Structure-Based Discovery of Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-κB Ligand (RANKL)-Induced Osteoclastogenesis Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structure-Based Discovery of the Inhibitors
2.2. Evaluation of the Compounds in Osteoclastogenesis Assays
2.3. Structure–Activity Relationships of the Hit Compounds
2.4. Hit-Based Discovery of Potent Inhibitors
2.5. Design and Synthesis of PRAN Compounds
3. Conclusions
4. Methods and Materials
4.1. Computational Methods
4.2. Expression, Purification and Electrophoresis of Human RANKL
4.3. Cell Culture of RAW264.7
4.4. RANKL-Induced Osteoclast Differentiation
4.5. Quantitative TRAP Activity Assay
4.6. Viability Assay
4.7. General Procedure for the Preparation of Compounds PRAN-1.1 to PRAN-3.10
4.8. Characterization and Purification Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Capulli, M.; Paone, R.; Rucci, N. Osteoblast and osteocyte: Games without frontiers. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 561, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.R.; Mundy, G.R. Advances in osteoclast biology: Old findings and new insights from mouse models. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullberg, B.; Johnell, O.; Kanis, J.A. World-wide projections for hip fracture. Osteoporos. Int. 1997, 7, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, D.L.; Timms, E.; Tan, H.L.; Kelley, M.J.; Dunstan, C.R.; Burgess, T.; Elliott, R.; Colombero, A.; Elliott, G.; Scully, S.; et al. Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell 1998, 93, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuller, K.; Wong, B.; Fox, S.; Choi, Y.; Chambers, T.J. TRANCE is necessary and sufficient for osteoblast-mediated activation of bone resorption in osteoclasts. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fata, J.E.; Kong, Y.Y.; Li, J.; Sasaki, T.; Irie-Sasaki, J.; Moorehead, R.A.; Elliott, R.; Scully, S.; Voura, E.B.; Lacey, D.L.; et al. The osteoclast differentiation factor osteoprotegerin-ligand is essential for mammary gland development. Cell 2000, 103, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takayanagi, H. Osteoimmunology: Shared mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanada, R.; Leibbrandt, A.; Hanada, T.; Kitaoka, S.; Furuyashiki, T.; Fujihara, H.; Trichereau, J.; Paolino, M.; Qadri, F.; Plehm, R.; et al. Central control of fever and female body temperature by RANKL/RANK. Nature 2009, 462, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.Y.; Yoshida, H.; Sarosi, I.; Tan, H.L.; Timms, E.; Capparelli, C.; Morony, S.; Oliveira-dos-Santos, A.J.; Van, G.; Itie, A.; et al. OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature 1999, 397, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougall, W.C.; Glaccum, M.; Charrier, K.; Rohrbach, K.; Brasel, K.; De Smedt, T.; Daro, E.; Smith, J.; Tometsko, M.E.; Maliszewski, C.R.; et al. RANK is essential for osteoclast and lymph node development. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 2412–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Douni, E.; Rinotas, V.; Makrinou, E.; Zwerina, J.; Penninger, J.M.; Eliopoulos, E.; Schett, G.; Kollias, G. A RANKL G278R mutation causing osteopetrosis identifies a functional amino acid essential for trimer assembly in RANKL and TNF. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 784–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sezer, O.; Heider, U.; Zavrski, I.; Kuhne, C.A.; Hofbauer, L.C. RANK ligand and osteoprotegerin in myeloma bone disease. Blood 2003, 101, 2094–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, X.; Lu, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, H.; Zhao, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Crystal structure of human RANKL complexed with its decoy receptor osteoprotegerin. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sisay, M.; Mengistu, G.; Edessa, D. The RANK/RANKL/OPG system in tumorigenesis and metastasis of cancer stem cell: Potential targets for anticancer therapy. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 3801–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostenuik, P.J.; Nguyen, H.Q.; McCabe, J.; Warmington, K.S.; Kurahara, C.; Sun, N.; Chen, C.; Li, L.; Cattley, R.C.; Van, G.; et al. Denosumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody to RANKL, inhibits bone resorption and increases BMD in knock-in mice that express chimeric (murine/human) RANKL. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2009, 24, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopeck, A.T.; Lipton, A.; Body, J.J.; Steger, G.G.; Tonkin, K.; de Boer, R.H.; Lichinitser, M.; Fujiwara, Y.; Yardley, D.A.; Viniegra, M.; et al. Denosumab compared with zoledronic acid for the treatment of bone metastases in patients with advanced breast cancer: A randomized, double-blind study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 5132–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watts, N.B.; Brown, J.P.; Papapoulos, S.; Lewiecki, E.M.; Kendler, D.L.; Dakin, P.; Wagman, R.B.; Wang, A.; Daizadeh, N.S.; Smith, S.; et al. Safety Observations with 3 Years of Denosumab Exposure: Comparison between Subjects Who Received Denosumab during the Randomized FREEDOM Trial and Subjects Who Crossed over to Denosumab During the FREEDOM Extension. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 1481–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Crockett, J.C. Osteoporosis—A current view of pharmacological prevention and treatment. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 7, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, K.W.; Martin, T.J. New therapeutics for osteoporosis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2014, 16, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chames, P.; Van Regenmortel, M.; Weiss, E.; Baty, D. Therapeutic antibodies: Successes, limitations and hopes for the future. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrari, S.; Langdahl, B. Mechanisms underlying the long-term and withdrawal effects of denosumab therapy on bone. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Kinosaki, M.; Takami, M.; Choi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Murali, R. Disabling of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB (RANK) receptor complex by novel osteoprotegerin-like peptidomimetics restores bone loss in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 8269–8277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ta, H.M.; Nguyen, G.T.; Jin, H.M.; Choi, J.; Park, H.; Kim, N.; Hwang, H.Y.; Kim, K.K. Structure-based development of a receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand (RANKL) inhibitor peptide and molecular basis for osteopetrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20281–20286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Kim, M.H.; Lee, S.; Bae, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, S.B. Discovery of novel benzopyranyl tetracycles that act as inhibitors of osteoclastogenesis induced by receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 8760–8764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.H.; Lin, R.W.; Chen, Y.L.; Wang, G.J.; Ho, M.L.; Tzeng, C.C. Discovery of indeno[1,2-c]quinoline derivatives as inhibitors of osteoclastogenesis induced by receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL). J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3103–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, J.; Kasahara, C.; Asano, T.; Ito, S.; Seki, N.; Kato, Y.; Morikawa, N.; Nozaki, K.; Nishimura, K.; Akamatsu, H.; et al. Orally available pyridinylpyrimidine derivatives as novel RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 5681–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Liu, F.L.; Lee, C.C.; Chen, T.C.; Ahmed Ali, A.A.; Sytwu, H.K.; Chang, D.M.; Huang, H.S. Modified salicylanilide and 3-phenyl-2H-benzo[e][1,3]oxazine-2,4(3H)-dione derivatives as novel inhibitors of osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 8072–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Liu, F.L.; Chen, C.L.; Chen, T.C.; Chang, D.M.; Huang, H.S. Discovery of 5-(2′,4′-difluorophenyl)-salicylanilides as new inhibitors of receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclastogenesis. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 98, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinotas, V.; Papakyriakou, A.; Violitzi, F.; Papaneophytou, C.; Ouzouni, M.D.; Alexiou, P.; Strongilos, A.; Couladouros, E.; Kontopidis, G.; Eliopoulos, E.; et al. Discovery of Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-kappaB Ligand with a Superior Therapeutic Index. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 12043–12059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melagraki, G.; Ntougkos, E.; Papadopoulou, D.; Rinotas, V.; Leonis, G.; Douni, E.; Afantitis, A.; Kollias, G. In Silico Discovery of Plant-Origin Natural Product Inhibitors of Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) and Receptor Activator of NF-kappaB Ligand (RANKL). Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.; Li, S.; Wang, T.; Yan, X.; He, Q.; Ning, R.; Xu, X.; Yao, W.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; et al. Development of an Orally Active Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-kappaB Ligand. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 10992–11009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soekanto, A.; Ohya, K.; Ogura, H. The effect of sodium salicylate on the osteoclast-like cell formation and bone resorption in a mouse bone marrow culture. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1994, 54, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.M.; Smith, A.S.; Oslob, J.D.; Flanagan, W.M.; Braisted, A.C.; Whitty, A.; Cancilla, M.T.; Wang, J.; Lugovskoy, A.A.; Yoburn, J.C.; et al. Small-molecule inhibition of TNF-alpha. Science 2005, 310, 1022–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Peng, L.; Yang, K.; Wang, T.; Yan, X.; Jiang, T.; Xu, J.; Qi, J.; Zhou, H.; Qian, N.; et al. Development of Small-Molecules Targeting Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-kappaB Ligand (RANKL)-Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-kappaB (RANK) Protein-Protein Interaction by Structure-Based Virtual Screening and Hit Optimization. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 5370–5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, R.M.; Kang, H.J.; McCorvy, J.D.; Glatfelter, G.C.; Jones, A.J.; Che, T.; Slocum, S.; Huang, X.P.; Savych, O.; Moroz, Y.S.; et al. Virtual discovery of melatonin receptor ligands to modulate circadian rhythms. Nature 2020, 579, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, B.J.; Gahbauer, S.; Luttens, A.; Lyu, J.; Webb, C.M.; Stein, R.M.; Fink, E.A.; Balius, T.E.; Carlsson, J.; Irwin, J.J.; et al. A practical guide to large-scale docking. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 4799–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beroza, P.; Crawford, J.J.; Ganichkin, O.; Gendelev, L.; Harris, S.F.; Klein, R.; Miu, A.; Steinbacher, S.; Klingler, F.M.; Lemmen, C. Chemical space docking enables large-scale structure-based virtual screening to discover ROCK1 kinase inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, A.; Smiesko, M.; Sellner, M.; Lill, M.A. Decision Making in Structure-Based Drug Discovery: Visual Inspection of Docking Results. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 2489–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A. Lead- and drug-like compounds: The rule-of-five revolution. Drug Discov. Today. Technol. 2004, 1, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettou, A.; Papaneophytou, C.; Melagraki, G.; Maranti, A.; Liepouri, F.; Alexiou, P.; Papakyriakou, A.; Couladouros, E.; Eliopoulos, E.; Afantitis, A.; et al. Aqueous Solubility Enhancement for Bioassays of Insoluble Inhibitors and QSPR Analysis: A TNF-alpha Study. SLAS Discov. Adv. Life Sci. R D 2018, 23, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villoutreix, B.O.; Labbe, C.M.; Lagorce, D.; Laconde, G.; Sperandio, O. A leap into the chemical space of protein-protein interaction inhibitors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 4648–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, J.J.; Sterling, T.; Mysinger, M.M.; Bolstad, E.S.; Coleman, R.G. ZINC: A free tool to discover chemistry for biology. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 1757–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hawkins, P.C.; Skillman, A.G.; Warren, G.L.; Ellingson, B.A.; Stahl, M.T. Conformer generation with OMEGA: Algorithm and validation using high quality structures from the Protein Databank and Cambridge Structural Database. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, T.; Freyss, J.; von Korff, M.; Rufener, C. DataWarrior: An open-source program for chemistry aware data visualization and analysis. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaneophytou, C.P.; Rinotas, V.; Douni, E.; Kontopidis, G. A statistical approach for optimization of RANKL overexpression in Escherichia coli: Purification and characterization of the protein. Protein Expr. Purif. 2013, 90, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertl, P.; Rohde, B.; Selzer, P. Fast Calculation of Molecular Polar Surface Area as a Sum of Fragment-Based Contributions and Its Application to the Prediction of Drug Transport Properties. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 3714–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

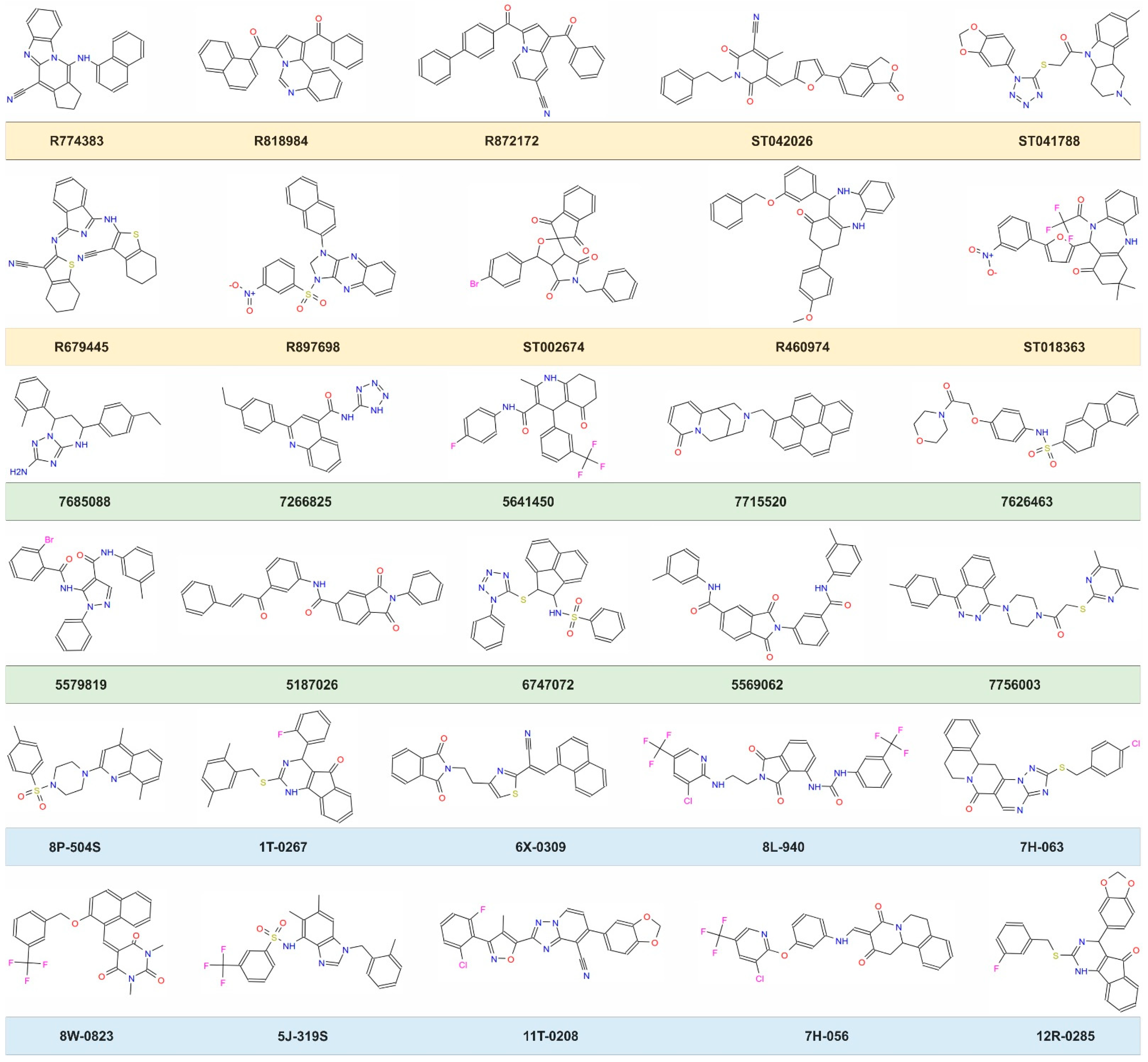
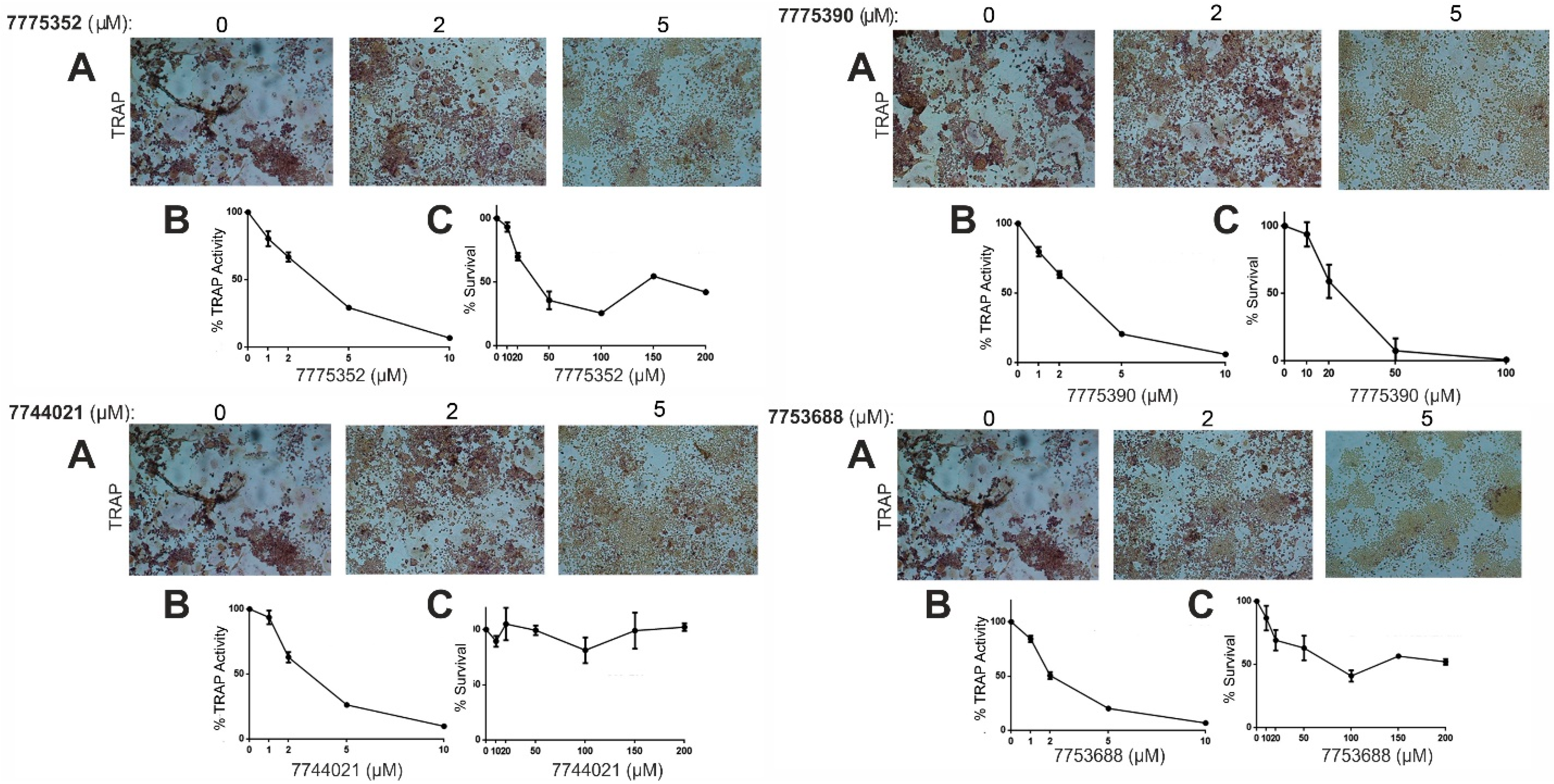

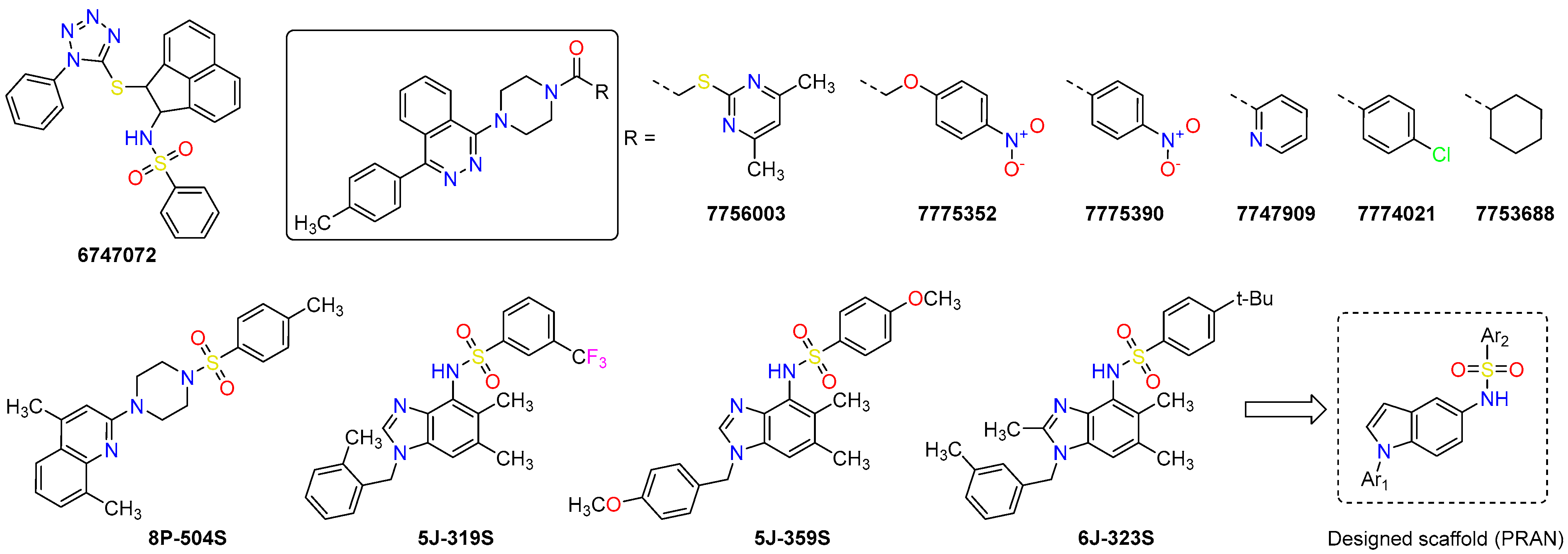
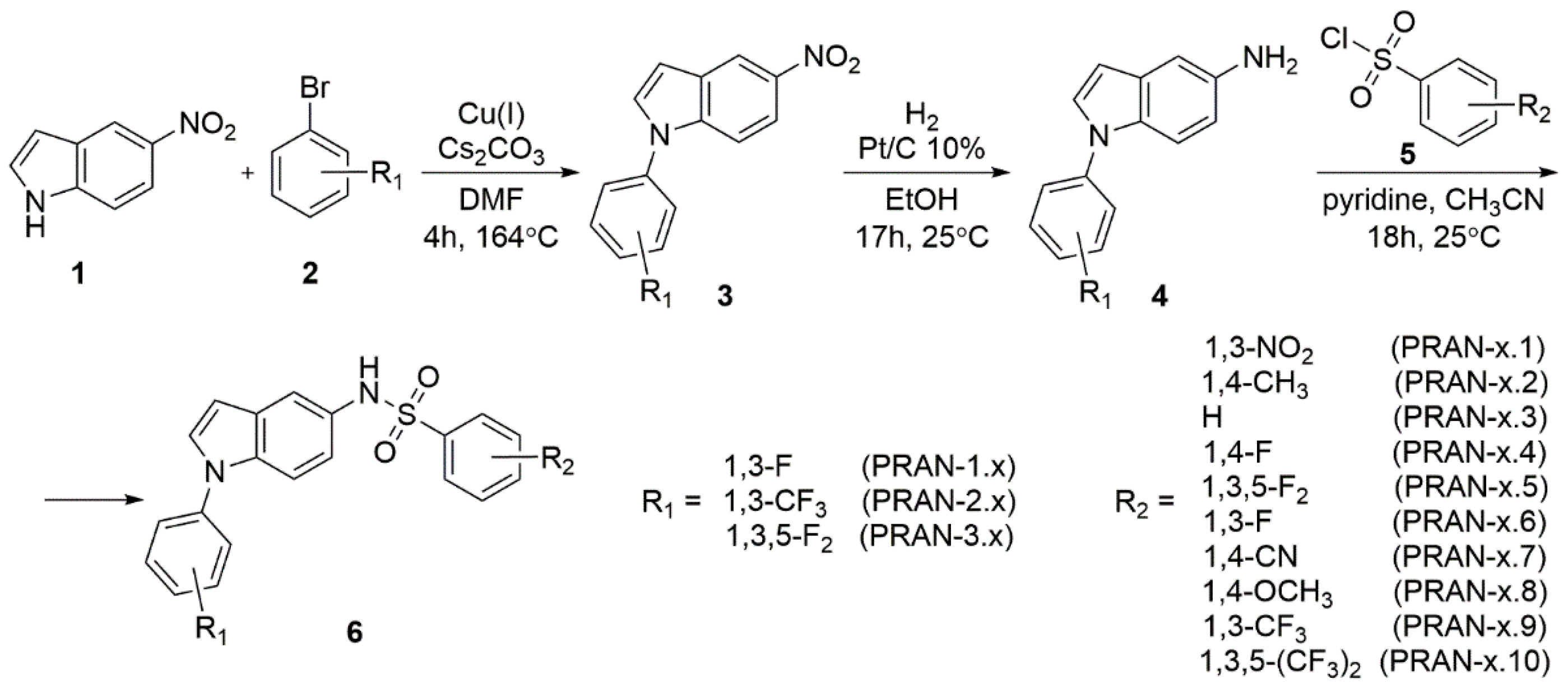
| Compound ID | MW (g/mol) | cLogP | Solubility in DMSO | Inhibition of Osteoclastogenesis | Activity IC50 (μΜ) | Toxicity LC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R774383 | 374.4 | 5.77 | Medium | Partial | n.d. | n.d. |
