Abstract
The Bdnf (brain-derived neurotrophic factor) gene contains eight regulatory exons (I–VIII) alternatively spliced to the protein-coding exon IX. Only exons I, II, IV, and VI are relatively well studied. The BDNF system and brain serotonergic system are tightly interconnected and associated with aggression. The benzopentathiepine TC-2153 affects both systems and exerts antiaggressive action. Our aim was to evaluate the effects of TC-2153 on the Bdnf exons I–IX’s expressions and serotonin receptors’ mRNA levels in the brain of rats featuring high aggression toward humans (aggressive) or its absence (tame). Aggressive and tame adult male rats were treated once with vehicle or 10 or 20 mg/kg of TC-2153. mRNA was quantified in the cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and midbrain with real-time PCR. Selective breeding for high aggression or its absence affected the serotonin receptors’ and Bdnf exons’ transcripts differentially, depending on the genotype (strain) and brain region. TC-2153 had comprehensive effects on the Bdnf exons’ expressions. The main trend was downregulation in the hypothalamus and midbrain. TC-2153 increased 5-HT1B receptor hypothalamusc mRNA expression. For the first time, an influence of TC-2153 on the expressions of Bdnf regulatory exons and the 5-HT1B receptor was shown, as was an association between Bdnf regulatory exons and fear-induced aggression involving genetic predisposition.
1. Introduction
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is the most abundant neurotrophin in the brain and is involved in neuro- and gliogenesis, neuroprotection, long- and short-term synaptic plasticity, and synaptogenesis (for a review, see [1]). This variety of functions is partly explained by its sophisticated gene structure. The rodent Bdnf gene consists of eight 5′ noncoding exons (I–VIII) alternatively spliced to a common 3′ protein-coding exon [2]. The numerous Bdnf RNA splice variants eventually encode the same BDNF protein. It has been shown that these eight regulatory exons undergo differential expression throughout distinct brain regions and brain developmental stages [3]. Moreover, 5′ regulatory exons serve to localize mRNAs to different parts of a neuron [4], where local translation and prompt availability of BDNF are crucial for neuroplasticity and synaptic functioning (for a review, see [5]). Disruption of untranslated exons I, II, IV, and VI diversely affects dendritic morphology and spine arborization in basal and apical dendrites [6]. Furthermore, data obtained over the last decade implicate the noncoding Bdnf exons in the regulation of behavior and pathological conditions. Downregulations of exons IV and VI are associated with elevated depressive-like behavior [7], while underexpression of exon VII is implicated in heightened depression and anxiety [8]. Reductions in exons II, IV, and VI’s expressions are observed in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease [9]. On the other hand, overexpression of the regulatory Bdnf exons is mainly associated with increased stress and fear conditioning. Enhanced transcriptions of exons I and IV in fear-conditioned animals have been documented [10,11]. Notably, distinct types of stress produce different alterations in the expressions of exons I, IV, and VI [12,13]. While single-immobilization stress leads to the downregulations of exons I and IV, these two exons are upregulated under the influence of foot shock stress [12]. At the same time, the expressions of exons IV and VI are increased after acute stress [13]. Although all these studies are mainly dedicated to exons I, II, IV, and VI, there is very little information on the cellular and behavioral roles of the other four regulatory Bdnf exons: III, V, VII, and VIII.
There is interest in the involvement of BDNF in the mechanism of aggressive behavior [14,15,16]. Some studies point to the elevation of aggression induced by central BDNF administration in mice [17] and a high BDNF protein level in the aggressive AB–Halle (ABH) mouse strain [15], while other research indicates an association between BDNF disruption and aggressiveness both in animals and humans [16,18,19]. Therefore, the participation of BDNF in the mechanism of aggression is controversial and may depend on the 5′ regulatory exons. At present, there is only one study showing associations between the different regulatory Bdnf exons’ expressions and aggression [20]. That report revealed that selective disruption of exons I and II, but not exons IV and VI, results in elevated offensive territorial aggression in mice [20]. These types of depletion are accompanied by changes in the serotonergic system: mutations of exons I and II are associated with an increase in serotonin transporter and 5-HT2A receptor gene expressions [20]. The connection between aggression and the serotonergic system is well known, and serotonin is considered one of the main neurotransmitters regulating this complex type of behavior (for a review, see [21]). Genetic variants of the serotonin receptors 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT2A, and 5-HT7 [22,23,24,25] are implicated in this type of behavior. Moreover, serotonin receptors and BDNF share a reciprocal modulating link: BDNF injection raises the expressions of genes encoding the 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, and 5-HT2A receptors [26,27], whereas activation of the 5-HT2A receptor in turn regulates Bdnf gene expression [28,29,30].
