Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Exposure on Human Glial Cells and Zebrafish Embryos
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of ZnO NPs
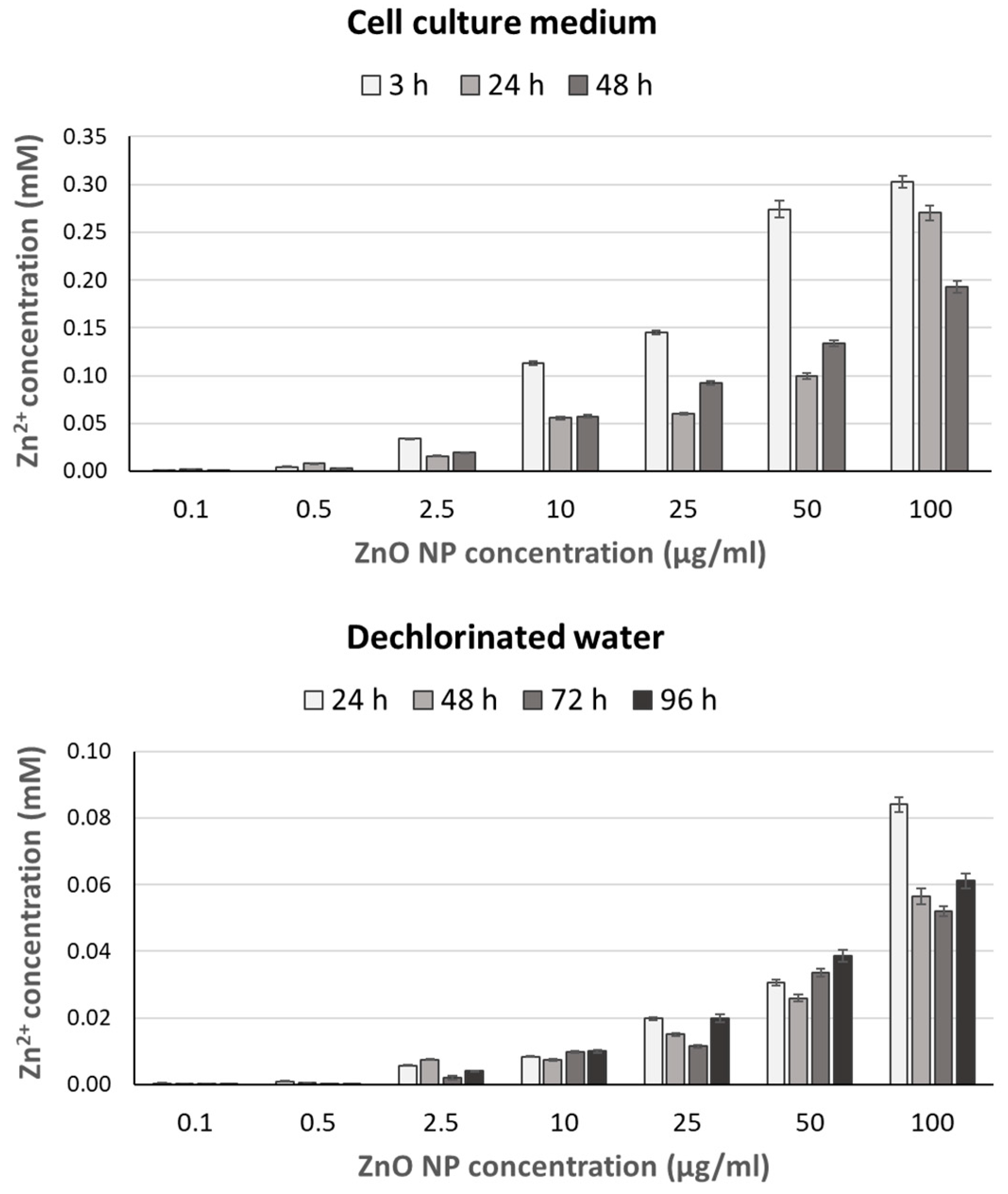
2.2. Zn2+ Ion Release
2.3. Cellular Morphology
2.4. Cell Viability Assay
2.5. Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity Assay
2.6. Zebrafish Morphological Alterations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Nanoparticle Suspension: Preparation and Characterization
4.3. Cell Culture and Treatments
4.4. Morphological Analysis
4.5. Cellular Viability
4.6. Zebrafish Husbandry and Embryo Collection
4.7. Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity Assay
4.8. Morphological Analysis of Zebrafish Embryos
4.9. Zinc Ions Released from the ZnO NPs
4.10. Toxicity of Zn2+ Ions
4.11. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, J.; Tang, J.; Xu, S.; Ge, J.; Dong, Y.; Li, H.; Jin, M. ZnO Nanoparticles: Recent Advances in Ecotoxicity and Risk Assessment. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 43, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.E.; Li, Z.H.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, Y.F.; Jin, Y.F.; Tang, Z.X. Synthesis, Antibacterial Activity, Antibacterial Mechanism and Food Applications of ZnO Nanoparticles: A Review. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2014, 31, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Impacts: Cytotoxicity, Genotoxicity, Developmental Toxicity, and Neurotoxicity. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2019, 29, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smaoui, S.; Chérif, I.; Ben Hlima, H.; Khan, M.U.; Rebezov, M.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Sarkar, T.; Shariati, M.A.; Lorenzo, J.M. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Meat Packaging: A Systematic Review of Recent Literature. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2023, 36, 101045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geremew, A.; Carson, L.; Woldesenbet, S.; Wang, H.; Reeves, S.; Brooks, N.; Saganti, P.; Weerasooriya, A.; Peace, E. Effect of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized from Carya Illinoinensis Leaf Extract on Growth and Antioxidant Properties of Mustard (Brassica Juncea). Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1108186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedda, G.; Abdelhamid, H.N.; Khan, M.S.; Wu, H.F. ZnO Nanoparticle-Modified Polymethyl Methacrylate-Assisted Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Coupled with MALDI-MS for Rapid Pathogenic Bacteria Analysis. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 45973–45983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Nadeem, S.; Bahadur, A.; Javed, M.; Ahmad, Z.; Ahmad, M.N.; Shoaib, M.; Liu, G.; Mohyuddin, A.; Raheel, M. The Effect of Ni-Doped ZnO NPs on the Antibacterial Activity and Degradation Rate of Polyacrylic Acid-Modified Starch Nanocomposite. JOM 2021, 73, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Zhao, S.; Wang, S.; Lu, Z. Proteomics of Streptococcus Mutans to Reveal the Antibiofilm Formation Mechanism of Ag/Zno Nanocomposites with Light-Emitting Diode Radiation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 7741–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bekkali, C.; Labrag, J.; Oulguidoum, A.; Chamkhi, I.; Laghzizil, A.; Nunzi, J.-M.; Robert, D.; Aurag, J. Porous ZnO/Hydroxyapatite Nanomaterials with Effective Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Activities for the Degradation of Antibiotics. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2022, 7, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizan, M.; Hayat, S.; Pichtel, J. Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Crop Plants: A Perspective Analysis. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 41; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Tang, M. Toxic Effects and Involved Molecular Pathways of Nanoparticles on Cells and Subcellular Organelles. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2020, 40, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowack, B.; Bucheli, T.D. Occurrence, Behavior and Effects of Nanoparticles in the Environment. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 150, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czyżowska, A.; Barbasz, A. A Review: Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles–Friends or Enemies? Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2022, 32, 885–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.M.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, D.W.; Sohn, M.H.; Lim, S.T. The Effect of Fluorination of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Evaluation of Their Biodistribution after Oral Administration. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 205102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, Y.Y.; Chiung, Y.M.; Chen, Y.C.; Cheng, T.J.; Liu, P.S. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Interfere with Zinc Ion Homeostasis to Cause Cytotoxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 125, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deore, M.S.; Naqvi, S.; Kumar, A.; Flora, S.J.S. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Protects Co-Exposure to Lead and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induced Neuro, Immuno and Male Reproductive Toxicity in Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 626238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxall, A.B.; Tiede, K.; Chaudhry, Q. Engineered Nanomaterials in Soils and Water: How Do They Behave and Could They Pose a Risk to Human Health? Nanomedicine 2007, 2, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Sinha, S.; Jothiramajayam, M.; Jana, A.; Nag, A.; Mukherjee, A. Cyto-Genotoxicity and Oxidative Stress Induced by Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle in Human Lymphocyte Cells in Vitro and Swiss Albino Male Mice in Vivo. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 97, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T.M.; Behal, A.; Sushkova, S.N.; Mandzhieva, S.; Singh, R.; Gorovtsov, A.; Tsitsuashvili, V.S.; Purvis, W.O.; Ghazaryan, K.A.; et al. Effects of Zinc-Oxide Nanoparticles on Soil, Plants, Animals and Soil Organisms: A Review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2018, 9, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, E. A Review on Nanotoxicity and Nanogenotoxicity of Different Shapes of Nanomaterials. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 118–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandurangan, M.; Kim, D.H. In Vitro Toxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: A Review. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdiglesias, V.; Costa, C.; Kiliç, G.; Costa, S.; Pásaro, E.; Laffon, B.; Teixeira, J.P. Neuronal Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity Induced by Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Environ. Int. 2013, 55, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Bertólez, N.; Costa, C.; Brandão, F.; Kiliç, G.; Teixeira, J.P.; Pásaro, E.; Laffon, B.; Valdiglesias, V. Neurotoxicity Assessment of Oleic Acid-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in SH-SY5Y Cells. Toxicology 2018, 406–407, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdolenova, Z.; Lorenzo, Y.; Collins, A.; Dusinska, M. Can Standard Genotoxicity Tests Be Applied to Nanoparticles? J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2012, 75, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthana, S.; Kumar, A. Potential Risks and Benefits of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: A Systematic Review. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2020, 50, 47–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laffon, B.; Fernández-Bertólez, N.; Costa, C.; Pásaro, E.; Valdiglesias, V. Comparative Study of Human Neuronal and Glial Cell Sensitivity for in Vitro Neurogenotoxicity Testing. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 102, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Bertólez, N.; Costa, C.; Brandão, F.; Kiliç, G.; Duarte, J.A.J.A.; Teixeira, J.P.J.P.; Pásaro, E.; Valdiglesias, V.; Laffon, B. Toxicological Assessment of Silica-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Human Astrocytes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 118, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y. Ecotoxicity Assessment of a Molybdenum Mining Effluent Using Acute Lethal, Oxidative Stress, and Osmoregulatory Endpoints in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 5137–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Cao, X.; Yan, B.; Guo, Z.; Xi, Z.; Li, J.; Ci, N.; Yan, M.; Ci, L. Ecotoxicological Evaluation of Functional Carbon Nanodots Using Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Model at Different Developmental Stages. Chemosphere 2023, 333, 138970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasamma, S.; Audira, G.; Juniardi, S.; Sampurna, B.; Liang, S.-T.; Hao, E.; Lai, Y.-H.; Hsiao, C.-D. Zinc Chloride Exposure Inhibits Brain Acetylcholine Levels, Produces Neurotoxic Signatures, and Diminishes Memory and Motor Activities in Adult Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarasamma, S.; Audira, G.; Siregar, P.; Malhotra, N.; Lai, Y.-H.; Liang, S.-T.; Chen, J.-R.; Chen, K.H.-C.; Hsiao, C.-D. Nanoplastics Cause Neurobehavioral Impairments, Reproductive and Oxidative Damages, and Biomarker Responses in Zebrafish: Throwing up Alarms of Wide Spread Health Risk of Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bugel, S.M.; Tanguay, R.L.; Planchart, A. Zebrafish: A Marvel of High-Throughput Biology for 21st Century Toxicology. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2014, 1, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, A.R.; Sharma, G.; Lee, S.-S. Zebrafish: A Complete Animal Model to Enumerate the Nanoparticle Toxicity. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 14, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horzmann, K.A.; Freeman, J.L. Making Waves: New Developments in Toxicology with the Zebrafish. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 163, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dang, Z.C.; van der Ven, L.T.M.; Kienhuis, A.S. Fish Embryo Toxicity Test, Threshold Approach, and Moribund as Approaches to Implement 3R Principles to the Acute Fish Toxicity Test. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beekhuijzen, M.; de Koning, C.; Flores-Guillén, M.E.; de Vries-Buitenweg, S.; Tobor-Kaplon, M.; van de Waart, B.; Emmen, H. From Cutting Edge to Guideline: A First Step in Harmonization of the Zebrafish Embryotoxicity Test (ZET) by Describing the Most Optimal Test Conditions and Morphology Scoring System. Reprod. Toxicol. 2015, 56, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malandrakis, A.A.; Kavroulakis, N.; Chrysikopoulos, C.V. Zinc Nanoparticles: Mode of Action and Efficacy against Boscalid-Resistant Alternaria Alternata Isolates. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.K.; Katuwal, S.; Tettey, F.; Gupta, A.; Bhattarai, S.; Jaisi, S.; Bhandari, D.P.; Shah, A.K.; Bhattarai, N.; Parajuli, N. Current Research on Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; You, H.; Lv, L. Acute ZnO Nanoparticles Exposure Induces Developmental Toxicity, Oxidative Stress and DNA Damage in Embryo-Larval Zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 136–137, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, H.S.; Othman, H.H.; Abdullah, R.; Edin, H.Y.A.S.; AL-Haj, N.A. Beneficial and Toxicological Aspects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Animals. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 1769–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sruthi, S.; Mohanan, P.V. Investigation on Cellular Interactions of Astrocytes with Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Rat C6 Cell Lines. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 133, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eixenberger, J.E.; Anders, C.B.; Hermann, R.J.; Brown, R.J.; Reddy, K.M.; Punnoose, A.; Wingett, D.G. Rapid Dissolution of ZnO Nanoparticles Induced by Biological Buffers Significantly Impacts Cytotoxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2017, 30, 1641–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, H. In Vitro Response of Immune Cells on Metal Oxide Nanoparticles with Different Solubility. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 5546–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Anderson, D.; Dhawan, A. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Oxidative DNA Damage and ROS-Triggered Mitochondria Mediated Apoptosis in Human Liver Cells (HepG2). Apoptosis 2012, 17, 852–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, G.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Chuai, M.; Brand-Saberi, B.; Chen, G.; Jiang, X.; Yang, X. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Exposure-Induced Oxidative Stress Restricts Cranial Neural Crest Development during Chicken Embryogenesis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 194, 110415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S. DLS and Zeta Potential—What They Are and What They Are Not? J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warheit, D.B. How Meaningful Are the Results of Nanotoxicity Studies in the Absence of Adequate Material Characterization? Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 101, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, I.; Dawson, K.A. Protein-Nanoparticle Interactions. Nano Today 2008, 3, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihari, P.; Vippola, M.; Schultes, S.; Praetner, M.; Khandoga, A.G.; Reichel, C.A.; Coester, C.; Tuomi, T.; Rehberg, M.; Krombach, F. Optimized Dispersion of Nanoparticles for Biological in Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Part. Fibre. Toxicol. 2008, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Yang, H.; Fang, Y.; Li, K.; Tian, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Tan, Y.; Lai, W.; Bian, L.; et al. Neurotoxicity and Biomarkers of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Main Functional Brain Regions and Dopaminergic Neurons. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, A.; Dierker, C.; Rommel, C.; Hahn, D.; Wohlleben, W.; Schulze-Isfort, C.; Göbbert, C.; Voetz, M.; Hardinghaus, F.; Schnekenburger, J. Cytotoxicity Screening of 23 Engineered Nanomaterials Using a Test Matrix of Ten Cell Lines and Three Different Assays. Part. Fibre. Toxicol. 2011, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kroll, A.; Pillukat, M.H.; Hahn, D.; Schnekenburger, J. Interference of Engineered Nanoparticles with in Vitro Toxicity Assays. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 1123–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquis, B.J.; Love, S.A.; Braun, K.L.; Haynes, C.L. Analytical Methods to Assess Nanoparticle Toxicity. Analyst 2009, 134, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, V.; Johnston, H.; Schins, R.P.F. Development of in Vitro Systems for Nanotoxicology: Methodological Considerations. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2009, 39, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Brandão, F.; Bessa, M.J.; Costa, S.; Valdiglesias, V.; Kiliç, G.; Fernández-Bertólez, N.; Quaresma, P.; Pereira, E.; Pásaro, E.; et al. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles on Neuronal and Glial Cells. Evaluation of Nanoparticle Interference with Viability Tests. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2016, 36, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holder, A.L.; Goth-Goldstein, R.; Lucas, D.; Koshland, C.P. Particle-Induced Artifacts in the MTT and LDH Viability Assays. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1885–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kroll, A.; Pillukat, M.H.; Hahn, D.; Schnekenburger, J. Current in Vitro Methods in Nanoparticle Risk Assessment: Limitations and Challenges. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Inman, A.O.; Zhang, L.W. Limitations and Relative Utility of Screening Assays to Assess Engineered Nanoparticle Toxicity in a Human Cell Line. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 234, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for in Vitro Cytotoxicity. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:10993:-5:ed-3:v1:en (accessed on 13 July 2023).
