Unraveling the Role of Epithelial Cells in the Development of Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
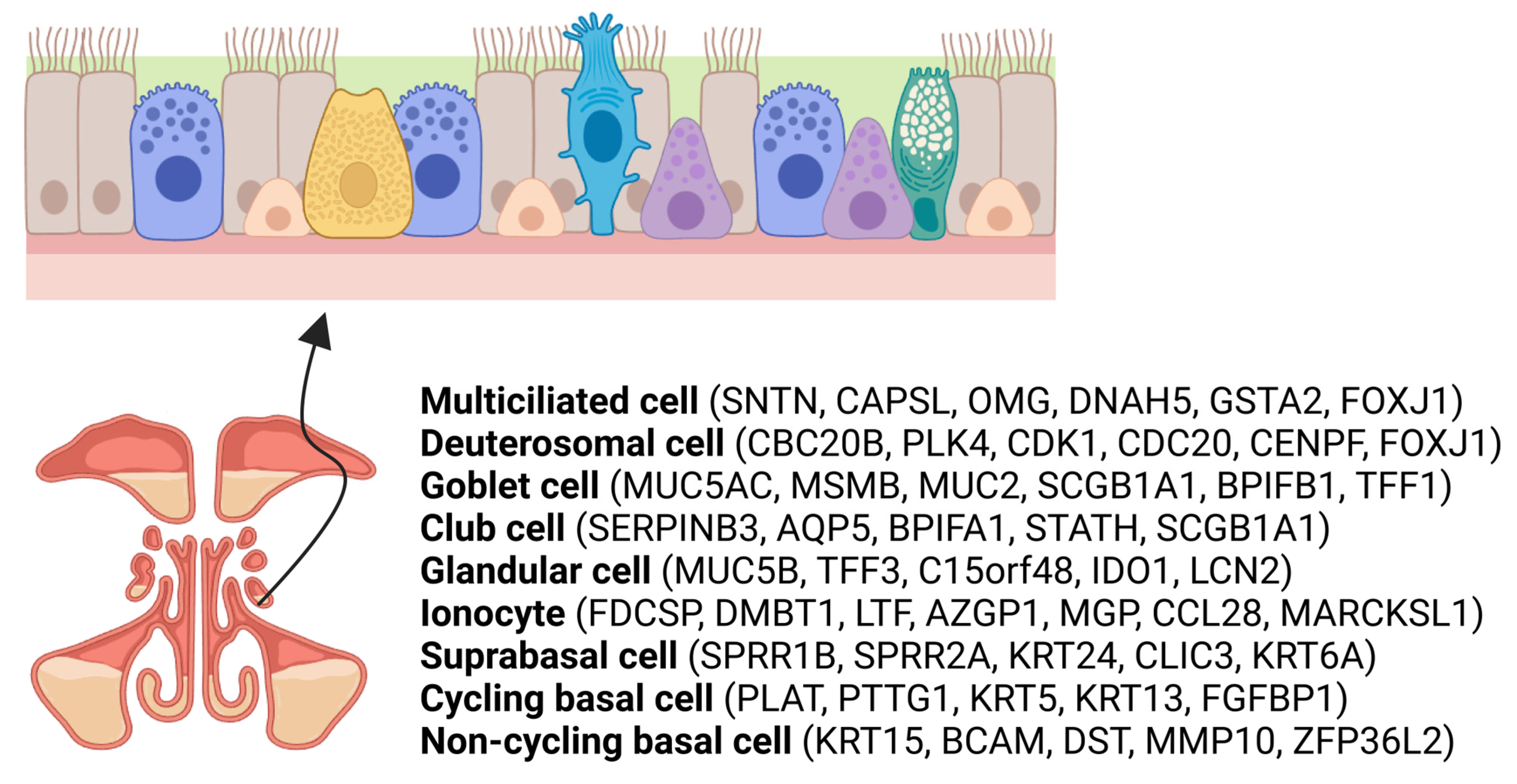
2. Overview of Sinonasal Epithelial Cell Subtypes
3. Histological Changes and Tissue Remodeling in CRS
3.1. Histological Characteristics of CRS
3.2. Tissue Remodeling
3.3. EMT in CRS
4. Sinonasal Barriers in CRS
4.1. Mucociliary Clearance
4.2. Physical Barriers and Epithelial Cell Dysfunction
5. Innate Immune Responses of Epithelial Cells in CRS
5.1. Chemical Barriers: Mucus and Defense Molecules
5.2. Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs)
6. Epithelial Cell–ECM Crosstalk
7. Nasal and Airway Epithelial Cell–Immune Cell Crosstalk
7.1. Nasal and Airway Epithelial Cell–Macrophage Crosstalk
7.2. Nasal and Airway Epithelial Cell–Neutrophil Crosstalk
7.3. Nasal and Airway Epithelial Cell–DC Crosstalk
7.4. Nasal and Airway Epithelial Cell–B-Cell Crosstalk
7.5. Nasal and Airway Epithelial Cell–T-Cell Crosstalk
7.6. Nasal and Airway Epithelial Cell–Eosinophil Crosstalk
7.7. Nasal and Airway Epithelial Cell–Mast Cell Crosstalk
7.8. Nasal and Airway Epithelial Cell–ILC Crosstalk
8. Therapeutic Approaches Impacting the Sinonasal Epithelium in CRS
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meltzer, E.O.; Hamilos, D.L.; Hadley, J.A.; Lanza, D.C.; Marple, B.F.; Nicklas, R.A.; Bachert, C.; Baraniuk, J.; Baroody, F.M.; Benninger, M.S.; et al. Rhinosinusitis: Establishing definitions for clinical research and patient care. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114 (Suppl. S6), 155–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Hopkins, C.; Hellings, P.W.; Kern, R.; Reitsma, S.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Mullol, J.; Alobid, I.; et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020. Rhinology 2020, 58 (Suppl. S29), 1–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponikau, J.U.; Sherris, D.A.; Kephart, G.M.; Kern, E.B.; Gaffey, T.A.; Tarara, J.E.; Kita, H. Features of airway remodeling and eosinophilic inflammation in chronic rhinosinusitis: Is the histopathology similar to asthma? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, A.; Schleimer, R.P.; Bleier, B.S. Mechanisms and pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 1491–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynne, M.; Atkinson, C.; Schlosser, R.J.; Mulligan, J.K. Contribution of Epithelial Cell Dysfunction to the Pathogenesis of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2019, 33, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, C.; Shi, L. Upper airway stem cells: Understanding the nose and role for future cell therapy. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2015, 15, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, M.B.; Gudis, D.A.; Cohen, N.A. Epithelium, cilia, and mucus: Their importance in chronic rhinosinusitis. Immunol. Allergy Clin. North. Am. 2009, 29, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watelet, J.B.; Bachert, C.; Claeys, C.; Van Cauwenberge, P. Matrix metalloproteinases MMP-7, MMP-9 and their tissue inhibitor TIMP-1: Expression in chronic sinusitis vs nasal polyposis. Allergy 2004, 59, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tos, M.; Larsen, P.L.; Møller, K. Goblet cell density in nasal polyps. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1990, 99 Pt 1, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.U.; Reynolds, S.D.; Watkins, S.; Fuchs, E.; Stripp, B.R. Basal cells are a multipotent progenitor capable of renewing the bronchial epithelium. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz García, S.; Deprez, M.; Lebrigand, K.; Cavard, A.; Paquet, A.; Arguel, M.J.; Magnone, V.; Truchi, M.; Caballero, I.; Leroy, S.; et al. Novel dynamics of human mucociliary differentiation revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing of nasal epithelial cultures. Development 2019, 146, 177428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordovas-Montanes, J.; Dwyer, D.F.; Nyquist, S.K.; Buchheit, K.M.; Vukovic, M.; Deb, C.; Wadsworth, M.H., 2nd; Hughes, T.K.; Kazer, S.W.; Yoshimoto, E.; et al. Allergic inflammatory memory in human respiratory epithelial progenitor cells. Nature 2018, 560, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.J.; Chung, Y.W.; Moon, S.; Seo, J.H.; Kang, M.; Nam, J.S.; Lee, S.N.; Kim, C.H.; Choi, A.M.K.; Yoon, J.H. IL-4 drastically decreases deuterosomal and multiciliated cells via alteration in progenitor cell differentiation. Allergy 2023, 78, 1866–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaragosi, L.E.; Deprez, M.; Barbry, P. Using single-cell RNA sequencing to unravel cell lineage relationships in the respiratory tract. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, R.J.; Lloyd, C.M. Regulation of immune responses by the airway epithelial cell landscape. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawankar, R.; Nonaka, M. Inflammatory mechanisms and remodeling in chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2007, 7, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudis, D.; Zhao, K.Q.; Cohen, N.A. Acquired cilia dysfunction in chronic rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2012, 26, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bruaene, N.; Derycke, L.; Perez-Novo, C.A.; Gevaert, P.; Holtappels, G.; De Ruyck, N.; Cuvelier, C.; Van Cauwenberge, P.; Bachert, C. TGF-beta signaling and collagen deposition in chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 253–259.