Conditional Deletion of Foxg1 Delayed Myelination during Early Postnatal Brain Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
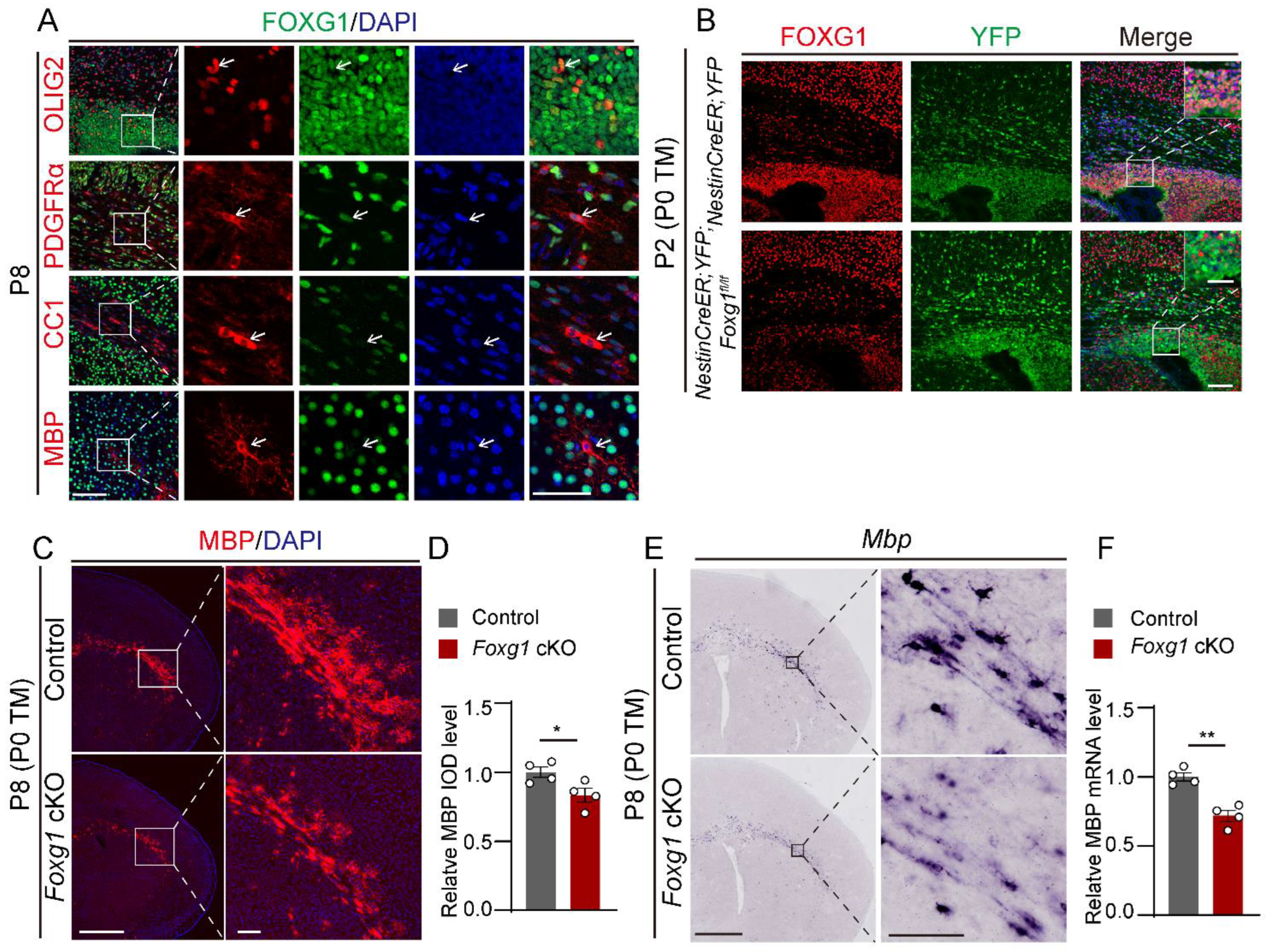
2.1. Foxg1 Deletion Leads to Defect in Myelination at Early Postnatal Period
2.2. Transient Defects in Myelination Are Observed in Foxg1 cKO Mice
2.3. Foxg1 Deletion Lead to Impaired OLs Maturation
2.4. Foxg1 Deletion Induces Cell−Autonomous Impairment in OLs Maturation
2.5. Foxg1 Promotes Cell Cycle Exit in OPCs while Maintaining Proliferation in NPCs
2.6. Foxg1 Deletion Leads to Imbalance of the Regulatory Mechanisms of Myelination
3. Discussion
3.1. Exploring OL Dysfunction in FOXG1 Syndrome from Animal Models
3.2. Foxg1 Modulates OL Diversely in Myelination and Remyelination
3.3. Potential Mechanisms of Foxg1 Regulation on Developmental Myelination
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.3. BrdU Administration
4.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. In Situ Hybridization
4.7. Cell Count and IOD Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bradl, M.; Lassmann, H. Oligodendrocytes: Biology and Pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews, E.S.; Appel, B. Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. Methods Cell Biol. 2016, 134, 69–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, D.M.S.; Brennan, E.J.; Brock, R.; Cocas, L.A. Neuron to Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cell Synapses: Protagonists in Oligodendrocyte Development and Myelination, and Targets for Therapeutics. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 779125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, K.L.; Dahl, K.D.; Gallo, V.; Macklin, W.B. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Regulators of Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Proliferation and Differentiation. Semin Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 116, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz, B.; Popko, B. Molecular Control of Oligodendrocyte Development. Trends Neurosci. 2019, 42, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, R.D. White Matter in Learning, Cognition and Psychiatric Disorders. Trends Neurosci. 2008, 31, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cainelli, E.; Arrigoni, F.; Vedovelli, L. White Matter Injury and Neurodevelopmental Disabilities: A Cross-Disease (Dis)Connection. Prog. Neurobiol. 2020, 193, 101845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuel, M.; Martynoga, B.; Yu, T.; West, J.D.; Mason, J.O.; Price, D.J. The Transcription Factor Foxg1 Regulates the Competence of Telencephalic Cells to Adopt Subpallial Fates in Mice. Development 2010, 137, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, A.; Wu, X.; Chen, H.; Bai, Q.-R.; Han, X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.; Ding, Z.; Shen, Q.; Zhao, C. Foxg1 Directly Represses Dbx1 to Confine the POA and Subsequently Regulate Ventral Telencephalic Patterning. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 4968–4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanashima, C.; Shen, L.; Li, S.C.; Lai, E. Brain Factor-1 Controls the Proliferation and Differentiation of Neocortical Progenitor Cells through Independent Mechanisms. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 6526–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shen, W.; Ni, Y.; Su, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, C. Impaired Interneuron Development after Foxg1 Disruption. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 27, 793–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cargnin, F.; Kwon, J.-S.; Katzman, S.; Chen, B.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, S.-K. FOXG1 Orchestrates Neocortical Organization and Cortico-Cortical Connections. Neuron 2018, 100, 1083–1096.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yang, M.; Su, M.; Liu, B.; Zhou, K.; Sun, C.; Ba, R.; Yu, B.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Z.; et al. FOXG1 Sequentially Orchestrates Subtype Specification of Postmitotic Cortical Projection Neurons. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabh3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, P.-S.; Miyoshi, G.; Hanashima, C. Sensory Cortex Wiring Requires Preselection of Short- and Long-Range Projection Neurons through an Egr-Foxg1-COUP-TFI Network. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, G.; Ueta, Y.; Natsubori, A.; Hiraga, K.; Osaki, H.; Yagasaki, Y.; Kishi, Y.; Yanagawa, Y.; Fishell, G.; Machold, R.P.; et al. FoxG1 Regulates the Formation of Cortical GABAergic Circuit during an Early Postnatal Critical Period Resulting in Autism Spectrum Disorder-like Phenotypes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, L.-C.; Singh, S.; Wang, H.-P.; Hsu, C.-J.; Hu, S.-C.; Lee, W.-T. FOXG1-Related Syndrome: From Clinical to Molecular Genetics and Pathogenic Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoichet, S.A.; Kunde, S.-A.; Viertel, P.; Schell-Apacik, C.; von Voss, H.; Tommerup, N.; Ropers, H.-H.; Kalscheuer, V.M. Haploinsufficiency of Novel FOXG1B Variants in a Patient with Severe Mental Retardation, Brain Malformations and Microcephaly. Hum. Genet. 2005, 117, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortum, F.; Das, S.; Flindt, M.; Morris-Rosendahl, D.J.; Stefanova, I.; Goldstein, A.; Horn, D.; Klopocki, E.; Kluger, G.; Martin, P.; et al. The Core FOXG1 Syndrome Phenotype Consists of Postnatal Microcephaly, Severe Mental Retardation, Absent Language, Dyskinesia, and Corpus Callosum Hypogenesis. J. Med. Genet. 2011, 48, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Liu, D.; Jiang, F.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Qu, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Fan, H.; Yao, R. Conditional Deletion of Foxg1 Alleviates Demyelination and Facilitates Remyelination via the Wnt Signaling Pathway in Cuprizone-Induced Demyelinated Mice. Neurosci. Bull. 2020, 37, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettige, N.C.; Ernst, C. FOXG1 Dose in Brain Development. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancaccio, M.; Pivetta, C.; Granzotto, M.; Filippis, C.; Mallamaci, A. Emx2 and Foxg1 Inhibit Gliogenesis and Promote Neuronogenesis. Stem Cells 2010, 28, 1206–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcone, C.; Santo, M.; Liuzzi, G.; Cannizzaro, N.; Grudina, C.; Valencic, E.; Peruzzotti-Jametti, L.; Pluchino, S.; Mallamaci, A. Foxg1 Antagonizes Neocortical Stem Cell Progression to Astrogenesis. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 4903–4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Li, J.; Marin-Husstege, M.; Kageyama, R.; Fan, Y.; Gelinas, C.; Casaccia-Bonnefil, P. A Molecular Insight of Hes5-Dependent Inhibition of Myelin Gene Expression: Old Partners and New Players. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 4833–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigenson, K.; Reid, M.; See, J.; Crenshaw, E.B.; Grinspan, J.B. Wnt Signaling Is Sufficient to Perturb Oligodendrocyte Maturation. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2009, 42, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braccioli, L.; Vervoort, S.J.; Puma, G.; Nijboer, C.H.; Coffer, P.J. SOX4 Inhibits Oligodendrocyte Differentiation of Embryonic Neural Stem Cells in Vitro by Inducing Hes5 Expression. Stem Cell Res. 2018, 33, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanta, J.; Kessler, J.A. Interactions between ID and OLIG Proteins Mediate the Inhibitory Effects of BMP4 on Oligodendroglial Differentiation. Development 2004, 131, 4131–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vegas, N.; Cavallin, M.; Maillard, C.; Boddaert, N.; Toulouse, J.; Schaefer, E.; Lerman-Sagie, T.; Lev, D.; Magalie, B.; Moutton, S.; et al. Delineating FOXG1 Syndrome: From Congenital Microcephaly to Hyperkinetic Encephalopathy. Neurol. Genet. 2018, 4, e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pringsheim, M.; Mitter, D.; Schröder, S.; Warthemann, R.; Plümacher, K.; Kluger, G.; Baethmann, M.; Bast, T.; Braun, S.; Büttel, H.; et al. Structural Brain Anomalies in Patients with FOXG1 Syndrome and in Foxg1+/− Mice. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilpert, N.