Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Influence Survival in Pleural Mesothelioma: Digital Gene Expression Analysis and Supervised Machine Learning Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Histologic and Immunohistochemical Evaluation
2.2. Association between DSR, FAP Immunohistochemistry, Gene Expression, and Survival
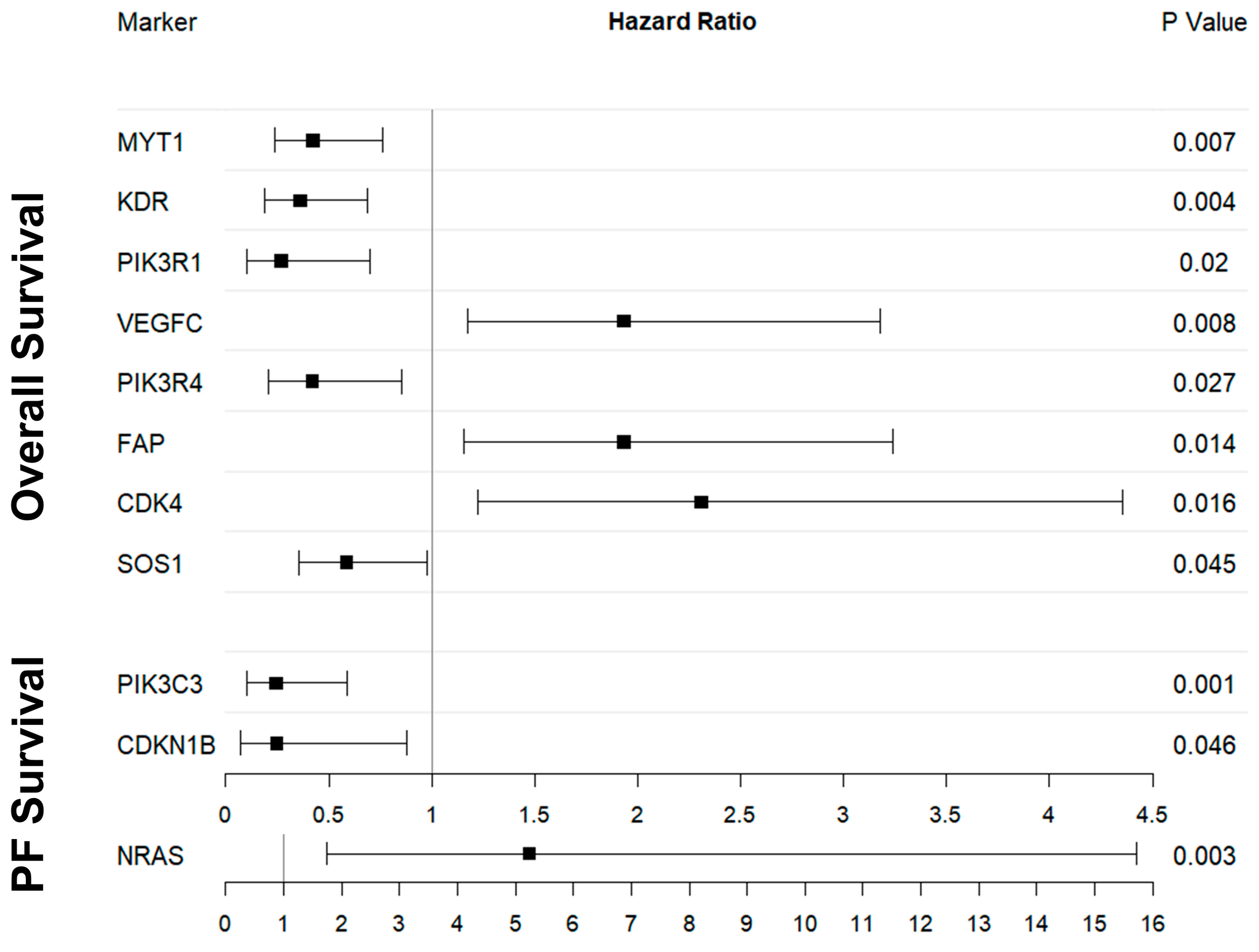
2.3. OS and Digital Gene Expression Analysis
2.4. PFS and Digital Gene Expression Analysis
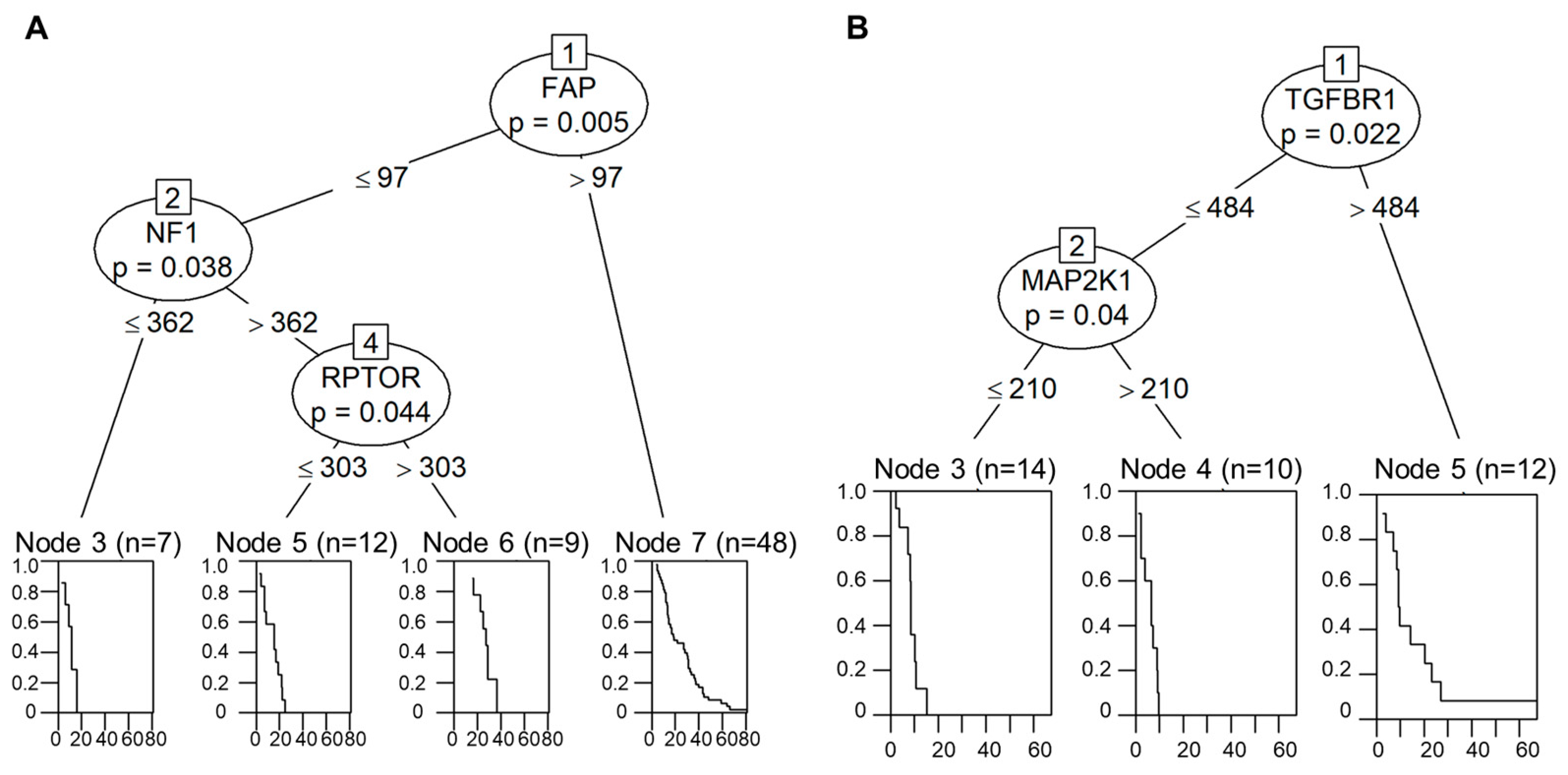
2.5. Decision-Tree-Based Analysis of OS and PFS
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Cohort
4.2. Immunohistochemistry
4.3. RNA Isolation and Quantification
4.4. Digital Gene Expression Analysis
4.5. NanoString Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
4.6. Machine Learning
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Minamoto, T.; Ooi, A.; Okada, Y.; Mai, M.; Nagai, Y.; Nakanishi, I. Desmoplastic reaction of gastric carcinoma: A light- and electron-microscopic immunohistochemical analysis using collagen type-specific antibodies. Hum. Pathol. 1988, 19, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheuba, C.; Kaserer, K.; Kaczirek, K.; Asari, R.; Niederle, B. Desmoplastic stromal reaction in medullary thyroid cancer-an intraoperative “marker” for lymph node metastases. World J. Surg. 2006, 30, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koperek, O.; Scheuba, C.; Cherenko, M.; Neuhold, N.; De Micco, C.; Schmid, K.W.; Niederle, B.; Kaserer, K. Desmoplasia in medullary thyroid carcinoma: A reliable indicator of metastatic potential. Histopathology 2008, 52, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcangelo, E.; Wu, N.C.; Cadavid, J.L.; McGuigan, A.P. The life cycle of cancer-associated fibroblasts within the tumour stroma and its importance in disease outcome. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasek, J.J.; Gabbiani, G.; Hinz, B.; Chaponnier, C.; Brown, R.A. Myofibroblasts and mechano-regulation of connective tissue remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasanen, K.; Vaheri, A. Activation of fibroblasts in cancer stroma. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 2713–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; Zeisberg, M. Fibroblasts in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostman, A.; Augsten, M. Cancer-associated fibroblasts and tumor growth—Bystanders turning into key players. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2009, 19, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Sun, P.L.; He, Y.; Yao, M.; Gao, H. Desmoplastic Reaction and Tumor Budding in Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma are Prognostic Factors for Distant Metastasis: A Retrospective Study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ueno, H.; Kanemitsu, Y.; Sekine, S.; Ishiguro, M.; Ito, E.; Hashiguchi, Y.; Kondo, F.; Shimazaki, H.; Mochizuki, S.; Kajiwara, Y.; et al. Desmoplastic Pattern at the Tumor Front Defines Poor-prognosis Subtypes of Colorectal Cancer. