Differentially Expressed Genes and Signalling Pathways Regulated by High Selenium Involved in Antioxidant and Immune Functions of Goats Based on Transcriptome Sequencing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Apparent Digestibility
2.2. Plasma Biochemical and Antioxidant Activity Parameters
2.3. Muscle Immune Parameters and Oxidation Products
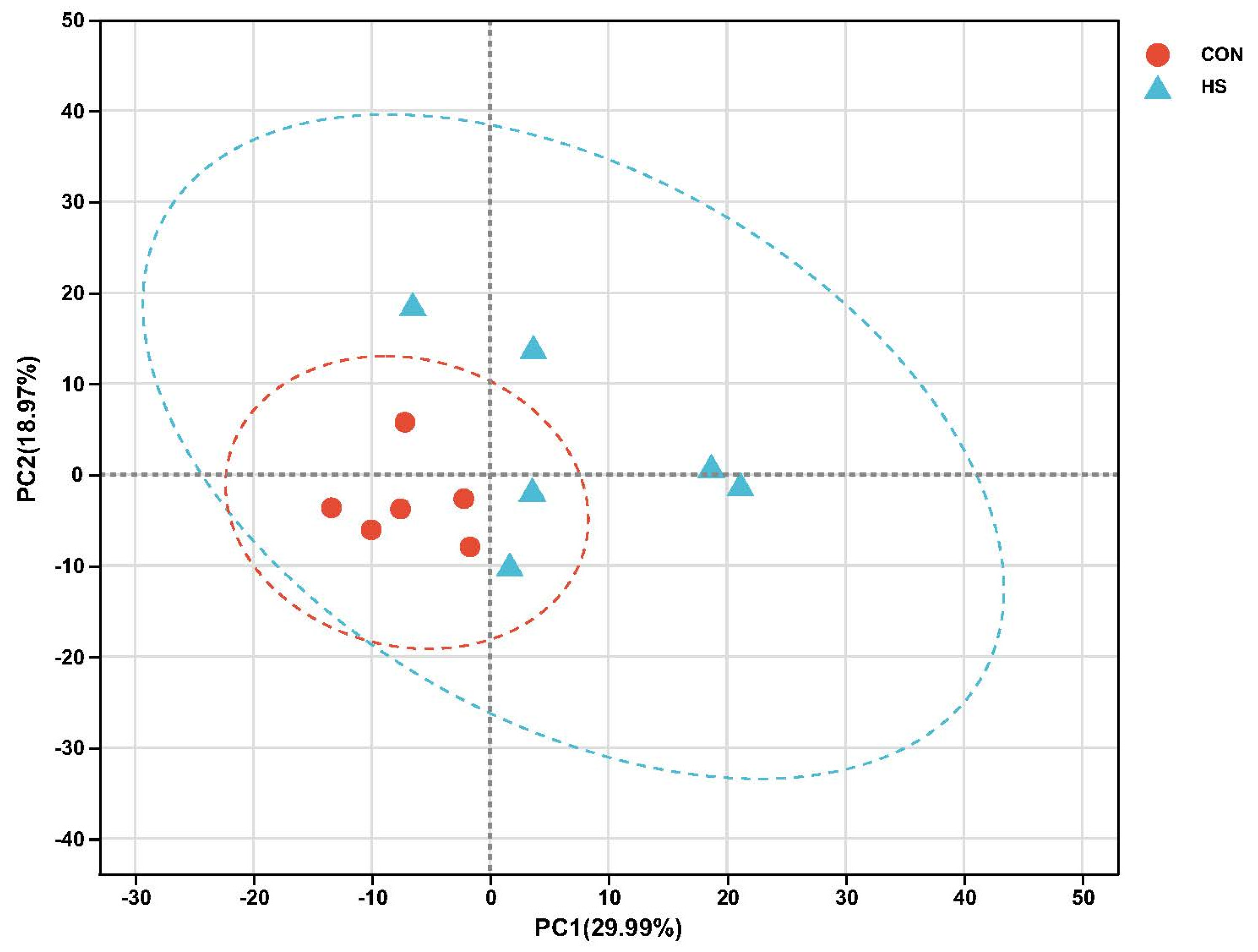
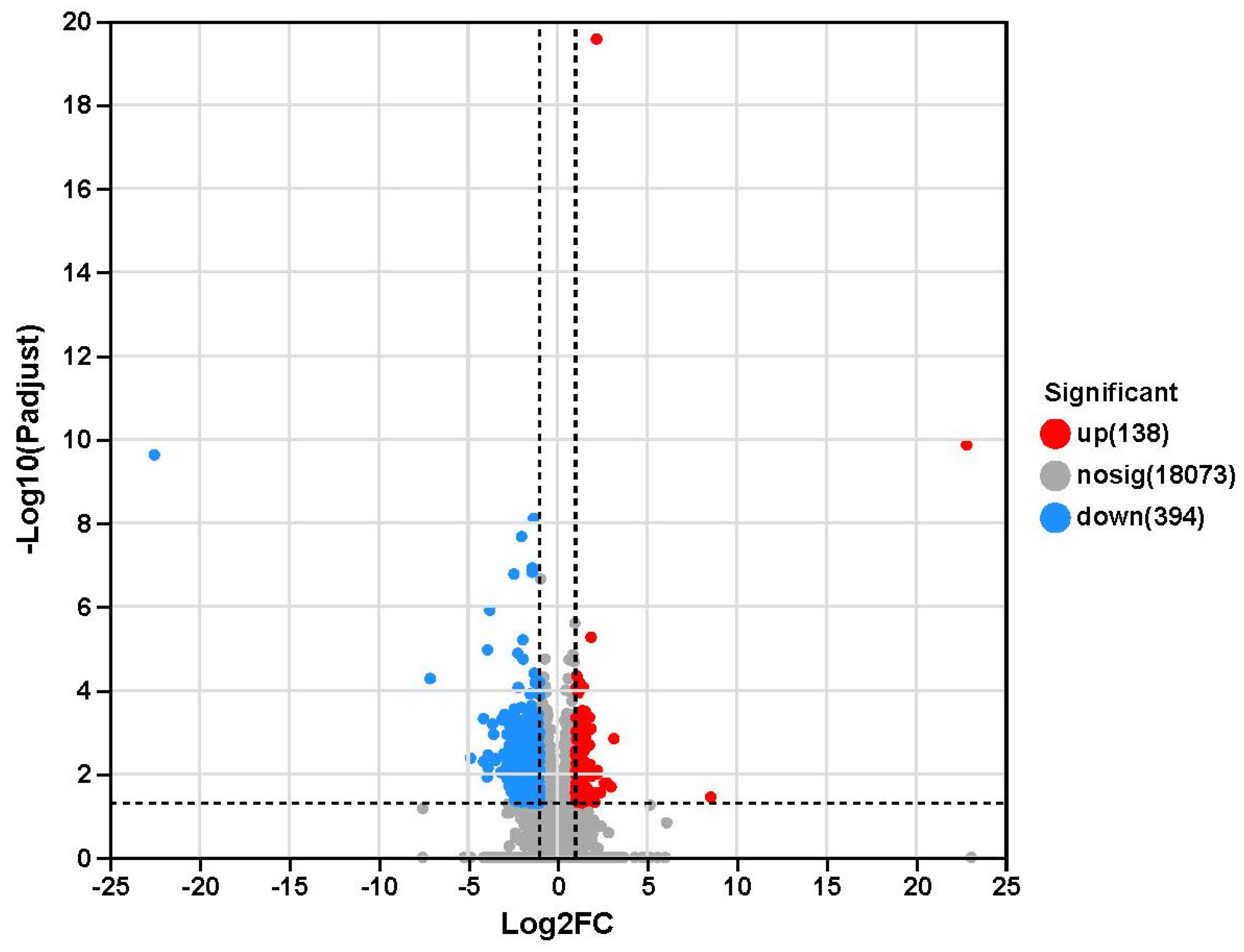
2.4. Transcriptome Sequencing Results
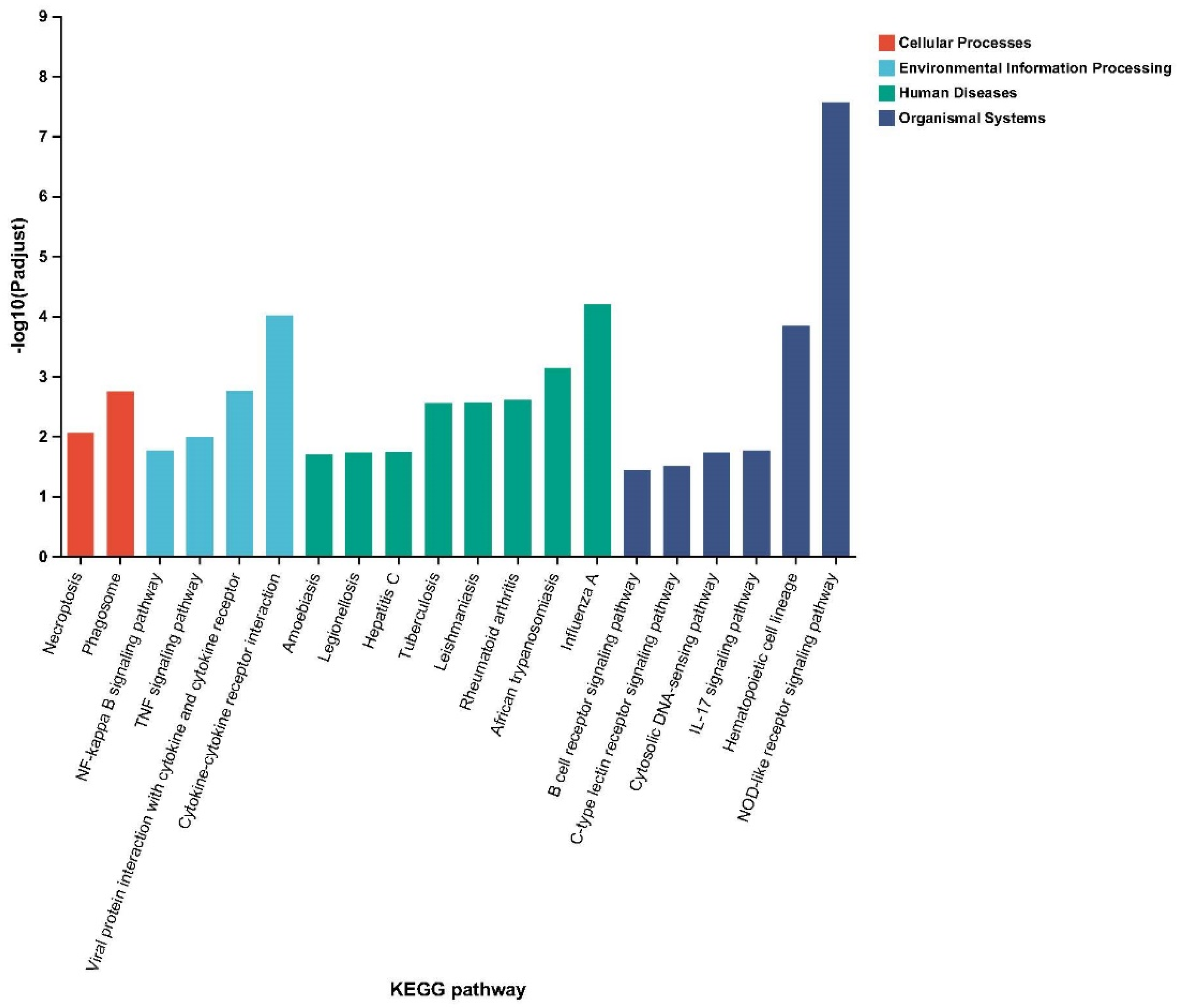
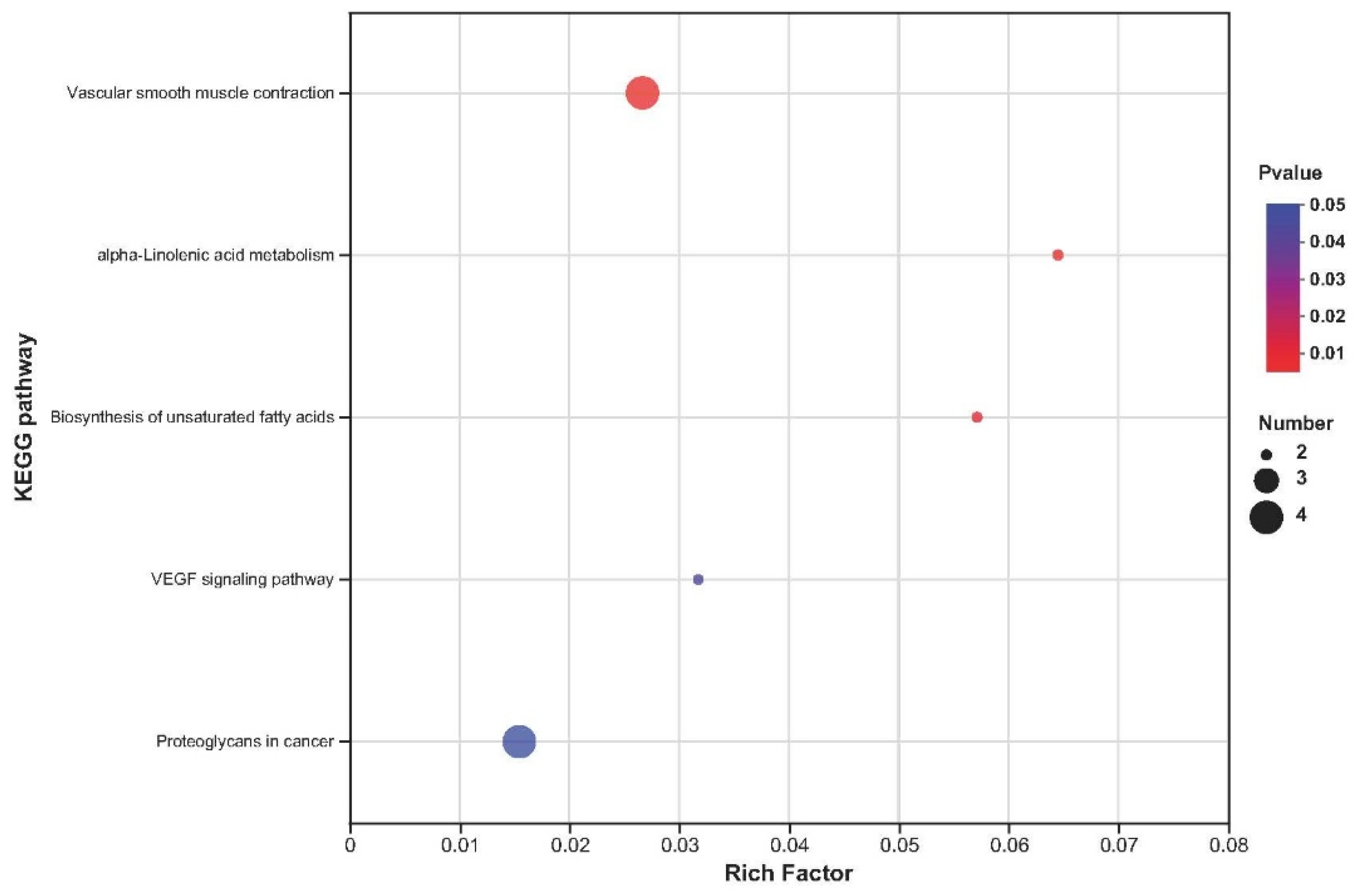
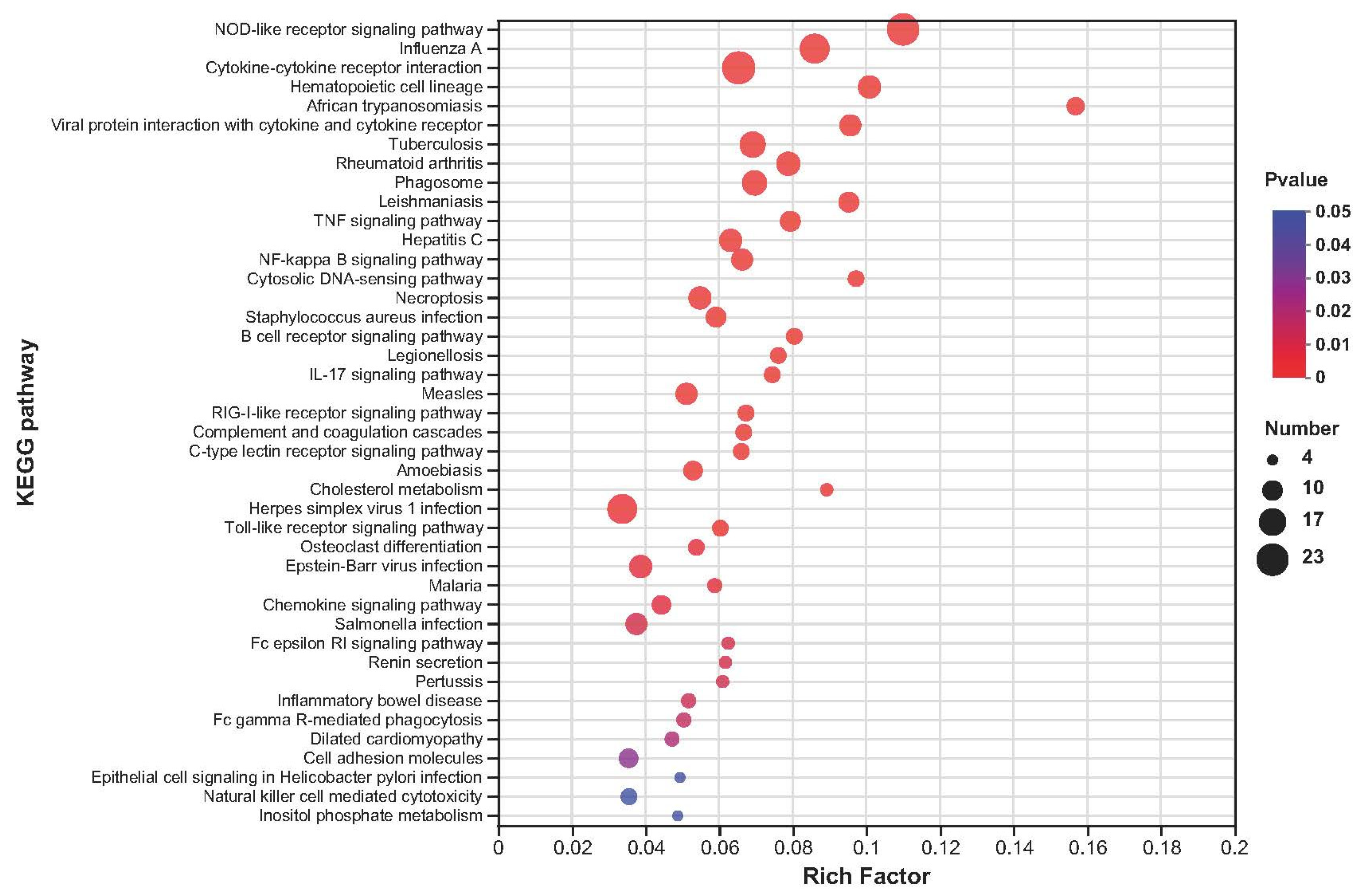
2.5. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes Enrichment Analysis
2.6. Gene Ontology Enrichment Analysis
2.7. Expression of Genes Related to Antioxidant Activity
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Experimental Design, Animals, and Diets
5.2. Chemical Composition
5.3. Apparent Digestibility
5.4. Plasma Biochemical and Antioxidant Activity Parameters
5.5. Muscle Immune and Oxidation Parameters
5.6. Transcriptome
5.6.1. RNA Extraction
5.6.2. Library Preparation and Illumina HiSeq xten/Nova Seq 6000 Sequencing
5.6.3. Read Mapping
5.6.4. Differential Expression Analysis and Functional Enrichment
5.6.5. Identification of Alternative Splicing Events
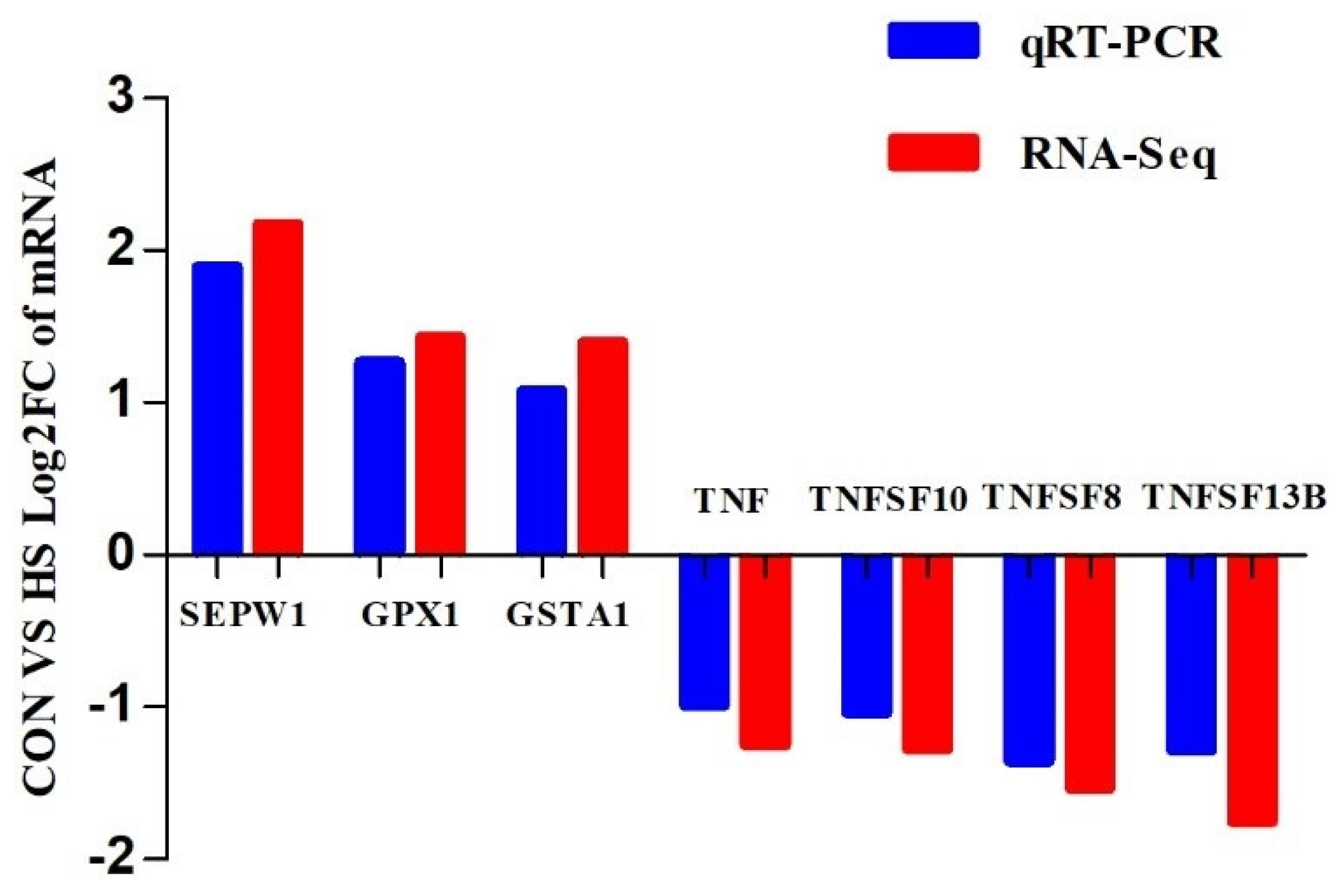
5.7. Validation of RNA-Seq Results via Real−Time PCR
5.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mazur, M.; Zwyrzykowska-Wodzińska, A.; Wojtas, E.; Zachwieja, A.; Salejda, A.M. Effect of yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis A. St.-Hil.) supplementation on oxidative stress in ruminants. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2019, 79, 316–322. [Google Scholar]
- Mattioli, G.A.; Rosa, D.E.; Turic, E.; Picco, S.J.; Raggio, S.J.; Minervino, A.H.H.; Fazzio, L.E. Effects of parenteral supplementation with minerals and vitamins on oxidative stress and humoral immune response of weaning calves. Animals 2020, 10, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wichtel, J.J. A review of selenium deficiency in grazing ruminants. part 1: New roles for selenium in ruminant metabolism. N. Z. Vet. J. 1998, 46, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrauzer, G.N. Selenium yeast: Composition, quality, analysis, and safety. Pure Appl. Chem. 2006, 78, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandour, A.S.; Samir, H.; El-Beltagy, M.A.