Localized Infections with P. aeruginosa Strains Defective in Zinc Uptake Reveal That Zebrafish Embryos Recapitulate Nutritional Immunity Responses of Higher Eukaryotes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
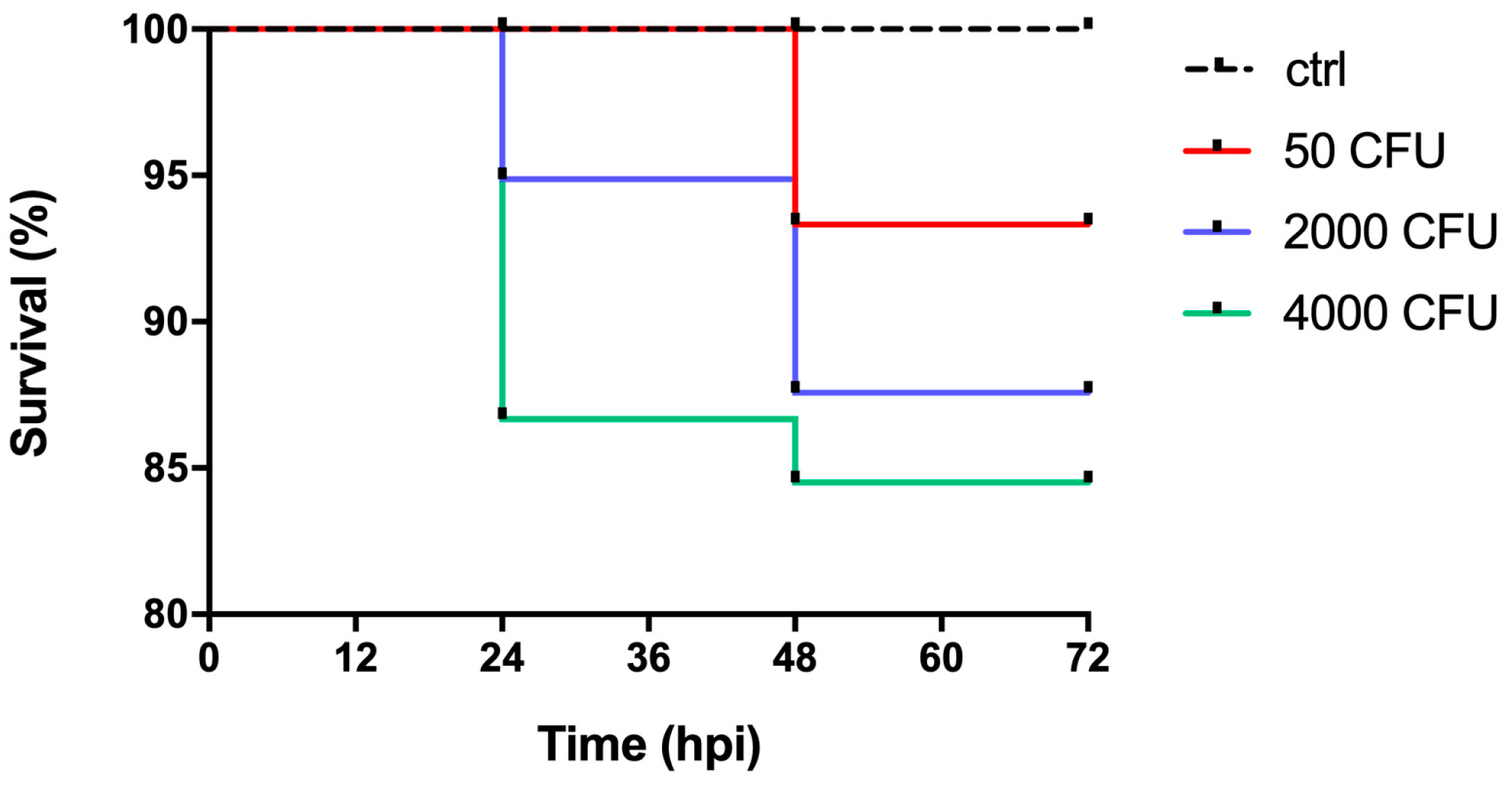
2.1. Development of an Experimental Model of P. aeruginosa Infection in Zebrafish Embryos
2.2. Mixed Infections Reveal a Contribution of Zn Uptake Systems to P. aeruginosa Virulence in Zebrafish
2.3. The Early Response of Zebrafish to P. aeruginosa Infections Involves Zn Intoxication
2.4. P. aeruginosa Adapts to Zebrafish by Modulating the Expression of Distinct Zn-Responsive Genes at Different Stages of Infection
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.2. Zebrafish Embryos Infection
4.3. Competition Assay in Zebrafish Embryos
4.4. RNA Extraction and Real Time-PCR
4.5. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical Statement
References
- Murdoch, C.C.; Skaar, E.P. Nutritional Immunity: The Battle for Nutrient Metals at the Host–Pathogen Interface. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldon, J.R.; Skaar, E.P. Metals as Phagocyte Antimicrobial Effectors. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2019, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Chávez, M.; Pérez-García, L.; Niño-Vega, G.; Mora-Montes, H. Fungal Strategies to Evade the Host Immune Recognition. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hood, M.I.; Skaar, E.P. Nutritional Immunity: Transition Metals at the Pathogen–Host Interface. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mastropasqua, M.C.; D’Orazio, M.; Cerasi, M.; Pacello, F.; Gismondi, A.; Canini, A.; Canuti, L.; Consalvo, A.; Ciavardelli, D.; Chirullo, B.; et al. Growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Zinc Poor Environments Is Promoted by a Nicotianamine-Related Metallophore. Mol. Microbiol. 2017, 106, 543–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Orazio, M.; Mastropasqua, M.C.; Cerasi, M.; Pacello, F.; Consalvo, A.; Chirullo, B.; Mortensen, B.; Skaar, E.P.; Ciavardelli, D.; Pasquali, P.; et al. The Capability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to Recruit Zinc under Conditions of Limited Metal Availability Is Affected by Inactivation of the ZnuABC Transporter. Metallomics 2015, 7, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pederick, V.G.; Eijkelkamp, B.A.; Begg, S.L.; Ween, M.P.; McAllister, L.J.; Paton, J.C.; McDevitt, C.A. ZnuA and Zinc Homeostasis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lhospice, S.; Gomez, N.O.; Ouerdane, L.; Brutesco, C.; Ghssein, G.; Hajjar, C.; Liratni, A.; Wang, S.; Richaud, P.; Bleves, S.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa zinc uptake in chelating environment is primarily mediated by the metallophore pseudopaline. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ammendola, S.; Secli, V.; Pacello, F.; Mastropasqua, M.C.; Romão, M.A.; Gomes, C.M.; Battistoni, A. Zinc-Binding Metallophores Protect Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Calprotectin-Mediated Metal Starvation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2022, 369, fnac071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonergan, Z.R.; Skaar, E.P. Nutrient Zinc at the Host–Pathogen Interface. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 1041–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrov, A.G.; Kirillina, O.; Fetherston, J.D.; Miller, M.C.; Burlison, J.A.; Perry, R.D. The Y Ersinia Pestis Siderophore, Yersiniabactin, and the ZnuABC System Both Contribute to Zinc Acquisition and the Development of Lethal Septicaemic Plague in Mice. Mol. Microbiol. 2014, 93, 759–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laffont, C.; Arnoux, P. The Ancient Roots of Nicotianamine: Diversity, Role, Regulation and Evolution of Nicotianamine-like Metallophores. Metallomics 2020, 12, 1480–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghssein, G.; Brutesco, C.; Ouerdane, L.; Fojcik, C.; Izaute, A.; Wang, S.; Hajjar, C.; Lobinski, R.; Lemaire, D.; Richaud, P.; et al. Biosynthesis of a Broad-Spectrum Nicotianamine-like Metallophore in Staphylococcus aureus. Science 2016, 352, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grim, K.P.; San Francisco, B.; Radin, J.N.; Brazel, E.B.; Kelliher, J.L.; Párraga Solórzano, P.K.; Kim, P.C.; McDevitt, C.A.; Kehl-Fie, T.E. The Metallophore Staphylopine Enables Staphylococcus aureus To Compete with the Host for Zinc and Overcome Nutritional Immunity. mBio 2017, 8, e01281-e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obritsch, M.D.; Fish, D.N.; MacLaren, R.; Jung, R. Nosocomial Infections Due to Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Epidemiology and Treatment Options. Pharmacotherapy 2005, 25, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Cystic Fibrosis: Pathogenesis and Persistence. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2002, 3, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, S.; Hayes, D.; Wozniak, D.J. Cystic Fibrosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: The Host-Microbe Interface. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00138-e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukavica-Ibrulj, I.; Levesque, R.C. Animal Models of Chronic Lung Infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Useful Tools for Cystic Fibrosis Studies. Lab. Anim. 2008, 42, 389–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maura, D.; Bandyopadhaya, A.; Rahme, L.G. Animal Models for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum Sensing Studies. In Quorum Sensing; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 227–241. [Google Scholar]
- McCarron, A.; Parsons, D.; Donnelley, M. Animal and Cell Culture Models for Cystic Fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yan, Z.; Yi, Y.; Li, Z.; Lei, D.; Rogers, C.S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Welsh, M.J.; Leno, G.H.; et al. Adeno-Associated Virus–Targeted Disruption of the CFTR Gene in Cloned Ferrets. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, C.S.; Hao, Y.; Rokhlina, T.; Samuel, M.; Stoltz, D.A.; Li, Y.; Petroff, E.; Vermeer, D.W.; Kabel, A.C.; Yan, Z.; et al. Production of CFTR-Null and CFTR-ΔF508 Heterozygous Pigs by Adeno-Associated Virus–Mediated Gene Targeting and Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 1571–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCarron, A.; Donnelley, M.; Parsons, D. Airway Disease Phenotypes in Animal Models of Cystic Fibrosis. Respir Res. 2018, 19, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilke, M.; Buijs-Offerman, R.M.; Aarbiou, J.; Colledge, W.H.; Sheppard, D.N.; Touqui, L.; Bot, A.; Jorna, H.; de Jonge, H.R.; Scholte, B.J. Mouse Models of Cystic Fibrosis: Phenotypic Analysis and Research Applications. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2011, 10, S152–S171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cafora, M.; Brix, A.; Forti, F.; Loberto, N.; Aureli, M.; Briani, F.; Pistocchi, A. Phages as Immunomodulators and Their Promising Use as Anti-Inflammatory Agents in a Cftr Loss-of-Function Zebrafish Model. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2021, 20, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, M.D.; Kremer, L. CFTR Depletion Confers Hypersusceptibility to Mycobacterium fortuitum in a Zebrafish Model. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phennicie, R.T.; Sullivan, M.J.; Singer, J.T.; Yoder, J.A.; Kim, C.H. Specific Resistance to Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in Zebrafish Is Mediated by the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 4542–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clatworthy, A.E.; Lee, J.S.-W.; Leibman, M.; Kostun, Z.; Davidson, A.J.; Hung, D.T. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection of Zebrafish Involves Both Host and Pathogen Determinants. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herbomel, P.; Thisse, B.; Thisse, C. Ontogeny and Behaviour of Early Macrophages in the Zebrafish Embryo. Development 1999, 126, 3735–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Sar, A.M.; Musters, R.J.P.; van Eeden, F.J.M.; Appelmelk, B.J.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.J.E.; Bitter, W. Zebrafish Embryos as a Model Host for the Real-Time Analysis of Salmonella Typhimurium Infections. Cell Microbiol. 2003, 5, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Tepaamorndech, S. The SLC30 Family of Zinc Transporters—A Review of Current Understanding of Their Biological and Pathophysiological Roles. Mol. Asp. Med. 2013, 34, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmiter, R.D.; Huang, L. Efflux and Compartmentalization of Zinc by Members of the SLC30 Family of Solute Carriers. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2004, 447, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastropasqua, M.C.; Lamont, I.; Martin, L.W.; Reid, D.W.; D’Orazio, M.; Battistoni, A. Efficient zinc uptake is critical for the ability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to express virulence traits and colonize the human lung. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 48, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prajsnar, T.K.; Cunliffe, V.T.; Foster, S.J.; Renshaw, S.A. A Novel Vertebrate Model of Staphylococcus Aureus Infection Reveals Phagocyte-Dependent Resistance of Zebrafish to Non-Host Specialized Pathogens. Cell Microbiol. 2008, 10, 2312–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brannon, M.K.; Davis, J.M.; Mathias, J.R.; Hall, C.J.; Emerson, J.C.; Crosier, P.S.; Huttenlocher, A.; Ramakrishnan, L.; Moskowitz, S.M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type III Secretion System Interacts with Phagocytes to Modulate Systemic Infection of Zebrafish Embryos. Cell Microbiol. 2009, 11, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meijer, H.A.; Spaink, H.P. Host-Pathogen Interactions Made Transparent with the Zebrafish Model. Curr. Drug Targets 2011, 12, 1000–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pont, S.; Blanc-Potard, A.-B. Zebrafish Embryo Infection Model to Investigate Pseudomonas aeruginosa Interaction With Innate Immunity and Validate New Therapeutics. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 745851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.C.; Mostowy, S. The Case for Modeling Human Infection in Zebrafish. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Hu, B. Establishment of Multi-Site Infection Model in Zebrafish Larvae for Studying Staphylococcus aureus Infectious Disease. J. Genet. Genom. 2012, 39, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, S.; Fries, F.; Müller, R.; Herrmann, J. Zebrafish: An Attractive Model to Study Staphylococcus aureus Infection and Its Use as a Drug Discovery Tool. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botella, H.; Peyron, P.; Levillain, F.; Poincloux, R.; Poquet, Y.; Brandli, I.; Wang, C.; Tailleux, L.; Tilleul, S.; Charrire, G.M.; et al. Mycobacterial P 1-Type ATPases Mediate Resistance to Zinc Poisoning in Human Macrophages. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 10, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapetanovic, R.; Bokil, N.J.; Achard, M.E.S.; Ong, C.L.Y.; Peters, K.M.; Stocks, C.J.; Phan, M.D.; Monteleone, M.; Schroder, K.; Irvine, K.M.; et al. Salmonella Employs Multiple Mechanisms to Subvert the TLR-Inducible Zinc-Mediated Antimicrobial Response of Human Macrophages. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 1901–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stocks, C.J.; Phan, M.D.; Achard, M.E.S.; Nhu, N.T.K.; Condon, N.D.; Gawthorne, J.A.; Lo, A.W.; Peters, K.M.; McEwan, A.G.; Kapetanovic, R.; et al. Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli Employs Both Evasion and Resistance to Subvert Innate Immune-Mediated Zinc Toxicity for Dissemination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 6341–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ong, C.L.Y.; Gillen, C.M.; Barnett, T.C.; Walker, M.J.; McEwan, A.G. An Antimicrobial Role for Zinc in Innate Immune Defense against Group A Streptococcus. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- von Pein, J.B.; Stocks, C.J.; Schembri, M.A.; Kapetanovic, R.; Sweet, M.J. An Alloy of Zinc and Innate Immunity: Galvanising Host Defence against Infection. Cell Microbiol. 2021, 23, e13268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian Vignesh, K.; Landero Figueroa, J.A.; Porollo, A.; Divanovic, S.; Caruso, J.A.; Deepe, G.S. IL-4 Induces Metallothionein 3- and SLC30A4-Dependent Increase in Intracellular Zn 2+ That Promotes Pathogen Persistence in Macrophages. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 3232–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vignesh, K.S.; Landero Figueroa, J.A.; Porollo, A.; Caruso, J.A.; Deepe, G.S. Zinc Sequestration: Arming Phagocyte Defense against Fungal Attack. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, H.; Morikawa, H.; Kamon, H.; Iguchi, M.; Hojyo, S.; Fukada, T.; Yamashita, S.; Kaisho, T.; Akira, S.; Murakami, M.; et al. Toll-like receptor-mediated regulation of zinc homeostasis influences dendritic cell function. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuzzi, J.P.; Lichten, L.A.; Rivera, S.; Blanchard, R.K.; Aydemir, T.B.; Knutson, M.D.; Ganz, T.; Cousins, R.J. Interleukin-6 regulates the zinc transporter Zip14 in liver and contributes to the hypozincemia of the acute-phase response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 6843–6848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keller, P.J.; Schmidt, A.D.; Wittbrodt, J.; Stelzer, E.H.K. Digital Scanned Laser Light-Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy (DSLM) of Zebrafish and Drosophila Embryonic Development. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2011, 2011, pdbprot065839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of Embryonic Development of the Zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, S.M.; Freeman, J.L. RNA Isolation from Embryonic Zebrafish and CDNA Synthesis for Gene Expression Analysis. J. Vis. Exp. 2009, 30, e1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koressaar, T.; Remm, M. Enhancements and Modifications of Primer Design Program Primer3. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1289–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing Real-Time PCR Data by the Comparative CT Method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Name | Strain | Relevant Genotype | Reference |
| wild-type | PA14 | Lab collection | |
| znuA | MDO101 | znuA::Gm | [6] |
| zrmA | MDO111 | zrmA::Gm | [5] |
| znuAzrmA | MDO113 | znuA::scar zrmA::Gm | [5] |
| Gene | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
| dksA2 | AAGCCCAGCAGGACTTCTTC | TGTCGAGCAGCTTCTTCTCC |
| ef1α | TTGAGAAGAAAATCGGTGGTGCTG | GGAACGGTGTGATTGAGGGAAATTC |
| oprI | ATTCTCTGCTCTGGCTCTGG | CGGTCTGCTGAGCTTTCTG |
| PA14_16660 | CATCAACGCCCTGATGAGTA | GACTTCGCCTCGATCAACTC |
| rpmE2 | GCCGACGTGTACTTCCTGAT | GCGTCACGTAGGGATAGGTC |
| rpoD | CATCGCCAAGAAGTACACCA | CCACGACGGTATTCGAACTT |
| slc30a1a | ACACAAGAACGGGAAGGTCC | GTGACACATATCGGCAGCCT |
| slc30a4 | TCCTCGATGTCGGGTCTGAT | GCAGATCCTCCGAGAAGTCG |
| slc30a5 | ACTCTGTGGACCACTCAGGA | GCACCCCTCGTCTTAGAAGG |
| slc30a7 | TGATGATCGCAGACCCCATC | GCATGGTCCAGAGAAGGAGG |
| zrmA | GACACCCGTATCGAGGACAT | GAAGCCACGGACGTTGTACT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Secli, V.; Di Biagio, C.; Martini, A.; Michetti, E.; Pacello, F.; Ammendola, S.; Battistoni, A. Localized Infections with P. aeruginosa Strains Defective in Zinc Uptake Reveal That Zebrafish Embryos Recapitulate Nutritional Immunity Responses of Higher Eukaryotes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24020944
Secli V, Di Biagio C, Martini A, Michetti E, Pacello F, Ammendola S, Battistoni A. Localized Infections with P. aeruginosa Strains Defective in Zinc Uptake Reveal That Zebrafish Embryos Recapitulate Nutritional Immunity Responses of Higher Eukaryotes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(2):944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24020944
Chicago/Turabian StyleSecli, Valerio, Claudia Di Biagio, Arianna Martini, Emma Michetti, Francesca Pacello, Serena Ammendola, and Andrea Battistoni. 2023. "Localized Infections with P. aeruginosa Strains Defective in Zinc Uptake Reveal That Zebrafish Embryos Recapitulate Nutritional Immunity Responses of Higher Eukaryotes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 2: 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24020944
APA StyleSecli, V., Di Biagio, C., Martini, A., Michetti, E., Pacello, F., Ammendola, S., & Battistoni, A. (2023). Localized Infections with P. aeruginosa Strains Defective in Zinc Uptake Reveal That Zebrafish Embryos Recapitulate Nutritional Immunity Responses of Higher Eukaryotes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(2), 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24020944







