The Effects of Early-Life Stress on Liver Transcriptomics and the Protective Role of EPA in a Mouse Model of Early-Life-Stress-Induced Adolescent Depression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
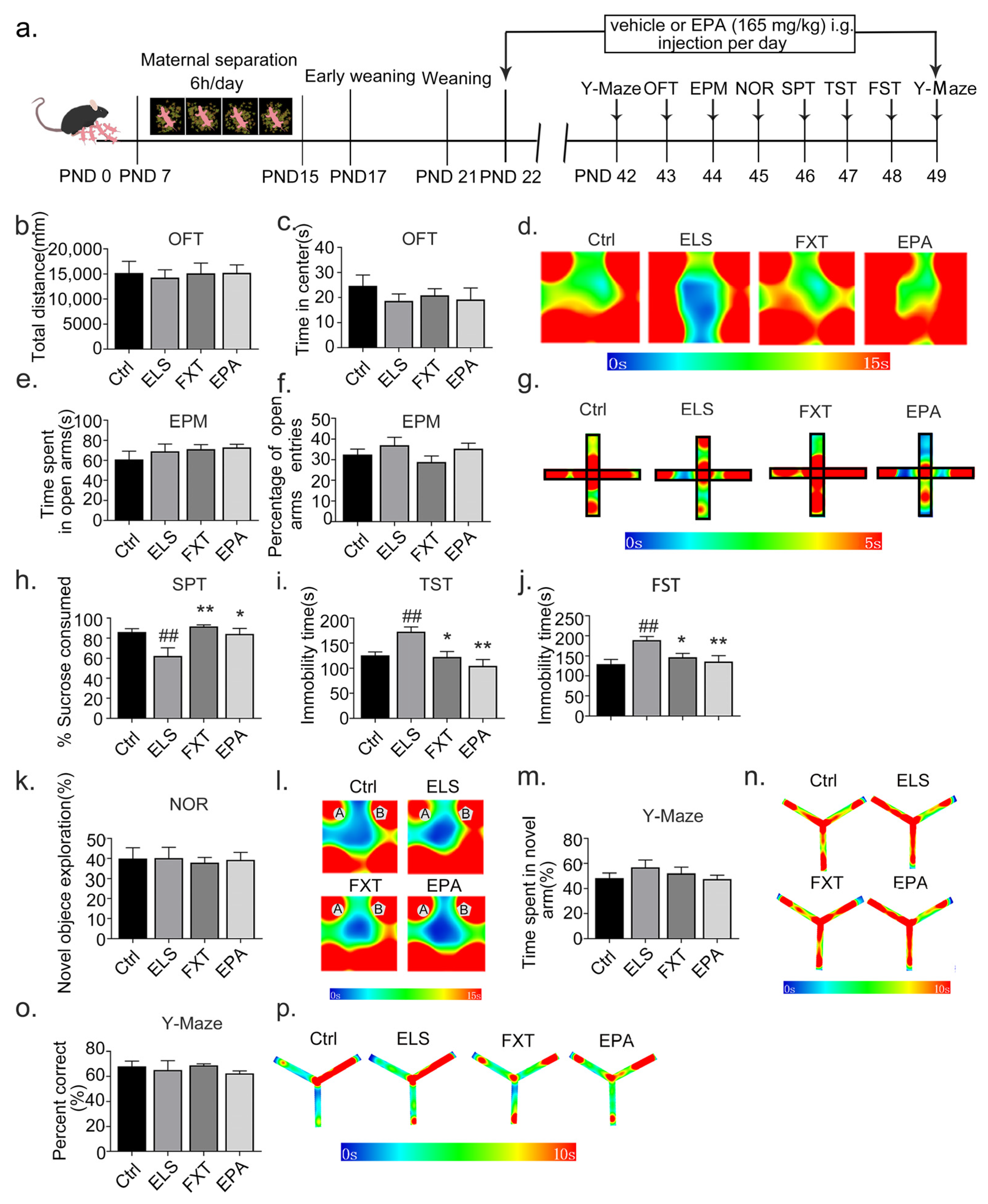
2.1. Early-Life-Stress-Induced Depression-like Behaviors Rather Than Anxiety-like Behavior in Adolescent Mice
2.2. The Effect of Early-Life Stress on the Transcriptional Patterns in the Liver of Adolescent Mice
2.3. The Effects of Early-Life Stress on the Liver and Brain Tissue Damage in Adolescent Mice
2.4. Administration of EPA Improved Depressive-like Behavior in Adolescent Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Early-Life-Stress Paradigm
4.3. Drug Administration
4.4. Anxiety-like Behavior Test
4.5. Depression-like Behavior Test
4.6. Learning and Memory Behavior Test
4.7. RNA-Sequencing Analysis
4.8. AST and AST Assay
4.9. Hematoxylin–Eosin Staining
4.10. Nissl Staining
4.11. EPA Assay
4.12. Western Blot (WB)
4.13. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (q-PCR)
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- LeMoult, J.; Humphreys, K.L.; Tracy, A.; Hoffmeister, J.A.; Ip, E.; Gotlib, I.H. Meta-analysis: Exposure to Early Life Stress and Risk for Depression in Childhood and Adolescence. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2020, 59, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Fry, D.A.; Ji, K.; Finkelhor, D.; Chen, J.; Lannen, P.; Dunne, M.P. The burden of child maltreatment in China: A systematic review. Bull. World Health Organ. 2015, 93, 176–185C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.I.; Yu, N.W.; Liu, C.Y.; Wu, K.Y.; Yang, C.H. The impact of the duration of an untreated episode on improvement of depression and somatic symptoms. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 2245–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.S.; Jansen, K.L.; Cloy, J.A. Treatment of childhood and adolescent depression. Am. Fam. Physician 2012, 86, 442–448. [Google Scholar]
- Solmi, M.; Fornaro, M.; Ostinelli, E.G.; Zangani, C.; Croatto, G.; Monaco, F.; Krinitski, D.; Fusar-Poli, P.; Correll, C.U. Safety of 80 antidepressants, antipsychotics, anti-attention-deficit/hyperactivity medications and mood stabilizers in children and adolescents with psychiatric disorders: A large scale systematic meta-review of 78 adverse effects. World Psychiatry 2020, 19, 214–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, G. Controversies in the Pharmacotherapy of Adolescent Depression. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2022, 28, 1975–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, L.; Lan, X.; Cohen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Ravindran, A.V.; Yuan, S.; Zheng, P.; Coghill, D.; Yang, L.; et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acids metabolism, purine metabolism and inosine as potential independent diagnostic biomarkers for major depressive disorder in children and adolescents. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkman, H.O.; Hersberger, M.; Walitza, S.; Berger, G.E. Disentangling the Molecular Mechanisms of the Antidepressant Activity of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalagala, P.C.R.; Sugasini, D.; Dasarathi, S.; Pahan, K.; Subbaiah, P.V. Dietary lysophosphatidylcholine-EPA enriches both EPA and DHA in the brain: Potential treatment for depression. J. Lipid. Res. 2019, 60, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.P.; Su, K.P. Nutritional Neuroscience as Mainstream of Psychiatry: The Evidence- Based Treatment Guidelines for Using Omega-3 Fatty Acids as a New Treatment for Psychiatric Disorders in Children and Adolescents. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2020, 18, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.E.; Park, Y. EPA and DHA, but not ALA, have antidepressant effects with 17beta-estradiol injection via regulation of a neurobiological system in ovariectomized rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 49, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guu, T.W.; Mischoulon, D.; Sarris, J.; Hibbeln, J.; McNamara, R.K.; Hamazaki, K.; Freeman, M.P.; Maes, M.; Matsuoka, Y.J.; Belmaker, R.H.; et al. International Society for Nutritional Psychiatry Research Practice Guidelines for Omega-3 Fatty Acids in the Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder. Psychother. Psychosom. 2019, 88, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, R.P.; Metherel, A.H.; Chen, C.T.; Shaikh, S.R.; Nadjar, A.; Joffre, C.; Laye, S. Brain eicosapentaenoic acid metabolism as a lead for novel therapeutics in major depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 85, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Song, C. EPA is More Effective than DHA to Improve Depression-Like Behavior, Glia Cell Dysfunction and Hippcampal Apoptosis Signaling in a Chronic Stress-Induced Rat Model of Depression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentini, K.J.; Pickens, C.A.; Wiesinger, J.A.; Fenton, J.I. The effect of fish oil supplementation on brain DHA and EPA content and fatty acid profile in mice. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 69, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lu, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, L.; Li, Y.; Bai, M.; Xu, E. Quantitative proteomic analysis of the liver reveals antidepressant potential protein targets of Sinisan in a mouse CUMS model of depression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.H.; Wu, Z.; Dong, J.H.; Zeng, Y.N.; Xiong, W.C.; Liu, C.; Wang, M.Y.; Zhu, M.Z.; Chen, W.J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Liver Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Regulates Behavioral and Cellular Effects of Chronic Stress. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 3223–3234 e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahl, K.G.; Krüger, T.; Eckermann, G.; Wedemeyer, H. Major depression and liver disease: The role of microbiome and inflammation. Fortschr. Neurol. Psychiatr. 2019, 87, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hernaez, R.; Kramer, J.R.; Khan, A.; Phillips, J.; McCallister, K.; Chaffin, K.; Hernandez, A.P.; Fullington, H.; Ortiz, C.; Blackwell, J.-M.; et al. Depression and Anxiety Are Common Among Patients With Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 194–203.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchenio, A.; Lecca, S.; Valentinova, K.; Mameli, M. Limiting habenular hyperactivity ameliorates maternal separation-driven depressive-like symptoms. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.P.-C.; Su, K.-P.; Mondelli, V.; Satyanarayanan, S.K.; Yang, H.-T.; Chiang, Y.-J.; Chen, H.-T.; Pariante, C.M. High-dose eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) improves attention and vigilance in children and adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and low endogenous EPA levels. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Featherstone, R.E.; Gifford, R.L.; Crown, L.M.; Amirfathi, F.; Alaniz, J.P.; Yi, J.; Tran, A.; Adomian, D.; Schwenk, A.; Melnychenko, O.; et al. Early life social instability stress causes lasting cognitive decrement and elevated hippocampal stress-related gene expression. Exp. Neurol. 