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zele, T.; Claeys, S.; Gevaert, P.; Van Maele, G.; Holtappels, G.; Van Cauwenberge, P.; Bachert, C. Differentiation of chronic sinus diseases by measurement of inflammatory mediators. Allergy 2006, 61, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bruaene, N.; Bachert, C. Tissue remodeling in chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 11, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleimer, R.P. Immunopathogenesis of Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyposis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2017, 12, 331–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bruaene, N.; Pérez-Novo, C.A.; Basinski, T.M.; Van Zele, T.; Holtappels, G.; De Ruyck, N.; Schmidt-Weber, C.; Akdis, C.; Van Cauwenberge, P.; Bachert, C.; et al. T-cell regulation in chronic paranasal sinus disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 1435–1441.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachert, C.; Gevaert, P.; Holtappels, G.; Cuvelier, C.; van Cauwenberge, P. Nasal polyposis: From cytokines to growth. Am. J. Rhinol. 2000, 14, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyo, J.S.; Kim, S.J. Relationship between histologic changes and inflammatory markers in chronic rhinosinusitis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2021, 14, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kotas, M.E.; Patel, N.N.; Cope, E.K.; Gurrola, J.G.; Goldberg, A.N.; Pletcher, S.D.; Seibold, M.A.; Moore, C.M.; Gordon, E.D. IL-13–associated epithelial remodeling correlates with clinical severity in nasal polyposis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, N.W.; Medzhitov, R. Pattern recognition receptors and control of adaptive immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 227, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.W.; Cho, K.; Kim, D.W.; Han, D.H.; Khalmuratova, R.; Kim, S.W.; Jeon, S.Y.; Min, Y.G.; Lee, C.H.; Rhee, C.S.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 mediates nasal polypogenesis by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 944–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; Neilson, E.G. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1776–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagalwalla, A.F.; Akhtar, N.; Woodruff, S.A.; Rea, B.A.; Masterson, J.C.; Mukkada, V.; Parashette, K.R.; Du, J.; Fillon, S.; Protheroe, C.A.; et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Epithelial mesenchymal transition contributes to esophageal remodeling and reverses with treatment. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 1387–1396.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Könnecke, M.; Burmeister, M.; Pries, R.; Böscke, R.; Bruchhage, K.L.; Ungefroren, H.; Klimek, L.; Wollenberg, B. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Chronic Rhinosinusitis: Differences Revealed Between Epithelial Cells from Nasal Polyps and Inferior Turbinates. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2017, 65, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lamouille, S.; Derynck, R. TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.E. Non-Smad pathways in TGF-beta signaling. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Tao, Y.; Li, X. Expression of MMP-9/TIMP-2 in nasal polyps and its functional implications. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 14556–14561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Weinberg, R.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development and tumor metastasis. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Wang, H.; Yin, J. The Role of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 183, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Ye, T.; Liang, N.; Huang, Z.; Cui, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, B. Differing roles for TGF-β/Smad signaling in osteitis in chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyps. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2015, 29, e152–e159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callejas-Díaz, B.; Fernandez, G.; Fuentes, M.; Martínez-Antón, A.; Alobid, I.; Roca-Ferrer, J.; Picado, C.; Tubita, V.; Mullol, J. Integrated mRNA and microRNA transcriptome profiling during differentiation of human nasal polyp epithelium reveals an altered ciliogenesis. Allergy 2020, 75, 2548–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, C.; Zhu, G.; Yuan, W.; Xiao, Z.A. TGF-β1 Induces Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Chronic Sinusitis with Nasal Polyps through MicroRNA-21. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 179, 304–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Xue, K.; Wang, Z. MicroRNA-761 suppresses remodeling of nasal mucosa and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in mice with chronic rhinosinusitis through LCN2. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Kim, D.W.; Yoon, H.; So, D.; Khalmuratova, R.; Rhee, C.-S.; Park, J.-W.; Shin, H.-W. Sirtuin 1 attenuates nasal polypogenesis by suppressing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 87–98.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Cheng, H.; Mo, Q.; Zhou, X.; Xie, M. miR-155-5p downregulation inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by targeting SIRT1 in human nasal epithelial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 3695–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majima, Y.; Sakakura, Y.; Matsubara, T.; Miyoshi, Y. Possible mechanisms of reduction of nasal mucociliary clearance in chronic sinusitis. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1986, 11, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.S.; Hsieh, J.F.; Tsai, S.C.; Ho, Y.J.; Kao, C.H. The role of rhinoscintigraphy in the evaluation of nasal mucociliary clearance function in patients with sinusitis. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2000, 21, 1029–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollin, M.; Seymour, K.; Hariri, M.; Harcourt, J. Rhinosinusitis, symptomatology & absence of polyposis in children with primary ciliary dyskinesia. Rhinology 2009, 47, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski, L.E.; Yin, W.; Rogers, T.D.; Busalacchi, K.B.; Chua, M.; O’Neal, W.K.; Grubb, B.R. Conditional deletion of dnaic1 in a murine model of primary ciliary dyskinesia causes chronic rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 43, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwany, S.; Hisham, M.; Gamaee, R. The effect of endoscopic sinus surgery on mucociliary clearance in patients with chronic sinusitis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 1998, 255, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallstrand, T.S.; Hackett, T.L.; Altemeier, W.A.; Matute-Bello, G.; Hansbro, P.M.; Knight, D.A. Airway epithelial regulation of pulmonary immune homeostasis and inflammation. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 151, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, M.H.; Lee, P.H.; Choi, S.M.; Hwang, D.; Kim, J.H.; Park, M.C.; Park, S.; Baek, A.R.; Jang, A.S. Impact of the Junction Adhesion Molecule-A on Asthma. Yonsei Med. J. 2023, 64, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, C.M. Tight junctions/adherens junctions: Basic structure and function. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 2525–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, S.; Comstock, A.T.; Sajjan, U.S. Barrier function of airway tract epithelium. Tissue Barriers 2013, 1, e24997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matter, K.; Balda, M.S. Signalling to and from tight junctions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, M.A.; Nelson, W.J.; Chavez, N. Cell-Cell Junctions Organize Structural and Signaling Networks. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a029181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieu, D.D.; Kern, R.C.; Schleimer, R.P. Alterations in epithelial barrier function and host defense responses in chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, R.; Deng, C.; Xu, J.; Dong, W.; Hong, Z.; Yu, H.; Situ, H.; Liu, C.; et al. Nasal epithelial barrier disruption by particulate matter ≤ 2.5 μm via tight junction protein degradation. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 38, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Y.; Liu, F.; Yi, X.; Liu, S.; Holtappels, G.; Bachert, C.; Zhang, N. The development of nasal polyp disease involves early nasal mucosal inflammation and remodelling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyka, M.B.; Wawrzyniak, P.; Eiwegger, T.; Holzmann, D.; Treis, A.; Wanke, K.; Kast, J.I.; Akdis, C.A. Defective epithelial barrier in chronic rhinosinusitis: The regulation of tight junctions by IFN-γ and IL-4. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 1087–1096.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Sun, Y.; Li, C.; Qu, J.; Zhou, B. Eosinophils Correlate with Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2022, 84, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahana, S.; Jaunmuktane, Z.; Stenkvist Asplund, M.; Roomans, G.M. Ultrastructural investigation of epithelial damage in asthmatic and non-asthmatic nasal polyps. Respir. Med. 2006, 100, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, G.A.; Den Beste, K.; Parkos, C.A.; Nusrat, A.; Delgaudio, J.M.; Wise, S.K. Epithelial tight junction alterations in nasal polyposis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2011, 1, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, K.; Obata, K.; Keira, T.; Miyata, R.; Hirakawa, S.; Takano, K.; Kohno, T.; Sawada, N.; Himi, T.; Kojima, T. Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase causes transient disruption of tight junctions and downregulation of PAR-2 in human nasal epithelial cells. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, Z.; Roscioli, E.; Murphy, J.; Ou, J.; Bassiouni, A.; Wormald, P.J.; Vreugde, S. Staphylococcus aureus impairs the airway epithelial barrier in vitro. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015, 5, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gevaert, E.; Zhang, N.; Krysko, O.; Lan, F.; Holtappels, G.; De Ruyck, N.; Nauwynck, H.; Yousefi, S.; Simon, H.U.; Bachert, C. Extracellular eosinophilic traps in association with Staphylococcus aureus at the site of epithelial barrier defects in patients with severe airway inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 1849–1860.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.J.; Kim, T.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Kim, C.H. Hypoxia increases epithelial permeability in human nasal epithelia. Yonsei Med. J. 2015, 56, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, G.D.; Jeney, E.V.; Baraniuk, J.N.; Kim, I.; Meredith, S.D.; Kaliner, M.A. Pathophysiology of rhinitis. Lactoferrin and lysozyme in nasal secretions. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 84, 1528–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corfield, A.P. Mucins: A biologically relevant glycan barrier in mucosal protection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 236–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, T.; Hansson, G.C.; Samuelsson, T. Gel-forming mucins appeared early in metazoan evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16209–16214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahy, J.V.; Dickey, B.F. Airway mucus function and dysfunction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2233–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Song, B.H.; Howe, C.L.; Chang, E.H. A Comprehensive Systematic Review of the Association Between Airway Mucins and Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2019, 33, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, P.; Loukoianov, A.; Wachi, S.; Wu, R. Regulation of airway mucin gene expression. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2008, 70, 405–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovenberg, H.W.; Davies, J.R.; Carlstedt, I. Different mucins are produced by the surface epithelium and the submucosa in human trachea: Identification of MUC5AC as a major mucin from the goblet cells. Biochem. J. 1996, 318 Pt 1, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucherat, O.; Boczkowski, J.; Jeannotte, L.; Delacourt, C. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of goblet cell metaplasia in the respiratory airways. Exp. Lung Res. 2013, 39, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalfaoui, L.; Symon, F.A.; Couillard, S.; Hargadon, B.; Chaudhuri, R.; Bicknell, S.; Mansur, A.H.; Shrimanker, R.; Hinks, T.S.C.; Pavord, I.D.; et al. Airway remodelling rather than cellular infiltration characterizes both type 2 cytokine biomarker-high and -low severe asthma. Allergy 2022, 77, 2974–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonser, L.R.; Erle, D.J. Airway Mucus and Asthma: The Role of MUC5AC and MUC5B. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkham, S.; Sheehan, J.K.; Knight, D.; Richardson, P.S.; Thornton, D.J. Heterogeneity of airways mucus: Variations in the amounts and glycoforms of the major oligomeric mucins MUC5AC and MUC5B. Biochem. J. 2002, 361 Pt 3, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rose, V.; Molloy, K.; Gohy, S.; Pilette, C.; Greene, C.M. Airway Epithelium Dysfunction in Cystic Fibrosis and COPD. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 1309746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Antón, A.; de Bolós, C.; Alobid, I.; Benítez, P.; Roca-Ferrer, J.; Picado, C.; Mullol, J. Corticosteroid therapy increases membrane-tethered while decreases secreted mucin expression in nasal polyps. Allergy 2008, 63, 1368–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, M.G.; Livraghi-Butrico, A.; Fletcher, A.A.; McElwee, M.M.; Evans, S.E.; Boerner, R.M.; Alexander, S.N.; Bellinghausen, L.K.; Song, A.S.; Petrova, Y.M.; et al. Muc5b is required for airway defence. Nature 2014, 505, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Guan, W.; Xiang, B.; Wang, W.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, J. MUC5B regulates goblet cell differentiation and reduces inflammation in a murine COPD model. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, S.; Sagara, H.; Fukuda, T.; Saito, H.; Okayama, Y. FcepsilonRI-mediated amphiregulin production by human mast cells increases mucin gene expression in epithelial cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, G.K.; Duffy, S.M.; Roach, K.M.; Hirst, R.A.; Shikotra, A.; Gaillard, E.A.; Bradding, P. KCa3.1 K+ Channel Expression and Function in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, T.; Velichko, S.; Thai, P.; Hung, L.Y.; Huang, F.; Wu, R. Regulation of airway MUC5AC expression by IL-1beta and IL-17A; the NF-kappaB paradigm. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6236–6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Derycke, L.; Holtappels, G.; Wang, X.D.; Zhang, L.; Bachert, C.; Zhang, N. Th2 cytokines orchestrate the secretion of MUC5AC and MUC5B in IL-5-positive chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Allergy 2019, 74, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 2006, 124, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wu, M. Pattern recognition receptors in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Q.; Truong-Tran, A.Q.; Plitt, J.R.; Beck, L.A.; Schleimer, R.P. Activation of airway epithelial cells by toll-like receptor agonists. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2004, 31, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, A.P.; Truong-Tran, Q.A.; Myers, A.; Bickel, C.; Schleimer, R.P. Serum amyloid A, properdin, complement 3, and toll-like receptors are expressed locally in human sinonasal tissue. Am. J. Rhinol. 2006, 20, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seshadri, S.; Lin, D.C.; Rosati, M.; Carter, R.G.; Norton, J.E.; Suh, L.; Kato, A.; Chandra, R.K.; Harris, K.E.; Chu, H.W.; et al. Reduced expression of antimicrobial PLUNC proteins in nasal polyp tissues of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergy 2012, 67, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, S.; Lu, X.; Purkey, M.R.; Homma, T.; Choi, A.W.; Carter, R.; Suh, L.; Norton, J.; Harris, K.E.; Conley, D.B.; et al. Increased expression of the epithelial anion transporter pendrin/SLC26A4 in nasal polyps of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 1548–1558.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, K.; Chang, A.; Hoggard, M.; Radcliff, F.J.; Jiang, Y.; Taylor, M.W.; Darveau, R.; Douglas, R.G. Toll-like receptor activation by sino-nasal mucus in chronic rhinosinusitis. Rhinology 2017, 55, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Meng, J.; Qiao, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, J.; Holtappels, G.; Luo, B.; Zhou, P.; et al. Expression of TGF, matrix metalloproteinases, and tissue inhibitors in Chinese chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. The role of transforming growth factor β in T helper 17 differentiation. Immunology 2018, 155, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chang, L.; Li, X.; Huang, J.; Yang, L.; Lai, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhao, J.; et al. Tc17/IL-17A Up-Regulated the Expression of MMP-9 via NF-κB Pathway in Nasal Epithelial Cells of Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramezanpour, M.; Moraitis, S.; Smith, J.L.; Wormald, P.J.; Vreugde, S. Th17 Cytokines Disrupt the Airway Mucosal Barrier in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 9798206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, C.; Ji, W.; Xu, Y.; Guo, H. Relationship of TLR2, TLR4 and tissue remodeling in chronic rhinosinusitis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 1199–1212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Imoto, Y.; Kato, A.; Takabayashi, T.; Stevens, W.; Norton, J.E.; Suh, L.A.; Carter, R.G.; Weibman, A.R.; Hulse, K.E.; Harris, K.E.; et al. Increased thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor levels in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 1566–1574.