Genome-Wide Identification of the Odorant Receptor Gene Family and Revealing Key Genes Involved in Sexual Communication in Anoplophora glabripennis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Genome-Wide Identification of OR Genes in A. glabripennis
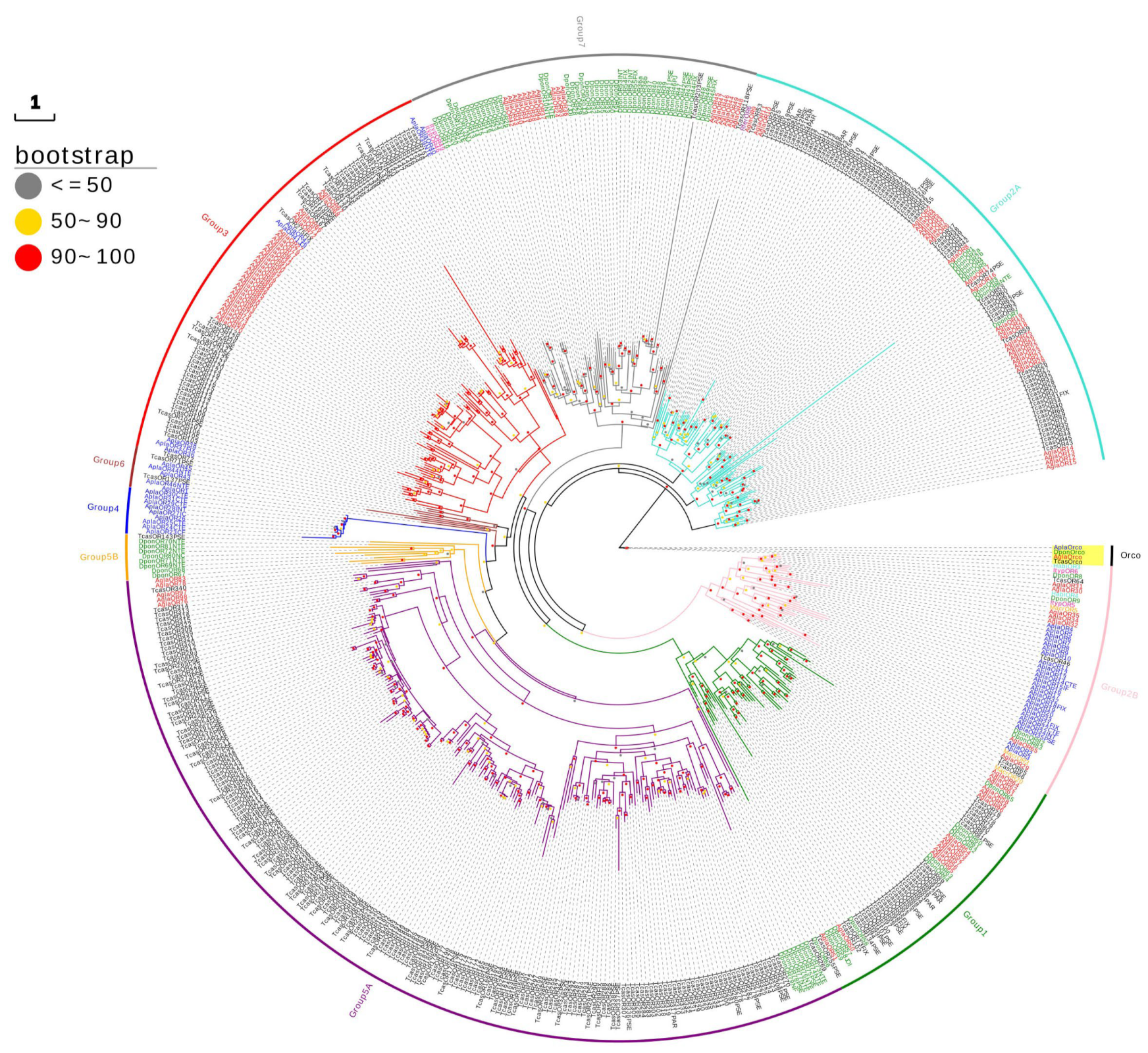
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of AglaORs
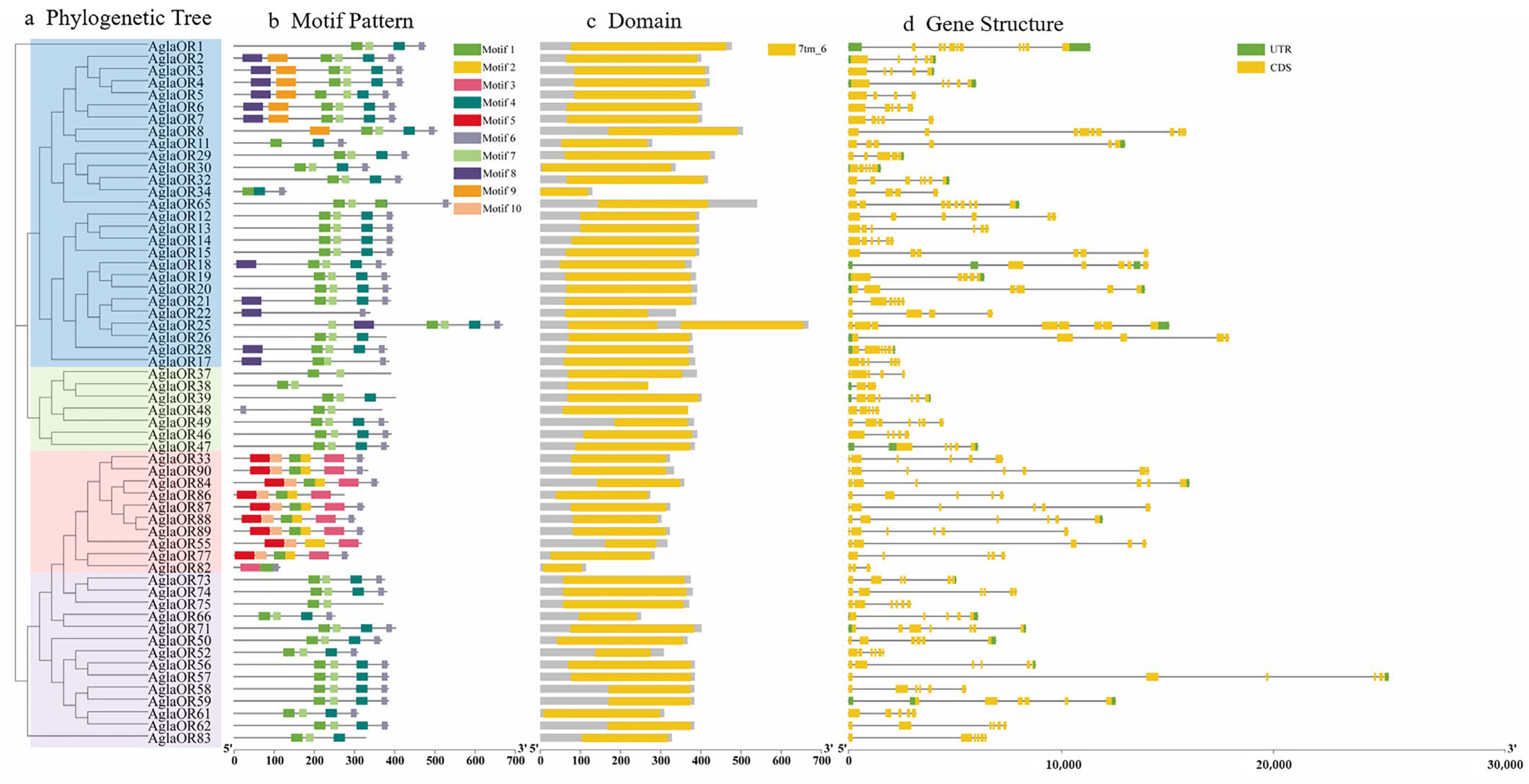
2.3. AglaOR Gene and Protein Structure
2.4. Spatial–Temporal Differential Expression Analysis of AglaORs
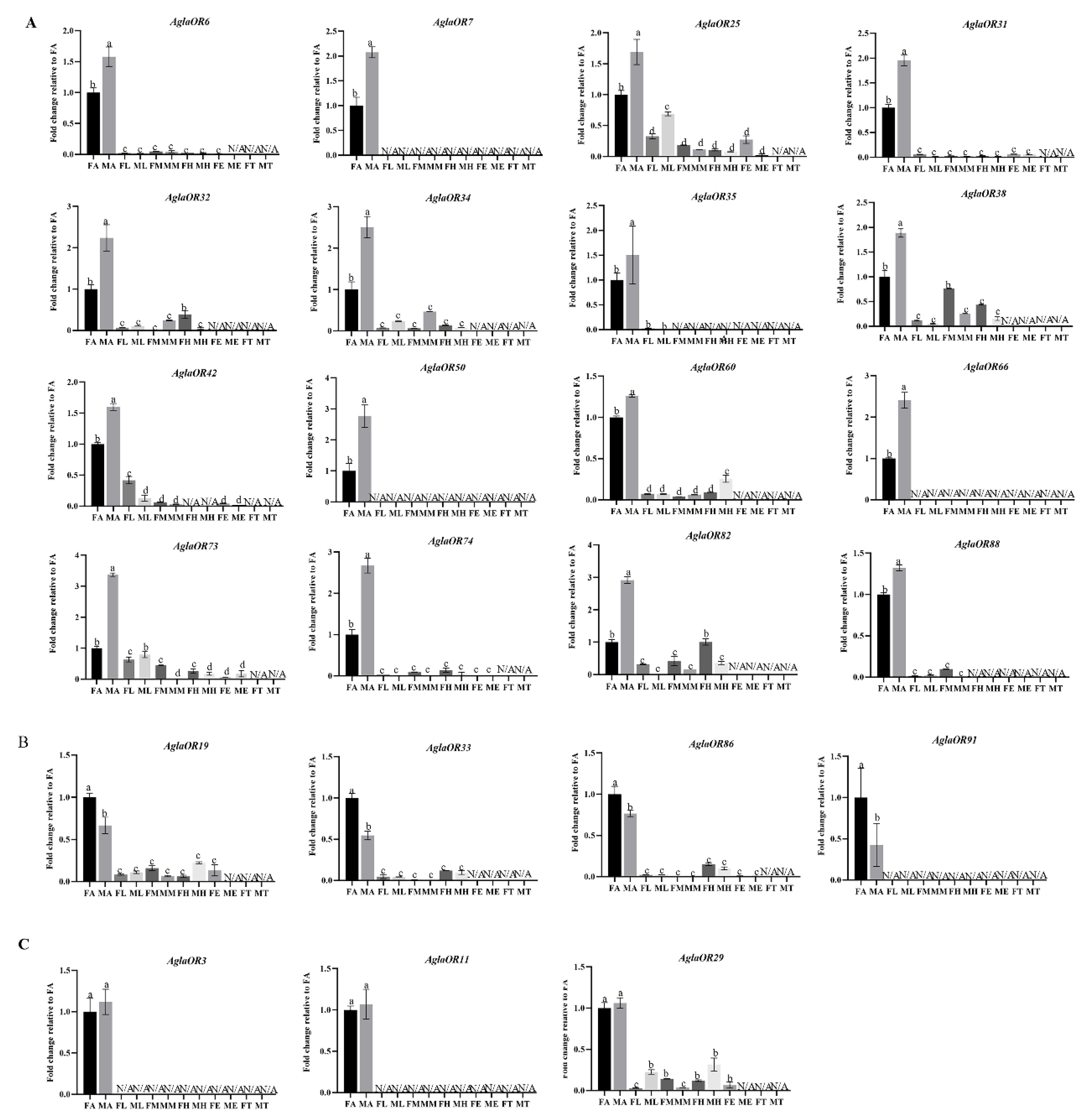
2.4.1. Analysis of Expression Pattern of AglaORs in Different Sex Tissues of Adults
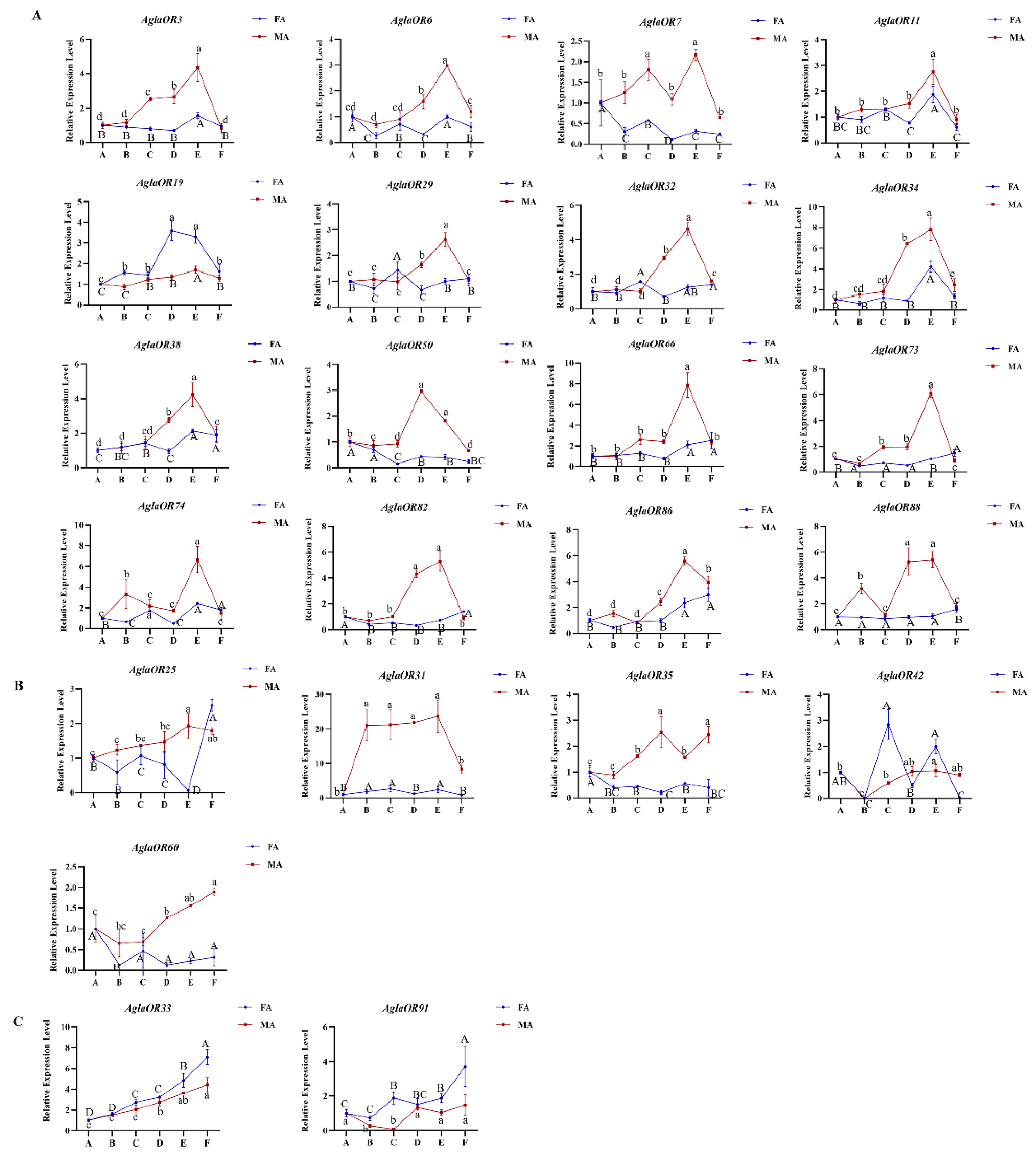
2.4.2. Analysis of Expression Patterns of AglaORs in Adults at Different Stages of Development
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification and Sequence Analysis of the AglaOR Gene Family
4.1.1. Identification of AglaOR Gene Family
4.1.2. Construction of Phylogenetic Tree
4.1.3. Structural Characteristics Analysis of AglaORs
4.2. Analysis of Expression Characteristics of AglaORs
4.2.1. Insect Collection and Processing
4.2.2. RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR Analysis
4.2.3. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hansson, B.S.; Stensmyr, M.C. Evolution of Insect Olfaction. Neuron 2011, 72, 698–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, S.W.; Liu, Y.; Jacquin-Joly, E.; Dong, S.L.; Wang, G.R. Identification and Functional Characterization of Sex Pheromone Receptors in the Common Cutworm (Spodoptera litura). Chem. Sens. 2015, 40, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaissling, K.E. Chemo-electrical transduction in insect olfactory receptors. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1986, 9, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, J.; Gänβle, H.; Raming, K. Odorant binding proteins of Heliothis virescens. Insect. Mol. Biol. 1993, 23, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallem, E.A.; Dahanukar, A.; Carlson, J.R. Insect odor and taste receptors. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2006, 51, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silbering, A.F.; Rytz, R.; Grosjean, Y.; Abuin, L.; Ramdya, P.; Jefferis, G.; Benton, R. Complementary Function and Integrated Wiring of the Evolutionarily Distinct Drosophila Olfactory Subsystems. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 13357–13375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, K.; Brady, R., Jr.; Cravchik, A.; Morozov, P.; Rzhetsky, A.; Zuker, C.; Axel, R. A chemosensory gene family encoding candidate gustatory and olfactory receptors in Drosophila. Cell 2001, 104, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touhara, K. Insect olfactory receptor complex functions as a ligand-gated lonotropic channel. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1170, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, L.; Axel, R. A novel multigene family may encode odorant receptors: A molecular basis for odor recognition. Cell 1991, 65, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troemel, E.R.; Chou, J.H.; Dwyer, N.D.; Colbert, H.A.; Bargmann, C.I. Divergent seven transmembrane receptors are candidate chemosensory receptors in C. elegans. Cell 1995, 83, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyne, P.J.; Warr, C.G.; Freeman, M.R.; Lessing, D.; Kim, J.; Carlson, J.R. A novel family of divergent seven-transmembrane proteins: Candidate odorant receptors in Drosophila. Neuron 1999, 22, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pierce, K.L.; Premont, R.T.