2022, 354, 114099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Liu, X.-X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Song, Y.; Zou, J.-X.; Pan, H.-Q.; Zhai, X.-Z.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Zhang, Y.-B.; et al. Early life stress induces anxiety-like behavior during adulthood through dysregulation of neuronal plasticity in the basolateral amygdala. Life Sci. 2021, 285, 119959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catale, C.; Bisicchia, E.; Carola, V.; Viscomi, M.T. Early life stress exposure worsens adult remote microglia activation, neuronal death, and functional recovery after focal brain injury. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 94, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yon, J.H.; Daniel-Johnson, J.; Carter, L.B.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. Anesthesia induces neuronal cell death in the developing rat brain via the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways. Neuroscience 2005, 135, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S.; Kang, J.-Y.; Son, C.-G. A Comparison of Isolation Stress and Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress for the Establishment of Mouse Models of Depressive Disorder. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 616389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, A.S.F.; López-López, J.A.; Hammerton, G.; Manley, D.; Timpson, N.J.; Leckie, G.; Pearson, R.M. Genetic and Environmental Risk Factors Associated With Trajectories of Depression Symptoms From Adolescence to Young Adulthood. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e196587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alteba, S.; Portugalov, A.; Hillard, C.J.; Akirav, I. Inhibition of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH) During Adolescence and Exposure to Early Life Stress may Exacerbate Depression-like Behaviors in Male and Female Rats. Neuroscience 2021, 455, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhu, C.; Zeng, X.; Zheng, S.; Li, W.; Yao, L.; Xia, Y.; Su, W.-W.; et al. Early Life Stress Induces Different Behaviors in Adolescence and Adulthood May Related With Abnormal Medial Prefrontal Cortex Excitation/Inhibition Balance. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 720286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, B.; Kapoor, D.; Gautam, S.; Singh, R.; Bhardwaj, S. Dietary Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFAs): Uses and Potential Health Benefits. Curr. Nutr. Rep3. 2021, 10, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-C.; Du, L.; Shi, H.-H.; Ding, L.; Yanagita, T.; Xue, C.-H.; Wang, Y.-M.; Zhang, T.-T. Dietary EPA-Enriched Phospholipids Alleviate Chronic Stress and LPS-Induced Depression- and Anxiety-Like Behavior by Regulating Immunity and Neuroinflammation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, e2100009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-H.; Wang, Q.; You, Q.-L.; Li, Z.-L.; Hu, N.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Z.-L.; Li, S.-J.; Li, X.-W.; Yang, J.-M.; et al. Acute EPA-induced learning and memory impairment in mice is prevented by DHA. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, A.; Slaby, A.; Tvrzicka, E.; Jachymova, M.; Macasek, J.; Vecka, M.; Zeman, M.; Stankova, B. Desaturases of fatty acids (FADS) and their physiological and clinical implication. Cas. Lek. Cesk. 2016, 155, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lattka, E.; Illig, T.; Koletzko, B.; Heinrich, J. Genetic variants of the FADS1 FADS2 gene cluster as related to essential fatty acid metabolism. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2010, 21, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanza, P.; Parmigiani, S. How does sex matter? Behavior, stress and animal models of neurobehavioral disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 76 Pt A, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Cui, Y.; Gan, S.; Xie, Z.; Cui, S.; Cao, K.; Wang, S.; Shi, G.; Yang, L.; Bai, S.; et al. Sinisan alleviates depression-like behaviors by regulating mitochondrial function and synaptic plasticity in maternal separation rats. Phytomedicine 2022, 106, 154395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ye, L.; Liu, Z.; Cui, Y.; Deng, D.; Bai, S.; Yang, L.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, R. Protective Effects of Resveratrol on Adolescent Social Isolation-Induced Anxiety-Like Behaviors via Modulating Nucleus Accumbens Spine Plasticity and Mitochondrial Function in Female Rats. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Lin, H.; Cui, Y.; Wen, W.; Cui, X.; Shen, C.; Mo, H.; Yang, L.; Bai, S.; Shi, Y.; et al. Depression promotes lung carcinoma progression by regulating the tumor microenvironment in tumor-bearing models of C57BL/6J mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 754, 135851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ying, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, N.; Tu, G.; Zhu, M.; Wu, Y.; Xiao, B.; Ye, L.; Li, J.; et al. Different roles of Rac1 in the acquisition and extinction of methamphetamine-associated contextual memory in the nucleus accumbens. Theranostics 2019, 9, 7051–7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Cao, K.; Cui, S.; Cui, Y.; Mo, H.; Wen, W.; Dong, Z.; Lin, H.; Bai, S.; Yang, L.; et al. SiNiSan ameliorates depression-like behavior in rats by enhancing synaptic plasticity via the CaSR-PKC-ERK signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 124, 109787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Ye, L.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Deng, D.; An, L.; Bai, S.; Yang, L.; Liu, B.; Shi, Y.; et al. The Effects of Early-Life Stress on Liver Transcriptomics and the Protective Role of EPA in a Mouse Model of Early-Life-Stress-Induced Adolescent Depression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713131
Zhao J, Ye L, Liu Z, Wu J, Deng D, An L, Bai S, Yang L, Liu B, Shi Y, et al. The Effects of Early-Life Stress on Liver Transcriptomics and the Protective Role of EPA in a Mouse Model of Early-Life-Stress-Induced Adolescent Depression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(17):13131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713131
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jinlan, Lihong Ye, Zuyi Liu, Jiayi Wu, Di Deng, Lin An, Shasha Bai, Lei Yang, Binjie Liu, Yafei Shi, and et al. 2023. "The Effects of Early-Life Stress on Liver Transcriptomics and the Protective Role of EPA in a Mouse Model of Early-Life-Stress-Induced Adolescent Depression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 17: 13131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713131
APA StyleZhao, J., Ye, L., Liu, Z., Wu, J., Deng, D., An, L., Bai, S., Yang, L., Liu, B., Shi, Y., Liu, Z., & Zhang, R. (2023). The Effects of Early-Life Stress on Liver Transcriptomics and the Protective Role of EPA in a Mouse Model of Early-Life-Stress-Induced Adolescent Depression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(17), 13131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713131








