Molecular Impact of Conventional and Electronic Cigarettes on Pulmonary Surfactant
Abstract
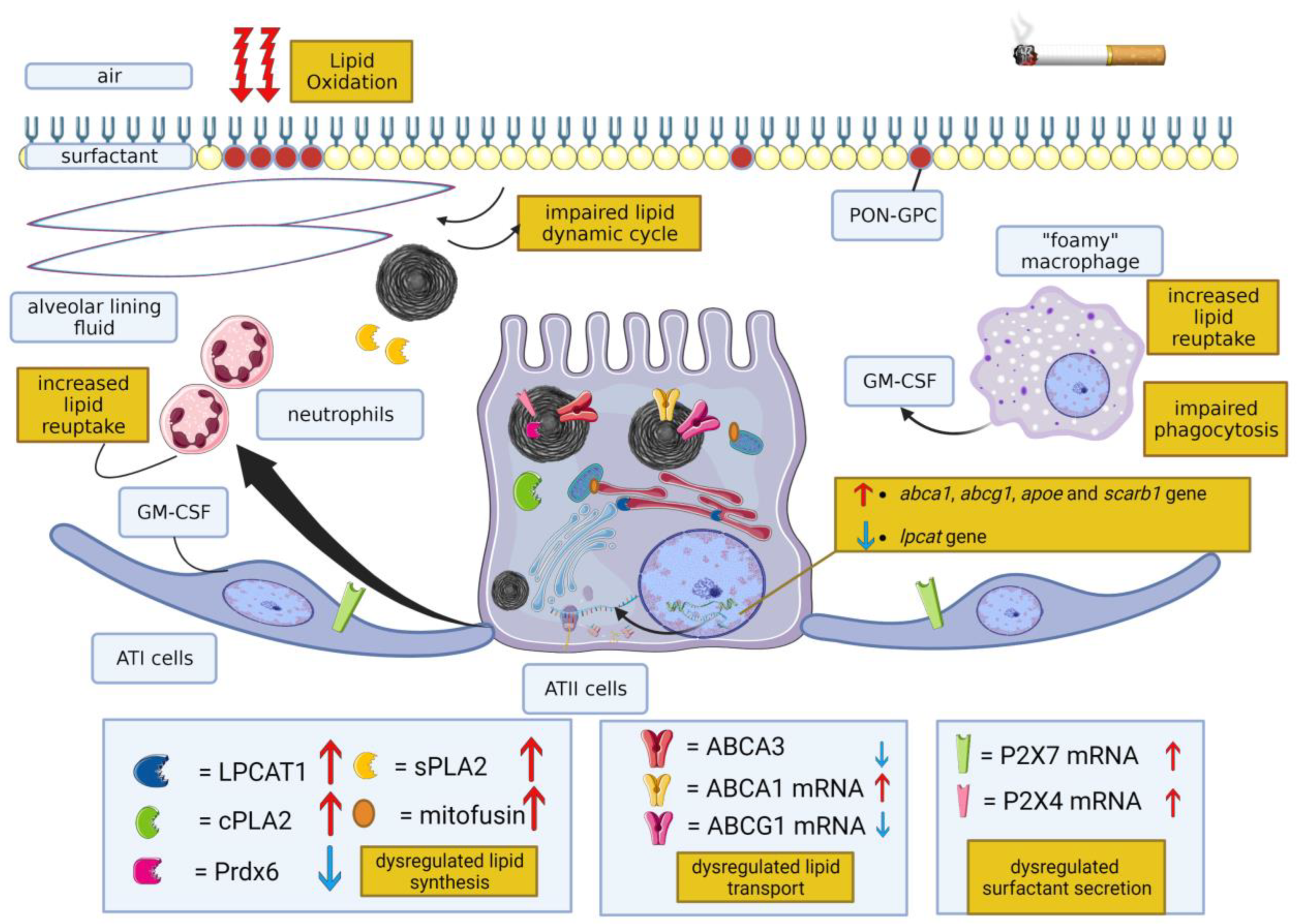
1. Introduction
2. Lipid and Protein Composition of Surfactant
3. Effect of Cigarette Smoke on the Lipid Components of Surfactant
3.1. Cigarette Smoke’s Effect on Composition and Abundance of Surfactant Lipids
| Subjects; Smoking Habit | Analysis | Tot. Lipids | FA | GL | Glycerophospholipids | Sphingolipids | Sterols | Prenols | Ref. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pa | PC | PG | APG | PE | PI | PS | SM | Cho | CE | |||||||
| Never smokers: 8, mean age 26 years. Current smokers: 8, mean age 24 years. HS | Acellular BAL |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | [96] | ||||
| Never smokers: 12, mean age 29.9 years. Current smokers: 14, mean age 28.5 years. ND | Acellular BAL |  |  |  |  |  |  | [97] | ||||||||
| Never smokers: 9, mean age 36 years. Current smokers13, mean age 44 years ND | Acellular BAL |  |  |  |  |  |  | [102] | ||||||||
| Never smokers: 11. Current smokers: 10. Mean age 36 years LS | Acellular BAL |  |  $ $ | [100] | ||||||||||||
| Never smokers: 20, mean age 32 years. Current smokers: 13, mean age 28 years. LS | Acellular BAL |  |  |  | [103] | |||||||||||
| Never smokers: 12 (aged 18 to 33 years). Current smokers: 8 (aged 24 to 48 years). LS and HS | Acellular BAL | Phospholipids | [98] | |||||||||||||
| Never smokers: 65, mean age 28 ± 8 years. Current smokers: 23, mean age 53 ± 5 years. LS | Acellular BAL | Phospholipids | [101] | |||||||||||||
| Never smokers: 14, mean age 54 years Current smokers: 20, mean age 42 years LS | Induced sputum |  |  |  |  |  | [99] | |||||||||
| Organism; Type and Time of Exposure | Analysis | Tot. Lipids | Glycerophospholipids | Sphingolipids | Sterols | Ref. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pa | PC | PON-GPC | PG | APG | PE | PI | PS | BMP | PCe | PeP | Cer | Chol | ||||
| 7 B6C3F1 mice; 2 cigarettes/day, 5 days/wk, for 14 days | Acellular BAL |  | [109] | |||||||||||||
| A/J mice: 16 control, 16 CS exposed; filtered cigarette smoke for 4 or 8 wks | primary ATII total cell lysates |  | [108] | |||||||||||||
| BALB/c C57BL/6 mice: 5 control, 5 CS exposed; twice daily smoke from 12 cigarettes 3R4F, for 4 days | Acellular BAL |  | [107] | |||||||||||||
| C57BL/6N mice; 2 rounds of smoke of 50 min each, 5 consecutive days, for 12 wks | Acellular BAL |  |  | [92] | ||||||||||||
| C57BL/6 mice: 11 control, 3 CS exposed; 4 h of smoke from 20 3R4F cigarettes/6 months | Acellular BAL |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | [44] | |||
3.2. Molecular Mechanisms Leading to Cigarette-Smoke-Induced Modification of Surfactant Lipid Homeostasis
4. Effect of Cigarette Smoke on the Protein Components of Surfactant
4.1. Cigarette Smoke Effect’s on Composition and Abundance of Surfactant Proteins
4.2. Molecular Mechanisms Leading to Cigarette-Smoke-Induced Modification of Surfactant Protein Homeostasis
5. Molecular Impact of Electronic Cigarette Vapor on Pulmonary Surfactant
6. Surfactant-Related Biomarkers Altered in Plasma by Cigarette Smoke or Electronic Cigarette Vapor
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, A.; Cherian, S.V.; Vassallo, R.; Yi, E.S.; Ryu, J.H. Current Concepts in Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Management of Smoking-Related Interstitial Lung Diseases. Chest 2018, 154, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saracen, A. Cigarette Smoking and Respiratory System Diseases in Adolescents. In Respiratory Treatment and Prevention; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Kolanjiyil, A.V.; Kleinstreuer, C. Modeling Airflow and Particle Deposition in a Human Acinar Region. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2019, 2019, 5952941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y. Recent Advances in the Understanding of Alveolar Flow. Biomicrofluidics 2022, 16, 021502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Nasu, F.; Harada, A.; Kunitomo, M. Oxidants in the Gas Phase of Cigarette Smoke Pass Through the Lung Alveolar Wall and Raise Systemic Oxidative Stress. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 103, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travaglini, K.J.; Nabhan, A.N.; Penland, L.; Sinha, R.; Gillich, A.; Sit, R.V.; Chang, S.; Conley, S.D.; Mori, Y.; Seita, J.; et al. A Molecular Cell Atlas of the Human Lung from Single-Cell RNA Sequencing. Nature 2020, 587, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastacky, J.; Lee, C.Y.; Goerke, J.; Koushafar, H.; Yager, D.; Kenaga, L.; Speed, T.P.; Chen, Y.; Clements, J.A. Alveolar Lining Layer Is Thin and Continuous: Low-Temperature Scanning Electron Microscopy of Rat Lung. J. Appl. Physiol. 1995, 79, 1615–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowicz-Kuśnierz, A.; Korchowiec, B.; Rogalska, E.; Korchowiec, J. The Lung Surfactant Activity Probed with Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 304, 102659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmeda, B.; Martínez-Calle, M.; Pérez-Gil, J. Pulmonary Surfactant Metabolism in the Alveolar Airspace: Biogenesis, Extracellular Conversions, Recycling. Ann. Anat.-Anat. Anz. 2017, 209, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañadas, O.; Olmeda, B.; Alonso, A.; Pérez-Gil, J. Lipid–Protein and Protein–Protein Interactions in the Pulmonary Surfactant System and Their Role in Lung Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diem, K.; Fauler, M.; Fois, G.; Hellmann, A.; Winokurow, N.; Schumacher, S.; Kranz, C.; Frick, M. Mechanical Stretch Activates Piezo1 in Caveolae of Alveolar Type I Cells to Trigger ATP Release and Paracrine Stimulation of Surfactant Secretion from Alveolar Type II Cells. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 12785–12804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokicki, W.; Rokicki, M.; Wojtacha, J.; Dżeljijli, A. The Role and Importance of Club Cells (Clara Cells) in the Pathogenesis of Some Respiratory Diseases. Pol. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2016, 1, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orgeig, S.; Morrison, J.L.; Daniels, C.B. Evolution, Development, and Function of the Pulmonary Surfactant System in Normal and Perturbed Environments. In Comprehensive Physiology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 363–422. [Google Scholar]
- Parra, E.; Pérez-Gil, J. Composition, Structure and Mechanical Properties Define Performance of Pulmonary Surfactant Membranes and Films. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2015, 185, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casals, C.; Campanero-Rhodes, M.A.; García-Fojeda, B.; Solís, D. The Role of Collectins and Galectins in Lung Innate Immune Defense. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidoni, R.; Caretti, A.; Signorelli, P. Role of Sphingolipids in the Pathobiology of Lung Inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 487508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochs, M.; Hegermann, J.; Lopez-Rodriguez, E.; Timm, S.; Nouailles, G.; Matuszak, J.; Simmons, S.; Witzenrath, M.; Kuebler, W.M. On Top of the Alveolar Epithelium: Surfactant and the Glycocalyx. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miserocchi, G. Mechanisms Controlling the Volume of Pleural Fluid and Extravascular Lung Water. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2009, 18, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodega, F.; Sironi, C.; Armilli, M.; Porta, C.; Agostoni, E. Evidence for Na+–Glucose Cotransporter in Type I Alveolar Epithelium. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 134, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londino, J.D.; Lazrak, A.; Collawn, J.F.; Bebok, Z.; Harrod, K.S.; Matalon, S. Influenza Virus Infection Alters Ion Channel Function of Airway and Alveolar Cells: Mechanisms and Physiological Sequelae. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 313, L845–L858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bove, P.F.; Grubb, B.R.; Okada, S.F.; Ribeiro, C.M.P.; Rogers, T.D.; Randell, S.H.; O’Neal, W.K.; Boucher, R.C. Human Alveolar Type II Cells Secrete and Absorb Liquid in Response to Local Nucleotide Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 34939–34949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, M.; Voelker, D.R. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Viral Actions of Anionic Pulmonary Surfactant Phospholipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2022, 1867, 159139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, W. Lung Surfactant: Function and Composition in the Context of Development and Respiratory Physiology. Ann. Anat.