On the other hand, the molecular mechanisms underlying aggression involve multiple brain systems and are associated with environmental as well as hereditary factors. Two strains of wild Norway rats selectively bred for 90 generations at the Institute of Cytology and Genetics (Novosibirsk, Russia) for enhancement (aggressive rats) or absence (tame rats) of aggression toward humans are a suitable model for investigating mechanisms of fear-induced aggression and domestication. These animals differ in a number of behavioral characteristics: the aggressive rats manifest greater fear [31,32], high anxiety [33], and a reduction in learning abilities and memory compared with the tame animals [34]. Moreover, the aggressive and tame rats demonstrate significant alterations in their brain serotonergic and BDNF systems [14,31,35,36,37,38,39,40]. Nonetheless, the function of the noncoding regulatory Bdnf exons in the mechanisms of aggression toward humans and domestication has not been studied yet.
Recently, it was shown that the novel antidepressant benzopentathiepine TC-2153—when administered acutely or chronically—significantly diminishes the fear-induced aggression in aggressive rats and, after acute administration, has an anxiolytic effect on both tame and aggressive Norway rats [41]. TC-2153 is known to elevate the expression of the common protein-coding exon IX of the Bdnf gene [42] and to influence the serotonergic system in mice [43,44,45,46]. Earlier, it has been shown that the 5′ untranslated regulatory exons can be affected by the administration of classic antidepressants [7,47,48]. On the basis of these findings, we propose in this study that the new antidepressant TC-2153 can differently affect the expressions of the Bdnf exons, and these results can shed light on the psychotropic effects of TC-2153.
Accordingly, the aim of this study was to investigate the expressions of all the Bdnf exons (I–IX) and serotonin receptors 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT2A, and 5-HT7 (encoded by genes Htr1a, Htr1b, Htr2a, and Htr7, respectively) in the model of genetically determined fear-induced aggression (or its absence) after acute administration of the novel antidepressant TC-2153.
In this work, for the first time, we showed that TC-2153 affects the regulatory Bdnf exons depending on the genotype (strain) and brain region and upregulates Htr1b mRNA. The regulatory Bdnf exons I–VIII were found to be associated with fear-induced aggression involving genetic predisposition.
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Acute TC-2153 Treatment on mRNA Levels of Bdnf Untranslated Exons I–VIII and Coding Exon IX in the Cortex of Aggressive and Tame Rats
The two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) revealed significant effects of the genotype factor on the expressions of exons I–III, V, VII, and VIII. At the same time, no effect of the drug factor or of the interaction of the two factors on the expressions of exons I–IX was detected (Table S1). Aggressive rats manifested higher expressions of exons I, II, III, V, VII, and VIII compared with the tame animals (Figure 1).
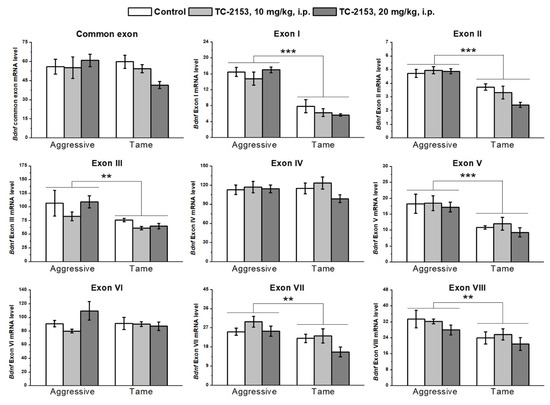
Figure 1.
Effects of acute administration of vehicle (control) or TC-2153 at a dose of 10 or 20 mg/kg on mRNA levels of Bdnf (brain-derived neurotrophic factor) regulatory exons I–VIII and coding (common) exon IX in the cortex of aggressive and tame rats. The expression levels were evaluated as the number of transcript copies per 100 copies of Polr2a mRNA. ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001 for the genotype effect (5–7 animals per group).
2.2. Effects of Acute TC-2153 Treatment on mRNA Levels of Bdnf Untranslated Exons I–VIII and Coding Exon IX in the Hippocampus of Aggressive and Tame Rats
We found significant effects of the genotype factor on the expressions of all 5′ noncoding exons and of the drug factor on exons V and VI, while there were no effects of the factors’ interaction on the expressions of the studied exons (Table S2). Expression levels of exons II–VIII were lower in the hippocampus of aggressive rats compared with tame ones, while expression of exon I proved to be elevated in aggressive rats. TC-2153 at the dose of 10 mg/kg increased the mRNA level of exon VI. At the same time, the post hoc analysis of exon V expression did not reveal any differences between the groups (Figure 2).
