Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Activation Reduces Pulmonary Vein Arrhythmogenesis and Regulates Calcium Homeostasis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
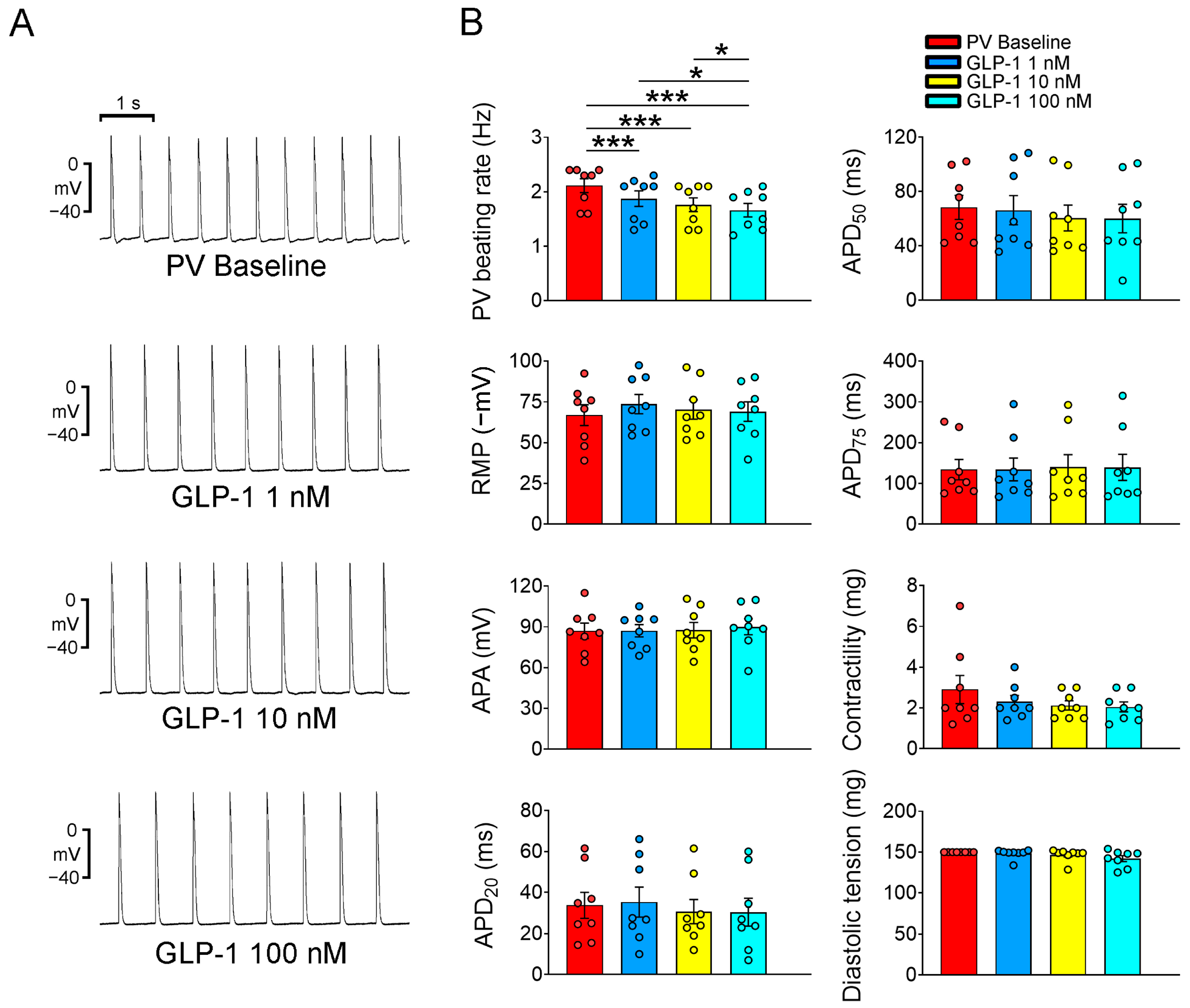
2.1. Electrophysiological Effects of the GLP-1 Receptor Agonist on PVs and Sinoatrial Node (SAN)
2.2. Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonist on PV Ionic Currents and Ca2+ Homeostasis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. PV and SAN Tissue Preparations
4.2. Electrophysiological Study in PV and SAN Tissue Preparations
4.3. Single PV Cardiomyocyte Isolation
4.4. Ionic Current Measurements
4.5. Measurements of SR Ca2+ Content
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchhof, P.; Benussi, S.; Kotecha, D.; Ahlsson, A.; Atar, D.; Casadei, B.; Castella, M.; Diener, H.C.; Heidbuchel, H.; Hendriks, J.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 50, e1–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahed, M.R.; Hashemzadeh, M.; Jamal, M.M. Diabetes mellitus is a strong, independent risk for atrial fibrillation and flutter in addition to other cardiovascular disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2005, 105, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatemi, O.; Yuriditsky, E.; Tsioufis, C.; Tsachris, D.; Morgan, T.; Basile, J.; Bigger, T.; Cushman, W.; Goff, D.; Soliman, E.Z.; et al. Impact of intensive glycemic control on the incidence of atrial fibrillation and associated cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (from the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 114, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudis, C.A.; Korantzopoulos, P.; Ntalas, I.V.; Kallergis, E.M.; Liu, T.; Ketikoglou, D.G. Diabetes mellitus and atrial fibrillation: Pathophysiological mechanisms and potential upstream therapies. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 184, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serban, R.C.; Scridon, A. Data linking diabetes mellitus and atrial fibrillation-how strong is the evidence? From epidemiology and pathophysiology to therapeutic implications. Can. J. Cardiol. 2018, 34, 1492–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohne, L.J.; Johnson, D.; Rose, R.A.; Wilton, S.B.; Gillis, A.M. The association between diabetes mellitus and atrial fibrillation: Clinical and mechanistic insights. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.W.; Lee, T.I.; Lin, Y.K.; Chen, Y.C.; Kao, Y.H.; Chen, Y.J. Effect of antidiabetic drugs on the risk of atrial fibrillation: Mechanistic insights from clinical evidence and translational studies. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Daniels, G.H.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Kristensen, P.; Mann, J.F.E.; Nauck, M.A.; Nissen, S.E.; Pocock, S.; Poulter, N.R.; Ravn, L.S.; et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Colhoun, H.M.; Dagenais, G.R.; Diaz, R.; Lakshmanan, M.; Pais, P.; Probstfield, J.; Riesmeyer, J.S.; Riddle, M.C.; Rydénet, L.; et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): A double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, A.F.; Green, J.B.; Janmohamed, S.; D’Agostino Sr, R.B.; Granger, C.B.; Jones, N.P.; Leiter, L.A.; Rosenberg, A.E.; Sigmon, K.N.; Somerville, M.C.; et al. Albiglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (Harmony Outcomes): A double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, L.E.; Holt, T.A.; Rees, K.; Randeva, H.S.; O’Hare, J.P. Effects of exenatide and liraglutide on heart rate, blood pressure and body weight: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e001986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggio, L.L.; Ussher, J.R.; McLean, B.A.; Cao, X.; Kabir, M.G.; Mulvihill, E.E.; Mighiu, A.S.; Zhang, H.; Ludwig, A.; Seeley, R.J.; et al. The autonomic nervous system and cardiac GLP-1 receptors control heart rate in mice. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, H.; Lee, C.E.; Marcus, J.N.; Williams, T.D.; Overton, J.M.; Lopez, M.E.; Hollenberg, A.N.; Baggio, L.; Saper, C.B.; Drucker, D.J.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor stimulation increases blood pressure and heart rate and activates autonomic regulatory neurons. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffioen, K.J.; Wan, R.; Okun, E.; Wang, X.; Lovett-Barr, M.R.; Li, Y.; Mughal, M.R.; Mendelowitz, D.; Mattson, M.P. GLP-1 receptor stimulation depresses heart rate variability and inhibits neurotransmission to cardiac vagal neurons. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 89, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Ren, G.; Wang, O.; Gao, L.; Chen, H.; Ding, C. Comparison of the effect of glucose-lowering agents on the risk of atrial fibrillation: A network meta-analysis. Heart Rhythm 2021, 18, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, X.; Xie, X.; Xu, M.; Xu, L.; Liu, P.; Luo, B. Comparison of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists for atrial fibrillation in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Systematic review with network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 79, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Kao, Y.H.; Lu, Y.Y.; Chen, S.A.; Chen, Y.J. Distinctive sodium and calcium regulation associated with sex differences in atrial electrophysiology of rabbits. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 4658–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzeshka, M.S.; Lip, G.Y.; Snezhitskiy, V.; Shantsila, E. Cardiac fibrosis in patients with atrial fibrillation: Mechanisms and clinical implications. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 943–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Niwano, S.; Niwano, H.; Fukaya, H.; Murakami, M.; Kishihara, J.; Satoh, A.; Yoshizawa, T.; Ishizue, N.; Igarashi, T.; et al. Liraglutide suppresses atrial electrophysiological changes. Heart Vessels 2019, 34, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, S.; Wang, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, P.; Deng, N.; Tang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wu, L.; Chen, J.; et al. Exendin-4 inhibits atrial arrhythmogenesis in a model of myocardial infarction-induced heart failure via the GLP-1 receptor signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 3669–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younce, C.W.; Burmeister, M.A.; Ayala, J.E. Exendin-4 attenuates high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis via inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress and activation of SERCA2a. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2013, 304, C508–C518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Lee, T.I.; Kao, Y.H.; Chao, T.F.; Chen, S.A.; Chen, Y.J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 regulates calcium homeostasis and electrophysiological activities of HL-1 cardiomyocytes. Peptides 2016, 78, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haissaguerre, M.; Jais, P.; Shah, D.C.; Takahashi, A.; Hocini, M.; Quiniou, G.; Garrigue, S.; Mouroux, A.L.; Métayer, P.L.; Clémenty, J. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.A.; Hsieh, M.H.; Tai, C.T.; Tsai, C.F.; Prakash, V.S.; Yu, W.C.; Hsu, T.L.; Ding, Y.A.; Chang, M.S. Initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating from the pulmonary veins: Electrophysiological characteristics, pharmacological responses, and effects of radiofrequency ablation. Circulation 1999, 100, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongcharoen, W.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Chen, S.Y.; Yeh, H.I.; Lin, C.I.; Chen, S.A. Aging increases pulmonary veins arrhythmogenesis and susceptibility to calcium regulation agents. Heart Rhythm 2007, 4, 1338–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jais, P.; Hocini, M.; Macle, L.; Choi, K.J.; Deisenhofer, I.; Weerasooriya, R.; Shah, D.C.; Garrigue, S.; Raybaud, F.; Scavee, C.; et al. Distinctive electrophysiological properties of pulmonary veins in patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2002, 106, 2479–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nattel, S.; Burstein, B.; Dobrev, D. Atrial remodeling and atrial fibrillation: Mechanisms and implications. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2008, 1, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Chen, S.A.; Chang, M.S.; Lin, C.I. Arrhythmogenic activity of cardiac muscle in pulmonary veins of the dog: Implication for the genesis of atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2000, 48, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnagarin, R.; Kiuchi, M.G.; Ho, J.K.; Matthews, V.B.; Schlaich, M.P. Sympathetic nervous system activation and its modulation: Role in atrial fibrillation. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.S.; Chen, L.S.; Fishbein, M.C.; Lin, S.F.; Nattel, S. Role of the autonomic nervous system in atrial fibrillation: Pathophysiology and therapy. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1500–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Chen, S.A.; Chen, Y.C.; Yeh, H.I.; Chan, P.; Chang, M.S.; Lin, C.I. Effects of rapid atrial pacing on the arrhythmogenic activity of single cardiomyocytes from pulmonary veins: Implication in initiation of atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2001, 104, 2849–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Chen, S.A.; Chen, Y.C.; Yeh, H.I.; Chang, M.S.; Lin, C.I. Electrophysiology of single cardiomyocytes isolated from rabbit pulmonary veins: Implication in initiation of focal atrial fibrillation. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2002, 97, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, T.F.; Pelzer, S.; Trautwein, W.; Pelzer, D.J. Regulation and modulation of calcium channels in cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle cells. Physiol. Rev. 1994, 74, 365–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasago, T.; Imagawa, T.; Shigekawa, M. Phosphorylation of the cardiac ryanodine receptor by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Biochem. 1989, 106, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindemann, J.P.; Jones, L.R.; Hathaway, D.R.; Henry, B.G.; Watanabe, A.M. β-Adrenergic stimulation of phospholamban phosphorylation and Ca2+-ATPase activity in guinea pig ventricles. J. Biochem. 1983, 258, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perchenet, L.; Hinde, A.K.; Patel, K.C.; Hancox, J.C.; Levi, A.J. Stimulation of Na+/Ca2+ exchange by the β-adrenergic/protein kinase A pathway in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes at 37 °C. Pflugers Arch. 2000, 439, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lo, L.W.