CD74 Promotes a Pro-Inflammatory Tumor Microenvironment by Inducing S100A8 and S100A9 Secretion in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
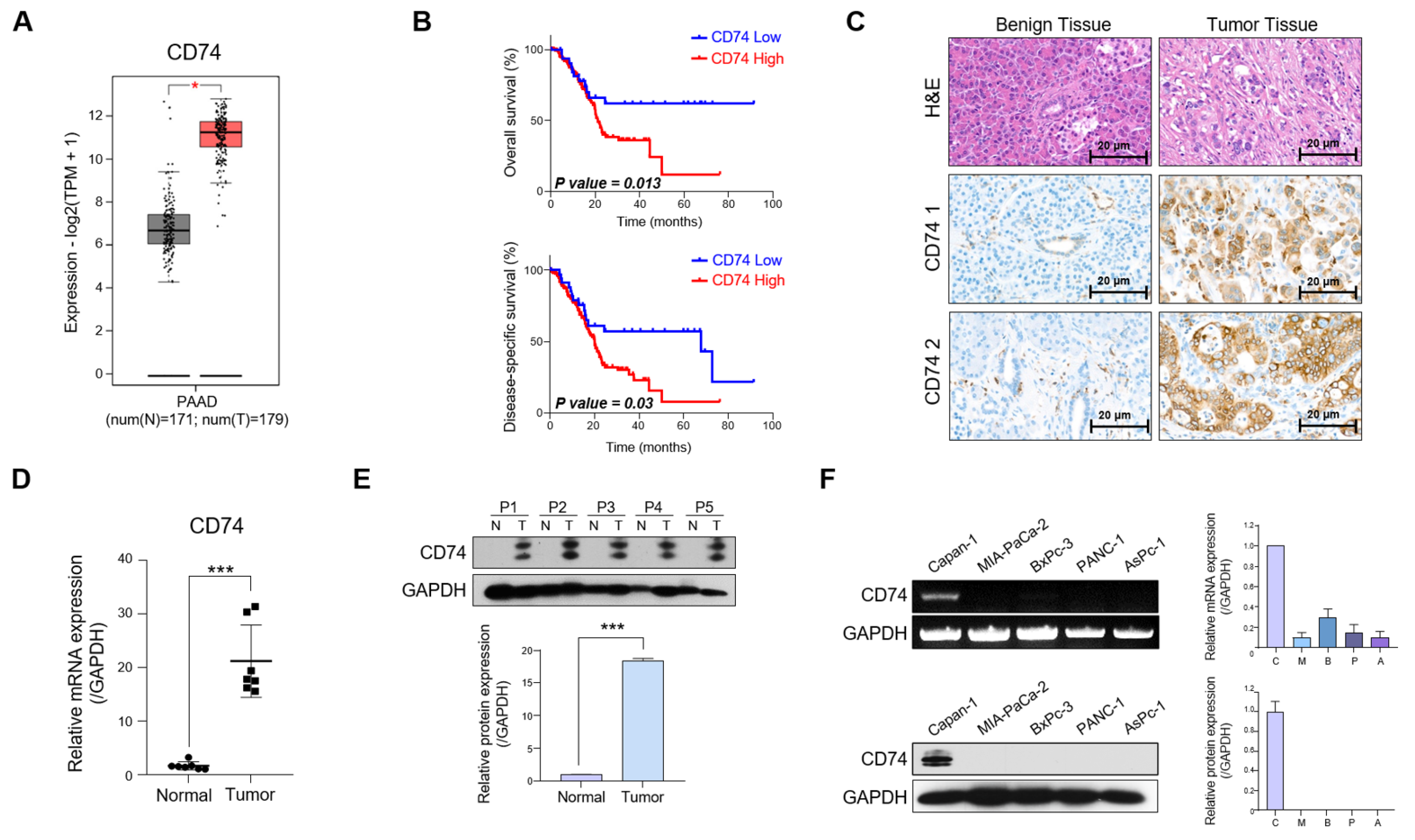
2.1. CD74 Expression Is Elevated in Patients with PDAC
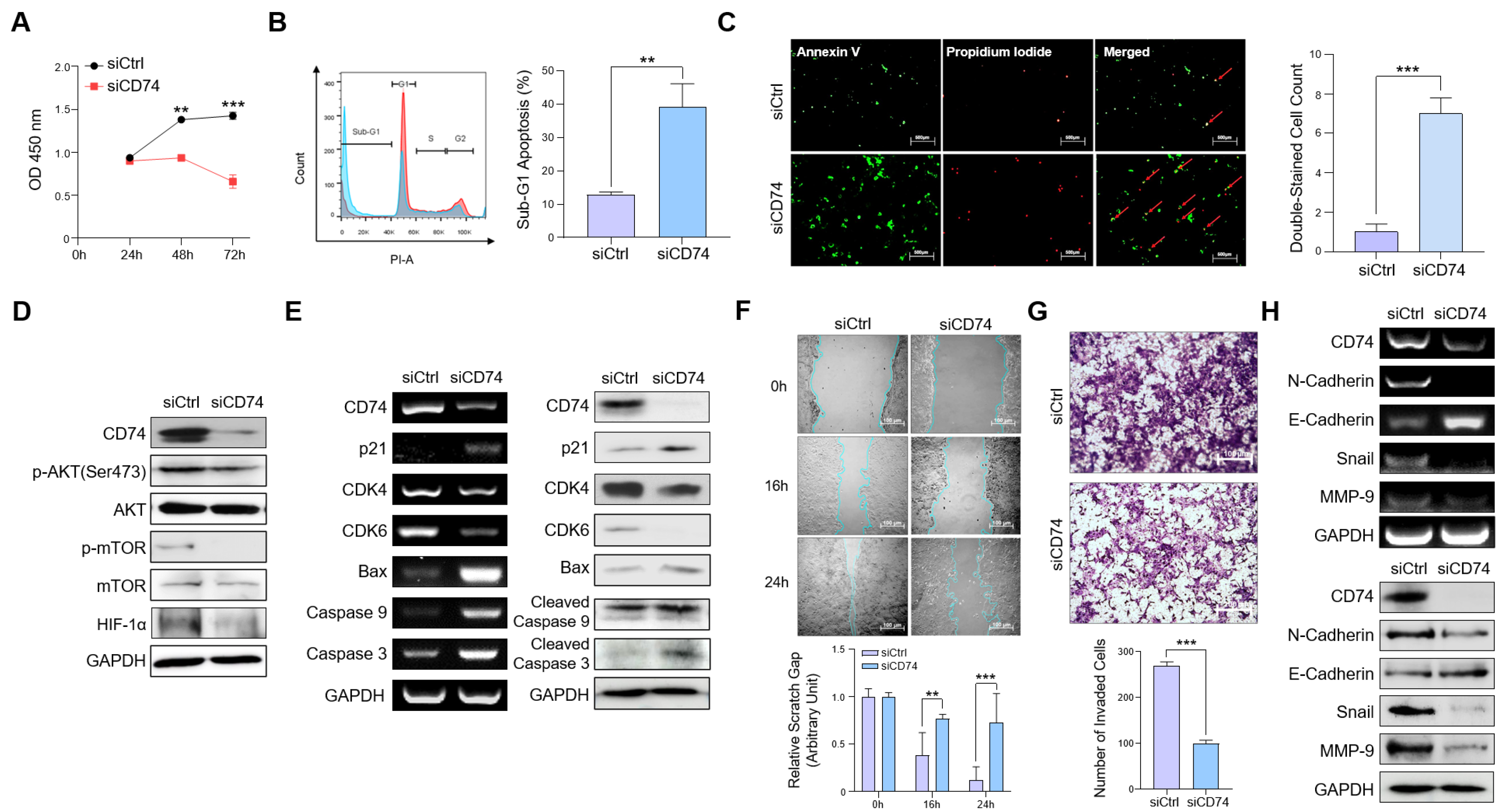
2.2. CD74 Suppression Reduces Oncogenic Properties of Tumor Cells In Vitro
2.3. CD74 Knockdown Decreases the Expression and Secretion of S100A8 and S100A9
2.4. S100A8 and S100A9 Induce the Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Normal Fibroblasts (NFs)
2.5. CD74 Knockdown Reduces Both Tumor Growth and Inflammatory Conditions in an Orthotopic Mouse Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Tissue Collection
4.2. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
4.3. Western Blotting
4.4. siRNA Transfection
4.5. Isolation and Culture of NFs and CAFs
4.6. Annexin V-FITC and PI Staining Assay
4.7. PI Staining Analysis
4.8. WST-1 Assay
4.9. CM Preparation
4.10. ELISA
4.11. RNA Isolation and PCR
4.12. qRT-PCR
4.13. RNA-Seq Analysis
4.14. Wound Healing Assay
4.15. Transwell Invasion Assay
4.16. Mouse Tumor Model
4.17. IHC Staining
4.18. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, F.; Huang, M.; Bai, Y.; Yin, X.; Yan, J.; Liu, F.; Chen, J.; Weng, X. Landmarks in pancreatic cancer studies. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uson Junior, P.L.S.; Carvalho, L.; Fernandes, M.L.C.; Botrus, G.; de Souza Martins, R.; da Silva, E.F.; Dos Santos, S.; Taniwaki, L.; Taranto, P.; Dutra, A.C.P.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy or upfront surgery in localized pancreatic cancer: A contemporary analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Tsang, Y.; Yang, Y. Identification of CEACAM5 as a stemness-related inhibitory immune checkpoint in pancreatic cancer. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miquel, M.; Zhang, S.; Pilarsky, C. Pre-clinical Models of Metastasis in Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 748631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, T.; Hiroshima, Y.; Matsuyama, R.; Homma, Y.; Hoffman, R.M.; Endo, I. Role of the tumor microenvironment in pancreatic cancer. Ann. Gastroenterol. Surg. 2019, 3, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Wei, Y.; Liu, S. The Interplay Between Inflammation and Stromal Components in Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 850093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landskron, G.; De la Fuente, M.; Thuwajit, P.; Thuwajit, C.; Hermoso, M.A. Chronic inflammation and cytokines in the tumor microenvironment. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 149185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Chu, S.; Yao, S.; Li, Y.; Fan, S.; Sun, X.; Su, L.; Liu, X. CD74 interacts with CD44 and enhances tumorigenesis and metastasis via RHOA-mediated cofilin phosphorylation in human breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 68303–68313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, K.T.; Nofchissey, R.A.; Pinchuk, I.V.; Beswick, E.J. Chronic macrophage migration inhibitory factor exposure induces mesenchymal epithelial transition and promotes gastric and colon cancers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Molina, A.; Yu, A.; Hanson, J.; Cheung, H.; Li, X.; Natkunam, Y. High frequency of CD74 expression in lymphomas: Implications for targeted therapy using a novel anti-CD74-drug conjugate. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2019, 5, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucala, R.; Shachar, I. The integral role of CD74 in antigen presentation, MIF signal transduction, and B cell survival and homeostasis. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Cai, W.; Yang, J.; Fu, X.; Putha, L.; Xia, Q.; Windsor, J.A.; Phillips, A.R.; Tyndall, J.D.A.; Du, D.; et al. Targeting Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor in Acute Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 638950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Yarom, N.; Radomir, L.; Sever, L.; Kramer, M.P.; Lewinsky, H.; Bornstein, C.; Blecher-Gonen, R.; Barnett-Itzhaki, Z.; Mirkin, V.; Friedlander, G.; et al. CD74 is a novel transcription regulator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beswick, E.J.; Reyes, V.E. CD74 in antigen presentation, inflammation, and cancers of the gastrointestinal tract. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 2855–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanese, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Berkova, Z.; Wang, Y.; Samaniego, F.; Lee, J.E.; Ekmekcioglu, S.; Grimm, E.A. Cell Surface CD74-MIF Interactions Drive Melanoma Survival in Response to Interferon-γ. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 2775–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narumi, K.; Miyakawa, R.; Ueda, R.; Hashimoto, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Aoki, K. Proinflammatory Proteins S100A8/S100A9 Activate NK Cells via Interaction with RAGE. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 5539–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Song, R.; Wang, Z.; Jing, Z.; Wang, S.; Ma, J. S100A8/A9 in Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedjadi, T.; Evans, A.; Sheikh, A.; Barerra, L.; Al-Ghamdi, S.; Oldfield, L.; Greenhalf, W.; Neoptolemos, J.P.; Costello, E. S100A8 and S100A9 proteins form part of a paracrine feedback loop between pancreatic cancer cells and monocytes. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclerc, E.; Vetter, S.W. The role of S100 proteins and their receptor RAGE in pancreatic cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 2706–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Guo, F.; Chen, M.; Tao, X.; Dong, D. S100 Proteins in Pancreatic Cancer: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 711180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, Y.; Bustos, M.A.; Cho, S.N.; Roszik, J.; Ryu, S.; Lopez, V.M.; Burks, J.K.; Lee, J.E.; Grimm, E.A.; Hoon, D.S.B.; et al. Interplay between soluble CD74 and macrophage-migration inhibitory factor drives tumor growth and influences patient survival in melanoma. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shachar, I.; Cohen, S.; Marom, A.; Becker-Herman, S. Regulation of CLL survival by hypoxia-inducible factor and its target genes. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 2906–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Carstens, J.L.; Kim, J.; Scheible, M.; Kaye, J.; Sugimoto, H.; Wu, C.C.; LeBleu, V.S.; Kalluri, R. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is dispensable for metastasis but induces chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015, 527, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiong, Q.; Wang, S.; Wu, Q.; et al. Correction: PSC-derived Galectin-1 inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells by activating the NF-κB pathway. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 2111–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibino, T.; Sakaguchi, M.; Miyamoto, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Motoyama, A.; Hosoi, J.; Shimokata, T.; Ito, T.; Tsuboi, R.; Huh, N.H. S100A9 is a novel ligand of EMMPRIN that promotes melanoma metastasis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, N.B.; Weide, B.; Gries, M.; Reith, M.; Tarnanidis, K.; Schuermans, V.; Kemper, C.; Kehrel, C.; Funder, A.; Lichtenberger, R.; et al. Tumor microenvironment-derived S100A8/A9 is a novel prognostic biomarker for advanced melanoma patients and during immunotherapy with anti-PD-1 antibodies. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, K.; Friedlander, G.; Pellegrino, B.; Radomir, L.; Lewinsky, H.; Leng, L.; Bucala, R.; Becker-Herman, S.; Shachar, I. CD74 as a regulator of transcription in normal B cells. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizian-Farsani, F.; Abedpoor, N.; Hasan Sheikhha, M.; Gure, A.O.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H.; Ghaedi, K. Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products Acts as a Fuel to Colorectal Cancer Development. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 552283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srikrishna, G. S100A8 and S100A9: New insights into their roles in malignancy. J. Innate Immun. 