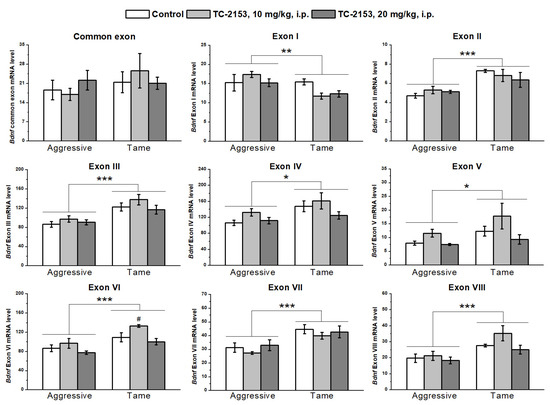
Figure 2.
The impact of acute administration of vehicle (control) or TC-2153 at a dose of 10 or 20 mg/kg on mRNA levels of Bdnf (brain-derived neurotrophic factor) regulatory exons I–VIII and coding (common) exon IX in the hippocampus of aggressive and tame rats. The expression levels were evaluated as the number of transcript copies per 100 copies of Polr2a mRNA. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001 for the genotype effect; # p < 0.05 in comparison with the control group (5–7 animals per group).
2.3. Effects of Acute TC-2153 Treatment on mRNA Levels of Bdnf Untranslated Exons I–VIII and Coding Exon IX in the Hypothalamus of Aggressive and Tame Rats
In the hypothalamus, the two-way ANOVA uncovered significant effects of the genotype on the expressions of common exon IX and exon I and of the drug factor on the expressions of exons I, V, and VII, while no effect of a genotype × drug interaction was observed (Table S3). Aggressive animals featured higher expressions of the common exon IX and of exon I than tame rats did. TC-2153 at the dose 20 mg/kg reduced the expression of exon I in both strains and the expression levels of exons V and VII in tame rats (Figure 3).
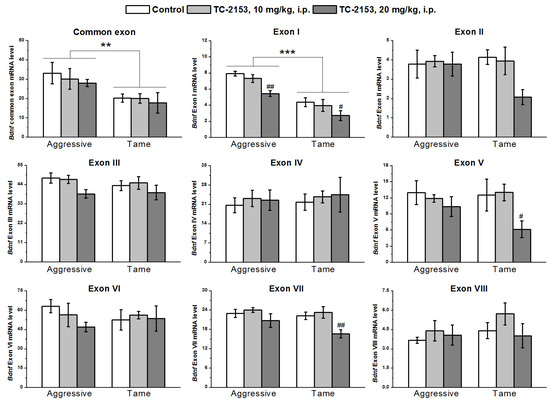
Figure 3.
The impact of acute administration of vehicle (control) or TC-2153 at a dose of 10 or 20 mg/kg on mRNA levels of Bdnf (brain-derived neurotrophic factor) regulatory exons I–VIII and coding (common) exon IX in the hypothalamus of aggressive and tame rats. The expression levels were evaluated as the number of transcript copies per 100 copies of Polr2a mRNA. ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001 for the genotype effect; # p < 0.05 and ## p < 0.01 in comparison with the control group (4–7 animals per group).
2.4. Effects of Acute TC-2153 Treatment on mRNA Levels of Bdnf Untranslated Exons I–VIII and Coding Exon IX in the Midbrain of Aggressive and Tame Rats
In the midbrain, with the two-way ANOVA, we found significant effects of the genotype on the expressions of exons I–V and effects of the drug factor on exons II, IV, V, VII, and VIII and common exon IX, while no effects of a genotype × drug interaction were seen (Table S4). The expressions of exons I–V were higher in aggressive rats than in tame ones. TC-2153 significantly reduced exons II and VIII’s mRNA levels in tame rats, while the expressions of exons IV, V, and VII were significantly diminished in both strains. TC-2153 at the dose of 20 mg/kg also reduced the expression of the common exon IX in tame rats (Figure 4).
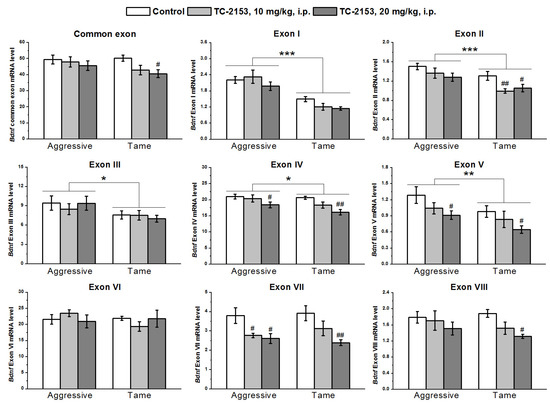
Figure 4.
Effects of acute administration of vehicle (control) or TC-2153 at a dose of 10 or 20 mg/kg on mRNA levels of Bdnf (brain-derived neurotrophic factor) regulatory exons I–VIII and coding (common) exon IX in the midbrain of aggressive and tame rats. The expression levels were evaluated as the number of transcript copies per 100 copies of Polr2a mRNA. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001 for the genotype effect; # p < 0.05 and ## p < 0.01 in comparison with the control group (5–7 animals per group).