| R818984 | 426.5 | 5.58 | Medium | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| R872172 | 426.5 | 5.13 | Low | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| ST042026 | 464.5 | 3.30 | High | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| ST041788 | 464.5 | 3.34 | High | Partial | n.d. | n.d. |
| R679445 | 467.6 | 5.85 | High | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| R897698 | 483.5 | 4.20 | Low | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| R460974 | 502.6 | 5.94 | High | Partial | n.d. | n.d. |
| ST002674 | 516.3 | 3.28 | High | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| ST018363 | 525.5 | 4.44 | High | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| 7685088 | 333.4 | 3.88 | Medium | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| 7266825 | 344.4 | 3.63 | High | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| 5641450 | 404.5 | 5.09 | High | Partial | n.d. | n.d. |
| 7715520 | 444.4 | 5.19 | Low | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| 7626463 | 464.5 | 3.23 | Low | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| 5187026 | 472.5 | 5.28 | High | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| 5579819 | 475.3 | 4.54 | High | None | n.d. | n.d. |
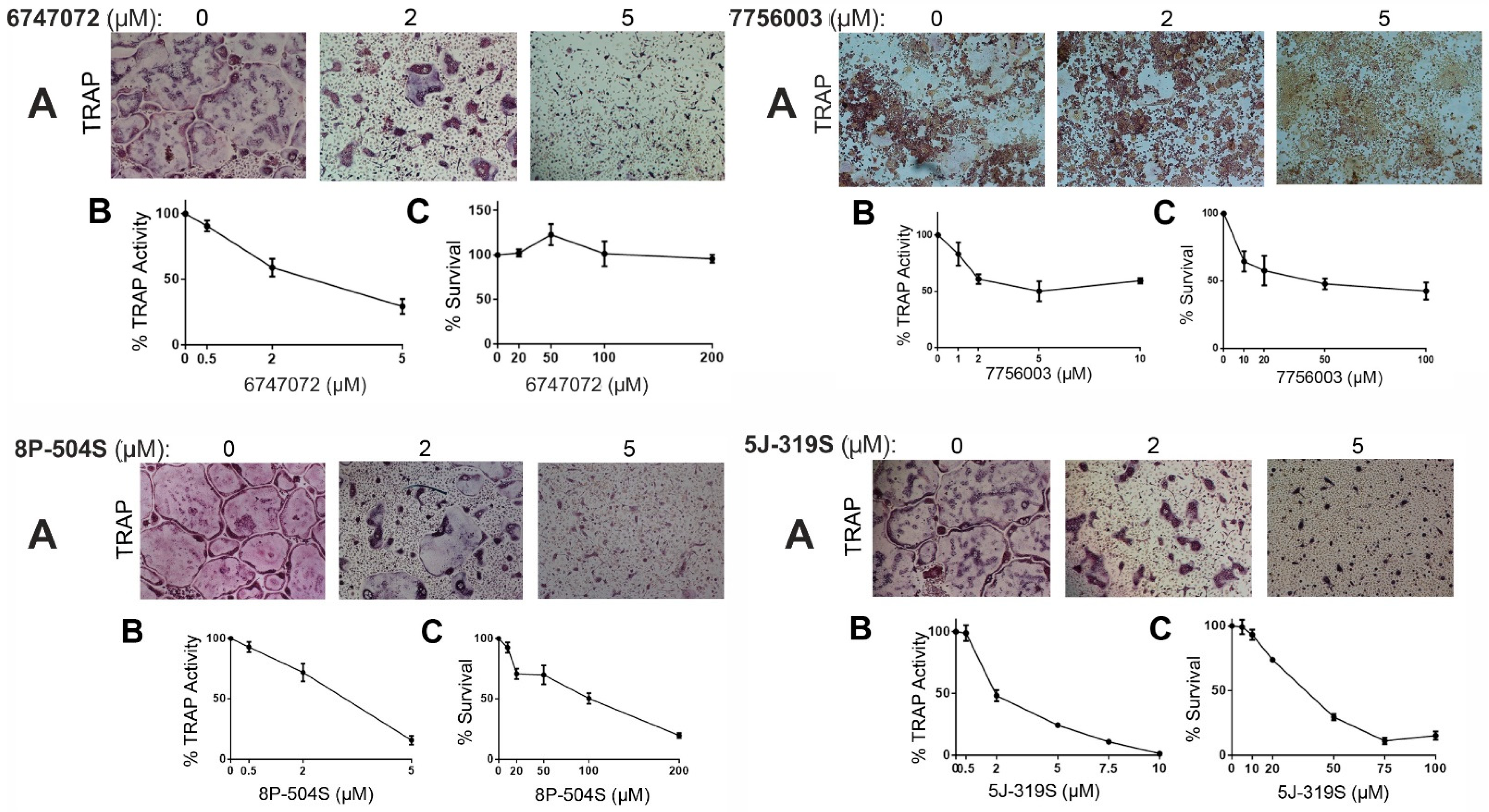
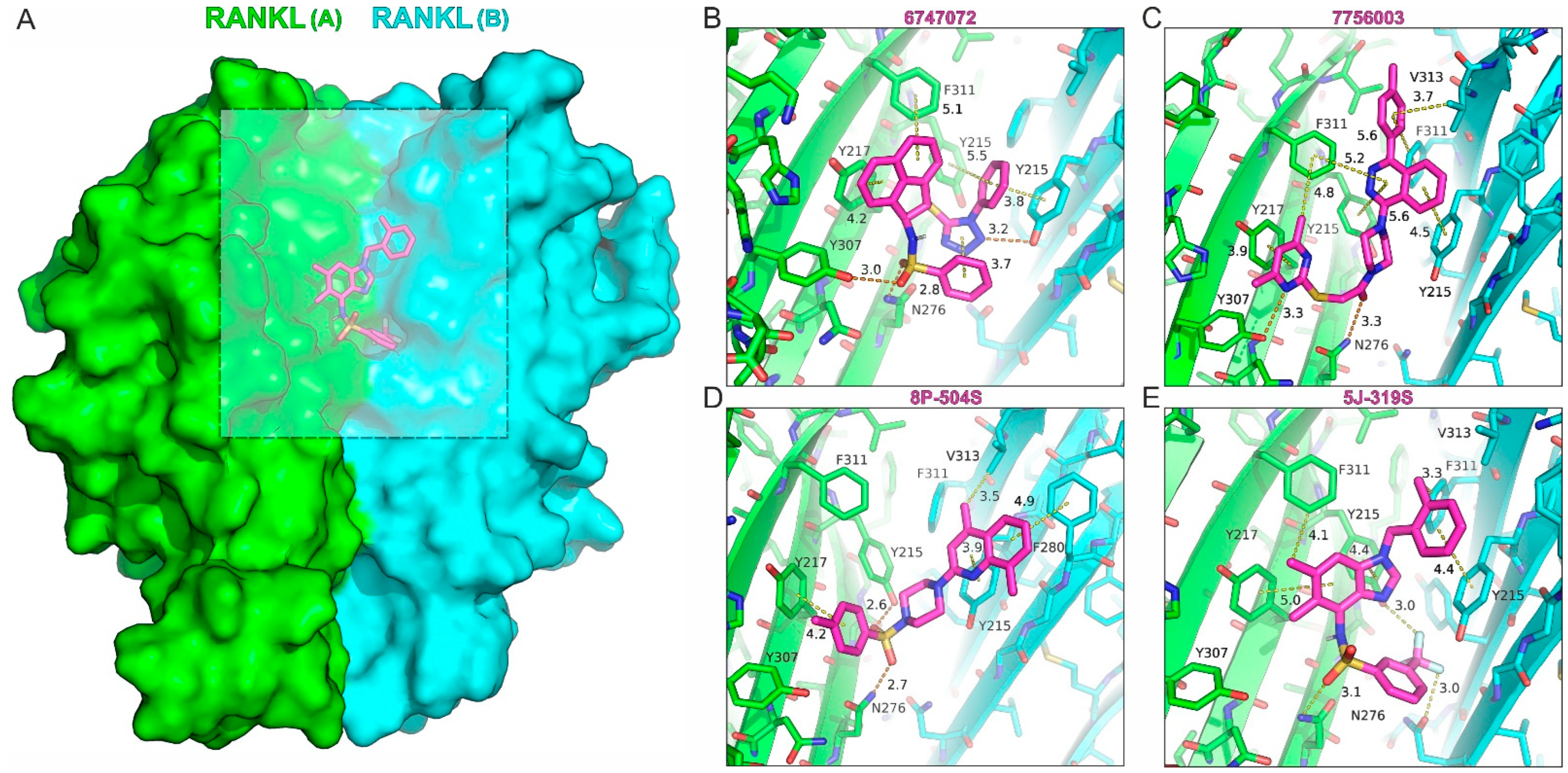
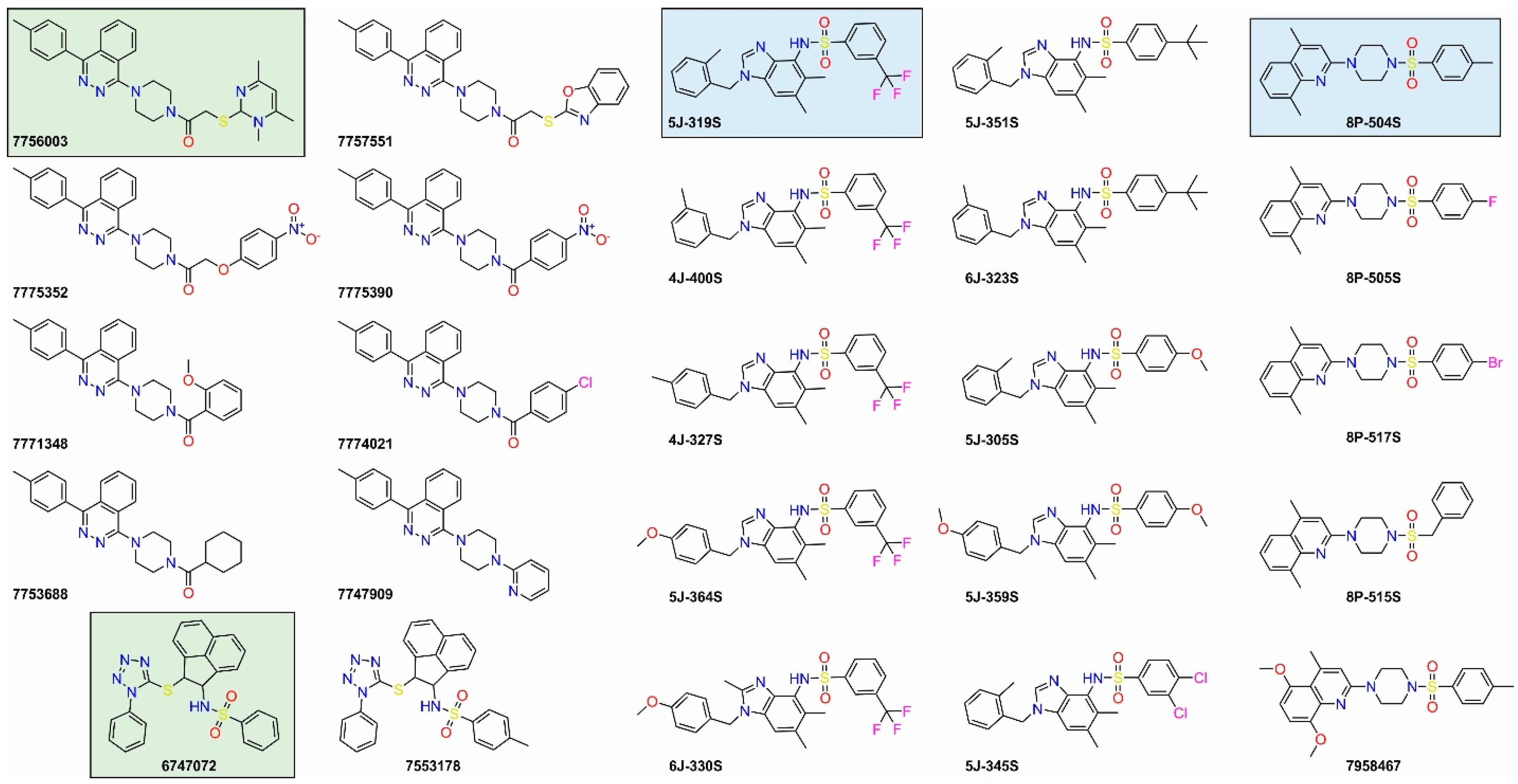
| 6747072 | 485.6 | 5.24 | High | Total | 2.90 ± 0.97 | >200 |
| 5569062 | 489.5 | 5.47 | Medium | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| 7756003 | 484.6 | 4.44 | High | Total | 4.63 ± 0.26 | 33.5 ± 14.5 |
| 8P-504S | 395.5 | 4.01 | High | Total | 3.53 ± 0.35 | 107 ± 2.0 |
| 1T-0267 | 428.5 | 5.47 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| 6X-0309 | 435.5 | 4.59 | Low | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| 12R-0285 | 444.5 | 4.90 | Medium | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| 7H-063 | 447.9 | 3.77 | Medium | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| 8W-0823 | 468.4 | 4.30 | Low | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| 5J-319S | 473.5 | 4.93 | High | Total | 1.11 ± 0.35 | 41.5 ± 0.1 |
| 11T-0208 | 473.9 | 4.55 | High | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| 7H-056 | 513.9 | 4.60 | Low | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| 8L-940 | 571.9 | 4.93 | High | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| Compound ID | MW (g/mol) | cLogP | Solubility in DMSO | Inhibition of Osteoclastogenesis | Activity IC50 (μΜ) | Toxicity LC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7757551 (a) | 495.6 | 5.22 | Medium | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| 7775352 (a) | 483.5 | 3.40 | High | Total | 3.31 ± 0.18 | 37.9 ± 1.8 |
