Evaluating the Classification Accuracy of Expression Quantitative Trait Loci Calculated Polygenic Risk Scores in Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
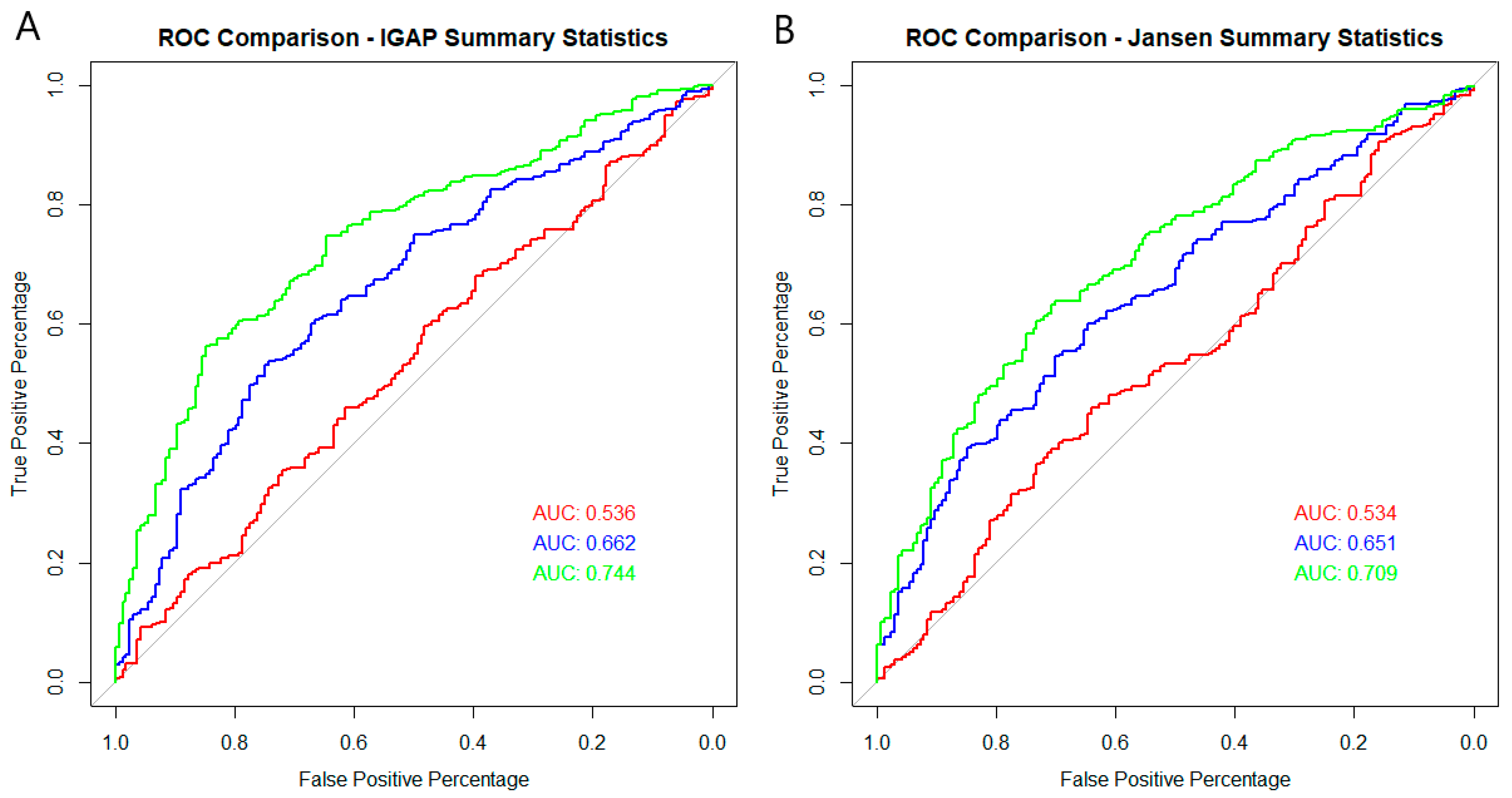
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barker, W.W.; Luis, C.A.; Kashuba, A.; Luis, M.; Harwood, D.G.; Loewenstein, D.; Waters, C.; Jimison, P.; Shepherd, E.; Sevush, S.; et al. Relative Frequencies of Alzheimer Disease, Lewy Body, Vascular and Frontotemporal Dementia, and Hippocampal Sclerosis in the State of Florida Brain Bank. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2002, 16, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatz, M.; Reynolds, C.A.; Fratiglioni, L.; Johansson, B.; Mortimer, J.A.; Berg, S.; Fiske, A.; Pedersen, N.L. Role of Genes and Environments for Explaining Alzheimer Disease. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2006, 63, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sims, R.; Hill, M.; Williams, J. The Multiplex Model of the Genetics of Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Sommerlad, A.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Brayne, C.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; Cooper, C.; et al. Dementia Prevention, Intervention, and Care: 2020 Report of the Lancet Commission. Lancet 2020, 396, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.R.; Zimmer, J.A.; Evans, C.D.; Lu, M.; Ardayfio, P.; Sparks, J.; Wessels, A.M.; Shcherbinin, S.; Wang, H.; Nery, E.S.M.; et al. Donanemab in Early Symptomatic Alzheimer Disease: The TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2023, 330, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, J.R.J.R.; Mistry, S.; Muskett, N.; Escott-Price, V.; Brookes, K. From Polygenic Scores to Precision Medicine in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 74, 1271–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, T.W.; Katzourou, I.K.; Stevenson-Hoare, J.O.; Bracher-Smith, M.R.; Ivanov, D.K.; Escott-Price, V. Machine Learning for the Life-Time Risk Prediction of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, A.C.J.W. Validity of Polygenic Risk Scores: Are We Measuring What We Think We Are? Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, R143–R150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecile, A.; Janssens, J.W.; Joyner, M.J. Polygenic Risk Scores That Predict Common Diseases Using Millions of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms: Is More, Better? Clin. Chem. 2019, 65, 609–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, F.K.; Tonk, E.C.M.; Janssens, A.C.J.W. Evaluation of Polygenic Risk Models Using Multiple Performance Measures: A Critical Assessment of Discordant Results. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.; Gallagher, E.; Koska, K.; Guetta-Baranes, T.; Morgan, K.; Thomas, A.; Brookes, K.J. Genome-Wide Association Findings from the Brains for Dementia Research Cohort. Neurobiol. Aging 2021, 107, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.-C.; Ibrahim-Verbaas, C.A.; Harold, D.; Naj, A.C.; Sims, R.; Bellenguez, C.; Jun, G.; DeStefano, A.L.; Bis, J.C.; Beecham, G.W.; et al. Meta-Analysis of 74,046 Individuals Identifies 11 New Susceptibility Loci for Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jansen, I.E.; Savage, J.E.; Watanabe, K.; Bryois, J.; Williams, D.M.; Steinberg, S.; Sealock, J.; Karlsson, I.K.; Hägg, S.; Athanasiu, L.; et al. Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis Identifies New Loci and Functional Pathways Influencing Alzheimer’s Disease Risk. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellenguez, C.; Küçükali, F.; Jansen, I.E.; Kleineidam, L.; Moreno-Grau, S.; Amin, N.; Naj, A.C.; Campos-Martin, R.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Andrade, V.; et al. New Insights into the Genetic Etiology of Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Dementias. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 412–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, R.; Van Der Lee, S.J.J.; Naj, A.C.C.; Bellenguez, C.; Badarinarayan, N.; Jakobsdottir, J.; Kunkle, B.W.W.; Boland, A.; Raybould, R.; Bis, J.C.C.; et al. Rare Coding Variants in PLCG2, ABI3, and TREM2 Implicate Microglial-Mediated Innate Immunity in Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, J.R.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, L.; Ueno, L.; Du, L.; Jonkers, M.; Yates, J.R.; Vogt, P.K. The Butterfly Effect in Cancer: A Single Base Mutation Can Remodel the Cell. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desi, N.; Tay, Y. The Butterfly Effect of RNA Alterations on Transcriptomic Equilibrium. Cells 2019, 8, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ospina-Romero, M.; Glymour, M.M.; Hayes-Larson, E.; Mayeda, E.R.; Graff, R.E.; Brenowitz, W.D.; Ackley, S.F.; Witte, J.S.; Kobayashi, L.C. Association Between Alzheimer Disease and Cancer With Evaluation of Study Biases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2025515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, K.; Soosaipillai, A.; Sando, S.B.; Lauridsen, C.; Berge, G.; Møller, I.; Grøntvedt, G.R.; Bråthen, G.; Begcevic, I.; Moussaud, S.; et al. Assessment of Kallikrein 6 as a Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2018, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angeli, S.; Kousiappa, I.; Stavrou, M.; Sargiannidou, I.; Georgiou, E.; Papacostas, S.S.; Kleopa, K.A. Altered Expression of Glial Gap Junction Proteins Cx43, Cx30, and Cx47 in the 5XFAD Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 582934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, F.; Hassan, R.; Adam, I.; Bansal, R.; Broersen, K. A Review of Oxidative Stress Products and Related Genes in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 83, 977–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkowski, K.; Pedersen, T.L.; Seyfried, N.T.; Lah, J.J.; Levey, A.I.; Hales, C.M.; Dammer, E.B.; Blach, C.; Louie, G.; Kaddurah-Daouk, R.; et al. Association of Plasma and CSF Cytochrome P450, Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase, and Ethanolamide Metabolism with Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarparast, M.; Dattmore, D.; Alan, J.; Lee, K.S.S. Cytochrome P450 Metabolism of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Neurodegeneration. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, K.J.; Guetta-Baranes, T.; Thomas, A.; Morgan, K. An Alternative Method of SNP Inclusion to Develop a Generalized Polygenic Risk Score Analysis across Alzheimer’s Disease Cohorts. Front. Dement. 