Perspectives of Proteomics in Respiratory Allergic Diseases
Abstract
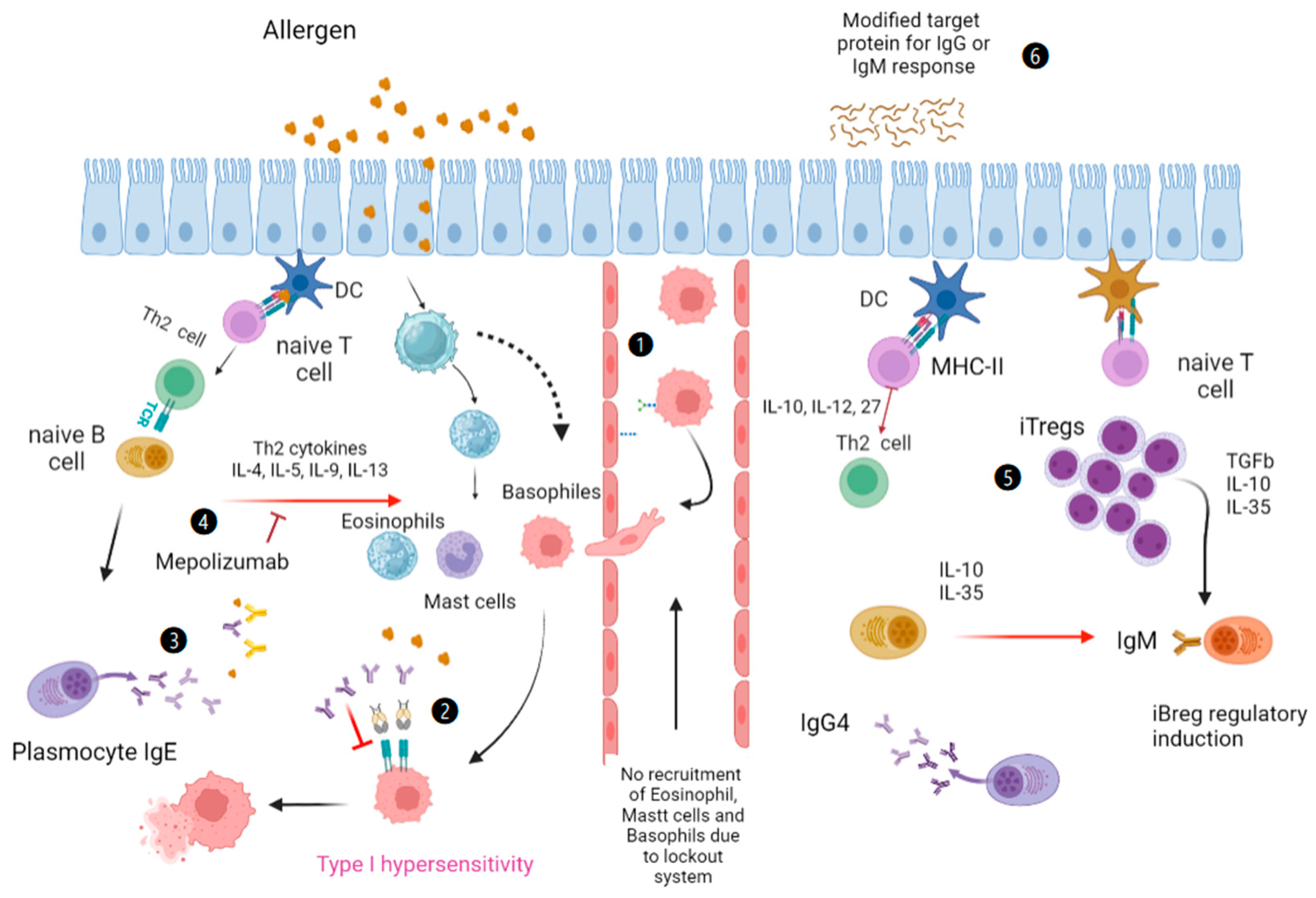
:1. Introduction
2. Global Characteristics of Allergies for Proteomics Studies
3. Proteomic Technologies for the Study of Respiratory Allergies
3.1. ELISA
3.2. Luminex
3.3. Western Blotting
3.4. Liquid Chromatography
3.5. Mass Spectrometry for Tree Allergen Homology
| Trees | Allergens | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Birch | Bet v 1, Bet v 2, Bet v 3, Bet v 4, Bet v 5, Bet v 6 | [62,63,65] |
| Alder | Aln g 1, Aln g 2, Aln g 3, Aln g 4 | [65] |
| Beech | Fag s 1 | [66] |
| Oak | Que a 1 | [67] |
| Ash | Fra e 1. Fra e 2, Fra e 3, Fra e 6, Fra e 10, Fra e 11, and Fra e 12 | [44,68] |
| Thunder | Lig v 1 | [69,70] |
| Olive | Ole e 1 to Ole e 12 | [71,72] |
| Lilac | Syr v 1, Syr v 2, Syr v 3 | [62,73] |
| Cypress | Cha o 1 | [74,75] |
| Japanese cedar | Cry j 1, Cry j 2 | [2,76] |
| Juniper | Jun a 1, Jun a 2 | [2,77] |
| Plantain | Pla a 1 to Pla a 4 | [78] |
| Ficus | Fic c 1 | [72] |
| Walnut | Jug r 5 | [79] |
3.6. Other Methods
4. Informatics for the Development of Protein Models
4.1. Protein Data Bank
4.2. Immune Epitope Database (IEDB)
4.3. UniProt
4.4. Swiss-Prot
4.5. Modeler
4.6. Rosetta Commons
4.7. AlphaFold Protein Structure Database
4.8. X-ray Cryptography
5. Discussion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilkins, M.R.; Christian, P.; Ron, D.A.; Ou, K.; Golaz, O.; Sanchez, J.-C.; Yan, J.X.; Gooley, A.A.; Hughes, G.; Humphery-Smith, I.; et al. From Proteins to Proteomes: Large Scale Protein Identification by Two-Dimensional Electrophoresis and Arnino Acid Analysis. Nat. Biotechnol. 1996, 1, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amrani, S.; Al-Jabri, Z.; Al-Zaabi, A.; Alshekaili, J.; Al-Khabori, M. Proteomics: Concepts and applications in human medicine. World. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 5, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphery-Smith, I. The 20th anniversary of proteomics and some of its origins. Proteomics 2015, 11, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, R.; Robert, P.A.; Pavlović, M.; Jeliazkov, J.R.; Snapkov, I.; Slabodkin, A.; Weber, C.R.; Scheffer, L.; Miho, E.; Haff, I.H.; et al. A compact vocabulary of paratope-epitope interactions enables predictability of antibody-antigen binding. Cell. Rep. 2021, 34, 108856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badotti, F.; Barbosa, A.S.; Reis, A.L.M.; do Valle, I.F.; Ambrósio, L.; Bitar, M. Comparative modeling of proteins: A method for engaging students’ interest in bioinformatics tools. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2014, 1, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlén, M.; Karlsson, M.J.; Hober, A.; Svensson, A.S.; Scheffel, J.; Kotol, D. The human secretome. Sci. Signal. 2019, 609, eaaz0274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizuet-de-Rueda, J.C.; Montero-Vargas, J.M.; Galván-Morales, M.A.; Gutiérrez-de-Velasco, P.R.; Teran, L.M. Current Insights on the Impact of Proteomics in Respiratory Allergie. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 10, 5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Krempski, J.W.; Nadeau, K. Advances and novel developments in mechanisms of allergic inflammation. Allergy 2020, 12, 3100–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.J.; Huang, M.T. Asthma in the Precision Medicine Era: Biologics and Probiotics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 9, 4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demoly, P. Respiratory allergic disease genes. Rev. Pneumol. Clin. 2003, 2 Pt 1, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Portelli, M.A.; Hodge, E.; Sayers, I. Genetic risk factors for the development of allergic disease identified by genome-wide association. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2015, 1, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, D.E.; Boyle, R.J.; Thornton, C.A.; Prescott, S.L. Mechanisms of allergic disease—Environmental and genetic determinants for the development of allergy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2015, 5, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevach, E.M.; Thornton, A.M. tTregs, pTregs, and iTregs: Similarities and differences. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 259, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzada, D.; Cremades-Jimeno, L.; López-Ramos, M.; Cárdaba, B. Peptide Allergen Immunotherapy: A New Perspective in Olive-Pollen Allergy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 7, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Alhamwe, B.A.; Santner-Nanan, B.; Miethe, B.; Harb, H.; Renz, H.; Potaczek, D.P.; Nanan, R.K. Short-Chain Fatty Acids Augment Differentiation and Function of Human Induced Regulatory T Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 10, 5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agache, I.; Beltran, J.; Akdis, C.; Akdis, M.; Canelo-Aybar, C.; Canonica, G.W.; Casale, T.; Chivato, T.; Corren, J.; Del Giacco, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of treatment with biologicals (benralizumab, dupilumab, mepolizumab, omalizumab and reslizumab) for severe eosinophilic asthma. A systematic review for the EAACI Guidelines—Recommendations on the use of biologicals in severe asthma. Allergy 2020, 5, 1023–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, N.; Mariotti-Ferrandiz, M.E.; Wang, Y.; Malissen, B.; Waldmann, H.; Hori, S. Heterogeneity of natural Foxp3+ T cells: A committed regulatory T-cell lineage and an uncommitted minor population retaining plasticity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1903–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Shumate, A.; Pertea, G.; Varabyou, A.; Breitwieser, F.P.; Chang, Y.C.; Madugundu, A.K.; Pandey, A.; Salzberg, S.L. CHESS: A new human gene catalog curated from thousands of large-scale RNA sequencing experiments reveals extensive transcriptional noise. Genome Biol. 2018, 1, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortuaire, G.; Marchetti, P.; Formstecher, P.; Danzé, P.M. Micro-array based technologies to study the proteome: Technological progress and applications. Ann. Biol. Clin. 2004, 2, 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Link, A.J.; Washburn, M.P. Analysis of protein composition using multidimensional chromatography and mass spectrometry. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2014, 78, 23.1.1–23.1.25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Seo, J.; Shin, S.K. Multi-functional MBIT for peptide tandem mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2015, 2, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Fonslow, B.R.; Shan, B.; Baek, M.C.; Yates, J.R. Protein Analysis by Shotgun/Bottom-up Proteomics. Chem. Rev. 2013, 4, 2343–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porebski, G.; Piotrowicz-Wojcik, K.; Spiewak, R. ELISpot assay as a diagnostic tool in drug hypersensitivity reactions. J. Immunol. Methods 2021, 495, 113062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, K.; Nishiyama, C. IL-10 in Mast Cell-Mediated Immune Responses: Anti-Inflammatory and Proinflammatory Roles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 9, 4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaillant, A.A.J.; Vashisht, R.; Zito, P.M. Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions; Stat Pearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.W.; McKinney, B.H.; Blankenship, K.D.; Morris, D.O. Detection and Inhibition of IgE for cross-reactive carbohydrate determinants evident in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of allergen-specific IgE in the sera of dogs and cats. Vet. Dermatol. 