2.5. The Influence of Acute TC-2153 Treatment on the Htr1a mRNA Levels in Brain Structures of Aggressive and Tame Rats
We found a significant effect of the genotype on the 5-HT1A receptor mRNA levels in the hippocampus (F1,33 = 9.42, p < 0.01) and midbrain (F1,32 = 5.69, p < 0.05): aggressive rats had lower Htr1a gene expression than the tame animals did. Nonetheless, no genotype effect was detectable in the cortex (F1,34 < 1) and hypothalamus (F1,36 = 2.06, p > 0.05). Acute TC-2153 administration had an impact on Htr1a mRNA expression in the hippocampus (F2,33 = 5.05, p < 0.05); however, the post hoc analysis did not show any difference between the groups. In other brain structures, no effect of the drug was found (cortex F2,34 < 1; hypothalamus F2,36 < 1; and midbrain F2,32 = 1.39, p > 0.05). Genotype × drug interactions were insignificant (cortex F2,34 < 1; hippocampus F2,33 < 1; hypothalamus F2,36 = 1.41, p > 0.05; and midbrain F2,32 = 1.02, p > 0.05) (Figure 5).
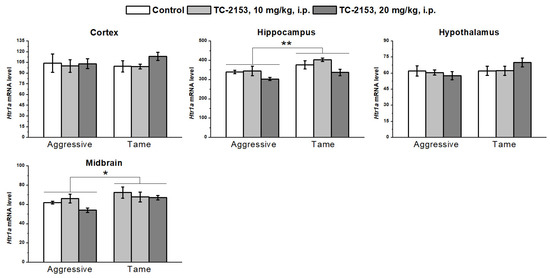
Figure 5.
Effects of acute administration of vehicle (control) or TC-2153 at a dose of 10 or 20 mg/kg on 5-HT1A receptor (Htr1a) mRNA levels in the cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and midbrain of aggressive and tame rats. The expression levels were assessed as the number of transcript copies per 100 copies of Polr2a mRNA. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 for the genotype effect (5–7 animals per group).
2.6. Effects of Acute TC-2153 Treatment on Htr7 mRNA Levels in Brain Structures of Aggressive and Tame Rats
We detected a higher level of 5-HT7 receptor mRNA in the cortex (genotype effect F1,32 = 15.79, p < 0.001) and hippocampus (genotype effect F1,36 = 4.45, p < 0.05) of aggressive rats compared with tame ones. No genotype effect was found in the hypothalamus (F1,35 = 1.11, p > 0.05) and midbrain (F1,36 = 1.52, p > 0.05). TC-2153 exerted no effect in any of the tested brain structures (cortex F2,32 < 1; hippocampus F2,36 < 1; hypothalamus F2,35 < 1; and midbrain F2,36 < 1). Genotype × drug interactions were insignificant (cortex F2,32 < 1; hippocampus F2,36 = 2.57, p > 0.05; hypothalamus F2,35 < 1; and midbrain F2,36 < 1) (Figure 6).
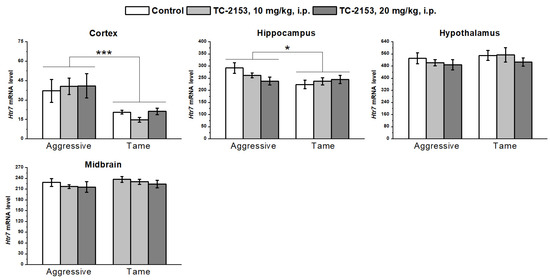
Figure 6.
Effects of acute administration of vehicle (control) or TC-2153 at a dose of 10 or 20 mg/kg on 5-HT7 receptor (Htr7) mRNA levels in the cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and midbrain of aggressive and tame rats. The expression levels were determined as the number of transcript copies per 100 copies of Polr2a mRNA. * p < 0.05 and *** p < 0.001 for the genotype effect (5–7 animals per group).
2.7. Effects of Acute TC-2153 Treatment on Htr1b mRNA Levels in Brain Structures of Aggressive and Tame Rats
Aggressive rats had an elevated expression of the 5-HT1B receptor gene in the frontal cortex (genotype effect F1,31 = 6.94, p < 0.05) and low expression in the midbrain (genotype effect F1,35 = 6.79, p < 0.05). No genotype effect was detectable in the hippocampus (F1,35 < 1) and hypothalamus (F1,35 < 1). Acute TC-2153 administration upregulated the mRNA of this receptor in the hypothalamus of both strains of rats (F2,35 = 4.25, p < 0.05). The drug did not affect 5-HT1B receptor expression in the cortex (F2,31 < 1), hippocampus (F2,35 < 1), and midbrain (F2,35 = 1.27, p > 0.05). At the same time, there were no effects of genotype × drug interaction (cortex F2,31 < 1; hippocampus F2,35 < 1; hypothalamus F2,35 = 1.49, p > 0.05; and midbrain F2,35 = 1.55, p > 0.05) (Figure 7).