2023, 2, 1120206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, J.S.; Bonham, L.W.; Sears, R.L.; Klein, E.; Karydas, A.; Kramer, J.H.; Miller, B.L.; Coppola, G. Decision Tree Analysis of Genetic Risk for Clinically Heterogeneous Alzheimer’s Disease. BMC Neurol. 2015, 15, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sleegers, K.; Bettens, K.; De Roeck, A.; Van Cauwenberghe, C.; Cuyvers, E.; Verheijen, J.; Struyfs, H.; Van Dongen, J.; Vermeulen, S.; Engelborghs, S.; et al. A 22-Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Alzheimer’s Disease Risk Score Correlates with Family History, Onset Age, and Cerebrospinal Fluid Abeta42. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 11, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Escott-Price, V.; Sims, R.; Bannister, C.; Harold, D.; Vronskaya, M.; Majounie, E.; Badarinarayan, N.; Morgan, K.; Passmore, P.; Holmes, C.; et al. Common Polygenic Variation Enhances Risk Prediction for Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain 2015, 138, 3673–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leonenko, G.; Baker, E.; Stevenson-Hoare, J.; Sierksma, A.; Fiers, M.; Williams, J.; de Strooper, B.; Escott-Price, V. Identifying Individuals with High Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Polygenic Risk Scores. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosto, G.; Bird, T.D.; Tsuang, D.; Bennett, D.A.; Boeve, B.F.; Cruchaga, C.; Faber, K.; Foroud, T.M.; Farlow, M.; Goate, A.M.; et al. Polygenic Risk Scores in Familial Alzheimer Disease. Neurology 2017, 88, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escott-Price, V.; Myers, A.J.; Huentelman, M.; Hardy, J. Polygenic Risk Score Analysis of Pathologically Confirmed Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escott-Price, V.; Myers, A.; Huentelman, M.; Shoai, M.; Hardy, J.; Hardy, J. Polygenic Risk Score Analysis of Alzheimer’s Disease in Cases without APOE4 or APOE2 Alleles. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. JPAD 2019, 6, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marigorta, U.M.; Denson, L.A.; Hyams, J.S.; Mondal, K.; Prince, J.; Walters, T.D.; Griffiths, A.; Noe, J.D.; Crandall, W.V.; Rosh, J.R.; et al. Transcriptional Risk Scores Link GWAS to EQTL and Predict Complications in Crohn’s Disease HHS Public Access Author Manuscript. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1517–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Pividori, M.; Manichaikul, A.; Palmer, A.A.; Cox, N.J.; Wheeler, H.E.; Im, H.K. Polygenic Transcriptome Risk Scores (PTRS) Can Improve Portability of Polygenic Risk Scores across Ancestries. Genome Biol. 2022, 23, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pain, O.; Glanville, K.P.; Hagenaars, S.; Selzam, S.; Fürtjes, A.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Rimfeld, K.; Breen, G.; Folkersen, L.; Lewis, C.M. Imputed Gene Expression Risk Scores: A Functionally Informed Component of Polygenic Risk. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 30, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, P.T.; Costello, H.; Hayes, G.M. Brains for Dementia Research: Evolution in a Longitudinal Brain Donation Cohort to Maximize Current and Future Value. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 66, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, S.; Patel, T.; Guetta-Baranes, T.; Sang, F.; Francis, P.T.; Morgan, K.; Brookes, K.J. Observations of Extensive Gene Expression Differences in the Cerebellum and Potential Relevance to Alzheimer’s Disease. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A Fast Spliced Aligner with Low Memory Requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. FeatureCounts: An Efficient General Purpose Program for Assigning Sequence Reads to Genomic Features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shabalin, A.A. Gene Expression Matrix EQTL: Ultra Fast EQTL Analysis via Large Matrix Operations. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.-C.; Müller, M. PROC: An Open-Source Package for R and S+ to Analyze and Compare ROC Curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| eQTLs | eQTLs Plus APOE | eQTLs in DE Genes | eQTLs in DE Genes Plus APOE | rs429358 & rs7412 Only | Best Model Using Thresholding without APOE Region | Best Model Using Thresholding Plus APOE Isoform SNPs | Best Model Using Thresholding with APOE Region | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGAP | # SNPs | 17,865 | 17,867 | 1614 | 1616 | 2 | 29 | 31 | 56 |
| Logisitic Regression p value | 9.22 × 10−6 | 1.52 × 10−8 | 0.184 | 3.18 × 10−8 | 6.89 × 10−15 | 6.73 × 10−5 | 2.61 × 10−16 | 9.20 × 10−18 | |
| Area Under the Curve | 0.6144 | 0.6508 | 0.5357 | 0.6616 | 0.7082 | 0.6078 | 0.7442 | 0.7633 | |
| Jansen | # SNPs | 34,894 | 34,896 | 3116 | 3118 | 2 | 62 | 64 | 164 |
| Logisitic Regression p value | 1.02 × 10−6 | 2.51 × 10−9 | 0.264 | 7.72 × 10−8 | 2.1 × 10−14 | 0.0002 | 1.93 × 10−12 | 3.72 × 10−16 | |
| Area Under the Curve | 0.6417 | 0.6738 | 0.5335 | 0.6511 | 0.7083 | 0.6033 | 0.7089 | 0.7543 | |
| Bellenguez | # SNPs | 30,863 | - | 2759 | - | - | 70,674 | - | - |
| Logisitic Regression p value | 1.76 × 10−5 | - | 0.03 | - | - | 2.73 × 10−11 | - | - | |
| Area Under the Curve | 0.6241 | - | 0.5586 | - | - | 0.6865 | - | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brookes, K.J. Evaluating the Classification Accuracy of Expression Quantitative Trait Loci Calculated Polygenic Risk Scores in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612799
Brookes KJ. Evaluating the Classification Accuracy of Expression Quantitative Trait Loci Calculated Polygenic Risk Scores in Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(16):12799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612799
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrookes, Keeley J. 2023. "Evaluating the Classification Accuracy of Expression Quantitative Trait Loci Calculated Polygenic Risk Scores in Alzheimer’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 16: 12799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612799
APA StyleBrookes, K. J. (2023). Evaluating the Classification Accuracy of Expression Quantitative Trait Loci Calculated Polygenic Risk Scores in Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(16), 12799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612799





