Toxic Effects and Mechanisms of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Liver Toxicity
2.1. Oxidative Damage and Apoptosis
2.2. Disturbance of Glucose and Lipid Metabolism
2.3. Mitochondrial Damage
2.4. Indirect Exposures
2.5. Combined Exposures
2.6. Others
3. Kidney Toxicity
3.1. Oxidative Damage and Apoptosis
3.2. Combined Exposures
3.3. Others
4. Gut Toxicity
4.1. Oxidative Damage and Apoptosis
4.2. Intestinal Microbiome Disturbance
5. Thyroid Toxicity
5.1. Hormonal Interferences
5.2. Oxidative Damage and Apoptosis
5.3. Indirect Exposures
5.4. Combined Exposures
5.5. Others
6. Embryotoxicity
6.1. Oxidative Damage and Apoptosis
6.2. Combined Exposures
6.3. Others
7. Reproductive Toxicity
7.1. Oxidative Damage and Apoptosis
7.2. Epigenetic Inheritance
7.3. Mitochondrial Damage
7.4. Combined Exposures
7.5. Others
8. Neurotoxicity
8.1. Apoptosis
8.2. Disease Induction
8.3. Intestinal Microbiome Disturbance
8.4. Combined Exposures
8.5. Others
9. Immunotoxicity
9.1. Oxidative Damage and Apoptosis
9.2. Inflammatory Response
9.3. Combined Exposures
10. Others
10.1. Diabetes Induction
10.2. Heart Toxicity
10.3. Eye Toxicity
10.4. Lung Toxicity
11. Discussion and Conclusions
12. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khalil, A.; Cevik, S.E.; Hung, S.; Kolla, S.; Roy, M.A.; Suvorov, A. Developmental Exposure to 2,2′,4,4′-Tetrabromodiphenyl Ether Permanently Alters Blood-Liver Balance of Lipids in Male Mice. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevrier, J.; Harley, K.G.; Bradman, A.; Gharbi, M.; Sjödin, A.; Eskenazi, B. Polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) flame retardants and thyroid hormone during pregnancy. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, C.; Li, L.Y. Filling the gap: Estimating physicochemical properties of the full array of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs). Environ. Pollut. 2013, 180, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Gong, A.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Bai, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, G. Cell changes and differential proteomic analysis during biodegradation of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 25048–25055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zou, W.; Zhong, Y.; An, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, M.; Yu, Z. The hormesis effect of BDE-47 in HepG2 cells and the potential molecular mechanism. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 209, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Song, J.; Ren, Z.; Yuan, H.; Yan, H.; Zhang, J.; Pei, Z.; He, Z. Environmental Characteristics of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers in Marine System, with Emphasis on Marine Organisms and Sediments. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1317232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, T.J.; Ball, A.S.; Clarke, B.O. Critical review of soil contamination by polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and novel brominated flame retardants (NBFRs); concentrations, sources and congener profiles. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 741–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.A.; Rylander, C.; Brustad, M.; Sandanger, T.M. Persistent organic pollutants in meat, liver, tallow and bone marrow from semi-domesticated reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus L.) in Northern Norway. Acta Vet. Scand. 2013, 55, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Driscoll, K.; Robinson, J.; Chiang, W.S.; Chen, Y.Y.; Kao, R.C.; Doherty, R. The environmental fate of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in western Taiwan and coastal waters: Evaluation with a fugacity-based model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 13222–13234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, N.A.; McConnell, L.L.; Torrents, A.; Ramirez, M. Persistence of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in agricultural soils after biosolids applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3077–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muresan, B.; Lorgeoux, C.; Gasperi, J.; Moilleron, R. Fate and spatial variations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the deposition within a heavily urbanized area: Case of Paris (France). Water Sci. Technol. A J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 2010, 62, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, S.; Cheng, L.; Jing, X.; Wang, X.; Guan, S.; Song, W.; Rao, Q. Determination of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers in Water Samples Using Effervescent-Assisted Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Icroextraction with Solidification of the Aqueous Phase. Molecules 2021, 26, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, K.L.; Man, Y.B.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Liang, Y.; Wong, M.H. Removal of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) using a combined system involving TiO(2) photocatalysis and wetland plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322 Pt A, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Klösener, J.; Flor, S.; Peters, T.M.; Ludewig, G.; Thorne, P.S.; Robertson, L.W.; Luthe, G. Toxicity assessment of air-delivered particle-bound polybrominated diphenyl ethers. Toxicology 2014, 317, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Huang, H.; Niu, Z.; Han, W. Characterization of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and hydroxylated and methoxylated PBDEs in soils and plants from an e-waste area, China. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imm, P.; Knobeloch, L.; Buelow, C.; Anderson, H.A. Household exposures to polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in a Wisconsin Cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1890–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, S.; Chen, X.; Kass, P.H.; Puschner, B. Polychlorinated biphenyl and polybrominated diphenyl ether profiles in serum from cattle, sheep, and goats across California. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Maryam, B.; Ji, Z.; Sun, J.; Liu, X. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers as hitchhikers on microplastics: Sorption behaviors and combined toxicities to Epinephelus moara. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 252, 106317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Che, S.; Li, S.; Ruan, Z. The combined impact of decabromodiphenyl ether and high fat exposure on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in vivo and in vitro. Toxicology 2021, 464, 153015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, M.; Gao, Y.; Cui, J. In vitro study on the joint hepatoxicity upon combined exposure of cadmium and BDE-209. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 57, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eick, S.M.; Goin, D.E.; Cushing, L.; DeMicco, E.; Park, J.S.; Wang, Y.; Smith, S.; Padula, A.M.; Woodruff, T.J.; Morello-Frosch, R. Mixture effects of prenatal exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and polybrominated diphenyl ethers on maternal and newborn telomere length. Environ. Health A Glob. Access Sci. Source 2021, 20, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midya, V.; Colicino, E.; Conti, D.V.; Berhane, K.; Garcia, E.; Stratakis, N.; Andrusaityte, S.; Basagaña, X.; Casas, M.; Fossati, S.; et al. Association of Prenatal Exposure to Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals With Liver Injury in Children. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2220176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowell, W.J.; Margolis, A.; Rauh, V.A.; Sjödin, A.; Jones, R.; Wang, Y.; Garcia, W.; Perera, F.; Wang, S.; Herbstman, J.B. Associations between prenatal and childhood PBDE exposure and early adolescent visual, verbal and working memory. Environ. Int. 2018, 118, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouidir, M.; Buck Louis, G.M.; Kanner, J.; Grantz, K.L.; Zhang, C.; Sundaram, R.; Rahman, M.L.; Lee, S.; Kannan, K.; Tekola-Ayele, F.; et al. Association of Maternal Exposure to Persistent Organic Pollutants in Early Pregnancy With Fetal Growth. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapleton, H.M.; Eagle, S.; Anthopolos, R.; Wolkin, A.; Miranda, M.L. Associations between polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) flame retardants, phenolic metabolites, and thyroid hormones during pregnancy. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1454–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Chen, X.; Gyimah, E.; Xu, H.; Chen, J. Hepatic oxidative stress, DNA damage and apoptosis in adult zebrafish following sub-chronic exposure to BDE-47 and BDE-153. Environ. Toxicol. 2020, 35, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casella, M.; Lori, G.; Coppola, L.; La Rocca, C.; Tait, S. BDE-47, -99, -209 and Their Ternary Mixture Disrupt Glucose and Lipid Metabolism of Hepg2 Cells at Dietary Relevant Concentrations: Mechanistic Insight through Integrated Transcriptomics and Proteomics Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schecter, A.; Johnson-Welch, S.; Tung, K.C.; Harris, T.R.; Päpke, O.; Rosen, R. Polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) levels in livers of U.S. human fetuses and newborns. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health. Part A 2007, 70, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Liu, X.; Mei, S.; Xu, G. Accumulative levels, temporal and spatial distribution of common chemical pollutants in the blood of Chinese adults. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 119980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, T.; Wang, D.; Du, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Bekir, M.; Yu, D.; Shi, Z. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and decabromodiphenyl ethane in paired hair/serum and nail/serum from corresponding chemical manufacturing workers and their correlations to thyroid hormones, liver and kidney injury markers. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 139049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Salamova, A.; He, K.; Hites, R.A. Analysis of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and emerging halogenated and organophosphate flame retardants in human hair and nails. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1406, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhai, J.X. Distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in breast milk, cord blood and placentas: A systematic review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 21548–21573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Hu, W.; Wu, R.; Zheng, S.; Wu, K. Bioinformatic analyses of hydroxylated polybrominated diphenyl ethers toxicities on impairment of adrenocortical secretory function. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2022, 27, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D.; Cao, K.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Feng, M.; Liu, H. Evaluation of the oxidative stress in liver of crucian carp (Carassius auratus) exposed to 3,4,4′-tri-CDE, 2-MeO-3′,4,4′-tri-CDE, and 2-HO-3′,4,4′-tri-CDE. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 5164–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, D.; Ghate, N.B.; Panja, S.; Basu, T.; Shendge, A.K.; Mandal, N. Glycoside rich fraction from Spondias pinnata bark ameliorate iron overload induced oxidative stress and hepatic damage in Swiss albino mice. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Kim, T.H.; Choi, J.S.; Nabanata, P.; Kim, N.Y.; Ahn, M.Y.; Jung, K.K.; Kang, I.H.; Kim, T.S.; Kwack, S.J.; et al. Evaluation of liver and thyroid toxicity in Sprague-Dawley rats after exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ether BDE-209. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 35, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado-Feliciano, M.; Bigsby, R.M. The polybrominated diphenyl ether mixture DE-71 is mildly estrogenic. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, M.; Liu, F.; Qin, L.; Qu, R.; Li, D.; Wang, Z. Subacute oral toxicity of BDE-15, CDE-15, and HODE-15 in ICR male mice: Assessing effects on hepatic oxidative stress and metals status and ascertaining the protective role of vitamin E. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 1924–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, J.M.; Burka, L.T.; Smith, C.S.; Black, W.; James, R.; Cunningham, M.L. Differential expression of CYP1A, 2B, and 3A genes in the F344 rat following exposure to a polybrominated diphenyl ether mixture or individual components. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2005, 88, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, M.; Yang, H.; Cromie, M.; Gu, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, L.; Yu, Y.; Gao, W.; et al. BDE47 induces rat CYP3A1 by targeting the transcriptional regulation of miR-23b. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, J.; Chan, K.M. BDE-99, but not BDE-47, is a transient aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist in zebrafish liver cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 305, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saquib, Q.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Ahmed, J.; Al-Salim, A.; Ansari, S.M.; Faisal, M.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Musarrat, J.; AlWathnani, H.A.; Alatar, A.A.; et al. Hazards of low dose flame-retardants (BDE-47 and BDE-32): Influence on transcriptome regulation and cell death in human liver cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 308, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Liu, H.; Yin, H.; Liu, X.; Peng, H.; Lu, G.; Dang, Z.; He, C. Effect of 2, 2′, 4, 4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47) and its metabolites on cell viability, oxidative stress, and apoptosis of HepG2. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, J.; White, C.C.; Dabrowski, M.J.; Kavanagh, T.J.; Eckert, M.L.; Gallagher, E.P. The role of mitochondrial and oxidative injury in BDE 47 toxicity to human fetal liver hematopoietic stem cells. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2008, 101, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, J.; Eckert, M.L.; Lee, L.E.; Gallagher, E.P. Comparative oxygen radical formation and toxicity of BDE 47 in rainbow trout cell lines. Mar. Environ. Res. 2008, 66, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Shan, Q.; Zhuang, J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, X.; Fan, S.H.; Lu, J.; Wu, D.M.; Hu, B.; Zheng, Y.L. Troxerutin inhibits 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47)-induced hepatocyte apoptosis by restoring proteasome function. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 233, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Fan, S.H.; Zhuang, J.; Zheng, Y.L.; Lu, J.; Wu, D.M.; Shan, Q.; Hu, B. Troxerutin protects against 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47)-induced liver inflammation by attenuating oxidative stress-mediated NAD+-depletion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albina, M.L.; Alonso, V.; Linares, V.; Bellés, M.; Sirvent, J.J.; Domingo, J.L.; Sánchez, D.J. Effects of exposure to BDE-99 on oxidative status of liver and kidney in adult rats. Toxicology 2010, 271, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.O.; Pereira, L.C.; Oliveira, D.P.; Dorta, D.J. BDE-99 congener induces cell death by apoptosis of human hepatoblastoma cell line-HepG2. Toxicol. Vitr. Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2013, 27, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, S.; Chen, S.; Li, S.; Ruan, Z. Decabromodiphenyl ether initiates mitochondria-dependent apoptosis by disrupting calcium homeostasis in mice livers. Chemosphere 2022, 291 Pt 1, 132767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Peng, L.; Fang, C.; Qin, Q.; Lv, X.; Liu, Z.; Yang, B.; Song, E.; Song, Y. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers quinone-induced intracellular protein oxidative damage triggers ubiquitin-proteasome and autophagy-lysosomal system activation in LO2 cells. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Sun, X.; Che, S.; Zhang, L.; Ruan, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, J. AhR-mediated CYP1A1 and ROS overexpression are involved in hepatotoxicity of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209). Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 352, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.Z.; Xu, Y.; Hu, D.C.; Hui, Y.; Yang, F.X. Apoptosis induction on human hepatoma cells Hep G2 of decabrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE-209). Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 171, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, A.; Liu, H.; Zhang, A.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Effect of BDE-209 on glutathione system in Carassius auratus. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 32, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.P.; Peng, Y.; Zhi, H.; Wu, S.K.; Chen, X.Y.; Zeng, Y.H.; Luo, X.J.; Mai, B.X. Contaminant-related oxidative distress in common kingfisher (Alcedo atthis) breeding at an e-waste site in South China. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.K.; Shi, Y.F.; Fong, C.C.; Chen, Y.; van de Merwe, J.P.; Chan, A.K.; Wei, F.; Bo, J.; Ye, R.; Au, D.W.; et al. Gender-specific transcriptional profiling of marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) liver upon BDE-47 exposure. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2013, 8, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.L.; Jiang, S.R.; Fan, Y.; Wang, J.S.; Wang, M.L.; Li, M.Y. 2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-Hexabromophenyl ether (BDE-153) causes abnormal insulin secretion and disorders of glucose and lipid metabolism in mice. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. JCMA 2023, 86, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvorov, A.; Naumov, V.; Shtratnikova, V.; Logacheva, M.; Shershebnev, A.; Wu, H.; Gerasimov, E.; Zheludkevich, A.; Pilsner, J.R.; Sergeyev, O. Rat liver epigenome programing by perinatal exposure to 2,2′,4′4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether. Epigenomics 2020, 12, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.T.; Szabo, D.T.; Carey, G.B. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers alter hepatic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase enzyme kinetics in male Wistar rats: Implications for lipid and glucose metabolism. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health. Part A 2013, 76, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowens, K.R.; Simpson, S.; Thomas, W.K.; Carey, G.B. Polybrominated Diphenyl Ether (PBDE)-Induced Suppression of Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase (PEPCK) Decreases Hepatic Glyceroneogenesis and Disrupts Hepatic Lipid Homeostasis. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health. Part A 2015, 78, 1437–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlova, E.V.; Chinthirla, B.D.; Pérez, P.A.; DiPatrizio, N.V.; Argueta, D.A.; Phillips, A.L.; Stapleton, H.M.; González, G.M.; Krum, J.M.; Carrillo, V.; et al. Maternal transfer of environmentally relevant polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) produces a diabetic phenotype and disrupts glucoregulatory hormones and hepatic endocannabinoids in adult mouse female offspring. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Jing, L.; Li, X.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Y.; Sang, Y.; Gao, L.; Liu, S.; Shi, Z.; Sun, Z.; et al. Decabromodiphenyl ether-induced PRKACA hypermethylation contributed to glycolipid metabolism disorder via regulating PKA/AMPK pathway in rat and L-02 cells. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 90, 103808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, B.; Pawlak, M.; Lefebvre, P.; Staels, B. PPARs in obesity-induced T2DM, dyslipidaemia and NAFLD. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrha, A.; Suvorov, A. Transcriptomic Analysis of Gonadal Adipose Tissue in Male Mice Exposed Perinatally to 2,2′,4,4′-Tetrabromodiphenyl Ether (BDE-47). Toxics 2018, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, M.; Webster, T.F.; Ferguson, P.L.; Stapleton, H.M. Characterizing the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPARγ) ligand binding potential of several major flame retardants, their metabolites, and chemical mixtures in house dust. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, E.W.; Boudreau, A.; Wade, M.G.; Atlas, E. Induction of adipocyte differentiation by polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in 3T3-L1 cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamstra, J.H.; Hruba, E.; Blumberg, B.; Janesick, A.; Mandrup, S.; Hamers, T.; Legler, J. Transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms underlying enhanced in vitro adipocyte differentiation by the brominated flame retardant BDE-47. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4110–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Jing, L.; Li, X.; Zheng, D.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Y.; Sang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, X. Decabromodiphenyl ether disturbs hepatic glycolipid metabolism by regulating the PI3K/AKT/GLUT4 and mTOR/PPARγ/RXRα pathway in mice and L02 cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 142936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, G.; Yu, Y.; Jing, L.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, X.; Sun, Z. The effects of decabromodiphenyl ether on glycolipid metabolism and related signaling pathways in mice. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, Z.Z.; Xiao, X.; Zhou, S.; Wang, X.C.; Gu, J.; Qiu, L.L.; Zhang, X.H.; Xu, Q.; Zhen, B.; et al. Mechanism of BDE209-induced impaired glucose homeostasis based on gene microarray analysis of adult rat liver. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1557–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.; Tang, J.; Liao, T.; Shi, X.; Dong, F.; Feng, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, T.; Wu, X.; Yang, L. Metabolism toxicity and susceptibility of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) exposure on BRL cells with insulin resistance. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 91306–91324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Feng, L.; Zheng, Y.L.; Lu, J.; Fan, S.H.; Shan, Q.; Zheng, G.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Wu, D.M.; Li, M.Q.; et al. 2, 2′, 4, 4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47) induces mitochondrial dysfunction and related liver injury via eliciting miR-34a-5p-mediated mitophagy impairment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazin, M.; Pereira, L.C.; Dorta, D.J. Toxicity of brominated flame retardants, BDE-47 and BDE-99 stems from impaired mitochondrial bioenergetics. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2015, 25, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.C.; Cabral Miranda, L.F.; Franco-Bernardes, M.F.; Tasso, M.J.; Duarte, F.V.; Inácio Varela, A.T.; Rolo, A.P.; Marques Palmeira, C.M.; Dorta, D.J. Mitochondrial damage and apoptosis: Key features in BDE-153-induced hepatotoxicity. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2018, 291, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L.C.; Souza, A.O.; Tasso, M.J.; Oliveira, A.M.C.; Duarte, F.V.; Palmeira, C.M.; Dorta, D.J. Exposure to decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) produces mitochondrial dysfunction in rat liver and cell death. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health. Part A 2017, 80, 1129–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunnick, J.K.; Shockley, K.R.; Pandiri, A.R.; Kissling, G.E.; Gerrish, K.E.; Ton, T.V.; Wilson, R.E.; Brar, S.S.; Brix, A.E.; Waidyanatha, S.; et al. PBDE-47 and PBDE mixture (DE-71) toxicities and liver transcriptomic changes at PND 22 after in utero/postnatal exposure in the rat. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 3415–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Mulero, M.; Domingo, J.L.; Sanchez, D.J. Perinatal exposure to BDE-99 causes decreased protein levels of cyclin D1 via GSK3β activation and increased ROS production in rat pup livers. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2014, 137, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhu, L.; Kang, Q.; Lee, H.K.; Li, D.; Chung, A.C.K.; Cai, Z. Chronic exposure to tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47) aggravates hepatic steatosis and liver fibrosis in diet-induced obese mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 378, 120766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, G.; Tian, L.; Kong, C.; Gao, D.; Chen, Y.; Junaid, M.; Wang, J. Neuro- and hepato-toxicity of polystyrene nanoplastics and polybrominated diphenyl ethers on early life stages of zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857 Pt 2, 159567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crump, D.; Chiu, S.; Egloff, C.; Kennedy, S.W. Effects of hexabromocyclododecane and polybrominated diphenyl ethers on mRNA expression in chicken (Gallus domesticus) hepatocytes. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2008, 106, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimbo, T.; Dunnick, J.K.; Brix, A.; Mav, D.; Shah, R.; Roberts, J.D.; Wade, P.A. DNA Methylation Changes in Tbx3 in a Mouse Model Exposed to Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers. Int. J. Toxicol. 2017, 36, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Søfteland, L.; Petersen, K.; Stavrum, A.K.; Wu, T.; Olsvik, P.A. Hepatic in vitro toxicity assessment of PBDE congeners BDE47, BDE153 and BDE154 in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 105, 246–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.J.; Dutta, M.; Dempsey, J.L.; Lehmler, H.J.; MacDonald, J.; Bammler, T.; Walker, C.; Kavanagh, T.J.; Gu, H.; Mani, S.; et al. Neonatal Exposure to BPA, BDE-99, and PCB Produces Persistent Changes in Hepatic Transcriptome Associated With Gut Dysbiosis in Adult Mouse Livers. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2021, 184, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Y.; Cui, J.Y. Regulation of protein-coding gene and long noncoding RNA pairs in liver of conventional and germ-free mice following oral PBDE exposure. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueyoshi, T.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Moore, R.; Kodavanti, P.R.; Lehmler, H.J.; Negishi, M.; Birnbaum, L.S. Flame retardant BDE-47 effectively activates nuclear receptor CAR in human primary hepatocytes. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2014, 137, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Li, C.Y.; Kelly, E.J.; Sheppard, L.; Cui, J.Y. Transcriptomic profiling of PBDE-exposed HepaRG cells unveils critical lncRNA- PCG pairs involved in intermediary metabolism. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0224644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liang, B.; Chen, T.; Zheng, D.; Zhao, X.; Jing, L.; Zhou, X.; Sun, Z.; Shi, Z. Hepatotoxicity of decabromodiphenyl ethane (DBDPE) and decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) in 28-day exposed Sprague-Dawley rats. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Cao, L.; Li, F.; Lian, P.; Zhao, J. Multiple biomarkers of the cytotoxicity induced by BDE-47 in human embryonic kidney cells. Chemosphere 2015, 126, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, P.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, G.; Cai, J.; Zhang, Z. Melatonin relieves 2,2,4,4-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47)-induced apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction through the AMPK-Sirt1-PGC-1α axis in fish kidney cells (CIK). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 232, 113276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Q.; Zhuang, J.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.; Zheng, Y. Troxerutin Reduces Kidney Damage against BDE-47-Induced Apoptosis via Inhibiting NOX2 Activity and Increasing Nrf2 Activity. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 6034692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Jin, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Rao, Q. Nephrotoxicity and possible mechanisms of decabrominated diphenyl ethers (BDE-209) exposure to kidney in broilers. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milovanovic, V.; Buha, A.; Matovic, V.; Curcic, M.; Vucinic, S.; Nakano, T.; Antonijevic, B. Oxidative stress and renal toxicity after subacute exposure to decabrominated diphenyl ether in Wistar rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 7223–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, B.; Qian, X.; Xu, G.; Jin, X.; Chen, D.; Tang, J.; Xu, L. Transcriptomics-based analysis of co-exposure of cadmium (Cd) and 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47) indicates mitochondrial dysfunction induces NLRP3 inflammasome and inflammatory cell death in renal tubular epithelial cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 241, 113790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Zhao, Z.; Rao, Q.; Li, X.; Ruan, Z.; Yang, J. BDE-47 induces nephrotoxicity through ROS-dependent pathways of mitochondrial dynamics in PK15 cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Qiao, S.; Ma, W.; Cai, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z. Melatonin administration alleviates 2,2,4,4-tetra-brominated diphenyl ether (PBDE-47)-induced necroptosis and secretion of inflammatory factors via miR-140-5p/TLR4/NF-κB axis in fish kidney cells. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 128, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Q.; Zheng, G.H.; Han, X.R.; Wen, X.; Wang, S.; Li, M.Q.; Zhuang, J.; Zhang, Z.F.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Troxerutin Protects Kidney Tissue against BDE-47-Induced Inflammatory Damage through CXCR4-TXNIP/NLRP3 Signaling. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 9865495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, C.; Lok-Shun Lai, N.; Zhang, W.; Hua, J.; Lam, P.K.S.; Lam, J.C.W.; Zhou, B. Acute exposure to PBDEs at an environmentally realistic concentration causes abrupt changes in the gut microbiota and host health of zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yuan, J.; Che, S.; Zhang, L.; Ruan, Z.; Sun, X. Decabromodiphenyl ether induces ROS-mediated intestinal toxicity through the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022, 36, e22995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Wan, X.; Xiao, B.; Yang, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, P.; Liu, L.; Xia, T.; Wang, A.; et al. Impacts of PBDE-47 exposure before, during and after pregnancy on the maternal gut microbiome and its association with host metabolism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoville, D.K.; Li, C.Y.; Wang, D.; Dempsey, J.L.; Raftery, D.; Mani, S.; Gu, H.; Cui, J.Y. Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Gut Microbiome Modulate Metabolic Syndrome-Related Aqueous Metabolites in Mice. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 2019, 47, 928–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, M.V.; Dutta, M.; Suvorov, A.; Shi, X.; Gu, H.; Mani, S.; Yue Cui, J. Early Life Exposure to Environmental Contaminants (BDE-47, TBBPA, and BPS) Produced Persistent Alterations in Fecal Microbiome in Adult Male Mice. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2021, 179, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popli, S.; Badgujar, P.C.; Agarwal, T.; Bhushan, B.; Mishra, V. Persistent organic pollutants in foods, their interplay with gut microbiota and resultant toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Yan, J.; Teng, M.; Yan, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, W. In utero and lactational exposure to BDE-47 promotes obesity development in mouse offspring fed a high-fat diet: Impaired lipid metabolism and intestinal dysbiosis. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 1847–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Y.; Dempsey, J.L.; Wang, D.; Lee, S.; Weigel, K.M.; Fei, Q.; Bhatt, D.K.; Prasad, B.; Raftery, D.; Gu, H.; et al. PBDEs Altered Gut Microbiome and Bile Acid Homeostasis in Male C57BL/6 Mice. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 2018, 46, 1226–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Wen, S.; Li, J.; Zhong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y. The human body burden of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and their relationships with thyroid hormones in the general population in Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466–467, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Lu, L.; Zhou, J.; Huang, H.; Fang, D.; Tao, G. Effect on metabolic enzymes and thyroid receptors induced by BDE-47 by activation the pregnane X receptor in HepG2, a human hepatoma cell line. Toxicol. Vitr. Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2014, 28, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macaulay, L.J.; Chen, A.; Rock, K.D.; Dishaw, L.V.; Dong, W.; Hinton, D.E.; Stapleton, H.M. Developmental toxicity of the PBDE metabolite 6-OH-BDE-47 in zebrafish and the potential role of thyroid receptor β. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 168, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.K.; Chan, K.M. Disruption of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis in zebrafish embryo-larvae following waterborne exposure to BDE-47, TBBPA and BPA. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 108, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yu, L.; Yang, L.; Zhou, B. Bioconcentration and metabolism of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) result in thyroid endocrine disruption in zebrafish larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 110–111, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis-Hutchings, R.G.; Cherr, G.N.; Hanna, L.A.; Keen, C.L. Polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE)-induced alterations in vitamin A and thyroid hormone concentrations in the rat during lactation and early postnatal development. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2006, 215, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowles, J.R.; Fairbrother, A.; Baecher-Steppan, L.; Kerkvliet, N.I. Immunologic and endocrine effects of the flame-retardant pentabromodiphenyl ether (DE-71) in C57BL/6J mice. Toxicology 1994, 86, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Zeng, X.; Lu, F.; Chen, A.; Huo, X. Elevated serum polybrominated diphenyl ethers and alteration of thyroid hormones in children from Guiyu, China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowell, W.J.; Sjödin, A.; Jones, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Whyatt, R.M.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Bradwin, G.; Hassoun, A.; Oberfield, S.; et al. Pre- and Postnatal Polybrominated Diphenyl Ether Concentrations in Relation to Thyroid Parameters Measured During Early Childhood. Thyroid Off. J. Am. Thyroid Assoc. 2019, 29, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Niu, P.; Kong, F.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Yu, D.; Jia, J.; Yang, L.; Fu, Z.; Li, R.; et al. Disruption of thyroid hormone levels by decabrominated diphenyl ethers (BDE-209) in occupational workers from a deca-BDE manufacturing plant. Environ. Int. 2018, 120, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Yang, J.; Rao, Q.; Liu, Z.; Song, W.; Guan, S.; Zhao, Z.; Song, W. Toxic effects of Decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) on thyroid of broiler chicks by transcriptome profile analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 219, 112305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chan, K.M. Evaluation of the toxic effects of brominated compounds (BDE-47, 99, 209, TBBPA) and bisphenol A (BPA) using a zebrafish liver cell line, ZFL. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 159, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zha, J.; Wu, F.; Wang, Z. Relationship between BDE 209 metabolites and thyroid hormone levels in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 122–123, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibhazehiebo, K.; Iwasaki, T.; Kimura-Kuroda, J.; Miyazaki, W.; Shimokawa, N.; Koibuchi, N. Disruption of thyroid hormone receptor-mediated transcription and thyroid hormone-induced Purkinje cell dendrite arborization by polybrominated diphenyl ethers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyes, P.D.; Lema, S.C.; Macaulay, L.J.; Douglas, N.K.; Stapleton, H.M. Low level exposure to the flame retardant BDE-209 reduces thyroid hormone levels and disrupts thyroid signaling in fathead minnows. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10012–10021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Ross, D.G.; DeVito, M.J.; Crofton, K.M. Effects of short-term in vivo exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers on thyroid hormones and hepatic enzyme activities in weanling rats. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2001, 61, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, V.M.; Staskal, D.F.; Ross, D.G.; Diliberto, J.J.; DeVito, M.J.; Birnbaum, L.S. Possible mechanisms of thyroid hormone disruption in mice by BDE 47, a major polybrominated diphenyl ether congener. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 226, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Liu, L.; Zhou, G.; Tian, Z.; Luo, C.; Xia, T.; Chen, J.; Niu, Q.; Dong, L.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Perigestational exposure to low doses of PBDE-47 induces excessive ER stress, defective autophagy and the resultant apoptosis contributing to maternal thyroid toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Gao, H.; Dong, L.; Liu, L.; Zhou, G.; Luo, C.; Tian, Z.; Xia, T.; Wang, A.; Zhang, S. Perinatal low-dose PBDE-47 exposure hampered thyroglobulin turnover and induced thyroid cell apoptosis by triggering ER stress and lysosomal destabilization contributing to thyroid toxicity in adult female rats. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Li, B.; Zhang, C.; Lei, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, A. Roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress in 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenylether-induced thyroid cell apoptosis and autophagy. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 214, 112077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, D.; Jing, L.; Zhou, X.; Sun, Z.; Shi, Z. A comparison of the thyroid disruption induced by decabrominated diphenyl ethers (BDE-209) and decabromodiphenyl ethane (DBDPE) in rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Técher, R.; Houde, M.; Verreault, J. Associations between organohalogen concentrations and transcription of thyroid-related genes in a highly contaminated gull population. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 545–546, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkoosh, M.R.; Van Gaest, A.L.; Strickland, S.A.; Hutchinson, G.P.; Krupkin, A.B.; Dietrich, J.P. Alteration of thyroid hormone concentrations in juvenile Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) exposed to polybrominated diphenyl ethers, BDE-47 and BDE-99. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lema, S.C.; Dickey, J.T.; Schultz, I.R.; Swanson, P. Dietary exposure to 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (PBDE-47) alters thyroid status and thyroid hormone-regulated gene transcription in the pituitary and brain. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1694–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Song, N.; Xu, H.; Dang, Y.; Liu, C.; Giesy, J.P.; Yu, H. Prenatal transfer of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) results in disruption of the thyroid system and developmental toxicity in zebrafish offspring. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 190, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, Å.K.; Verreault, J.; François, A.; Houde, M.; Giraudo, M.; Dam, M.; Jenssen, B.M. Flame retardants and their associations with thyroid hormone-related variables in northern fulmars from the Faroe Islands. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806 Pt 2, 150506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.M.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, B.M.; Kim, I.C.; Jeong, C.B.; Lee, J.S. Adverse effects of BDE-47 on in vivo developmental parameters, thyroid hormones, and expression of hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis genes in larvae of the self-fertilizing fish Kryptolebias marmoratus. Chemosphere 2017, 176, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Li, Y.; Ru, H.; Xie, H.; Yao, F.; Ni, Z.; Zhong, L. Parental exposure to 2,2′,4,4′ -pentain polybrominated diphenyl ethers (BDE-99) causes thyroid disruption and developmental toxicity in zebrafish. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 372, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Deng, J.; Shi, X.; Liu, C.; Yu, K.; Zhou, B. Exposure to DE-71 alters thyroid hormone levels and gene transcription in the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis of zebrafish larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 97, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, H.; Giesy, J.P.; Hecker, M.; Lam, M.H.; Yu, H. Accumulation and biotransformation of BDE-47 by zebrafish larvae and teratogenicity and expression of genes along the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12943–12951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuong, A.M.; Webster, G.M.; Romano, M.E.; Braun, J.M.; Zoeller, R.T.; Hoofnagle, A.N.; Sjödin, A.; Yolton, K.; Lanphear, B.P.; Chen, A. Maternal Polybrominated Diphenyl Ether (PBDE) Exposure and Thyroid Hormones in Maternal and Cord Sera: The HOME Study, Cincinnati, USA. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Hernandez-Moreno, D.; Main, K.M.; Skakkebæk, N.E.; Kiviranta, H.; Toppari, J.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U.; Shen, H.; Schramm, K.W.; De Angelis, M. Association of In Utero Persistent Organic Pollutant Exposure With Placental Thyroid Hormones. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 3473–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Albrecht, M.; Fromme, H.; Schramm, K.W.; De Angelis, M. Persistent Organic Pollutants in Human Breast Milk and Associations with Maternal Thyroid Hormone Homeostasis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; He, C.T.; Chen, S.J.; Yan, X.; Guo, M.N.; Wang, M.H.; Yu, Y.J.; Yang, Z.Y.; Mai, B.X. Disruption of thyroid hormone (TH) levels and TH-regulated gene expression by polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), and hydroxylated PCBs in e-waste recycling workers. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernest, S.R.; Wade, M.G.; Lalancette, C.; Ma, Y.Q.; Berger, R.G.; Robaire, B.; Hales, B.F. Effects of chronic exposure to an environmentally relevant mixture of brominated flame retardants on the reproductive and thyroid system in adult male rats. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2012, 127, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makey, C.M.; McClean, M.D.; Braverman, L.E.; Pearce, E.N.; He, X.M.; Sjödin, A.; Weinberg, J.M.; Webster, T.F. Polybrominated Diphenyl Ether Exposure and Thyroid Function Tests in North American Adults. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turyk, M.E.; Persky, V.W.; Imm, P.; Knobeloch, L.; Chatterton, R.; Anderson, H.A. Hormone disruption by PBDEs in adult male sport fish consumers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1635–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.M.; Chen, F.A.; Huang, Y.F.; Hsing, L.L.; Chen, L.L.; Wu, L.S.; Liu, T.S.; Chang-Chien, G.P.; Chen, K.C.; Chao, H.R. Negative associations between PBDE levels and thyroid hormones in cord blood. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2011, 214, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Colborn, T.; Hayes, T.B.; Heindel, J.J.