studied | 24 | 24 | 30 | 29 | |
| with skeletal anomalies (%) | 0 | 0 | 7 (23.3) | 2 (6.8) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalinina, A.; Semenova, M.; Bruter, A.; Varlamova, E.; Kubekina, M.; Pavlenko, N.; Silaeva, Y.; Deikin, A.; Antoshina, E.; Gorkova, T.; et al. Cyclophilin A as a Pro-Inflammatory Factor Exhibits Embryotoxic and Teratogenic Effects during Fetal Organogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411279
Kalinina A, Semenova M, Bruter A, Varlamova E, Kubekina M, Pavlenko N, Silaeva Y, Deikin A, Antoshina E, Gorkova T, et al. Cyclophilin A as a Pro-Inflammatory Factor Exhibits Embryotoxic and Teratogenic Effects during Fetal Organogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(14):11279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411279
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalinina, Anastasiia, Maria Semenova, Alexandra Bruter, Ekaterina Varlamova, Marina Kubekina, Natalia Pavlenko, Yulia Silaeva, Alexey Deikin, Elena Antoshina, Tatyana Gorkova, and et al. 2023. "Cyclophilin A as a Pro-Inflammatory Factor Exhibits Embryotoxic and Teratogenic Effects during Fetal Organogenesis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 14: 11279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411279
APA StyleKalinina, A., Semenova, M., Bruter, A., Varlamova, E., Kubekina, M., Pavlenko, N., Silaeva, Y., Deikin, A., Antoshina, E., Gorkova, T., Trukhanova, L., Salmina, A., Novikova, S., Voronkov, D., Kazansky, D., & Khromykh, L. (2023). Cyclophilin A as a Pro-Inflammatory Factor Exhibits Embryotoxic and Teratogenic Effects during Fetal Organogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(14), 11279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411279






