Bradykinin Metabolism and Drug-Induced Angioedema
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Overview on Epidemiology of BK-Mediated AE
3. Diagnostic Approach in Drug-Induced BK-Mediated AE
4. Metabolism of BK and Its Receptors
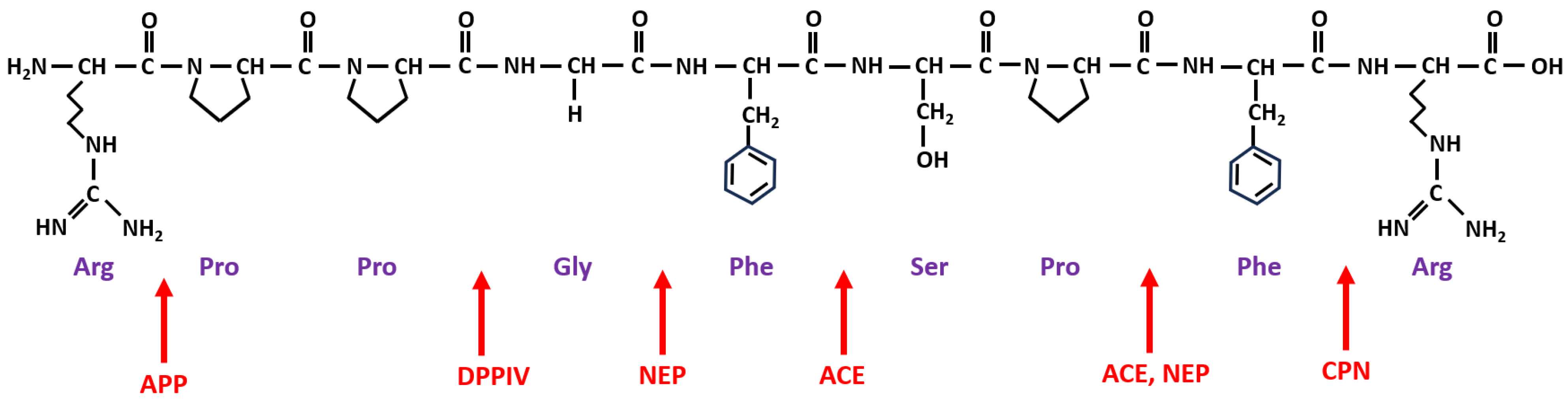
| Enzyme Name and Role in BK Metabolism | Abbreviation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Proteases involved in BK formation | type | location | |
| plasma kallikrein | Pka | serine | plasma |
| tissue kallikreins | TK | serine | plasma, tissue |
| factor XIIa | αFXIIa | serine | plasma |
| plasmin | Pla | serine | plasma |
| Peptidases involved in BK degradation | alias | products | |
| angiotensin-converting enzyme | ACE | kininase II | BK-(1-5), BK-(1-7) |
| carboxypeptidase N | CPN | kininase I | BK-(1-8) [des-Arg9-BK] |
| aminopeptidase P | APP | X-Pro aminopeptidase | BK-(2-9) |
| aminopeptidase N | APN | CD13 | BK-(2-9) |
| neutral endopeptidase | NEP | neprilysin, CD10 | BK-(1-7), BK-(1-4) |
| dipeptidyl peptidase IV | DPP-IV | CD26 | BK-(4-9) |
5. Drug-Induced BK-Mediated AE
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernstein, J.A.; Moellman, J. Emerging concepts in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with undifferentiated angioedema. Int. J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mudd, P.A.; Hooker, E.A.; Stolz, U.; Hart, K.W.; Bernstein, J.A.; Moellman, J.J. Emergency department evaluation of patients with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor associated angioedema. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 38, 2596–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, M.; Rodriguez-Garijo, N.; Sabate-Bresco, M. Medical algorithm: Diagnosis and management of histaminergic angioedema. Allergy 2023, 78, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J.A.; Cremonesi, P.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Hollingsworth, J. Angioedema in the emergency department: A practical guide to differential diagnosis and management. Int. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.J.; Koyfman, A.; Gottlieb, M. Evaluation and Management of Angioedema in the Emergency Department. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 20, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerji, A.; Blumenthal, K.G.; Lai, K.H.; Zhou, L. Epidemiology of ACE Inhibitor Angioedema Utilizing a Large Electronic Health Record. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, T.; Gonzalez, J.; Monteleone, C. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema: A review of the literature. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2017, 19, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Straka, B.T.; Ramirez, C.E.; Byrd, J.B.; Stone, E.; Woodard-Grice, A.; Nian, H.; Yu, C.; Banerji, A.; Brown, N.J. Effect of bradykinin receptor antagonism on ACE inhibitor-associated angioedema. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 242–248.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beltrami, L.; Zingale, L.C.; Carugo, S.; Cicardi, M. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-related angioedema: How to deal with it. Expert. Opin. Drug Saf. 2006, 5, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aygoren-Pursun, E.; Magerl, M.; Maetzel, A.; Maurer, M. Epidemiology of Bradykinin-mediated angioedema: A systematic investigation of epidemiological studies. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfaue, A.; Schuler, P.J.; Mayer, B.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Greve, J.; Hahn, J. Clinical features of angioedema induced by renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibition: A retrospective analysis of 84 patients. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2019, 9, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreau, M.E.; Dubreuil, P.; Molinaro, G.; Chagnon, M.; Muller-Esterl, W.; Lepage, Y.; Marceau, F.; Adam, A. Expression of metallopeptidases and kinin receptors in swine oropharyngeal tissues: Effects of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibition and inflammation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 315, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoover, T.; Lippmann, M.; Grouzmann, E.; Marceau, F.; Herscu, P. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor induced angio-oedema: A review of the pathophysiology and risk factors. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 40, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, A.P.; Joseph, K.; Silverberg, M. Pathways for bradykinin formation and inflammatory disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 109, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, J.; Boursiquot, J.N.; Chapdelaine, H.; Laramee, B.; Desjardins, M.; Gagnon, R.; Payette, N.; Lepeshkina, O.; Vincent, M. Bradykinin-induced angioedema in the emergency department. Int. J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 15, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainer, J.V.; Morrow, J.D.; Loveland, A.; King, D.J.; Brown, N.J. Effect of bradykinin-receptor blockade on the response to angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, M.; Rosenbaum, D.; Vaughan, D.E.; Brown, N.J. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition increases human vascular tissue-type plasminogen activator release through endogenous bradykinin. Circulation 2003, 107, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seyedi, N.; Maruyama, R.; Levi, R. Bradykinin activates a cross-signaling pathway between sensory and adrenergic nerve endings in the heart: A novel mechanism of ischemic norepinephrine release? J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 290, 656–663. [Google Scholar]
- Fryer, R.M.; Segreti, J.; Banfor, P.N.; Widomski, D.L.; Backes, B.J.; Lin, C.W.; Ballaron, S.J.; Cox, B.F.; Trevillyan, J.M.; Reinhart, G.A.; et al. Effect of bradykinin metabolism inhibitors on evoked hypotension in rats: Rank efficacy of enzymes associated with bradykinin-mediated angioedema. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adam, A.; Cugno, M.; Molinaro, G.; Perez, M.; Lepage, Y.; Agostoni, A. Aminopeptidase P in individuals with a history of angio-oedema on ACE inhibitors. Lancet 2002, 359, 2088–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.B.; Shreevatsa, A.; Putlur, P.; Foretia, D.; McAlexander, L.; Sinha, T.; Does, M.D.; Brown, N.J. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV deficiency increases susceptibility to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced peritracheal edema. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinaro, G.; Cugno, M.; Perez, M.; Lepage, Y.; Gervais, N.; Agostoni, A.; Adam, A. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-associated angioedema is characterized by a slower degradation of des-arginine(9)-bradykinin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 303, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinheiro, A.S.; Silbak, S.; Schmaier, A.H. Bradykinin—An elusive peptide in measuring and understanding. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 6, e12673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cugno, M.; Nussberger, J.; Cicardi, M.; Agostoni, A. Bradykinin and the pathophysiology of angioedema. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2003, 3, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.J.; Snowden, M.; Griffin, M.R. Recurrent angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor--associated angioedema. JAMA 1997, 278, 232–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabroe, R.A.; Black, A.K. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angio-oedema. Br. J. Dermatol. 1997, 136, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quan, M. Case study. ACE inhibitor-induced angioedema. Clin. Cornerstone 2009, 9 (Suppl. 3), S34–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, P.; Fernandez, T.D.; Canto, G.; Mayorga, C. Angioedema induced by angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 13, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.M.; Chung, P.; Chao, S.; Chao, L.; Chao, J. Differential regulation of kininogen gene expression by estrogen and progesterone in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1992, 1131, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binkley, K.E. Factor XII mutations, estrogen-dependent inherited angioedema, and related conditions. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2010, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, N.J.; Ray, W.A.; Snowden, M.; Griffin, M.R. Black Americans have an increased rate of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor-associated angioedema. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1996, 60, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, C.R.; Lip, G.Y.; Beevers, D.G. Angioedema due to ACE inhibitors: Increased risk in patients of African origin. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 48, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreau, M.E.; Garbacki, N.; Molinaro, G.; Brown, N.J.; Marceau, F.; Adam, A. The kallikrein-kinin system: Current and future pharmacological targets. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 99, 6–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cilia La Corte, A.L.; Carter, A.M.; Rice, G.I.; Duan, Q.L.; Rouleau, G.A.; Adam, A.; Grant, P.J.; Hooper, N.M. A functional XPNPEP2 promoter haplotype leads to reduced plasma aminopeptidase P and increased risk of ACE inhibitor-induced angioedema. Hum. Mutat. 2011, 32, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.L.; Nikpoor, B.; Dube, M.P.; Molinaro, G.; Meijer, I.A.; Dion, P.; Rochefort, D.; Saint-Onge, J.; Flury, L.; Brown, N.J.; et al. A variant in XPNPEP2 is associated with angioedema induced by angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 77, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blais, C., Jr.; Marc-Aurele, J.; Simmons, W.H.; Loute, G.; Thibault, P.; Skidgel, R.A.; Adam, A. Des-Arg9-bradykinin metabolism in patients who presented hypersensitivity reactions during hemodialysis: Role of serum ACE and aminopeptidase P. Peptides 1999, 20, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulec, M.; Caliskaner, Z.; Tunca, Y.; Ozturk, S.; Bozoglu, E.; Gul, D.; Erel, F.; Kartal, O.; Karaayvaz, M. The role of ace gene polymorphism in the development of angioedema secondary to angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2008, 36, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pare, G.; Kubo, M.; Byrd, J.B.; McCarty, C.A.; Woodard-Grice, A.; Teo, K.K.; Anand, S.S.; Zuvich, R.L.; Bradford, Y.; Ross, S.; et al. Genetic variants associated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-associated angioedema. Pharmacogenet Genom. 2013, 23, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quyyumi, A.A.; Ozkor, M. Vasodilation by hyperpolarization: Beyond NO. Hypertension 2006, 48, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mombouli, J.V.; Ballard, K.D.; Vanhoutte, P.M. Kininase-independent potentiation of endothelium-dependent relaxations to kinins by converting enzyme inhibitor perindoprilat. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2002, 23, 203–207. [Google Scholar]
- Kostis, J.B.; Kim, H.J.; Rusnak, J.; Casale, T.; Kaplan, A.; Corren, J.; Levy, E. Incidence and characteristics of angioedema associated with enalapril. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banerji, A.; Clark, S.; Blanda, M.; LoVecchio, F.; Snyder, B.; Camargo, C.A., Jr. Multicenter study of patients with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema who present to the emergency department. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008, 100, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiner, G.I.; Giclas, P.; Stadtmauer, G.; Cunningham-Rundles, C. Unmasking of acquired autoimmune C1-inhibitor deficiency by an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001, 86, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, T.; Gandhi, T.K.; Fiskio, J.M.; Seger, A.C.; So, J.W.; Cook, E.F.; Fukui, T.; Bates, D.W. An evaluation of risk factors for adverse drug events associated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2004, 10, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gompels, M.M.; Lock, R.J. C1 inhibitor deficiency: Diagnosis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2005, 30, 460–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, Z.; Zsilinszky, Z.; Polai, Z.; Andrasi, N.; Kohalmi, K.V.; Csuka, D.; Varga, L.; Farkas, H. The Importance of Complement Testing in Acquired Angioedema Related to Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.; Magerl, M.; Betschel, S.; Aberer, W.; Ansotegui, I.J.; Aygoren-Pursun, E.; Banerji, A.; Bara, N.A.; Boccon-Gibod, I.; Bork, K.; et al. The international WAO/EAACI guideline for the management of hereditary angioedema—The 2021 revision and update. World Allergy Organ. J. 2022, 15, 100627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasekar, M.; Craig, T.J. ACE inhibitor-induced angioedema. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012, 12, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrmizakis, D.E.; Papadakis, C.E.; Liolios, A.D.; Karatzanis, A.D.; Malandrakis, S.; Skoulakis, C.E.; Bizakis, J.G.; Velegrakis, G.A. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2004, 130, 1416–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykewicz, M.S. Cough and angioedema from angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: New insights into mechanisms and management. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 4, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanmart, H.; Malo, O.; Carrier, M.; Nickner, C.; Desjardins, N.; Perrault, L.P. Comparative study of cyclosporine and tacrolimus vs newer immunosuppressants mycophenolate mofetil and rapamycin on coronary endothelial function. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2002, 21, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duerr, M.; Glander, P.; Diekmann, F.; Dragun, D.; Neumayer, H.H.; Budde, K. Increased incidence of angioedema with ACE inhibitors in combination with mTOR inhibitors in kidney transplant recipients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rothermundt, C.; Gillessen, S. Angioedema in a patient with renal cell cancer treated with everolimus in combination with an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, e57–e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Charmillon, A.; Deibener, J.; Kaminsky, P.; Louis, G. Angioedema induced by angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, potentiated by m-TOR inhibitors: Successful treatment with icatibant. Intensive Care Med. 2014, 40, 893–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.B.; Woodard-Grice, A.; Stone, E.; Lucisano, A.; Schaefer, H.; Yu, C.; Eyler, A.E.; Salloum, N.E.; Brown, N.J. Association of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-associated angioedema with transplant and immunosuppressant use. Allergy 2010, 65, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mannucci, E.; Pala, L.; Ciani, S.; Bardini, G.; Pezzatini, A.; Sposato, I.; Cremasco, F.; Ognibene, A.; Rotella, C.M. Hyperglycaemia increases dipeptidyl peptidase IV activity in diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.B.; Touzin, K.; Sile, S.; Gainer, J.V.; Yu, C.; Nadeau, J.; Adam, A.; Brown, N.J. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV in angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor associated angioedema. Hypertension 2008, 51, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, D.R.; Oliveria, S.A.; Berlowitz, D.R.; Fincke, B.G.; Stang, P.; Lillienfeld, D.E. Angioedema incidence in US veterans initiating angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Hypertension 2008, 51, 1624–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stauber, T.; Confino-Cohen, R.; Goldberg, A. Life-threatening angioedema induced by angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: Characteristics and risk factors. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2014, 28, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrami, L.; Zanichelli, A.; Zingale, L.; Vacchini, R.; Carugo, S.; Cicardi, M. Long-term follow-up of 111 patients with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-related angioedema. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 2273–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosbaum, A.; Bouillet, L.; Floccard, B.; Javaud, N.; Launay, D.; Boccon-Gibod, I.; Fain, O.; Groupe d’experts du CREAK; French National Center for Angioedema. Management of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-related angioedema: Recommendations from the French National Center for Angioedema. Rev. Med. Interne 2013, 34, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.B.; Adam, A.; Brown, N.J. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-associated angioedema. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2006, 26, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bas, M.; Adams, V.; Suvorava, T.; Niehues, T.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Kojda, G. Nonallergic angioedema: Role of bradykinin. Allergy 2007, 62, 842–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, D.L.; Coop, C.A. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-associated angioedema treated with c1-esterase inhibitor: A case report and review of the literature. Allergy Rhinol. 2016, 7, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greve, J.; Bas, M.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Schuler, P.J.; Weller, P.; Kojda, G.; Strassen, U. Effect of C1-Esterase-inhibitor in angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, E198–E202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibfried, M.; Kovary, A. C1 Esterase Inhibitor (Berinert) for ACE Inhibitor-Induced Angioedema: Two Case Reports. J. Pharm. Pract. 