BRD4 Inhibition Enhances the Antitumor Effects of Radiation Therapy in a Murine Breast Cancer Model
Abstract
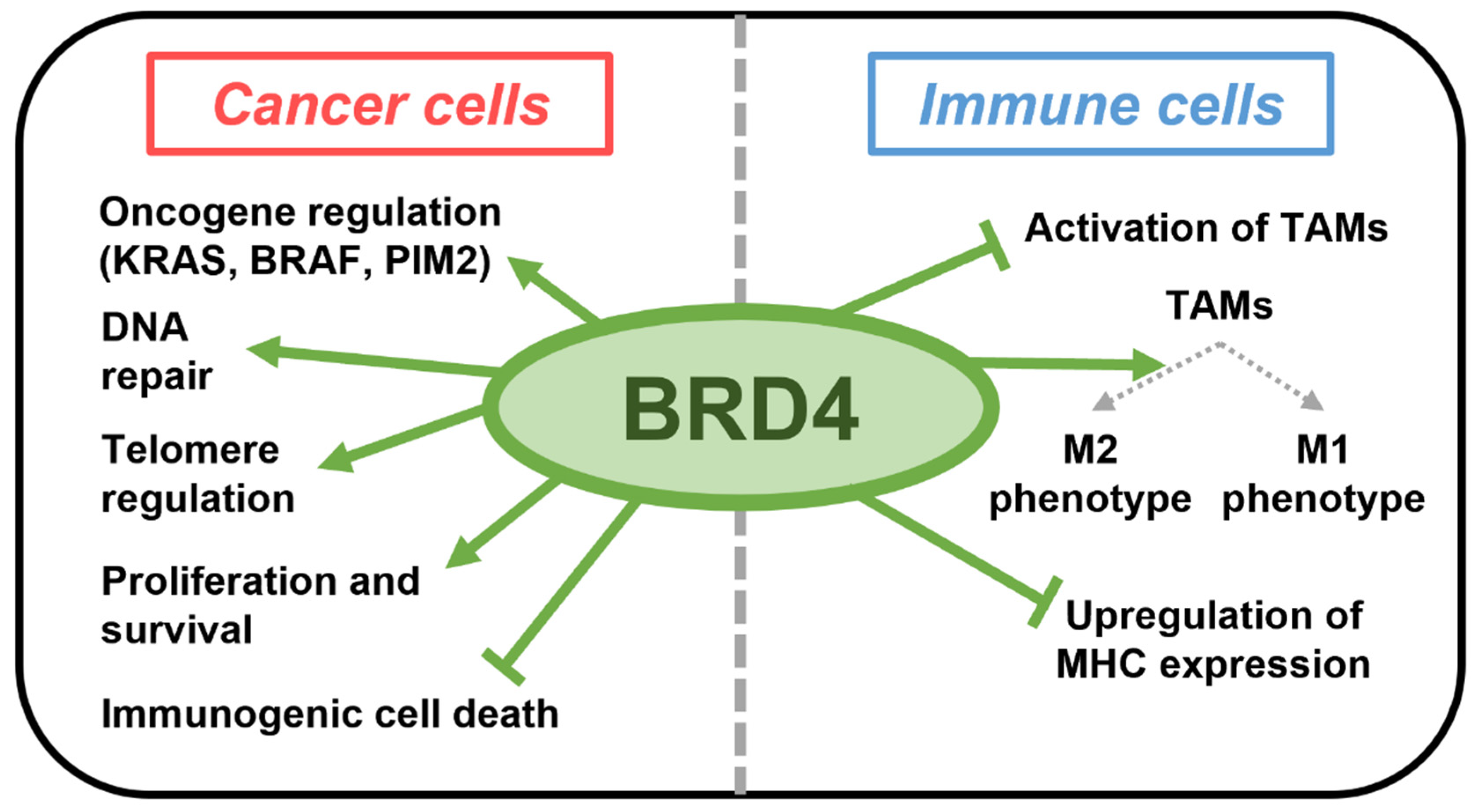
1. Introduction
2. Results
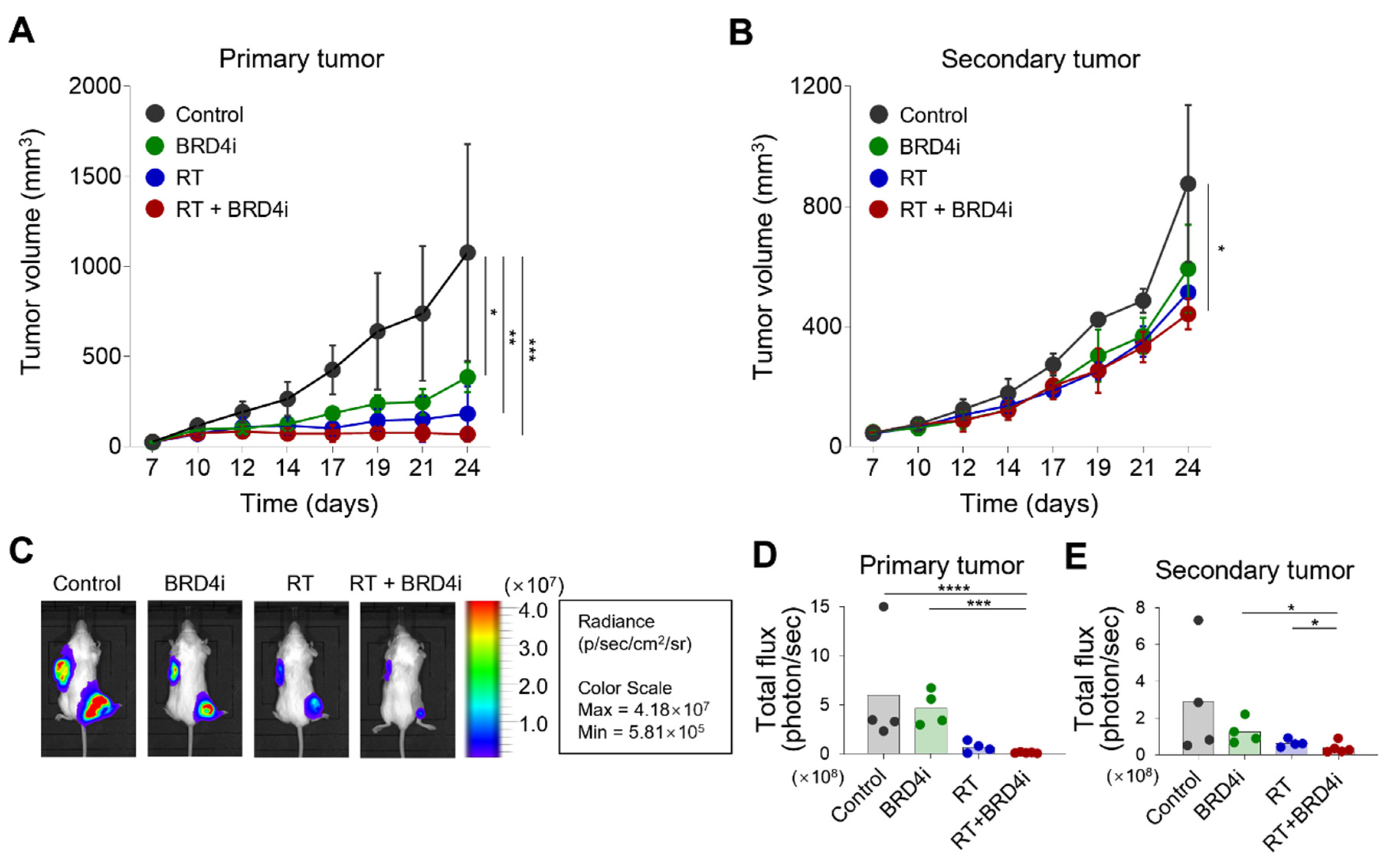
2.1. Effects of Local RT and BRD4 Inhibition on Tumor Growth
2.2. Effects of the BRD4 Inhibitor on the Abscopal Effects of Local RT
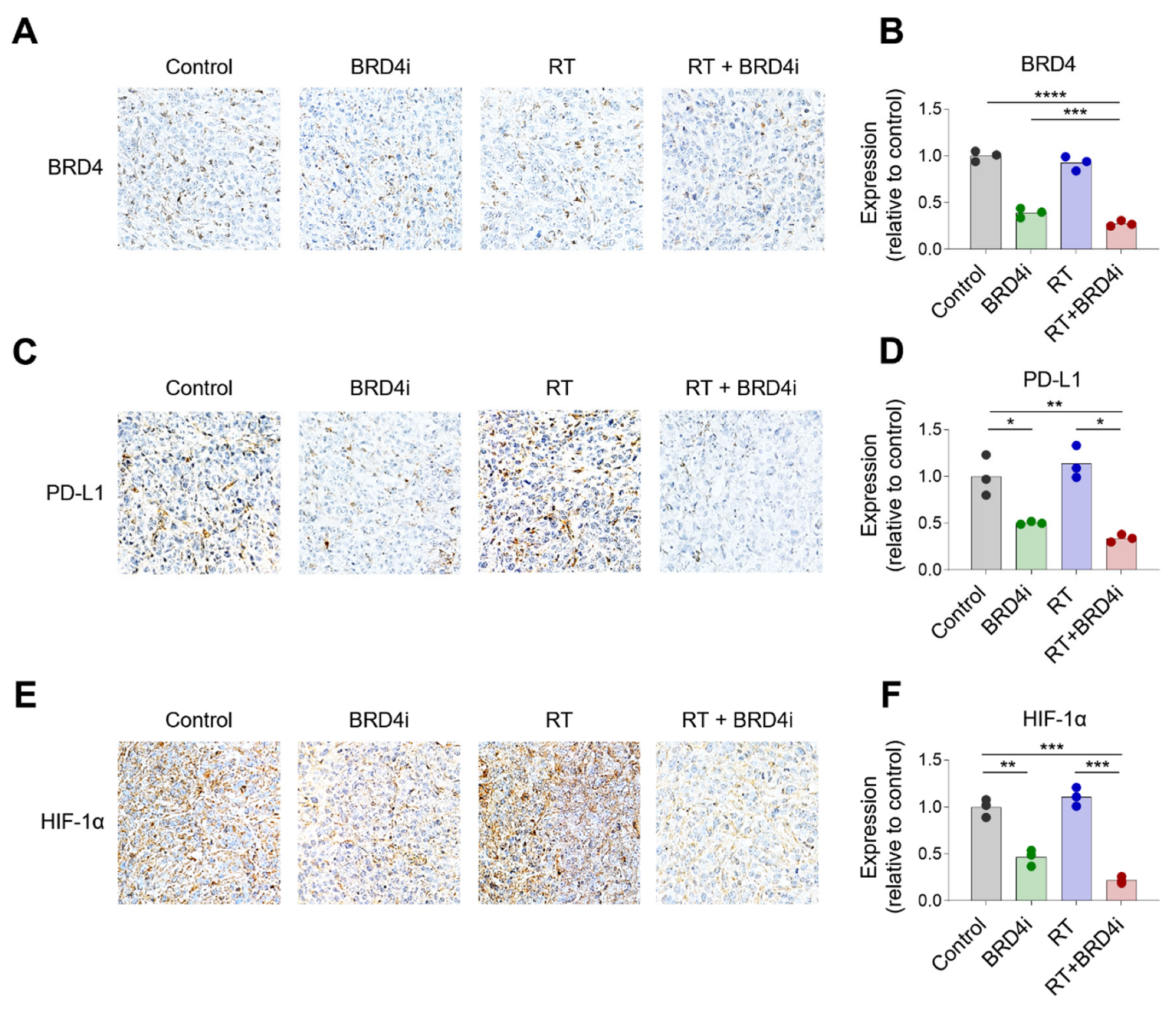
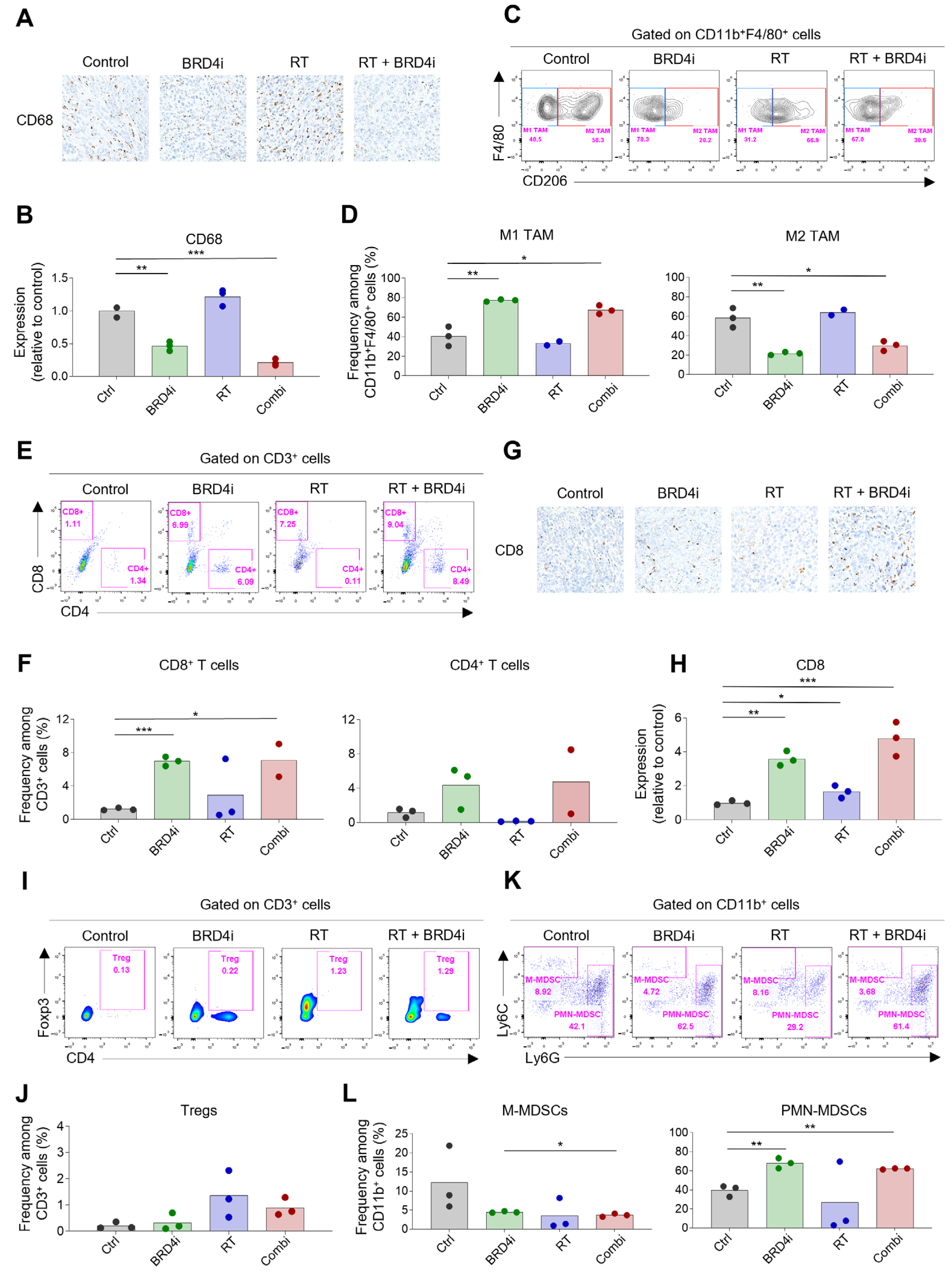
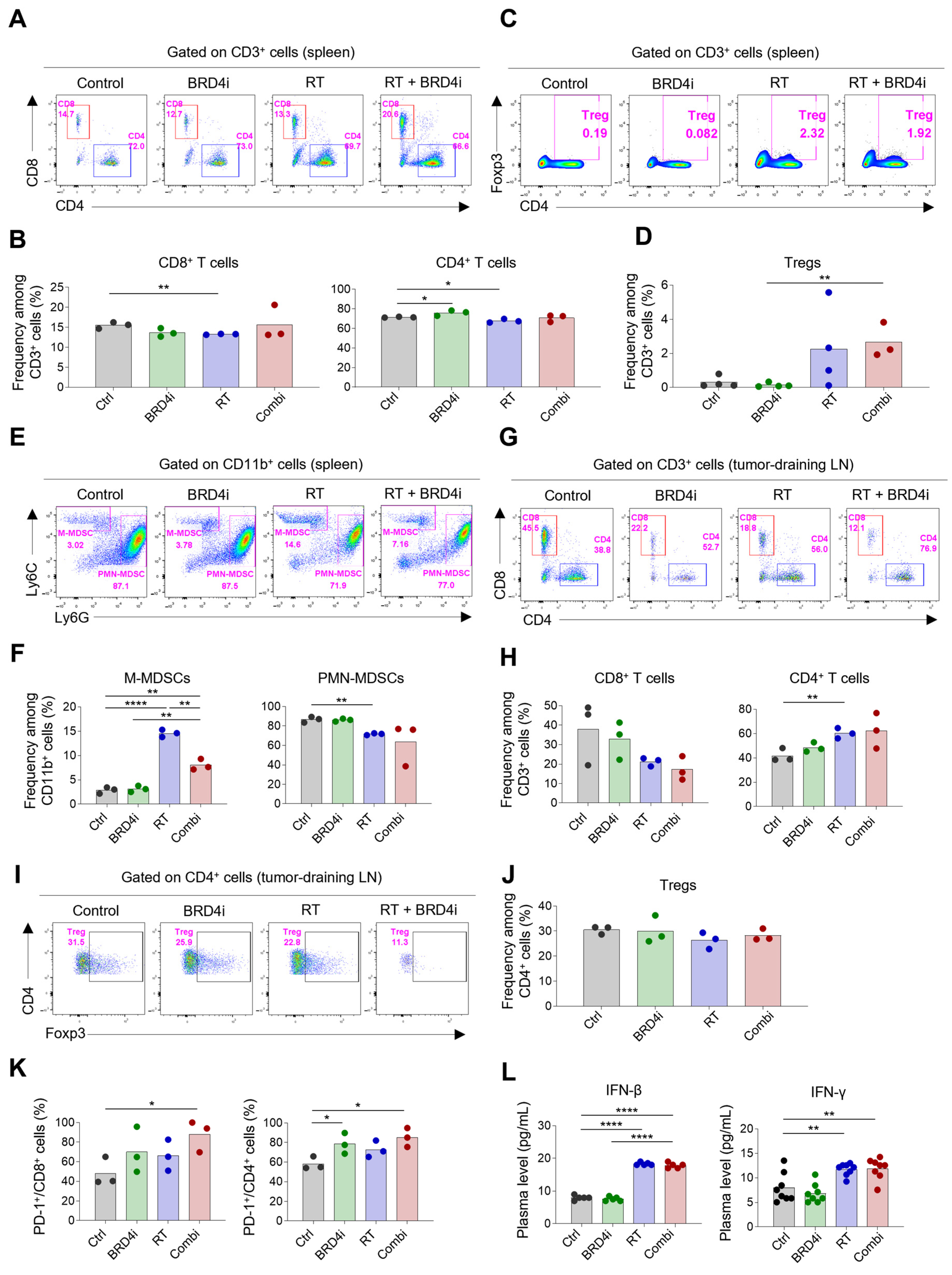
2.3. Treatment Effects on the TME
2.4. Treatment Effects on Systemic Immune Responses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Mouse Tumor Model
4.3. Treatments
4.4. Tumor Growth
4.5. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
4.6. Flow Cytometric Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thariat, J.; Hannoun-Levi, J.M.; Sun Myint, A.; Vuong, T.; Gérard, J.P. Past, Present, and Future of Radiotherapy for the Benefit of Patients. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, C.; Al-Hilli, Z.; Vicini, F. Advances in Breast Cancer Radiotherapy: Implications for Current and Future Practice. JCO Oncol. Pract. 2021, 17, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, M.; Krause, M.; Overgaard, J.; Debus, J.; Bentzen, S.M.; Daartz, J.; Richter, C.; Zips, D.; Bortfeld, T. Radiation Oncology in the Era of Precision Medicine. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Mu, X.; He, H.; Zhang, X.D. Cancer Radiosensitizers. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 24–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwa, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Nam, J.M.; Harada, H. Tumor Microenvironment and Radioresistance. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichselbaum, R.R.; Liang, H.; Deng, L.; Fu, Y.X. Radiotherapy and Immunotherapy: A Beneficial Liaison? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tie, Y.; Tang, F.; Wei, Y.-Q.; Wei, X.-W. Immunosuppressive Cells in Cancer: Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Targets. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassetta, L.; Pollard, J.W. A Timeline of Tumour-Associated Macrophage Biology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2023, 23, 238–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, C.; Tanaka, A.; Sakaguchi, S. Tumor-Infiltrating Regulatory T Cells as Targets of Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muroyama, Y.; Nirschl, T.R.; Kochel, C.M.; Lopez-Bujanda, Z.; Theodros, D.; Mao, W.; Carrera-Haro, M.A.; Ghasemzadeh, A.; Marciscano, A.E.; Velarde, E.; et al. Stereotactic Radiotherapy Increases Functionally Suppressive Regulatory T Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 992–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Kane, N.; Kobayashi, N.; Kono, E.A.; Yamashiro, J.M.; Nickols, N.G.; Reiter, R.E. High-Dose per Fraction Radiotherapy Induces Both Antitumor Immunity and Immunosuppressive Responses in Prostate Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sia, J.; Hagekyriakou, J.; Chindris, I.; Albarakati, H.; Leong, T.; Schlenker, R.; Keam, S.P.; Williams, S.G.; Neeson, P.J.; Johnstone, R.W.; et al. Regulatory T Cells Shape the Differential Impact of Radiation Dose-Fractionation Schedules on Host Innate and Adaptive Antitumor Immune Defenses. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 111, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Cortegana, C.; Galassi, C.; Klapp, V.; Gabrilovich, D.I.; Galluzzi, L. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Radiotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2022, 10, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiao, S.L.; Ruffell, B.; De Nardo, D.G.; Faddegon, B.A.; Park, C.C.; Coussens, L.M. TH2-Polarized CD4+ T Cells and Macrophages Limit Efficacy of Radiotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, D.; Song, C.; Li, Y.; Xia, J.; Wu, Y.; Jia, J.; Cui, X.; Yu, S.; Gu, J. Combination of Radiotherapy and Suppression of Tregs Enhances Abscopal Antitumor Effect and Inhibits Metastasis in Rectal Cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donati, B.; Lorenzini, E.; Ciarrocchi, A. BRD4 and Cancer: Going beyond Transcriptional Regulation. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmore, J.E.; Issa, G.C.; Lemieux, M.E.; Rahl, P.B.; Shi, J.; Jacobs, H.M.; Kastritis, E.; Gilpatrick, T.; Paranal, R.M.; Qi, J.; et al. BET Bromodomain Inhibition as a Therapeutic Strategy to Target C-Myc. Cell 2011, 146, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, C.J.; Kopp, N.; Bird, L.; Paranal, R.M.; Qi, J.; Bowman, T.; Rodig, S.J.; Kung, A.L.; Bradner, J.E.; Weinstock, D.M. BET Bromodomain Inhibition Targets Both C-Myc and IL7R in High-Risk Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2012, 120, 2843–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fu, Y.; Yang, B.; Guo, E.; Wu, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, R.; Li, K.; Wang, B.; et al. BRD4 Inhibition by AZD5153 Promotes Antitumor Immunity via Depolarizing M2 Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Hu, Y.; Miao, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, X. A BRD4 PROTAC Nanodrug for Glioma Therapy via the Intervention of Tumor Cells Proliferation, Apoptosis and M2 Macrophages Polarization. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 2658–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Guo, Y.; Hu, R.; Cai, W.L.; Li, Y.; Pei, S.; Sun, H.; Peng, C.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; et al. Potent BRD4 Inhibitor Suppresses Cancer Cell-Macrophage Interaction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, G.; Ma, Z.; Xiong, G.; Wang, W.; Huang, Z.; Wan, Y.; Xu, X.; Hoyle, R.G.; Yi, C.; et al. BET Inhibition Triggers Antitumor Immunity by Enhancing MHC Class I Expression in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 3394–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riganti, C.; Lingua, M.F.; Salaroglio, I.C.; Falcomatà, C.; Righi, L.; Morena, D.; Picca, F.; Oddo, D.; Kopecka, J.; Pradotto, M.; et al. Bromodomain Inhibition Exerts Its Therapeutic Potential in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma by Promoting Immunogenic Cell Death and Changing the Tumor Immune-Environment. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1398874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.G.; Jang, B.S.; Kang, M.H.; Na, D.; Kim, I.A. PI3Kγδ Inhibitor plus Radiation Enhances the Antitumour Immune Effect of PD-1 Blockade in Syngenic Murine Breast Cancer and Humanised Patient-Derived Xenograft Model. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 157, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.I.; Han, M.G.; Kang, M.H.; Park, J.M.; Kim, E.E.; Bae, J.; Ahn, S.; Kim, I.A. PI3Kαδ Inhibitor Combined With Radiation Enhances the Antitumor Immune Effect of Anti-PD1 in a Syngeneic Murine Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Model. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 110, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, L.; Werba, G.; Tiwari, S.; Giao Ly, N.N.; Nguy, S.; Alothman, S.; Alqunaibit, D.; Avanzi, A.; Daley, D.; Barilla, R.; et al. Radiation Therapy Induces Macrophages to Suppress T-Cell Responses Against Pancreatic Tumors in Mice. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1659–1672.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Hu, X.; Zeng, F.; Cheng, J.; Jin, H.; Lin, X.; Chen, L.F. Brd4 Modulates the Innate Immune Response through Mnk2-EIF4E Pathway-Dependent Translational Control of IκBα. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3993–E4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.S.; Gatchalian, J.; Ho, J.; Burns, M.J.; Hah, N.; Wei, Z.; Downes, M.; Evans, R.M.; Hargreaves, D.C. BRD9 Regulates Interferon-Stimulated Genes during Macrophage Activation via Cooperation with BET Protein BRD4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2110812119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Sun, P.; Ma, Z.; Sun, P. BRD4 Promotes Tumor Progression and NF-ΚB/CCL2-Dependent Tumor-Associated Macrophage Recruitment in GIST. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Xu, F.; Cheng, J.; Yu, M.; Ke, G.; Wu, X. BRD4 Inhibition Sensitizes Cervical Cancer to Radiotherapy by Attenuating DNA Repair. Oncogene 2021, 40, 2711–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clambey, E.T.; McNamee, E.N.; Westrich, J.A.; Glover, L.E.; Campbell, E.L.; Jedlicka, P.; De Zoeten, E.F.; Cambier, J.C.; Stenmark, K.R.; Colgan, S.P.; et al. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Alpha-Dependent Induction of FoxP3 Drives Regulatory T-Cell Abundance and Function during Inflammatory Hypoxia of the Mucosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2784–E2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noman, M.Z.; Desantis, G.; Janji, B.; Hasmim, M.; Karray, S.; Dessen, P.; Bronte, V.; Chouaib, S. PD-L1 Is a Novel Direct Target of HIF-1α, and Its Blockade under Hypoxia Enhanced MDSC-Mediated T Cell Activation. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colegio, O.R.; Chu, N.Q.; Szabo, A.L.; Chu, T.; Rhebergen, A.M.; Jairam, V.; Cyrus, N.; Brokowski, C.E.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; Phillips, G.M.; et al. Functional Polarization of Tumour-Associated Macrophages by Tumour-Derived Lactic Acid. Nature 2014, 513, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciscano, A.E.; Ghasemzadeh, A.; Nirschl, T.R.; Theodros, D.; Kochel, C.M.; Francica, B.J.; Muroyama, Y.; Anders, R.A.; Sharabi, A.B.; Velarde, E.; et al. Elective Nodal Irradiation Attenuates the Combinatorial Efficacy of Stereotactic Radiation Therapy and Immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5058–5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchwald, Z.S.; Nasti, T.H.; Lee, J.; Eberhardt, C.S.; Wieland, A.; Im, S.J.; Lawson, D.; Curran, W.; Ahmed, R.; Khan, M.K. Tumor-Draining Lymph Node Is Important for a Robust Abscopal Effect Stimulated by Radiotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dammeijer, F.; van Gulijk, M.; Mulder, E.E.; Lukkes, M.; Klaase, L.; van den Bosch, T.; van Nimwegen, M.; Lau, S.P.; Latupeirissa, K.; Schetters, S.; et al. The PD-1/PD-L1-Checkpoint Restrains T Cell Immunity in Tumor-Draining Lymph Nodes. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 685–700.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wein, L.; Luen, S.J.; Savas, P.; Salgado, R.; Loi, S. Checkpoint Blockade in the Treatment of Breast Cancer: Current Status and Future Directions. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.; Cortes, J.; Pusztai, L.; McArthur, H.; Kümmel, S.; Bergh, J.; Denkert, C.; Park, Y.H.; Hui, R.; Harbeck, N.; et al. Pembrolizumab for Early Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.; Cescon, D.W.; Rugo, H.S.; Nowecki, Z.; Im, S.A.; Yusof, M.M.; Gallardo, C.; Lipatov, O.; Barrios, C.H.; Holgado, E.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy versus Placebo plus Chemotherapy for Previously Untreated Locally Recurrent Inoperable or Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (KEYNOTE-355): A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Phase 3 Clinical Trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 1817–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, K.; Patel, A.A.; Kong, W.T.; Piot, C.; Halitzki, E.; Dunsmore, G.; Khalilnezhad, S.; Irac, S.E.; Dubuisson, A.; Chevrier, M.; et al. Cross-Tissue Single-Cell Landscape of Human Monocytes and Macrophages in Health and Disease. Immunity 2021, 54, 1883–1900.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Acevedo, J.A.; Kimbrough, E.M.O.; Lou, Y. Next Generation of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Beyond. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shorstova, T.; Foulkes, W.D.; Witcher, M. Achieving Clinical Success with BET Inhibitors as Anti-Cancer Agents. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 1478–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theelen, W.S.M.E.; Chen, D.; Verma, V.; Hobbs, B.P.; Peulen, H.M.U.; Aerts, J.G.J.V.; Bahce, I.; Niemeijer, A.L.N.; Chang, J.Y.; de Groot, P.M.; et al. Pembrolizumab with or without Radiotherapy for Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Pooled Analysis of Two Randomised Trials. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.; Jeon, S.H.; Han, M.G.; Kang, M.H.; Kim, I.A. BRD4 Inhibition Enhances the Antitumor Effects of Radiation Therapy in a Murine Breast Cancer Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13062. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713062
Kim S, Jeon SH, Han MG, Kang MH, Kim IA. BRD4 Inhibition Enhances the Antitumor Effects of Radiation Therapy in a Murine Breast Cancer Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(17):13062. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713062
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Seongmin, Seung Hyuck Jeon, Min Guk Han, Mi Hyun Kang, and In Ah Kim. 2023. "BRD4 Inhibition Enhances the Antitumor Effects of Radiation Therapy in a Murine Breast Cancer Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 17: 13062. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713062
APA StyleKim, S., Jeon, S. H., Han, M. G., Kang, M. H., & Kim, I. A. (2023). BRD4 Inhibition Enhances the Antitumor Effects of Radiation Therapy in a Murine Breast Cancer Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(17), 13062. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713062





