The Expression of P35 Plays a Key Role in the Difference in Apoptosis Induced by AcMNPV Infection in Different Spodoptera exigua Cell Lines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
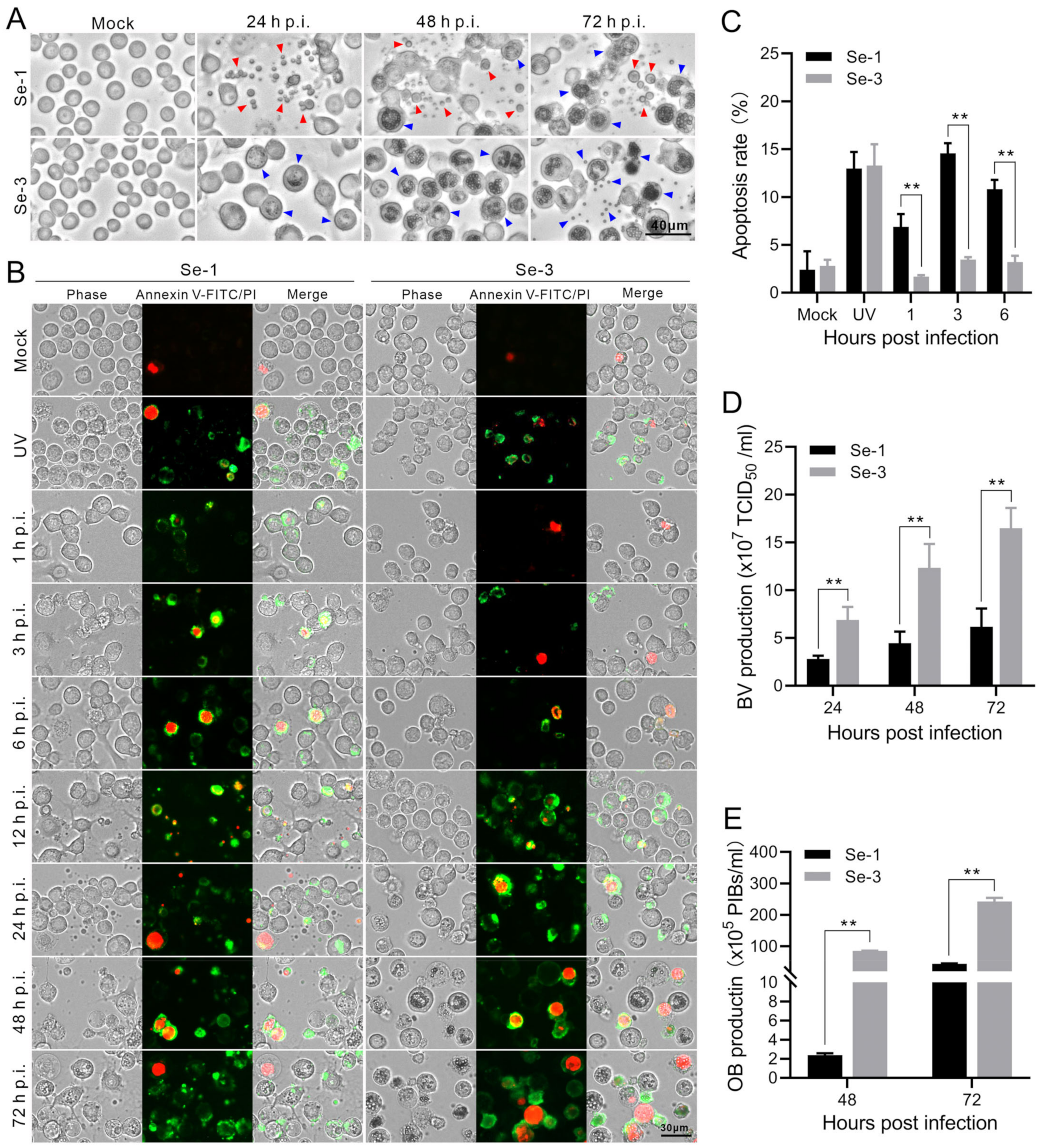
2.1. Apoptosis and Virus Production Analysis of the Two Different S. exigua Cell Lines Infected with AcMNPV
2.2. Analysis of the Apoptosis Process in Two Different S. exigua Cell Lines Infected with AcMNPV
2.3. Transcription Analysis of the Core Apoptosis Gene Caspases in Two Different S. exigua Cell Lines during AcMNPV Infection
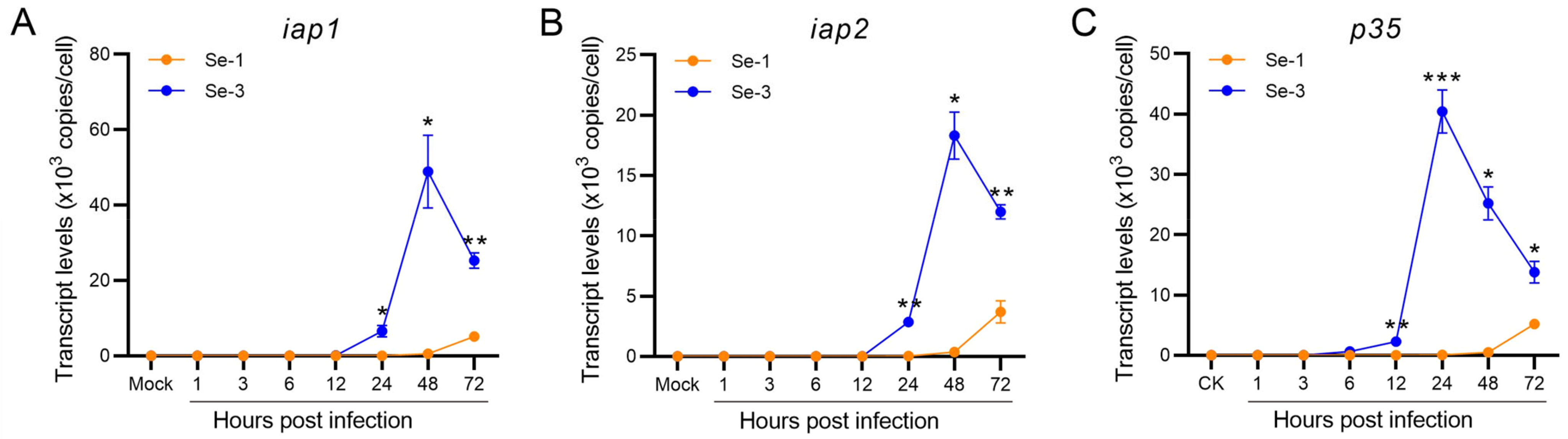
2.4. Transcription Analysis of the Antiapoptotic Genes in Two Different S. exigua Cell Lines during AcMNPV Infection
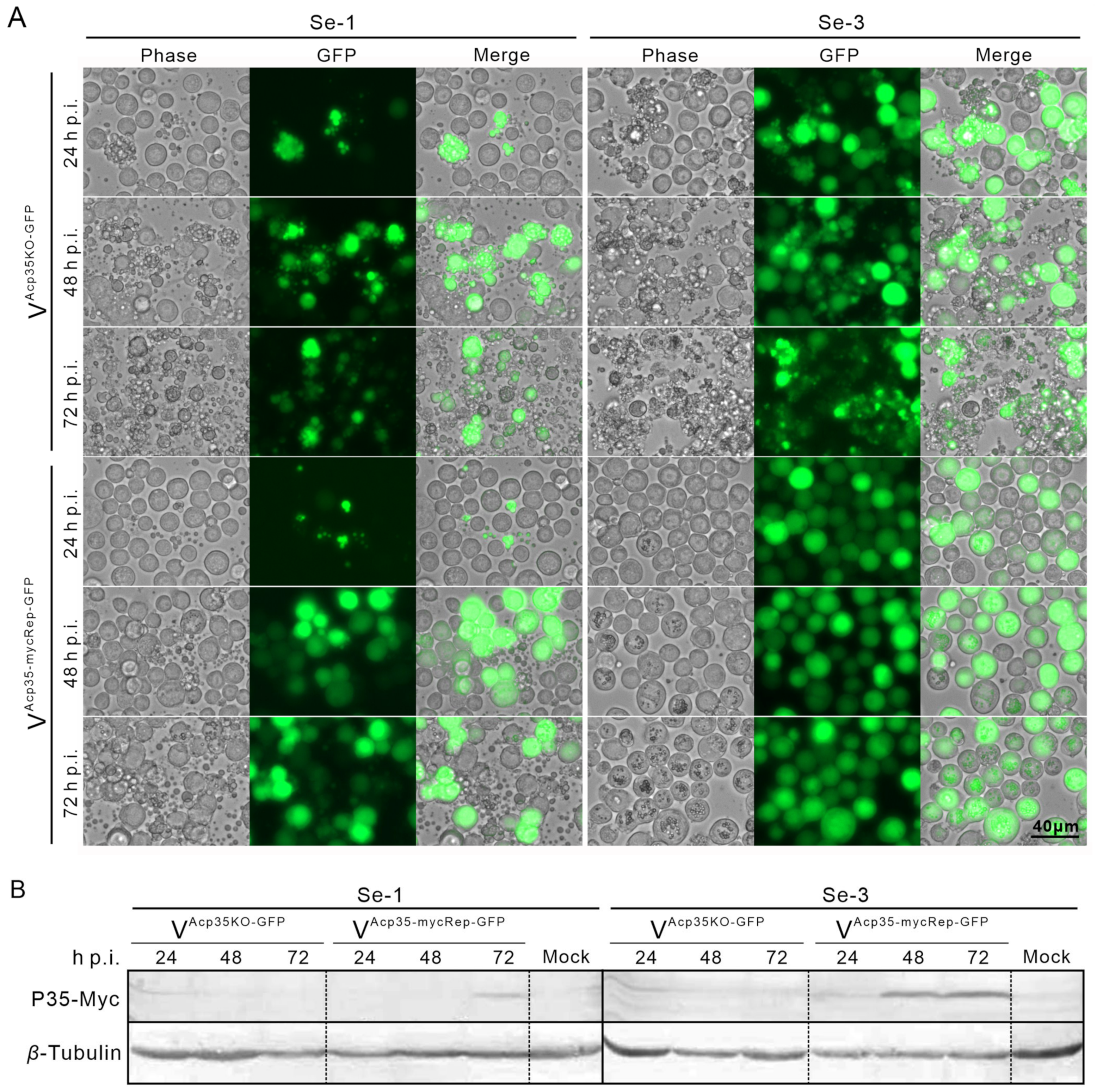
2.5. Expression of P35 Protein in Two Different S. exigua Cell Lines Infected with Recombinant AcMNPV
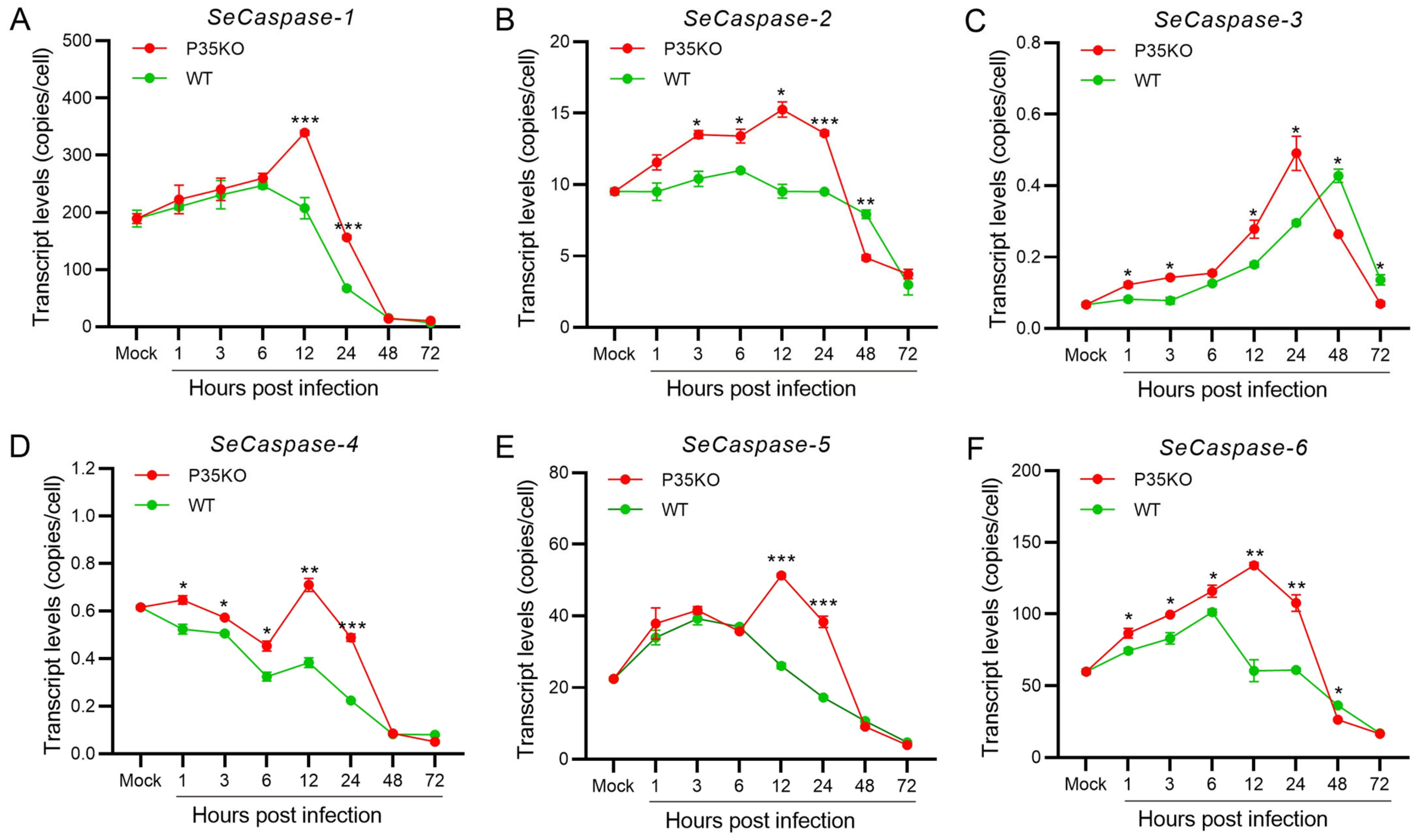
2.6. Transcription Analysis of SeCaspases in Se-3 Cell Lines during Recombinant VAcp35KO-GFP Infection
2.7. Expression Change Analysis of the Genes of the Two Different S. exigua Cell Lines during AcMNPV Infection
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Viruses
4.2. Virus Infection and Productions Determination
4.3. Apoptosis Process and Rate Analysis
4.4. Expression Analysis of Cell and Virus Genes by Reverse Transcription Quantitative PCR
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Analysis of the Differentially Expressed Genes from Apoptosis-associated Pathways
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blissard, G.W.; Theilmann, D.A. Baculovirus entry and egress from insect cells. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2018, 5, 113–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrmann, G.F. Baculovirus Molecular Biology [Internet], 4th ed.; National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Federici, B.A. Naturally occurring baculoviruses for insect pest control. In Biopesticides: Use and Delivery; Hall, F.R., Menn, J.J., Eds.; Humana Press Inc: Totowa, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 301–320. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, C.; Yang, S.; Lei, W.; Nyamwasa, I.; Hu, J.; Sun, X. Displaying enhancing factors on the surface of occlusion bodies improves the insecticidal efficacy of a baculovirus. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricarte-Bermejo, A.; Simón, O.; Fernández, A.B.; Williams, T.; Caballero, P. Bacmid expression of granulovirus enhancin En3 accumulates in cell soluble fraction to potentiate nucleopolyhedrovirus infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, T.E.; Clem, R.J. Insect defenses against virus infection: The role of apoptosis. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 22, 401–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clem, R.J. The role of apoptosis in defense against baculovirus infection in insects. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 289, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clem, R.J.; Fechheimer, M.; Miller, L.K. Prevention of apoptosis by a baculovirus gene during infection of insect cells. Science 1991, 254, 1388–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lannan, E.; Vandergaast, R.; Friesen, P.D. Baculovirus caspase inhibitors P49 and P35 block virus-induced apoptosis downstream of effector caspase DrICE activation in Drosophila melanogaster cells. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 9319–9330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Opdenbosch, N.; Lamkanfi, M. Caspases in cell death, inflammation, and disease. Immunity 2019, 50, 1352–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; López-Soto, A.; Kumar, S.; Kroemer, G. Caspases connect cell-death signaling to organismal homeostasis. Immunity 2016, 44, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, O.; Wells, J.A. Caspases and their substrates. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.M.; Granville, D.J.; Lowenberger, C. The insect caspases. Apoptosis 2009, 14, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalini, S.; Dorstyn, L.; Dawar, S.; Kumar, S. Old, new and emerging functions of caspases. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Texada, D.E.; Duggan, C.; Deng, Y.; Redens, T.B.; Langford, M.P. Caspase-3 and -7 mediate apoptosis of human Chang’s conjunctival cells induced by enterovirus 70. Virology 2006, 347, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koganti, S.; Burgula, S.; Bhaduri-McIntosh, S. STAT3 activates the anti-apoptotic form of caspase 9 in oncovirus-infected B lymphocytes. Virology 2020, 540, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masalova, O.V.; Lesnova, E.I.; Solyev, P.N.; Zakirova, N.F.; Prassolov, V.S.; Kochetkov, S.N.; Ivanov, A.V.; Kushch, A.A. Modulation of cell death pathways by hepatitis C virus proteins in Huh7.5 hepatoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, H.L.; Wang, L.; Gardner, C.L.; Corkum, C.P.; Grant, M.D.; Hirasawa, K.; Russell, R.S. Crosstalk between pyroptosis and apoptosis in hepatitis C virus-induced cell death. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 788138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtiade, J.; Pauchet, Y.; Vogel, H.; Heckel, D.G. A comprehensive characterization of the caspase gene family in insects from the order Lepidoptera. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Li, Z.Q.; Ou-Yang, Y.Y.; Huang, G.H. Identification of four caspase genes from Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and their regulations toward different apoptotic stimulations. Insect Sci. 2020, 27, 1158–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, Z.; Li, A.; Lu, Z.; Wu, C.; Yin, H.; Yuan, M.; Pang, Y. The Spodoptera frugiperda effector caspase Sf-caspase-1 becomes unstable following its activation. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2013, 83, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Civciristov, S.; Hawkins, C.J.; Clem, R.J. SfDronc, an initiator caspase involved in apoptosis in the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clem, R.J. Viral IAPs, then and now. Semi Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 39, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, R.; Meng, Q.; Miao, L.; Liang, H.; Chen, J.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Jin, W.; Qin, Q.; Zhang, H. Genome analysis of a novel clade b betabaculovirus isolated from the legume pest Matsumuraeses phaseoli (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Viruses 2020, 12, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Yamada, H.; Hamajima, R.; Kobayashi, M. Baculovirus genes modulating intracellular innate antiviral immunity of lepidopteran insect cells. Virology 2013, 435, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bump, N.J.; Hackett, M.; Hugunin, M.; Seshagiri, S.; Brady, K.; Chen, P.; Ferenz, C.; Franklin, S.; Ghayur, T.; Li, P.; et al. Inhibition of ICE family proteases by baculovirus antiapoptotic protein p35. Science 1995, 269, 1885–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, C.G.; Valdes, J.J.; Bentley, W.E. Investigating apoptosis: Characterization and analysis of Trichoplusia ni-caspase-1 through overexpression and RNAi mediated silencing. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Rich, R.L.; Steegborn, C.; Min, T.; Huang, Y.; Myszka, D.G.; Wu, H. Mutational analyses of the p35-caspase interaction: A bowstring kinetic model of caspase inhibition by p35. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 5455–5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Yu, M.; Wu, W.; Yu, Q.; Weng, Q.; Yang, K.; Yuan, M.; Pang, Y. Functional analysis of Spodoptera litura nucleopolyhedrovirus p49 gene during Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus infection of SpLi-221 cells. Virus Genes 2010, 41, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Reske, G.; Huang, Q.; Hammock, B.D.; Qi, Y.; Chejanovsky, N. Characterization of the apoptosis suppressor protein P49 from the Spodoptera littralis nucleopolyhedrovirus. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 48677–48684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, H.; Kitaguchi, K.; Hamajima, R.; Kobayashi, M.; Ikeda, M. Novel apoptosis suppressor Apsup from the baculovirus Lymantria dispar multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus precludes apoptosis by preventing proteolytic processing of initiator caspase Dronc. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 12925–12934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, N.M.; Vandergaast, R.L.; Friesen, P.D. Baculovirus inhibitor-of-apoptosis Op-IAP3 blocks apoptosis by interaction with and stabilization of a host insect cellular IAP. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Kang, T.T.; Bao, X.Y.; Dong, Z.Q.; Zhu, Y.; Xiao, W.F.; Pan, M.H.; Lu, C. Evolutionary and functional analyses of the interaction between the Bombyx mori inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) and nucleopolyhedrovirus IAPs. Insect Sci. 2020, 27, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Lin, T.; Feng, G.; Yang, K.; Pang, Y. Functional analysis of the putative antiapoptotic genes, p49, and iap4, of Spodoptera litura nucleopolyhedrovirus with RNAi. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clem, R.J.; Miller, L.K. Control of programmed cell death by the baculovirus genes p35 and iap. Mol. Cell Biol. 1994, 14, 5212–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, C.M.; Barnett, A.L.; Ayres, M.D.; Windass, J.; King, L.A.; Possee, R.D. In vitro host range of Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus recombinants lacking functional p35, iap1 or iap2. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Y. miR-34-5p, encoded by Spodoptera frugiperda, participates in anti-baculovirus by regulating innate immunity in the insect host. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222 Pt B, 2190–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Huang, X.M.; Ding, X.Y.; Zhao, C.X.; Li, M.W.; Wu, Y.C.; Liu, Q.N.; Wang, X.Y. Bmcas-1 plays an important role in response against BmNPV infection in vitro. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 107, e21793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, K.; Ou, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, H. Development of a baculovirus vector carrying a small hairpin RNA for suppression of sf-caspase-1 expression and improvement of recombinant protein production. BMC Biotechnol. 2018, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, K.; Lan, L.; Shi, N.; Nan, H.; Shi, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, H. Improvement of protein production by engineering a novel antiapoptotic baculovirus vector to suppress the expression of Sf-caspase-1 and Tn-caspase-1. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2021, 118, 2977–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Malmanche, H.; Marcellin, E.; Reid, S. Knockout of Sf-Caspase-1 generates apoptosis-resistant Sf9 cell lines: Implications for baculovirus expression. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 17, e2100532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaguchi, K.; Hamajima, R.; Yamada, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Ikeda, M. Cloning and functional characterization of the Lymantria dispar initiator caspase dronc. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 436, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Song, J.; Bao, X.Y.; Chen, P.; Yi, H.S.; Pan, M.H.; Lu, C. BmDredd is an initiator caspase and participates in Emodin-induced apoptosis in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Gene 2016, 591, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Liang, A.; Fu, Y. Baculovirus antiapoptotic protein P35 regulated the host apoptosis to enhance virus multiplication. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2016, 423, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Deng, Z.; Long, Z.; Cai, Y.; Ying, Z.; Yin, H.; Yuan, M.; Clem, R.J.; Yang, K.; Pang, Y. Generating a host range-expanded recombinant baculovirus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, J.; Mendrysa, S.M.; LaCount, D.J.; Gaur, S.; Krebs, J.F.; Armstrong, R.C.; Tomaselli, K.J.; Friesen, P.D. Apoptotic suppression by baculovirus P35 involves cleavage by and inhibition of a virus-induced CED-3/ICElike protease. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 6251–6259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddins, M.J.; Lemongello, D.; Friesen, P.D.; Fisher, A.J. Crystallization and low-resolution structure of an effector-caspase/P35 complex: Similarities and differences to an initiator-caspase/P35 complex. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2002, 58, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Cirilli, M.; Huang, Y.; Rich, R.L.; Myszka, D.G.; Wu, H. Covalent inhibition revealed by the crystal structure of the caspase-8/p35 complex. Nature 2001, 410, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, R.; Zheng, G.L.; Wan, F.H.; Li, C.Y. Establishment and characterization of three embryonic cell lines of beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Cytotechnology 2016, 68, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Yue, Q.; Gao, J.L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.R.; Blissard, G.W.; Liu, T.X.; Li, Z.F. Roles of cellular NSF protein in entry and nuclear egress of budded virions of Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01111-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.T.; Li, Y.Y.; Qiao, B.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Ji, N.; Li, Z.F. Disrupting the association of Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus Ac93 with cellular ESCRT-III/Vps4 hinders nuclear egress of nucleocapsids and intranuclear microvesicles formation. Virology 2020, 541, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckow, V.A.; Lee, S.C.; Barry, G.F.; Olins, P.O. Efficient generation of infectious recombinant baculoviruses by site-specific transposon-mediated insertion of foreign genes into a baculovirus genome propagated in Escherichia coli. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 4566–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, D.R.; Miller, L.K.; Luckow, V.A. Baculovirus Expression Vectors: A Laboratory Manual; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, B.; Huang, C.; Xing, L.S.; Li, Z.Y.; Liu, C.H.; Zhou, H.X.; Zheng, G.L.; Li, J.; Han, J.C.; et al. A chromosome-level genome assembly of the beet armyworm Spodoptera exigua. Genomics 2023, 115, 110571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.K.; Feng, Z.X.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.W.; Zhang, X.G. DEGseq: An R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene Name | KEGG ID (Name) | Gene ID | Log2 (Fold Change) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mock | 1 h p.i. | 12 h p.i. | |||
