Docking Studies, Cytotoxicity Evaluation and Interactions of Binuclear Copper(II) Complexes with S-Isoalkyl Derivatives of Thiosalicylic Acid with Some Relevant Biomolecules
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. DNA Interactions Studies
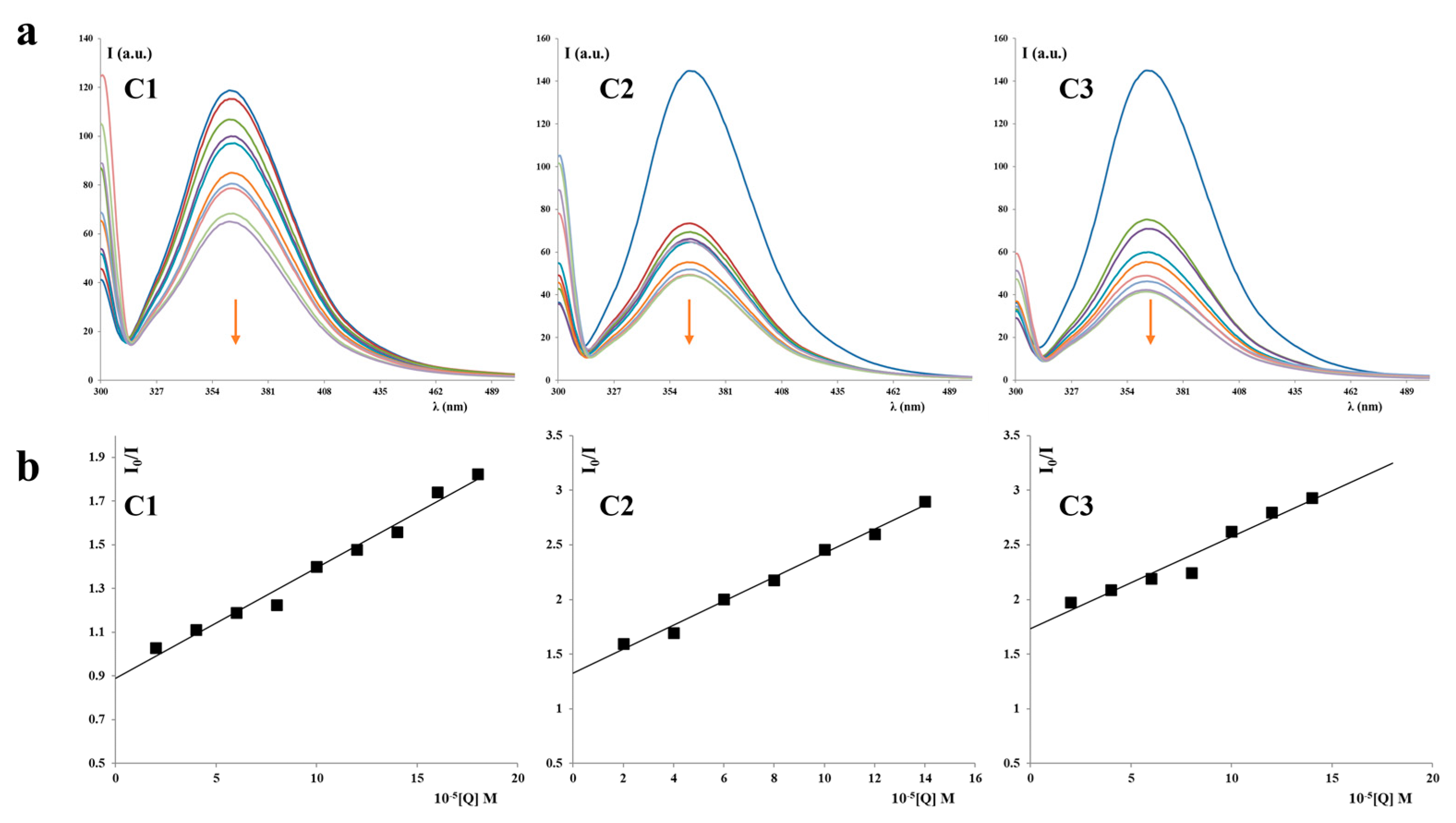
2.1.1. UV–Vis Absorption Studies
2.1.2. Ethidium Bromide (EB) Displacement Studies
2.1.3. Viscosity
2.1.4. Protein Binding Studies
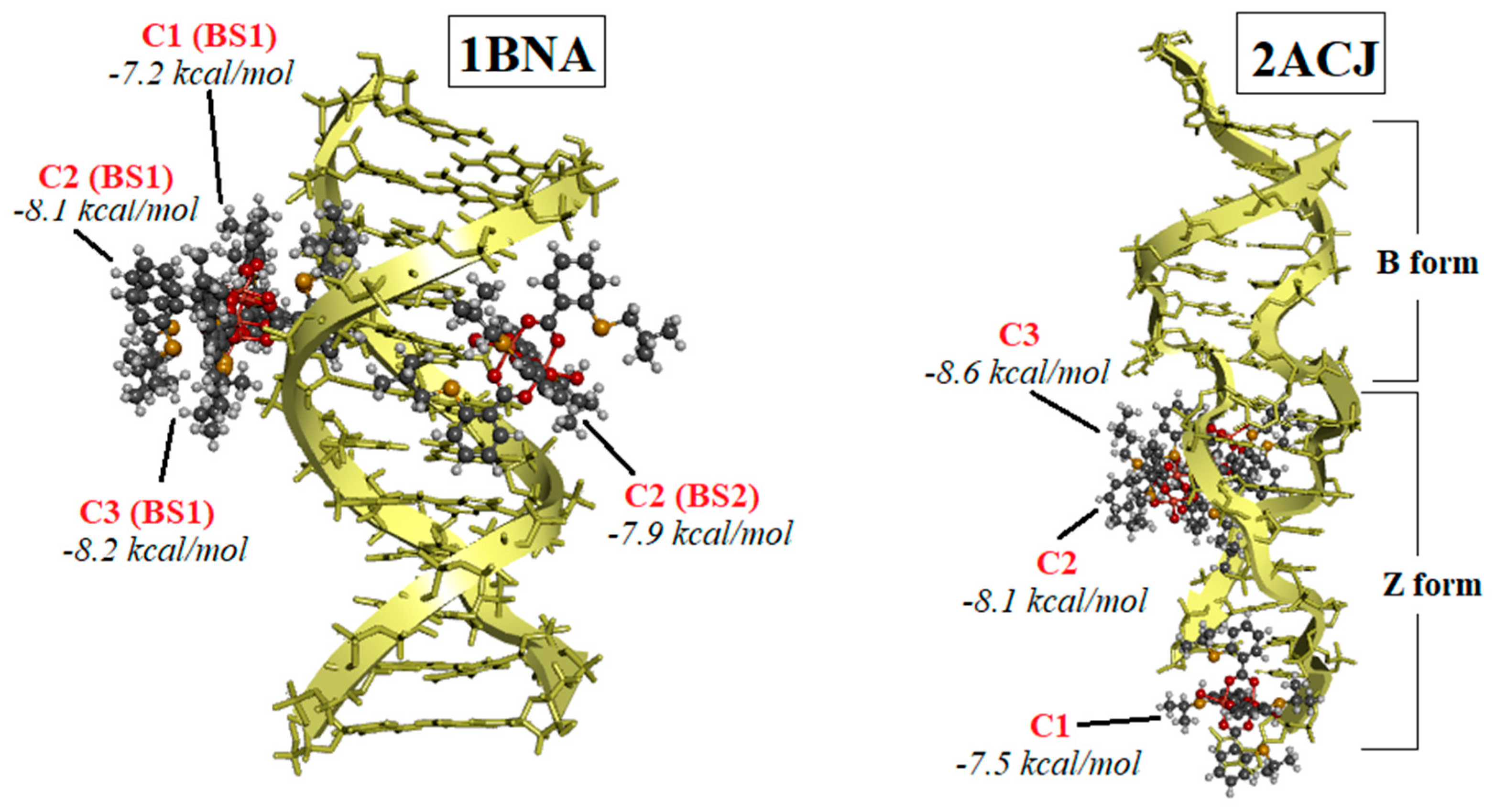
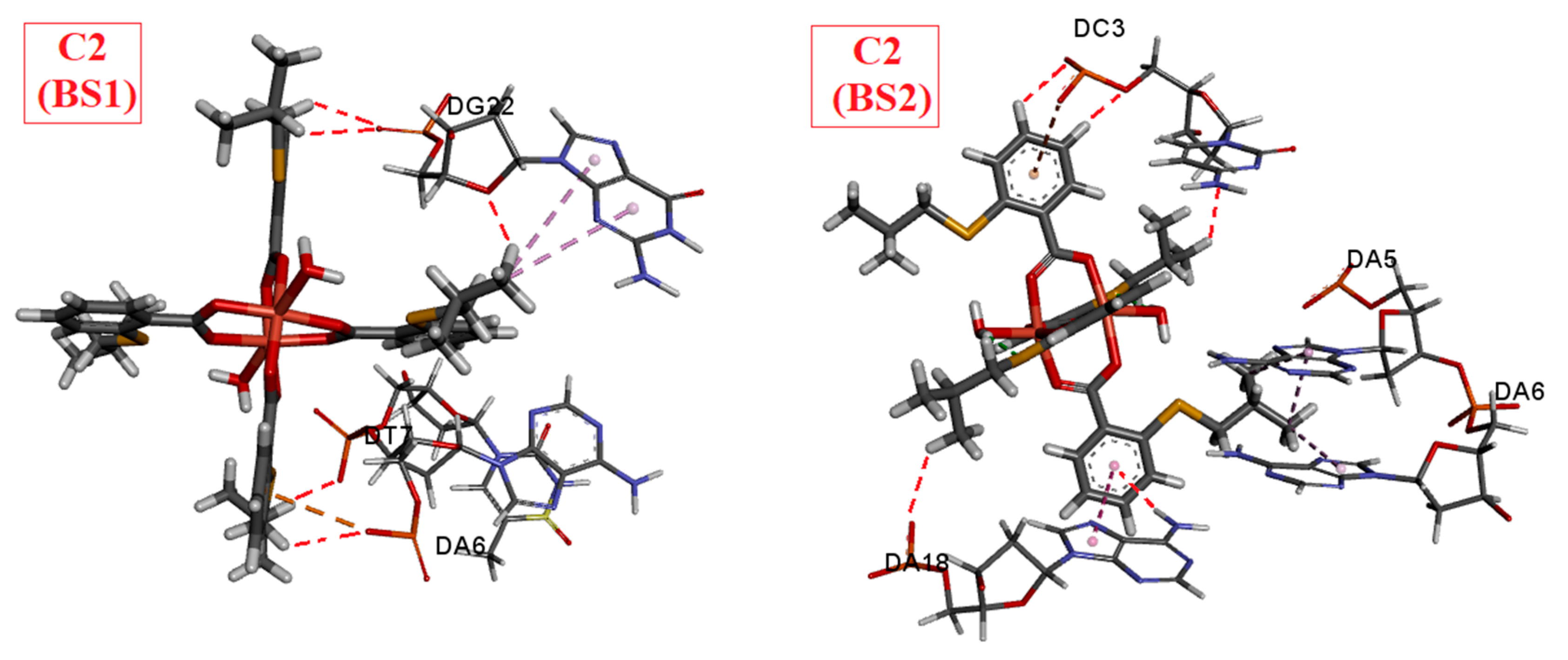
2.2. Results of Docking
2.3. Results Antitumor Activity
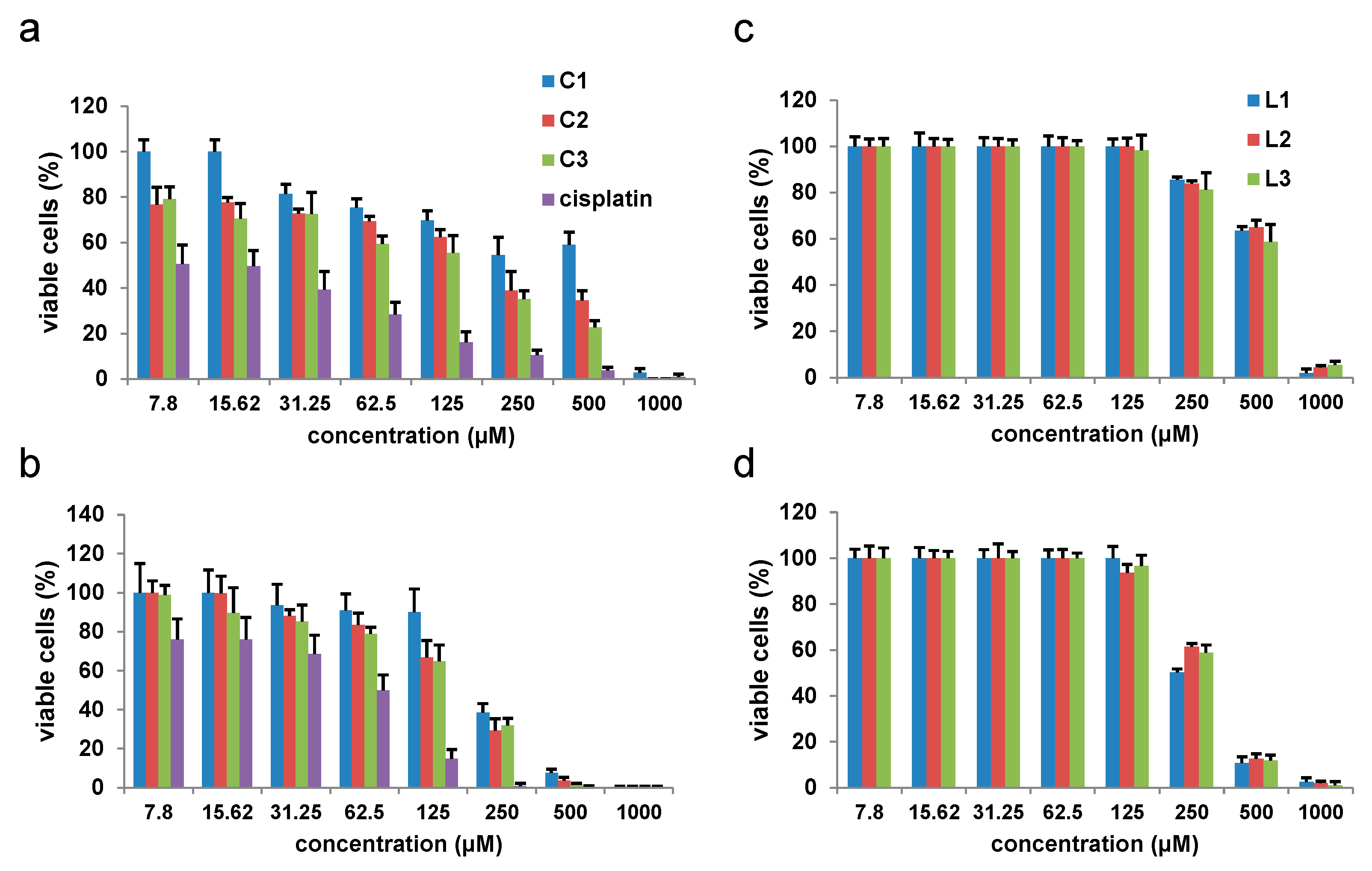
2.3.1. Effects of Copper(II) Complexes on Tumor Murine Colon Carcinoma Cells Viability In Vitro
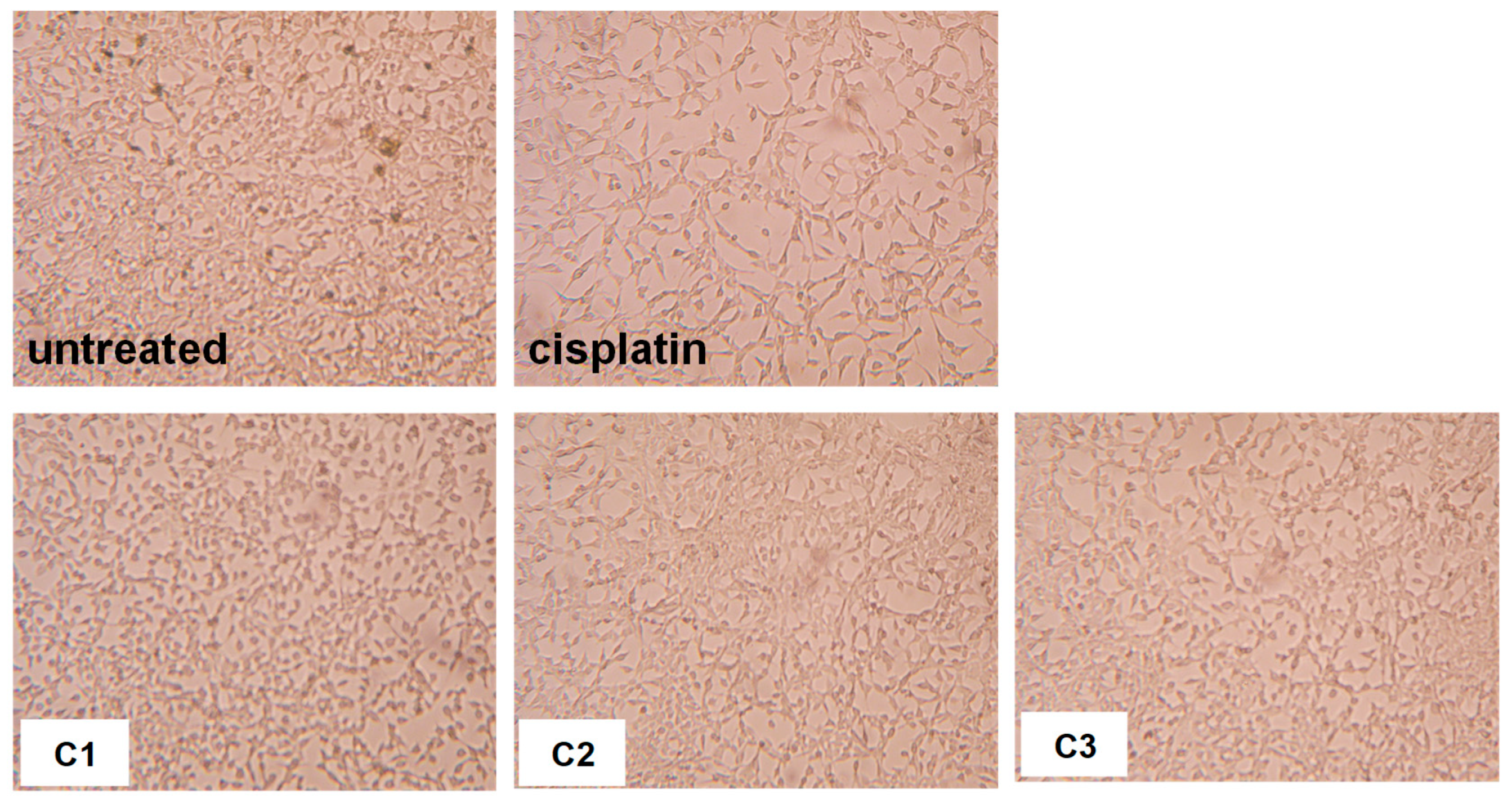
2.3.2. Effects of Copper(II) Complexes on Tumor Cell Apoptosis
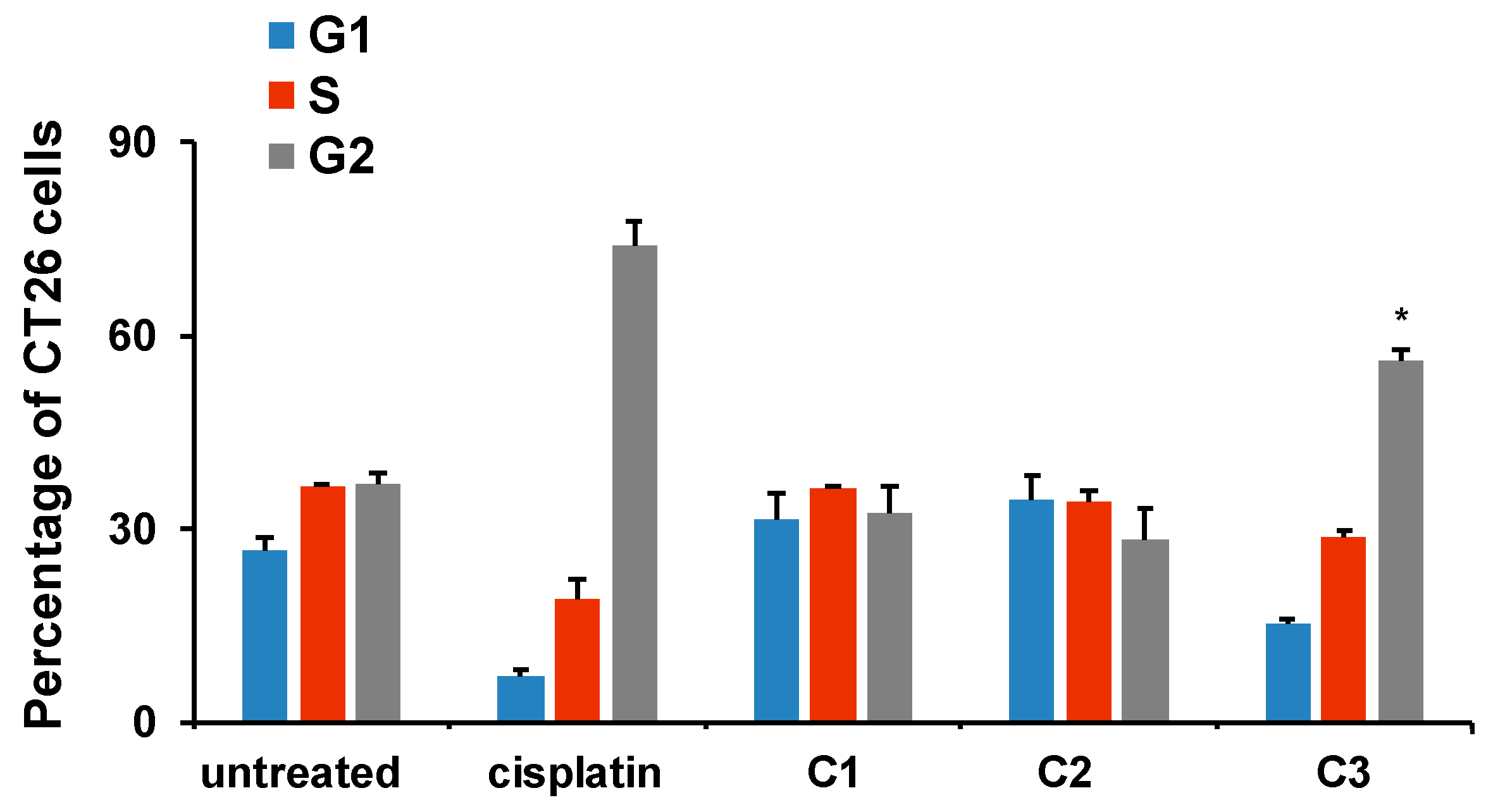
2.3.3. Effects of C3 on Cell Cycle in CT26 Cells
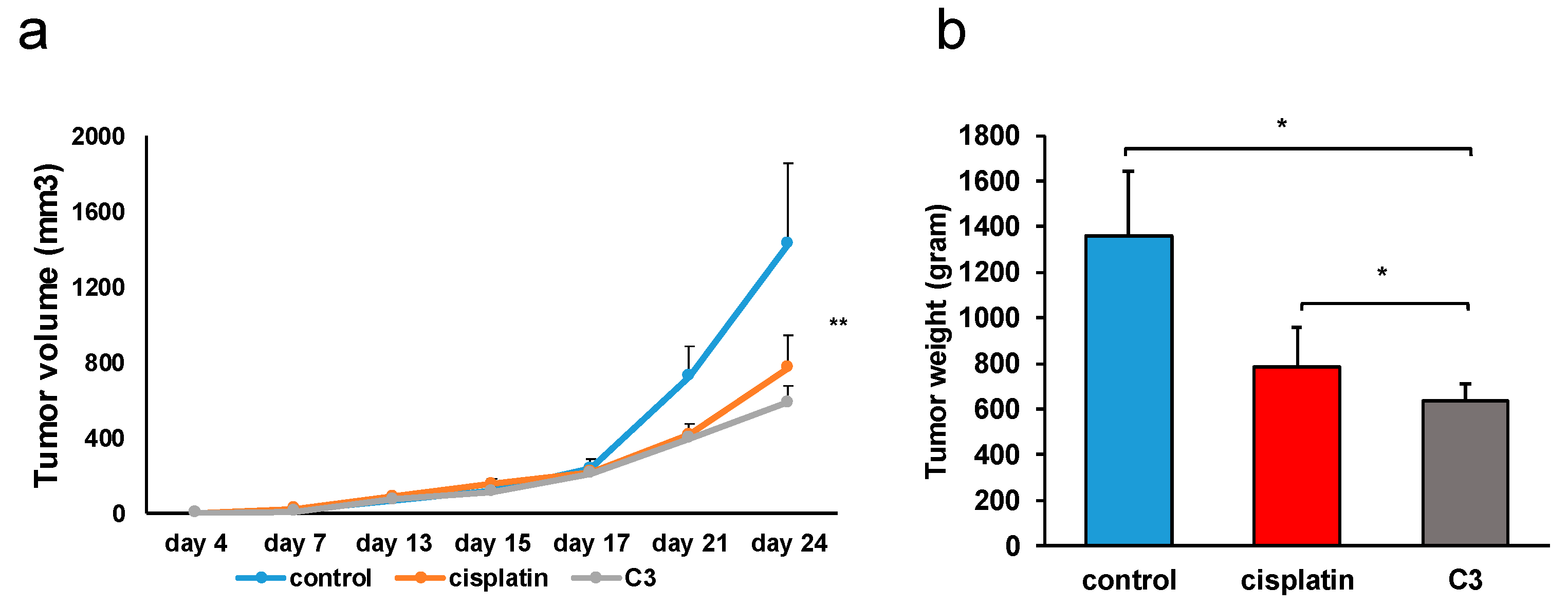
2.3.4. Effects of C3 on the Growth and Metastasis of Murine Primary Heterotopic Colon Cancer
2.3.5. C3 Reduces Liver and Lung Metastases of Mice with Primary Heterotopic Colon Cancer CT26
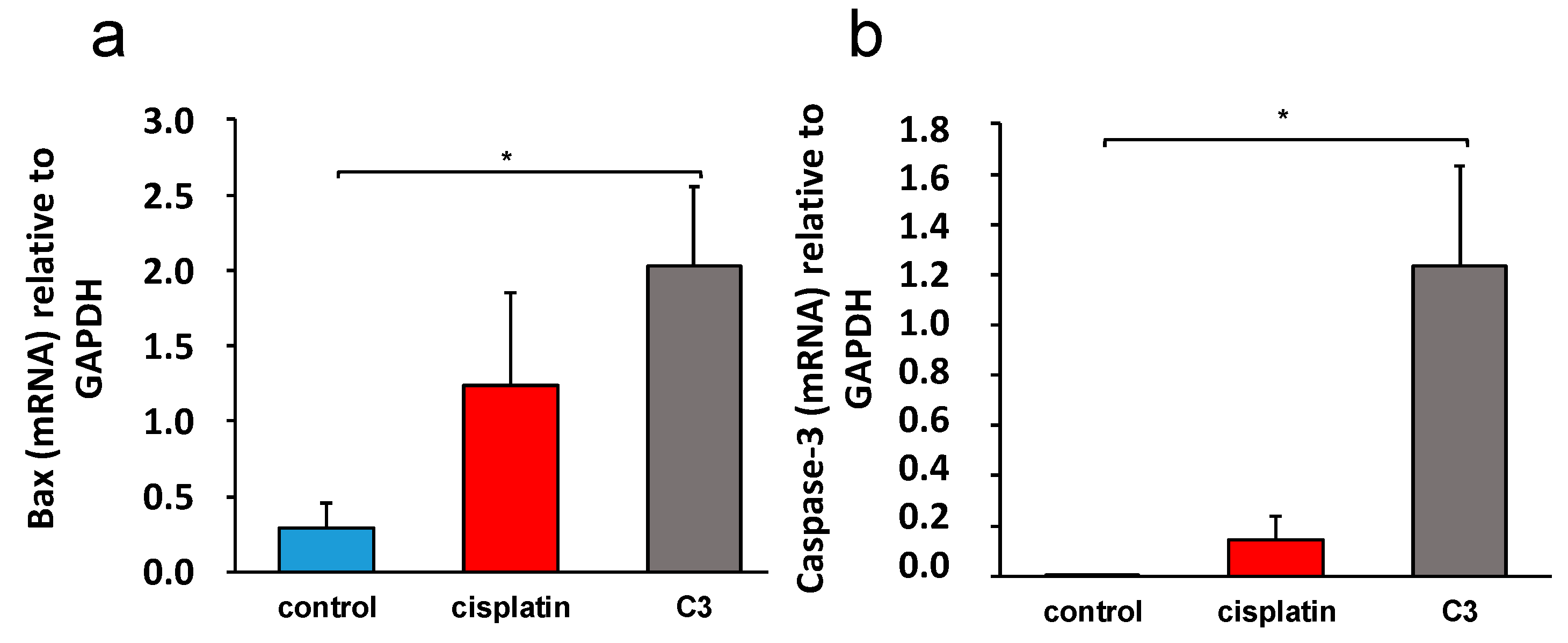
2.3.6. C3 Reduces the Expression of Inflammation Markers in Tissue of Primary Murine Heterotopic Colon Cancer
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Measurements
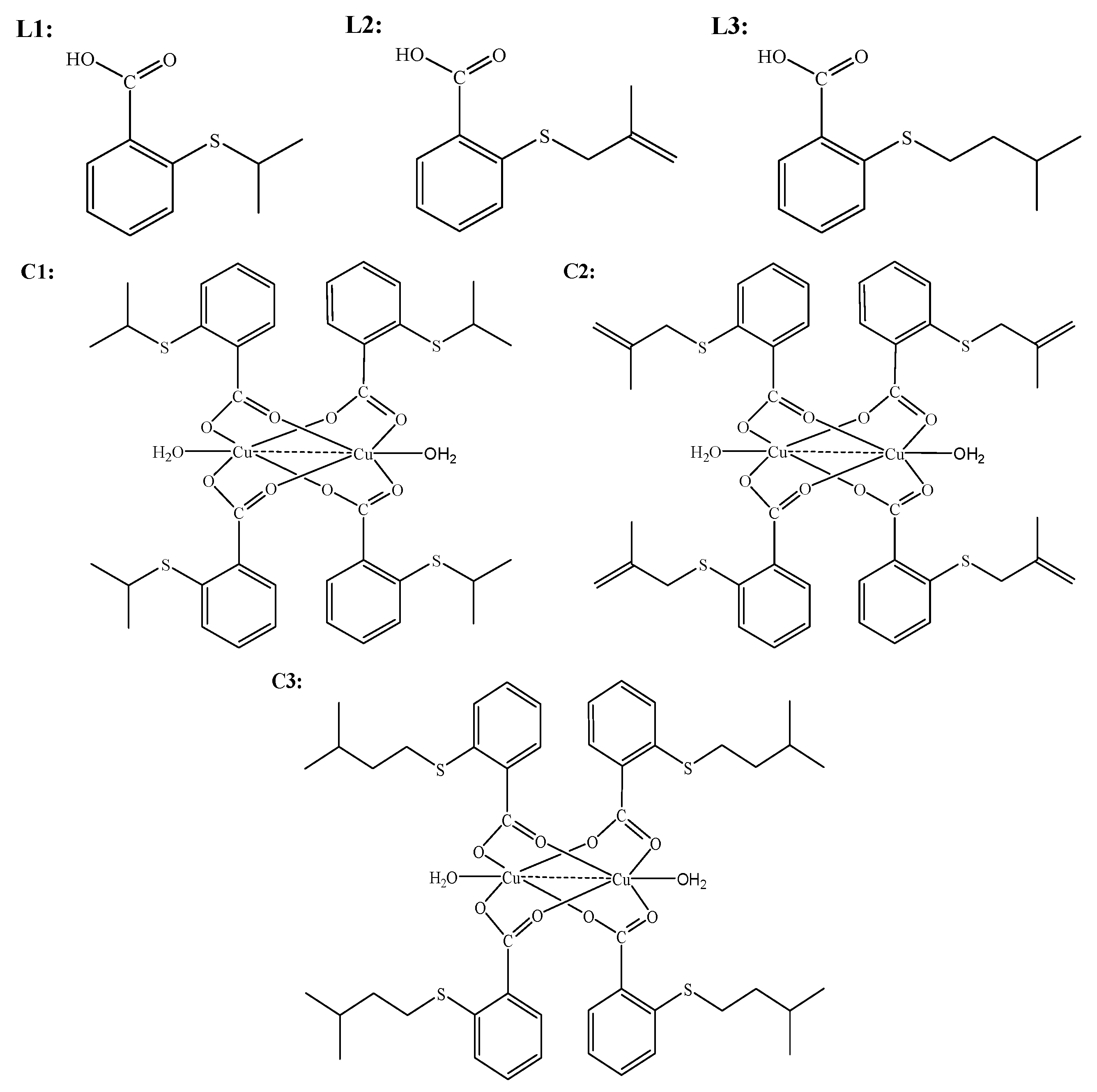
4.2. Syntheses
4.2.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of S-Isoalkyl Derivatives of Thiosalicylic Acid (L1)–(L3)
4.2.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Copper(II)-Complexes with S-Isoalkyl Derivatives of Thiosalicylic Acid (C1)–(C3)
4.3. UV–Vis DNA Interactions
4.4. UV–Vis Absorption Studies
4.5. Ethidium Bromide (EB) Displacement Studies
4.6. Viscosity Measurements
4.7. Protein Binding Studies
4.8. Methodology of Docking
4.9. Cytotoxic Activity
4.9.1. Cell Culture
4.9.2. MTT Assay
4.9.3. Annexin V Propidium Iodide Double Staining Assay
4.9.4. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.9.5. Experimental Animals
4.9.6. Heterotopic Model of Murine Colon Cancer and Drug Treatment
4.9.7. Estimation of Colon Cancer Growth
4.9.8. Histological Analysis
4.9.9. RNA Extraction and Real-Time qRT-PCR
4.9.10. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tisato, F.; Marzano, C.; Porchia, M.; Pellei, M.; Santini, C. Copper in diseases and treatments, and copper-based anticancer strategies. Med. Res. Rev. 2010, 30, 708–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.R.; Swamy, M.K.; Satyanarayana, B. In silico DNA topo IIβ binding and in vitro DNA interaction, anti-proliferative, and anti-bacterial activities of two new ternary Copper (II) schiff base complexes. Chem. Data Collect. 2018, 17–18, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathiresana, S.; Mugeshb, S.; Muruganb, M.; Ahamedb, F.; Annaraj, J. Mixed-ligand copper(II)-phenolate complexes: Structure and studies on DNA/protein binding profiles, DNA cleavage, molecular docking and cytotoxicity. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 1810–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Guo, Z. Functionalization of platinum complexes for biomedical applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 2622–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, F.; Sarmad, H.; Di, C.; Andrew, D.; Sara, S.; Dajena, T.; Ping Dou, Q. Novel metals and metal complexes as platforms for cancer therapy. Curr. Phram. Des. 2010, 16, 1813–1825. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, E.; Giandomenico, C.M. Current status of platinum-based antitumor drugs. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2451–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeles-Boza, A.M.; Bradley, P.M.; Fu, P.K.-L.; Wicke, S.E.; Bacsa, J.; Dunbar, K.R.; Turro, C. DNA binding and photocleavage in vitro by new dirhodium(ii) dppz complexes: Correlation to cytotoxicity and photocytotoxicity. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 8510–8519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarski, P.J.; Mackay, F.S.; Sadler, P.J. Photoactivatable platinum complexes. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajda, N.; Kralovánszky, J.; Gal, F.; Kiss, F.; Kerpel-Fronius, S. Evaluation of side effects of platinum complexes (CDDP, CBDCA, CHIP) on rat bone marrow. Vivo 1989, 3, 267–270. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, P.A.; Xiao, H.; Yu, C.; Liu, J.; Cheng, Z.; Song, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Waqng, J.; Gu, Z.; et al. Enhanced cisplatin chemotherapy by iron oxide nanocarriermediated generation of highly toxic reactive oxygen species. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 928–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthi, P.; Mahendiran, D.; Shobana, S.; Srinivasan, P.; Kalilur Rahiman, A. Theoretical, biological and in silico studies of pen-dant-armed heteroleptic copper(II) phenolate complexes. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1161, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ramos, J.C.; Galindo-Murillo, R.; Cortés-Guzmán, F.; Ruiz-Azuara, L. Metal-Based Drug-DNA Interactions. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2013, 57, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalaivani, P.; Prabhakaran, R.; Vaishnavi, E.; Rueffer, T.; Lang, H.; Poornima, P.; Renganathan, R.; Padma, V.V.; Natarajan, K. Synthesis, structure, DNA/protein binding and in vitro cytotoxicity of new ruthenium metallates. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2014, 1, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagesan, M.; Bhuvanesh, N.S.P.; Dharmaraj, N. Potentially cytotoxic new copper(II) hydrazone complexes: Synthesis, crystal structure and biological properties. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 7210–7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, C.; Pellei, M.; Gandin, V.; Porchia, M.; Tisato, F.; Marzano, C. Advances in copper complexes as anticancer agents. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 815–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbu, S.; Kandaswamy, M.; Selvaraj, M. DNA binding, DNA hydrolysis and phosphatase-like activity of new macrobicyclic dicopper(II) complexes. Polyhedron 2011, 33, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, A.W.; Ali, S.; Tahir, M.N.; Zahoor, M.; Wadood, A.; Iqbal, M. Binuclear copper(II) complexes: Synthesis, structural characterization, DNA binding and in silico studies. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2020, 85, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowndes, S.A.; Harris, A.L. The role of copper in tumour angiogenesis. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2005, 10, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.-F. Copper stimulates proliferation of human endothelial cells under culture. J. Cell. Biochem. 1998, 69, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, G.; Vuyyuru, H.; Muthuvel, B.; Natrajan, S.K. CTR1 silencing inhibits angiogenesis by limiting copper entry into endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soncin, F.; Guitton, J.-D.; Cartwright, T.; Badet, J. Interaction of human angiogenin with copper modulates angiogenin binding to endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 236, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wee, N.K.; Weinstein, D.C.; Fraser, S.T.; Assinder, S.J. The mammalian copper transporters CTR1 and CTR2 and their roles in de-velopment and disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 960–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, A.; AlAjmi, M.F.; Rehman, T.; Amir, S.; Husain, F.M.; Alsalme, A.; Siddiqui, M.A.; AlKhedhairy, A.A.; Khan, R.A. Copper(II) complexes as potential anticancer and Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents: In vitro and in vivo studies. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dimitrijević, J.; Arsenijević, A.N.; Milovanović, M.Z.; Arsenijević, N.N.; Milovanović, J.Z.; Stanković, A.S.; Bukonjić, A.M.; Tomović, D.L.; Ratković, Z.R.; Potočňák, I.; et al. Synthesis, characterization and cytotoxic activity of binuclear cop-per(II)-complexes with some S-isoalkyl derivatives of thiosalicylic acid. Crystal structure of the binuclear copper(II)-complex with S-isopropyl derivative of thiosalicylic acid. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2020, 208, 111078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancar, A.; Lindsey-Boltz, L.A.; Ünsal-Kaçmaz, K.; Linn, S. Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the DNA damage checkpoints. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004, 73, 39–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sazonova, E.V.; Petrichuk, S.V.; Kopeina, G.S.; Zhivotovsky, B. A link between mitotic defects and mitotic catastrophe: Detection and cell fate. Biol. Direct 2021, 16, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y. Aspirin suppresses chemoresistance and enhances antitumor activity of 5-Fu in 5-Fu-resistant colorectal cancer by abolishing 5-Fuinduced NF-κB activation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koumousi, E.S.; Zampakou, M.; Raptopoulou, C.P.; Psycharis, V.; Beavers, C.M.; Teat, S.J.; Psomas, G.; Stamatatos, T.C. First Palla-dium(II) and Platinum(II) Complexes from Employment of 2,6-Diacetylpyridine Dioxime: Synthesis, Structural and Spectroscopic Characterization, and Biological Evaluation. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 7699–7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, M.A.; Zaki, M.; Afzal, M.; Mane, M.; Kumar, M.; Shah, B.A.; Srivastav, S.; Srikrishna, S.; Peerzada, G.M.; Tabassum, S. Nuclear blebbing of biologically active organoselenium compound towards human cervical cancer cell (HeLa): In vitro DNA/HSA binding, cleavage and cell imaging studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 90, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.M.; Tossi, A.B.; McConnell, D.J.; Ohuigin, C. A study of the interactions of some polypyridylruthenium(II) complexes with DNA using fluorescence spectroscopy, topoisomerisation and thermal denaturation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985, 13, 6017–6034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boger, D.L.; Fink, B.E.; Brunette, S.R.; Tse, W.C.; Hedrick, M.P. A Simple, High-Resolution Method for Establishing DNA Binding Affinity and Sequence Selectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 5878–5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, A.; Sen, T.K.; Ghorai, A.; Musie, G.T.; Mandal, S.K.; Ghosh, U.; Bera, M. Synthesis, Structure, Spectroscopic Characterization, and Protein Binding Affinity of New Water-Soluble Hetero- and Homometallic Tetranuclear [CuII2ZnII2] and [CuII4] Clusters. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 2880–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.C.; Barton, J.K. On demonstrating DNA intercalation. Acc. Chem. Res. 1990, 23, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasternack, R.F.; Gibbs, E.J.; Villafranca, J.J. Interactions of porphyrins with nucleic acids. Biochemistry 1983, 22, 5409–5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rippe, K. Analysis of protein-DNA binding at equilibrium. B. I. F. Futura 1997, 12, 20–26; Qu, X.; Chaires, J.B. Analysis of drug-DNA binding data. Methods Enzymol. 2000, 321, 353–369. [Google Scholar]
- Raja, D.S.; Bhuvanesh, N.S.P.; Natarajan, K. Effect of N(4)-Phenyl Substitution in 2-Oxo-1,2-dihydroquinoline-3-carbaldehyde Semicarbazones on the Structure, DNA/Protein Interaction, and Antioxidative and Cytotoxic Activity of Cu(II) Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 12852–12866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-D.; Tian, J.-L.; Gu, W.; Liu, X.; Yan, S.-P. A novel 1,2,4-triazole-based copper(II) complex: Synthesis, characterization, magnetic property and nuclease activity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2010, 104, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Li, Y.-T.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Yan, C.-W. Synthesis, crystal structure, cytotoxic activities and DNA-binding properties of new binuclear copper(II) complexes bridged by N,N′-bis(N-hydroxyethylaminoethyl)oxamide. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2009, 103, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Majumdar, R.; Roy, M.; Dighe, R.R.; Chakravarty, A.R. An Iron Complex of Dipyridophenazine as a Potent Photocytotoxic Agent in Visible Light. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 2652–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Guo, Q.; Dong, J.; Xu, T.; Li, J. DNA binding, DNA cleavage and BSA interaction of a mixed-ligand copper(II) complex with taurine Schiff base and 1,10-phenanthroline. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2013, 125, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paitandi, R.P.; Gupta, R.K.; Singh, R.S.; Sharma, G.; Koch, B.; Pandey, D.S. Interaction of ferrocene appended Ru(II), Rh(III) and Ir(III) dipyrrinato complexes with DNA/protein, molecular docking and antitumor activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 84, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.N. Recent advances in molecular luminescence analysis. Proc. Anal. Div. Chem. Soc. 1979, 16, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Huang, W.; Dai, Z.X. Spectroscopic investigation of the interaction between riboflavin and bovine serum albumin. J. Mol. Struct. 2008, 875, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, S.; Subramani, V.K.; Kim, K.K. Z-DNA in the genome: From structure to disease. Biophys. Rev. 2019, 11, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krall, J.B.; Nichols, P.J.; Henen, M.A.; Vicens, Q.; Vögeli, B. Structure and Formation of Z-DNA and Z-RNA. Molecules 2023, 28, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schottel, B.L.; Chifotides, H.T.; Dunbar, K.R. Anion-p interactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, V.K.; Ravichandran, S.; Bansal, V.; Kim, K.K. Chemical-induced formation of BZ-junction with base extrusion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 508, 1215–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yin, C.; Fedorov, A.; Qiao, L.; Bao, H.; Beknazarov, N.; Wang, S.; Gautam, A.; Williams, R.M.; Crawford, J.C.; et al. ADAR1 masks the cancer immunotherapeutic promise of ZBP1-driven necroptosis. Nature 2022, 606, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, H.R.; Lindén, S.K. The aspirin metabolite salicylate inhibits lysine acetyltransferases and MUC1 induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paterson, J.R.; Lawrence, J.R. Salicylic acid: A link between aspirin, diet and the prevention of colorectal cancer. Qjm Int. J. Med. 2001, 94, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greten, F.R.; Grivennikov, S.I. Inflammation and Cancer: Triggers, Mechanisms, and Consequences. Immunity 2019, 51, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijajlović, M.Ž.; Nikolić, M.V.; Tomović, D.L.; Bukonjić, A.M.; Kočović, A.; Jevtić, V.V.; Ratković, Z.R.; Klisurić, O.; Trifunović, S.R.; Radić, G.P. Synthesis and characterization of platinum(IV)- complexes with some S-alkyl derivatives of thiosalicylic acid. Crystal structure of the S-butyl derivative of thiosalicylic acid. Serbian J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2017, 18, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikolic, M.; Mijajlovic, M.; Jevtic, V.; Ratković, Z.; Novakovic, S.; Bogdanovic, G.; Milovanovic, J.; Arsenijevic, A.; Stojanovic, B.; Trifunovic, S.; et al. Cytotoxicity of copper(II)-complexes with some S-alkyl derivatives of thiosalicylic acid. Crystal structure of the binuclear copper(II)-complex with S-ethyl derivative of thiosalicylic acid. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1116, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijajlović, M.