-M.; Marguet, F.; Maillard, C.; Guimiot, F.; Martinovic, J.; Drunat, S.; Attié-Bitach, T.; Razavi, F.; Tessier, A.; Capri, Y.; et al. Human Neuropathology Confirms Projection Neuron and Interneuron Defects and Delayed Oligodendrocyte Production and Maturation in FOXG1 Syndrome. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2021, 64, 104282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Adams, H.R.; Seltzer, L.E.; Dobyns, W.B.; Paciorkowski, A.R. Phenotype Differentiation of FOXG1 and MECP2 Disorders: A New Method for Characterization of Developmental Encephalopathies. J. Pediatr. 2016, 178, 233–240.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporali, C.; Signorini, S.; De Giorgis, V.; Pichiecchio, A.; Zuffardi, O.; Orcesi, S. Early-Onset Movement Disorder as Diagnostic Marker in Genetic Syndromes: Three Cases of FOXG1-Related Syndrome. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2018, 22, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, L.-C.; Wu, Y.-T.; Hsu, C.-J.; Weng, W.-C.; Tsai, W.-C.; Lee, W.-T. Cognition and Evolution of Movement Disorders of FOXG1-Related Syndrome. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Madaan, P.; Vyas, S.; Sankhyan, N. FOXG1 Variant Presenting as Unexplained Irritability and Peculiar Crying Spells. Seizure 2021, 93, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Thacker, S.; Sarn, N.; Dutta, R.; Eng, C. Constitutional Mislocalization of Pten Drives Precocious Maturation in Oligodendrocytes and Aberrant Myelination in Model of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedel, M.; Fröb, F.; Elsesser, O.; Wittmann, M.-T.; Lie, D.C.; Reis, A.; Wegner, M. Transcription Factor Tcf4 Is the Preferred Heterodimerization Partner for Olig2 in Oligodendrocytes and Required for Differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 4839–4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, A.; Katayama, Y.; Nishiyama, M.; Shoji, H.; Tokuoka, K.; Ueta, Y.; Miyata, M.; Isa, T.; Miyakawa, T.; Hayashi-Takagi, A.; et al. Oligodendrocyte Dysfunction Due to Chd8 Mutation Gives Rise to Behavioral Deficits in Mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2020, 29, 1274–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, P.-S.; hAilín, D.Ó.; Vogel, T.; Hanashima, C. Transcription and Beyond: Delineating FOXG1 Function in Cortical Development and Disorders. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacey, L.K.K.; Xuan, I.C.Y.; Guan, S.; Sussman, D.; Henkelman, R.M.; Chen, Y.; Thomsen, C.; Hampson, D.R. Delayed Myelination in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 3920–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergles, D.E.; Richardson, W.D. Oligodendrocyte Development and Plasticity. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a020453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, S.; Gritti, L.; Crooks, D.; Dombrowski, Y. Oligodendrocytes in Development, Myelin Generation and Beyond. Cells 2019, 8, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.-H.; Biswas, S.; Selvaraj, V.; Liu, X.-B.; Sohn, J.; Jiang, P.; Chen, C.; Chmilewsky, F.; Marzban, H.; Horiuchi, M.; et al. The P38α Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Is a Key Regulator of Myelination and Remyelination in the CNS. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, I.K.; Richardson, W.D.; Bolsover, S.R.; Raff, M.C. PDGF and Intracellular Signaling in the Timing of Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. J. Cell Biol. 1989, 109, 3411–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calver, A.R.; Hall, A.C.; Yu, W.-P.; Walsh, F.S.; Heath, J.K.; Betsholtz, C.; Richardson, W.D. Oligodendrocyte Population Dynamics and the Role of PDGF In Vivo. Neuron 1998, 20, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Qiu, W.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Dai, Z.; Yang, A.; Tang, T.; Zhao, X.; Qiu, M. ADAMTS4 Enhances Oligodendrocyte Differentiation and Remyelination by Cleaving NG2 Proteoglycan and Attenuating PDGFRα Signaling. J. Neurosci. 