- Leung, S. Exposure to Titanium Dioxide and Other Metallic Oxide Nanoparticles Induces Cytotoxicity on Human Neural Cells and Fibroblasts. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sudhakaran, S.; Athira, S.S.; Mohanan, P.V. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Induced Neurotoxic Potential upon Interaction with Primary Astrocytes. Neurotoxicology 2019, 73, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Singh, V.; Gera, R.; Purohit, M.P.; Ghosh, D. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Induces Microglial Death by NADPH-Oxidase-Independent Reactive Oxygen Species as Well as Energy Depletion. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 6273–6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, S.; Sasidharan, A.; Divya Rani, V.V.; Menon, D.; Nair, S.; Manzoor, K.; Raina, S. Role of Size Scale of ZnO Nanoparticles and Microparticles on Toxicity toward Bacteria and Osteoblast Cancer Cells. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.; Kansara, K.; Senapati, V.A.; Shanker, R.; Dhawan, A.; Kumar, A. Cell Cycle Dependent Cellular Uptake of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Human Epidermal Cells. Mutagenesis 2016, 31, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.W.Y.; Leung, P.T.Y.; Djurišić, A.B.; Leung, K.M.Y. Toxicities of Nano Zinc Oxide to Five Marine Organisms: Influences of Aggregate Size and Ion Solubility. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Nallathamby, P.D.; Browning, L.M.; Osgood, C.J.; Nancy Xu, X.H. In Vivo Imaging of Transport and Biocompatibility of Single Silver Nanoparticles in Early Development of Zebrafish Embryos. ACS Nano 2007, 1, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chun, H.S.; Park, D.; Eun Lim, S.; Jeong, K.H.; Park, J.S.; Park, H.J.; Kang, S.; Kang, K.S.; Park, H.G.; An, H.R.; et al. Two Zinc-Aminoclays’ in-Vitro Cytotoxicity Assessment in HeLa Cells and in-Vivo Embryotoxicity Assay in Zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 137, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.H.; Lin, C.C.; Meng, P.J. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Alter Hatching and Larval Locomotor Activity in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 277, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, N.R.; Lenz, M.; Wehrli, B.; Fent, K. Comparative Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Dissolved Zinc on Zebrafish Embryos and Eleuthero-Embryos: Importance of Zinc Ions. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476–477, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Amora, M.; Schmidt, T.J.N.; Konstantinidou, S.; Raffa, V.; De Angelis, F.; Tantussi, F. Effects of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles in Zebrafish. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.K.; Panda, P.K.; Jha, E.; Suar, M.; Parashar, S.K.S. Altered Physiochemical Properties in Industrially Synthesized ZnO Nanoparticles Regulate Oxidative Stress; Induce in Vivo Cytotoxicity in Embryonic Zebrafish by Apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Ren, X.; Zhu, R.; Luo, Z.; Ren, B. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Oxidative DNA Damage and ROS-Triggered Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis in Zebrafish Embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 180, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, C.S.; Igartúa, D.E.; Calienni, M.N.; Feas, D.A.; Siri, M.; Montanari, J.; Chiaramoni, N.S.; Alonso, S.D.V.; Prieto, M.J. Relation between Biophysical Properties of Nanostructures and Their Toxicity on Zebrafish. Biophys. Rev. 2017, 9, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kteeba, S.M.; El-Adawi, H.I.; El-Rayis, O.A.; El-Ghobashy, A.E.; Schuld, J.L.; Svoboda, K.R.; Guo, L. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Toxicity in Embryonic Zebrafish: Mitigation with Different Natural Organic Matter. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 1125–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansjosten, I.; Takamiya, M.; Rapp, J.; Reiner, L.; Fritsch-Decker, S.; Mattern, D.; Andraschko, S.; Anders, C.; Pace, G.; Dickmeis, T.; et al. Surface Functionalisation-Dependent Adverse Effects of Metal Nanoparticles and Nanoplastics in Zebrafish Embryos. Environ. Sci. Nano 2022, 9, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, A.; Sano, K.; Nagata, K.; Yasumasu, S.; Ohtsuka, J.; Yamamura, A.; Kubota, K.; Iuchi, I.; Tanokura, M. Crystal Structure of Zebrafish Hatching Enzyme 1 from the Zebrafish Danio Rerio. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 402, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, Z.; Ear, J.; Chang, C.H.; Zhang, H.; Low-Kam, C.; Yamada, K.; Meng, H.; Wang, X.; et al. Zebrafish High-Throughput Screening to Study the Impact of Dissolvable Metal Oxide Nanoparticles on the Hatching Enzyme, ZHE1. Small 2013, 9, 1776–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Son, J.; Harper, B.; Zhou, Z.; Harper, S. Influence of Surface Chemical Properties on the Toxicity of Engineered Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles to Embryonic Zebrafish. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1568–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- OECD. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2013; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cellular Growth and Survival: Application to Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleström, P.; D’Angelo, L.; Midtlyng, P.J.; Schorderet, D.F.; Schulte-Merker, S.; Sohm, F.; Warner, S. Zebrafish: Housing and Husbandry Recommendations. Lab. Anim. 2020, 54, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Cell culture medium | Time (h) | 0 | 3 | 24 | 48 | |
| Hydrodynamic diameter (nm) a | 302.09 ± 0.84 | 315.01 ± 3.16 | 269.16 ± 1.36 | 273.97 ± 5.91 | ||
| Zeta potential (mV) a | −1.73 ± 4.05 | 2.79 ± 3.01 | −20.25 ± 2.03 | −13.46 ± 2.36 | ||
| Dechlorinated water | Time (h) | 0 | 24 | 48 | 72 | 96 |
| Hydrodynamic diameter (nm) a | 301.36 ± 6.74 | 269.72 ± 0.12 | 242.46 ± 1.67 | 224.71 ± 2.38 | 238.15 ± 1.56 | |
| Zeta potential (mV) a | −23.23 ± 2.11 | −18.22 ± 1.09 | −26.73 ± 1.69 | −22.22 ± 0.55 | −22.49 ± 3.39 |
| Exposure Time (h) | 3 | 24 | 48 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO NPs IC50 (µg/mL) a | 120.51 ± 9.50 | 34.76 ± 1.92 | 17.08 ± 1.20 |
| ZnSO4 IC50 (mM) a | 3.24 ± 1.43 | 0.41 ± 0.002 | 0.22 ± 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valdiglesias, V.; Alba-González, A.; Fernández-Bertólez, N.; Touzani, A.; Ramos-Pan, L.; Reis, A.T.; Moreda-Piñeiro, J.; Yáñez, J.; Laffon, B.; Folgueira, M. Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Exposure on Human Glial Cells and Zebrafish Embryos. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512297
Valdiglesias V, Alba-González A, Fernández-Bertólez N, Touzani A, Ramos-Pan L, Reis AT, Moreda-Piñeiro J, Yáñez J, Laffon B, Folgueira M. Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Exposure on Human Glial Cells and Zebrafish Embryos. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(15):12297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512297
Chicago/Turabian StyleValdiglesias, Vanessa, Anabel Alba-González, Natalia Fernández-Bertólez, Assia Touzani, Lucía Ramos-Pan, Ana Teresa Reis, Jorge Moreda-Piñeiro, Julián Yáñez, Blanca Laffon, and Mónica Folgueira. 2023. "Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Exposure on Human Glial Cells and Zebrafish Embryos" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 15: 12297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512297
APA StyleValdiglesias, V., Alba-González, A., Fernández-Bertólez, N., Touzani, A., Ramos-Pan, L., Reis, A. T., Moreda-Piñeiro, J., Yáñez, J., Laffon, B., & Folgueira, M. (2023). Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Exposure on Human Glial Cells and Zebrafish Embryos. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(15), 12297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512297