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 41, 1506–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudino, G.; Xue, J.; Yang, H. How asbestos and other fibers cause mesothelioma. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, S39–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, M.; Yang, H. Molecular pathways: Targeting mechanisms of asbestos and erionite carcinogenesis in mesothelioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sekido, Y. Molecular pathogenesis of malignant mesothelioma. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.; Cukierman, E. Stromal dynamic reciprocity in cancer: Intricacies of fibroblastic-ECM interactions. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2016, 42, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heneberg, P. Paracrine tumor signaling induces transdifferentiation of surrounding fibroblasts. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 97, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaeth, E.L.; Dembinski, J.L.; Sasser, A.K.; Watson, K.; Klopp, A.; Hall, B.; Andreeff, M.; Marini, F. Mesenchymal stem cell transition to tumor-associated fibroblasts contributes to fibrovascular network expansion and tumor progression. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Cheng, L.; Fan, Y.; Mao, W. Tumor Microenvironment-Associated Immune-Related Genes for the Prognosis of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 544789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, M.; Jesenofsky, R.; Faissner, R.; Weidenauer, C.; Hagmann, W.; Michl, P.; Heuchel, R.L.; Haas, S.L.; Lohr, J.M. Desmoplasia and chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Cancers 2014, 6, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, J.; Ding, L.; Zhang, D.; Shi, G.; Xu, Q.; Shen, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Hou, Y. Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts promote the stemness and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer by transferring exosomal lncRNA H19. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3932–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, A.J.; Cortes, E.; Lachowski, D.; Cheung, B.C.H.; Karim, S.A.; Morton, J.P.; Del Rio Hernandez, A. Matrix stiffness induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, e352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, S.; Chen, J.; Yao, H.; Liu, J.; Yu, S.; Lao, L.; Wang, M.; Luo, M.; Xing, Y.; Chen, F.; et al. CD10(+)GPR77(+) Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Promote Cancer Formation and Chemoresistance by Sustaining Cancer Stemness. Cell 2018, 172, 841–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesweg, M.; Mairinger, F.; Reis, H.; Goetz, M.; Kollmeier, J.; Misch, D.; Stephan-Falkenau, S.; Mairinger, T.; Walter, R.F.H.; Hager, T.; et al. Machine learning reveals a PD-L1-independent prediction of response to immunotherapy of non-small cell lung cancer by gene expression context. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 140, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesweg, M.; Mairinger, F.; Reis, H.; Goetz, M.; Walter, R.F.H.; Hager, T.; Metzenmacher, M.; Eberhardt, W.E.E.; McCutcheon, A.; Koster, J.; et al. Machine learning-based predictors for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy of non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 655–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayers, M.; Lunceford, J.; Nebozhyn, M.; Murphy, E.; Loboda, A.; Kaufman, D.R.; Albright, A.; Cheng, J.D.; Kang, S.P.; Shankaran, V.; et al. IFN-γ-related mRNA profile predicts clinical response to PD-1 blockade. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 2930–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danaher, P.; Warren, S.; Lu, R.; Samayoa, J.; Sullivan, A.; Pekker, I.; Wallden, B.; Marincola, F.M.; Cesano, A. Pan-cancer adaptive immune resistance as defined by the Tumor Inflammation Signature (TIS): Results from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suwanabol, P.A.; Seedial, S.M.; Zhang, F.; Shi, X.; Si, Y.; Liu, B.; Kent, K.C. TGF-β and Smad3 modulate PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 302, H2211–H2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martini, M.; De Santis, M.C.; Braccini, L.; Gulluni, F.; Hirsch, E. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: An updated review. Ann. Med. 2014, 46, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Guillermet-Guibert, J.; Graupera, M.; Bilanges, B. The emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific PI3K signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimbalkar, D.; Henry, M.K.; Quelle, F.W. Cytokine activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase sensitizes hematopoietic cells to cisplatin-induced death. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Shekar, S.C.; Wu, H.; Fu, Z.; Yip, S.C.; Cahill, S.M.; Girvin, M.E.; Backer, J.M. Mechanism of constitutive phosphoinositide 3-kinase activation by oncogenic mutants of the p85 regulatory subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 27850–27855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaiswal, B.S.; Janakiraman, V.; Kljavin, N.M.; Chaudhuri, S.; Stern, H.M.; Wang, W.; Kan, Z.; Dbouk, H.A.; Peters, B.A.; Waring, P.; et al. Somatic mutations in p85alpha promote tumorigenesis through class IA PI3K activation. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parsons, D.W.; Jones, S.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.C.; Leary, R.J.; Angenendt, P.; Mankoo, P.; Carter, H.; Siu, I.M.; Gallia, G.L.; et al. An integrated genomic analysis of human glioblastoma multiforme. Science 2008, 321, 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urick, M.E.; Rudd, M.L.; Godwin, A.K.; Sgroi, D.; Merino, M.; Bell, D.W. PIK3R1 (p85α) is somatically mutated at high frequency in primary endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4061–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheung, L.W.T.; Hennessy, B.T.; Li, J.; Yu, S.; Myers, A.P.; Djordjevic, B.; Lu, Y.; Stemke-Hale, K.; Dyer, M.D.; Zhang, F.; et al. High Frequency of PIK3R1 and PIK3R2 Mutations in Endometrial Cancer Elucidates a Novel Mechanism for Regulation of PTEN Protein Stability. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jané, P.; Gógl, G.; Kostmann, C.; Bich, G.; Girault, V.; Caillet-Saguy, C.; Eberling, P.; Vincentelli, R.; Wolff, N.; Travé, G.; et al. Interactomic affinity profiling by holdup assay: Acetylation and distal residues impact the PDZome-binding specificity of PTEN phosphatase. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Chen, C.; Sun, L.; Li, S.; Ding, X. New PTEN mutation identified in a patient with rare bilateral choroidal ganglioneuroma. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020, 20, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. mTOR Signaling in Cancer and mTOR Inhibitors in Solid Tumor Targeting Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Eilers, G.; Kuang, Y.; Shi, S.; Yan, Z.; Li, X.; Corson, J.M.; Meng, F.; et al. Multipoint targeting of the PI3K/mTOR pathway in mesothelioma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2479–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackel, M.C.; Tausch-Treml, R.; Kopf-Maier, P. Cytokinetic effects of cisplatin on diverse human head and neck carcinomas in vitro: Dependence on the tumor sensitivity to cisplatin. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 1996, 122, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, D.E.; Ng, C.E.; Raaphorst, G.P. Cell cycle perturbations in cisplatin-sensitive and resistant human ovarian carcinoma cells following treatment with cisplatin and low dose rate irradiation. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1997, 40, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherr, C.J. D-type cyclins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1995, 20, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogl, M.; Rosenmayr, A.; Bohanes, T.; Scheed, A.; Brndiar, M.; Stubenberger, E.; Ghanim, B. Biomarkers for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma-A Novel View on Inflammation. Cancers 2021, 13, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, B. Prognostic factors in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowell, J.E.; Dunphy, F.R.; Taub, R.N.; Gerber, D.E.; Ngov, L.; Yan, J.; Xie, Y.; Kindler, H.L. A multicenter phase II study of cisplatin, pemetrexed, and bevacizumab in patients with advanced malignant mesothelioma. Lung Cancer 2012, 77, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, J.L.; Dacic, S.; Galateau-Salle, F.; Attanoos, R.L.; Butnor, K.J.; Churg, A.; Husain, A.N.; Kadota, K.; Khoor, A.; Nicholson, A.G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Pleura: Advances Since the 2015 Classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, J.D.; Gospodarowicz, M.K.; Wittekind, C. International Union against Cancer. In TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, 8th ed.; Wiley: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, M.J.; Nowak, A.K. Modified RECIST criteria for assessment of response in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceresoli, G.L.; Chiti, A.; Zucali, P.A.; Cappuzzo, F.; De Vincenzo, F.; Cavina, R.; Rodari, M.; Poretti, D.; Lutman, F.R.; Santoro, A. Assessment of tumor response in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2007, 33, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, L.R.; Lee, H.O.; Lee, J.S.; Klein-Szanto, A.; Watts, P.; Ross, E.A.; Chen, W.T.; Cheng, J.D. Clinical implications of fibroblast activation protein in patients with colon cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1736–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brcic, L.; Mathilakathu, A.; Walter, R.F.H.; Wessolly, M.; Mairinger, E.; Beckert, H.; Kreidt, D.; Steinborn, J.; Hager, T.; Christoph, D.C.; et al. Digital Gene Expression Analysis of Epithelioid and Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma Reveals Differences in Immunogenicity. Cancers 2021, 13, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hothorn, T.; Hornik, K.; Zeileis, A. Unbiased Recursive Partitioning: A Conditional Inference Framework. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2006, 15, 651–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
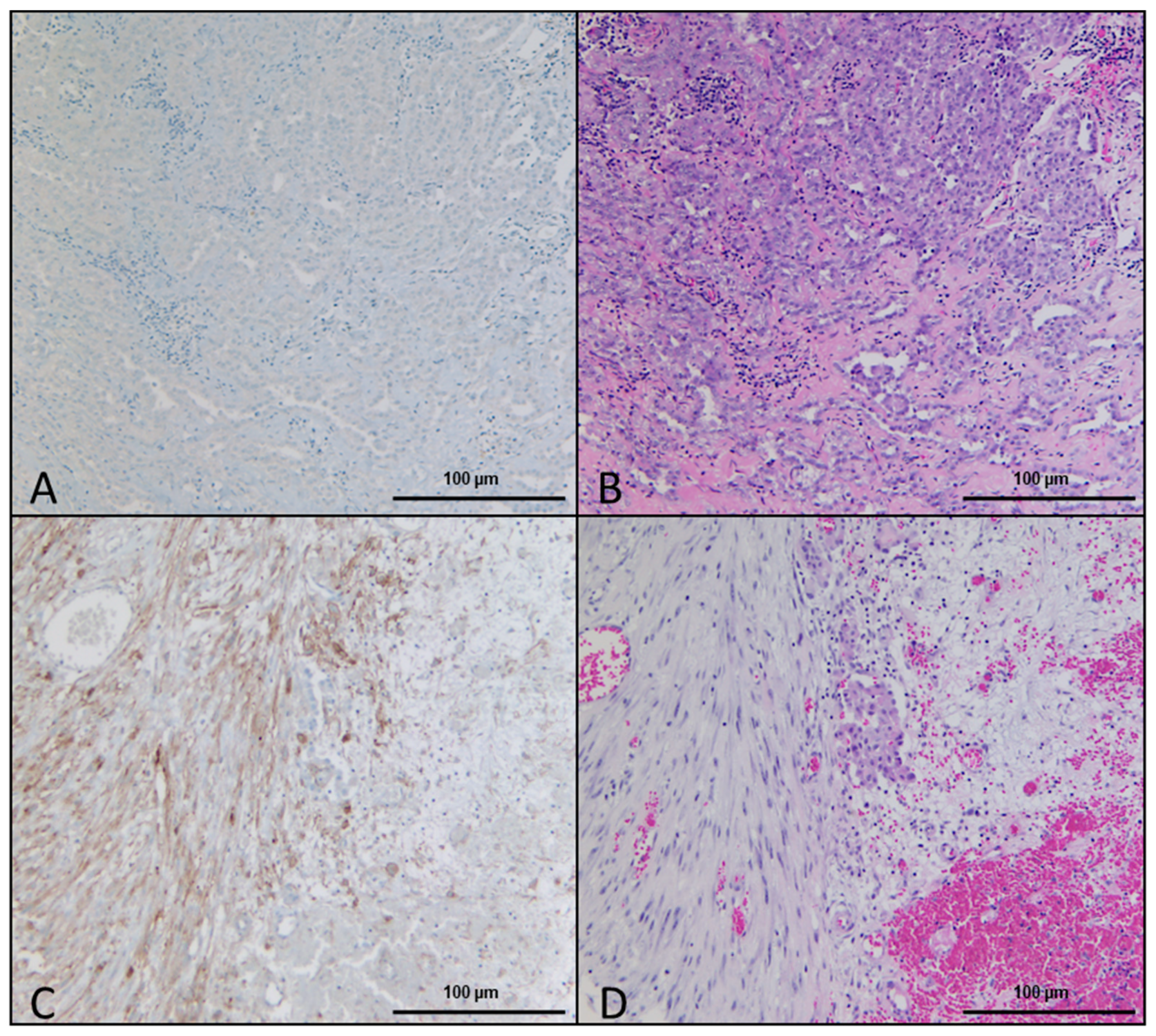
| Histological Observation. | Percentage of Samples | Number of Samples |
|---|---|---|
| Overall DSR in HE-stained slides | 67.5% | 52/77 |
| DSR-low | 45.5% | 35/77 |
| DSR-high | 22.1% | 17/77 |
| DSR absent in HE staining | 32.5% | 25/77 |
| FAP-negative samples in DSR absent samples | 20% | 5/25 |
| Score of 1 in DSR-low samples | 25.7% | 9/35 |
| Score of 2 in DSR-low samples | 48.6% | 17/35 |
| Score of 3 in DSR-low samples | 25.7% | 9/35 |
| Score of 1 in DSR-high samples | 23.5% | 4/17 |
| Score of 2 in DSR-high samples | 47.1% | 8/17 |
| Score of 3 in DSR-high samples | 29.4% | 5/17 |