-Anat. Anz. 2016, 208, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo, C.W.; Samaha, G.; Garcia-Arcos, I. Alveolar Lipids in Pulmonary Disease. A Review. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milad, N.; Morissette, M.C. Revisiting the Role of Pulmonary Surfactant in Chronic Inflammatory Lung Diseases and Environmental Exposure. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 210077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldhuizen, R.; Nag, K.; Orgeig, S.; Possmayer, F. The Role of Lipids in Pulmonary Surfactant. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Mol. Basis Dis. 1998, 1408, 90–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Sánchez, J.C.; Cruz, A.; Pérez-Gil, J. Structural Hallmarks of Lung Surfactant: Lipid-Protein Interactions, Membrane Structure and Future Challenges. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 703, 108850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhard, W.; Hoffmann, S.; Dombrowsky, H.; Rau, G.A.; Kamlage, A.; Kappler, M.; Haitsma, J.J.; Freihorst, J.; von der Hardt, H.; Poets, C.F. Phosphatidylcholine Molecular Species in Lung Surfactant. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2001, 25, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, K.; Sun, L.; Luo, Z.; Cao, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, K.; Faizy, A.; Piomelli, D.; Lu, X.; Shan, J.; et al. Reduced DMPC and PMPC in Lung Surfactant Promote SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Obesity. Metabolism 2022, 131, 155181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Gil, J. A Recipe for a Good Clinical Pulmonary Surfactant. Biomed. J. 2022, 45, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessler, M.B.; Summer, R.S. Surfactant Lipids at the Host–Environment Interface. Metabolic Sensors, Suppressors, and Effectors of Inflammatory Lung Disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 54, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkov, V.N.; Oskolkova, O.V.; Birukov, K.G.; Levonen, A.-L.; Binder, C.J.; Stöckl, J. Generation and Biological Activities of Oxidized Phospholipids. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2010, 12, 1009–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vockeroth, D.; Gunasekara, L.; Amrein, M.; Possmayer, F.; Lewis, J.F.; Veldhuizen, R.A.W. Role of Cholesterol in the Biophysical Dysfunction of Surfactant in Ventilator-Induced Lung Injury. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2010, 298, L117–L125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekara, L.; Al-Saiedy, M.; Green, F.; Pratt, R.; Bjornson, C.; Yang, A.; Michael Schoel, W.; Mitchell, I.; Brindle, M.; Montgomery, M.; et al. Pulmonary Surfactant Dysfunction in Pediatric Cystic Fibrosis: Mechanisms and Reversal with a Lipid-Sequestering Drug. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2017, 16, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markart, P.; Ruppert, C.; Wygrecka, M.; Colaris, T.; Dahal, B.; Walmrath, D.; Harbach, H.; Wilhelm, J.; Seeger, W.; Schmidt, R.; et al. Patients with ARDS Show Improvement but Not Normalisation of Alveolar Surface Activity with Surfactant Treatment: Putative Role of Neutral Lipids. Thorax 2007, 62, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liekkinen, J.; Enkavi, G.; Javanainen, M.; Olmeda, B.; Pérez-Gil, J.; Vattulainen, I. Pulmonary Surfactant Lipid Reorganization Induced by the Adsorption of the Oligomeric Surfactant Protein B Complex. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 3251–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, P.; Zarini, S.; Chan, E.D.; Leslie, C.C.; Murphy, R.C.; Voelker, D.R. Pulmonary Surfactant Phosphatidylglycerol Inhibits Mycoplasma Pneumoniae-Stimulated Eicosanoid Production from Human and Mouse Macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 7841–7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liekkinen, J.; Olżyńska, A.; Cwiklik, L.; Bernardino de la Serna, J.; Vattulainen, I.; Javanainen, M. Surfactant Proteins SP-B and SP-C in Pulmonary Surfactant Monolayers: Physical Properties Controlled by Specific Protein–Lipid Interactions. Langmuir 2023, 39, 4338–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingenito, E.P.; Mora, R.; Mark, L. Pivotal Role of Anionic Phospholipids in Determining Dynamic Behavior of Lung Surfactant. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavarha, M.; Khoojinian, H.; Schulwitz, L.E.; Biswas, S.C.; Rananavare, S.B.; Hall, S.B. Hydrophobic Surfactant Proteins Induce a Phosphatidylethanolamine to Form Cubic Phases. Biophys. J. 2010, 98, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-de-Lara, L.; Tlatelpa-Romero, B.; Romero, Y.; Fernández-Tamayo, N.; Vazquez-de-Lara, F.; Justo-Janeiro, J.M.; Garcia-Carrasco, M.; de-la-Rosa Paredes, R.; Cisneros-Lira, J.; Mendoza-Milla, C.; et al. Phosphatidylethanolamine Induces an Antifibrotic Phenotype in Normal Human Lung Fibroblasts and Ameliorates Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porras-Gómez, M.; Shoaib, T.; Steer, D.; Espinosa-Marzal, R.M.; Leal, C. Pathological Cardiolipin-Promoted Membrane Hemifusion Stiffens Pulmonary Surfactant Membranes. Biophys. J. 2022, 121, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, R.; Rong, P.; Wang, J.; Parvin, R.; Deng, Y. The Potential Role of Bioactive Plasmalogens in Lung Surfactant. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 618102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agudelo, C.W.; Kumley, B.K.; Area-Gomez, E.; Xu, Y.; Dabo, A.J.; Geraghty, P.; Campos, M.; Foronjy, R.; Garcia-Arcos, I. Decreased Surfactant Lipids Correlate with Lung Function in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Rojo, N.; Riezman, H. On the Road to Unraveling the Molecular Functions of Ether Lipids. FEBS Lett. 2019, 593, 2378–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, A.J.; McCoy, D.M.; McGowan, S.E.; Salome, R.G.; Mallampalli, R.K. Alveolar Sphingolipids Generated in Response to TNF-α Modifies Surfactant Biophysical Activity. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 94, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griese, M.; Bonella, F.; Costabel, U.; de Blic, J.; Tran, N.-B.; Liebisch, G. Quantitative Lipidomics in Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, M.; Roddick, V.; Thornburg, T.; King, L.; Cochran, F. Conversion of Phosphatidylglycerol to Lyso(Bis)Phosphatidic Acid by Alveolar Macrophages. FASEB J. 1987, 1, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paget, T.L.; Parkinson-Lawrence, E.J.; Trim, P.J.; Autilio, C.; Panchal, M.H.; Koster, G.; Echaide, M.; Snel, M.F.; Postle, A.D.; Morrison, J.L.; et al. Increased Alveolar Heparan Sulphate and Reduced Pulmonary Surfactant Amount and Function in the Mucopolysaccharidosis IIIA Mouse. Cells 2021, 10, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Kadambi, P.; Dave, V.; Lu, L.J.; Whitsett, J.A. A Systems Approach to Mapping Transcriptional Networks Controlling Surfactant Homeostasis. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambiar, S.; Bong How, S.; Gummer, J.; Trengove, R.; Moodley, Y. Metabolomics in Chronic Lung Diseases. Respirology 2020, 25, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargagli, E.; Refini, R.M.; d’Alessandro, M.; Bergantini, L.; Cameli, P.; Vantaggiato, L.; Bini, L.; Landi, C. Metabolic Dysregulation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, F.X.; Whitsett, J.A. The Pulmonary Collectins, SP-A and SP-D, Orchestrate Innate Immunity in the Lung. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viklund, E.; Bake, B.; Hussain-Alkhateeb, L.; Koca Akdeva, H.; Larsson, P.; Olin, A.-C. Current Smoking Alters Phospholipid- and Surfactant Protein A Levels in Small Airway Lining Fluid: An Explorative Study on Exhaled Breath. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapnell, B.C.; Nakata, K.; Bonella, F.; Campo, I.; Griese, M.; Hamilton, J.; Wang, T.; Morgan, C.; Cottin, V.; McCarthy, C. Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Calle, M.; Alonso, A.; Pérez-Gil, J.; Olmeda, B. Native Supramolecular Protein Complexes in Pulmonary Surfactant: Evidences for SP-A/SP-B Interactions. J. Proteom. 