| Apoptosis | |||||
| Aif | K04727(AIFM1) | SeL15G011396 | −1.8 | nc | −3.4 |
| dTspo | K05770(TSPO) | SeL24G017306 | nc | nc | 1 |
| Bicaudal | K01527(EGD1) | SeL24G017329 | nc | nc | 1.2 |
| Lamin | K07611(LMNB) | SeL02G001429 | nc | nc | 1.2 |
| Buffy | K20017(BUFFY) | SeL04G003073 | 2.7 | 2.0 | 3.5 |
| Drp1 | K17065(DNM1L) | SeL13G009814 | nc | nc | 1.4 |
| Htra2 | K08669(HTRA2) | SeL24G017609 | nc | nc | 1.1 |
| Apaf-1 | K02084(APAF1) | SeL09G006996 | nc | −1.5 | nc |
| P53 pathway | |||||
| Mdm2 | K06643(MDM2) | SeL09G006582 | nc | 1 | 3 |
| Pigs | K10133(TP53I3)/K10134(EI24) | SeL07G005232 | nc | nc | 1 |
| Siah | K04506(SIAH1) | SeL06G005033 | nc | −1.5 | −1.2 |
| SeL03G002261 | 1.1 | nc | 1.3 | ||
| JAK-STAT signalling pathway | |||||
| Stat1-6 | K11220(STAT1)/K11221(STAT2)/K04692(STAT3)/K11222(STAT4)/K11223(STAT5A, B)/K11225(STAT6) | SeL31G020844 | nc | −1.1 | nc |
| Pias1-2 | K04706 (PIAS1)/K16063(PIAS2) | SeL27G018744 | nc | nc | −1.6 |
| SeL08G006116 | nc | nc | 1.1 | ||
| Cbp/p300 | K04498(EP300) | SeL31G020863 | −1.6 | −1.6 | −1.1 |
| Cis | K04701(CISH) | SeL17G012537 | nc | −1.2 | 3.4 |
| Socs | K04694(SOCS1)/K04695(SOCS2)/K04696(SOCS3)/K04697(SOCS4)/K04698(SOCS5)/K04699(SOCS6_7) | SeL11G008507 | −1.3 | nc | 1.9 |
| SeL29G019826 | 1.1 | 1 | 2.4 | ||
| SeL01G000204 | nc | −1.1 | nc | ||
| PI3K-Akt pathway | |||||
| Pi3k | K00929(PIK3CA_B_D)/K02649(PIK3R1_2_3) | SeL05G003720 | −1.5 | −1.1 | −1.6 |
| SeL07G005570 | nc | −1.1 | nc | ||
| SeL06G004934 | nc | nc | 1.1 | ||
| Pten | K01110(PTEN) | SeL18G013590 | nc | nc | 1 |
| Magi | K05629(AIP1)/K05631(AIP3) | SeL26G018583 | nc | nc | 1 |
| Pdk1 | K06276(PDPK1) | SeL20G014856 | nc | nc | 1 |
| Pp2a | K04382(PPP2C)/K03456(PPP2R1)/K04354(PPP2R2)/K11583(PPP2R3)/K11584(PPP2R5) | SeL19G014057 | nc | −1.2 | −1.1 |
| SeL24G017678 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.9 | ||
| SeL03G002068 | nc | nc | 2.5 | ||
| Cdc37 | K09554(CD37) | SeL13G009955 | −1.5 | −1.1 | −1.2 |
| Phlpp | K16340(PHLPP) | SeL04G003119 | nc | nc | −4.5 |
| Creb | K05870(CREB1)/K04450(ATF2)/K04374(ATF4)/K09048(CREB3)/K09047(CREB5)/K09049(ATF6B) | SeL13G009595 | nc | nc | 3 |
| SeL17G012601 | −1.1 | −1.3 | nc | ||
| NIK-NF-kB pathway | |||||
| Ikk | K04467(IKBKA) | SeL18G013302 | nc | nc | −3.2 |