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Izumi, W.; Ma, D.; Matsuura, K.; Tanaka, R.; Watanabe, G. Effect of supra-nutritional selenium-enriched probiotics on hematobiochemical, hormonal, and Doppler hemodynamic changes in male goats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 19447–19460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čobanová, K.; Faix, Š.; Plachá, I.; Mihaliková, K.; Váradyová, Z.; Kišidayová, S.; Grešáková, Ľ. Effects of different dietary selenium sources on antioxidant status and blood phagocytic activity in sheep. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 175, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, K.; Tang, C.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Effects of dietary supplementation with different levels of selenium yeast on growth performance, carcass characteristics, antioxidant capacity, and meat quality of Tan sheep. Livest. Sci. 2022, 255, 104783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juniper, D.T.; Phipps, R.H.; Givens, D.I.; Jones, A.K.; Green, C.; Bertin, G. Tolerance of ruminant animals to high dose in-feed administration of a selenium-enriched yeast. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 86, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristaldi, L.A.; McDowell, L.R.; Buergelt, C.D.; Davis, P.A.; Wilkinson, N.S.; Martin, F.G. Tolerance of inorganic selenium in wether sheep. Small Rumin. Res. 2005, 56, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, P.R.; Berry, M.J. The influence of selenium on immune responses. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Pérez, A.; García-García, E.; Zavaleta-Mancera, A.; Ramírez-Bribiesca, J.E.; Revilla-Vázquez, A.; Hernández-Calva, L.M.; López-Arellano, R.; Cruz-Monterrosa, R.G. Designing and evaluation of sodium selenite nanoparticles in vitro to improve selenium absorption in ruminants. Vet. Res. Commun. 2010, 34, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, L.W. Designing mineral supplementation of forage programs for beef cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2000, 77, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsolak, F.; Milos, P.M. RNA sequencing: Advances, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, P.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; El-Samahy, M.A.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y. Dietary supplementation with metformin improves testis function and semen quality and increases antioxidants and autophagy capacity in goats. Theriogenology 2022, 188, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Yang, C.; Tan, Z.; He, Z. Changes of intestinal oxidative stress, inflammation, and gene expression in neonatal diarrhoea kids. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 598691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yue, W.; Lei, F. Effects of organic selenium (Se-enriched yeast) supplementation in gestation diet on antioxidant status, hormone profile and haemato-biochemical parameters in Taihang black goats. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2018, 238, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Dowell, L.R.; Davis, P.A.; Cristaldi, L.A.; Wilkinson, N.S.; Buergelt, C.D.; Van Alstyne, R. Selenium toxicity for ruminants–Paranoia or precaution? In Proceedings of the Florida Ruminant Nutrition Symposium Proceedings, Gainesville, FL, USA, 1–2 February 2005; pp. 38–49. [Google Scholar]
- Suganthi, R.; Ghosh, J.; Malik, P.; Awachat, V.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Pal, D.; Nongkhlaw, S. Effect of dietary organic selenium (Se) on immune response, hepatic antioxidant status, selenoprotein gene expression and meat oxidative stability in lambs. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2019, 28, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.Z.; Li, J.X.; Luo, Q.Y.; Wang, X.; Xiao, M.M.; Zhou, D.; Lu, Q.; Chen, X. Effect of supplementation with selenium-yeast on muscle antioxidant activity, meat quality, fatty acids and amino acids in goats. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 8, 813672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Luo, Q.; Ban, C.; Lu, Q. The effects of selenium on rumen fermentation parameters and microbial metagenome in goats. Fermentation 2022, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.A.; Ebeid, H.M.; Hassan, F. Revisiting the effects of different dietary sources of selenium on the health and performance of dairy animals: A review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 3319–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Wang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Chang, S.; Zheng, H.; Wang, H.; Yan, T.; Guru, T.; Hou, F. Selenium yeast dietary supplement affects rumen bacterial population dynamics and fermentation parameters of Tibetan sheep (Ovis aries) in Alpine meadow. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 663945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermauw, V.; Yisehak, K.; Dierenfeld, E.S.; Du Laing, G.; Buyse, J.; Wuyts, B.; Janssens, G.P.J. Effects of trace element supplementation on apparent nutrient digestibility and utilisation in grass-fed zebu (Bos indicus) cattle. Livest. Sci. 2013, 155, 225–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Cui, X.; Chang, S.; Xiao, X.; Yan, T.; Wang, H.; Hou, F. Effect of different levels of selenium yeast on the antioxidant status, nutrient digestibility, selenium balances and nitrogen metabolism of Tibetan sheep in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Small Rumin. Res. 2019, 180, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, A.; El-Zaiat, H.M.; Saber, A.M.; Anwer, M.M.; Sallam, S.M. Impact of organic selenium and vitamin E on rumen fermentation, milk production, feed digestibility, blood parameters and parasitic response of lactating goats. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2019, 21, 1793–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Li, K.; Zou, C.; Tong, C.; Sun, L.; Cao, Z.; Yang, S.; Lyu, Q. Selenium yeast alleviates ochratoxin A-induced hepatotoxicity via modulation of the PI3K/AKT and Nrf2/Keap1 signaling pathways in chickens. Toxins 2020, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesaratto, L.; Vascotto, C.; Calligaris, S.; Tell, G. The importance of redox state in liver damage. Ann. Hepatol. 2004, 3, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sordillo, L.M.; Mavangira, V. The nexus between nutrient metabolism, oxidative stress and inflammation in transition cows. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2014, 54, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, D.; Ceriello, A.; Paolisso, G. Diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease: Which role for oxidative stress? Metabolism 1995, 44, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Li, J.; Luo, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Zhou, D.; Xie, L.; Ban, C.; Lu, Q. Effects of purple corn anthocyanin on growth performance, meat quality, muscle antioxidant status, and fatty acid profiles in goats. Foods 2022, 11, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Gao, C.S.; Du, X.Y.; Zhao, L.; Niu, X.T.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, D.M. Effect of sub-chronic exposure to selenium and astaxanthin on Channa argus: Bioaccumulation, oxidative stress and inflammatory response. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, Y.; Dufrasne, I. Selenium in cattle: A review. Molecules 2016, 21, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Khan, M.Z.; Ma, Y.; Alugongo, G.M.; Ma, J.; Chen, T.; Khan, A.; Cao, Z. The antioxidant properties of selenium and vitamin E; their role in periparturient dairy cattle health regulation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Yoo, S.; Su, J.; Han, H.R.; Wang, M.; Qu, W.; Zhong, D. Effects of selenium, copper and magnesium on antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation in bovine fluorosis. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. 2004, 17, 1695–1699. [Google Scholar]