Ž.; Nikolić, M.V.; Jevtić, V.V.; Ratković, Z.R.; Simović Marković, B.; Volarević, V.; Arsenijević, N.N.; Novaković, S.B.; Bogdanović, G.A.; Trifunović, S.R.; et al. Cytotoxicity of palladium(II) complexes with alkyl derivates of thiosalicylic acids. Crystal structure of the bis(S- butyl-thiosalicylate)palladium(II) complex, [Pd(S-bu-thiosal)2]. Polyhedron 2015, 90, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazic, S.; Silconi, Z.B.; Jevtovic, A.; Jurisevic, M.; Milovanovic, J.; Mijajlovic, M.; Nikolic, M.; Kanjevac, T.; Potočňák, I.; Samoľová, E.; et al. The Zn(S-pr-thiosal)2 complex attenu-ates murine breast cancer growth by inducing apoptosis and G1/S cell cycle arrest. Future Med. Chem. 2020, 12, 897–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besser Silconi, Z.; Benazic, S.; Milovanovic, J.; Jurisevic, M.; Djordjevic, D.; Nikolic, M.; Mijajlovic, M.; Ratkovic, Z.; Radić, G.; Radisavljevic, S.; et al. DNA binding and antitumor activities of plati-num(IV) and zinc(II) complexes with some S-alkyl derivatives of thiosalicylic acid. Trans. Met. Chem. 2018, 43, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walencik, P.K.; Stokowa-Sołtys, K.; Wieczorek, R.; Komarnicka, U.K.; Kyzioł, A.; JeżowskaBojczuk, M. Impact of the Cu(II) ions on the chemical and biological properties of goserelin—Coordination pattern, DNA degradation, oxidative reactivity and in vitro cyto-toxicity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2017, 175, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaran, E.; Sogukomerogullari, H.G.; Cakmak, R.; Akkoc, S.; Taskin-Tok, T.; Köse, A. Novel chiral Schiff base Palladium(II), Nickel(II), Copper(II) and Iron(II) complexes: Synthesis, characterization, anticancer activity and molecular docking studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 129, 106176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouda, A.M.; El-Ghamry, H.A.; Bawazeer, T.M.; Farghaly, T.A.; Abdalla, A.N.; Aslam, A. Antitumor activity of pyrrolizines and their Cu(II) complexes: Design, synthesis and cytotoxic screening with potential apoptosis-inducing activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 145, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordestani, N.; Rudbari, H.A.; Fernandes, A.R.; Raposo, L.R.; Luz, A.; Baptista, P.V.; Bruno, G.; Scopelliti, R.; Fateminia, Z.; Micale, N.; et al. Copper(II) complexes with tridentate halogen-substituted Schiff base ligands: Synthesis, crystal structures and investigating the effect of halogenation, leaving groups and ligand flexibility on antiproliferative activities. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 3990–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’connor, M.; Kellett, A.; McCann, M.; Rosair, G.; McNamara, M.; Howe, O.; Creaven, B.S.; McClean, S.; Kia, A.F.-A.; O’shea, D.; et al. Copper(II) complexes of salicylic acid combining superoxide dismutase mimetic properties with dna binding and cleaving capabilities display promising chemotherapeutic potential with fast acting in vitro cytotoxicity against cisplatin sensitive and resistant cancer cell lines. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 1957–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianferrara, T.; Bratsos, I.; Alessio, E. A categorization of metal anticancer compounds based on their mode of action. Dalton Trans. 2009, 37, 7588–7598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, M.C.; Perelmulter, K.; Levín, P.; Romo, A.I.B.; Lemus, L.; Fogolín, M.B.; León, I.E.; Di Virgilio, A.L. Antiproliferative activity of two copper (II) complexes on colorectal cancer cell models: Impact on ROS production, apoptosis induction and NF-κB inhibition. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 169, 106092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arikrishnan, S.; Loh, J.S.; Teo, X.W.; Bin Norizan, F.; Low, M.L.; Lee, S.H.; Foo, J.B.; Tor, Y.S. Ternary Copper (II) Complex Induced Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Mishra, S.; Kamaal, S.; Alarifi, A.; Afzal, M.; Das Saha, K.; Ahmad, M. Evaluation of catacholase mimicking activity and apoptosis in human colorectal carcinoma cell line by activating mitochondrial pathway of copper(II) complex coupled with 2-(quinolin-8-yloxy)(methyl)benzonitrile and 8-hydroxyquinoline. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 106, 104479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vančo, J.; Trávníček, Z.; Hošek, J.; Malina, T.; Dvořák, Z. Copper(II) Complexes Containing Natural Flavonoid Pomiferin Show Considerable In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Anti-inflammatory Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarnicka, U.K.; Starosta, R.; Płotek, M.; de Almeida, R.F.M.; Jeżowska-Bojczuk, M.; Kyzioł, A. Copper(I) complexes with phosphine derived from sparfloxacin. Part II: A first insight into the cytotoxic action mode. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 5052–5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacopetta, B. TP53 mutation in colorectal cancer. Hum. Mutat. 2003, 21, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.A.; Fridman, J.S.; Yang, M.; Baranov, E.; Hoffman, R.M.; Lowe, S.W. Dissecting p53 tumor suppressor functions in vivo. Cancer Cell 2002, 1, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bunz, F.; Hwang, P.M.; Torrance, C.; Waldman, T.; Zhang, Y.; Dillehay, L.; Williams, J.; Lengauer, C.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. Disruption of p53 in human cancer cells alters the responses to therapeutic agents. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castedo, M.; Perfettini, J.-L.; Roumier, T.; Andreau, K.; Medema, R.; Kroemer, G. Cell death by mitotic catastrophe: A molecular definition. Oncogene 2004, 23, 2825–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Q.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, C.; Mo, F.; Chen, L.; Peng, G.; Cai, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Liu, X. Dioscin inhibits the growth of human osteosarcoma by inducing G2/M-phase arrest, apoptosis, and GSDME-dependent cell death in vitro and in vivo. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 2911–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, S.; Rajendiran, V.; Palaniandavar, M.; Periasamy, V.S.; Srinag, B.S.; Krishnamurthy, H.; Akbarsha, M.A. Induction of cell death by ternary copper(II) complexes of L-tyrosine and diimines: Role of coligands on DNA binding and cleavage and anticancer activity. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 1309–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandler, R.S.; Halabi, S.; Baron, J.A.; Budinger, S.; Paskett, E.; Keresztes, R.; Petrelli, N.; Pipas, J.M.; Karp, D.D.; Loprinzi, C.L.; et al. A randomized trial of aspirin to prevent colorectal adenomas in patients with previous colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, J.A.; Cole, B.F.; Sandler, R.S.; Haile, R.W.; Ahnen, D.; Bresalier, R.; McKeown-Eyssen, G.; Summers, R.W.; Rothstein, R.; Burke, C.A.; et al. A Randomized trial of aspirin to prevent colorectal Adenomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, R.F.A.; Grainge, M.J.; Shepherd, V.C.; Armitage, N.C.; Muir, K.R. ukCAP Trial Group. Aspirin and folic acid for the pre-vention of recurrent colorectal adenomas. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, H.; Mutoh, M.; Suzuki, S.; Tokudome, S.; Saida, Y.; Abe, T.; Okamura, S.; Tajika, M.; Joh, T.; Tanaka, S.; et al. The preventive effects of low-dose enteric-coated aspirin tablets on the development of colorectal tumours in Asian patients: A randomised trial. Gut 2014, 63, 1755–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friis, S.; Riis, A.H.; Erichsen, R.; Baron, J.A.; Sørensen, H.T. Low-dose aspirin or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use and col-orectal cancer risk: A population-based, case-control study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 163, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Rodríguez, L.A.; Soriano-Gabarró, M.; Bromley, S.; Lanas, A.; Cea Soriano, L. New use of low-dose aspirin and risk of colo-rectal cancer by stage at diagnosis: A nested casecontrol study in UK general practice. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.T.; Ogino, S.; Fuchs, C.S. Aspirin and the risk of colorectal cancer in relation to the expression of COX-2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 2131–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronov, E.; Apte, R.N. IL-1 in Colon Inflammation, Colon Carcinogenesis and Invasiveness of Colon Cancer. Cancer Microenviron. 