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Wongcharoen, W.; Lin, C.I.; Chen, S.A. Calmodulin kinase II inhibition prevents arrhythmic activity induced by alpha and beta-adrenergic agonists in rabbit pulmonary veins. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 571, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.K.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, S.A.; Chen, Y.J. Ion channel remodeling in pulmonary vein arrhythmogenesis for atrial fibrillation. J. Exp. Clin. Med. 2011, 3, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.L.; Chen, Y.C.; Yeh, Y.H.; Lin, Y.K.; Wu, T.J.; Lin, C.I.; Chen, S.A.; Chen, Y.J. Heart failure enhanced pulmonary vein arrhythmogenesis and dysregulated sodium and calcium homeostasis with increased calcium sparks. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2011, 22, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, G.; Liu, J.; Qin, S.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yu, H.; Lu, K.; Zhang, N.; Cao, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Cardioprotection by exenatide: A novel mechanism via improving mitochondrial function involving the GLP-1 receptor/cAMP/PKA pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1693–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.Q.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, T.F.; Zhang, M.Q.; Qin, X.M. Exendin-4 promotes endothelial barrier enhancement via PKA- and Epac1-dependent Rac1 activation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2015, 308, C164–C175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, L.S. A novel mechanism for the treatment of angina, arrhythmias, and diastolic dysfunction: Inhibition of late INa using ranolazine. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2009, 54, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, A.; Amin, G.; Abidi, E.; Altara, R.; Booz, G.W.; Zouein, F.A. Role of ranolazine in heart failure: From cellular to clinic perspective. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 919, 174787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Shryock, J.C.; Belardinelli, L. An increase of late sodium current induces delayed afterdepolarizations and sustained triggered activity in atrial myocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2008, 294, H2031–H2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicouri, S.; Glass, A.; Belardinelli, L.; Antzelevitch, C. Antiarrhythmic effects of ranolazine in canine pulmonary vein sleeve preparations. Heart Rhythm 2008, 5, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, H.S.; Wittert, G.A.; Leong, D.P.; Shirazi, M.G.; Bahrami, B.; Middeldorp, M.E.; Lorimer, M.F.; Lau, D.H.; Antic, N.A.; Brooks, A.G.; et al. Effect of weight reduction and cardiometabolic risk factor management on symptom burden and severity in patients with atrial fibrillation: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013, 310, 2050–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.S.; Lin, F.J.; Liu, C.M.; Lin, Y.K.; Chen, Y.C.; Hsu, C.C.; Higa, S.; Chen, S.A.; Chen, Y.J. Mirabegron, a β3-adrenoreceptor agonist, regulates right and left atrial arrhythmogenesis differentially. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 24, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Wongcharoen, W.; Lin, C.I.; Chen, S.A. Effect of K201, a novel antiarrhythmic drug on calcium handling and arrhythmogenic activity of pulmonary vein cardiomyocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suenari, K.; Chen, Y.C.; Kao, Y.H.; Cheng, C.C.; Lin, Y.K.; Chen, Y.J.; Chen, S.A. Discrepant electrophysiological characteristics and calcium homeostasis of left atrial anterior and posterior myocytes. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2011, 106, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hove-Madsen, L.; Llach, A.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Roura, S.; Font, E.R.; Aris, A.; Cinca, J. Atrial fibrillation is associated with increased spontaneous calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in human atrial myocytes. Circulation 2004, 110, 1358–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Kao, Y.H.; Lin, Y.K.; Yeh, Y.H.; Chen, S.A.; Chen, Y.J. Colchicine modulates calcium homeostasis and electrical property of HL-1 cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 1182–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| T1 | T2 | E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaCl (mM) | 137 | 137 | 5 | 130 | 140 | 5 | 20 | |||
| NaHCO3 (mM) | 15 | 15 | ||||||||
| NaH2PO4 (mM) | 0.5 | 0.5 | ||||||||
| KCl (mM) | 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| CaCl2 (mM) | 2.7 | 1.8 | 1 | 1.8 | 2 | 1.75 | ||||
| MgCl2 (mM) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | |
| Dextrose (mM) | 11 | 11 | ||||||||
| CsCl (mM) | 133 | 5 | 133 | 133 | 130 | 130 | 110 | |||
| Nifedipine (mM) | 0.002 | |||||||||
| HEPES (mM) | 5 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 10 | ||
| MgATP (mM) | 5 | 5 | 5 | |||||||
| EGTA (mM) | 10 | 10 | 10 | |||||||
| TEACl (mM) | 20 | 20 | 20 | |||||||
| Glucose (mM) | 5 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 5 | |||||
| Na2ATP (mM) | 4 | |||||||||
| NaGTP (mM) | 0.1 | |||||||||
| Na2phosphocreatine (mM) | 5 | |||||||||
| Strophanthidin (mM) | 10 | |||||||||
| Nitrendipine (mM) | 10 | |||||||||
| niflumic acid (mM) | 100 | |||||||||
| BAPTA (mM) | 5 | |||||||||
| Tetrodotoxin (mM) | 10 | |||||||||
| 4-aminopyridine (mM) | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chan, C.-S.; Lin, F.-J.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-K.; Higa, S.; Chen, S.-A.; Chen, Y.-J. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Activation Reduces Pulmonary Vein Arrhythmogenesis and Regulates Calcium Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713100
Chan C-S, Lin F-J, Chen Y-C, Lin Y-K, Higa S, Chen S-A, Chen Y-J. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Activation Reduces Pulmonary Vein Arrhythmogenesis and Regulates Calcium Homeostasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(17):13100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713100
Chicago/Turabian StyleChan, Chao-Shun, Fong-Jhih Lin, Yao-Chang Chen, Yung-Kuo Lin, Satoshi Higa, Shih-Ann Chen, and Yi-Jen Chen. 2023. "Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Activation Reduces Pulmonary Vein Arrhythmogenesis and Regulates Calcium Homeostasis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 17: 13100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713100
APA StyleChan, C.-S., Lin, F.-J., Chen, Y.-C., Lin, Y.-K., Higa, S., Chen, S.-A., & Chen, Y.-J. (2023). Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Activation Reduces Pulmonary Vein Arrhythmogenesis and Regulates Calcium Homeostasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(17), 13100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713100