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Lee, D.H.; Shioda, T.; Soto, A.M.; vom Saal, F.S.; Welshons, W.V.; et al. Hormones and endocrine-disrupting chemicals: Low-dose effects and nonmonotonic dose responses. Endocr. Rev. 2012, 33, 378–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, C.A.; McCoy, G.L.; Hui, Y.Y.; LaVoie, H.A. Perinatal exposure to low-dose DE-71 increases serum thyroid hormones and gonadal osteopontin gene expression. Exp. Biol. Med. 2011, 236, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbstman, J.B.; Sjödin, A.; Apelberg, B.J.; Witter, F.R.; Halden, R.U.; Patterson, D.G.; Panny, S.R.; Needham, L.L.; Goldman, L.R. Birth delivery mode modifies the associations between prenatal polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) and polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) and neonatal thyroid hormone levels. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1376–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tian, L.; Gao, D.; Liao, H.; Kong, C.; Chen, X.; Junaid, M.; Wang, J. Toxic effects of polystyrene nanoplastics and polybrominated diphenyl ethers to zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 126, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Cheng, Y.; Shang, X.; Wang, R.; Wang, R.; Hao, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Disturbance of the Dlk1-Dio3 imprinted domain may underlie placental Dio3 suppression and extracellular thyroid hormone disturbance in placenta-derived JEG-3 cells following decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE209) exposure. Toxicology 2021, 458, 152837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Tan, Y.Q.; Leung, L.K. Exposure to 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether at late gestation modulates placental signaling molecules in the mouse model. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xia, R.; Yu, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.L. Isoliquiritigenin as an antioxidant phytochemical ameliorates the developmental anomalies of zebrafish induced by 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Pan, Z.J.; Mengqiu, L.; Hong, F.S.; Zhu, C.K.; Wu, N.; Chang, G.; Wang, H.; Zhao, X.X. BDE-47 induced apoptosis in zebrafish embryos through mitochondrial ROS-mediated JNK signaling. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Sun, W.; Zhang, H.; Chen, D. BDE-209 inhibits pluripotent genes expression and induces apoptosis in human embryonic stem cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. JAT 2016, 36, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Yu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Z.; Huang, X.; Xu, B.; Zhou, K.; Chen, X.; Xia, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Effects of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether on the development of mouse embryonic stem cells. Reprod. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, S.J.; Huang, C.P.; Chen, P.C.; Huang, C. Teratogenic responses of zebrafish embryos to decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) in the presence of nano-SiO(2) particles. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, R.G.; Lefèvre, P.L.; Ernest, S.R.; Wade, M.G.; Ma, Y.Q.; Rawn, D.F.; Gaertner, D.W.; Robaire, B.; Hales, B.F. Exposure to an environmentally relevant mixture of brominated flame retardants affects fetal development in Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicology 2014, 320, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Liu, F.; Liu, H.; Wei, Z.; Sun, P.; Wang, Z. Evaluation of HODE-15, FDE-15, CDE-15, and BDE-15 toxicity on adult and embryonic zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 14047–14057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattner, B.A.; Lazarus, R.S.; Heinz, G.H.; Karouna-Renier, N.K.; Schultz, S.L.; Hale, R.C. Comparative embryotoxicity of a pentabrominated diphenyl ether mixture to common terns (Sterna hirundo) and American kestrels (Falco sparverius). Chemosphere 2013, 93, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tanaka, Y.; Fujiwara, M.; Shindo, A.; Yin, G.; Kitazawa, T.; Teraoka, H. Aroclor 1254 and BDE-47 inhibit dopaminergic function manifesting as changes in locomotion behaviors in zebrafish embryos. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Kang, J.; Qiu, J.; Zhong, X.; Shi, X.; Zhou, B.; Wei, Y. Waterborne exposure to low concentrations of BDE-47 impedes early vascular development in zebrafish embryos/larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 203, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Cho, Y.H.; Won, S.; Ku, J.L.; Moon, H.B.; Park, J.; Choi, G.; Kim, S.; Choi, K. Maternal exposures to persistent organic pollutants are associated with DNA methylation of thyroid hormone-related genes in placenta differently by infant sex. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, S.; Zhou, Q.; Fu, Z.; Liu, P.; Cao, X.; Xi, S. 2, 2′, 4, 4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether induces placental toxicity via activation of p38 MAPK signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 244, 114034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.F.; Kapidzic, M.; Hamilton, E.G.; Chen, H.; Puckett, K.W.; Zhou, Y.; Ona, K.; Parry, E.; Wang, Y.; Park, J.S.; et al. Genomic Profiling of BDE-47 Effects on Human Placental Cytotrophoblasts. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2019, 167, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Song, Q.; Ge, W.; Jin, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Y. Associations between in utero exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers, pathophysiological state of fetal growth and placental DNA methylation changes. Environ. Int. 2019, 133 Pt B, 105255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Xia, H.; Su, M.; Song, P.; Qi, X.; Cui, Y.; Cao, Y.; Chen, T.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, A.; et al. Metabonomic phenotyping reveals an embryotoxicity of deca-brominated diphenyl ether in mice. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1976–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Li, Z.; Du, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, W.; Xiao, X.; He, Y.; Sun, B.; Yu, Y.; et al. The effects of PBDE-209 exposure during pregnancy on placental ET-1 and eNOS expression and the birth weight of offspring. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. Off. J. Int. Soc. Dev. Neurosci. 2015, 43, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Fan, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, J.; Jin, L. Gestational exposure to BDE-209 induces placental injury via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated PERK/ATF4/CHOP signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 233, 113307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zezza, D.; Tait, S.; Della Salda, L.; Amorena, M.; Merola, C.; Perugini, M. Toxicological, gene expression and histopathological evaluations of environmentally realistic concentrations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers PBDE- 47, PBDE-99 and PBDE-209 on zebrafish embryos. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 183, 109566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Zhou, G.; Jing, L.; Shi, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, X. BDE-209 induces male reproductive toxicity via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis mediated by DNA damage response signaling pathways. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255 Pt 1, 113097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, L.H.; Hsu, P.C.; Lee, C.W.; Tsai, S.S.; Pan, M.H.; Li, M.H. Developmental exposure to decabrominated diphenyl ether (BDE-209): Effects on sperm oxidative stress and chromatin DNA damage in mouse offspring. Environ. Toxicol. 2013, 28, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, G.; Sang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, L.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, X.; Sun, Z. BDE-209 and DBDPE induce male reproductive toxicity through telomere-related cell senescence and apoptosis in SD rat. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Jing, L.; Zhou, G.; Sang, Y.; Gao, L.; Jiang, S.; Shi, Z.; Ge, W.; Sun, Z.; et al. Decabromodiphenyl ether induces male reproductive toxicity by activating mitochondrial apoptotic pathway through glycolipid metabolism dysbiosis. Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Singh, S.K. Maternal exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ether (BDE-209) during lactation affects germ cell survival with altered testicular glucose homeostasis and oxidative status through down-regulation of Cx43 and p27Kip1 in prepubertal mice offspring. Toxicology 2017, 386, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, D.; Singh, S.K. Inhibition of testicular steroidogenesis and impaired differentiation of Sertoli cells in peripubertal mice offspring following maternal exposure to BDE-209 during lactation suppress germ cell proliferation. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 290, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, D.; Singh, V.K.; Singh, S.K. Maternal BDE-209 exposure during lactation perturbs steroidogenesis, germ cell kinetics and THRα1 expression in testes of prepubertal mice offspring. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2018, 122, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Joshi, D.; Singh, S.K. Maternal BDE-209 exposure during lactation causes testicular and epididymal toxicity through increased oxidative stress in peripubertal mice offspring. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 311, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, D.; Singh, S.K. Decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) exposure to lactating mice perturbs steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis in adult male offspring. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 209, 111783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tang, X.; Sha, J.; Chen, H.; Sun, T.; Wang, Y. The reproductive toxicity on the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis induced by BDE-47 and studies on the effective mechanism based on antioxidant defense system changes. Chemosphere 2015, 135, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Z.; Dong, H.; Qiu, L.; Gu, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.L. Cytochrome P450 3A1 mediates 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether-induced reduction of spermatogenesis in adult rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.H.; Li, X.H.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Sun, S.C. Exposure to PBDE47 affects mouse oocyte quality via mitochondria dysfunction-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 198, 110662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Cui, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Lu, Y.; Bi, Y.; Huang, X.; Lin, M.; Xia, Y.; et al. 2,2′,4,4′-Tetrabromodiphenyl ether disrupts spermatogenesis, impairs mitochondrial function and induces apoptosis of early leptotene spermatocytes in rats. Reprod. Toxicol. 2015, 51, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, J.; Cui, Y. 2,2′,4,4′-Tetrabromodiphenyl ether injures cell viability and mitochondrial function of mouse spermatocytes by decreasing mitochondrial proteins Atp5b and Uqcrc1. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 46, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Tang, X.; Li, D.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, R.; Shu, F.; Jia, W.; Fu, W.; Xia, H.; Liu, G. Prenatal exposure to environmentally relevant levels of PBDE-99 leads to testicular dysgenesis with steroidogenesis disorders. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424 Pt B, 127547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoraszczuk, E.L.; Siembida, M.; Grzyb, D.; Rak-Mardyła, A. Polybrominated diphenylethers (PBDEs) act as apoptotic factors in the corpus luteum in addition to having a short-term stimulatory effect on progesterone secretion by luteal cells. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2012, 22, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Dong, Y.; Tian, E.; Xie, L.; Wang, G.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Lv, Y.; Ni, C.; et al. 4-Bromodiphenyl ether delays pubertal Leydig cell development in rats. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 986–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, F.; Li, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yan, H.; Tahir, A.; Zheng, W.; Li, X.; Huang, T.; Ge, R.S. Exposure to 4-bromodiphenyl ether during pregnancy blocks testis development in male rat fetuses. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 342, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, X.; Xi, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Luan, Y. 4-Bromodiphenyl Ether Induces Germ Cell Apoptosis by Induction of ROS and DNA Damage in Caenorhabditis elegans. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2017, 157, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, X.; Xi, J.; Liu, W.; Cao, Y.; Tang, W.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Luan, Y. 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether induces germ cell apoptosis through oxidative stress by a MAPK-mediated p53-independent pathway. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242 Pt A, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.; Parker, M.; Brown, S.E.; Cevik, S.E.; Guo, L.W.; Jensen, J.; Olmsted, A.; Portman, D.; Wu, H.; Suvorov, A. Perinatal exposure to 2,2′,4′4′ -Tetrabromodiphenyl ether induces testicular toxicity in adult rats. Toxicology 2017, 389, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suvorov, A.; Shershebnev, A.; Wu, H.; Medvedeva, Y.; Sergeyev, O.; Pilsner, J.R. Perinatal exposure to low dose 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47) alters sperm DNA methylation in adult rats. Reprod. Toxicol. 2018, 75, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.C.; Li, Z.K.; Lai, C.S.; Tseng, L.H.; Lee, C.W.; Cheng, F.J.; Chang, C.Y.; Chen, J.R. Transgenerational effects of BDE-209 on male reproduction in F3 offspring rats. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, L.; Yang, X.; Zhou, G.; Sang, Y.; Xue, J.; Shi, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, X. BDE-209 induced spermatogenesis disorder by inhibiting SETD8/H4K20me1 related histone methylation in mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 864, 161162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhou, G.; Sang, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhou, X.; Sun, Z. DNA methylation changes induced by BDE-209 are related to DNA damage response and germ cell development in GC-2spd. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 109, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelouahab, N.; Ainmelk, Y.; Takser, L. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and sperm quality. Reprod. Toxicol. 2011, 31, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, O.; Huang, J.Y.; Aleksa, K.; Hales, B.F.; Goodyer, C.G.; Robaire, B.; Chevrier, J.; Chan, P. Exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers and phthalates in healthy men living in the greater Montreal area: A study of hormonal balance and semen quality. Environ. Int. 2018, 116, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, J.A.; Olivier, H.M.; Draugelis-Dale, R.O.; Eilts, B.E.; Torres, L.; Patiño, R.; Nilsen, E.; Goodbred, S.L. Assessing reproductive and endocrine parameters in male largescale suckers (Catostomus macrocheilus) along a contaminant gradient in the lower Columbia River, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 484, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, S.; Che, S.; Chen, S.; Ruan, Z.; Zhang, L. Hesperidin partly ameliorates the decabromodiphenyl ether-induced reproductive toxicity in pubertal mice. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 90391–90403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Xia, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, T.; Wang, J.; Liu, T.; Xu, S.; Liang, G. 2,2′,4,4′-Tetrabromodiphenyl ether disrupts spermatogenesis in mice by interfering with the ER-Nrf1-Tfam-mitochondria pathway. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2022, 38, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, A.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Yan, M.; Xian, P.; Chang, Y.; Chen, X.; Tang, N.J. BDE-47 Decreases Progesterone Levels in BeWo Cells by Interfering with Mitochondrial Functions and Genes Related to Cholesterol Transport. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2019, 32, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talsness, C.E.; Shakibaei, M.; Kuriyama, S.N.; Grande, S.W.; Sterner-Kock, A.; Schnitker, P.; de Souza, C.; Grote, K.; Chahoud, I. Ultrastructural changes observed in rat ovaries following in utero and lactational exposure to low doses of a polybrominated flame retardant. Toxicol. Lett. 2005, 157, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, C.; Ji, M.; Gu, J.; Yang, L.; Zhu, J.; Dong, H.; Wang, S.L. High-fat diet aggravates 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether-inhibited testosterone production via DAX-1 in Leydig cells in rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 323, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Wei, Y.; Geng, W.; Zhang, T.; Ding, T.; Xu, J.; He, H.; Gao, X.; Zhai, J. BDE-209 disrupted the blood-testis barrier integrity by inhibiting estrogen receptor α signaling pathway in Sprague-Dawley rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 47349–47365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Geng, X.; Ding, T.; Li, J.; Tang, J.; Chen, D.; Cui, L.; Wang, Q. An increase of estrogen receptor α protein level regulates BDE-209-mediated blood-testis barrier disruption during spermatogenesis in F1 mice. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 4801–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.B.; Li, Y.Y.; Shen, Y.P.; Zhu, M.; Li, X.H.; Qin, Z.F. 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodipheny ether (BDE-47) disrupts gonadal development of the Africa clawed frog (Xenopus laevis). Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 221, 105441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Won, E.J.; Lee, M.C.; Seo, J.S.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.S. Developmental retardation, reduced fecundity, and modulated expression of the defensome in the intertidal copepod Tigriopus japonicus exposed to BDE-47 and PFOS. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 165, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Yang, D.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Liao, J.; Xu, T.; Bai, C.; Chen, J.; Lin, K.; Huang, C.; et al. Chronic zebrafish low dose decabrominated diphenyl ether (BDE-209) exposure affected parental gonad development and locomotion in F1 offspring. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Peng, L.; Ni, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, K. Effect of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47) on sexual behaviors and reproductive function in male zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 111, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefèvre, P.L.C.; Nardelli, T.C.; Son, W.Y.; Sadler, A.R.; Rawn, D.F.K.; Goodyer, C.; Robaire, B.; Hales, B.F. Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers in Human Follicular Fluid Dysregulate Mural and Cumulus Granulosa Cell Gene Expression. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Geng, W.; Zhang, T.; Wei, Y.; He, H.; Chen, W. BDE-209 induce spermatocytes arrest at early-pachytene stage during meiotic prophase I in mice. Toxicology 2022, 467, 153061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, L.H.; Lee, C.W.; Pan, M.H.; Tsai, S.S.; Li, M.H.; Chen, J.R.; Lay, J.J.; Hsu, P.C. Postnatal exposure of the male mouse to 2,2′,3,3′,4,4′,5,5′,6,6′-decabrominated diphenyl ether: Decreased epididymal sperm functions without alterations in DNA content and histology in testis. Toxicology 2006, 224, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; He, H.; Wei, Y.; Geng, W.; Zhai, J. Vitamin C supplementation rescued meiotic arrest of spermatocytes in Balb/c mice exposed to BDE-209. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 242, 113846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaso, H.; Nakamura, N.; Naito, M.; Hirai, S.; Matsuno, Y.; Itoh, M.; Mori, C. Early postnatal exposure to a low dose of decabromodiphenyl ether affects expression of androgen and thyroid hormone receptor-alpha and its splicing variants in mouse Sertoli cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, C.C.; Shi, Y.F.; Yu, W.K.; Wei, F.; van de Merwe, J.P.; Chan, A.K.; Ye, R.; Au, D.W.; Wu, R.S.; Yang, M.S. iTRAQ-based proteomic profiling of the marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) gonad exposed to BDE-47. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Miao, J.; Song, Y.; Pan, L.; Yin, P. Effects of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodipheny ether (BDE-47) on gonadogenesis of the manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 193, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Ma, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, B.; Niu, Q.; Chen, J.; Xia, T.; Li, P.; et al. Roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress, apoptosis and autophagy in 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether-induced rat ovarian injury. Reprod. Toxicol. 2016, 65, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, L.M.; Path, E.M.; Nystrom, G.S.; Venables, B.J.; Sellin Jeffries, M.K. Early Life Stage Exposure to BDE-47 Causes Adverse Effects on Reproductive Success and Sexual Differentiation in Fathead Minnows (Pimephales promelas). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7834–7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.B.; Yuen, K.W.; Wu, R.S. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers affect the reproduction and development, and alter the sex ratio of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marteinson, S.C.; Bird, D.M.; Shutt, J.L.; Letcher, R.J.; Ritchie, I.J.; Fernie, K.J. Multi-generational effects of polybrominated diphenylethers exposure: Embryonic exposure of male American kestrels (Falco sparverius) to DE-71 alters reproductive success and behaviors. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 1740–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arowolo, O.; Pilsner, J.R.; Sergeyev, O.; Suvorov, A. Mechanisms of Male Reproductive Toxicity of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ao, H.; Chen, L.; Sottas, C.M.; Ge, R.S.; Zhang, Y. Effect of brominated flame retardant BDE-47 on androgen production of adult rat Leydig cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 205, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tang, X.; Zhou, B.; Xu, N.; Wang, Y. Mechanism of Deca-BDE-induced apoptosis in Neuro-2a cells: Role of death-receptor pathway and reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial pathway. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 46, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Chen, D. The environmental pollutant BDE-209 regulates NO/cGMP signaling through activation of NMDA receptors in neurons. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 3397–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Du, L.; Tang, W.; Kuang, L.; Du, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, D. PBDE-209 exposure damages learning and memory ability in rats potentially through increased autophagy and apoptosis in the hippocampus neuron. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 50, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Nie, J.; Niu, Q. Lactation exposure to BDE-153 damages learning and memory, disrupts spontaneous behavior and induces hippocampus neuron death in adult rats. Brain Res. 2013, 1517, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, L.G.; Tagliaferri, S.; Roqué, P.J.; Pellacani, C. Role of glutamate receptors in tetrabrominated diphenyl ether (BDE-47) neurotoxicity in mouse cerebellar granule neurons. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 241, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassmann, K.; Schreiber, T.; Dingemans, M.M.; Krause, G.; Roderigo, C.; Giersiefer, S.; Schuwald, J.; Moors, M.; Unfried, K.; Bergman, Å.; et al. BDE-47 and 6-OH-BDE-47 modulate calcium homeostasis in primary fetal human neural progenitor cells via ryanodine receptor-independent mechanisms. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1537–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Wang, A.G.; Xia, T.; Gao, P.; Niu, Q.; Guo, L.J.; Chen, X.M. Mechanisms underlying the developmental neurotoxic effect of PBDE-47 and the enhanced toxicity associated with its combination with PCB153 in rats. Neurotoxicology 2009, 30, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Mulero, M.; López, M.; Domingo, J.L.; Sánchez, D.J. BDE-99 deregulates BDNF, Bcl-2 and the mRNA expression of thyroid receptor isoforms in rat cerebellar granular neurons. Toxicology 2011, 290, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Mulero, M.; Heredia, L.; Pujol, A.; Domingo, J.L.; Sánchez, D.J. Perinatal exposure to BDE-99 causes learning disorders and decreases serum thyroid hormone levels and BDNF gene expression in hippocampus in rat offspring. Toxicology 2013, 308, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Gu, J.; Ma, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, W. Neurobehavioural effects, redox responses and tissue distribution in rat offspring developmental exposure to BDE-99. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltier, M.R.; Fassett, M.J.; Arita, Y.; Chiu, V.Y.; Takhar, H.S.; Getahun, D. Exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ether-47 increases the risk of post-partum depression. J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022, 35, 8350–8354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viberg, H.; Mundy, W.; Eriksson, P. Neonatal exposure to decabrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE 209) results in changes in BDNF, CaMKII and GAP-43, biochemical substrates of neuronal survival, growth, and synaptogenesis. Neurotoxicology 2008, 29, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viberg, H. Exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers 203 and 206 during the neonatal brain growth spurt affects proteins important for normal neurodevelopment in mice. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2009, 109, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutic, A.D.; Barr, D.B.; Hertzberg, V.S.; Brennan, P.A.; Dunlop, A.L.; McCauley, L.A. Polybrominated Diphenyl Ether Serum Concentrations and Depressive Symptomatology in Pregnant African American Women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; You, M.; Che, X.; Dai, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y. Perinatal exposure to BDE-47 exacerbated autistic-like behaviors and impairments of dendritic development in a valproic acid-induced rat model of autism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 212, 112000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Wu, Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, Q.; Han, J.; Guo, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhou, B. The developmental neurotoxicity of polybrominated diphenyl ethers: Effect of DE-71 on dopamine in zebrafish larvae. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Li, N.; Ma, M.; Zhou, B. The neurotoxicity of DE-71: Effects on neural development and impairment of serotonergic signaling in zebrafish larvae. J. Appl. Toxicol. JAT 2016, 36, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, L.; Cai, X.; Liu, W.; Song, J.; Li, M.; Cai, Z. 6-OH-BDE-47 exposure-induced Parkinson’s disease pathology in Sprague Dawley rat. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 135184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Gao, H.; Yu, F.; Xiao, B.; Li, X.; Cai, B.; Ge, L.; Lu, Y.; Wan, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. Perinatal exposure to low-level PBDE-47 programs gut microbiota, host metabolism and neurobehavior in adult rats: An integrated analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 154150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, R.; Tang, S.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, S.; Yan, Z.; Chen, J. Single and mixture toxicities of BDE-47, 6-OH-BDE-47 and 6-MeO-BDE-47 on the feeding activity of Daphnia magna: From behavior assessment to neurotoxicity. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, M.; Alfonso, S.; Bégout, M.L.; Barrachina, C.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Keiter, S.H.; Cousin, X. An environmentally relevant mixture of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polybrominated diphenylethers (PBDEs) disrupts mitochondrial function, lipid metabolism and neurotransmission in the brain of exposed zebrafish and their unexposed F2 offspring. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, S.; Blanc, M.; Joassard, L.; Keiter, S.H.; Munschy, C.; Loizeau, V.; Bégout, M.L.; Cousin, X. Examining multi- and transgenerational behavioral and molecular alterations resulting from parental exposure to an environmental PCB and PBDE mixture. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 208, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, H.; Zheng, H.; Bai, C.; Pan, W.; Zhou, H.; Liao, M.; Huang, C.; Dong, Q. Maternal exposure to low dose BDE209 and Pb mixture induced neurobehavioral anomalies in C57BL/6 male offspring. Toxicology 2019, 418, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Wang, Q.; Shi, X.; Guo, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhou, B. Effect of combined exposure to lead and decabromodiphenyl ether on neurodevelopment of zebrafish larvae. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1646–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, P.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Huang, C.; Wang, X.; Lin, K.; Zhou, B. Bioconcentration and metabolism of BDE-209 in the presence of titanium dioxide nanoparticles and impact on the thyroid endocrine system and neuronal development in zebrafish larvae. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8 (Suppl. 1), 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Cheng, J.; Gu, J.; Liu, Y.; Fujimura, M.; Wang, W. Assessment of neurotoxic effects and brain region distribution in rat offspring prenatally co-exposed to low doses of BDE-99 and methylmercury. Chemosphere 2014, 112, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Seifikar, H.; Larocque, N.; Kim, Y.; Khatib, I.; Fernandez, C.J.; Abello, N.; Robinson, J.F. Using a Multi-Stage hESC Model to Characterize BDE-47 Toxicity During Neurogenesis. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2019, 171, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alm, H.; Kultima, K.; Scholz, B.; Nilsson, A.; Andrén, P.E.; Fex-Svenningsen, A.; Dencker, L.; Stigson, M. Exposure to brominated flame retardant PBDE-99 affects cytoskeletal protein expression in the neonatal mouse cerebral cortex. Neurotoxicology 2008, 29, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alm, H.; Scholz, B.; Kultima, K.; Nilsson, A.; Andrén, P.E.; Savitski, M.M.; Bergman, A.; Stigson, M.; Fex-Svenningsen, A.; Dencker, L. In vitro neurotoxicity of PBDE-99: Immediate and concentration-dependent effects on protein expression in cerebral cortex cells. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvorov, A.; Girard, S.; Lachapelle, S.; Abdelouahab, N.; Sebire, G.; Takser, L. Perinatal exposure to low-dose BDE-47, an emergent environmental contaminant, causes hyperactivity in rat offspring. Neonatology 2009, 95, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, R.; Shi, X.; Peng, J.; Tan, W.; Huang, W.; Wu, K.; Liu, C. Behavioral changes and transcriptomic effects at embryonic and post-embryonic stages reveal the toxic effects of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether on neurodevelopment in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 248, 114310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.T.; Hsiao, Y.C.; Ko, F.C.; Cheng, J.O.; Cheng, Y.M.; Chen, T.H. Chronic exposure of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (PBDE-47) alters locomotion behavior in juvenile zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 98, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Liang, S.; Zhou, H.; Yin, N.; Faiola, F. Typical halogenated flame retardants affect human neural stem cell gene expression during proliferation and differentiation via glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta and T3 signaling. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 183, 109498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azar, N.; Booij, L.; Muckle, G.; Arbuckle, T.E.; Séguin, J.R.; Asztalos, E.; Fraser, W.D.; Lanphear, B.P.; Bouchard, M.F. Prenatal exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and cognitive ability in early childhood. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Chen, T.; Gao, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z. The protective effects of insulin-like growth factor-1 on neurochemical phenotypes of dorsal root ganglion neurons with BDE-209-induced neurotoxicity in vitro. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2017, 33, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C.M.; Small, D.; Bell, T.; David-Drori, J.; Hansen, C.; Morris-Schaffer, K.; Canale, C.; Ng, J.; Markowski, V.P. Early postnatal decabromodiphenyl ether exposure reduces thyroid hormone and astrocyte density in the juvenile mouse dentate gyrus. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 216, 112798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branchi, I.; Alleva, E.; Costa, L.G. Effects of perinatal exposure to a polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE 99) on mouse neurobehavioural development. Neurotoxicology 2002, 23, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dach, K.; Bendt, F.; Huebenthal, U.; Giersiefer, S.; Lein, P.J.; Heuer, H.; Fritsche, E. BDE-99 impairs differentiation of human and mouse NPCs into the oligodendroglial lineage by species-specific modes of action. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, W.J.; Wall, P.M.; Nakai, J.S.; Yagminas, A.; Wade, M.; Li, N. Behavioral and thyroid effects of in utero and lactational exposure of Sprague-Dawley rats to the polybrominated diphenyl ether mixture DE71. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2015, 52 Pt B, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, C.; Hu, C.; Yu, K.; Yang, L.; Zhou, B. Acute exposure to DE-71: Effects on locomotor behavior and developmental neurotoxicity in zebrafish larvae. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 2338–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Shi, Q.; Guo, Y.; Hua, J.; Han, J.; Yang, L. DE-71 affected the cholinergic system and locomotor activity via disrupting calcium homeostasis in zebrafish larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 250, 106237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.; Hou, Y.; Li, N.; Pulido, O.; Bowers, W. Developmental neurotoxicity of polybrominated diphenyl ethers mixture de71 in Sprague-Dawley rats. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health. Part A 2016, 79, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Bai, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Dong, Q.; Yang, D. BDE-47 disrupts axonal growth and motor behavior in developing zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 120–121, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Huang, W.; Liu, C.; Xiao, J.; Wu, R.; Wang, X.; Cai, Z.; Wu, K. Behavioral change and transcriptomics reveal the effects of 2, 2′, 4, 4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether exposure on neurodevelopmental toxicity to zebrafish (Danio rerio) in early life stage. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazer, L.; Wells, C.N.; Drastal, M.; Odamah, K.A.; Galat, R.E.; Behl, M.; Levin, E.D. Developmental exposure to low concentrations of two brominated flame retardants, BDE-47 and BDE-99, causes life-long behavioral alterations in zebrafish. Neurotoxicology 2018, 66, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Streifel, K.M.; Singh, V.; Yang, D.; Mangini, L.; Wulff, H.; Lein, P.J. From the Cover: BDE-47 and BDE-49 Inhibit Axonal Growth in Primary Rat Hippocampal Neuron-Glia Co-Cultures via Ryanodine Receptor-Dependent Mechanisms. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2017, 156, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Tang, X.; Zhou, B.; Xu, N.; Zhou, Z.; Fang, K.; Wang, Y. BDE-47 and BDE-209 inhibit proliferation of Neuro-2a cells via inducing G1-phase arrest. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 50, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Tang, X.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, N.; Wang, Y. A ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway and Nrf2 pathway activation are involved in BDE-47 induced apoptosis in Neuro-2a cells. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, T.; Chen, L.; Tao, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, J.; Ruan, D.Y. Effects of decabrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE 209) exposure at different developmental periods on synaptic plasticity in the dentate gyrus of adult rats In vivo. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2009, 110, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, A.; Fanelli, R.; Re Depaolini, A.; De Paola, M. Decabrominated diphenyl ether and methylmercury impair fetal nervous system development in mice at documented human exposure levels. Dev. Neurobiol. 2015, 75, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Huang, Y.; Li, K.; Cheng, X.; Li, G.; Liu, M.; Nie, Y.; Geng, S.; Zhao, S. Developmental exposure of decabromodiphenyl ether impairs subventricular zone neurogenesis and morphology of granule cells in mouse olfactory bulb. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.; Wang, C.; Zhao, C.; Jiang, R.; Song, J. Effects of maternal exposure to BDE209 on neuronal development and transcription of iodothyronine deiodinase in offspring mice. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2019, 29, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.; Zen, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, C.; Song, J. A preliminary study on the mechanism of the neurosteroid-mediated ionotropic receptor dysfunction in neurodevelopmental toxicity induced by decabromodiphenyl ether. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 217, 112198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, S.C.; Bianco, A.C.; Stapleton, H.M. Disruption of type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase activity in cultured human glial cells by polybrominated diphenyl ethers. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, G.; Yu, J.; Cui, C.; Chen, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, Y. Association between prenatal exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers and young children’s neurodevelopment in China. Environ. Res. 2015, 142, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, S.; Li, S.; Ma, Y.; Hu, D.; Xiao, F. Curcumin hinders PBDE-47-induced neutrophil extracellular traps release via Nrf2-associated ROS inhibition. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 225, 112779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, J. In vitro immunotoxicity and possible mechanisms of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47) on Ruditapes philippinarum hemocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 127, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Tang, X.; Sun, T.; Wang, Y. BDE-47 exposure changed the immune function of haemocytes in Mytilus edulis: An explanation based on ROS-mediated pathway. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 182, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.Y.; Wan, B.; Guo, L.H.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Y. In vitro immune toxicity of polybrominated diphenyl ethers on murine peritoneal macrophages: Apoptosis and immune cell dysfunction. Chemosphere 2015, 120, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frouin, H.; Lebeuf, M.; Hammill, M.; Masson, S.; Fournier, M. Effects of individual polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) congeners on harbour seal immune cells in vitro. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, V.; Longo, A.; Adamo, G.; Fiannaca, A.; Picciotto, S.; La Paglia, L.; Romancino, D.; La Rosa, M.; Urso, A.; Cibella, F.; et al. 2,2′4,4′-Tetrabromodiphenyl Ether (PBDE-47) Modulates the Intracellular miRNA Profile, sEV Biogenesis and Their miRNA Cargo Exacerbating the LPS-Induced Pro-Inflammatory Response in THP-1 Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 664534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamkin, D.M.; Chen, S.; Bradshaw, K.P.; Xu, S.; Faull, K.F.; Sloan, E.K.; Cole, S.W. Low-dose exposure to PBDE disrupts genomic integrity and innate immunity in mammary tissue. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 904607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, V.; Aloi, N.; Lo Presti, E.; Fiannaca, A.; Longo, A.; Adamo, G.; Urso, A.; Meraviglia, S.; Bongiovanni, A.; Cibella, F.; et al. Impact of the flame retardant 2,2′4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (PBDE-47) in THP-1 macrophage-like cell function via small extracellular vesicles. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1069207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, V.; Longo, A.; Di Sano, C.; Cigna, D.; Cibella, F.; Di Felice, G.; Colombo, P. In vitro exposure to 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (PBDE-47) impairs innate inflammatory response. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, D.; Wei, J.; Lu, W.; Xia, B.; Li, S.; Liu, D.; Liu, N.; Wang, X.; Lin, G. BDE-47 disturbs the immune response of lymphocytes to LPS by downregulating NF-κB pathway. Chemosphere 2022, 308 Pt 3, 136562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zota, A.R.; Geller, R.J.; Romano, L.E.; Coleman-Phox, K.; Adler, N.E.; Parry, E.; Wang, M.; Park, J.S.; Elmi, A.F.; Laraia, B.A.; et al. Association between persistent endocrine-disrupting chemicals (PBDEs, OH-PBDEs, PCBs, and PFASs) and biomarkers of inflammation and cellular aging during pregnancy and postpartum. Environ. Int. 2018, 115, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwood, P.; Schauer, J.; Pessah, I.N.; Van de Water, J. Preliminary evidence of the in vitro effects of BDE-47 on innate immune responses in children with autism spectrum disorders. J. Neuroimmunol. 2009, 208, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornton, L.M.; Path, E.M.; Nystrom, G.S.; Venables, B.J.; Sellin Jeffries, M.K. Embryo-larval BDE-47 exposure causes decreased pathogen resistance in adult male fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 80, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Jian, X.; Zhou, B.; Lu, K.; Wang, Y. Changes in the immune function of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) provide insights into strategies against BDE-47 stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zeng, W.; Wang, Y.; Shen, H.; Wang, Y. Long-term exposure to high levels of decabrominated diphenyl ether inhibits CD4 T-cell functions in C57Bl/6 mice. J. Appl. Toxicol. JAT 2016, 36, 1112–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Khanniche, A.; Hu, Q.; Feng, Y.; Ye, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, L.; et al. Long-term exposure to decabrominated diphenyl ether impairs CD8 T-cell function in adult mice. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 11, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, W.; Chen, Y.; Ding, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhao, T.; Mao, G.; Wu, X.; et al. Short-term exposure of decabromodiphenyl ether in female adult Balb/c mice: Immune toxicity and self-recovery. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 342, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhan, H.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, D. The PBDE-209 exposure during pregnancy and lactation impairs immune function in rats. Mediat. Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 692467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Rao, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Song, W.; Guan, S.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, T.; Zhao, Z.; Song, W. The immunotoxicity of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) on broiler chicks by transcriptome profiling analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 232, 113284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.K.; Sohn, K.H.; Kim, I.Y.; Lee, J.K.; Ju, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lim, C.H.; Han, B.S.; Jung, H.C.; Lee, J.Y.; et al. Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers Orally Administration to Mice Were Tansferred to Offspring during Gestation and Lactation with Disruptions on the Immune System. Immune Netw. 2010, 10, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Rajput, I.R.; Sanganyado, E.; Yajing, S.; Yu, F.; Liang, B.; Liu, W. Immune stimulation effect of PBDEs via prostaglandin pathway in pantropical spotted dolphin: An in vitro study. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa-Ruiz, C.; Manuguerra, S.; Morghese, M.; García-Beltrán, J.M.; Esteban, M.; Giuga, M.; Messina, C.M.; Santulli, A. Immunity and inflammatory responses in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) exposed to sub-lethal mixture of carbamazepine, cadmium chloride and polybrominated diphenyl ether. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 111, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Xiao, X.; Sun, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, M.; Li, L.; et al. Environmental exposure to BDE47 is associated with increased diabetes prevalence: Evidence from community-based case-control studies and an animal experiment. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Meng, G.; Chi, M.; Li, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y. A nested case-control study of the association between exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus. Environ. Int. 2018, 119, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, R.; Koike, E.; Win-Shwe, T.T.; Takano, H. Decabromodiphenyl ether exacerbates hyperglycemia in diet-induced obese mice. Toxicology 2019, 412, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liang, B.; Chen, T.; Zheng, D.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, X.; Sun, Z.; Shi, Z. Cardiovascular toxicity of decabrominated diphenyl ethers (BDE-209) and decabromodiphenyl ethane (DBDPE) in rats. Chemosphere 2019, 223, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Fu, J.; Sun, S.; Jin, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. BDE-209 induces autophagy and apoptosis via IRE1α/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, Y.; Huang, C.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhou, B. Acute exposure to DE-71 causes alterations in visual behavior in zebrafish larvae. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 1370–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zeng, Y.; Ge, L.; Gong, J.; Weng, C.; Yang, C.; Yang, J.; Fang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zou, T.; et al. Evaluation of the influences of low dose polybrominated diphenyl ethers exposure on human early retinal development. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhao, J.; Yin, D.; Zhao, Q.; Dong, B. High-throughput RNA sequencing reveals the effects of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether on retina and bone development of zebrafish larvae. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, C.; Huang, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Zhou, B. Alterations in retinoid status after long-term exposure to PBDEs in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 120–121, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Chen, L.; Hu, C.; Zhou, B. Effects of acute exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers on retinoid signaling in zebrafish larvae. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 35, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mao, P.; Li, G.; Hu, J.; Yu, Y.; An, T. Delineation of 3D dose-time-toxicity in human pulmonary epithelial Beas-2B cells induced by decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE209). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243 Pt A, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, G.D.; Moscato, M.; Montalbano, A.M.; Anzalone, G.; Gagliardo, R.; Bonanno, A.; Giacomazza, D.; Barone, R.; Drago, G.; Cibella, F.; et al. Can PBDEs affect the pathophysiologic complex of epithelium in lung diseases? Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzalone, G.; Moscato, M.; Montalbano, A.M.; Albano, G.D.; Gagliardo, R.; Marchese, R.; Fucarino, A.; Nigro, C.L.; Drago, G.; Profita, M. PBDEs affect inflammatory and oncosuppressive mechanisms via the EZH2 methyltransferase in airway epithelial cells. Life Sci. 2021, 282, 119827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbano, A.M.; Albano, G.D.; Anzalone, G.; Moscato, M.; Gagliardo, R.; Di Sano, C.; Bonanno, A.; Ruggieri, S.; Cibella, F.; Profita, M. Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of the flame retardants (PBDE-47, PBDE-99 and PBDE-209) in human bronchial epithelial cells. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandona, A.; Jagić, K.; Dvoršćak, M.; Madunić, J.; Klinčić, D.; Katalinić, M. PBDEs Found in House Dust Impact Human Lung Epithelial Cell Homeostasis. Toxics 2022, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, R.; Cunha, S.C.; Casal, S. Brominated flame retardants and seafood safety: A review. Environ. Int. 2015, 77, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, A.J.; Webster, T.F.; McClean, M.D. Diet contributes significantly to the body burden of PBDEs in the general U.S. population. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1520–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yan, Z.; Zheng, X.; Wang, S.; Fan, J.; Sun, Q.; Xu, J.; Men, S. Health risk assessment and development of human health ambient water quality criteria for PBDEs in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Li, J.; Deng, X.; Xia, B.; Song, Q.; Zhao, Y.; He, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xie, A.; et al. Association between fetal growth restriction and maternal exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 198, 110623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapleton, H.M.; Letcher, R.J.; Baker, J.E. Debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ether congeners BDE 99 and BDE 183 in the intestinal tract of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpeta, A.; Warzecha, K.; Jerzak, J.; Ptak, A.; Gregoraszczuk, E.L. Activation of the enzymes of phase I (CYP2B1/2) and phase II (SULT1A and COMT) metabolism by 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE47) in the pig ovary. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 34, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xi, B.; Tan, W. Release, transformation, and risk factors of polybrominated diphenyl ethers from landfills to the surrounding environments: A review. Environ. Int. 2021, 157, 106780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmens, H.; Foan, L.; Simon, V.; Mills, G. Terrestrial mosses as biomonitors of atmospheric POPs pollution: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 173, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Jin, L.; Luthy, R.G. Kinetics and pathways for the debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by bimetallic and nanoscale zerovalent iron: Effects of particle properties and catalyst. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, N.; Zhao, X.; Meng, X.Z.; Chen, L. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in a conventional wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) from Shanghai, the Yangtze River Delta: Implication for input source and mass loading. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

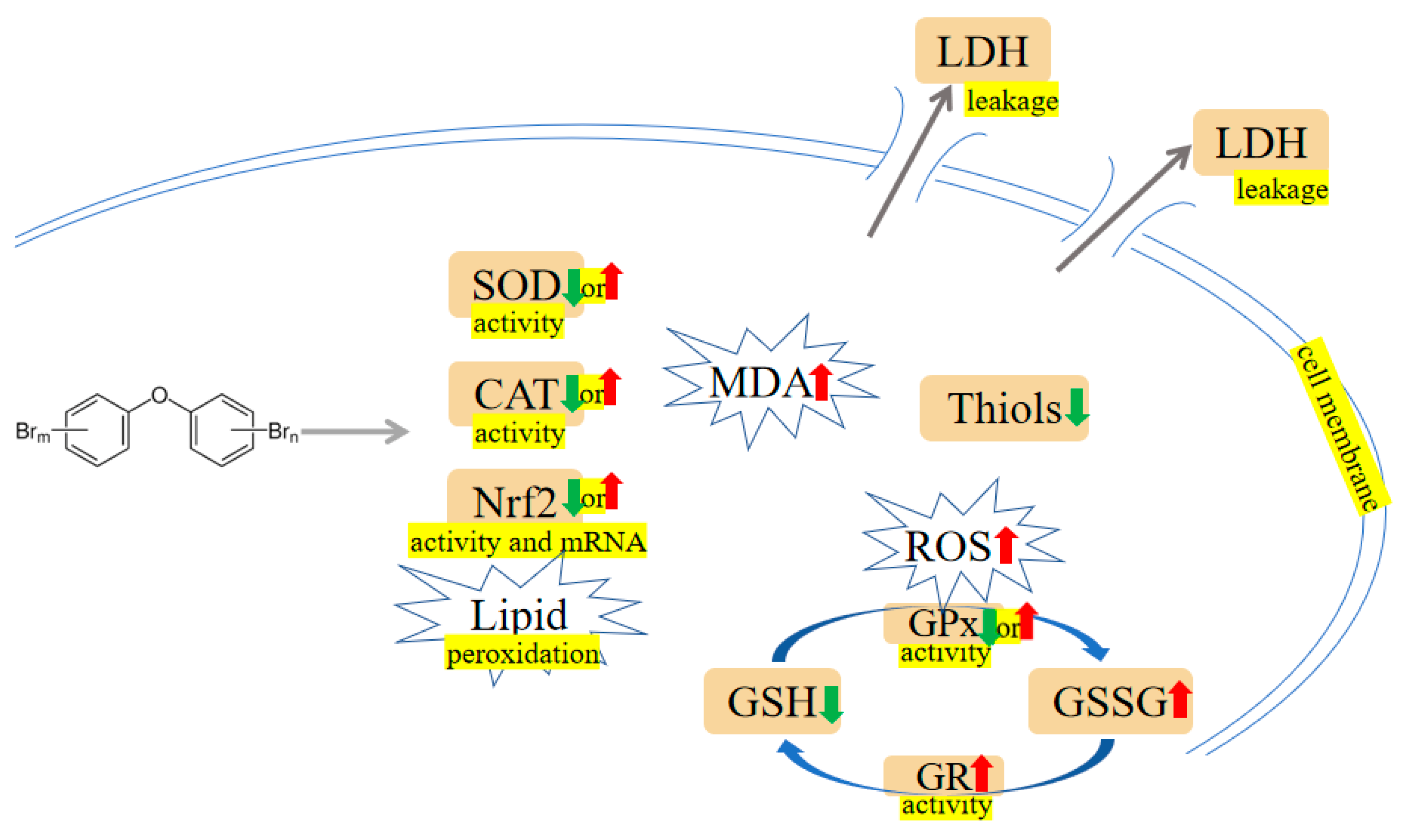
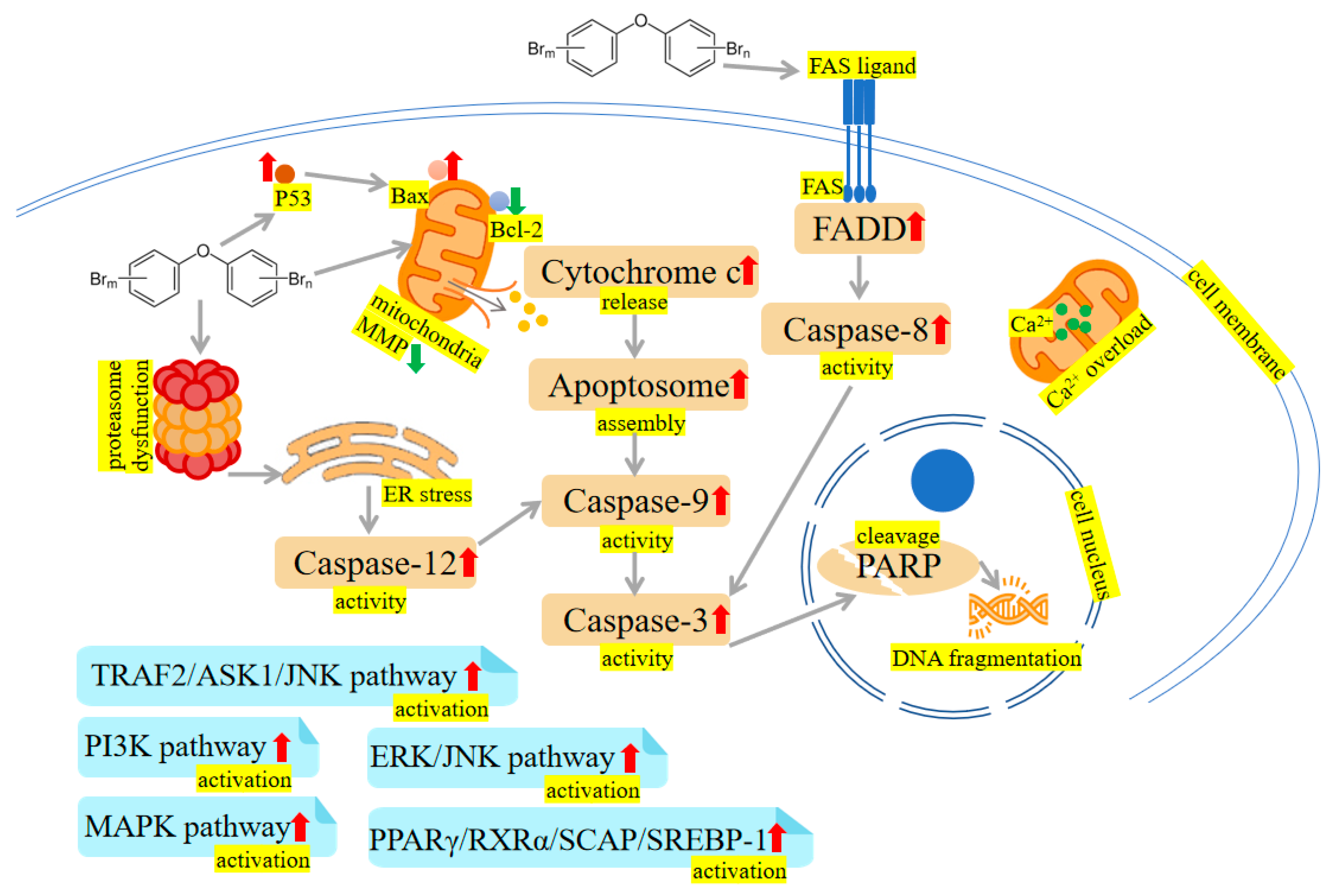

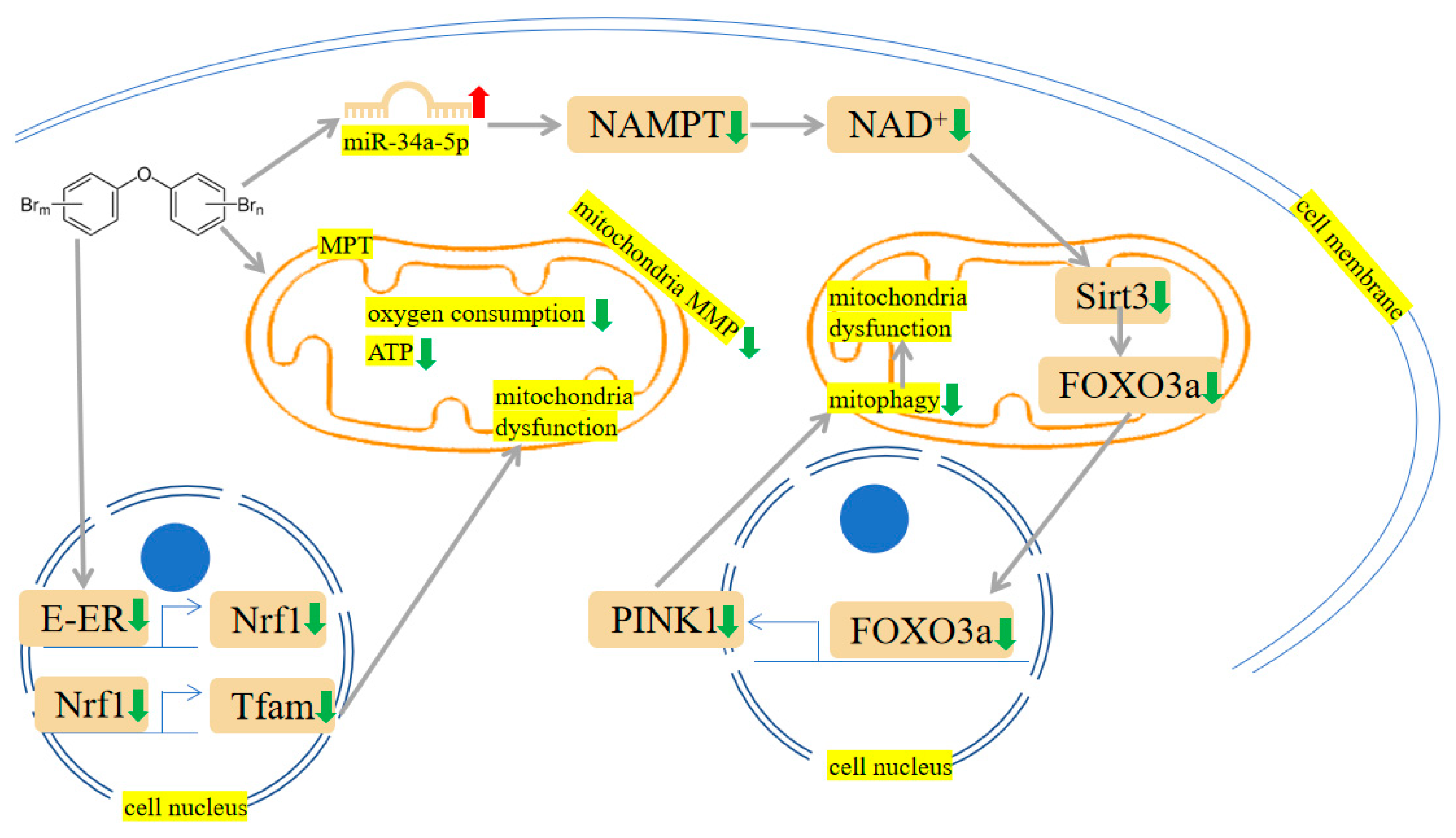


| Treatments | Effects and Mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|
| PBDE-47 or -153, zebrafish | CAT activity↑, SOD activity↑, Caspase-3↑, P53↑, Bcl-2↓ | [26] |
| PBDE-47 or -32, HepG2 cells, trout liver cells | Cell viability↓, ROS↑, apoptosis, DNA damage, mitochondrial impairment | [42,43,45] |
| PBDE-47, HSCs | ROS↑, lipid peroxidation, MMP↓ | [44] |
| PBDE-47, -99, -209, HepG2 cells | ERα↑, PPARα↑, intracellular lipid accumulation | [27] |
| PBDE-47, CAR and PXR null mice | CYP2B6↑, CYP2B6↑ | [85] |
| PBDE-47 or -99, isolated Wistar rat liver mitochondria | oxygen consumption↓, mitochondrial swelling, calcium release, ATP↓ | [73] |
| PBDE-47, CD-1 mice, ICR mice, C57 BL/6 mice | Proteasome dysfunction, TRAF2/ASK1/JNK pathway↑, NAD+ depletion, Sirt1↓, inflammation↑, abnormal insulin secretion, miR-34a-5p↑, Sirt3/FOXO3α/PINK1 pathway↓, mitochondrial dysfunction | [1,46,47,57,72] |
| PBDE-99, SD rats, HepG2 cells | SOD activity↑, CAT activity↓, GSSG↑, GSH↓, Caspase-3 activity↑, Caspase-9 activity↑, apoptosis | [48,49] |
| PBE-99, C57BL/6 mice | Inflammation, acetate↑, succinate↑ | [83] |
| PBDE-209, C57BL/6 mice, ICR mice, LO2 cells | ER stress↑, mitochondrial Ca2+ overload, apoptosis, ROS↑, PI3K/AKT/GLUT4 pathway↓, mTOR/PPARγ/RXRα pathway↑, Glucose↑, TG↑, HDL↓, liver and adipose structures damage | [50,68,69] |
| PBDE-209, SD rats | Hyperglycemia, GSH↓, SOD activity↓, liver weight↑, liver/body weight ratio↑, serum total bilirubin and indirect bilirubin↑, oxidative stress, PXR↓, CAR↓, CYP3A↓ | [70,87] |
| PBDE-209, IR-BRL cells | TC↑, TG↑, AST activity↑, ALT activity↑, MDA↑, IRS-1/PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway↓, IRS-1/GLUT4↓ | [71] |
| PBDE quinone, LO2 cells | ER stress↑, autophagy-lysosomal system↑, ROS↑ | [51] |
| PBDE-209, SD rats, LO2 cells | PRKACA-1 hypermethylation, TG↑, Glucose↑, PI3K/AKT/GLUT4 pathway↓, mTOR/PPARγ/RXRα pathway↑ | [62,68] |
| PBDE-209, HepG2 cells, isolated mitochondria | Mitochondrial Ca2+ overload, apoptosis, ROS↑, LDH leakage, matrix swelling, ATP↓, cell viability↓ | [52,53,75] |
| PBDE-209, Carassius auratus | GR activity↑, GSH↓ | [54] |
| PBDEs in e-waste site, kingfisher (Alcedo atthis) | MDA↑, ROS↑, CAT activity↓, SOD activity↓ | [55] |
| PBDE-47, marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) | PI3K pathway activity↑, MAPK pathway activity↑ | [56] |
| PBDE-71, Wistar rats | Glucose:insulin ratio↑ | [59,60] |
| PBDE-71, C57BL/6 mice | Glucose intolerance, fasting hyperglycemia, retarded glucose clearance, diminished thermogenic brown adipose tissue mass | [61] |
| PBDE-153, isolated rat liver mitochondria | MMP↓, ATP↓, ROS↑ | [74] |
| PBDE-47, Wistar Han rats, indirect exposure | Centrilobular hypertrophy, fatty change, cytochrome p450↑, Nrf2↑, lipid↑, oncogenes change, epigenetic change | [76] |
| PBDE-99, SD rats, indirect exposure | PIP3K/AKT pathway↓ | [77] |
| PBDE-47 and high-fat diet, HepG2 cells, C57BL/6J mice, combined exposure | CPT1α↓, fatty acid oxidation↓, microsomal triglyceride transfer protein↓, sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1↑, stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1↑, fatty acid synthase↑, lipid deposition, NAFLD, MDA↑, ROS↑, lipid accumulation | [19,78] |
| PBDE-47 and nanoplastics, zebrafish, combined exposure | Darker/browner liver colour, atrophied liver, liver degeneration or necrosis, gpx1a↓, CYP1A1↑, mortality↑, voluntary movements↑, hatching rate↑, heart rate↓ | [79] |
| PBDE-47 and microplastics, grouper (Epinephelus moara), combined exposure | PPAR-related genes↑, IL-17-related genes↓ | [18] |
| PBDE-71, hepatocytes derived from embryonic chickens | TTR↓, THRSP14-α↓, FABP↓ | [80] |
| PBDE-71, B6C3F1/N mice | Tbx3 hypomethylation | [81] |
| PBDE-47, PBDE-153 and PBDE-154 (alone or in combination), primary Atlantic salmon hepatocytes | VTG↑, ZP3↑ | [82] |
| Treatments | Effects and Mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|
| PBDE-99, SD rats | CAT activity↓, GSSG/GSH↑ | [48] |
| PBDE-47, HEK293 cells | Cell apoptosis, ROS↑, Bax↑, Bad↑, Bcl-2↑, Hrk↑, ethanol↑, GSH↓, creatine↓, aspartate↓, UDP-glucose↓, NAD+↓ | [88] |
| PBDE-47, CIK cells | CAT activity↓, SOD activity↓, GPx activity↓, T-AOC↓, Bax↑, Cytochrome C↑, Caspase-3↑ | [89] |
| PBDE-47, C57BL/6 mice | Cytochrome c release, caspase activation, PARP cleavage, CAT activity↓, SOD activity↓, GPx activity↓, Nrf2 activity↓, ROS↑, NF-κB↑, ACR↑, NLRP3↑, CXCR4/TXNIP/NLRP3↑ | [90,96] |
| PBDE-209, broilers | Swelling and granular degeneration of the renal tubular epithelium, atrophy and necrosis of glomeruli, MDA↑, GSH-Px↓, GSH↓, SOD↓, Bax/Bcl-2 ratio↑, p-ERK1/2↑, p-JNK1/2↑, Bax↑, Cytochrome c↑, Caspase-3↑ | [91] |
| PBDE-209, Wistar rats | GSH↑, TBARS↑, -SH↓ | [92] |
| PBDE-47 and Cd, HKC cells, combined exposure | Cell rounding, cell swelling, renal tubular epithelial cell damage, LDH release, NLRP3↑, cleaved Caspase-1↑, cleaved GSDMD↑, mitochondrial dysfunction, pyroptosis | [93] |
| PBDE-47, PK 15 cells | Mitochondrial fusion and fission↓, MMP↓, ROS↑, ATP↓, cellular disintegration | [94] |
| PBDE-47, CIK cells | AMPK-Sirt1-PGC-1α pathway↓, cytoplasmic Ca2+↑, miR-140-5p miRNA↓, TLR4↑, NF-κB↑ | [89,95] |
| Treatments | Effects and Mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|
| PBDE-71, zebrafish | Disruption of epithelial barrier integrity, inflammatory response, and anti-oxidant capacity | [97] |
| PBDE-209, Caco-2 cells | Nrf2↓, FAS↑, CYP1A1↑ | [98] |
| PBDE-47, SD rats | AF12↓, Oscillospira↓, Actinobacteria phylum↑, Blautia↑, Gemella↑, Phascolarctobacterium↑ | [99] |
| PBDE-47, CD-1 mice, ICR mice | Fecal and liver bile acids↑, CYP7A1↑, FXR signaling↓, microbial diversity↓, microbial compositional alterations, worsen HFD-induced obesity, hepatic steatosis, and injury | [101,102,103] |
| PBDE-47 and -99, C57BL/6 mice | Unconjugated bile acids↑, Akkermansia muciniphila↑, acetate↑, succinate↑, Ntcp↓, Oatp1b2↓ | [83,104] |
| Treatments | Effects and Mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|
| PBDE-47, HepG2 cells | TRα1↓, TRα1↓, TRβ1↓, TRβ1↓ | [106] |
| PBDE-47, zebrafish | TR↓, head trunk angle↓, otic vesicle length↑, eye pigmentation↓, developmental delays | [107] |
| PBDE-47, zebrafish | TTR↓, TG↓, TRβ↓, TSHβ↓, NIS↑, TPO↑, TRα↑ | [108] |
| PBDE-209, zebrafish | CRH↑, TSHβ↑, NIS↑, TG↑, Dio1↑, Dio2↑, TRα↑, TRβ↑, TTR↓, UGT1ab↓ | [109] |