| 7775390 (a) | 453.5 | 3.83 | High | Total | 2.91 ± 0.08 | 25.0 ± 5.6 |
| 7771348 (a) | 438.5 | 4.68 | Medium | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| 7774021 (a) | 442.9 | 5.35 | High | Total | 3.03 ± 0.16 | >200 |
| 7753688 (a) | 414.6 | 4.65 | High | Total | 2.18 ± 0.31 | 75.1 ± 9.3 |
| 7747909 (a) | 381.5 | 4.09 | High | Total | 3.03 ± 0.40 | 12.3 ± 1.1 |
| 7553178 (b) | 499.6 | 5.59 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| 4J-400S (c) | 473.5 | 4.93 | High | Partial | n.d. | n.d. |
| 4J-327S (c) | 473.5 | 4.93 | High | Partial | n.d. | n.d. |
| 5J-364S (c) | 489.5 | 4.51 | High | Partial | n.d. | n.d. |
| 6J-330S (c) | 503.5 | 4.75 | High | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| 5J-351S (c) | 461.6 | 5.66 | High | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| 6J-323S (c) | 475.7 | 5.90 | Medium | Total | 3.77 ± 1.05 | >50 |
| 5J-305S (c) | 435.5 | 4.01 | High | Partial | n.d. | n.d. |
| 5J-359S (c) | 451.5 | 3.60 | High | Total | 2.03 ± 0.17 | 17.2 ±1.2 |
| 5J-345S (c) | 474.4 | 5.29 | Medium | Partial | n.d. | n.d. |
| 8P-505S (d) | 399.5 | 3.76 | High | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| 8P-517S (d) | 460.4 | 4.39 | High | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| 8P-515S (d) | 395.5 | 3.90 | High | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| 7958467 (d) | 441.6 | 3.52 | High | None | n.d. | n.d. |
| Compound ID | MW (g/mol) | cLogP | Solubility in DMSO | Inhibition of Osteoclastogenesis | Activity IC50 (μΜ) | Toxicity LC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRAN-1.1 | 411.4 | 2.64 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-1.2 | 380.4 | 3.91 | High | Total | 4.13 ± 0.87 | 23.9 ± 2.5 |
| PRAN-1.3 | 366.4 | 3.56 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-1.4 | 384.4 | 3.66 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-1.5 | 402.4 | 3.76 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-1.6 | 384.4 | 3.66 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-1.7 | 391.4 | 3.40 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-1.8 | 396.4 | 3.49 | High | Total | 2.03 ± 0.81 | 13.2 ± 1.1 |
| PRAN-1.9 | 434.4 | 4.41 | High | Total | 2.59 ± 0.96 | 20.8 ± 1.9 |
| PRAN-1.10 | 502.4 | 5.26 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-2.1 | 461.4 | 3.39 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-2.2 | 430.4 | 4.65 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-2.3 | 416.4 | 4.31 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-2.4 | 434.4 | 4.41 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-2.5 | 452.4 | 4.51 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-2.6 | 434.4 | 4.41 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-2.7 | 441.4 | 4.14 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-2.8 | 446.4 | 4.24 | High | Total | 4.26 ± 1.16 | 11.4 ± 0.4 |
