Pyk2/FAK Signaling Is Upregulated in Recurrent Glioblastoma Tumors in a C57BL/6/GL261 Glioma Implantation Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Pyk2 and FAK Phosphorylation Is Upregulated in Tumors That Have Regrown after Resection
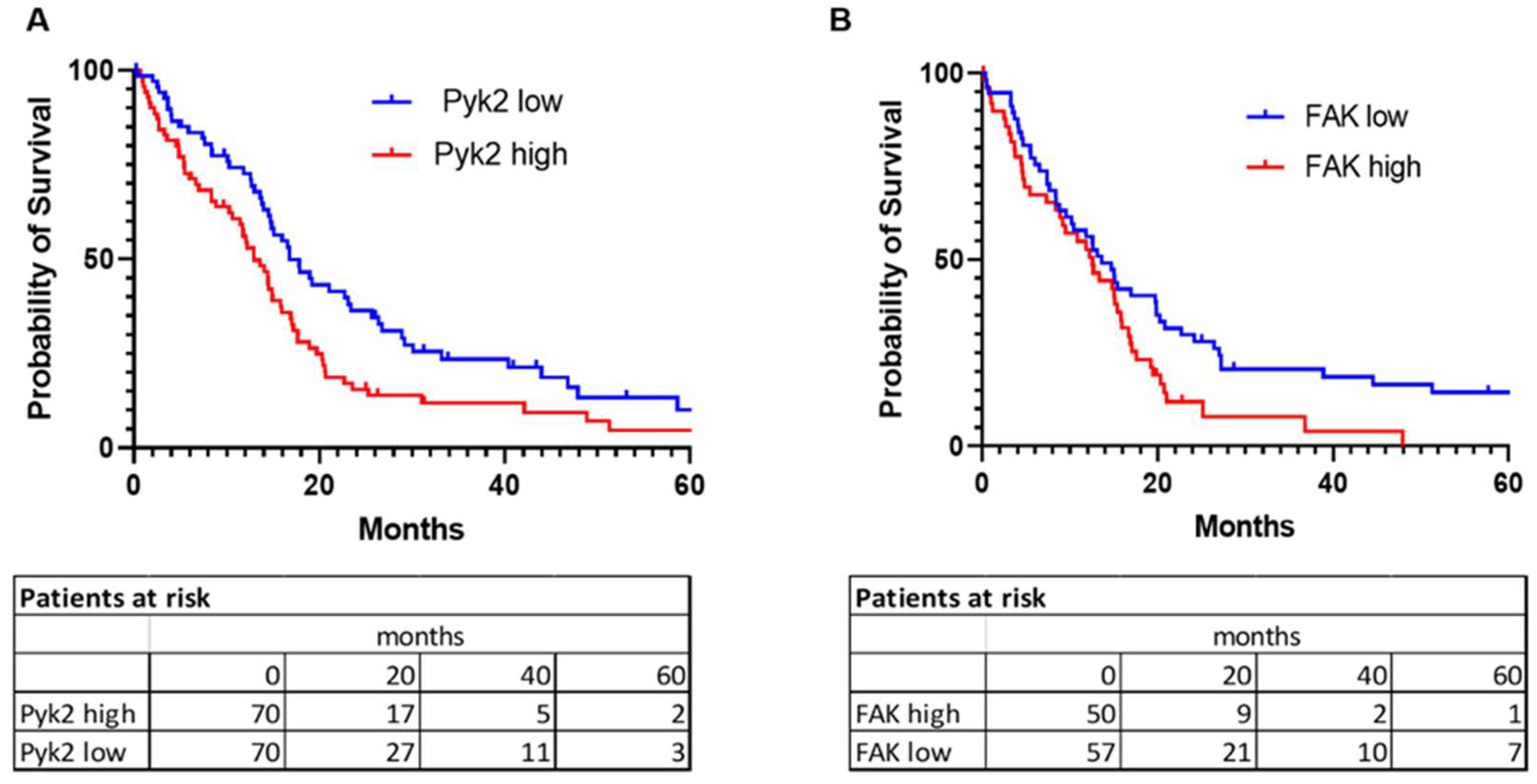
2.2. Pyk2 and FAK Gene-Expression Pattern in Glioblastoma Tumors Associate with Overall Patient Survival
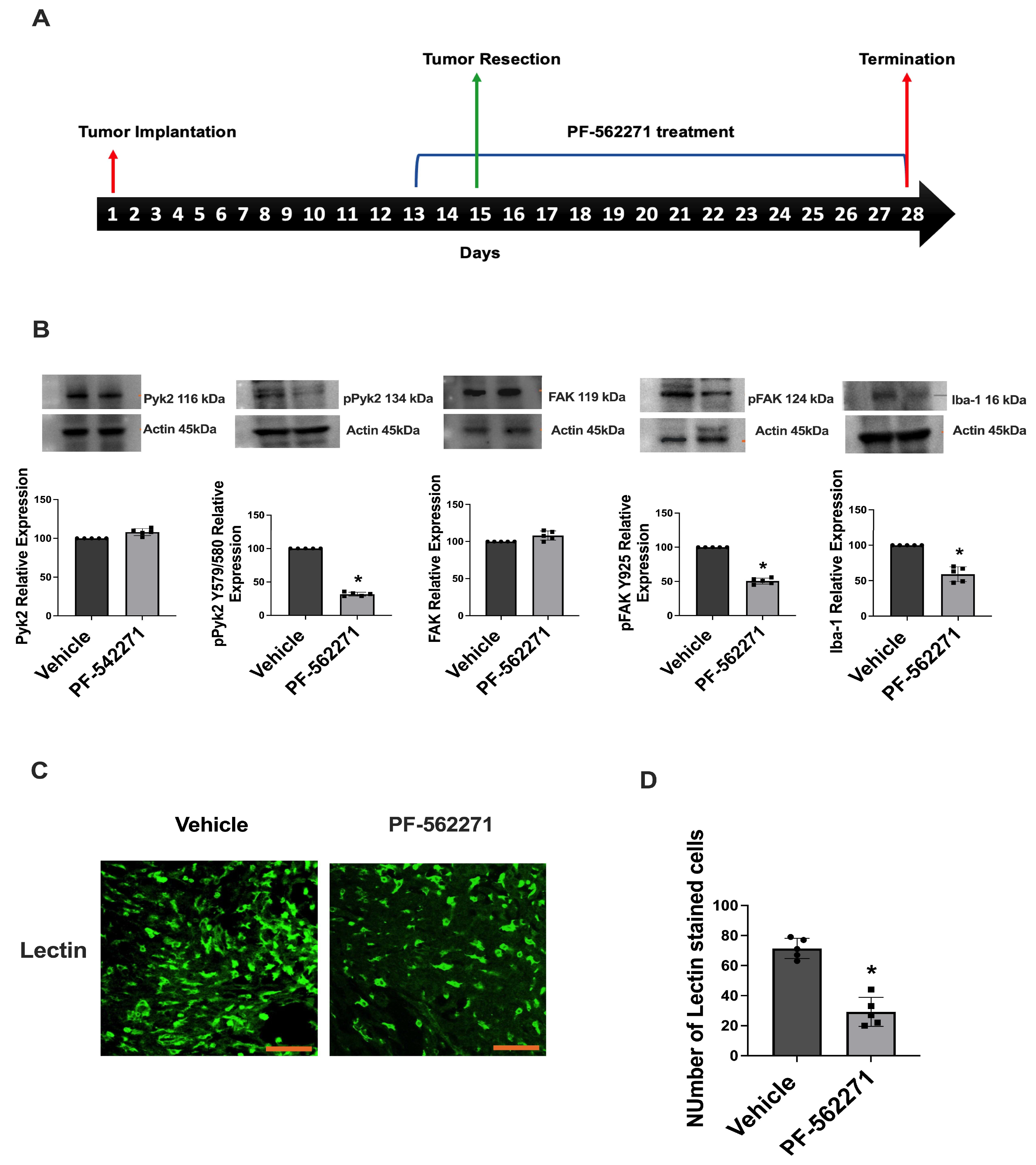
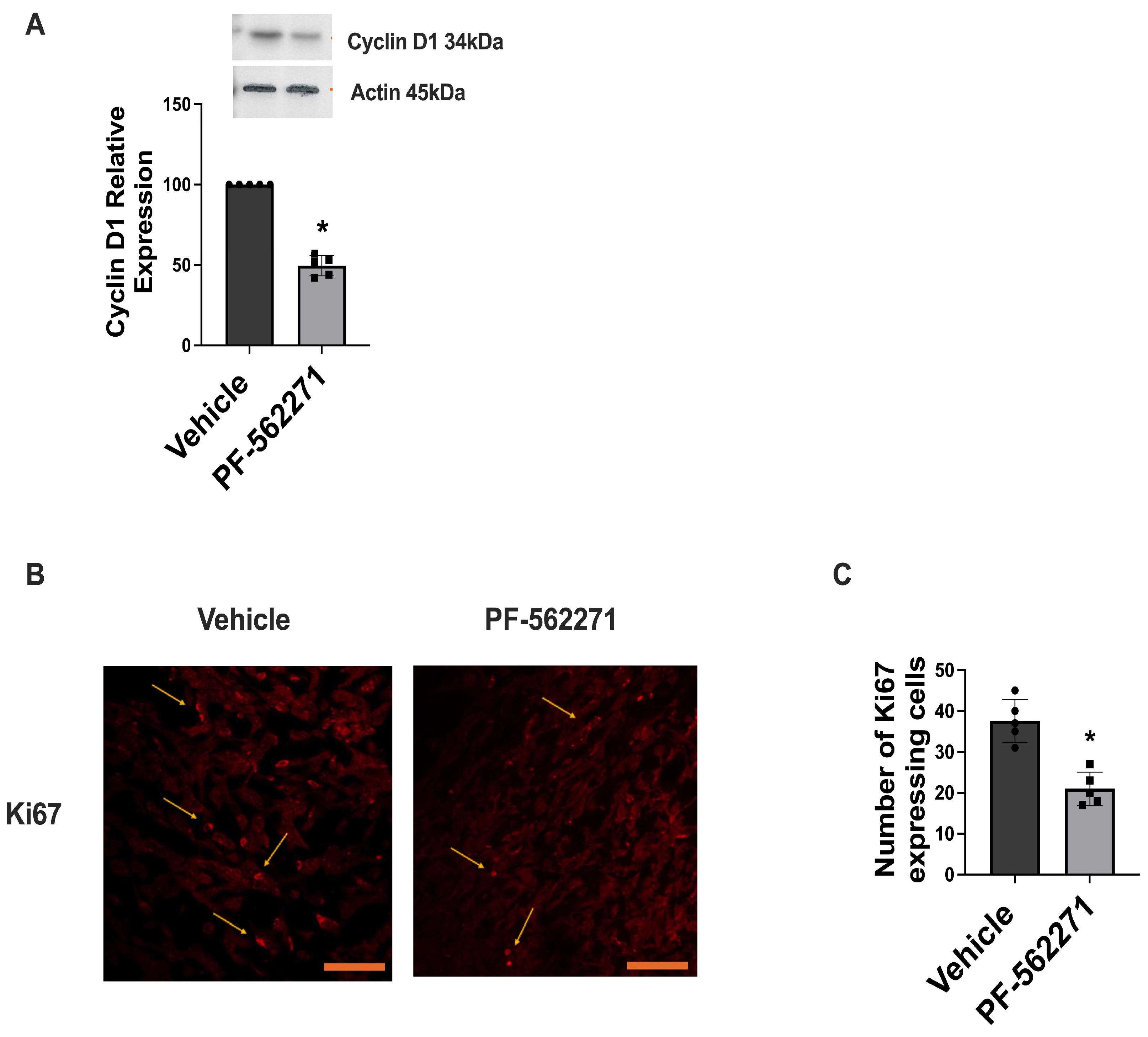
2.3. PF-562271 Reduces Pyk2 and FAK Phosphorylation and the Ki67 Proliferation Index in Tumors Regrown after Surgical Resection
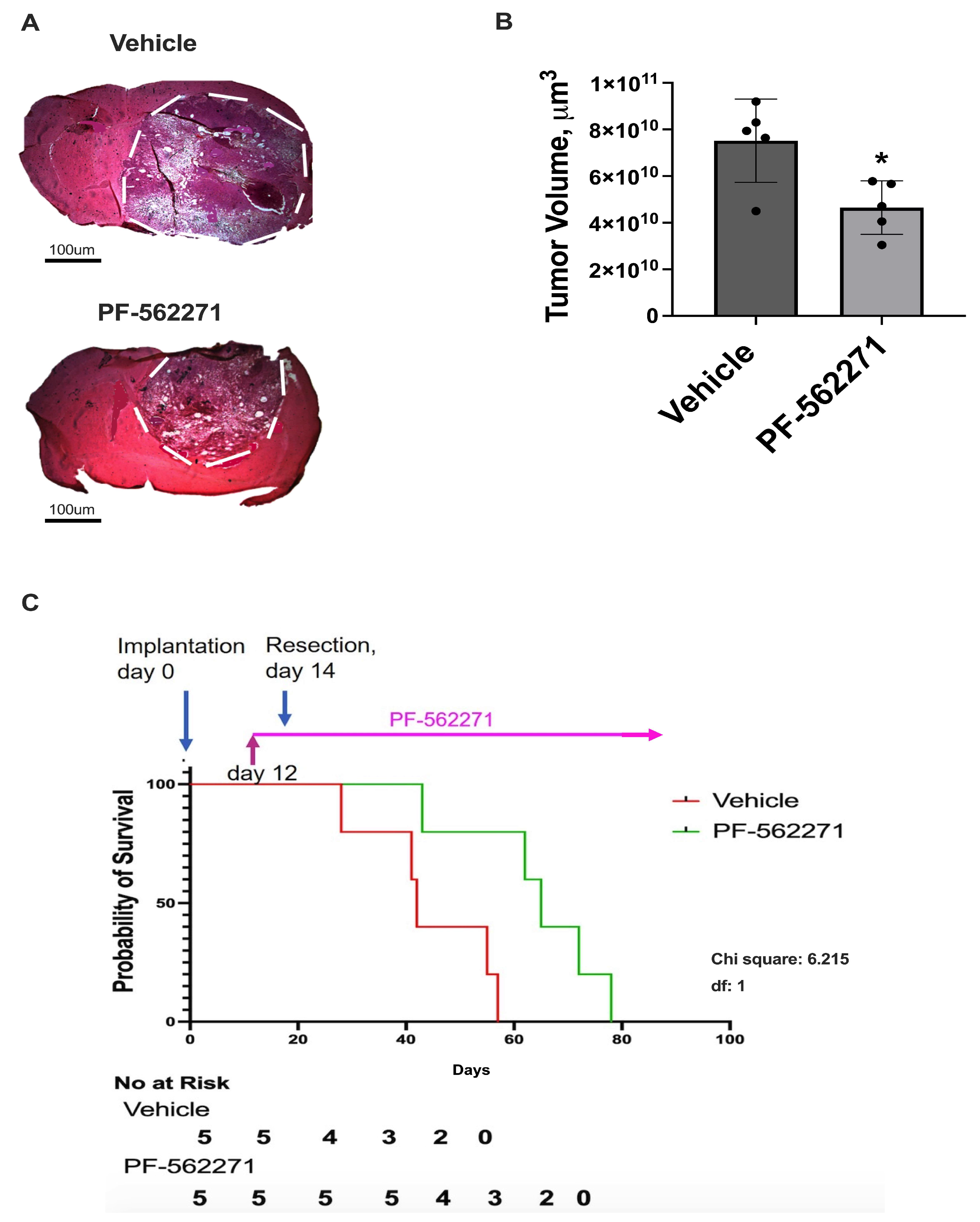
2.4. PF-562271 Reduces the Growth of Recurrent Tumors and Increases Animal Survival
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Intracranial Glioma Implantation and Tumor Resection
4.3. Oral Gavage
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Tumor Size Evaluation
4.6. Immunofluorescence Imaging
4.7. Survival Analysis
4.8. Human Pyk2 and FAK Gene Expression Analysis and Survival Probability Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stupp, R.; Brada, M.J.; van den Bent, M.; Tonn, J.-C.; Pentheroudakis, G.; ESMO Guidelines Working Group. High-grade glioma: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Liao, P.; Rouse, C.; Chen, Y.; Dowling, J.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2007–2011. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 16, iv1–iv63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, L.J.M.; Kannegieter, N.M.; Haerkens, F.; Toth, E.; Kros, J.M.; Hov, D.A.S.; Fillebeen, J.; Verschuren, L.; Leenstra, S.; Ressa, A.; et al. Multiomics profiling of paired primary and recurrent glioblastoma patient tissues. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2020, 2, vdaa083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noch, E.K.; Ramakrishna, R.; Magge, R. Challenges in the Treatment of Glioblastoma: Multisystem Mechanisms of Therapeutic Resistance. World Neurosurg. 2018, 116, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacko, O.; Benouaich-Amiel, A.; Brandicourt, P.; Niaré, M.; Charni, S.; Cavandoli, C.; Brauge, D.; Catalaa, I.; Brenner, A.; Moyal, E.C.-J.; et al. The Impact of Surgery on the Survival of Patients with Recurrent Glioblastoma. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2021, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Huang, T.; Wang, Y.; Chang, L.; Zheng, W.; Ma, Y.; Chen, F.; Gong, X.; et al. Genomic analysis of primary and recurrent gliomas reveals clinical outcome related molecular features. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirzkall, A.; McGue, C.; Saraswathy, S.; Cha, S.; Liu, R.; Vandenberg, S.; Lamborn, K.R.; Berger, M.S.; Chang, S.M.; Nelson, S.J. Tumor regrowth between surgery and initiation of adjuvant therapy in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2009, 11, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, N.; Kim, H.-S.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, E.-J.; Maeng, L.-S.; Yoon, W.S. Targeted Genomic Sequencing Reveals Different Evolutionary Patterns Between Locally and Distally Recurrent Glioblastomas. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2020, 17, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, X.; You, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Yan, W. Comprehensive portrait of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme in molecular and clinical characteristics. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 30968–30974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, M.D.; Reis, G.F.; Reuss, D.E.; Phillips, J.J. Protein Analysis of Glioblastoma Primary and Posttreatment Pairs Suggests a Mesenchymal Shift at Recurrence. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 75, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, H.S.; Kharbanda, S.; Chen, R.; Forrest, W.F.; Soriano, R.H.; Wu, T.D.; Misra, A.; Nigro, J.M.; Colman, H.; Soroceanu, L.; et al. Molecular subclasses of high-grade glioma predict prognosis, delineate a pattern of disease progression, and resemble stages in neurogenesis. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arteaga, C.L. Epidermal Growth Factor receptor dependence in human tumors: More than just expression? Oncology 2002, 7 (Suppl. S4), 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, A.; Ott, M.; Fang, D.; Heimberger, A.B. The Role and Therapeutic Targeting of JAK/STAT Signaling in Glioblastoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbison, R.A.; Kubik, M.; Konnick, E.