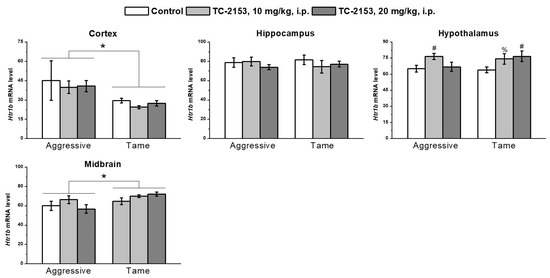
Figure 7.
The influence of acute administration of vehicle (control) or TC-2153 at a dose of 10 or 20 mg/kg on 5-HT1B receptor (Htr1b) mRNA levels in the cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and midbrain of aggressive and tame rats. The expression levels were evaluated as the number of transcript copies per 100 copies of Polr2a mRNA. * p < 0.05 for the genotype effect; # p < 0.05 and % p = 0.062 in comparison with the control group (5–7 animals per group).
2.8. Effects of Acute TC-2153 Treatment on Htr2a mRNA Levels in Brain Structures of Aggressive and Tame Rats
The investigation of 5-HT2A receptor expression revealed a genotype effect in all the tested brain structures, except for in the cortex (cortex F1,35 = 3.12, p > 0.05; hippocampus F1,35 = 17.90, p < 0.001; hypothalamus F1,35 = 4.73, p < 0.05; and midbrain F1,36 = 5.06, p < 0.05): aggressive rats had higher mRNA levels relative to the tame animals. At the same time, no influence of the drug (cortex F2,35 < 1; hippocampus F2,35 = 1.95, p > 0.05; hypothalamus F2,35 = 2.53, p > 0.05; and midbrain F2,36 < 1) or of a genotype × drug interaction (cortex F2,35 < 1; hippocampus F2,35 < 1; hypothalamus F2,35 = 1.82, p > 0.05; and midbrain F2,36 < 1) was registered in any of the analyzed brain structures (Figure 8).
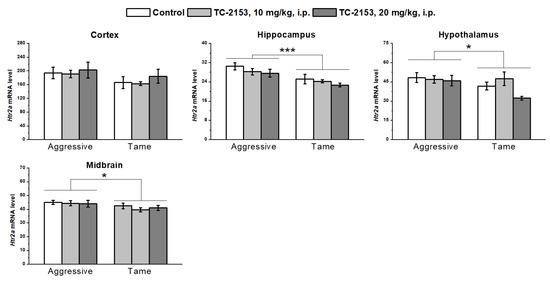
Figure 8.
Effects of acute administration of vehicle (control) or TC-2153 at the dose 10 or 20 mg/kg on 5-HT2A receptor (Htr2a) mRNA levels in the cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and midbrain of aggressive and tame rats. The expression levels were assessed as the number of transcript copies per 100 copies of Polr2a mRNA. * p < 0.05 and *** p < 0.001 for the genotype effect (6–7 animals per group).
3. Discussion
In this study, primers for all eight 5′ untranslated exons of the rat Bdnf gene were designed, and the mRNA levels of these regulatory exons were assessed in the cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and midbrain of Norway rats (which had a genetic predisposition to fear-induced aggression or its absence) after acute treatment with the novel antidepressant TC-2153.
We obtained quite diverse results. Compared with the tame rats, the aggressive rats featured elevated expression levels of exons I, II, III, V, VII, and VIII in the cortex; exons I and IX in the hypothalamus; and exons I, II, III, IV, and V in the midbrain, and underexpression of all the regulatory exons in the hippocampus except for exon I, which was upregulated (Figure 9). The genotype effects in the cortex, hypothalamus, and midbrain are in agreement with multiple research articles that indicate an association between aggression and elevated levels of the BDNF protein and its isoforms [15,49]. It should be noted that earlier, we revealed a difference between the same rat strains in the expression of protein-coding exon IX in the cortex [14]. These results failed to be replicated in the current study. As opposed to the current study, in the previous work, the animals received neither drug nor vehicle administration. The differences in the experimental design could explain the discrepancies between our present results and previously published data.