2019, 207, 103466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehlmeyer, K.; Ruwisch, J.; Roldan, N.; Lopez-Rodriguez, E. Alveolar Dynamics and Beyond—The Importance of Surfactant Protein C and Cholesterol in Lung Homeostasis and Fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beileke, S.; Claassen, H.; Wagner, W.; Matthies, C.; Ruf, C.; Hartmann, A.; Garreis, F.; Paulsen, F.; Schicht, M.; Bräuer, L. Expression and Localization of Lung Surfactant Proteins in Human Testis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräuer, L.; Johl, M.; Paulsen, F.P.; Börgermann, J.; Pleyer, U.; Tsokos, M. Detection and Localization of the Hydrophobic Surfactant Proteins B and C in Human Tear Fluid and the Human Lacrimal System. Curr. Eye Res. 2009, 32, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräuer, L.; Schicht, M.; Stengl, C.; Heinemann, F.; Götz, W.; Scholz, M.; Paulsen, F. Detection of Surfactant Proteins A, B, C, and D in Human Gingiva and Saliva. Biomed. Tech. 2012, 57, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahlman, M.T.; Gray, M.P.; Falconieri, M.W.; Whitsett, J.A.; Weaver, T.E. Lamellar Body Formation in Normal and Surfactant Protein B-Deficient Fetal Mice. Lab. Investig. 2000, 80, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, C.D.; Zhang, P.X.; Gonzales, L.W.; Guttentag, S.H. In Vitro Surfactant Protein B Deficiency Inhibits Lamellar Body Formation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003, 29, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Calle, M.; Olmeda, B.; Dietl, P.; Frick, M.; Pérez-Gil, J. Pulmonary Surfactant Protein SP-B Promotes Exocytosis of Lamellar Bodies in Alveolar Type II Cells. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 4600–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Calle, M.; Prieto, M.; Olmeda, B.; Fedorov, A.; Loura, L.M.S.; Pérez-Gil, J. Pulmonary Surfactant Protein SP-B Nanorings Induce the Multilamellar Organization of Surfactant Complexes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2020, 1862, 183216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobi, N.; Giolai, M.; Olmeda, B.; Miklavc, P.; Felder, E.; Walther, P.; Dietl, P.; Frick, M.; Pérez-Gil, J.; Haller, T. A Small Key Unlocks a Heavy Door: The Essential Function of the Small Hydrophobic Proteins SP-B and SP-C to Trigger Adsorption of Pulmonary Surfactant Lamellar Bodies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2016, 1863, 2124–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaccaro, A.M.; Salvioli, R.; Tatti1, M.; Ciaffoni1, F. Saposins and Their Interaction with Lipids. Neurochem. Res. 1999, 24, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Gil, J.; Casals, C.; Marsh, D. Interactions of Hydrophobic Lung Surfactant Proteins SP-B and SP-C with Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine and Dipalmitoylphosphatidylglycerol Bilayers Studied by Electron Spin Resonance Spectroscopy. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 3964–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, J.M.; Mayo, J.; Tan, W.; Tammemagi, C.M.; Liu, G.; Peacock, S.; Shepherd, F.A.; Goffin, J.; Goss, G.; Nicholas, G.; et al. Plasma Pro-Surfactant Protein B and Lung Function Decline in Smokers. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.B.; Rohatgi, A.; Garcia, C.K.; Ayers, C.R.; Das, S.R.; Lakoski, S.G.; Berry, J.D.; Khera, A.; McGuire, D.K.; de Lemos, J.A. Interactions Between Smoking, Pulmonary Surfactant Protein B, and Atherosclerosis in the General Population. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 2136–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttentag, S. Posttranslational Regulation of Surfactant Protein B Expression. Semin. Perinatol. 2008, 32, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmeda, B.; García-Álvarez, B.; Gómez, M.J.; Martínez-Calle, M.; Cruz, A.; Pérez-Gil, J. A Model for the Structure and Mechanism of Action of Pulmonary Surfactant Protein B. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 4236–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, A.J.; Whitelegge, J.P.; Sharma, S.K.; Gordon, L.M.; Walther, F.J. Emulation of the Structure of the Saposin Protein Fold by a Lung Surfactant Peptide Construct of Surfactant Protein B. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, M.; Dong, P.; Hermans, C.; Bernard, A.; Bersten, A.D.; Doyle, I.R. Serum Levels of CC16, SP-A and SP-B Reflect Tobacco-Smoke Exposure in Asymptomatic Subjects. Eur. Respir. J. 2002, 20, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, J.; Szyperski, T.; Wüthrich, K. Pulmonary Surfactant-Associated Polypeptide SP-C in Lipid Micelles: CD Studies of Intact SP-C and NMR Secondary Structure Determination of Depalmitoyl-SP-C(1-17). FEBS Lett. 1995, 362, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plasencia, I.; Baumgart, F.; Andreu, D.; Marsh, D.; Pérez-Gil, J. Effect of Acylation on the Interaction of the N-Terminal Segment of Pulmonary Surfactant Protein SP-C with Phospholipid Membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Biomembr. 2008, 1778, 1274–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schürch, D.; Ospina, O.L.; Cruz, A.; Pérez-Gil, J. Combined and Independent Action of Proteins SP-B and SP-C in the Surface Behavior and Mechanical Stability of Pulmonary Surfactant Films. Biophys. J. 2010, 99, 3290–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saiedy, M.; Tarokh, A.; Nelson, S.; Hossini, K.; Green, F.; Ling, C.C.; Prenner, E.J.; Amrein, M. The Role of Multilayers in Preventing the Premature Buckling of the Pulmonary Surfactant. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 1372–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, W.R.; Ross, G.F.; Singleton, F.M.; Dingle, S.; Whitsett, J.A.; Divkion, P.; Surfczctant, J.A.W. Surfactant-Associated Protein Inhibits Phospholipid Secretion from Type II Cells. J. Appl. Physiol. 1987, 63, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S. P63 (CKAP4) as an SP-A Receptor: Implications for Surfactant Turnover. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 25, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegami, M.; Grant, S.; Korfhagen, T.; Scheule, R.K.; Whitsett, J.A. Surfactant Protein-D Regulates the Postnatal Maturation of Pulmonary Surfactant Lipid Pool Sizes. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Xiong, P.; Fu, Y. Surfactant Protein A Expression and Distribution in Human Lung Samples from Smokers with or without Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in China. Medicine 2020, 99, e19118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spragg, R.G.; Lewis, J.F. Pathology of the Surfactant System of the Mature Lung Second San Diego Conference. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casals, C.; García-Fojeda, B.; Minutti, C.M. Soluble Defense Collagens: Sweeping up Immune Threats. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 112, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamiya, R.; Uchida, K.; Shibata, T.; Maeno, T.; Kato, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Ariki, S.; Hasegawa, Y.; Saito, A.; Miwa, S.; et al. Disruption of the Structural and Functional Features of Surfactant Protein A by Acrolein in Cigarette Smoke. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.R. Immunoregulatory Functions of Surfactant Proteins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariki, S.; Nishitani, C.; Kuroki, Y. Diverse Functions of Pulmonary Collectins in Host Defense of the Lung. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 532071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, A.; Phipps, M.J.S.; Clark, H.W.; Skylaris, C.-K.; Madsen, J. Surfactant Proteins A and D: Trimerized Innate Immunity Proteins with an Affinity for Viral Fusion Proteins. J. Innate Immun. 2019, 11, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhardt, A.; Wehle, M.; Geissner, A.; Crouch, E.C.; Kang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Anish, C.; Santer, M.; Seeberger, P.H. Structure Binding Relationship of Human Surfactant Protein D and Various Lipopolysaccharide Inner Core Structures. J. Struct. Biol. 2016, 195, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douda, D.N.; Jackson, R.; Grasemann, H.; Palaniyar, N. Innate Immune Collectin Surfactant Protein D Simultaneously Binds Both Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and Carbohydrate Ligands and Promotes Bacterial Trapping. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 1856–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issac, M.S.M.; Ashur, W.; Mousa, H. Genetic Polymorphisms of Surfactant Protein D Rs2243639, Interleukin (IL)-1β Rs16944 and IL-1RN Rs2234663 in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Healthy Smokers, and Non-Smokers. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2014, 18, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milad, N.; Pineault, M.; Lechasseur, A.; Routhier, J.; Beaulieu, M.