2017, 30, 668–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, E.R.; Bygum, A. ACE-inhibitor induced angio-oedema treated with complement C1-inhibitor concentrate. BMJ Case Rep. 2013, 2013, bcr2013200652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassen, G.W.; Kalantari, H.; Parraga, M.; Chirurgi, R.; Meletiche, C.; Chan, C.; Ciarlo, J.; Gazi, F.; Lobaito, C.; Tadayon, S.; et al. Fresh frozen plasma for progressive and refractory angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema. J. Emerg. Med. 2013, 44, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkerson, R.G.; Dakessian, A.; Moellman, J.J.; Bernstein, J.A. Clinical trial of C1-INH for treatment of ACEi-induced angioedema. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2023, 68, 196–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, J.A.; Moellman, J.J.; Collins, S.P.; Hart, K.W.; Lindsell, C.J. Effectiveness of ecallantide in treating angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema in the emergency department. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015, 114, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, L.M.; Graffeo, C.; Crosley, P.; Klausner, H.A.; Clark, C.L.; Frank, A.; Miner, J.; Iarrobino, R.; Chyung, Y. Ecallantide for the acute treatment of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema: A multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2015, 65, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoldt, J.; Cox, C.; Matusz, E. Tranexamic acid use in the setting of ACE inhibitor induced angioedema. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 55, 230.e3–230.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.H.; Tsai, K.C.; Ho, M.P. Tranexamic acid use for ACE inhibitor induced angioedema. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 59, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartal, C.; Zeldetz, V.; Stavi, V.; Barski, L. The role of icatibant-the B2 bradykinin receptor antagonist-in life-threatening laryngeal angioedema in the ED. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 33, 479.e1–479.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bova, M.; Guilarte, M.; Sala-Cunill, A.; Borrelli, P.; Rizzelli, G.M.; Zanichelli, A. Treatment of ACEI-related angioedema with icatibant: A case series. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2015, 10, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crooks, N.H.; Patel, J.; Diwakar, L.; Smith, F.G. Icatibant in the treatment of Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema. Case Rep. Crit. Care 2014, 2014, 864815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fok, J.S.; Katelaris, C.H.; Brown, A.F.; Smith, W.B. Icatibant in angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor-associated angioedema. Intern. Med. J. 2015, 45, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinert, R.; Levy, P.; Bernstein, J.A.; Body, R.; Sivilotti, M.L.A.; Moellman, J.; Schranz, J.; Baptista, J.; Kimura, A.; Nothaft, W.; et al. Randomized Trial of Icatibant for Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor-Induced Upper Airway Angioedema. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 1402–1409.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, B.; Nair, A.P.; Misra, A.; Scott, C.Z.; Mahar, J.H.; Fedson, S. Neprilysin Inhibitors in Heart Failure: The Science, Mechanism of Action, Clinical Studies, and Unanswered Questions. JACC Basic. Transl. Sci. 2023, 8, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eworuke, E.; Welch, E.C.; Haug, N.; Horgan, C.; Lee, H.S.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, T.Y. Comparative Risk of Angioedema With Sacubitril-Valsartan vs Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Inhibitors. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, J.L.; Jaramillo, J.C.; Fernandez, C.; Enriquez, A.; Mielgo, R. Severe angioedema associated with olmesartan. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011, 107, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taki, M.; Watanabe, H.; Hasegawa, T.; Bamba, H.; Shimada, T.; Hisa, Y. Angioedema: 6 years experience with fourteen cases. Auris Nasus Larynx 2010, 37, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Investigators, O.; Yusuf, S.; Teo, K.K.; Pogue, J.; Dyal, L.; Copland, I.; Schumacher, H.; Dagenais, G.; Sleight, P.; Anderson, C. Telmisartan, ramipril, or both in patients at high risk for vascular events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1547–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rijnsoever, E.W.; Kwee-Zuiderwijk, W.J.; Feenstra, J. Angioneurotic edema attributed to the use of losartan. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998, 158, 2063–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, R.; Dong, V.M.; Lee, C.J.; Ntoso, K.A. Angiotensin II receptor blocker-associated angioedema: On the heels of ACE inhibitor angioedema. Pharmacotherapy 2002, 22, 1173–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, S.A.; Meyboom, R.H.; van Puijenbroek, E.P.; Guchelaar, H.J. Use of angiotensin receptor antagonists in patients with ACE inhibitor induced angioedema. Pharm. World Sci. 2004, 26, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudey, S.N.; Westermann-Clark, E.; Lockey, R.F. Cardiovascular and Diabetic Medications That Cause Bradykinin-Mediated Angioedema. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonde, M.M.; Olsen, K.B.; Erikstrup, N.; Speerschneider, T.; Lyngso, C.; Haunso, S.; Nielsen, M.S.; Sheikh, S.P.; Hansen, J.L. The angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist Losartan binds and activates bradykinin B2 receptor signaling. Regul. Pept. 2011, 167, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haymore, B.R.; Yoon, J.; Mikita, C.P.; Klote, M.M.; DeZee, K.J. Risk of angioedema with angiotensin receptor blockers in patients with prior angioedema associated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: A meta-analysis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008, 101, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beavers, C.J.; Dunn, S.P.; Macaulay, T.E. The role of angiotensin receptor blockers in patients with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema. Ann. Pharmacother. 2011, 45, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makani, H.; Messerli, F.H.; Romero, J.; Wever-Pinzon, O.; Korniyenko, A.; Berrios, R.S.; Bangalore, S. Meta-analysis of randomized trials of angioedema as an adverse event of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors. Am. J. Cardiol. 2012, 110, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, E.R.; Pottegard, A.; Bygum, A.; von Buchwald, C.; Homoe, P.; Hallas, J. Angiotensin II receptor blockers are safe in patients with prior angioedema related to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors—A nationwide registry-based cohort study. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 285, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, S.; Reichman, M.E.; Houstoun, M.; Ross Southworth, M.; Ding, X.; Hernandez, A.F.; Levenson, M.; Li, L.; McCloskey, C.; Shoaibi, A.; et al. Comparative risk for angioedema associated with the use of drugs that target the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 1582–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cicardi, M.; Zingale, L.C.; Bergamaschini, L.; Agostoni, A. Angioedema associated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor use: Outcome after switching to a different treatment. Arch. Intern. Med. 2004, 164, 910–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campbell, D.J.; Zhang, Y.; Kelly, D.J.; Gilbert, R.E.; McCarthy, D.J.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. Aliskiren increases bradykinin and tissue kallikrein mRNA levels in the heart. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2011, 38, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzaldua, D.A.; Schmitz, P.G. Aliskiren as an alternative in a patient with life-threatening ACE inhibitor-induced angioedema. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008, 51, 532–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlienger, R.G.; Korn, J.R.; Wehler, E.; Lopez Leon, S.; Yeaw, J. Angioedema Among Hypertensive Patients Treated with Aliskiren or Other Antihypertensive Medications in the United States. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2017, 17, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottomeyer, C.; Hennerici, M.G.; Szabo, K. Raising awareness of orolingual angioedema as a complication of thrombolysis in acute stroke patients. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2009, 27, 307–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, R.M.; Pollack, C.V., Jr. Successful cricothyrotomy after thrombolytic therapy for acute myocardial infarction: A report of two cases. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2000, 35, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapostolle, A.; Weisenburger-Lile, D.; Yger, M.; Alamowitch, S.; Fain, O. Bradykinin-Mediated Angioedema Following Tenecteplase Administration in an Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2022, 53, e446–e447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneron, C.; Lecluse, A.; Ronziere, T.; Bouillet, L.; Boccon-Gibod, I.; Gayet, S.; Doche, E.; Smadja, D.; Di Legge, S.; Dumont, F.; et al. Angioedema associated with thrombolysis for ischemic stroke: Analysis of a case-control study. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 286, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Lin, H. Alteplase associated Orolingual angioedema: A case report and literature review. Medicine 2022, 101, e32474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sczepanski, M.; Bozyk, P. Institutional Incidence of Severe tPA-Induced Angioedema in Ischemic Cerebral Vascular Accidents. Crit. Care Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 9360918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Groger, M.; Lebesgue, D.; Pruneau, D.; Relton, J.; Kim, S.W.; Nussberger, J.; Plesnila, N. Release of bradykinin and expression of kinin B2 receptors in the brain: Role for cell death and brain edema formation after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2005, 25, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cassano, N.; Nettis, E.; Di Leo, E.; Ambrogio, F.; Vena, G.A.; Foti, C. Angioedema associated with dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitors. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2021, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.J.; Byiers, S.; Carr, D.; Maldonado, M.; Warner, B.A. Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor use associated with increased risk of ACE inhibitor-associated angioedema. Hypertension 2009, 54, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voloshyna, D.; Al Barznji, S.; Shaik, T.A.; Rizvi, A.; Sachdev, R.; Pritwani, P.; Saleem, F.; Ghaffari, M.A.Z. Atorvastatin as a Rare Primary Cause of Drug-Induced Angioedema: A Case Report. Cureus 2022, 14, e28788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, S.; Saleem, M.W.; Haider, A.W. Angioedema; An Unreported Adverse Effect Of Pitavastatin. J. Ayub Med. Coll. Abbottabad 2018, 30, 603–604. [Google Scholar]
- Can, P.K.; Degirmentepe, E.N.; Etikan, P.; Kiziltaç, K.; Gelincik, A.; Demir, S.; Buyukozturk, S.; Haşal, E.; Başkan, E.B.; Aydin, Ö.; et al. Assessment of disease activity and quality of life in patients with recurrent bradykinin-mediated versus mast cell-mediated angioedema. World Allergy Organ. J. 2021, 14, 100554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moellman, J.J.; Bernstein, J.A.; Lindsell, C.; Banerji, A.; Busse, P.J.; Camargo, C.A., Jr.; Collins, S.P.; Craig, T.J.; Lumry, W.R.; Nowak, R.; et al. A consensus parameter for the evaluation and management of angioedema in the emergency department. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2014, 21, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souza-Silva, I.M.; de Paula, C.A.; Bolais-Ramos, L.; Santos, A.K.; da Silva, F.A.; de Oliveira, V.L.S.; da Rocha, I.D.; Antunes, M.M.; Cordeiro, L.P.B.; Teixeira, V.P.; et al. Peptide fragments of bradykinin show unexpected biological activity not mediated by B(1) or B(2) receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 3061–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Feature | ACEI-AE | HAE |
|---|---|---|
| age of onset | adult | usually 2–13 years |
| location of AE attacks | lips, tongue, face | facial, laryngeal, peripheral, abdominal area |
| speed of AE attack onset | gradual, over few hours | gradual, over few hours rapid onset, possibly <1 h |
| duration of AE attacks | usually 24–48 h after drug discontinuation | 3–5 days without treatment |
| association with urticaria | no | no |
| abdominal pain presentation | yes | usually not |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smolinska, S.; Antolín-Amérigo, D.; Popescu, F.-D. Bradykinin Metabolism and Drug-Induced Angioedema. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411649
Smolinska S, Antolín-Amérigo D, Popescu F-D. Bradykinin Metabolism and Drug-Induced Angioedema. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(14):11649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411649
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmolinska, Sylwia, Darío Antolín-Amérigo, and Florin-Dan Popescu. 2023. "Bradykinin Metabolism and Drug-Induced Angioedema" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 14: 11649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411649
APA StyleSmolinska, S., Antolín-Amérigo, D., & Popescu, F.-D. (2023). Bradykinin Metabolism and Drug-Induced Angioedema. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(14), 11649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411649