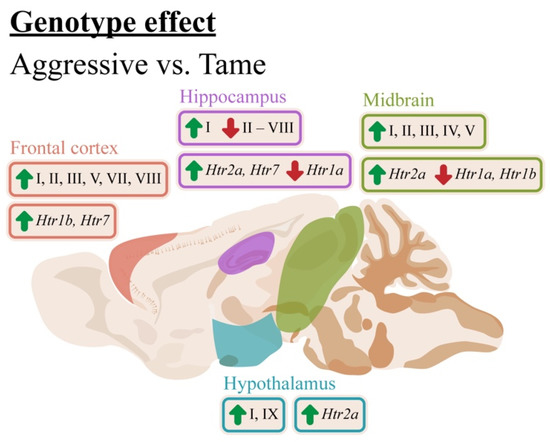
Figure 9.
The influence of the genotype on mRNA levels of Bdnf (brain-derived neurotrophic factor) untranslated exons I–VIII and protein-coding exon IX and on Htr1a, Htr7, Htr1b, and Htr2a in the frontal cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and midbrain of aggressive and tame rats. Green arrows indicate an elevation and red arrows indicate a reduction of expression in aggressive rats compared to the tame ones.
In the hippocampus, the expressions of almost all the 5′ regulatory were higher in the tame rats. At the same time, in this project, we detected no difference between the rat strains in the expression of protein-coding exon IX in the hippocampus, in good agreement with the previously obtained data [14]. It is well known that the hippocampus plays a crucial part in memory, learning, and neural plasticity. Previously, it has been reported that aggressive rats show impaired learning abilities in the Morris water maze test [34]. These disturbances in the spatial memory of aggressive rats may be explained by the reduction in the expression of Bdnf regulatory exons in the hippocampus revealed in the current paper.
To date, the association between Bdnf regulatory exons and aggression has been observed only in one paper (by Maynard and colleagues), who investigated whether a mutation of exon I, II, IV, or VI leads to territorially induced intermale aggression [20]. They showed that the lack of exon I or II aggravates such behavior, while disruption of exons IV or VI does not have such an effect. The other four exons were not tested in that study. At first glance, our results contradict these findings: exon I expression turned out to be elevated in the cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and midbrain of aggressive rats, exon II was upregulated in the cortex and midbrain and underexpressed in the hippocampus, exon IV was also upregulated in the midbrain and downregulated in the hippocampus, while the expression of exon VI was lower in the hippocampus of aggressive rats. Nonetheless, it should be mentioned that territorial intermale aggression is not the same type of aggressive behavior as fear-induced aggression, and they are probably regulated by different mechanisms. Moreover, it has been reported that a knockout of Bdnf causes aggressive behavior [16,50,51]. On the contrary, genetic and ethological models of aggression indicate a positive association between BDNF level and aggressive behavior [14,15,17]. Thus, our study confirmed the involvement of exons I and II in aggressive behavior, as documented by Maynard and colleagues. On the other hand, our findings indicate the participations of exons IV and VI as well, which may be explained by the difference in the type of aggression. Moreover, in this study we, for the first time, detected changes in the expression of the other four regulatory exons—III, V, VII, and VIII—in the brains of aggressive rats in the model of fear-induced aggression compared with tame animals. Overall, the patterns of the 5′ exons’ expressions depend on the brain region.
We detected a higher mRNA level for the majority of the regulatory Bdnf exons in the midbrain of aggressive rats compared with tame ones. It is well known that the cell bodies of 5-HT (serotonin) neurons are located in the midbrain raphe nuclei [52], ensuring neurotransmitter synthesis. The brain 5-HT system is known to play a central role in mechanisms of aggression [21]. On the other hand, BDNF takes part in the development of serotonin neurons at the early stages of ontogenesis of the central nervous system [53,54]. In a mature brain, these two systems are interdependent and regulate each other (for a review, see [55]). Nevertheless, it is still unclear what function the regulatory Bdnf exons perform in the interaction between the BDNF system and the 5-HT system and in the involvement of this crosstalk in the mechanisms of genetically determined aggressive behavior. Pharmacological and genetic studies suggest that the serotonin receptors 5-HT1A, 5-HT7, 5-HT1B, and 5-HT2A (encoded by genes Htr1a, Htr7, Htr1b, and Htr2a, respectively) participate in the regulation of different types of aggression [22,23,24,25]. Therefore, to research the potential connection between the regulatory Bdnf exons and the 5-HT system, we measured the mRNA levels of these 5-HT receptors in the brains of rats with a genetic predisposition to fear-induced aggression or its absence.
We noticed differences in the expressions of 5-HT receptors between the tested rat strains. Aggressive rats were found to have lower Htr1a mRNA levels in the hippocampus and midbrain relative to tame rats. It is known that 5-HT1A receptor agonists exert an antiaggressive effect [38,56]. Our findings suggest that a higher expression of this receptor’s mRNA can also be associated with the absence of aggression in tame animals. Moreover, in a previous report, we noted that aggressive rats have higher anxiety than tame rats in the elevated plus maze test [41]. On the other hand, a knockout of the Htr1a gene also aggravates anxious behavior [57]. Consequently, the revealed difference in 5-HT1A receptor expression between these rat strains can offer an explanation for the previous findings.