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Lee, S.-G.; Park, H.; Zhang, J.; Carlson, C.S.; Chen, C.; Schwartz, S.M.; et al. The mutational landscape of recurrent versus nonrecurrent human papillomavirus–related oropharyngeal cancer. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e99327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Tran, N.L.; Menashi, E.; Rohl, C.; Kloss, J.; Bay, R.C.; Berens, M.E.; Loftus, J.C. The tyrosine kinase pyk2 promotes migration and invasion of glioma cells. Neoplasia 2005, 7, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, C.R.; Hsia, D.A.; Schlaepfer, D.D. The focal adhesion kinase—A Regulator of cell migration and invasion. IUBMB Life 2002, 53, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunty, J.M.; Schaller, M.D. The N Termini of Focal adhesion kinase family members regulate substrate phosphorylation, localization, and cell morphology. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 45644–45654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, D.; Yang, Z.; Kloss, J.; Loftus, J.C. The Pyk2 FERM regulates Pyk2 complex formation and phosphorylation. Cell. Signal. 2011, 23, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avraham, H.; Park, S.-Y.; Schinkmann, K.; Avraham, S. RAFTK/Pyk2-mediated cellular signalling. Cell. Signal. 2000, 12, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaepfer, D.D.; Hanks, S.K.; Hunter, T.; van der Geer, P. Integrin-mediated signal transduction linked to Ras pathway by GRB2 binding to focal adhesion kinase. Nature 1994, 372, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.R.; Bradley, R.; Ganju, R.K. LPS-induced MCP-1 expression in human microvascular endothelial cells is mediated by the tyrosine kinase, Pyk2 via the p38 MAPK/NF-kappaB-dependent pathway. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftus, J.C.; Yang, Z.; Tran, N.L.; Kloss, J.; Viso, C.; Berens, M.E.; Lipinski, C.A. The Pyk2 FERM domain as a target to inhibit glioma migration. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulino, V.M.; Yang, Z.; Kloss, J.; Ennis, M.J.; Armstrong, B.A.; Loftus, J.C.; Tran, N.L. TROY (TNFRSF19) is overexpressed in advanced glial tumors and promotes glioblastoma cell invasion via Pyk2-Rac1 signaling. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 1558–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Tran, N.L.; Viso, C.; Kloss, J.; Yang, Z.; Berens, M.E.; Loftus, J.C. Extended survival of Pyk2 or FAK deficient orthotopic glioma xenografts. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2008, 90, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Golubovskaya, V.M.; Huang, G.; Ho, B.; Yemma, M.; Morrison, C.D.; Lee, J.; Eliceiri, B.P.; Cance, W.G. Pharmacologic Blockade of FAK Autophosphorylation Decreases Human Glioblastoma Tumor Growth and Synergizes with Temozolomide. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, R.E.; del Valle, M.M.; Ortiz, K.; Almodovar, L.; Kucheryavykh, L. Microglial cytokines induce invasiveness and proliferation of human glioblastoma through Pyk2 and FAK activation. Cancers 2021, 13, 6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolón-Reyes, K.; Kucheryavykh, Y.V.; Cubano, L.A.; Inyushin, M.; Skatchkov, S.N.; Eaton, M.J.; Harrison, J.K.; Kucheryavykh, L.Y. Microglia activate migration of glioma cells through a Pyk2 intra-cellular pathway. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, l1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.; Cloughesy, T.; Perry, J.R.; Wick, W. Standards of care for treatment of recurrent glioblastoma—Are we there yet? Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 4–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keles, G.; Anderson, B.; Berger, M.S. The effect of extent of resection on time to tumor progression and survival in patients with glioblastoma multiforme of the cerebral hemisphere. Surg. Neurol. 1999, 52, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Tran, N.L.; Bay, C.; Kloss, J.; McDonough, W.S.; Beaudry, C.; Berens, M.E.; Loftus, J.C. Differential role of proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 and focal adhesion kinase in determining glioblastoma migration and proliferation. Mol. Cancer Res. 2003, 1, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Dai, D.; Zhou, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Inhibition of Cyclin D1 Expression in Human Glioblastoma Cells is Associated with Increased Temozolomide Chemosensitivity. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 2496–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holien, T.; Våtsveen, T.K.; Hella, H.; Waage, A.; Sundan, A. Addiction to c-MYC in multiple myeloma. Blood 2012, 120, 2450–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, J.B.; Adair, S.J.; Slack-Davis, J.K.; Walters, D.M.; Tilghman, R.W.; Hershey, E.D.; Lowrey, B.; Thomas, K.S.; Bouton, A.H.; Hwang, R.F.; et al. Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase by PF-562,271 inhibits the growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer concomitant with altering the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, W.G.; Ung, E.; Whalen, P.; Cooper, B.; Hulford, C.; Autry, C.; Richter, D.; Emerson, E.; Lin, J.; Kath, J.; et al. Antitumor Activity and Pharmacology of a Selective Focal Adhesion Kinase Inhibitor, PF-562,271. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1935–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Wen, J.; Gong, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Liang, J.; Hu, F.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, L.; et al. Antitumor effect of focal adhesion kinase inhibitor PF562271 against human osteosarcoma in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1347–1356, Correction in Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 3663–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmanis, S.; Sloan, S.A.; Croote, D.; Mignardi, M.; Chernikova, S.; Samghababi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Neff, N.; Kowarsky, M.; Caneda, C.; et al. Single-Cell RNA-Seq analysis of infiltrating neoplastic cells at the migrating front of human glioblastoma. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 1399–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, L.J.; Parrinello, S. Vascular regulation of glioma stem-like cells: A balancing act. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2017, 47, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfried, T.N.; Arismendi-Morillo, G.; Zuccoli, G.; Lee, D.C.; Duraj, T.; Elsakka, A.M.; Maroon, J.C.; Mukherjee, P.; Ta, L.; Shelton, L.; et al. Metabolic management of microenvironment acidity in glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 968351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Czaplinska, D.; Ialchina, R.; Schnipper, J.; Liu, B.; Sandelin, A.; Pedersen, S.F. Cancer