2020, 6, 439-e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinou, G.N. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA). Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1592, 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, D.K.; Grammer, L.C. An overview of allergens. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2019, 6, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Grammer, L.C. Chapter 1: An overview of allergens. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2012, 33 (Suppl. S1), 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.Y.; Williams, K.D. Hypersensitivity to molds in New York City in adults who have asthma. Alergia Asthma Proc. 2003, 1, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Huss, K.; Adkinson, N.F., Jr.; Eggleston, P.A.; Dawson, C.; Van Natta, M.L.; Hamilton, R.G. House dust mite and cockroach exposure are strong risk factors for positive allergy skin test responses in the Childhood Asthma Management Program. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 1, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lee, H.; Choi, A.R.; Park, K.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Oh, E.J. Comparison of allergen-specific IgE levels between Immulite 2000 and ImmunoCAP systems against six inhalant allergens and ten food allergens. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2018, 7–8, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasilova, N.; Girault, H.H. Bioanalytical methods for food allergy diagnosis, allergen detection and new allergen discovery. Bioanalysis 2015, 9, 1175–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saff, R.R. Skin testing as a biomarker in drug allergy. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023, 2, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Uchida, T.; Chazono, H.; Ookawa, T.; Sakurai, D.; Okamoto, Y. Seasonal changes in antigen-specific T-helper clone sizes in patients with Japanese cedar pollinosis: A 2-year study. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2008, 3, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, N.C.; Wang, K.; Wadhwa, P.D.; Culhane, J.F.; Nelson, E.L. Validation and comparison of luminex multiplex cytokine analysis kits with ELISA: Determinations of a panel of nine cytokines in clinical sample culture supernatants. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2005, 2, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognon, B.; Reboux, G.; Roussel, S.; Barrera, C.; Dalphin, J.C.; Fellrath, J.M.; Monod, M.; Millon, L. Western blotting as a tool for the serodiagnosis of farmer’s lung disease: Validation with Lichtheimia corymbifera protein extracts. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, D.G.; Milner, F.H.; Johnson, P. The Allergenic Activity and Stability of Purified Allergens from the Pollen of Common Rye Grass (Lolium perenne). Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1966, 6, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakalarski, C.E.; Kirkpatrick, D.S. A Biologist’s Field Guide to Multiplexed Quantitative Proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2016, 5, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavski, N.; Peters, U.; Brettschneider, R.; Oldenburg, M.; Baur, X.; Bittner, C. Cof a 1: Identification, expression and immunoreactivity of the first coffee allergen. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 159, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, K.S.; Gadermaier, G.; Vejvar, E.; Arcuri, H.A.; Galvão, C.E.; Yang, A.C.; Resende, V.M.F.; de Oliviera Martins, C.; Himly, M.; Mari, A.; et al. Novel allergens from ancient foods: Man e 5 from manioc (Manihot esculenta Crantz) cross reacts with Hev b 5 from latex. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelle, J.L.; Green, R. One-dimensional SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (1D SDS-PAGE). Methods Enzymol. 2014, 541, 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- Gargan, E.; Ohlendieck, K. Sample Preparation and Protein Determination for 2D-DIGE Proteomics. In Difference Gel Electrophoresis. Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 2596, pp. 325–337. [Google Scholar]