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Seven-transmembrane receptors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 3, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benton, R.; Sachse, S.; Michnick, S.; Vosshall, L. Atypical membrane topology and heteromeric function of Drosophila odorant receptors in vivo. Chem. Sens. 2006, 31, A5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, K.; Pellegrino, M.; Nakagawa, T.; Nakagawa, T.; Vosshall, L.B.; Touhara, K. Insect Olfactory Receptors are Heteromeric Ligand-Gated Ion Channels. Chem. Sens. 2008, 33, S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicher, D.; Schafer, R.; Bauernfeind, R.; Stensmyr, M.C.; Heller, R.; Heinemann, S.H.; Hansson, B.S. Drosophila odorant receptors are both ligand-gated and cyclic-nucleotide-activated cation channels. Nature 2008, 452, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallem, E.A.; Carlson, J.R. Coding of odors by a receptor repertoire. Cell 2006, 125, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirkness, E.F.; Haas, B.J.; Sun, W.L.; Braig, H.R.; Perotti, M.A.; Clark, J.M. Genome sequences of the human body louse and its primary endosymbiont provide insights into the permanent parasitic lifestyle . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12168, Correction in Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6335–6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engsontia, P.; Sanderson, A.P.; Cobb, M.; Walden, K.K.O.; Robertson, H.M.; Brown, S. The red flour beetle’s large nose: An expanded odorant receptor gene family in Tribolium castaneum. Insect. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.F.; Schneider, T.M.; Schwartz, A.M.; Andersson, M.N.; McKenna, D.D. The diversity and evolution of odorant receptors in beetles (Coleoptera). Insect. Mol. Biol. 2020, 29, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ju, Q.; Jie, W.C.; Li, F.; Jiang, X.J.; Hu, J.J.; Qu, M.J. Chemosensory Gene Families in Adult Antennae of Anomala corpulenta Motschulsky (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Rutelinae). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121504. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, J.K.; Yang, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.X.; Liu, Y.; Xi, J.H. Identification of candidate chemosensory receptors in the antennal transcriptome of the large black chafer Holotrichia parallela Motschulsky (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 28, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.N.; Grosse-Wilde, E.; Keeling, C.I.; Bengtsson, J.M.; Yuen, M.M.S.; Li, M.; Hillbur, Y.; Bohlmann, J.; Hansson, B.S.; Schlyter, F. Antennal transcriptome analysis of the chemosensory gene families in the tree killing bark beetles, Ips typographus and Dendroctonus ponderosae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae). BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andersson, M.N.; Keeling, C.I.; Mitchell, R.F. Genomic content of chemosensory genes correlates with host range in wood-boring beetles (Dendroctonus ponderosae, Agrilus planipennis, and Anoplophora glabripennis). BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Li, D.Z.; Min, S.F.; Mi, F.; Zhou, S.S.; Wang, M.Q. Analysis of chemosensory gene families in the beetle Monochamus alternatus and its parasitoid Dastarcus helophoroides. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2014, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.F.; Hall, L.P.; Reagel, P.F.; McKenna, D.D.; Baker, T.C.; Hildebrand, J.G. Odorant receptors and antennal lobe morphology offer a new approach to understanding olfaction in the Asian longhorned beetle. J. Comp. Physiol. A. Neuroethol. Sens. Neural. Behav. Physiol. 2017, 203, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, R.F.; Hughes, D.T.; Luetje, C.W.; Millar, J.G.; Soriano-Agaton, F.; Hanks, L.M.; Robertson, H.M. Sequencing and characterizing odorant receptors of the cerambycid beetle Megacyllene caryae. Insect. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, H.B.; Wang, J.T.; Wen, M.; Xi, J.H.; Ren, B.Z. Identification and evolution of olfactory genes in the small poplar longhorn beetle Saperda populnea. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 26, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhu, J.Y.; Liu, N.Y. Identification and characterization of detoxification genes in two cerambycid beetles, Rhaphuma horsfieldi and Xylotrechus quadripes (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae: Clytini). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 243–244, 110431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.M.; Liu, Y.Y.; Chen, X.S. Genomic content of chemosensory receptors in two sister blister beetles facilitates characterization of chemosensory evolution. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, J.K.; Roberts, R.E.; Sonntag, Y.; Hou, X.Q.; Grosse-Wilde, E.; Machara, A.; Zhang, D.D.; Hansson, B.S.; Johanson, U.; Lofstedt, C.; et al. Putative ligand binding sites of two functionally characterized bark beetle odorant receptors. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.E.; Biswas, T.; Yuvaraj, J.K.; Grosse-Wilde, E.; Powell, D.; Hansson, B.S.; Lofstedt, C.; Andersson, M.N. Odorant receptor orthologues in conifer-feeding beetles display conserved responses to ecologically relevant odours. Mol. Ecol. 2022, 31, 3693–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, T.L.; Xu, Z.; Jia, Q.C.; Wang, G.R.; Hou, Y.M. Non-palm Plant Volatile alpha-Pinene Is Detected by Antenna-Biased Expressed Odorant Receptor 6 in the Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 701545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, L.; Xu, T.; Wickham, J.; Chen, Y.; Hao, D.; Hanks, L.M.; Millar, J.G.; Teale, S.A. Identification of a Male-Produced Pheromone Component of the Citrus Longhorned Beetle, Anoplophora chinensis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hérard, F.; Ciampitti, M.; Maspero, M.; Krehan, H.; Benker, U.; Boegel, C.; Schrage, R.; Bouhot-Delduc, L.; Bialooki, P. Anoplophora species in Europe: Infestations and management processes. EPPO Bull. 2006, 36, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javal, M.; Lombaert, E.; Tsykun, T.; Courtin, C.; Kerdelhué, C.; Prospero, S.; Roques, A.; Roux, G. Deciphering the worldwide invasion of the Asian long-horned beetle: A recurrent invasion process from the native area together with a bridgehead effect. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 951–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.D.; Liu, Y.N. Relationship among same-age sexual development, nutritional supplementation and mating in adult Anoplophora glabriformis. J. Northwest For. Univ. 1997, 4, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; Teale, S.A. Chemical Ecology of the Asian Longhorn Beetle, Anoplophora glabripennis. J. Chem. Ecol. 2021, 47, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, D.J.; Lance, D.R.; Mastro, V.C. Identification of a Potential Third Component of the Male-Produced Pheromone of Anoplophora glabripennis and its Effect on Behavior. J. Chem. Ecol. 2014, 40, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, A.; Oliver, J.E.; Aldrich, J.R.; Wang, B.; Mastro, V.C. Stimulatory beetle volatiles for the Asian longhorned beetle, Anoplophora glabripennis (Motschulsky). Z. Fur Nat. C. J. Biosci. 2002, 57, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.J.; Oliver, J.E.; Chauhan, K.; Zhao, B.G.; Xia, L.Q.; Xu, Z.C. Evidence for contact sex recognition pheromone of the Asian longhorned beetle, Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Naturwissenschaften 2003, 90, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Hansen, L.; Teale, S.A. Female calling behaviour in the Asian longhorned beetle (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Can. Entomol. 