| PBDE-71, SD rats | Plasma T4↓, liver vitamin A↓, body weight↓, T3 (F1 Female)↑, T4 (F1 Female)↑, thyroid gland weight↑, osteopontin↑ | [110,144] |
| PBDE-71, C57BL/6 mice | TT4↓, FT4↓ | [111] |
| PBDE-209, workers | Positive relationship between serum PBDE-209 levels and total TH | [114] |
| PBDE-209, rainbow trout | OH-BDE metabolites negatively correlated with the plasma FT4 levels | [117] |
| PBDE-209, fathead minnows | TT4↓, TT3↓ | [119] |
| PBDE-47, C57 BL/6 mice | TT4↓, Ugt1a1↑, Ugt1a7↑, Ugt2b5↑, CYP2B10↑, Mrp3↑ | [121] |
| PBDE-47, SD rats | Apoptosis, Caspase-3 activation, PARP cleavage, DNA fragmentation↑, GRP78↑, ATF4↑, CHOP↑, p62 accumulation, ER stress, defective autophagy | [122,123,124] |
| PBDE-28 or -47, human | TT4↑, FT4↑, TT3↑, FT3↑ | [135] |
| PBDEs, human | Placental T4↓ (PBDE-99, or -100) | [136] |
| PBDEs, human | TT4↓ (PBDE-99, -154 or -196), TT3↓ (PBDE-47, -99, -100, -197, -203 or -207) | [137] |
| PBDEs, human | TT3↑ (PBDE-47, -66 or 85), TT4↑ (PBDE-66, -85, 153 or -154), TT4↓ (PBDE-209) | [138] |
| PBDEs, human | TT4↓ (PBDE-28, -47, -99, -100 or -153) | [140] |
| PBDEs, human | TT3↓ (PBDE-154), FT3↓ (PBDE-153, -183), T4/T3 ratio↑ (PBDE-100) | [142] |
| PBDE-47 and PS-NPs, zebrafish, combined exposure | Deformity in pericardial edema, yolk sac edema, the curvature of the tail, TSHβ↑, TG↑, Dio2↑, TRβ↑ | [146] |
| PBDE-209, JEG-3 cells | Dio3↓, Dio3↓, has-miR-668-3p↓, has-miR409-3p↓ | [147] |
| Treatments | Effects and Mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|
| PBDE-47, ICR mice | MAPK signaling↑, changed placental function, low birth weight, stillbirth rate↑, plasma testosterone↓, progesterone↓, growth hormone↓, compromised fetal development | [148] |
| PBDE-47, zebrafish | Embryonic development abnormalities, ROS↑, JNK activity↑ | [149,150] |
| PBDE-209 or -47, hESCs, mESCs | ROS↑, OCT4↓, apoptosis, OCT4↓, SOX2↓, NANOG↓ | [151,152] |
| PBDE-209 and nSiO2, zebrafish, combined exposure | Postpone hatching, heartbeat↓, arrhythmia↑, malformation↑ | [153] |
| PBDEs, SD rats, zebrafish, common terns, kestrels | Soft tissue syndactyly or malposition of the distal phalanges and decreased ossification of the sixth sternebra (rats), embryo yolk sac, pericardial edema, spine deformation, neurobehavioral abnormalities, and blood vessels damage (zebrafish), shorter humerus length and reduced total thyroid weight (kestrels) | [154,155,156,157,158] |
| PBDE-47, human | Placental Dio3 methylation (female infants)↑ | [159] |
| PBDE-47, ICR mice | Adverse pregnancy results, VEGF-A↓, placental angiogenesis↓ | [160] |
| PBDE-47, CTB | Cell viability↓, Global CpG methylation↑ | [161] |
| PBDEs, human | Fetal growth retardation (PBDE-206, PBDE-17-190, PBDE-196-209), aberrant methylation of HSD11B2 and IGF2 | [162] |
| PBDE-209, C57 mice | Fetal growth and development↓, TCA cycle↓, accelerated lipolysis, TH↓ | [163] |
| PBDE-209, SD rats | ET-1↑, iNOS↑, eNOS↓, birth weight of the newborns↓ | [164] |
| PBDE-209, C57BL/6 mice | Placental vascular growth↓, placental cell death, GRP78↑, PERK signaling↑ | [165] |
| PBDEs, zebrafish | Yolk and pericardial edema, tail, and head malformation, reduced and extremely reduced heartbeat rate, blood stasis and spinal curvature, cardiac edema, damage of eye structure and hydrocephaly, liver vacuolization (PBDE-47, -99, -209), TSHβ↑, TTR↑, Tbg↑, Dio1↑ (PBDE-47, -99), Dio1↑ (PBDE-209) | [166] |
| Treatments | Effects and Mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|
| PBDE-209, ICR mice, CD-1 mice, Parkes strain mice, Balb/c mice, Sertoli cells | Oxidative stress, testosterone↓, DNA damage, ATM/Chk2↑, ATR/Chk1↑, DNA-PKcs/XRCC4/DNA ligase IV pathways↑, impaired germ cell proliferation, germ cell apoptosis↑, cx43↓, p27Kip1↓, ER signaling↑, impaired blood-testis barrier, sperm quality↓, arrested meiotic prophase I, testicular size↓, spermatogenesis↓ | [167,168,171,172,173,174,175,201,207,208,209,210] |
| PBDE-209, SD rats | Mitochondrial function↓, telomeres length↓, telomerase activity↓, PPARγ/RXRα/SCAP/SREBP-1↑, cell apoptosis, anogenital distance↓, abnormal sperm morphology, blood-testis barrier ultrastructure damage, tight junctions damage, ectoplasmic specialization structures with broken tight junctions, actin microfilaments↓ | [169,170,189,200] |
| PBDE-47, Brachionus plicatilis, SD rats | Reproductive rate↓, intrinsic increase rate↓, impaired ultrastructure of the ovary, ROS↑ | [176,177] |
| PBDE-47, marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma), manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum | Histone variants↓, parvalbumins↓, spermatogenesis↓, infertility, vitellogenins↑, apolipoprotein A-I↑, reproductive dysfunction | [211,212] |
| PBDE-47, mice, SD rats | Mitochondrial disruption, aberrant distribution, MMP↓, apoptosis | [178,179] |
| PBDE-47, Wistar rats, SD rats | Histone-protamine exchange↓, aberrant sperm epigenome, DMRs↑, autophagy↑, ovary damage, testosterone signaling disruption, AR antagonism, mTORC1 signaling↑, replacement of thyroid hormone from transporting proteins, cAMP↑ | [187,188,213,217] |
| PBDE-47, GC2 cells, ICR mice | Cell viability↓, condensation of nuclear, vacuolated mitochondria, Atp5b↓, Uqcrc↓, MMP↓, apoptosis, ER-Nrf1-Tfam-mitochondria pathway disturbance, mitochondria function↓, spermatogenesis↓, germ cells damage | [180,196] |
| PBDE-47, Fathead Minnows (Pimephales promelas) | Clutch size↓, fecundity↓ | [214] |
| PBDE-47, BeWo Cells | Mitochondria function↓, cholesterol transport↓, progesterone synthesis↓ | [197] |
| PBDE-47, ICR mice, GC-2 cells | Spermatogenesis damage, SETD8/H4K20me1-linked histone methylation disturbance, meiosis initiation↓, cell cycle progression↓, male reproductive toxicity | [190,191] |
| PBDE-71, zebrafish, male American kestrels (Falco sparverius) | Malformation, percentage of male↑, male courtship behaviors↓ | [215,216] |
| PBDE-99, Leydig cells | ROS↑, ERK1/2 pathway↑, ubiquitination degradation pathway↓, apoptosis | [181] |
| PBDE-99, Wistar rats | Adverse ultrastructural changes of mitochondria | [198] |
| PBDEs, Luteal cells | Malfunction of the corpus luteum, initiating apoptosis (PBDE-47, -99, -100) | [182] |
| PBDE-3, SD rats | ROS↑, serum testosterone↓, Leydig cell size↓, p-ERK1/2↓, p-AKT↓, p-AMPK↓ | [183,184] |
| PBDE-3 or -47, Caenorhabditis elegans | Life spans↓, fecundity↓, delayed egg-laying, ROS↑, DNA damage | [185,186] |
| PBDE-47 and high-fat diet, SD rats, combined exposure | Exacerbated the damage to the seminiferous epithelia, testosterone↓, spermatozoa↓, DAX-1↑, StAR↓, 3β-HSD↓ | [199] |
| Treatments | Effects and Mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|
| PBDE-209, Neuro-2a cells, HT-22 cells | FAS↑, FADD↑, Caspase-8↑, Caspase-3↑, apoptosis, PDEs↑, Bcl-2/Bax↓ | [219,220] |
| PBDE-47 or -209, Neuro-2a cells | P53↑, P21↑, cycline D1↓, CDK2↓, Nrf2↑, MMP↓, Cytochrome c release↑, Caspase-9↑, Caspase-3↑, ROS↑, MDA↑, GSSG/GSH ratio↑ | [265,266] |
| PBDE-209, SD rats, Wistar rats | LC3-Ⅱ↑, Beclin-1↑, P62↓, cleaved caspase-3↑, cleaved PARP↑, Bcl-2↓, neurons death, synaptic plasticity↓ | [221,267] |
| PBDE-153, SD rats | Learning ability↓, spontaneous activity↓, neuron apoptosis | [222] |
| PBDE-47, C57BL/6 mice cerebellar granule neurons, hNPCs | Extracellular glutamate↑, ionotropic glutamate receptors↑, calcium↑, oxidative stress, cell death | [223,224] |
| PBDE-47, SD rats | Caspase3↑, Caspase12↑, Cytochrome C↑, Caspase3↑, Caspase12↑, Cytochrome C↑, dendrites length↓, spines density↓, the behavior of autism, motor defect, impaired dopaminergic system, α-synuclein aggregation, ubiquitination↓, autophagy↓, PD risk↑, hyperactivity and anxiety-like behavior, Ruminococcaceae and Moraxella↓, Escherichia-Shigella↑, Pseudomonas and Peptococcus↑ | [225,233,236,237] |
| PBDE-99, cerebellar granular neurons, SD rats | BDNF↓, Bcl-2↓, learning difficulties, free radicals↑ | [226,227,228] |
| PBDE-99, CD-1 Swiss mice | Altered thigmotaxis, time in the centre of the arena↑ | [255] |
| PBDE-47, human | BDNF↓, risk of post-partum depression↑ | [229] |
| PBDEs, NMRI mice | BDNF↓, Ca/CaMKII↑ (PBDE-209, -206, -203) | [230,231] |
| PBDEs, human | Depression symptoms (PBDE-47, -99) | [232] |
| PBDE-71, zebrafish | Serotonin↓, TH↓, dopamine transporter protein↓, hyperactivity (low concentrations), activity during the dark period↓ (high concentrations), calcium balance disruption, cholinergic function↓, locomotor activity↓ | [234,235,258,259] |
| PBDE-47 and PS-NPs, zebrafish, combinde exposure | Accelerated voluntary movements, mortality↑, darker/browner liver colour, atrophied liver, ache↓, chrn7↓ | [79] |
| PBDE-71, SD rats | Delayed effects on sensory reactivity↓, startle reactions↑ | [257] |
| PBDEs, Daphnia magna | AChe activity↓ (PBDE-47, 6-OH-PBDE-47 and 6-MeO-PBDE-47) | [238] |
| PBDEs and PCB, zebrafish, combinde exposure | Neurobehavioral defects, mitochondrial function↓, lipid metabolism regulation↓ | [239,240] |
| PBDE-209 and Pb, C57BL/6 mice, combined exposure | TNFα↑, IFNγ↑, IL-4↑, IL-6↑, IL-10↑, IL-17 A↑, neuronal cells↓, impaired learning behavior | [241] |
| PBDE-209, C57BL/6 mice, ICR mice | Glial cell activity↓, hippocampal growth↓, behavioral difficulties, dendritic branches↓, synaptic proteins↓, doublecortin↑, weight gain↓, litter size of maternal mice↓, TT3↑, TT4↑, FT3↑, FT4↑, dio1↓ (livers), dio2↓ (livers), dio3↓ (livers), dio1↑ (brains), dio3↓ (brains), dio3↓, calcium overload, impaired learning and memory | [254,268,269,270,271] |
| PBDE-209 and Pb, zebrafish, combined exposure | Locomotor dysfunction, ROS↑, lipid peroxidation, DNA damage, antioxidant system↓ | [242] |
| PBDE-209 and nano-TiO2, zebrafish, combined exposure | Locomotion activity↓, mbp↓, a1-tubulin↓, gap-43↓ | [243] |
| PBDE-99 and MeHg, SD rats, combined exposure | Developmental neurotoxic effects, impaired negative geotaxis reflexes, impaired motor coordination | [244] |
| PBDE-99 or PBDE-47, NMRI mice, cerebral cortex cells, Wistar rats, human glial cells | Development of the brain↓, spontaneous behavior disturbance, Gap 43↑, Dio2 activity↓, neurodevelopmental deficits | [246,247,248,272] |
| PBDE-47, zebrafish | Spontaneous coil activity↑, locomotion↓, touch response↓, swimming speed↓, axonal growth↓, motor deficits, Hedgehog signaling↓ | [249,250,261,262] |
| PBDE-47 or -209, hNSC | NOTCH, GSK3β and T3 signaling interference | [251] |
| PBDE-47 or -49, SD rats, primary hippocampal cell cultures | Neuronal polarization delay, axonal outgrowth↓, RyR activity↑ | [264] |
| Treatments | Effects and Mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|
| PBDE-47, SD rats | NETs formation, ROS↑ | [274] |
| PBDE-47, Ruditapes philippinarum hemocytes, Mytilus edulis | Phagocytic ability↓, bacteriolytic activity↓, ROS↑, alteration of MAPKs pathways, lysosomal membrane damage | [275,276] |
| PBDE-47 or- 209, Kunming mice | ROS↑, GSH↓, macrophage accessory cell function↓ | [277] |
| PBDEs, harbour seal immune cells | ROS↑, thiols↓ (PBDE-47, -99, -153) | [278] |
| PBDE-47, THP-1 macrophage-like cells, spleen-derived lymphocytes, BALB/c mice, human | Perturb the innate immune response, disrupt the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6 and TNF-α) and interfere with basophil activation | [279,281,282,283,284] |
| PBDE-47, human PBMC | Higher response to LPS | [285] |
| PBDE-47, fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas), rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) | Resistance to the pathogen↓, survival rate↓, head kidney impairment, immune factors↓, respiratory burst activity↑, immune-related genes↓, impaired immune organs | [286,287] |
| PBDE-209, C57BL/6 mice, Balb/c mice, SD rats | Proliferative effects↓, production of cytokines↓, atrophying immune organs, humoral and cellular immunity changes | [288,289,290,291] |
| PBDE-209, Broiler chicks | Damaged and necrotic lymphocytes, lymphoid cells in the thymic gland↓ | [292] |
| PBDEs, pantropical spotted dolphin | Inflammatory cytokine↑, PGE2↑, cAMP↑, COX-2↑ (PBDE-47, -100, -209) | [294] |
| PBDE-47, CBZ and CdCl2, gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.), combined exposure | Dysregulation of pro-inflammatory factors and humoral response in the serum or skin mucus | [295] |
| Treatments | Effects and Mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|
| PBDE-47, SD rats | Risk of diabetes prevalence↑, hyperglycemia, scattered microvesicular steatosis | [296] |
| PBDEs, human | Glucose homeostasis disturbance, gestational diabetes mellitus↑ | [297] |
| PBDE-209 and high-fat diet, C57BL/6 mice | Blood glucose↑, insulin signaling pathway↑, GLUT4↓, TRα↓, AR↓, Insr↓ | [298] |
| PBDE-209, SD rats | Impaired morphology and ultrastructure of the heart and abdominal aorta, serum creatine kinase↑, LDH↑, IL-1β↑, IL-6↑, IL-10↑, TNFα↑, endothelial dysfunction, cardiovascular injury | [299] |
| PBDE-209, human umbilical vein endothelial cells | ROS↑, IRE1α/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway↑, autophagy↑, apoptosis | [300] |
| PBDE-71, zebrafish | Area of inner plexiform layer↓, inner nuclear layer↑, density of ganglion cells↓, hyperactive responses, retinal and retinyl ester content↑, raldh2↑, rdh1↓, crabp1a↓, crabp2a↓, raraa↓ zfrho↑, zfuv↑, zfred↑, zfblue↑, and zfgr1↑ | [301,304,305] |
| PBDE-47, hESC-ROs, zebrafish | Thickness and area of the neural retina↓, cell proliferation↓, cell apoptosis, aberrant differentiation, abnormal eye morphogenesis | [302,303] |
| PBDE-209, human lung epithelial cell | LDH leakage↑, cell viability↓, IL-6↑, IL-8↑, IL-6↑, IL-8↑ | [306] |
| PBDE-47, -99 or -209, A549 cells, pNHBE cells, human bronchial epithelial cells | Inflammation, oxidation stress, barrier integrity↓, uncontrolled production of mucous, alterations in physics and biochemical properties of airway fluids, NOX-4↑, ROS↑, DNA damage and repair processes↑ | [307,308,309] |
| PBDEs, human lung epithelial cells | Membrane disruption, LDH leakage↑, oxidation stress, MMP↓, ROS↑ | [310] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, J.; Xiao, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, D.; Wang, X. Toxic Effects and Mechanisms of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713487
Xue J, Xiao Q, Zhang M, Li D, Wang X. Toxic Effects and Mechanisms of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(17):13487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713487
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Jinsong, Qingqing Xiao, Min Zhang, Dan Li, and Xiaofei Wang. 2023. "Toxic Effects and Mechanisms of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 17: 13487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713487
APA StyleXue, J., Xiao, Q., Zhang, M., Li, D., & Wang, X. (2023). Toxic Effects and Mechanisms of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(17), 13487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713487