- Mas, S.; Garrido-Arandia, M.; Batanero, E.; Purohit, A.; Pauli, G.; Rodríguez, R.; Barderas, R.; Villalba, M. Characterization of profilin and polcalcin panallergens from ash pollen. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 4, 257–266. [Google Scholar]
- Yagami, A.; Ebisawa, M. New findings, pathophysiology, and antigen analysis in pollen-food allergy syndrome. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 3, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, M.; Roulias, A.; Ferreira, F.; Egger, M. Panallergens and their impact on the allergic patient. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2010, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papia, F.; Incorvaia, C.; Genovese, L.; Gangemi, S.; Minciullo, P.L. Allergic reactions to genus Morus plants: A review. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2020, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Ahanathapillai, V.; Sharma, N.R.; Jan, S.; Roy, A.; Upadhyay, A.K. Structural insights into the amino acid usage variations in the profilin gene family. Amino Acids 2022, 3, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, O. Separation techniques: Chromatography. North Clin. Istanb. 2016, 2, 156–160. [Google Scholar]
- Barderas, R.; Purohit, A.; Rodríguez, R.; Pauli, G.; Villalba, M. Isolation of the main allergen Fra e 1 from ash (Fraxinus excelsior) pollen: Comparison of the natural and recombinant forms. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006, 4, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohman, J., Jr.; Lowell, F.; Bloch, K. Allergens of mammalian origin: Characterization of allergen extracted from cat pelts. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1973, 4, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, N.; Brieva, A. Purification of allergens by high-performance liquid chromatography: V. Purification of cat and dog ephithelial allergens. J. Chromutography 1987, 404, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.K.; Leung, D.Y.M. Dog and Cat Allergies: Current State of Diagnostic Approaches and Challenges. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2018, 2, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahlbusch, B.; Rudeschko, O.; Szilagyi, U.; Schlott, B.; Henzgen, M.; Schlenvoigt, G.; Schubert, H. Purification and partial characterization of the major allergen, Cav p 1, from guinea pig Cavia porcellus. Allergy 2002, 5, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilger, C.; Swiontek, K.; Kler, S.; Diederich, C.; Lehners, C.; Vogel, L.; Vieths, S.; Hentges, F. Evaluation of two new recombinant guinea-pig lipocalins, Cav p 2 and Cav p 3, in the diagnosis of guinea-pig allergy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2011, 1, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.; Tee, R.D.; Stuart, M.C.; Newman-Taylor, A.J. Analysis of allergens in rat fur and saliva. Allergy 2001, 6, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foo, A.C.; Thompson, P.M.; Mueller, G.A. Removal and Replacement of Endogenous Ligands from Lipid-Bound Proteins and Allergens. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 168, e61780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Múnera, M.; Sanchez, A.; Sánchez, J.; Nordmann, M.; Perez, M.; Aparicio, D. Allergy to Mus m 1: Allergy to Mus m 1: A review of structural, and immunological features. Immunol. Lett. 2019, 209, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, R.G. Assessment of indoor allergen exposure. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2005, 5, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablos, I.; Wildner, S.; Asam, C.; Wallner, M.; Gadermaier, G. Pollen Allergens for Molecular Diagnosis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, E.; Breda, D.; Spisni, A.; Burastero, S.E. Component-Resolved Diagnosis Based on a Recombinant Variant of Mus m 1 Lipocalin Allergen. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 2, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, J.T.; Chen, K.H.; Sheu, F. Determination of the soybean allergen Gly m 6 and its stability in food processing using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry coupled with stable-isotope dimethyl labelling. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo Risk Assess. 2022, 6, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acunha, T.; Nardini, V.; Ferranti-Peti, A.P.; Borges-Prado, M.K.; Beraldo-Moraes, L.A.; Faccioli, L.H. Targeted analysis of eicosanoids derived from cytochrome P450 pathway by high-resolution multiple-reaction monitoring mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 7, e4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamloo, F.; Schmitz, N.; Scheurer, S.; Foetisch, K.; Hoffmann, A.; Haustein, D.; Vieths, S. Molecular cloning and characterization of a birch pollen minor allergen, Bet v 5, belonging to a family of isoflavone reductase-related proteins. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 5, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mari, A.; Wallner, M.; Ferreira, F. Fagales pollen sensitization in a birch-free area: A respiratory cohort survey using Fagales pollen extracts and birch recombinant allergens (rBet v 1, rBet v 2, rBet v 4). Clin. Exp. Allergy 2003, 10, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heath, M.D.; Collis, J.; Batten, T.; Hutchings, J.W.; Swan, N.; Skinner, M.A. Molecular, proteomic and immunological parameters of allergens provide inclusion criteria for new candidates within established grass and tree homologous groups. World Allergy Organ. J. 2015, 1, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Yang, M.; Jeong, K.Y.; Sim, D.W.; Park, J.H.; Park, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.W. Characterization of a Major Allergen from Mongolian Oak, Quercus mongolica, a Dominant Species of Oak in Korea. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 2, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, B.M.; Huerta-Ocampo, J.A.; Garcia-Sanchez, J.R.; Barrera-Pacheco, A.; de la Rosa, A.P.; Teran, L.M. Identification of Ligustrum lucidum pollen allergens using a proteomics approach. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 468, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robledo-Retana, T.; Mani, B.M.; Teran, L.M. Ligustrum pollen: New insights into allergic disease. World Allergy Organ J. 2020, 2, 100104. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, R.; Villalba, M.; Monsalve, R.I.; Batanero, E. The spectrum of olive pollen allergens. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2001, 3, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, E.; Villalba, M.; Rodríguez, R. Immunological and molecular characterization of the major allergens from lilac and privet pollens overproduced in Pichia pastoris. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2001, 2, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cases, B.; Ibañez, M.D.; Tudela, J.I.; Sanchez-Garcia, S.; Rodriguez Del Rio, P.; Fernandez, E.A.; Escudero, C.; Fernandez-Caldas, E. Immunological cross-reactivity between olive and grass pollen: Implication of major and minor allergens. World Allergy Organ. J. 2014, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Kuroki, M.; Maeda, M.; Okano, M.; Yokoyama, M.; Kino, K. Glycoform analysis of Japanese cypress pollen allergen, Cha o 1: A comparison of the glycoforms of cedar and cypress pollen allergens. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 2, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, M.; Kamamoto, M.; Hino, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Kimura, M.; Okano, M.; Kimura, Y. Glycoform analysis of Japanese cedar pollen allergen, Cry j 1. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 9, 1700–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osada, T.; Okano, M. Japanese cedar and cypress pollinosis updated: New allergens, cross-reactivity, and treatment. Allergol. Int. 2021, 3, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Kamamoto, M.; Maeda, M.; Okano, M.; Yokoyama, M.; Kino, K. Occurrence of Lewis a epitope in N-glycans of a glycoallergen, Jun a 1, from mountain cedar (Juniperus ashei) pollen. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 1, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansotegui, I.J.; Melioli, G.; Canonica, G.W.; Caraballo, L.; Villa, E.; Ebisawa, M.; Passalacqua, G.; Savi, E.; Ebo, D.; Gomez, R.M.; et al. IgE allergy diagnostics and other relevant tests in allergy, a World Allergy Organization position paper. World Allergy Organ. J. 2021, 7, 100557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheerbrant, H.; Guillien, A.; Vernet, R.; Lupinek, C.; Pison, C.; Pin, I.; Demenais, F.; Nadif, R.; Bousquet, J.; Pickl, W.F.; et al. Associations between specific IgE sensitization to 26 respiratory allergen molecules and HLA class II alleles in the EGEA cohort. Allergy 2021, 8, 2575–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenta, R.; Breiteneder, H.; Petternburger, K.; Breitenbach, M.; Rumpold, H.; Kraft, D.; Scheiner, O. Homology of the major birch-pollen allergen, Bet v I, with the major pollen allergens of alder, hazel, and hornbeam at the nucleic acid level as determined by cross-hybridization. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1991, 3, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, T.; Dairiki, K.; Morikubo, K.; Shimizu, K.; Tsunoo, H.; Mori, T.; Kino, K. Identification of human T cell epitopes in Japanese cypress pollen allergen, Cha o 1, elucidates the intrinsic mechanism of cross-allergenicity between Cha o 1 and Cry j 1, the major allergen of Japanese cedar pollen, at the T cell level. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2005, 5, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.; Palomares, O.; Quiralte, J.; Pauli, G.; Rodríguez, R.; Villalba, M. An Enzymatically Active β-1,3-Glucanase from Ash Pollen with Allergenic Properties: A Particular Member in the Oleaceae Family. PLoS ONE 2015, 7, e0133066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedermann, T.; Winther, L.; Till, S.J.; Panzner, P.; Knulst, A.; Valovirta, E. Birch pollen allergy in Europe. Allergy 2019, 7, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedermann, T.; Winther, L.; Till, S.J.; Panzner, P.; Knulst, A.; Valovirta, E. The allergen profile of ash (Fraxinus excelsior) pollen: Cross-reactivity with allergens from various plant species. Allergy 2019, 32, 933–941. [Google Scholar]
- Rivas, M.F. Cross-reactivity between fruit and vegetables. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2003, 3, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Huerta-Ocampo, J.A.; Valenzuela-Corral, A.; Robles-Burgueño, M.R.; Guzmán-Partida, A.M.; Hernández-Oñate, M.A.; Vázquez-Moreno, L.; Pavón-Romero, G.F.; Terán, L.M. Proteomic identification of allergenic proteins in red oak (Quercus rubra) pollen. World Allergy Organ. J. 2020, 3, 100111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Amparano, M.B.; Valenzuela-Corral, A.; Ramos-Clamont Montfort, G.; Vázquez-Moreno, L.; Escobedo-Moratilla, A.; Pastor-Palacios, G.; Ovando-Vázquez, C.; Teran, L.M.; Huerta-Ocampo, J.A. Immunoproteomic identification of allergenic proteins in pecan (Carya illinoinensis) pollen. J. Proteom. 