2019, 151, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.T.; Ge, X.Z.; Zou, Y.; Guo, S.W.; Wang, T.; Zong, S.X. Prediction of the potential global distribution of the Asian longhorned beetle Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) under climate change. Agric. For. Entomol. 2021, 23, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, J.D.; Xu, Z.C.; Teale, S.A. Evidence for a female-produced, long range pheromone of Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Insect. Sci. 2012, 19, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehme, M.E.; Keena, M.A.; Zhang, A.; Baker, T.C.; Hoover, K. Attraction of Anoplophora glabripennis to Male-Produced Pheromone and Plant Volatiles. Environ. Entomol. 2009, 38, 1745–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.J.; Wang, Z.N.; Qin, H.W.; Wang, D.P.; Shi, J. Effects of lures to trap Anoplophora glabripennis (Motschulsky) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in the coastal protection forest in Zhejiang, China. Environ. Entomol. 2017, 39, 694–700. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.G.W.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, W. Electroantennogram response of Anoplophora glabripennis (Motsch.) to Acernegundo volatiles. For. Pest Dis. 2016, 35, 9–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meng, P.S.; Trotter, R.T.; Keena, M.A.; Baker, T.C.; Yan, S.; Schwartzberg, E.G.; Hoover, K. Effects of Pheromone and Plant Volatile Release Rates and Ratios on Trapping Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in China. Environ. Entomol. 2014, 43, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.R.; Zhou, Q.; Hall, L.; Myrick, A.; Hoover, K.; Shields, K.; Baker, T.C. Olfactory Sensory Neurons of the Asian Longhorned Beetle, Anoplophora glabripennis, Specifically Responsive to its two Aggregation-Sex Pheromone Components. J. Chem. Ecol. 2018, 44, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Wang, J.Z.; Cui, M.M.; Tao, J.; Luo, Y.Q. Antennal transcriptome analysis of the Asian longhorned beetle Anoplophora glabripennis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, D.P.; Liu, Y.; Walker, W.B.; Li, J.H.; Wang, G.R. Molecular Characterization of the Aphis gossypii Olfactory Receptor Gene Families. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, H.B.; Ren, B.Z. Identification and Comparison of Candidate Olfactory Genes in the Olfactory and Non-Olfactory Organs of Elm Pest Ambrostoma quadriimpressum (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) Based on Transcriptome Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.F.; Yang, P.C.; Chen, D.F.; Jiang, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.H.; Kang, L. Identification and functional analysis of olfactory receptor family reveal unusual characteristics of the olfactory system in the migratory locust. Cell. Mol. Life. Sci. 2015, 72, 4429–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Hir, H.; Nott, A.; Moore, M.J. How introns influence and enhance eukaryotic gene expression. Trends. Biochem. Sci. 2003, 28, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffares, D.C.; Penkett, C.J.; Bahler, J. Rapidly regulated genes are intron poor. Trends. Genetics. 2008, 24, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vité; J.P.; Bakke, A.; Renwick, J.A.A. Pheromones in Ips (Coleoptera: Scolytidae)—Occurrence and production. Can. Entomol. 1972, 104, 1967–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizumi, H.; Miyashita, A.; Inoue, N.; Inokuchi, K.; Aoki, M.; Sakano, H. Primary dendrites of mitral cells synapse unto neighboring glomeruli independent of their odorant receptor identity. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, L.N.; Zhao, H.T.; Xu, B.; Jiang, Y.S. Odorant receptor might be related to sperm DNA integrity in Apis cerana cerana. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2018, 193, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, K.; Keena, M.; Nehme, M.; Wang, S.F.; Meng, P.; Zhang, A.J. Sex-Specific Trail Pheromone Mediates Complex Mate Finding Behavior in Anoplophora glabripennis. J. Chem.Ecol. 2014, 40, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.S.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, C.H.; Song, J.Y.; Kong, E.B.; Kim, J.F. Algorithm for Predicting Functionally Equivalent Proteins from BLAST and HMMER Searches. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 1054–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast Approximation for Phylogenetic Bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New Algorithms and Methods to Estimate Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies: Assessing the Performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.H.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol Plant. 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Z.; Gao, P.; Luo, Y.Q.; Tao, J. Characterization and expression profiling of odorant-binding proteins in Anoplophora glabripennis Motsch. Gene 2019, 693, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.B.; Li, Y.R.; Wang, Q.Q.; Zheng, C.C.; Zhao, D.F.; Shi, F.M.; Liu, X.H.; Tao, J.; Zong, S.X. Identification of key genes associated with overwintering in Anoplophora glabripennis larva using geneco-expressionnetwork analysis. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Z.; Hu, P.; Gao, P.; Tao, J.; Luo, Y.Q. Antennal transcriptome analysis and expression profiles of olfactory genes in Anoplophora chinensis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)). Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| GeneName | GeneID | CDS (bp) | Amino Acid Residues | Status | Molecular Weight (KDa) | Isoelectric Points | Grand Average of Hydropathicity | Transmembrane Helices | Subcellular Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AglaOR1 | XP_018568191.1 | 1431 | 477 | complete ORF | 53.81 | 7.73 | 0.19 | 7 | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| AglaOR2 | XP_018560835.2 | 1203 | 401 | complete ORF | 46.93 | 8.49 | 0.318 | 7 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR3 | XP_023313104.1 | 1263 | 421 | complete ORF | 49.13 | 8.64 | 0.483 | 7 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR4 | XP_018560865.2 | 1266 | 422 | complete ORF | 49.49 | 8.88 | 0.495 | 7 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR5 | XP_023313097.1 | 1161 | 387 | complete ORF | 45.03 | 9.14 | 0.31 | 6 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR6 | XP_023313106.1 | 1209 | 403 | complete ORF | 47.3 | 8.88 | 0.331 | 7 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR7 | XP_023313105.1 | 1209 | 403 | complete ORF | 47.44 | 8.79 | 0.276 | 7 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR8 | XP_023310030.1 | 1515 | 505 | complete ORF | 58.08 | 6.6 | 0.08 | 7 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR9 | XP_018575345.1 | 555 | 185 | 5’ lost | 21.81 | 7.8 | 0.349 | 3 | Cytoskeleton |
| AglaOR10 | XP_023310521.1 | 855 | 285 | 5’ lost | 33.66 | 9 | 0.189 | 5 | Cytoskeleton |
| AglaOR11 | XP_018567483.1 | 1152 | 384 | complete ORF | 44.49 | 6.6 | 0.235 | 4 | Cytoskeleton |