2015, 8, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Han, G.C.; Wang, R.X.; Xiao, H.; Hou, C.M.; Guo, R.F.; Dou, Y.; Shen, B.F.; Li, Y.; et al. Neutrophil infil-tration favors colitis-associated tumorigenesis by activating the interleukin-1 (IL-1)/IL-6 axis. Mucosal Immunol. 2014, 7, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zins, K.; Abraham, D.; Sioud, M.; Aharinejad, S. Colon cancer cell–derived tumor necrosis factor-α mediates the tumor growth–promoting response in macrophages by up-regulating the colony-stimulating factor-1 pathway. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Popivanova, B.K.; Kitamura, K.; Wu, Y.; Kondo, T.; Kagaya, T.; Kaneko, S.; Oshima, M.; Fujii, C.; Mukaida, N. Blocking TNF-α in mice reduces colorectal carcinogenesis associated with chronic colitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, C.A.; Friess, H.; Kretschmann, B.; Wildi, S.; Müller, C.; Graber, H.; Schilling, M.; Büchler, M.W. Over-expression of ICAM-1, VCAM-1 and ELAM-1 might influence tumor progression in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 1998, 79, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Chan, S.T.; Yang, T.L.; Tzeng, C.C.; Chen, C.C. Inhibition of ICAM-1 gene expression, monocyte adhesion and cancer cell invasion by targeting IKK complex: Molecular and functional study of novel alpha-methylene-gamma-butyrolactone derivatives. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 1925–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dymicka-Piekarska, V.; Kemona, H. Does colorectal cancer clinical advancement affect adhesion molecules (sP-selectin, sE-selectin and ICAM-1) concentration? Thromb Res. 2009, 124, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Shun, C.T.; Wu, M.S.; Chen, C.C. A novel anticancer effect of thalidomide: Inhibition of intercellular adhesion mole-cule-1-mediated cell invasion and metastasis through suppression of nuclear factor-kappaB. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 7165–7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schellerer, V.S.; Langheinrich, M.; Hohenberger, W.; Croner, R.S.; Merkel, S.; Rau, T.T.; Stürzl, M.; Naschberger, E. Tumor-associated fibroblasts isolated from colorectal cancer tissues exhibit increased ICAM-1 expression and affinity for monocytes. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ionescu, C.; Braicu, C.; Chiorean, R.; Petric, R.C.; Neagoe, E.; Pop, L.; Chira, S.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. TIMP-1 Expression in human colorectal cancer is associated with smad3 gene expression levels: A pilot study. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2014, 23, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tachimori, A.; Yamada, N.; Sakate, Y.; Yashiro, M.; Maeda, K.; Ohira, M.; Nishino, H.; Hirakawa, K. Up regulation of ICAM-1 gene expression inhibits tumour growth and liver metastasis in colorectal carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 1802–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gho, Y.S.; Kim, P.N.; Li, H.C.; Elkin, M.; Kleinman, H.K. Stimulation of tumor growth by human soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 4253–4257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, R.; Peng, Y.; Tang, W.; Xi, Y.; Tian, G.; Zhang, Y. Roles of intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in colorectal cancer: Expression, functions, prognosis, tumorigenesis, polymorphisms and therapeutic implications. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1052672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meadows, K.A.; Liu, F.; Sou, J.; Hudson, B.P.; McMillin, D.R. Spectroscopic and photophysical studies of the binding interactions between copper phenanthroline complexes and RNA. Inorg. Chem. 1993, 32, 2919–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harel, M.; Schalk, I.; Ehret-Sabatier, L.; Bouet, F.; Goeldner, M.; Hirth, C.; Axelsen, P.H.; Silman, I.; Sussman, J.L. Quaternary ligand binding to aromatic residues in the active-site gorge of acetylcholinesterase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 9031–9035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, H.R.; Wing, R.M.; Takano, T.; Broka, C.; Tanaka, S.; Itakura, K.; Dickerson, R.E. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer: Confor-mation and dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 2179–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oleg, T.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dassault Systèmes BIOVIA. Discovery Studio Modeling Environment (Release 2017); Dassault Systèmes: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]







