The Effect of Dietary Phospholipids on the Ultrastructure and Function of Intestinal Epithelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
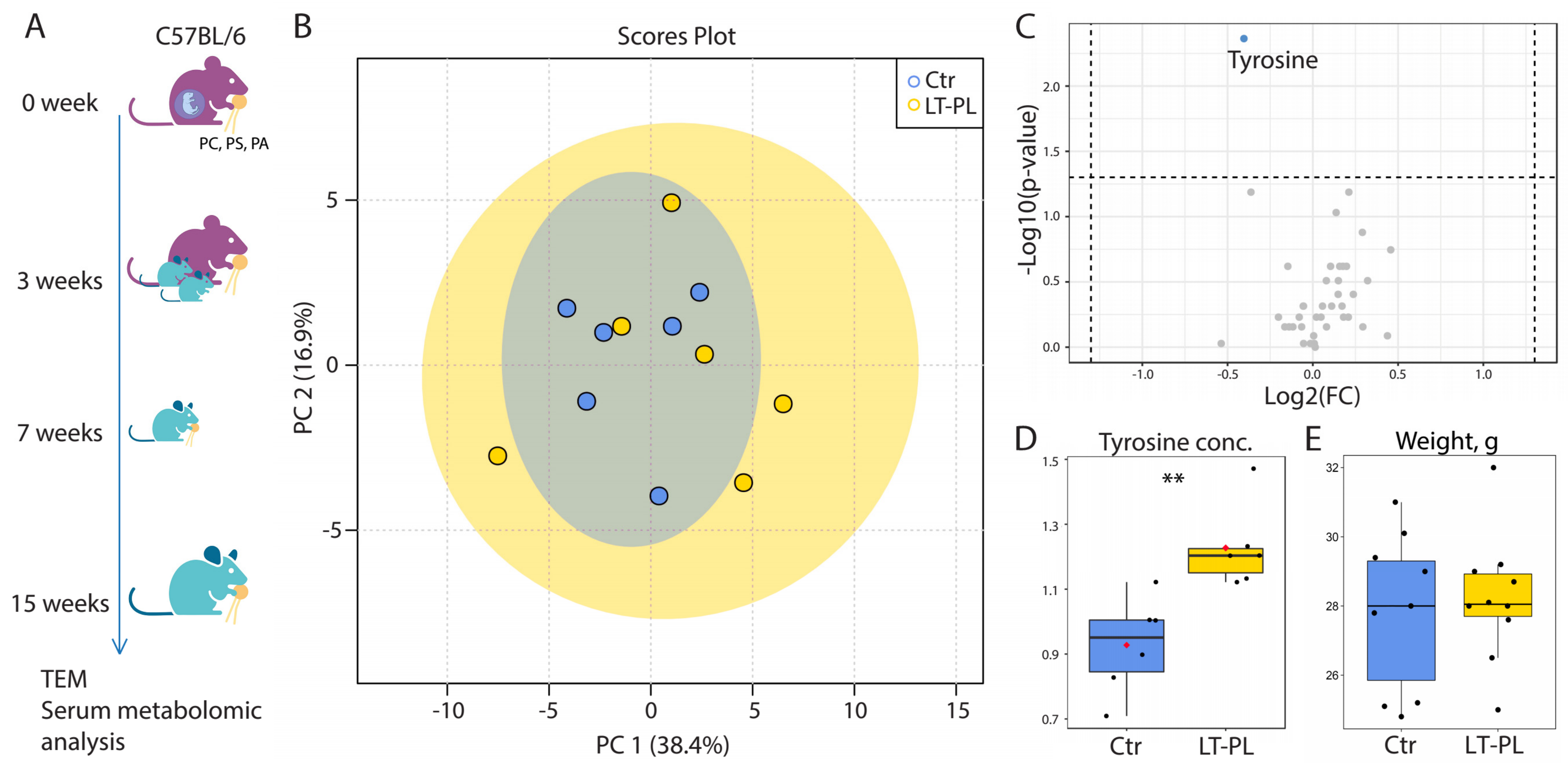
2.1. Long-Term Dietary PL Supplementation Does Not Significantly Affects Systemic Metabolism
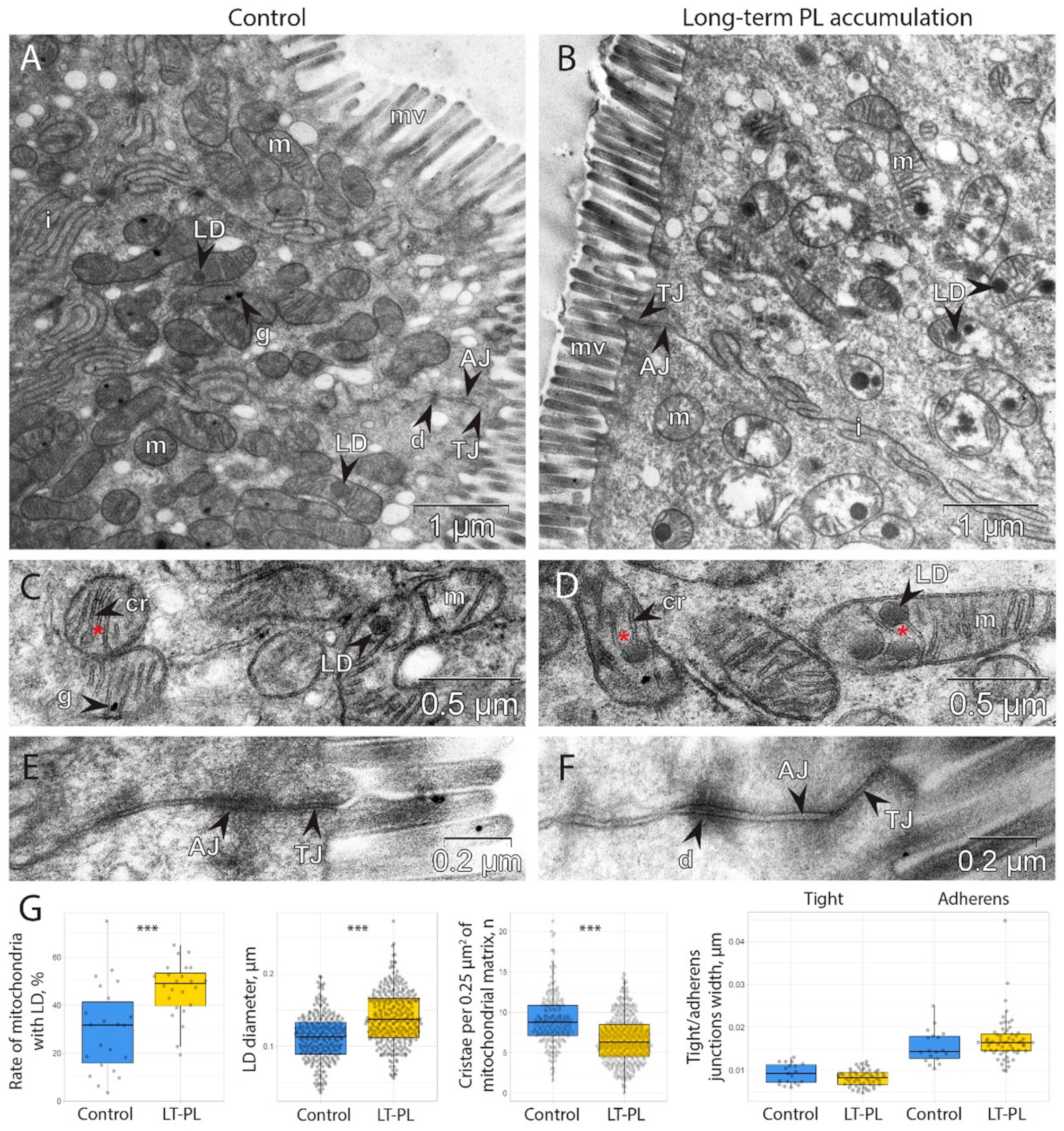
2.2. Long-Term Dietary PL Supplementation Results in Mitochondrial Damage and Lipid Droplets Accumulation in Mitochondria
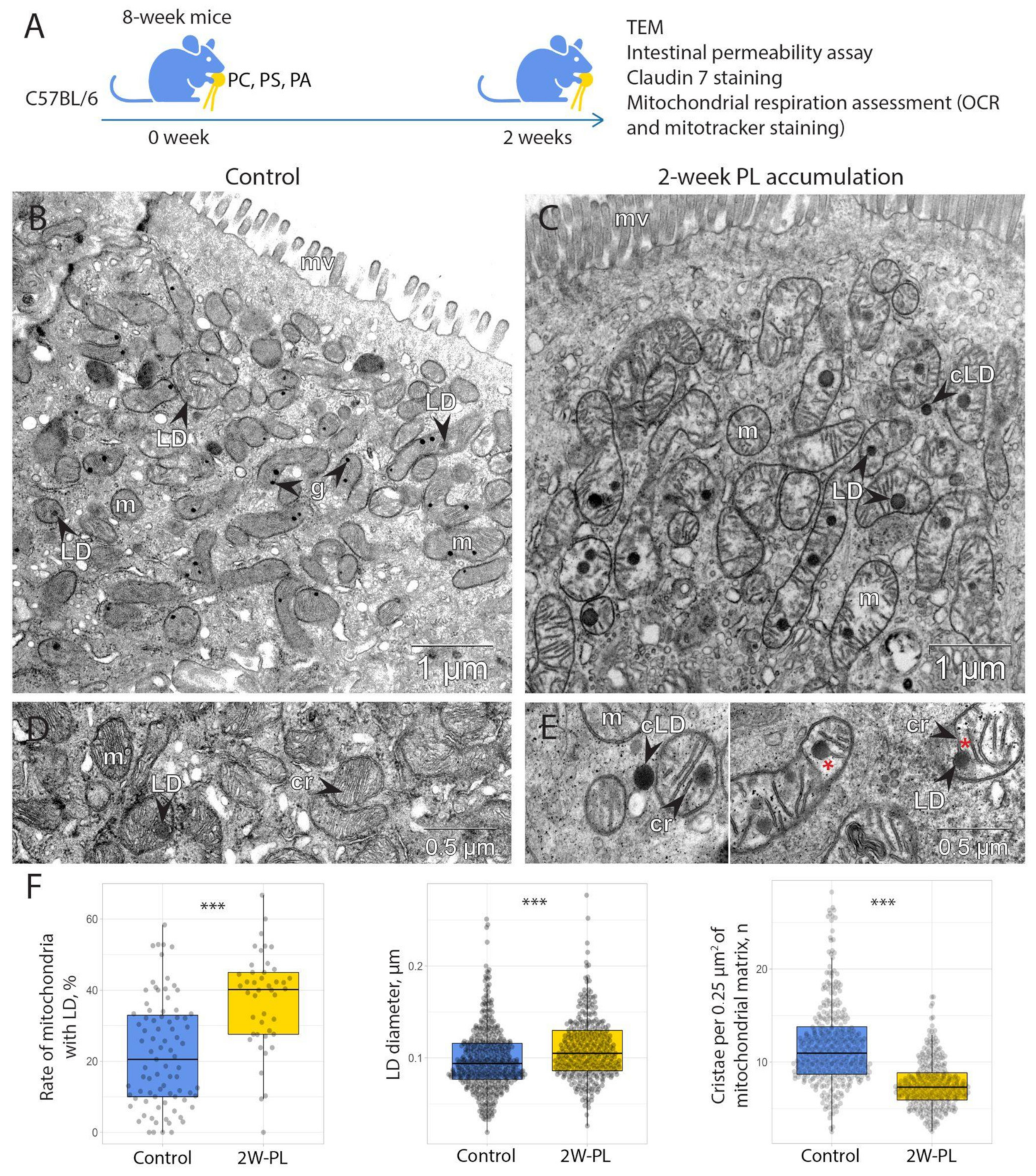
2.3. Two-Week Dietary PL Supplementation Is Sufficient to Induce Mitochondrial Damage and Lipid Drop Accumulation
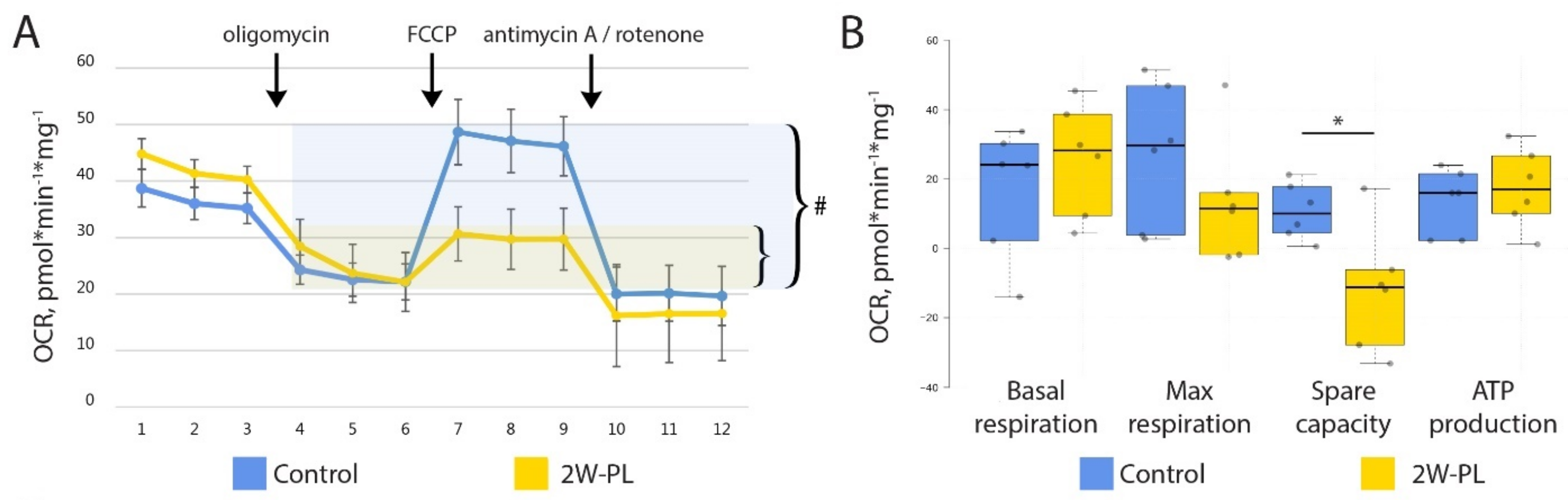
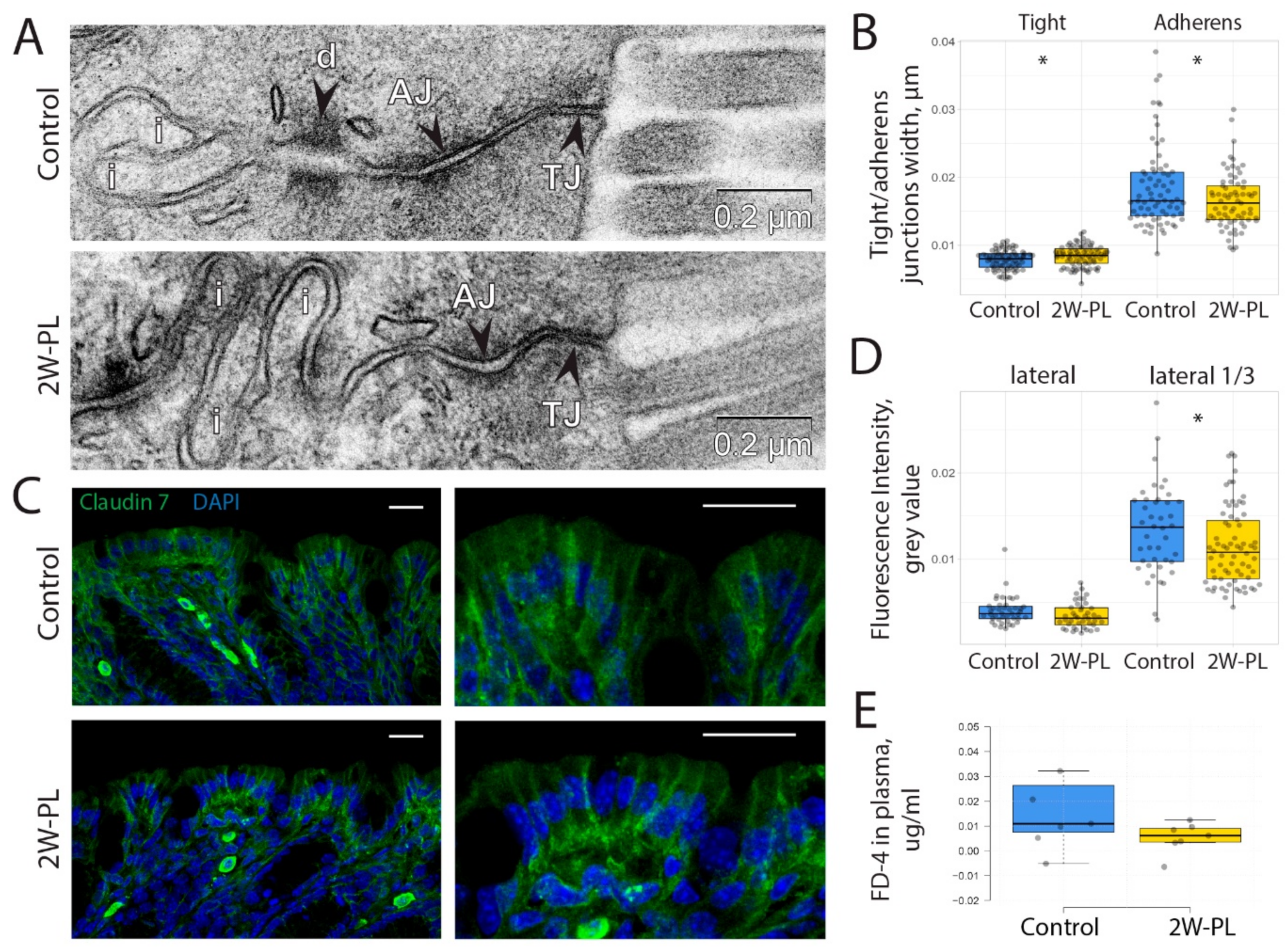
2.4. Mitochondrial Damage via PL Supplementation Is Insufficient to Induce an Increase in Intestinal Permeability
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Metabolite Extraction and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
4.3. Immunohistochemistry
4.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.5. Crypt Isolation
4.6. OCR Measurement
4.7. Intestinal Barrier Permeability Assessment
4.8. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Longo, V.D.; Anderson, R.M. Nutrition, longevity and disease: From molecular mechanisms to interventions. Cell 2022, 185, 1455–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Daniele, N.; Noce, A.; Vidiri, M.F.; Moriconi, E.; Marrone, G.; Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli, M.; D’Urso, G.; Tesauro, M.; Rovella, V.; De Lorenzo, A. Impact of Mediterranean diet on metabolic syndrome, cancer and longevity. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 8947–8979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, W. How Western Diet And Lifestyle Drive The Pandemic Of Obesity And Civilization Diseases. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 2221–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Montero, C.; Fraile-Martinez, O.; Gomez-Lahoz, A.M.; Pekarek, L.; Castellanos, A.J.; Noguerales-Fraguas, F.; Coca, S.; Guijarro, L.G.; Garcia-Honduvilla, N.; Asunsolo, A.; et al. Nutritional Components in Western Diet Versus Mediterranean Diet at the Gut Microbiota-Immune System Interplay. Implications for Health and Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eng, J.M.; Estall, J.L. Diet-Induced Models of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Food for Thought on Sugar, Fat, and Cholesterol. Cells 2021, 10, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. Functional amino acids in nutrition and health. Amino Acids 2013, 45, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisel, S. Choline, Other Methyl-Donors and Epigenetics. Nutrients 2017, 9, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruins, M.J.; Van Dael, P.; Eggersdorfer, M. The Role of Nutrients in Reducing the Risk for Noncommunicable Diseases during Aging. Nutrients 2019, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, T.A.; Hafekost, K.; Mitrou, F.; Lawrence, D. Food sources of saturated fat and the association with mortality: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Public Health 2013, 103, e31–e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Otto, M.C.; Mozaffarian, D.; Kromhout, D.; Bertoni, A.G.; Sibley, C.T.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Nettleton, J.A. Dietary intake of saturated fat by food source and incident cardiovascular disease: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordan, R.; Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I. Phospholipids of Animal and Marine Origin: Structure, Function, and Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Molecules 2017, 22, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayebati, S.K. Phospholipid and Lipid Derivatives as Potential Neuroprotective Compounds. Molecules 2018, 23, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsley, M. Effects of Phosphatidylserine Supplementation on Exercising Humans. Sport. Med. 2006, 36, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldyreva, L.V.; Morozova, M.V.; Saydakova, S.S.; Kozhevnikova, E.N. Fat of the Gut: Epithelial Phospholipids in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harayama, T.; Riezman, H. Understanding the diversity of membrane lipid composition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drin, G. Topological regulation of lipid balance in cells. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2014, 83, 51–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balla, T. Phosphoinositides: Tiny lipids with giant impact on cell regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1019–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musille, P.M.; Kohn, J.A.; Ortlund, E.A. Phospholipid--driven gene regulation. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klasen, K.; Corey, E.A.; Kuck, F.; Wetzel, C.H.; Hatt, H.; Ache, B.W. Odorant-stimulated phosphoinositide signaling in mammalian olfactory receptor neurons. Cell Signal. 2010, 22, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowder, M.K.; Seacrist, C.D.; Blind, R.D. Phospholipid regulation of the nuclear receptor superfamily. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2017, 63, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullenberg, D.; Taylor, L.A.; Schneider, M.; Massing, U. Health effects of dietary phospholipids. Lipids Health Dis. 2012, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Veen, J.N.; Kennelly, J.P.; Wan, S.; Vance, J.E.; Vance, D.E.; Jacobs, R.L. The critical role of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine metabolism in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 1558–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, J.E. Phospholipid synthesis and transport in mammalian cells. Traffic 2015, 16, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lee, M.; Fairn, G.D. Phospholipid subcellular localization and dynamics. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 6230–6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss-Hersh, K.; Garcia, A.L.; Marosvolgyi, T.; Szklenar, M.; Decsi, T.; Ruhl, R. Saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids in membranes are determined by the gene expression of their metabolizing enzymes SCD1 and ELOVL6 regulated by the intake of dietary fat. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 2759–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Carvalho, C.; Caramujo, M.J. The Various Roles of Fatty Acids. Molecules 2018, 23, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberle, F.A.; Feigenson, G.W. Phase separation in lipid membranes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garba, L.; Mohamad Yussoff, M.A.; Abd Halim, K.B.; Ishak, S.N.H.; Mohamad Ali, M.S.; Oslan, S.N.; Raja Abd Rahman, R.N.Z. Homology modeling and docking studies of a Delta9-fatty acid desaturase from a Cold-tolerant Pseudomonas sp. AMS8. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, I.; Ichimura, A.; Ohue-Kitano, R.; Igarashi, M. Free Fatty Acid Receptors in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2020, 100, 171–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vihma, V.; Tikkanen, M.J. Fatty acid esters of steroids: Synthesis and metabolism in lipoproteins and adipose tissue. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 124, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.R.; Raskin, S. The eicosapentaenoic acid:arachidonic acid ratio and its clinical utility in cardiovascular disease. Postgrad. Med. 2019, 131, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes. Nutrients 2010, 2, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Ripon, M.A.R.; Begum, R.; Bhowmik, D.R.; Amin, M.T.; Islam, M.A.; Ahmed, F.; Hossain, M.S. Arachidonic acid supplementation attenuates adipocyte inflammation but not adiposity in high fat diet induced obese mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 608, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simopoulos, A.P. Omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids: Endocannabinoids, genetics and obesity. OCL 2020, 27, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzner, L.; Ostermann, A.I.; Konrad, T.; Riegel, D.; Hellhake, S.; Schuchardt, J.P.; Schebb, N.H. Lipid Class Specific Quantitative Analysis of n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Food Supplements. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, W.; Bockmann, K.; Maas, C.; Mathes, M.; Hovelmann, J.; Shunova, A.; Hund, V.; Schleicher, E.; Poets, C.F.; Franz, A.R. Combined choline and DHA supplementation: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorissen, B.L.; Brouns, F.; Van Boxtel, M.P.; Riedel, W.J. Safety of soy-derived phosphatidylserine in elderly people. Nutr. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, A.; Giacomelli, L.; Togni, S.; Franceschi, F.; Eggenhoffner, R.; Zuccarini, M.C.; Belcaro, G. Oral administration of a lecithin-based delivery form of boswellic acids (Casperome®) for the prevention of symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized clinical study. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2019, 65, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glade, M.J.; Smith, K. Phosphatidylserine and the human brain. Nutrition 2015, 31, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, M.; Ghasemi, H.A.; Hajkhodadadi, I.; Moradi, M.H. De-oiled soy lecithin positively influenced growth performance, nutrient digestibility, histological intestinal alteration, and antioxidant status in turkeys fed with low energy diets. Br. Poult. Sci. 2021, 62, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholmie, Y.; Lozinsky, A.C.; Godwin, H.; Reeve, K.; Dzubiak, R.; Shah, N.; Meyer, R. Tolerance of soya lecithin in children with non-immunoglobulin E-mediated soya allergy: A randomised, double-blind, cross-over trial. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 33, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, S.; Terasawa, K.; Rabeler, R.; Hirayama, T.; Inoue, T.; Tatsumi, Y.; Purpura, M.; Jager, R. The effect of phosphatidylserine administration on memory and symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 27 (Suppl. 2), 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Chong, J.; Zhou, G.; de Lima Morais, D.A.; Chang, L.; Barrette, M.; Gauthier, C.; Jacques, P.E.; Li, S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W388–W396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, E.A.; Mollen, K.P. Mitochondrial dysfunction in inflammatory bowel disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 3, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisova, M.A.; Achasova, K.M.; Morozova, K.N.; Andreyeva, E.N.; Litvinova, E.A.; Ogienko, A.A.; Morozova, M.V.; Berkaeva, M.B.; Kiseleva, E.; Kozhevnikova, E.N. Mucin-2 knockout is a model of intercellular junction defects, mitochondrial damage and ATP depletion in the intestinal epithelium. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnason, I.; Scarpignato, C.; Holmgren, E.; Olszewski, M.; Rainsford, K.D.; Lanas, A. Mechanisms of Damage to the Gastrointestinal Tract from Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 500–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treede, I.; Braun, A.; Sparla, R.; Kuhnel, M.; Giese, T.; Turner, J.R.; Anes, E.; Kulaksiz, H.; Fullekrug, J.; Stremmel, W.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of phosphatidylcholine. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 27155–27164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stremmel, W.; Merle, U.; Zahn, A.; Autschbach, F.; Hinz, U.; Ehehalt, R. Retarded release phosphatidylcholine benefits patients with chronic active ulcerative colitis. Gut 2005, 54, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stremmel, W.; Ehehalt, R.; Autschbach, F.; Karner, M. Phosphatidylcholine for Steroid-Refractory Chronic Ulcerative Colitis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2007, 147, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karner, M.; Kocjan, A.; Stein, J.; Schreiber, S.; von Boyen, G.; Uebel, P.; Schmidt, C.; Kupcinskas, L.; Dina, I.; Zuelch, F.; et al. First Multicenter Study of Modified Release Phosphatidylcholine “LT-02” in Ulcerative Colitis: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial in Mesalazine-Refractory Courses. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Yang, B.; Miao, Z. Phosphatidylserine, inflammation, and central nervous system diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 975176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Huang, B.X.; Spector, A.A. Phosphatidylserine in the brain: Metabolism and function. Prog. Lipid Res. 2014, 56, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shu, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, W.; Ward, N.; Wang, J. Phosphatidylserine in the Nervous System: Cytoplasmic Regulator of the AKT and PKC Signaling Pathways and Extracellular “Eat-Me” Signal in Microglial Phagocytosis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante, G.; Alencar, M.; Haddock, B.; Harvey, P. The effects of phosphatidic acid supplementation on strength, body composition, muscular endurance, power, agility, and vertical jump in resistance trained men. J. Int. Soc. Sport. Nutr. 2016, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carman, G.M.; Han, G.S. Fat-regulating phosphatidic acid phosphatase: A review of its roles and regulation in lipid homeostasis. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, D.A. Phosphatidic acid and lipid-sensing by mTOR. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 24, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Shi, X.; Guo, X.; Li, H.; Xu, C. Ionic protein-lipid interaction at the plasma membrane: What can the charge do? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Tontonoz, P. Phospholipid Remodeling in Physiology and Disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2019, 81, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holic, R.; Pokorna, L.; Griac, P. Metabolism of phospholipids in the yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast 2020, 37, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olzmann, J.A.; Carvalho, P. Dynamics and functions of lipid droplets. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Liu, P. Two Types of Contact Between Lipid Droplets and Mitochondria. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 618322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benador, I.Y.; Veliova, M.; Mahdaviani, K.; Petcherski, A.; Wikstrom, J.D.; Assali, E.A.; Acin-Perez, R.; Shum, M.; Oliveira, M.F.; Cinti, S.; et al. Mitochondria Bound to Lipid Droplets Have Unique Bioenergetics, Composition, and Dynamics that Support Lipid Droplet Expansion. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 869–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Tham, D.K.L.; Liang, F.X.; Chang, J.; Wei, Y.; Sudhir, P.R.; Sall, J.; Ren, S.J.; Chicote, J.U.; Arnold, L.L.; et al. Mitochondrial lipid droplet formation as a detoxification mechanism to sequester and degrade excessive urothelial membranes. Mol. Biol. Cell 2019, 30, 2969–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, T.H.; Dencher, N.A. Cardiolipin: A proton trap for oxidative phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 2002, 528, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennington, E.R.; Funai, K.; Brown, D.A.; Shaikh, S.R. The role of cardiolipin concentration and acyl chain composition on mitochondrial inner membrane molecular organization and function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 1039–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added to Food (ANS); Mortensen, A.; Aguilar, F.; Crebelli, R.; Di Domenico, A.; Frutos, M.J.; Galtier, P.; Gott, D.; Gundert-Remy, U.; Lambré, C.; et al. Re-evaluation of lecithins (E 322) as a food additive. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akesson, B. Content of phospholipids in human diets studied by the duplicate-portion technique. Br. J. Nutr. 1982, 47, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, J.R.; Stout, J.R.; Williams, D.R.; Wells, A.J.; Fragala, M.S.; Mangine, G.T.; Gonzalez, A.M.; Emerson, N.S.; McCormack, W.P.; Scanlon, T.C.; et al. Efficacy of phosphatidic acid ingestion on lean body mass, muscle thickness and strength gains in resistance-trained men. J. Int. Soc. Sport. Nutr. 2012, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maev, I.V.; Samsonov, A.A.; Palgova, L.K.; Pavlov, C.S.; Shirokova, E.N.; Vovk, E.I.; Starostin, K.M. Effectiveness of phosphatidylcholine as adjunctive therapy in improving liver function tests in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic comorbidities: Real-life observational study from Russia. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2020, 7, e000368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stremmel, W.; Vural, H.; Evliyaoglu, O.; Weiskirchen, R. Delayed-Release Phosphatidylcholine Is Effective for Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis: A Meta-Analysis. Dig. Dis. 2021, 39, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholey, A.B.; Camfield, D.A.; Hughes, M.E.; Woods, W.; Stough, C.K.K.; White, D.J.; Gondalia, S.V.; Frederiksen, P.D. A randomized controlled trial investigating the neurocognitive effects of Lacprodan® PL-20, a phospholipid-rich milk protein concentrate, in elderly participants with age-associated memory impairment: The Phospholipid Intervention for Cognitive Ageing Reversal (PLICAR): Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2013, 14, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JanssenDuijghuijsen, L.M.; Grefte, S.; de Boer, V.C.J.; Zeper, L.; van Dartel, D.A.M.; van der Stelt, I.; Bekkenkamp-Grovenstein, M.; van Norren, K.; Wichers, H.J.; Keijer, J. Mitochondrial ATP Depletion Disrupts Caco-2 Monolayer Integrity and Internalizes Claudin 7. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suurna, M.V.; Ashworth, S.L.; Hosford, M.; Sandoval, R.M.; Wean, S.E.; Shah, B.M.; Bamburg, J.R.; Molitoris, B.A. Cofilin mediates ATP depletion-induced endothelial cell actin alterations. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2006, 290, F1398–F1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mähler Convenor, M.; Berard, M.; Feinstein, R.; Gallagher, A.; Illgen-Wilcke, B.; Pritchett-Corning, K.; Raspa, M. FELASA recommendations for the health monitoring of mouse, rat, hamster, guinea pig and rabbit colonies in breeding and experimental units. Lab. Anim. 2014, 48, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morozova, M.V.; Borisova, M.A.; Snytnikova, O.A.; Achasova, K.M.; Litvinova, E.A.; Tsentalovich, Y.P.; Kozhevnikova, E.N. Colitis-associated intestinal microbiota regulates brain glycine and host behavior in mice. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisova, M.A.; Snytnikova, O.A.; Litvinova, E.A.; Achasova, K.M.; Babochkina, T.I.; Pindyurin, A.V.; Tsentalovich, Y.P.; Kozhevnikova, E.N. Fucose Ameliorates Tryptophan Metabolism and Behavioral Abnormalities in a Mouse Model of Chronic Colitis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snytnikova, O.A.; Khlichkina, A.A.; Sagdeev, R.Z.; Tsentalovich, Y.P. Evaluation of sample preparation protocols for quantitative NMR-based metabolomics. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Guo, A.; Oler, E.; Wang, F.; Anjum, A.; Peters, H.; Dizon, R.; Sayeeda, Z.; Tian, S.; Lee, B.L.; et al. HMDB 5.0: The Human Metabolome Database for 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D622–D631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinskikh, A.; Snytnikova, O.; Zelentsova, E.; Borisova, M.; Tsentalovich, Y.; Akulov, A. The Effect of Blood Contained in the Samples on the Metabolomic Profile of Mouse Brain Tissue: A Study by NMR Spectroscopy. Molecules 2021, 26, 3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.Y.; Davidson, L.A.; Callaway, E.S.; Wright, G.A.; Safe, S.; Chapkin, R.S. A bioassay to measure energy metabolism in mouse colonic crypts, organoids, and sorted stem cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 309, G1–G9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saydakova, S.; Morozova, K.; Snytnikova, O.; Morozova, M.; Boldyreva, L.; Kiseleva, E.; Tsentalovich, Y.; Kozhevnikova, E. The Effect of Dietary Phospholipids on the Ultrastructure and Function of Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021788
Saydakova S, Morozova K, Snytnikova O, Morozova M, Boldyreva L, Kiseleva E, Tsentalovich Y, Kozhevnikova E. The Effect of Dietary Phospholipids on the Ultrastructure and Function of Intestinal Epithelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(2):1788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021788
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaydakova, Snezhanna, Ksenia Morozova, Olga Snytnikova, Maryana Morozova, Lidiya Boldyreva, Elena Kiseleva, Yuri Tsentalovich, and Elena Kozhevnikova. 2023. "The Effect of Dietary Phospholipids on the Ultrastructure and Function of Intestinal Epithelial Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 2: 1788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021788
APA StyleSaydakova, S., Morozova, K., Snytnikova, O., Morozova, M., Boldyreva, L., Kiseleva, E., Tsentalovich, Y., & Kozhevnikova, E. (2023). The Effect of Dietary Phospholipids on the Ultrastructure and Function of Intestinal Epithelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(2), 1788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021788