| AglaOR12 | XP_023310034.1 | 1188 | 396 | complete ORF | 45.55 | 8.03 | 0.361 | 4 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR13 | XP_023310033.1 | 1188 | 396 | complete ORF | 45.89 | 6.15 | 0.416 | 5 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR14 | XP_018566518.1 | 1188 | 396 | complete ORF | 45.49 | 5.75 | 0.51 | 5 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR15 | XP_018566530.1 | 1188 | 396 | complete ORF | 45.54 | 5.99 | 0.42 | 5 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR16 | XP_023309742.1 | 693 | 231 | 5’ lost | 26.47 | 7.81 | 0.49 | 4 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR17 | XP_018566967.1 | 1158 | 386 | complete ORF | 44.08 | 8.85 | 0.398 | 7 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR18 | XP_018569520.1 | 1131 | 377 | complete ORF | 43.78 | 8.49 | 0.307 | 5 | Mitochondrion |
| AglaOR19 | XP_018568462.1 | 1164 | 388 | complete ORF | 44.95 | 7.94 | 0.351 | 5 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR20 | XP_023313058.1 | 1173 | 391 | complete ORF | 45.37 | 6.05 | 0.431 | 5 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR21 | XP_023311850.1 | 1167 | 389 | complete ORF | 45.27 | 7.54 | 0.427 | 6 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR22 | XP_023311848.1 | 1014 | 338 | complete ORF | 38.8 | 8.13 | 0.205 | 4 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR23 | XP_023312636.1 | 699 | 233 | 3’ lost | 26.98 | 6.01 | 0.309 | 2 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR24 | XP_023310658.1 | 759 | 253 | 3’ lost | 29.91 | 8.65 | 0.211 | 5 | Cytoskeleton |
| AglaOR25 | XP_023311847.1 | 1041 | 347 | complete ORF | 77.26 | 7.44 | 0.372 | 10 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR26 | XP_023311849.1 | 1137 | 379 | complete ORF | 43.84 | 6.31 | 0.377 | 6 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR27 | XP_023309851.1 | 600 | 200 | 5’ lost | 23.12 | 4.85 | 0.315 | 3 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR28 | XP_018564120.1 | 1143 | 381 | complete ORF | 44.27 | 8.11 | 0.397 | 7 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR29 | XP_018564808.2 | 1305 | 435 | complete ORF | 51.09 | 8.36 | 0.32 | 7 | Cytoskeleton |
| AglaOR30 | XP_018575063.1 | 1011 | 337 | complete ORF | 38.7 | 9.03 | 0.258 | 5 | Cytoskeleton |
| AglaOR31 | XP_018560873.1 | 861 | 287 | 5’ lost | 32.1 | 8.64 | 0.365 | 6 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR32 | XP_018577142.1 | 1254 | 418 | complete ORF | 48.37 | 8.14 | 0.409 | 6 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR33 | XP_023311544.1 | 969 | 323 | complete ORF | 37.69 | 7.33 | 0.505 | 5 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR34 | XP_023310447.1 | 1263 | 421 | complete ORF | 14.9 | 8.47 | 0.617 | 1 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR35 | XP_023310446.1 | 390 | 130 | 5’ lost | 14.73 | 7.12 | 0.58 | 3 | Extracell |
| AglaOR36 | XP_023310818.1 | 315 | 105 | 5’ lost | 12.28 | 5.75 | 0.523 | 1 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR37 | XP_018570370.1 | 1170 | 390 | complete ORF | 45.77 | 9.55 | 0.167 | 6 | Mitochondrion |
| AglaOR38 | XP_023312982.1 | 1185 | 395 | complete ORF | 31.64 | 5.63 | 0.35 | 4 | Extracell |
| AglaOR39 | XP_023309827.1 | 1206 | 402 | complete ORF | 47.2 | 5.27 | 0.397 | 6 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR40 | XP_023312071.1 | 894 | 298 | 3’ lost | 35.08 | 6.24 | 0.286 | 3 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR41 | XP_023310498.1 | 774 | 258 | 3’ lost | 29.93 | 9.27 | 0.316 | 4 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR42 | XP_018567067.2 | 612 | 204 | 5’ lost | 24.02 | 8.95 | 0.362 | 2 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR43 | XP_023310496.1 | 372 | 124 | 5’ lost | 14.42 | 5.76 | 0.591 | 1 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR44 | XP_018577261.2 | 534 | 178 | 5’ lost | 20.5 | 7.19 | 0.213 | 2 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR45 | XP_018562952.1 | 603 | 201 | 5’ lost | 22.77 | 5.58 | 0.42 | 2 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR46 | XP_023311401.1 | 1173 | 391 | complete ORF | 45.43 | 6.24 | 0.437 | 6 | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| AglaOR47 | XP_018569507.1 | 1155 | 385 | complete ORF | 44.69 | 6.78 | 0.329 | 6 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR48 | XP_023313160.1 | 1104 | 368 | complete ORF | 43.55 | 9.16 | 0.285 | 6 | Cytoskeleton |