2021, 248, 104348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lee, B.; Du, W.X.; Lyu, S.C.; Nadeau, K.C.; Grauke, L.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Fan, Y.; Yi, J.; et al. Identification and Characterization of a New Pecan [Carya illinoinensis (Wangenh.) K. Koch] Allergen, Car i 2. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 20, 4146–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordas-Le Floch, V.; Le Mignon, M.; Bouley, J.; Groeme, R.; Jain, K.; Baron-Bodo, V.; Nony, E.; Mascarell, L.; Moingeon, P. Identification of Novel Short Ragweed Pollen Allergens Using Combined Transcriptomic and Immunoproteomic Approaches. PLoS ONE 2015, 8, e0136258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, S.; Torres, M.; Garrido-Arandia, M.; Salamanca, G.; Castro, L.; Barral, P.; Purohit, A.; Pauli, G.; Rodríguez, R.; Batanero, E.; et al. Ash pollen immunoproteomics: Identification, immunologic characterization, and sequencing of 6 new allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 3, 923–926.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez-Borque, E.; Betancor, D.; Fernández-Bravo, S.; Gómez-Cardeñosa, A.; Esteban, V.; Garrido-Arandia, M.; de las Herras, M.; Pastor-Vargas, C.; Cuesta-Herranz, J. Allergen Profile of London Plane Tree Pollen: Clinical and Molecular Pattern in Central Spain. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 5, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Li, B.; Zhan, X.; Schlüter, H.; Jungblut, P.R.; Coorssen, J.R. Innovating the Concept and Practice of Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis in the Analysis of Proteomes at the Proteoform Level. Proteomes 2019, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, J.; Sassmann, A.; Kasper, C.; Nimptsch, A.; Schubert, S. Extracellular Matrix Synthesis and Remodeling by Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Is Context-Sensitive. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 3, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhrik, L.; Henek, T.; Planas-Iglesias, J.; Kucera, J.; Damborsky, J.; Marek, M.; Hernychova, L. Study of Protein Conformational Dynamics Using Hydrogen/Deuterium Exchange Mass Spectrometry. Methods Mol Biol. 2023, 2652, 293–318. [Google Scholar]
- Adkins, J.N.; Varnum, S.M.; Auberry, K.J.; Moore, R.J.; Angell, N.H.; Smith, R.D.; Springer, D.L.; Pounds, J.G. Toward a human blood serum proteome: Analysis by multidimensional separation coupled with mass spectrometry. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2002, 12, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, J.K.; Jahan, T.A.; Hoopmann, M.R. Comet: An open-source MS/MS sequence database search tool. Proteomics 2013, 1, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyssié, D.; Gonzalez de Peredo, A.; Mouton, E.; Albigot, R.; Roussel, L.; Ortega, N.; Cayrol, C.; Burlet-Schiltz, O.; Girard, J.P.; Monsarrat, B. Mascot file parsing and quantification (MFPaQ), a new software to parse, validate, and quantify proteomics data generated by ICAT and SILAC mass spectrometric analyses: Application to the proteomics study of membrane proteins from primary human endothelial cells. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2007, 9, 1621–1637. [Google Scholar]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Cox, J. The MaxQuant computational platform for mass spectrometry-based shotgun proteomics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 12, 2301–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Chan, C.; Meng, F.; Hu, Y.; Chen, L.; Lin, G.; Zhang, S.; Wheeler, A.R. Comparison of Database Searching Programs for the Analysis of Single-Cell Proteomics Data. J. Proteome Res. 2023, 4, 1298–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soman, K.V.; Midoro-Horiuti, T.; Ferreon, J.C.; Goldblum, R.M.; Brooks, E.G.; Kurosky, A.; Braun, W.; Schei, C.H. Homology modeling and characterization of IgE binding epitopes of mountain cedar allergen Jun a 3. Biophys. J. 2000, 3, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, S.K.; Berman, H.M.; Kleywegt, G.J.; Markley, J.L.; Nakamura, H.; Velankar, S. Protein Data Bank (PDB): The Single Global Macromolecular Structure Archive. Methods Mol Biol. 2017, 1607, 627–641. [Google Scholar]