2012, 4, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteran, L.; Erez, N. The Dark Side of Fibroblasts: Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts as Mediators of Immunosuppression in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, S.; Coles, M.; Thomas, T.; Kollias, G.; Ludewig, B.; Turley, S.; Brenner, M.; Buckley, C.D. Fibroblasts as immune regulators in infection, inflammation and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 704–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamitopoulou, E. Tumour microenvironment of pancreatic cancer: Immune landscape is dictated by molecular and histopathological features. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Francesco, E.M.; Lappano, R.; Santolla, M.F.; Marsico, S.; Caruso, A.; Maggiolini, M. HIF-1α/GPER signaling mediates the expression of VEGF induced by hypoxia in breast cancer associated fibroblasts (CAFs). Breast. Cancer Res. 2013, 15, R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwörer, S.; Cimino, F.V.; Ros, M.; Tsanov, K.M.; Ng, C.; Lowe, S.W.; Carmona-Fontaine, C.; Thompson, C.B. Hypoxia Potentiates the Inflammatory Fibroblast Phenotype Promoted by Pancreatic Cancer Cell-Derived Cytokines. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 1596–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarantis, P.; Koustas, E.; Papadimitropoulou, A.; Papavassiliou, A.G.; Karamouzis, M.V. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Treatment hurdles, tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2020, 12, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padoan, A.; Plebani, M.; Basso, D. Inflammation and Pancreatic Cancer: Focus on Metabolism, Cytokines, and Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.H.; Zheng, J.H.; Jia, Q.Y.; Duan, Z.H.; Yao, H.F.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.W.; Jiang, S.H.; Liu, D.J.; Huo, Y.M. Immunosuppression, immune escape, and immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer: Focused on the tumor microenvironment. Cell Oncol. 2023, 46, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, L.; Ghosh, S.; Jiang, N.; Watanabe, K.; Parlak, M.; Bucala, R.; Moonah, S. CD74 Signaling Links Inflammation to Intestinal Epithelial Cell Regeneration and Promotes Mucosal Healing. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 10, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noe, J.T.; Mitchell, R.A. MIF-Dependent Control of Tumor Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 609948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, X.; Tang, L.; Liu, Z.; Yang, K.; Cheng, Q. CD74 Correlated With Malignancies and Immune Microenvironment in Gliomas. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 706949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkova, Z.; Wang, S.; Ao, X.; Wise, J.F.; Braun, F.K.; Rezaeian, A.H.; Sehgal, L.; Goldenberg, D.M.; Samaniego, F. CD74 interferes with the expression of fas receptor on the surface of lymphoma cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 33, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, P.J.; Lai, T.Y.; Cao, J.; Hsu, L.C.; Chiang, T.C.; Ou-Yang, P.; Tsai, C.Y.; Tsai, Y.F.; Lin, C.W.; Chen, C.C.; et al. The role of S100A9 in the interaction between pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells and stromal cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2022, 71, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balachander, G.M.; Talukdar, P.M.; Debnath, M.; Rangarajan, A.; Chatterjee, K. Inflammatory Role of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Invasive Breast Tumors Revealed Using a Fibrous Polymer Scaffold. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33814–33826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Yu, D.H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, C.Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.H.; Ni, C.R.; Zhu, M.H. Expression of fibroblast activation protein in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma and its clinicopathological significance. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.; Choi, S.; Yoo, S.; Lee, M.; Kim, I.-S. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in the Hypoxic Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2022, 14, 3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, W.C.; Lee, D.E.; Kang, H.W.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.H.; Fang, S.; Kim, H.J.; Park, J.S. CD74 Promotes a Pro-Inflammatory Tumor Microenvironment by Inducing S100A8 and S100A9 Secretion in Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12993. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612993
Hong WC, Lee DE, Kang HW, Kim MJ, Kim M, Kim JH, Fang S, Kim HJ, Park JS. CD74 Promotes a Pro-Inflammatory Tumor Microenvironment by Inducing S100A8 and S100A9 Secretion in Pancreatic Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(16):12993. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612993
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Woosol Chris, Da Eun Lee, Hyeon Woong Kang, Myeong Jin Kim, Minsoo Kim, Ju Hyun Kim, Sungsoon Fang, Hyo Jung Kim, and Joon Seong Park. 2023. "CD74 Promotes a Pro-Inflammatory Tumor Microenvironment by Inducing S100A8 and S100A9 Secretion in Pancreatic Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 16: 12993. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612993
APA StyleHong, W. C., Lee, D. E., Kang, H. W., Kim, M. J., Kim, M., Kim, J. H., Fang, S., Kim, H. J., & Park, J. S. (2023). CD74 Promotes a Pro-Inflammatory Tumor Microenvironment by Inducing S100A8 and S100A9 Secretion in Pancreatic Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(16), 12993. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612993