| AglaOR49 | XP_018571376.1 | 1149 | 383 | complete ORF | 45.21 | 9.18 | 0.311 | 6 | Mitochondrion |
| AglaOR50 | XP_018570955.1 | 1101 | 367 | complete ORF | 42.11 | 7.72 | 0.469 | 6 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR51 | XP_023309856.1 | 345 | 115 | 5’ lost | 13.11 | 8.19 | 0.731 | 2 | Cytoskeleton |
| AglaOR52 | XP_018578983.2 | 924 | 308 | complete ORF | 35.1 | 8.58 | 0.212 | 4 | Cytoskeleton |
| AglaOR53 | XP_023310132.1 | 450 | 150 | 5’ lost | 17.36 | 9.5 | 0.255 | 3 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR54 | XP_018578651.1 | 804 | 268 | 5’ lost | 30.51 | 9.2 | 0.484 | 4 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR55 | XP_023311538.1 | 951 | 317 | complete ORF | 36.83 | 7.31 | 0.52 | 6 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR56 | XP_018579026.2 | 1155 | 385 | complete ORF | 43.78 | 7.8 | 0.502 | 7 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR57 | XP_018579015.2 | 1155 | 385 | complete ORF | 43.29 | 7.07 | 0.543 | 7 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR58 | XP_018567969.1 | 1152 | 384 | complete ORF | 44.31 | 9.79 | 0.25 | 7 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR59 | XP_023313053.1 | 1152 | 384 | complete ORF | 44.05 | 9.49 | 0.268 | 7 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR60 | XP_023309848.1 | 735 | 245 | 5’ lost | 29.07 | 8.64 | 0.134 | 2 | Cytoskeleton |
| AglaOR61 | XP_018578867.1 | 927 | 309 | complete ORF | 35.54 | 8.43 | 0.267 | 5 | Cytoskeleton |
| AglaOR62 | XP_023310463.1 | 1152 | 384 | complete ORF | 44.41 | 6.43 | 0.321 | 6 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR63 | XP_018560823.2 | 624 | 208 | 5’ lost | 24.3 | 9.13 | 0.399 | 3 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR64 | XP_023310462.1 | 612 | 204 | 5’ lost | 23.56 | 6.5 | 0.426 | 3 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR65 | XP_023311417.1 | 1620 | 540 | complete ORF | 62.83 | 8.64 | 0.362 | 6 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR66 | XP_023312511.1 | 1215 | 405 | complete ORF | 46.23 | 8.4 | 0.355 | 2 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR67 | XP_023310753.1 | 822 | 274 | 5’ lost | 31.76 | 7.69 | 0.333 | 4 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR68 | XP_023310752.1 | 822 | 274 | 5’ lost | 31.58 | 6.24 | 0.452 | 4 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR69 | XP_023309980.1 | 507 | 169 | 5’ lost | 19.42 | 8.58 | 0.304 | 1 | Cytoskeleton |
| AglaOR70 | XP_018561943.1 | 660 | 220 | 5’ lost | 25.16 | 7.8 | 0.161 | 1 | Mitochondrion |
| AglaOR71 | XP_023312510.1 | 1206 | 402 | complete ORF | 46.2 | 6.77 | 0.334 | 6 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR72 | XP_018575789.2 | 810 | 270 | 5’ lost | 30.38 | 6.12 | 0.303 | 3 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR73 | XP_018561953.2 | 1125 | 375 | complete ORF | 43.83 | 7.52 | 0.377 | 5 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR74 | XP_023310232.1 | 1140 | 380 | complete ORF | 44.34 | 6.72 | 0.285 | 4 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR75 | XP_023309981.1 | 1113 | 371 | complete ORF | 42.52 | 8.52 | 0.505 | 4 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR76 | XP_018568489.1 | 318 | 106 | 5’ lost | 12.68 | 6.22 | 0.154 | 0 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR77 | XP_023309849.1 | 1155 | 385 | complete ORF | 33.44 | 8.73 | 0.541 | 4 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR78 | XP_018563443.1 | 588 | 196 | 5’ lost | 22.71 | 8.93 | 0.196 | 2 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR79 | XP_023309850.1 | 552 | 184 | 5’ lost | 21.39 | 9.05 | 0.207 | 0 | Cytoskeleton |