-J.; Aubin, S.; Morissette, M.C. Neutrophils and IL-1α Regulate Surfactant Homeostasis during Cigarette Smoking. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 1923–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilecki, B.; Wulf-Johansson, H.; Støttrup, C.; Jørgensen, P.T.; Djiadeu, P.; Nexøe, A.B.; Schlosser, A.; Hansen, S.W.K.; Madsen, J.; Clark, H.W.; et al. Surfactant Protein D Deficiency Aggravates Cigarette Smoke-Induced Lung Inflammation by Upregulation of Ceramide Synthesis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeidat, M.; Li, X.; Burgess, S.; Zhou, G.; Fishbane, N.; Hansel, N.N.; Bossé, Y.; Joubert, P.; Hao, K.; Nickle, D.C.; et al. Surfactant Protein D Is a Causal Risk Factor for COPD: Results of Mendelian Randomisation. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahy, E.; Subramaniam, S.; Brown, H.A.; Glass, C.K.; Merrill, A.H.; Murphy, R.C.; Raetz, C.R.H.; Russell, D.W.; Seyama, Y.; Shaw, W.; et al. A Comprehensive Classification System for Lipids. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 839–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, K.R.; Ha, D.M.; Schwarz, M.I.; Chan, E.D. Bronchoalveolar Lavage as a Diagnostic Procedure: A Review of Known Cellular and Molecular Findings in Various Lung Diseases. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 4991–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finley, T.N.; Ladman, A.J. Low Yield of Pulmonary Surfactant in Cigarette Smokers. N. Engl. J. Med. 1972, 286, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, R.B.; Davis, G.S.; Giancola, M.S. Biochemical Analyses of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluids of Healthy Human Volunteer Smokers and Nonsmokers. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1978, 118, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Honda, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Kuroki, Y.; Akino, T.; Abe, S. Decreased Contents of Surfactant Proteins A and D in BAL Fluids of Healthy Smokers. Chest 1996, 109, 1006–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telenga, E.D.; Hoffmann, R.F.; t’Kindt, R.; Hoonhorst, S.J.M.; Willemse, B.W.M.; van Oosterhout, A.J.M.; Heijink, I.H.; van den Berge, M.; Jorge, L.; Sandra, P.; et al. Untargeted Lipidomic Analysis in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Uncovering Sphingolipids. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmekel, B.; Khan, A.R.; Linden, M.; Wollmer, P. Recoveries of Phosphatidylcholine and Alveolar Macrophages in Lung Lavage from Healthy Light Smokers. Clin. Physiol. 1991, 11, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moré, J.M.; Voelker, D.R.; Silveira, L.J.; Edwards, M.G.; Chan, E.D.; Bowler, R.P. Smoking Reduces Surfactant Protein D and Phospholipids in Patients with and without Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. BMC Pulm. Med. 2010, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.A.; Haslam, P.L. Effect of Smoking on the Lipid Composition of Lung Lining Fluid and Relationship between Immunostimulatory Lipids, Inflammatory Cells and Foamy Macrophages in Extrinsic Allergic Alveolitis. Eur. Respir. J. 1990, 3, 1128–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, N.M.; Béné, M.C.; Gérard, H.; Chabot, F.; Faure, G.; Polu, J.M.; Lesur, O. Early Effects of Short-Time Cigarette Smoking on the Human Lung: A Study of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluids. Lung 1993, 171, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moliva, J.I.; Rajaram, M.V.S.; Sidiki, S.; Sasindran, S.J.; Guirado, E.; Pan, X.J.; Wang, S.-H.; Ross, P.; Lafuse, W.P.; Schlesinger, L.S.; et al. Molecular Composition of the Alveolar Lining Fluid in the Aging Lung. Age 2014, 36, 9633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.; Wakefield, M.; Owen, N.; Roberts, L. Characteristics of Heavy Smokers. Prev. Med. 1992, 21, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rydell-Törmänen, K.; Johnson, J.R. The Applicability of Mouse Models to the Study of Human Disease. In Mouse Cell Culture: Methods and Protocols; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Morissette, M.C.; Shen, P.; Thayaparan, D.; Stämpfli, M.R. Disruption of Pulmonary Lipid Homeostasis Drives Cigarette Smoke-Induced Lung Inflammation in Mice. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.R.; Yin, F.; Cadenas, E. Short-Term Cigarette Smoke Exposure Leads to Metabolic Alterations in Lung Alveolar Cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 51, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Shibata, Y.; Yamauchi, K.; Igarashi, A.; Inoue, S.; Abe, S.; Fujita, K.; Uosaki, Y.; Kubota, I. Oxidized Phospholipid, 1-Palmitoyl-2-(9′-Oxo-Nonanoyl)-Glycerophosphocholine (PON-GPC), Produced in the Lung Due to Cigarette Smoking, Impairs Immune Function in Macrophages. Lung 2012, 190, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morissette, M.C.; Lamontagne, M.; Bérubé, J.C.; Gaschler, G.; Williams, A.; Yauk, C.; Couture, C.; Laviolette, M.; Hogg, J.C.; Timens, W.; et al. Impact of Cigarette Smoke on the Human and Mouse Lungs: A Gene-Expression Comparison Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churg, A.; Cosio, M.; Wright, J.L. Mechanisms of Cigarette Smoke-Induced COPD: Insights from Animal Models. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2008, 294, L612–L631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, S. Biochemical and Biophysical Characterization of Pulmonary Surfactant in Rats Exposed Chronically to Cigarette Smoke. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1995, 27, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvin, C.G.; Bates, J.H.T. Measuring the Lung Function in the Mouse: The Challenge of Size. Respir. Res. 2003, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titz, B.; Szostak, J.; Sewer, A.; Phillips, B.; Nury, C.; Schneider, T.; Dijon, S.; Lavrynenko, O.; Elamin, A.; Guedj, E.; et al. Multi-Omics Systems Toxicology Study of Mouse Lung Assessing the Effects of Aerosols from Two Heat-Not-Burn Tobacco Products and Cigarette Smoke. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1056–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elamin, A.; Titz, B.; Dijon, S.; Merg, C.; Geertz, M.; Schneider, T.; Martin, F.; Schlage, W.K.; Frentzel, S.; Talamo, F.; et al. Quantitative Proteomics Analysis Using 2D-PAGE to Investigate the Effects of Cigarette Smoke and Aerosol of a Prototypic Modified Risk Tobacco Product on the Lung Proteome in C57BL/6 Mice. J. Proteom. 2016, 145, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, V.B. New Appreciation for an Old Pathway: The Lands Cycle Moves into New Arenas in Health and Disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2022, 50, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiba, S.; Dodia, C.; Chen, X.; Fisher, A.B. Characterization of Acidic Ca2+-Independent Phospholipase A2 of Bovine Lung. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998, 120, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titz, B.; Boué, S.; Phillips, B.; Talikka, M.; Vihervaara, T.; Schneider, T.; Nury, C.; Elamin, A.; Guedj, E.; Peck, M.J.; et al. Effects of Cigarette Smoke, Cessation, and Switching to Two Heat-Not-Burn Tobacco Products on Lung Lipid Metabolism in C57BL/6 and Apoe −/− Mice—An Integrative Systems Toxicology Analysis. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 149, 441–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beers, M.F.; Mulugeta, S. The Biology of the ABCA3 Lipid Transporter in Lung Health and Disease. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 367, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Pu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Ye, S.; Ma, Q.; Ren, J.; Cao, Z.; Zhong, G.; Zhang, X.; et al. The Effects and Mechanisms of SLC34A2 in Tumorigenesis and Progression of Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 22, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanosaki, T.; Mikami, Y.; Shindou, H.; Suzuki, T.; Hashidate-Yoshida, T.; Hosoki, K.; Kagawa, S.; Miyata, J.; Kabata, H.; Masaki, K.; et al. Lysophosphatidylcholine Acyltransferase 1 Deficiency Promotes Pulmonary Emphysema via Apoptosis of Alveolar Epithelial Cells. Inflammation 2022, 45, 1765–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rijt, S.H.; Keller, I.E.; John, G.; Kohse, K.; Yildirim, A.Ö.; Eickelberg, O.; Meiners, S. Acute Cigarette Smoke Exposure Impairs Proteasome Function in the Lung. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2012, 303, L814–L823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammerl, I.E.; Caniard, A.; Merl-Pham, J.; Ben-Nissan, G.; Mayr, C.H.; Mossina, A.; Geerlof, A.; Eickelberg, O.; Hauck, S.M.; Sharon, M.; et al. Dissecting the Molecular Effects of Cigarette Smoke on Proteasome Function. J. Proteom. 