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, S.; Gabazza, E.C.; Ogawa, T.; Tojima, I.; Hoshi, E.; Kouzaki, H.; Shimizu, T. Role of thrombin in chronic rhinosinusitis-associated tissue remodeling. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2011, 25, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samarakoon, R.; Higgins, S.P.; Higgins, C.E.; Higgins, P.J. TGF-beta1-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells requires pp60(c-src)/EGFR(Y845) and Rho/ROCK signaling. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2008, 44, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Shu, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Shen, Y.; Yang, Y. The development of nasal polyps involves early middle meatus mucous remodeling via TGF-β1 mediated PAI-1 reduction. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 89, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.J.; Hao, S.P.; Chen, C.L.; Wu, W.B. Thromboxane A2 Regulates CXCL1 and CXCL8 Chemokine Expression in the Nasal Mucosa-Derived Fibroblasts of Chronic Rhinosinusitis Patients. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bissonnette, E.Y.; Lauzon-Joset, J.F.; Debley, J.S.; Ziegler, S.F. Cross-Talk Between Alveolar Macrophages and Lung Epithelial Cells is Essential to Maintain Lung Homeostasis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 583042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wermuth, P.J.; Jimenez, S.A. The significance of macrophage polarization subtypes for animal models of tissue fibrosis and human fibrotic diseases. Clin. Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, K.; Nguyen, H.N.; Brenner, M.B. Fibroblast pathology in inflammatory diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e149538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krysko, O.; Holtappels, G.; Zhang, N.; Kubica, M.; Deswarte, K.; Derycke, L.; Claeys, S.; Hammad, H.; Brusselle, G.G.; Vandenabeele, P.; et al. Alternatively activated macrophages and impaired phagocytosis of S. aureus in chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergy 2011, 66, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Sun, X.; Tan, S.; Luo, C.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Lin, H.; Zhang, W. M2 macrophage-related gene signature in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1047930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Liu, P.; Zhou, H.; Jin, J.; Gong, W.; Liu, K.; Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Fan, W.; Tao, Z.; et al. TIM-4 in macrophages contributes to nasal polyp formation through the TGF-β1-mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition in nasal epithelial cells. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 941608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Xie, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, Y.; Lin, W.; Li, M. Immune cell infiltration and related core genes expression characteristics in eosinophilic and non-eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Bandi, V.; Guntupalli, K.K.; Jeffery, P.K. Bronchial mucosal inflammation and upregulation of CXC chemoattractants and receptors in severe exacerbations of asthma. Thorax 2007, 62, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeachy, M.J.; Cua, D.J.; Gaffen, S.L. The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Health and Disease. Immunity 2019, 50, 892–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traves, S.L.; Donnelly, L.E. Th17 cells in airway diseases. Curr. Mol. Med. 2008, 8, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rate, A.; Bosco, A.; McKenna, K.L.; Holt, P.G.; Upham, J.W. Airway epithelial cells condition dendritic cells to express multiple immune surveillance genes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallal, L.E.; Schaller, M.A.; Lindell, D.M.; Lira, S.A.; Lukacs, N.W. CCL20/CCR6 blockade enhances immunity to RSV by impairing recruitment of DC. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.C.; Ziegler, S.F. Inducible expression of the proallergic cytokine thymic stromal lymphopoietin in airway epithelial cells is controlled by NFkappaB. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Liao, S.; Chen, F.; Yang, Q.; Wang, D.Y. Role of IL-25, IL-33, and TSLP in triggering united airway diseases toward type 2 inflammation. Allergy 2020, 75, 2794–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Cao, P.P.; Zeng, M.; Zhen, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.N.; Hu, C.Y.; Ma, J.; Li, Z.Y.; Song, J.; et al. Interaction of thymic stromal lymphopoietin, IL-33, and their receptors in epithelial cells in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Allergy 2015, 70, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paplinska-Goryca, M.; Misiukiewicz-Stepien, P.; Nejman-Gryz, P.; Proboszcz, M.; Mlacki, M.; Gorska, K.; Krenke, R. Epithelial-macrophage-dendritic cell interactions impact alarmins expression in asthma and COPD. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 215, 108421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allakhverdi, Z.; Comeau, M.R.; Jessup, H.K.; Yoon, B.R.; Brewer, A.; Chartier, S.; Paquette, N.; Ziegler, S.F.; Sarfati, M.; Delespesse, G. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin is released by human epithelial cells in response to microbes, trauma, or inflammation and potently activates mast cells. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezato, R.; Perez-Novo, C.A.; Holtappels, G.; De Ruyck, N.; Van Crombruggen, K.; De Vos, G.; Bachert, C.; Derycke, L. The expression of dendritic cell subsets in severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps is altered. Immunobiology 2014, 219, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Schryver, E.; Devuyst, L.; Derycke, L.; Dullaers, M.; Van Zele, T.; Bachert, C.; Gevaert, P. Local immunoglobulin e in the nasal mucosa: Clinical implications. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2015, 7, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miljkovic, D.; Psaltis, A.; Wormald, P.J.; Vreugde, S. Naive and effector B-cell subtypes are increased in chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2018, 32, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulse, K.E.; Norton, J.E.; Suh, L.; Zhong, Q.; Mahdavinia, M.; Simon, P.; Kern, R.C.; Conley, D.B.; Chandra, R.K.; Tan, B.K.; et al. Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps is characterized by B-cell inflammation and EBV-induced protein 2 expression. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 1075–1083.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.P.; Li, H.B.; Wang, B.F.; Wang, S.B.; You, X.J.; Cui, Y.H.; Wang, D.Y.; Desrosiers, M.; Liu, Z. Distinct immunopathologic characteristics of various types of chronic rhinosinusitis in adult Chinese. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 478–484.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, J.Y.; Nayak, J.V.; Hulse, K.E.; Stevens, W.W.; Raju, P.A.; Huang, J.H.; Suh, L.A.; Van Roey, G.A.; Norton, J.E.; Carter, R.G.; et al. Evidence for altered levels of IgD in the nasal airway mucosa of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 1562–1571.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.K.; Li, Q.Z.; Suh, L.; Kato, A.; Conley, D.B.; Chandra, R.K.; Zhou, J.; Norton, J.; Carter, R.; Hinchcliff, M.; et al. Evidence for intranasal antinuclear autoantibodies in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 1198–1206.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Schryver, E.; Calus, L.; Bonte, H.; Natalie, R.; Gould, H.; Donovan, E.; Elewaut, D.; Valenta, R.; Mittermann, I.; Gutermuth, J.; et al. The quest for autoreactive antibodies in nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 893–895.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, G.; Kim, D.K.; Dhong, H.J.; Eun, K.M.; Lee, K.E.; Kong, I.G.; Kim, H.; Chung, S.K.; Kim, D.Y.; Rhee, C.S.; et al. Immunological Characteristics in Refractory Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps Undergoing Revision Surgeries. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2019, 11, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Huang, J.H.; Price, C.P.E.; Schauer, J.M.; Suh, L.A.; Harmon, R.; Conley, D.B.; Welch, K.C.; Kern, R.C.; Shintani-Smith, S.; et al. Prognostic factors for polyp recurrence in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 352–361.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Roey, G.A.; Vanison, C.C.; Wu, J.; Huang, J.H.; Suh, L.A.; Carter, R.G.; Norton, J.E.; Shintani-Smith, S.; Conley, D.B.; Welch, K.C.; et al. Classical complement pathway activation in the nasal tissue of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 89–100.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; He, B.; Chiu, A.; Chadburn, A.; Shan, M.; Buldys, M.; Ding, A.; Knowles, D.M.; Santini, P.A.; Cerutti, A. Epithelial cells trigger frontline immunoglobulin class switching through a pathway regulated by the inhibitor SLPI. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Williams, L.K.; Kato, A.; Peterson, E.L.; Favoreto, S., Jr.; Hulse, K.; Wang, D.; Beckman, K.; Thyne, S.; LeNoir, M.; et al. Genetic variation in B cell-activating factor of the TNF family (BAFF) and asthma exacerbations among African American subjects. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 996–999.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alturaiki, W. The roles of B cell activation factor (BAFF) and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL) in allergic asthma. Immunol. Lett. 2020, 225, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Truong-Tran, A.Q.; Scott, A.L.; Matsumoto, K.; Schleimer, R.P. Airway epithelial cells produce B cell-activating factor of TNF family by an IFN-beta-dependent mechanism. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 7164–7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilidaer; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Hu, L.; Han, M.; Wang, D.; Li, H. Increased BAFF expression in nasal polyps is associated with local IgE production, Th2 response and concomitant asthma. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 274, 1883–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Sun, C.; Luo, X.; Han, M.; Zhou, L.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Luo, R.; Li, H. Elevated B cell-activating factor (BAFF) in children with allergic rhinitis. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 78, 2156–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Li, M.; Zheng, J.; Zhan, J.; Zheng, H.; Li, R.; Wei, X. Circulating BAFF as novel biomarker in distinguishing chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps endotypes and predicting postoperative recurrence. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 104, 108515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurosawa, S.; Myers, A.C.; Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Ni, J.; Plitt, J.R.; Heller, N.M.; Bochner, B.S.; Schleimer, R.P. Expression of the costimulatory molecule B7-H2 (inducible costimulator ligand) by human airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003, 28, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.V.; Maris, C.H.; Hipkiss, E.L.; Flies, A.S.; Zhen, L.; Tuder, R.M.; Grosso, J.F.; Harris, T.J.; Getnet, D.; Whartenby, K.A.; et al. Role of PD-1 and its ligand, B7-H1, in early fate decisions of CD8 T cells. Blood 2007, 110, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saatian, B.; Yu, X.Y.; Lane, A.P.; Doyle, T.; Casolaro, V.; Spannhake, E.W. Expression of genes for B7-H3 and other T cell ligands by nasal epithelial cells during differentiation and activation. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2004, 287, L217–L225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Myers, A.C.; Chen, L.; Pardoll, D.M.; Truong-Tran, Q.A.; Lane, A.P.; McDyer, J.F.; Fortuno, L.; Schleimer, R.P. Constitutive and inducible expression of b7 family of ligands by human airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2005, 33, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.S. The role of the T cell in asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witherden, D.A.; Havran, W.L. Molecular aspects of epithelial gammadelta T cell regulation. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acacia de Sa Pinheiro, A.; Morrot, A.; Chakravarty, S.; Overstreet, M.; Bream, J.H.; Irusta, P.M.; Zavala, F. IL-4 induces a wide-spectrum intracellular signaling cascade in CD8+ T cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohn, L.; Elias, J.A.; Chupp, G.L. Asthma: Mechanisms of disease persistence and progression. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 22, 789–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Lee, H.J.; Im, N.R.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, H.K.; Kang, C.Y.; Park, I.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.M.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Decreased expression of CCL17 in the disrupted nasal polyp epithelium and its regulation by IL-4 and IL-5. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschberg, A.; Kiss, M.; Kadocsa, E.; Polyanka, H.; Szabo, K.; Razga, Z.; Bella, Z.; Tiszlavicz, L.; Kemeny, L. Different activations of toll-like receptors and antimicrobial peptides in chronic rhinosinusitis with or without nasal polyposis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 273, 1779–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Chi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Lv, Z.; Wang, J.; Yuan, L.; Huang, P.; et al. Kinetics of the accumulation of group 2 innate lymphoid cells in IL-33-induced and IL-25-induced murine models of asthma: A potential role for the chemokine CXCL16. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingler, A.I.; Stevens, W.W.; Tan, B.K.; Peters, A.T.; Poposki, J.A.; Grammer, L.C.; Welch, K.C.; Smith, S.S.; Conley, D.B.; Kern, R.C.; et al. Mechanisms and biomarkers of inflammatory endotypes in chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 1306–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Tang, X.Y.; Yang, Y.C.; Ke, X.; Kou, W.; Pan, C.K.; Hong, S.L. Impaired balance of Th17/Treg in patients with nasal polyposis. Scand. J. Immunol. 2011, 74, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Watanabe, S.; Sivam, A.; Wang, J.; Neuwirth, S.J.; Perez, R.I.; De Tineo, M.; Baroody, F.M.; Naclerio, R.M.; Pinto, J.M. Peripheral blood and tissue T regulatory cells in chronic rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2012, 26, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, C.; Schmidtmann, I.; Bopp, T.; Brieger, J.; Fruth, K. Treg activation and their role in different subtypes of chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergy 2020, 75, 2687–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.M.; Munoz, A.; Hwang, P.H.; Nadeau, K.C. Migration of regulatory T cells toward airway epithelial cells is impaired in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 137, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Vizuet, R.; Vega-Miranda, A.; Valencia-Maqueda, E.; Negrete-García, M.C.; Velásquez, J.R.; Teran, L.M. CC chemokine ligand 1 is released into the airways of atopic asthmatics. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettelli, E.; Carrier, Y.; Gao, W.; Korn, T.; Strom, T.B.; Oukka, M.; Weiner, H.L.; Kuchroo, V.K. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature 2006, 441, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Huang, C.; Zhou, B.; Ziegler, S.F. Isoform-specific inhibition of ROR alpha-mediated transcriptional activation by human FOXP3. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 4785–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Lopes, J.E.; Chong, M.M.; Ivanov, I.I.; Min, R.; Victora, G.D.; Shen, Y.; Du, J.; Rubtsov, Y.P.; Rudensky, A.Y.; et al. TGF-beta-induced Foxp3 inhibits T(H)17 cell differentiation by antagonizing RORgammat function. Nature 2008, 453, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poddighe, D.; Vangelista, L. Staphylococcus aureus Infection and Persistence in Chronic Rhinosinusitis: Focus on Leukocidin ED. Toxins 2020, 12, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W. Asthma Phenotype with Metabolic Dysfunction. Yonsei Med. J. 2022, 63, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulkerson, P.C.; Rothenberg, M.E. Targeting eosinophils in allergy, inflammation and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venge, P. The eosinophil and airway remodelling in asthma. Clin. Respir. J. 2010, 4 (Suppl. S1), 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wetering, S.; Zuyderduyn, S.; Ninaber, D.K.; van Sterkenburg, M.A.; Rabe, K.F.; Hiemstra, P.S. Epithelial differentiation is a determinant in the production of eotaxin-2 and -3 by bronchial epithelial cells in response to IL-4 and IL-13. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Ou, H.; Wu, F.; Ma, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Dang, H.; Zou, H. Interleukin-4-induced posttranscriptional gene regulation of CCL26 by the RNA-binding protein HuR in primary human nasal polyp-derived epithelial cells. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zeng, M.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, X.; Trudeau, J.B.; Goldschmidt, E.; Moore, J.A.; Chu, H.; Zhang, W.; et al. 15-Lipoxygenase 1 in nasal polyps promotes CCL26/eotaxin 3 expression through extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 1228–1241.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabayashi, T.; Kato, A.; Peters, A.T.; Suh, L.A.; Carter, R.; Norton, J.; Grammer, L.C.; Tan, B.K.; Chandra, R.K.; Conley, D.B.; et al. Glandular mast cells with distinct phenotype are highly elevated in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 410–420.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.P.; Zhang, Y.N.; Liao, B.; Ma, J.; Wang, B.F.; Wang, H.; Zeng, M.; Liu, W.H.; Schleimer, R.P.; Liu, Z. Increased local IgE production induced by common aeroallergens and phenotypic alteration of mast cells in Chinese eosinophilic, but not non-eosinophilic, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2014, 44, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavinia, M.; Carter, R.G.; Ocampo, C.J.; Stevens, W.; Kato, A.; Tan, B.K.; Kern, R.C.; Conley, D.B.; Chandra, R.; Hulse, K.E.; et al. Basophils are elevated in nasal polyps of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis without aspirin sensitivity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1759–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, A. Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Airway Diseases. Chest 2019, 156, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, W.W.; Kato, A. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells in nasal polyposis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 126, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzanka, A.; Misiołek, M.; Golusiński, W.; Jarząb, J. Molecular mechanisms of glucocorticoids action: Implications for treatment of rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2011, 268, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, K.; Chong, L.Y.; Hopkins, C.; Philpott, C.; Schilder, A.G.; Burton, M.J. Short-course oral steroids as an adjunct therapy for chronic rhinosinusitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 4, CD011992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ow, R.A.; McGinnis, J.P., 2nd; Sacks, H.J.; Mehle, M.E. The Effect of EDS-FLU on Objective and Patient-Reported Subjective Outcomes for Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Ear Nose Throat J. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachert, C.; Zhang, N.; Cavaliere, C.; Weiping, W.; Gevaert, E.; Krysko, O. Biologics for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 725–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.K.; Bachert, C.; Fokkens, W.; Desrosiers, M.; Wagenmann, M.; Lee, S.E.; Smith, S.G.; Martin, N.; Mayer, B.; Yancey, S.W.; et al. Mepolizumab for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (SYNAPSE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diver, S.; Khalfaoui, L.; Emson, C.; Wenzel, S.E.; Menzies-Gow, A.; Wechsler, M.E.; Johnston, J.; Molfino, N.; Parnes, J.R.; Megally, A.; et al. Effect of tezepelumab on airway inflammatory cells, remodelling, and hyperresponsiveness in patients with moderate-to-severe uncontrolled asthma (CASCADE): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 1299–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachert, C.; Mannent, L.; Naclerio, R.M.; Mullol, J.; Ferguson, B.J.; Gevaert, P.; Hellings, P.; Jiao, L.; Wang, L.; Evans, R.R.; et al. Effect of Subcutaneous Dupilumab on Nasal Polyp Burden in Patients With Chronic Sinusitis and Nasal Polyposis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 315, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, P.; Saenz, R.; Corren, J.; Han, J.K.; Mullol, J.; Lee, S.E.; Ow, R.A.; Zhao, R.; Howard, M.; Wong, K.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of omalizumab for nasal polyposis in an open-label extension study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 957–965.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ha, J.-G.; Cho, H.-J. Unraveling the Role of Epithelial Cells in the Development of Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814229
Ha J-G, Cho H-J. Unraveling the Role of Epithelial Cells in the Development of Chronic Rhinosinusitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(18):14229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814229
Chicago/Turabian StyleHa, Jong-Gyun, and Hyung-Ju Cho. 2023. "Unraveling the Role of Epithelial Cells in the Development of Chronic Rhinosinusitis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 18: 14229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814229
APA StyleHa, J.-G., & Cho, H.-J. (2023). Unraveling the Role of Epithelial Cells in the Development of Chronic Rhinosinusitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(18), 14229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814229