It is well established that 5-HT1A receptors can form heterodimeric complexes with 5-HT7 receptors [58] and thereby can regulate each other’s activity. There are contradictory data about the link between 5-HT7 receptors and anxiety [59,60]. At the same time, it has been previously shown that aggressive rats have a high Htr7 mRNA level in the frontal cortex and a reduced level in the midbrain and hypothalamus [22]. In the present study, we documented an elevated expression of this receptor in the frontal cortex of aggressive rats, and (in contrast to previous data) in the hippocampus, while no difference was observed in the midbrain and hypothalamus. 5-HT7 receptors are reported to be involved in the regulation of memory [61]. Perhaps the elevated expressions of these receptors in the hippocampus and cortex are related to memory consolidation. At the same time, the current study provides additional evidence of the alteration of 5-HT7 receptor expression in the brains of rats with genetically predisposed fear-induced aggression compared with tame ones.
The observed effect of the genotype (strain) on the 5-HT1B receptor was dependent on the brain region. Although in the frontal cortex, aggressive rats had a higher Htr1b mRNA level compared with the tame animals, and in the midbrain, the pattern was the opposite. It is well known that 5-HT1B receptor agonists tend to inhibit aggressive behavior [62], whereas a knockout of this gene leads to more profound aggression [63]. Therefore, the decrease in Htr1b expression in the midbrain, where cell bodies of serotonergic neurons are located, may be linked with the aggression enhancement, whereas the Htr1b upregulation in the cortex probably represents a compensatory mechanism.
At the same time, in aggressive rats, Htr2a mRNA levels proved to be elevated in the hippocampus, hypothalamus, and midbrain, pointing to the importance of this gene during the selection for high aggression toward humans or its absence. The 5-HT2A receptor is known to partake in other types of aggression as well, although its action is ambiguous: agonists [64], as well as antagonists [65], show an antiaggressive effect. In the present work, we demonstrated that 5-HT2A receptor expression is elevated in the brains of rats with increased fear-induced aggression. Furthermore, our data indicate a possible association between 5-HT2A receptor expression and Bdnf exon I mRNA levels. Both were elevated in the brains of aggressive rats compared with tame ones in almost all the tested brain structures. By contrast, Maynard and colleagues have previously observed an opposite association between these two genes: Bdnf exon I knockouts yield 5-HT2A receptor overexpression in the prefrontal cortex [20]. Nevertheless, based on the current results, it is possible to hypothesize that exon I may play a part in the regulation of 5-HT2A receptor expression. As described above, aggressive rats manifested a lower expression of the 5-HT1A receptor in the midbrain, where it was mainly expressed presynaptically, and its activation leads to the hyperpolarization of serotonergic neurons and inhibition of serotonin signaling (for a review, see [66]). On the other hand, 5-HT2A receptors are known activators of the 5-HT system (for a review, see [67]), and thus, via such expression patterns of these two receptor types, aggressive rats possess a more activated 5-HT system than tame rats do. This finding is consistent with earlier data suggesting that aggressive rats have a higher level of 5-HT in the cingulate cortex, nucleus accumbens, and putamen [33] compared with tame ones.
Furthermore, in this paper, we present an effect of acute administration of the benzopentathiepine TC-2153 on the expressions of the Bdnf 5′ regulatory exons (Figure 10). This influence is differentially exerted among distinct brain structures and depends on the genotype. The main impact of acute TC-2153 administration was seen in the hypothalamus and midbrain. The drug downregulated the Bdnf exons’ expressions in these brain structures. In tame rats, TC-2153 lowered the expressions of exons I, V, and VII in the hypothalamus and of exons II, IV, V, VII, VIII, and IX in the midbrain. In addition, in response to TC-2153 administration, aggressive rats showed a reduction in exon I expression in the hypothalamus and in the expressions of exons IV, V, and VII in the midbrain. Taking into account the results on the antiaggressive effect of TC-2153 obtained earlier [41], it is not surprising to see the main effects of this drug in the hypothalamus and midbrain because these brain structures are deeply involved in the regulation of aggressive behavior [68]. It is noteworthy that TC-2153 at the dose of 10 mg/kg elevated the expression of exon VI in the hippocampus. Therefore, TC-2153 decreased the expression of various Bdnf exons in the brain, except for exon VI in the hippocampus. Taken together, all our data suggest that TC-2153 is the first known drug to have such a comprehensive effect on Bdnf regulation, partly because the effects of other drugs have been investigated only on exons I, II, IV, and VI [7,47,69].