| K07209(IKBKB) | SeL04G003156 | −1.3 | −1.5 | nc | |
| Primer Name | Sequences (5′to 3′) | Plasmids |
|---|---|---|
| SeCaspase-1qF | gcgaggatgccagtggataga | pMD18-T-SeCaspase-1 |
| SeCaspase-1qR | ccttgaggactttggataggttgt | |
| SeCaspase-2qF | ccgagacagacggctggtat | pMD18-T-SeCaspase-2 |
| SeCaspase-2qR | cacggtcacggtttctccac | |
| SeCaspase-3qF | aatgccttgtacgacatgagc | pMD18-T-SeCaspase-3 |
| SeCaspase-3qR | ggttcttgttgatggctgctt | |
| SeCaspase-4qF | atctgcctcggcttggga | pMD18-T-SeCaspase-4 |
| SeCaspase-4qR | cgccacgcagccatagtc | |
| SeCaspase-5qF | ttgcccatctggtagacgcttta | pMD18-T-SeCaspase-5 |
| SeCaspase-5qR | ctgctgttcttgttcgggttgta | |
| SeCaspase-6qF | tttcaacgagtttccaacgatg | pMD18-T-SeCaspase-6 |
| SeCaspase-6qR | tgcattgacattcagtcccagt | |
| IAP1qF | gtgcgagtattgcgaagcag | pMD18-T-IAP1 |
| IAP1qR | acacacacttgggtttgcct | |
| IAP2qF | taggctgtcgcacgattttg | pMD18-T-IAP2 |
| IAP2qR | tgtcaacgaccacggattgt | |
| P35qF | tcgacgtgtcccagacgatt | pMD18-T-P35 |
| P35qR | cttgcgcgtaacgcttcgta |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Q.; Wang, M.; Ding, X.; Han, J.; Ma, H.; Li, J.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, B.; Li, C. The Expression of P35 Plays a Key Role in the Difference in Apoptosis Induced by AcMNPV Infection in Different Spodoptera exigua Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713228
Yu Q, Wang M, Ding X, Han J, Ma H, Li J, Zheng G, Zhang B, Li C. The Expression of P35 Plays a Key Role in the Difference in Apoptosis Induced by AcMNPV Infection in Different Spodoptera exigua Cell Lines. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(17):13228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713228
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Qianlong, Minghui Wang, Xuemeng Ding, Jiachen Han, Hancheng Ma, Jie Li, Guiling Zheng, Bin Zhang, and Changyou Li. 2023. "The Expression of P35 Plays a Key Role in the Difference in Apoptosis Induced by AcMNPV Infection in Different Spodoptera exigua Cell Lines" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 17: 13228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713228
APA StyleYu, Q., Wang, M., Ding, X., Han, J., Ma, H., Li, J., Zheng, G., Zhang, B., & Li, C. (2023). The Expression of P35 Plays a Key Role in the Difference in Apoptosis Induced by AcMNPV Infection in Different Spodoptera exigua Cell Lines. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(17), 13228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713228