2019, 193, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betsuyaku, T.; Kuroki, Y.; Nagai, K.; Nasuhara, Y.; Nishimura, M. Effects of Ageing and Smoking on SP-A and SP-D Levels in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 24, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, C.; Atochina-Vasserman, E.N.; Holz, O.; Beers, M.F.; Erpenbeck, V.J.; Krug, N.; Roepcke, S.; Lauer, G.; Elmlinger, M.; Hohlfeld, J.M. Comprehensive Characterisation of Pulmonary and Serum Surfactant Protein D in COPD. Respir. Res. 2011, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moazed, F.; Burnham, E.L.; Vandivier, R.W.; O’Kane, C.M.; Shyamsundar, M.; Hamid, U.; Abbott, J.; Thickett, D.R.; Matthay, M.A.; McAuley, D.F.; et al. Cigarette Smokers Have Exaggerated Alveolar Barrier Disruption in Response to Lipopolysaccharide Inhalation. Thorax 2016, 71, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koca, H.; Farbrot, A.; Olin, A.-C.; Emilsson, Ö.I. Surfactant Protein A in Particles in Exhaled Air and Plasma. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2022, 301, 103899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, S.; Whitsett, J.A.; Hull, W.; Gairola, C.G. Alteration of Pulmonary Surfactant Proteins in Rats Chronically Exposed to Cigarette Smoke. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1996, 140, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirama, N.; Shibata, Y.; Otake, K.; Machiya, J.I.; Wada, T.; Inoue, S.; Abe, S.; Takabatake, N.; Sata, M.; Kubota, I. Increased Surfactant Protein-D and Foamy Macrophages in Smoking-Induced Mouse Emphysema. Respirology 2007, 12, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.W.; Lin, Y.N.; Ding, Y.J.; Li, S.Q.; Li, H.P.; Zhou, J.P.; Zhang, L.; Shen, J.M.; Li, Q.Y. Surfaxin Attenuates PM2.5-Induced Airway Inflammation via Restoring Surfactant Proteins in Rats Exposed to Cigarette Smoke. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.S.; Yadav, B.; Yadav, E.; Hus, A.; Yadav, N.; Kaur, P.; Rosen, L.; Jandarov, R.; Yadav, J.S. Differential Modulation of Lung Aquaporins among Other Pathophysiological Markers in Acute (Cl2 Gas) and Chronic (Carbon Nanoparticles, Cigarette Smoke) Respiratory Toxicity Mouse Models. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 880815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Ikegami, M.; Moon, C.; Naren, A.P.; Shannon, J.M. Lysophosphatidylcholine Acyltransferase 1 (LPCAT1) Specifically Interacts with Phospholipid Transfer Protein StarD10 to Facilitate Surfactant Phospholipid Trafficking in Alveolar Type II Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 18559–18574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stormberg, T.; Vemulapalli, S.; Filliaux, S.; Lyubchenko, Y.L. Effect of Histone H4 Tail on Nucleosome Stability and Internucleosomal Interactions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, I.K.; Chung, S.; Hwang, J.-W.; Arunachalam, G.; Cook, S.; Yao, H.; Mazur, W.; Kinnula, V.L.; Fisher, A.B.; Rahman, I. Peroxiredoxin 6 Differentially Regulates Acute and Chronic Cigarette Smoke–Mediated Lung Inflammatory Response and Injury. Exp. Lung Res. 2010, 36, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, A.B.; Dodia, C.; Manevich, Y.; Chen, J.-W.; Feinstein, S.I. Phospholipid Hydroperoxides Are Substrates for Non-Selenium Glutathione Peroxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 21326–21334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokina, E.M.; Dodia, C.; Zhou, S.; Tao, J.-Q.; Gao, L.; Raabe, T.; Feinstein, S.I.; Fisher, A.B. Mutation of Serine 32 to Threonine in Peroxiredoxin 6 Preserves Its Structure and Enzymatic Function but Abolishes Its Trafficking to Lamellar Bodies. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 9268–9280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, A.B.; Dodia, C.; Sorokina, E.M.; Li, H.; Zhou, S.; Raabe, T.; Feinstein, S.I. A Novel Lysophosphatidylcholine Acyl Transferase Activity Is Expressed by Peroxiredoxin 6. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M. The Phospholipase A2 Superfamily as a Central Hub of Bioactive Lipids and Beyond. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 244, 108382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraj, P.; Sivaprakasam, C.; Varthini, L.V.; Sarkar, M.; Nachiappan, V. In Vitro Exposure of Tobacco Specific Nitrosamines Decreases the Rat Lung Phospholipids by Enhanced Phospholipase A2 Activity. Toxicol. In Vitro 2014, 28, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballweg, K.; Mutze, K.; Königshoff, M.; Eickelberg, O.; Meiners, S. Cigarette Smoke Extract Affects Mitochondrial Function in Alveolar Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 307, L895–L907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Sundar, I.K.; Lerner, C.A.; Gerloff, J.; Tormos, A.M.; Yao, H.; Rahman, I. Impaired Mitophagy Leads to Cigarette Smoke Stress-induced Cellular Senescence: Implications for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 2912–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravamudan, B.; Kiel, A.; Freeman, M.; Delmotte, P.; Thompson, M.; Vassallo, R.; Sieck, G.C.; Pabelick, C.M.; Prakash, Y.S. Cigarette Smoke-Induced Mitochondrial Fragmentation and Dysfunction in Human Airway Smooth Muscle. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L840–L854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.F.; Zarrintan, S.; Brandenburg, S.M.; Kol, A.; de Bruin, H.G.; Jafari, S.; Dijk, F.; Kalicharan, D.; Kelders, M.; Gosker, H.R.; et al. Prolonged Cigarette Smoke Exposure Alters Mitochondrial Structure and Function in Airway Epithelial Cells. Respir. Res. 2013, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandhok, G.; Lazarou, M.; Neumann, B. Structure, Function, and Regulation of Mitofusin-2 in Health and Disease. Biol. Rev. 2018, 93, 933–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.-P.; Hsu, C.-L.; Fan, L.-C.; Huang, Z.; Bhatia, D.; Chen, Y.-J.; Hisata, S.; Cho, S.J.; Nakahira, K.; Imamura, M.; et al. Mitofusins Regulate Lipid Metabolism to Mediate the Development of Lung Fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacharioudakis, E.; Agianian, B.; Kumar Mv, V.; Biris, N.; Garner, T.P.; Rabinovich-Nikitin, I.; Ouchida, A.T.; Margulets, V.; Nordstrøm, L.U.; Riley, J.S.; et al. Modulating Mitofusins to Control Mitochondrial Function and Signaling. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yue, J.; Fang, Q.; Gong, X. Cryo-EM Structures of the Human Surfactant Lipid Transporter ABCA3. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindlbeck, U.; Wittmann, T.; Höppner, S.; Kinting, S.; Liebisch, G.; Hegermann, J.; Griese, M. ABCA3 Missense Mutations Causing Surfactant Dysfunction Disorders Have Distinct Cellular Phenotypes. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; Fang, X.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, S.; Song, J. Cigarette Smoke Extract Combined with LPS Reduces ABCA3 Expression in Chronic Pulmonary Inflammation May Be Related to PPARγ/P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 244, 114086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubinville, É.; Talbot, M.; Bérubé, J.-C.; Hamel-Auger, M.; Maranda-Robitaille, M.; Beaulieu, M.-J.; Aubin, S.; Paré, M.-È.; Kallend, D.G.; Arsenault, B.; et al. Interplay between Cigarette Smoking and Pulmonary Reverse Lipid Transport. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.R.; Tao, J.-Q.; Collins, H.L.; Francone, O.L.; Rothblat, G.H. Pulmonary Abnormalities Due to ABCA1 Deficiency in Mice. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2005, 289, L980–L989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietl, P.; Frick, M. Channels and Transporters of the Pulmonary Lamellar Body in Health and Disease. Cells 2021, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, H.; Schmidt, M. Acute Influence of Cigarette Smoke on Secretion of Pulmonary Surfactant in Rat Alveolar Type II Cells in Culture. Eur. Respir. J. 1996, 9, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Merfort, I.; Idzko, M.; Zech, A. Blocking P2X Purinoceptor 4 Signalling Alleviates Cigarette Smoke Induced Pulmonary Inflammation. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucattelli, M.; Cicko, S.; Müller, T.; Lommatzsch, M.; De Cunto, G.; Cardini, S.; Sundas, W.; Grimm, M.; Zeiser, R.; Dürk, T.; et al. P2X7 Receptor Signaling in the Pathogenesis of Smoke-Induced Lung Inflammation and Emphysema. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 44, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirsching, E.; Fauler, M.; Fois, G.; Frick, M. P2 Purinergic Signaling in the Distal Lung in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringezu, F.; Pinkerton, K.E.; Zasadzinski, J.A. Environmental Tobacco Smoke Effects on the Primary Lipids of Lung Surfactant. Langmuir 2003, 19, 2900–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenger, P.C.; Alonso, C.; Zasadzinski, J.A.; Waring, A.J.; Jung, C.-L.; Pinkerton, K.E. Environmental Tobacco Smoke Effects on Lung Surfactant Film Organization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Biomembr. 2009, 1788, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, E.; Vogel, U.; Hougaard, K.S.; Pérez-Gil, J.; Zuo, Y.Y.; Sørli, J.B. An Adverse Outcome Pathway for Lung Surfactant Function Inhibition Leading to Decreased Lung Function. Curr. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 2, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowicz-Kuśnierz, A.; Cwiklik, L.; Korchowiec, J.; Rogalska, E.; Korchowiec, B. The Impact of Lipid Oxidation on the Functioning of a Lung Surfactant Model. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 24968–24978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; Leach, A.G.; Fullwood, D.; Mistry, D.; Hope, A. The PH Dependent Interaction between Nicotine and Simulated Pulmonary Surfactant Monolayers with Associated Molecular Modelling. Surf. Interface Anal. 2017, 49, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhivaki, D.; Kagan, J.C. Innate Immune Detection of Lipid Oxidation as a Threat Assessment Strategy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Xie, F.; Liu, K.; Liu, H.; Xie, J. Evaluation of Whole Cigarette Smoke Induced Oxidative Stress in A549 and BEAS–2B Cells. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 54, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataya, A.; Knight, V.; Carey, B.C.; Lee, E.; Tarling, E.J.; Wang, T. The Role of GM-CSF Autoantibodies in Infection and Autoimmune Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis: A Concise Review. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 752856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugg, S.T.; Scott, A.; Parekh, D.; Naidu, B.; Thickett, D.R. Cigarette Smoke Exposure and Alveolar Macrophages: Mechanisms for Lung Disease. Thorax 2022, 77, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamiya, R.; Takahashi, M.; Maeno, T.; Saito, A.; Kato, M.; Shibata, T.; Uchida, K.; Ariki, S.; Nakano, M. Acrolein in Cigarette Smoke Attenuates the Innate Immune Responses Mediated by Surfactant Protein D. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Gen. Subj. 2020, 1864, 129699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.H.; Chen, P.C.; Hsu, H.Y.; Liu, J.C.; Ho, Y.S.; Lin, Y.J.; Kuo, C.W.; Kuo, W.S.; Kao, H.F.; Wang, S.-D.; et al. Surfactant Protein D Inhibits Lipid-Laden Foamy Macrophages and Lung Inflammation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 20, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Lu, W.; Sun, D. Pulmonary Surfactant-associated Protein B Regulates Prostaglandin-endoperoxide Synthase-2 and Inflammation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Exp. Physiol. 2021, 106, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, M.; Horiuchi, T.; Nagai, J.; Yumoto, R. Effect of Cigarette Smoke Extract on Insulin Transport in Alveolar Epithelial Cell Line A549. Lung 2012, 190, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, U.M.; Ashna, U.; Kumar, S.S.P.; Nandkumar, A.M. Effect of Tobacco Extract on Surfactant Synthesis and Its Reversal by Retinoic Acid—Role of Cell–Cell Interactions in Vitro. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2013, 49, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puthusseri, B.; Marudamuthu, A.; Tiwari, N.; Fu, J.; Idell, S.; Shetty, S. Regulation of P53-Mediated Changes in the UPA-Fibrinolytic System and in Lung Injury by Loss of Surfactant Protein C Expression in Alveolar Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 312, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Gil, J.; Weaver, T.E. Pulmonary Surfactant Pathophysiology: Current Models and Open Questions. Physiology 2010, 25, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsen, S.G.; Duan, X.; Ji, R.; Perez, O.; Liu, C.; Merali, S. Cigarette Smoke Induces an Unfolded Protein Response in the Human Lung. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noutsios, G.T.; Ghattas, P.; Bennett, S.; Floros, J. 14-3-3 Isoforms Bind Directly Exon B of the 5′-UTR of Human Surfactant Protein A2 MRNA. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2015, 309, L147–L157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floros, J.; Tsotakos, N. Differential Regulation of Human Surfactant Protein A Genes, SFTPA1 and SFTPA2, and Their Corresponding Variants. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 766719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, K.N.; Mendelson, C.R. Potential Role of Nuclear Factor ΚB and Reactive Oxygen Species in CAMP and Cytokine Regulation of Surfactant Protein-A Gene Expression in Lung Type II Cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2002, 16, 1428–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Tian, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, W.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, W. Apoptosis and Surfactant Protein-C Expression Inhibition Induced by Lipopolysaccharide in AEC II Cell May Associate with NF-ΚB Pathway. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 42, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.-L.; Chuang, C.-Y.; Tai, Y.-T.; Tang, H.-L.; Chen, T.-G.; Chen, T.-L.; Chen, R.-M. Lipoteichoic Acid Induces Surfactant Protein-A Biosynthesis in Human Alveolar Type II Epithelial Cells through Activating the MEK1/2-ERK1/2-NF-ΚB Pathway. Respir. Res. 2012, 13, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhane, K.; Margana, R.K.; Boggaram, V. Characterization of Rabbit SP-B Promoter Region Responsive to Downregulation by Tumor Necrosis Factor-α. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2000, 279, L806–L814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitsett, J.A.; Glasser, S.W. Regulation of Surfactant Protein Gene Transcription. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Mol. Basis Dis. 1998, 1408, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Crouch, E. Surfactant Protein D Gene regulation: Interactions among the conserved CCAAT/Enhancer-binding protein elements. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 19530–19537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Crouch, E.C.; Rust, K.; Spaite, E.; Brody, S.L. Proximal Promoter of the Surfactant Protein D Gene: Regulatory roles of AP-1, forkhead box, and GT box binding proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 31051–31060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, P.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, M.; Shi, F.; Li, N.; Jin, Y. Silica Nanoparticle Exposure Inhibits Surfactant Protein A and B in A549 Cells through ROS-Mediated JNK/c-Jun Signaling Pathway. Environ. Toxicol. 2022, 37, 2291–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasnick, R.; Korfei, M.; Piskulak, K.; Henneke, I.; Wilhelm, J.; Mahavadi, P.; Dartsch, R.C.; von der Beck, D.; Koch, M.; Shalashova, I.; et al. Notch1 Induces Defective Epithelial Surfactant Processing and Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladenburger, A.; Seehase, M.; Kramer, B.W.; Thomas, W.; Wirbelauer, J.; Speer, C.P.; Kunzmann, S. Glucocorticoids Potentiate IL-6-Induced SP-B Expression in H441 Cells by Enhancing the JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2010, 299, L578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, Y.; Besnard, V.; Clark, J.C.; Xu, Y.; Wert, S.E.; Ikegami, M.; Whitsett, J.A. STAT3 Regulates ABCA3 Expression and Influences Lamellar Body Formation in Alveolar Type II Cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 38, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiappara, G.; Di Vincenzo, S.; Sangiorgi, C.; Di Sano, C.; D’Anna, C.; Zito, G.; Cipollina, C.; Vitulo, P.; Bertani, A.; Pace, E. Cigarette Smoke Upregulates Notch-1 Signaling Pathway and Promotes Lung Adenocarcinoma Progression. Toxicol. Lett. 2022, 355, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borggrefe, T.; Oswald, F. The Notch Signaling Pathway: Transcriptional Regulation at Notch Target Genes. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 1631–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, C.G.; Mosley, D.D.; Kharbanda, K.K.; Katafiasz, D.M.; Bailey, K.L.; Wyatt, T.A. Malondialdehyde Acetaldehyde-Adduction Changes Surfactant Protein D Structure and Function. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.W.; Neff, L.J.; Park-Lee, E.; Ren, C.; Cullen, K.A.; King, B.A. E-Cigarette Use Among Middle and High School Students—United States, 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1310–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalininskiy, A.; Kittel, J.; Nacca, N.E.; Misra, R.S.; Croft, D.P.; McGraw, M.D. E-Cigarette Exposures, Respiratory Tract Infections, and Impaired Innate Immunity: A Narrative Review. Pediatr. Med. 2021, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; English, S.; Ogilvie, J.A.; Siu, M.K.M.; Tammara, A.; Haas, C.J. All up in Smoke: Vaping-Associated Lung Injury. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2020, 10, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blount, B.C.; Karwowski, M.P.; Shields, P.G.; Morel-Espinosa, M.; Valentin-Blasini, L.; Gardner, M.; Braselton, M.; Brosius, C.R.; Caron, K.T.; Chambers, D.; et al. Vitamin E Acetate in Bronchoalveolar-Lavage Fluid Associated with EVALI. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivarelli, F.; Granata, S.; Rullo, L.; Mussoni, M.; Candeletti, S.; Romualdi, P.; Fimognari, C.; Cruz-Chamorro, I.; Carrillo-Vico, A.; Paolini, M.; et al. On the Toxicity of E-Cigarettes Consumption: Focus on Pathological Cellular Mechanisms. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 182, 106315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goniewicz, M.L.; Knysak, J.; Gawron, M.; Kosmider, L.; Sobczak, A.; Kurek, J.; Prokopowicz, A.; Jablonska-Czapla, M.; Rosik-Dulewska, C.; Havel, C.; et al. Levels of Selected Carcinogens and Toxicants in Vapour from Electronic Cigarettes. Tob. Control 2014, 23, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, E.; McCaig, L.; Shui-Kei Lau, G.; Tejura, A.; Cao, A.; Zuo, Y.Y.; Veldhuizen, R. E-Cigarette Aerosol Exposure of Pulmonary Surfactant Impairs Its Surface Tension Reducing Function. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; Birkett, J.W.; Kotwa, M.; Tomlinson, L.; Woldetinsae, R. The Impact of Cigarette/e-Cigarette Vapour on Simulated Pulmonary Surfactant Monolayers under Physiologically Relevant Conditions. Surf. Interface Anal. 2017, 49, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipasquale, M.; Gbadamosi, O.; Nguyen, M.H.L.; Castillo, S.R.; Rickeard, B.W.; Kelley, E.G.; Nagao, M.; Marquardt, D. A Mechanical Mechanism for Vitamin E Acetate in E-Cigarette/Vaping-Associated Lung Injury. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 2432–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayeck, N.; Zoghzoghi, C.; Karam, E.; Salman, R.; Karaoghlanian, N.; Shihadeh, A.; Eissenberg, T.; Zein, S.; Dine, E.; Saliba, N.A. Carrier Solvents of Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems Alter Pulmonary Surfactant. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 34, 1572–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bavel, N.; Lai, P.; Loebenberg, R.; Prenner, E.J. Vaping Additives Negatively Impact the Stability and Lateral Film Organization of Lung Surfactant Model Systems. Nanomedicine 2022, 17, 827–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyla, R.J.; Wright, J.; Parthiban, R.; Nazemidashtarjandi, S.; Kaya, S.; Farnoud, A.M. Electronic Cigarette Vapor Alters the Lateral Structure but Not Tensiometric Properties of Calf Lung Surfactant. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnowski, T.R.; Jabłczyńska, K.; Odziomek, M.; Schlage, W.K.; Kuczaj, A.K. Physicochemical Studies of Direct Interactions between Lung Surfactant and Components of Electronic Cigarettes Liquid Mixtures. Inhal. Toxicol. 2018, 30, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, M.C.; Landers, C.T.; Gu, B.H.; Chang, C.Y.; Tung, H.Y.; You, R.; Hong, M.J.; Baghaei, N.; Song, L.Z.; Porter, P.; et al. Electronic Cigarettes Disrupt Lung Lipid Homeostasis and Innate Immunity Independent of Nicotine. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 129, 4290–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szafran, B.N.; Pinkston, R.; Perveen, Z.; Ross, M.K.; Morgan, T.; Paulsen, D.B.; Penn, A.L.; Kaplan, B.L.F.; Noël, A. Electronic-Cigarette Vehicles and Flavoring Affect Lung Function and Immune Responses in a Murine Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ji, X.; Rahman, I. Dysregulated Metabolites Serve as Novel Biomarkers for Metabolic Diseases Caused by E-Cigarette Vaping and Cigarette Smoking. Metabolites 2021, 11, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, N.D.; Grimmer, J.A.; Tanwar, V.; Schwieterman, N.; Mohler, P.J.; Wold, L.E. Cardiovascular Risk of Electronic Cigarettes: A Review of Preclinical and Clinical Studies. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, R.P.; Jacobson, S.; Cruickshank, C.; Hughes, G.J.; Siska, C.; Ory, D.S.; Petrache, I.; Schaffer, J.E.; Reisdorph, N.; Kechris, K. Plasma Sphingolipids Associated with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Phenotypes. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberg, A.J.; Armeson, K.; Pierce, J.S.; Bielawski, J.; Bielawska, A.; Visvanathan, K.; Hill, E.G.; Ogretmen, B. Plasma Sphingolipids and Lung Cancer: A Population-Based, Nested Case–Control Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2013, 22, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, I.R.; Bersten, A.D.; Nicholas, T.E. Surfactant Proteins-A and-B Are Elevated in Plasma of Patients with Acute Respiratory Failure. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banfi, C.; Brioschi, M.; Mapelli, M.; Gianazza, E.; Mallia, A.; Zoanni, B.; Salvioni, E.; Gugliandolo, P.; Capra, N.; Veglia, F.; et al. Immature Circulating SP-B, Bound to HDL, Represents an Early Sign of Smoke-Induced Pathophysiological Alterations. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgård, C.; Wang, F.; Titlestad, I.L.; Kyvik, K.O.; Vestbo, J.; Sorensen, G.L. Increased Serum SP-D in Identification of High-Risk Smokers at High Risk of COPD. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2021, 320, L1005–L1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinci Ozyurek, B.; Sarinc Ulasli, S.; Savas Bozbas, S.; Bayraktar, N.; Akcay, S. Value of Serum and Induced Sputum Surfactant Protein-D in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2013, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulf-Johansson, H.; Støttrup, C.; Hansen, S.; Schlosser, A.; Stevenson, C.; Holmskov, U.; Sorensen, G. Surfactant Protein D and It Role on Inflammatory Responses in the Cigarette-Induced COPD Model. Pneumologie 2012, 66, P2_009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkesson, H.G.; Matthay, M.A.; Westrom, B.R.; Kim, K.J.; Karlsson, B.W.; Hastings, R.H.; Westriim, B.R.; Karlsson, B.W.; Hastings, R.H. Alveolar Epithelial Clearance of Protein. J. Appl. Physiol. 1996, 80, 1431–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthiaume, Y.; Albertine, K.H.; Grady, M.; Fick, G.; Matthay, M.A. Protein clearance from the air spaces and lungs of unanesthetized sheep over 144 h. J. Appl. Physiol. 1989, 67, 1887–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, I.R.; Nicholas, T.E.; Bersten, A.D. Partitioning Lung and Plasma Proteins: Circulating Surfactant Proteins as Biomarkers of Alveolocapillary Permeability. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1999, 26, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waseem, H.M.; Khan, R.A.; Parvez Lone, K. Plasma surfactant protein—A levels in healthy subjects and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. J. Ayub Med. Coll. Abbottabad 2020, 32, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Agustama, A.; Surgean Veterini, A.; Utariani, A. Correlation of Surfactant Protein-D (SP-D) Serum Levels with ARDS Severity and Mortality in Covid-19 Patients in Indonesia. Acta Med. Acad. 2022, 51, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayadi; Airlangga, P.S.; Kusuma, E.; Waloejo, C.S.; Salinding, A.; Lestari, P. Correlation between Serum Surfactant Protein-D Level with Respiratory Compliance and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Observational Study. Int. J. Crit. Illn. Inj. Sci. 2022, 12, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvioni, L.; Testa, F.; Sulejmani, A.; Pepe, F.; Giorgio Lovaglio, P.; Berta, P.; Dominici, R.; Leoni, V.; Prosperi, D.; Vittadini, G.; et al. Surfactant Protein D (SP-D) as a Biomarker of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Clin. Chim. Acta 2022, 537, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiezzi, M.; Morra, S.; Seminerio, J.; Van Muylem, A.; Godefroid, A.; Law-Weng-Sam, N.; Van Praet, A.; Corbière, V.; Orte Cano, C.; Karimi, S.; et al. SP-D and CC-16 Pneumoproteins’ Kinetics and Their Predictive Role During SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Front. Med. 2022, 8, 761299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togashi, Y.; Kono, Y.; Okuma, T.; Shioiri, N.; Mizushima, R.; Tanaka, A.; Ishiwari, M.; Toriyama, K.; Kikuchi, R.; Takoi, H.; et al. Surfactant Protein D: A Useful Biomarker for Distinguishing COVID-19 Pneumonia from COVID-19 Pneumonia-like Diseases. Health Sci. Rep. 2022, 5, e622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, C.; Xu, H.; Zheng, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Zou, L.; Xiao, X.; Chen, F.; Yan, X.; et al. Serum Surfactant Protein D in COVID-19 Is Elevated and Correlated with Disease Severity. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, A.; Hanash, S.; Rundle, A.; McKeague, I.W.; Tang, D.; Darakjy, S.; Gaziano, J.M.; Sesso, H.D.; Perera, F. Circulating Pro-Surfactant Protein B as a Risk Biomarker for Lung Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2013, 22, 1756–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sin, D.; Tammemagi, C.M.; Lam, S.; Barnett, M.J.; Duan, X.; Tam, A.; Auman, H.; Feng, Z.; Goodman, G.E.; Hanash, S.; et al. Pro-Surfactant Protein B as a Biomarker for Lung Cancer Prediction. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 4536–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guida, F.; Sun, N.; Bantis, L.E.; Muller, D.C.; Li, P.; Taguchi, A.; Dhillon, D.; Kundnani, D.L.; Patel, N.J.; Yan, Q.; et al. Assessment of Lung Cancer Risk on the Basis of a Biomarker Panel of Circulating Proteins. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, e182078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourad, B.H. Prediction of Lung Cancer Risk Using Circulating Pro-Surfactant Protein B and High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein among Egyptian Workers in the Rubber Industry. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2020, 36, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiels, M.S.; Kirk, G.D.; Drummond, M.B.; Dhillon, D.; Hanash, S.M.; Taguchi, A.; Engels, E.A. HIV Infection and Circulating Levels of Prosurfactant Protein B and Surfactant Protein D. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 217, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Subjects | Smoking Habit | Analysis | SP-A | SP-B | SP-C | SP-D | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Never smokers: 12 (aged 18 to 33 years). Current smokers: 8 (aged 24 to 48 years). | LS and HS | Acellular BAL |  |  | [98] | ||
| Never smokers: 22 (15 young, 7 elderly). Current smokers: 82 (20 young, 62 elderly). | ND | Acellular BL and BAL |  |  | [124] | ||
| Never smokers: 10 (21–36 years), young smokers: 10 (21–49 years), elderly smokers: 20 (40–75 years), elderly smokers with COPD: 20 (40–75 years). | ND | Acellular BAL |  | [125] | |||
| Never smokers: 10, mean age 40 years. Current smokers: 10, mean age 40 years | ND | Acellular BAL |  | [126] | |||
| Never smokers: 29, mean age 52 years. Current smokers: 37, mean age 59 years | LS | PEx |  | [54] | |||
| Never smokers: 97, age 42–67 years. Current smokers: 12, age 42–67 years | ND | PEx |  | [127] |
| Organism | Type and Time of Exposure | Analysis | SP-A | SP-B | SP-C | SP-D | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female Sprague-Dawley rats, 10 controls (5 not treated, 5 sham-treated), 5 CS exposed. | 2 cigarettes/day, 7 days/week, for 70 weeks | Acellular BAL Total mRNA and proteins from lung tissue |   |   | [128] | ||
| Male B6C3F1 mice, 20 controls, 20 CS exposed. | 2 cigarettes/day, 5 days/week, for 6 months | Acellular BAL and total mRNA from lung tissue |  | [129] | |||
| Male C57BL/6N wild type (WT) n = 5–7 | 2 rounds of exposure to CS of 50 min each, with a smoke-free interval of 30 min, 5 day/week for 12 weeks or for 3 days | Acellular BAL |  | [92] | |||
| Female BALB/c mice, 5 controls, 5 CS exposed | 2 h every morning for 4 days to the mainstream CS of 24 cigarettes with filters removed | Acellular BAL |  |  | [91] | ||
| Male Wistar rats, 10 controls, 10 CS exposed | 2 cigarettes/day for 45 days | Total proteins of lung tissue |  |  |  |  | [130] |
| C57BL/6J mice, 4 controls, 4 CS exposed | 30 µL/day of CSE administered via oropharyngeal instillation for 4 weeks | Total mRNA of lung tissue |  | [131] |
| Cell Line | Type and Time of Exposure | Analysis | SP-A | SP-B | SP-C | SP-D | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-549 | 30 mg/mL CSE for 48 h | Total mRNA |  | [169] | |||
| A-549 | Tobacco extract (100 μg/mL) for 1 h | Total mRNA |  |  |  |  | [170] |
| Primary HAEC | 2.5% CSE for 48 h | Total mRNA |  | [171] | |||
| A-549 | 10% CSE for 24 h | Total mRNA and proteins |  | [168] |
| Nature of Lipid Film | Component Tested | Method | Results | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixture of DPPC, POPG and PA | E-cigarette vapor | Langmuir trough simulating the alveolar environment | Reduced compressibility of surfactant film and impaired capacity to reduce the surface tension. | [197] |
| Calf lung surfactant extract | Different volumes of cigarette smoke or e-cigarette vapor bubbled in the subphase | Langmuir trough and atomic force microscopy | Both e-cigarette vapor and conventional cigarette smoke affect surfactant lateral structure; only cigarette smoke disrupts surfactant interfacial properties. | [201] |
| Calf lung surfactant extract | PG and VG at different proportions and concentrations added to the surfactant | Dynamic surface tension measured under a simulated breathing cycle using drop shape method | Only e-liquid concentrations > 200× higher than the estimated average dose after a single puffing session induced measurable changes in surfactant biophysical activity and only ultra-high concentrations inactivated the surfactant. | [202] |
| Pure DPPC or lipid mixture (DPPC/POPC/POPG/Chol) | Vitamin E acetate added to the lipid mixture | Neutron spin echo spectroscopy | Vitamin E acetate increased phospholipids membrane fluidity and compressibility. | [198] |
| Pure DPPC | Aerosol of liquid composed by PG and VG | Attenuated total reflectance-Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy | PG and VG modified the molecular alignment of the DPPC surfactant, affecting the surface tension at the air-water interface. | [199] |
| DPPC and POPG mixture | 5 mol% of vaping additives (vitamins and/or cannabinoids) added to the DPPC and POPG mixture | Langmuir-Blodgett trough and Brewster angle microscopy | Vaping additives negatively impact lipid packing and film stability, induce material loss upon cycling and significantly reduce functionally relevant lipid domains. | [200] |
| Bovine lipid extract surfactant | Vapor of a mixture of PG and VG at different ratios and with different devices with or without flavoring and nicotine | Constrained drop surfactometer | Minimum surface tension increased significantly after exposure to the e-cigarette aerosol. Variations in device used, addition of nicotine and temperature of the aerosol had no additional effect. Two e-liquid flavors, menthol and red wedding, had further detrimental effects. | [196] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garavaglia, M.L.; Bodega, F.; Porta, C.; Milzani, A.; Sironi, C.; Dalle-Donne, I. Molecular Impact of Conventional and Electronic Cigarettes on Pulmonary Surfactant. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11702. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411702
Garavaglia ML, Bodega F, Porta C, Milzani A, Sironi C, Dalle-Donne I. Molecular Impact of Conventional and Electronic Cigarettes on Pulmonary Surfactant. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(14):11702. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411702
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaravaglia, Maria Lisa, Francesca Bodega, Cristina Porta, Aldo Milzani, Chiara Sironi, and Isabella Dalle-Donne. 2023. "Molecular Impact of Conventional and Electronic Cigarettes on Pulmonary Surfactant" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 14: 11702. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411702
APA StyleGaravaglia, M. L., Bodega, F., Porta, C., Milzani, A., Sironi, C., & Dalle-Donne, I. (2023). Molecular Impact of Conventional and Electronic Cigarettes on Pulmonary Surfactant. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(14), 11702. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411702