2023, 43, 4405–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pol, S.U.; Polanco, J.J.; Seidman, R.A.; O’Bara, M.A.; Shayya, H.J.; Dietz, K.C.; Sim, F.J. Network-Based Genomic Analysis of Human Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Differentiation. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 9, 710–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, K.; Li, H.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Mastracci, T.; Wegner, M.; Chen, Y.; Sussel, L.; et al. Genetic Evidence That Nkx2.2 and Pdgfra Are Major Determinants of the Timing of Oligodendrocyte Differentiation in the Developing CNS. Development 2014, 141, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabretta, S.; Vogel, G.; Yu, Z.; Choquet, K.; Darbelli, L.; Nicholson, T.B.; Kleinman, C.L.; Richard, S. Loss of PRMT5 Promotes PDGFRα Degradation during Oligodendrocyte Differentiation and Myelination. Dev. Cell 2018, 46, 426–440.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardona, H.J.; Somasundaram, A.; Crabtree, D.M.; Gadd, S.L.; Becher, O.J. Prenatal Overexpression of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor A Results in Central Nervous System Hypomyelination. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, R.; Yang, L.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, P.; Ding, Z.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, C. FOXG1 Drives Transcriptomic Networks to Specify Principal Neuron Subtypes during the Development of the Medial Pallium. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Du, J.; Wu, H.; Ge, X.; Xu, X.; Yang, A.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, X.; Zheng, K.; Zhu, Q.; et al. Differential Inhibition of Sox10 Functions by Notch-Hes Pathway. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 40, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popko, B. Notch Signaling: A Rheostat Regulating Oligodendrocyte Differentiation? Dev. Cell 2003, 5, 668–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.D.; Cui, X.Y.; Ng, Y.K.; Xiao, Z.C. Notch Axoglial Interaction via the Notch Receptor in Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. Ann. Acad. Med. 2004, 33, 581–588. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, C.; Gong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shen, W.; Wang, K.; Liu, J.; Xu, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, C. Foxg1 Has an Essential Role in Postnatal Development of the Dentate Gyrus. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 2931–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.B.; Clarke, L.E.; Burzomato, V.; Kessaris, N.; Anderson, P.N.; Attwell, D.; Richardson, W.D. Dorsally and Ventrally Derived Oligodendrocytes Have Similar Electrical Properties but Myelinate Preferred Tracts. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 6809–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, R.; Qiu, W.; Yang, Y.; Xu, S.; Rao, Y.; Li, Q.; Luo, Y.; Huang, H.; Yang, A.; Tao, H.; et al. Evidence That DDR1 Promotes Oligodendrocyte Differentiation during Development and Myelin Repair after Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, G.; Sun, C.; Shen, H.; Qu, D.; Shen, C.; Lu, H. Conditional Deletion of Foxg1 Delayed Myelination during Early Postnatal Brain Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241813921
Cao G, Sun C, Shen H, Qu D, Shen C, Lu H. Conditional Deletion of Foxg1 Delayed Myelination during Early Postnatal Brain Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(18):13921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241813921
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Guangliang, Congli Sun, Hualin Shen, Dewei Qu, Chuanlu Shen, and Haiqin Lu. 2023. "Conditional Deletion of Foxg1 Delayed Myelination during Early Postnatal Brain Development" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 18: 13921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241813921
APA StyleCao, G., Sun, C., Shen, H., Qu, D., Shen, C., & Lu, H. (2023). Conditional Deletion of Foxg1 Delayed Myelination during Early Postnatal Brain Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(18), 13921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241813921