Cell Acid Adaptation Gene Expression Response Is Correlated to Tumor-Specific Tissue Expression Profiles and Patient Survival. Cancers 2020, 12, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Rivera, J.; Nuñez, R.; Kucheryavykh, Y.; Kucheryavykh, L. The PYK2 inhibitor PF-562271 enhances the effect of temozolomide on tumor growth in a C57Bl/6-Gl261 mouse glioma model. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2023, 161, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Hong, J.-H. Activated PyK2 and Its Associated Molecules Transduce Cellular Signaling from the Cancerous Milieu for Cancer Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanio, C.; Binder, Z.A.; Chang, R.B.; Nasrallah, M.P.; Delman, D.; Li, J.H.; Tang, O.Y.; Zhang, L.Y.; Zhang, J.V.; Wherry, E.J.; et al. Immunologic Features in De Novo and Recurrent Glioblastoma Are Associated with Survival Outcomes. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2022, 10, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Chanoch-Myers, R.; Mathewson, N.D.; Myskiw, C.; Atta, L.; Bussema, L.; Eichhorn, S.W.; Greenwald, A.C.; Kinker, G.S.; Rodman, C.; et al. Interactions between cancer cells and immune cells drive transitions to mesenchymal-like states in glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 779–792.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, A.M.; Kato, S.; Bazhenova, L.; Patel, S.P.; Frampton, G.M.; Miller, V.; Stephens, P.J.; Daniels, G.A.; Kurzrock, R. Tumor Mutational Burden as an Independent Predictor of Response to Immunotherapy in Diverse Cancers. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 2598–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Diaz, C.; Pöysti, A.; Mereu, E.; Clements, M.P.; Brooks, L.J.; Galvez-Cancino, F.; Castillo, S.P.; Tang, W.; Beattie, G.; Courtot, L.; et al. Glioblastoma cell fate is differentially regulated by the microenvironments of the tumor bulk and infiltrative margin. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Rivera, J.; Albors, A.; Kucheryavykh, Y.; Harrison, J.K.; Kucheryavykh, L. The Dynamics of Tumor-Infiltrating Myeloid Cell Activation and the Cytokine Expression Profile in a Glioma Resection Site during the Post-Surgical Period in Mice. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pombo Antunes, A.R.; Scheyltjens, I.; Lodi, F.; Messiaen, J.; Antoranz, A.; Duerinck, J.; Kancheva, D.; Martens, L.; De Vlaminck, K.; Van Hove, H.; et al. Single-cell profiling of myeloid cells in glioblastoma across species and disease stage reveals macrophage competition and specialization. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebel, E.; Kapolou, K.; Unger, S.; Núñez, N.G.; Utz, S.; Rushing, E.J.; Regli, L.; Weller, M.; Greter, M.; Tugues, S.; et al. Single-Cell Mapping of Human Brain Cancer Reveals Tumor-Specific Instruction of Tissue-Invading Leukocytes. Cell 2020, 181, 1626–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Li, Q.; Gao, Q.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, K.; Huang, X.; Pan, J.; Yan, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. IL-17 induces AKT-dependent IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 activation and tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortiz Rivera, J.; Velez Crespo, G.; Inyushin, M.; Kucheryavykh, Y.; Kucheryavykh, L. Pyk2/FAK Signaling Is Upregulated in Recurrent Glioblastoma Tumors in a C57BL/6/GL261 Glioma Implantation Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713467
Ortiz Rivera J, Velez Crespo G, Inyushin M, Kucheryavykh Y, Kucheryavykh L. Pyk2/FAK Signaling Is Upregulated in Recurrent Glioblastoma Tumors in a C57BL/6/GL261 Glioma Implantation Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(17):13467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713467
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtiz Rivera, Jescelica, Grace Velez Crespo, Mikhail Inyushin, Yuriy Kucheryavykh, and Lilia Kucheryavykh. 2023. "Pyk2/FAK Signaling Is Upregulated in Recurrent Glioblastoma Tumors in a C57BL/6/GL261 Glioma Implantation Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 17: 13467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713467
APA StyleOrtiz Rivera, J., Velez Crespo, G., Inyushin, M., Kucheryavykh, Y., & Kucheryavykh, L. (2023). Pyk2/FAK Signaling Is Upregulated in Recurrent Glioblastoma Tumors in a C57BL/6/GL261 Glioma Implantation Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(17), 13467. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713467