| AglaOR80 | XP_018560827.2 | 564 | 188 | 5’ lost | 21.94 | 9.56 | 0.282 | 2 | Nucleus |
| AglaOR81 | XP_023309854.1 | 501 | 167 | 5’ lost | 19.2 | 8.45 | 0.334 | 3 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR82 | XP_023312904.1 | 1080 | 360 | complete ORF | 41.71 | 8.75 | 0.467 | 2 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR83 | XP_018570369.1 | 984 | 328 | complete ORF | 38.23 | 7.73 | 0.514 | 4 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR84 | XP_023309845.1 | 1077 | 359 | complete ORF | 41.76 | 8.51 | 0.463 | 4 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR85 | XP_023309844.1 | 882 | 294 | 5’ lost | 34.42 | 7.39 | 0.488 | 4 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR86 | XP_023309852.1 | 1029 | 343 | complete ORF | 39.98 | 7.5 | 0.52 | 4 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR87 | XP_023311541.1 | 972 | 324 | complete ORF | 37.55 | 6.35 | 0.539 | 5 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR88 | XP_023309846.1 | 906 | 302 | complete ORF | 35.1 | 8.32 | 0.497 | 4 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR89 | XP_023309847.1 | 969 | 323 | complete ORF | 37.45 | 7.68 | 0.557 | 5 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR90 | XP_023311539.1 | 999 | 333 | complete ORF | 38.51 | 7.26 | 0.471 | 4 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR91 | XP_023311540.1 | 771 | 257 | 5’ lost | 29.63 | 8.69 | 0.038 | 2 | Cytoskeleton |
| AglaOR92 | XM_023456081.1 | 1206 | 402 | 5’ lost | 42.21 | 6.38 | 0.394 | 5 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR93 | XM_018713238.2 | 529 | 176 | 5’ lost | 10.87 | 8.78 | 0.484 | 0 | Extracell |
| AglaOR94 | XM_023454061.1 | 775 | 258 | 5’ lost | 12.21 | 5.24 | 0.679 | 1 | Extracell |
| AglaOR95 | XM_018723466.1 | 768 | 256 | 5’ lost | 9.04 | 43.98 | 0.226 | 7 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR96 | XM_018712442.2 | 1248 | 416 | 5’ lost | 7.96 | 44.72 | 0.429 | 7 | Plasma membrane |
| AglaOR97 | XM_018712974.1 | 832 | 277 | 5’ lost | 8.63 | 44.81 | 0.378 | 6 | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| AglaOR98 | XM_018712973.1 | 832 | 277 | 5’ lost | 9.28 | 44.92 | 0.367 | 6 | Plasma membrane |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, Y.; Zong, S.; Tao, J. Genome-Wide Identification of the Odorant Receptor Gene Family and Revealing Key Genes Involved in Sexual Communication in Anoplophora glabripennis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021625
Zhang S, Li M, Xu Y, Zhao Y, Niu Y, Zong S, Tao J. Genome-Wide Identification of the Odorant Receptor Gene Family and Revealing Key Genes Involved in Sexual Communication in Anoplophora glabripennis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(2):1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021625
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Sainan, Meng Li, Yabei Xu, Yuxuan Zhao, Yiming Niu, Shixiang Zong, and Jing Tao. 2023. "Genome-Wide Identification of the Odorant Receptor Gene Family and Revealing Key Genes Involved in Sexual Communication in Anoplophora glabripennis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 2: 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021625
APA StyleZhang, S., Li, M., Xu, Y., Zhao, Y., Niu, Y., Zong, S., & Tao, J. (2023). Genome-Wide Identification of the Odorant Receptor Gene Family and Revealing Key Genes Involved in Sexual Communication in Anoplophora glabripennis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(2), 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021625