| PRAN-2.9 | 484.4 | 5.16 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-2.10 | 552.4 | 6.01 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-3.1 | 429.4 | 2.74 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-3.2 | 398.4 | 4.01 | High | Partial | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-3.3 | 384.4 | 3.66 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-3.4 | 402.4 | 3.76 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-3.5 | 420.4 | 3.86 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-3.6 | 402.4 | 3.76 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-3.7 | 409.4 | 3.50 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-3.8 | 414.4 | 3.59 | High | Partial | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-3.9 | 452.4 | 4.51 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
| PRAN-3.10 | 520.4 | 5.36 | High | none | n.d. | n.d. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rinotas, V.; Liepouri, F.; Ouzouni, M.-D.; Chalkidi, N.; Papaneophytou, C.; Lampropoulou, M.; Vidali, V.P.; Kontopidis, G.; Couladouros, E.; Eliopoulos, E.; et al. Structure-Based Discovery of Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-κB Ligand (RANKL)-Induced Osteoclastogenesis Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411290
Rinotas V, Liepouri F, Ouzouni M-D, Chalkidi N, Papaneophytou C, Lampropoulou M, Vidali VP, Kontopidis G, Couladouros E, Eliopoulos E, et al. Structure-Based Discovery of Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-κB Ligand (RANKL)-Induced Osteoclastogenesis Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(14):11290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411290
Chicago/Turabian StyleRinotas, Vagelis, Fotini Liepouri, Maria-Dimitra Ouzouni, Niki Chalkidi, Christos Papaneophytou, Mariza Lampropoulou, Veroniki P. Vidali, George Kontopidis, Elias Couladouros, Elias Eliopoulos, and et al. 2023. "Structure-Based Discovery of Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-κB Ligand (RANKL)-Induced Osteoclastogenesis Inhibitors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 14: 11290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411290
APA StyleRinotas, V., Liepouri, F., Ouzouni, M.-D., Chalkidi, N., Papaneophytou, C., Lampropoulou, M., Vidali, V. P., Kontopidis, G., Couladouros, E., Eliopoulos, E., Papakyriakou, A., & Douni, E. (2023). Structure-Based Discovery of Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-κB Ligand (RANKL)-Induced Osteoclastogenesis Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(14), 11290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411290