- Sathya, A.; Prabhakar, S.; Sangha, S.P.S.; Ghuman, S.P.S. Vitamin E and selenium supplementation reduces plasma cortisol and oxidative stress in Dystocia-affected buffaloes. Vet. Res. Commun. 2007, 31, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiremidjian-Schumacher, L.; Stotzky, G. Selenium and immune responses. Environ. Res. 1987, 42, 277–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galbraith, M.L.; Vorachek, W.R.; Estill, C.T.; Whanger, P.D.; Bobe, G.; Davis, T.Z.; Hall, J.A. Rumen microorganisms decrease bioavailability of inorganic selenium supplements. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 171, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoda, K.; Kuramoto, K.; Eruden, B.; Nishida, T.; Shioya, S. The effects of three herbs as feed supplements on blood metabolites, hormones, antioxidant activity, IgG concentration, and ruminal fermentation in Holstein steers. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. 2006, 19, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Xun, W.; Yue, W.; Zhang, C.; Ren, Y.; Lei, S.; Wang, Q.; Yang, R.; Lei, F. Effect of sodium selenite, Se-yeast and nano-elemental selenium on growth performance, Se concentration and antioxidant status in growing male goats. Small Rumin. Res. 2011, 96, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arain, M.; Kamboh, A.A.; Arshed, M.J. Effects of selenium supplementation on hematological profile, gut microflora composition, in vitro biofilm formation assay and serum IgG concentration in goats. Pak. J. Zool. 2022, 54, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Miao, E.A.; Ting, J.P.Y. Mechanisms of NOD-like receptor-associated inflammasome activation. Immunity 2013, 39, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Lv, H.; Wen, Z.; Ci, X.; Peng, L. Isoliquiritigenin activates nuclear factor erythroid-2 related factor 2 to suppress the NOD-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome and inhibits the NF-κB pathway in macrophages and in acute lung injury. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sordillo, L.M. Selenium-dependent regulation of oxidative stress and immunity in periparturient dairy cattle. Vet. Med. Int. 2013, 2013, 154045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Cui, X.; Xu, W.; Fang, S.; Li, Z.; Lu, M.; Wu, Y.; Ma, X.; Chi, X.; et al. Ginseng stem-leaf saponins in combination with selenium promote the immune response in neonatal mice with maternal antibody. Vaccines 2020, 8, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlata, L.; Misurova, L.; Pechova, A.; Dvorak, R. The effect of inorganic and organically bound forms of selenium on glutathione peroxidase activity in the blood of goats. Vet. Med. 2011, 56, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaoka, M.; Ooka, R.; Nakazato, T.; Yoshida, S.; Oishi, S. Synthesis of selenocysteine and selenomethionine derivatives from sulfur-containing amino acids. Chem. Biodivers. 2008, 5, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M.P. The use of high-selenium yeast to raise selenium status: How does it measure up? Brit. J. Nutr. 2004, 92, 557–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Liu, J.; Du, X.; Zhang, J.; Pan, K.; Shan, W.; Xie, Y.; Song, W.; Zhao, J. The protective effects of selenium supplementation on ambient PM2.5-induced cardiovascular injury in rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 22153–22162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammerman, C.B.; Miller, S.M. Selenium in ruminant nutrition: A review. J. Dairy Sci. 1975, 58, 1561–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surai, P.F.; Kochish, I.I.; Fisinin, V.I.; Juniper, D.T. Revisiting oxidative stress and the use of organic selenium in dairy cow nutrition. Animals 2019, 9, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spears, J.W.; Weiss, W.P. Role of antioxidants and trace elements in health and immunity of transition dairy cows. Vet. J. 2008, 176, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ÇİÇek, S.; Turhan, S.; Sevda, I.Ş. Application of selenium nanoparticles diets in ruminants. Atatürk Üniv. Ziraat Fakültesi Derg. 2021, 52, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, J. TNF-mediated inflammatory disease. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosnedlova, B.; Kepinska, M.; Skalickova, S.; Fernandez, C.; Ruttkay-Nedecky, B.; Malevu, T.D.; Sochor, J.; Baron, M.; Melcova, M.; Zidkova, J.; et al. A summary of new findings on the biological effects of selenium in selected animal species—A critical review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddox, J.F.; Aherne, K.M.; Reddy, C.C.; Sordillo, L.M. Increased neutrophil adherence and adhesion molecule mRNA expression in endothelial cells during selenium deficiency. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1999, 65, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.S.; Celi, P.; Fahri, F.T.; Leury, B.J.; Dunshea, F.R. Dietary antioxidants at supranutritional doses modulate skeletal muscle heat shock protein and inflammatory gene expression in sheep exposed to heat stress. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 4897–4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, S.S.; Ponnampalam, E.N.; Celi, P.; Hopkins, D.L.; Leury, B.J.; Dunshea, F.R. High dietary vitamin E and selenium improves feed intake and weight gain of finisher lambs and maintains redox homeostasis under hot conditions. Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 137, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Nutrient Requirements of Goats: Angora, Dairy, and Meat Goats in Temperate and Tropical Countries; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Association of Official Analytical Chemists Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed.; AOAC: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, X.Z.; Li, J.X.; Luo, Q.Y.; Zhou, D.; Long, Q.M.; Wang, X.; Lu, Q.; Wen, G.L. Effects of purple corn anthocyanin on blood biochemical indexes, ruminal fluid fermentation, and rumen microbiota in goats. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 715710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Item, % | Treatment | SEM | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | LS | HS | |||
| DM | 87.69 | 87.21 | 87.47 | 0.3803 | 0.6865 |
| OM | 74.97 | 77.20 | 76.32 | 0.6703 | 0.1371 |
| GE | 74.07 | 75.38 | 74.80 | 0.5289 | 0.2852 |
| CP | 69.77 | 71.40 | 68.62 | 1.0650 | 0.2555 |
| EE | 71.63 a | 72.07 a | 74.21 b | 0.3730 | 0.0058 |
| NDF | 53.28 | 54.56 | 57.16 | 2.7704 | 0.6250 |
| ADF | 48.60 | 50.67 | 49.14 | 1.3658 | 0.5707 |
| Item | Treatment | SEM | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | LS | HS | |||
| Glu (mmol/L) | 4.47 | 4.74 | 4.31 | 0.2052 | 0.3343 |
| UN (mmol/L) | 4.90 | 5.20 | 4.94 | 0.3118 | 0.7675 |
| ALT (U/L) | 5.07 | 5.24 | 5.78 | 0.3941 | 0.4888 |
| AST (U/L) | 31.92 a | 25.58 b | 20.17 c | 1.1854 | <0.0001 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.40 | 3.91 | 4.04 | 0.9733 | 0.6569 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 0.53 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.0639 | 0.8553 |
| Cr (μmol/L) | 67.24 | 64.83 | 66.45 | 2.5398 | 0.8008 |
| TP (gprot/L) | 4.20 a | 4.35 ab | 4.44 b | 0.0610 | 0.0246 |
| Alb (g/L) | 24.42 | 22.58 | 23.35 | 0.9950 | 0.4299 |