| Score of 0 in overall samples | 7.7% | 5/65 |
| Score of 1 in overall samples | 32.3% | 21/65 |
| Score of 2 in overall samples | 38.4% | 25/65 |
| Score of 3 in overall samples | 21.5% | 14/65 |
| Number of Patients | 77 |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Male | 64 |
| Female | 13 |
| Histological subtype | |
| Epithelioid | 62 |
| Biphasic | 8 |
| Sarcomatoid | 7 |
| Age | |
| Mean/median age at diagnosis (years) | 64.6/65.2 |
| Range (years) | 37.6–82.9 |
| OS | |
| Deceased | 76 |
| Alive | 0 |
| Loss of Follow-Up | 1 |
| Median/mean OS (months) | 17.1/22.2 |
| 95% CI | 15.2–24.4 |
| Range (months) | 3.1–80.6 |
| PFS | |
| Partial remission (initial) | 3 |
| Stable disease (initial) | 32 |
| Progressive disease (initial) | 40 |
| Unknown response | 2 |
| Median/mean PFS (months) | 8.6/10.0 |
| 95% CI | 7.4–9.7 |
| Range (months) | 1.2–67.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borchert, S.; Mathilakathu, A.; Nath, A.; Wessolly, M.; Mairinger, E.; Kreidt, D.; Steinborn, J.; Walter, R.F.H.; Christoph, D.C.; Kollmeier, J.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Influence Survival in Pleural Mesothelioma: Digital Gene Expression Analysis and Supervised Machine Learning Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12426. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512426
Borchert S, Mathilakathu A, Nath A, Wessolly M, Mairinger E, Kreidt D, Steinborn J, Walter RFH, Christoph DC, Kollmeier J, et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Influence Survival in Pleural Mesothelioma: Digital Gene Expression Analysis and Supervised Machine Learning Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(15):12426. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512426
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorchert, Sabrina, Alexander Mathilakathu, Alina Nath, Michael Wessolly, Elena Mairinger, Daniel Kreidt, Julia Steinborn, Robert F. H. Walter, Daniel C. Christoph, Jens Kollmeier, and et al. 2023. "Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Influence Survival in Pleural Mesothelioma: Digital Gene Expression Analysis and Supervised Machine Learning Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 15: 12426. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512426
APA StyleBorchert, S., Mathilakathu, A., Nath, A., Wessolly, M., Mairinger, E., Kreidt, D., Steinborn, J., Walter, R. F. H., Christoph, D. C., Kollmeier, J., Wohlschlaeger, J., Mairinger, T., Brcic, L., & Mairinger, F. D. (2023). Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Influence Survival in Pleural Mesothelioma: Digital Gene Expression Analysis and Supervised Machine Learning Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(15), 12426. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512426