- Sidney, J.; Peters, B.; Sett, A. Epitope prediction and identification-adaptive T cell responses in humans. Semin. Immunol. 2020, 50, 101418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D480–D489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratilová, B.; Řehulka, P.; Garajová, S.; Řehulková, H.; Stratilová, E.; Hrmova, M.; Kozmon, S. Structural characterization of the Pet c 1.0201 PR-10 protein isolated from roots of Petroselinum crispum (Mill.) Fuss. Phytochemistry 2020, 175, 112368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajaejun, T.; Reamtong, O.; Lohnoo, T.; Yingyong, W.; Thammasudjarit, R. Assessment of temperature-dependent proteomes of Pythium insidiosum by using the SWISS-PROT database. Med. Mycol. 2019, 7, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaezzadeh, A.R.; Hernandez, C.; Vadas, O.; Deshusses, J.J.; Lescuyer, P.; Lisacek, F.; Hochstrasser, D.F. PICarver: A software tool and strategy for peptides isoelectric focusing. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 10, 4336–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, M.; Howell, S.; Sachdeva, R.; Dumont, C. Allergen cross-reactivity in allergic rhinitis and oral-allergy syndrome: A bioinformatic protein sequence analysis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014, 7, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using MODELLER. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2014, 47, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marze, N.A.; Roy-Burman, S.S.; Sheffler, W.; Gray, J.J. Efficient flexible backbone protein-protein docking for challenging targets. Bioinformatics 2018, 20, 3461–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadi, M.; Velankar, S. The impact of AlphaFold Protein Structure Database on the fields of life sciences. Proteomics 2022, e2200128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoline, L.; Lima, A.N.; Krieger, J.E.; Teixeira, S.K. Before and after AlphaFold2: An overview of protein structure prediction. Front. Bioinform. 2023, 3, 1120370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessau, M.A.; Modis, Y. Protein crystallization for X-ray crystallography. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 47, 2285. [Google Scholar]
- Gaudet, A.; Portier, L.; Prin, M.; Copin, M.C.; Tsicopoulos, A.; Mathieu, D.; Lassalle, P.; De Freitas-Caires, N. Endocan regulates acute lung inflammation through control of leukocyte diapedesis. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 3, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galván-Morales, M.Á. Perspectives of Proteomics in Respiratory Allergic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612924
Galván-Morales MÁ. Perspectives of Proteomics in Respiratory Allergic Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(16):12924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612924
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalván-Morales, Miguel Ángel. 2023. "Perspectives of Proteomics in Respiratory Allergic Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 16: 12924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612924
APA StyleGalván-Morales, M. Á. (2023). Perspectives of Proteomics in Respiratory Allergic Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(16), 12924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612924