| TAC (U/mL) | 1.92 b | 2.15 b | 3.74 a | 0.3329 | 0.0054 |
| SOD (U/mL) | 16.94 | 17.19 | 17.47 | 0.6525 | 0.8475 |
| GPX (U/mL) | 330.88 | 331.37 | 342.77 | 6.1516 | 0.3130 |
| GSH (mg/L) | 4.73 | 5.71 | 4.31 | 0.4591 | 0.7397 |
| GST (U/mL) | 42.21 a | 64.55 b | 57.38 ab | 5.1805 | 0.0403 |
| CAT (U/mL) | 1.75 a | 2.87 b | 2.02 ab | 0.3068 | 0.0355 |
| MDA (nmol/mL) | 2.03 a | 0.72 b | 1.03 b | 0.2059 | 0.0061 |
| Item | CON | HS | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgA (μg/mL) | 85.86 | 79.94 | 4.3429 | 0.3896 |
| IgG (mg/mL) | 1.30 | 1.28 | 0.1738 | 0.9377 |
| IgM (μg/mL) | 440.20 a | 505.52 b | 10.0882 | 0.0486 |
| SEPP (ng/mL) | 8.43 | 7.56 | 1.2584 | 0.6500 |
| IL−1 (pg/mL) | 12.61 | 11.17 | 1.0881 | 0.4008 |
| NF-κB (pg/mL) | 4.69 a | 3.06 b | 0.3585 | 0.0322 |
| 8-OHdG (ng/mL) | 0.91 | 0.79 | 0.0753 | 0.3301 |
| NO (μmol/L) | 20.92 | 35.23 | 4.8268 | 0.1580 |
| O2− (U/L) | 201.98 a | 181.51 b | 4.5181 | 0.0094 |
| OH (U/mL) | 81.29 | 82.62 | 0.6687 | 0.1884 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Ban, C.; Li, J.-X.; Luo, Q.-Y.; Qin, J.-X.; Xu, Y.-Q.; Lu, Q.; Tian, X.-Z. Differentially Expressed Genes and Signalling Pathways Regulated by High Selenium Involved in Antioxidant and Immune Functions of Goats Based on Transcriptome Sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021124
Wang X, Ban C, Li J-X, Luo Q-Y, Qin J-X, Xu Y-Q, Lu Q, Tian X-Z. Differentially Expressed Genes and Signalling Pathways Regulated by High Selenium Involved in Antioxidant and Immune Functions of Goats Based on Transcriptome Sequencing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(2):1124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021124
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xu, Chao Ban, Jia-Xuan Li, Qing-Yuan Luo, Ji-Xiao Qin, Yi-Qing Xu, Qi Lu, and Xing-Zhou Tian. 2023. "Differentially Expressed Genes and Signalling Pathways Regulated by High Selenium Involved in Antioxidant and Immune Functions of Goats Based on Transcriptome Sequencing" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 2: 1124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021124
APA StyleWang, X., Ban, C., Li, J.-X., Luo, Q.-Y., Qin, J.-X., Xu, Y.-Q., Lu, Q., & Tian, X.-Z. (2023). Differentially Expressed Genes and Signalling Pathways Regulated by High Selenium Involved in Antioxidant and Immune Functions of Goats Based on Transcriptome Sequencing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(2), 1124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021124