| Kb [M−1] | Ksv [M−1] | Kbin [M−1] | n | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | (4.5 ± 0.1) × 104 | (1.0 ± 0.1) × 103 | (1.0 ± 0.1) × 103 | 1 |
| C2 | (2.0 ± 0.1) × 105 | (2.7 ± 0.1) × 103 | (6.5 ± 0.1) × 106 | 1.7 |
| C3 | (1.7 ± 0.1) × 104 | (0.9 ± 0.1) × 103 | (1.9 ± 0.1) × 102 | 0.6 |
| Complex | Ksv [M−1] | Kbin [M−1] | n |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | (5.9 ± 0.1) × 104 | (7.2 ± 0.1) × 106 | 1.5 |
| C2 | (1.1 ± 0.1) × 105 | (1.6 ± 0.1) × 1012 | 2.6 |
| C3 | (1.0 ± 0.1) × 105 | (2.2 ± 0.1) × 103 | 0.6 |
| Cell Line | IC50 ± SD (μg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | Cisplatin | |
| SW480 | 188.52 ± 25.87 | 172.54 ± 30.18 | 170.19 ± 42.27 | 17.31 ± 4.26 |
| CT26 | 274.51 ± 47.5 | 142.47 ± 30.21 | 53.57 ± 9.54 | 64.87 ± 6.85 |
| Selectivity Index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | Cisplatin | |
| SW480 | 1.84 | 1.39 | 1.41 | 3.74 |
| CT26 | 1.26 | 1.69 | 4.47 | 1.04 |
| Untreated | Cisplatin | C3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage of mice with liver metastases | 88.89 | 50 | 25 |
| Percentage of mice with lung metastases | 88.89 | 50 | 25 |
| Sense (5′ to 3′) | Antisense (5′ to 3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| Mouse Bax | ACACCTGAGCTGACCTTG | AGCCCATGATGGTTCTGATC |
| Mouse Caspase-3 | AAATTCAAGGGACGGGTCAT | ATTGACACAATACACGGGATCTGT |
| Mouse ICAM-1 | CAATTTCTCATGCCGCACAG | AGCTGGAAGATCGAAAGTCCG |
| Mouse VCAM-1 | TGAACCCAAACAGAGGCAGAGT | GGTATCCCATCACTTGAGCAGG |
| Mouse TNF-α | CCACATCTCCCTCCAGAAAA | AGGGTCTGGGCCATAGAACT |
| Mouse IL-1β | TCTTTGAAGTTGACGGACCC | TGAGTGATACTGCCTGCCTG |
| Mouse GAPDH | CATCACTGCCACCCAGAAGACTG | ATGCCAGTGAGCTTCCCGTTCAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dimitrijević, J.D.; Solovjova, N.; Bukonjić, A.M.; Tomović, D.L.; Milinkovic, M.; Caković, A.; Bogojeski, J.; Ratković, Z.R.; Janjić, G.V.; Rakić, A.A.; et al. Docking Studies, Cytotoxicity Evaluation and Interactions of Binuclear Copper(II) Complexes with S-Isoalkyl Derivatives of Thiosalicylic Acid with Some Relevant Biomolecules. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512504
Dimitrijević JD, Solovjova N, Bukonjić AM, Tomović DL, Milinkovic M, Caković A, Bogojeski J, Ratković ZR, Janjić GV, Rakić AA, et al. Docking Studies, Cytotoxicity Evaluation and Interactions of Binuclear Copper(II) Complexes with S-Isoalkyl Derivatives of Thiosalicylic Acid with Some Relevant Biomolecules. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(15):12504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512504
Chicago/Turabian StyleDimitrijević, Jelena D., Natalija Solovjova, Andriana M. Bukonjić, Dušan Lj. Tomović, Mirjana Milinkovic, Angelina Caković, Jovana Bogojeski, Zoran R. Ratković, Goran V. Janjić, Aleksandra A. Rakić, and et al. 2023. "Docking Studies, Cytotoxicity Evaluation and Interactions of Binuclear Copper(II) Complexes with S-Isoalkyl Derivatives of Thiosalicylic Acid with Some Relevant Biomolecules" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 15: 12504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512504
APA StyleDimitrijević, J. D., Solovjova, N., Bukonjić, A. M., Tomović, D. L., Milinkovic, M., Caković, A., Bogojeski, J., Ratković, Z. R., Janjić, G. V., Rakić, A. A., Arsenijevic, N. N., Milovanovic, M. Z., Milovanovic, J. Z., Radić, G. P., & Jevtić, V. V. (2023). Docking Studies, Cytotoxicity Evaluation and Interactions of Binuclear Copper(II) Complexes with S-Isoalkyl Derivatives of Thiosalicylic Acid with Some Relevant Biomolecules. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(15), 12504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241512504