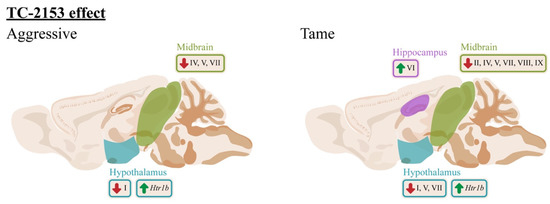
Figure 10.
The effects of acute TC-2153 administration on mRNA levels of Bdnf (brain-derived neurotrophic factor) untranslated exons I–VIII and protein-coding exon IX and Htr1a, Htr7, Htr1b, and Htr2a in the frontal cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and midbrain of aggressive and tame rats. Green arrows indicate an upregulation and red arrows indicate a downregulation of expression after acute administration of TC-2153.
Earlier, it was shown that chronic TC-2153 administration raises the expression of the Bdnf protein-coding exon IX in the hippocampus of ASC mice [42]. In this study, we demonstrated that acute TC-2153 administration diminishes the expression of the protein-coding exon IX in the midbrain and hypothalamus of tame rats. These results are in good concordance with those obtained with the classic antidepressants fluoxetine, tranylcypromine, and desipramine. These drugs also cause a reduction in the expression of various Bdnf exons after acute administration but upregulate their expression during chronic administration [47,48]. The only known target for TC-2153 is striatal-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase (STEP) [44,46,70], which is known to exert a downregulating effect on BDNF levels [71] through the dephosphorylation of kinases ERK1/2, which then fail to cease the phosphorylation of CREB: the main regulatory factor of Bdnf promoters. Via this mechanism, TC-2153, through the deactivation of STEP, should cause the upregulation of BDNF. We, however, revealed a downregulating effect on the expression of the Bdnf regulatory exons. These results may indicate the existence of another pharmacological target for TC-2153. Recently, it was found that fluoxetine binds directly to the receptor TrkB [72]. Taking into account the similarities between the effects of TC-2153 administration and those of fluoxetine [73,74,75], it is fair to assume that TC-2153 may also directly interact with TrkB. In this case, acute activation of this receptor may lead to a short-term compensatory decrease in Bdnf expression (as observed in a previous study after acute administration of fluoxetine [47,48]) and then to Bdnf upregulation when administered chronically. This hypothesis requires further research.
In this study, we found that TC-2153 increases the Htr1b mRNA level in the hypothalamus, suggesting that the acute antiaggressive effect of the drug may be mediated via regulation of this receptor’s expression. Furthermore, the 5-HT1B receptor is a Gi protein-coupled receptor, and its activation induces a decrease in cAMP levels and then the dephosphorylation of protein kinase A and CREB [76], which regulate Bdnf transcription. This observation suggests that the downregulating effect of TC-2153 on the Bdnf exons’ expressions may be mediated by the influence of this drug on the 5-HT1B receptor. By contrast, acute TC-2153 administration failed to affect the mRNA levels of Htr1a, Htr7, and Htr2a. Previously, it has been shown that chronic TC-2153 administration reduces the mRNA level of Htr1a [43] and inhibits functional activity and the protein level of the 5-HT2A receptor [45]. Perhaps the changes in the expressions of the Bdnf regulatory exons—as seen after acute administration—lead to a more lasting effect on these serotonin receptors, which is attributed to the chronic TC-2153 administration.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Experimental Procedures
The experiments were performed on adult outbred male rats (Rattus norvegicus) (4–5 months old, weighing 300–350 g) selectively bred from wild rats for 90 generations at the Institute of Cytology and Genetics (Novosibirsk, Russia) for the absence (tame rats, n = 21) or enhancement (aggressive rats, n = 21) of fear-induced aggressive behavior toward humans [77,78].
The animals were housed in metal cages (50 × 33 × 20 cm) under standard laboratory conditions on a natural light–dark cycle with free access to water and feed in groups of four individuals. The study was conducted at the Centre for Genetic Resources of Laboratory Animals at the federal research center of the Institute of Cytology and Genetics, SB RAS (Novosibirsk, Russia) (RFMEFI62119X0023).
Forty-two rats (twenty-one aggressive and twenty-one tame) were used to evaluate the influence of acute administration of TC-2153 on the expression of different Bdnf transcripts and serotonin receptors. The new-generation antidepressant TC-2153 [8-(trifluoromethyl)benzo[f][1–5]pentathiepin-6-amine, N.N. Vorozhtsov Novosibirsk Institute of Organic Chemistry, Novosibirsk, Russia] was diluted in a solution of 0.05% Tween 20 and 0.05% DMSO as described before [45]. Rats were injected intraperitoneally (100 µL/100 g of body weight) with 10 or 20 mg/kg of TC-2153 or vehicle (a 0.05% solution of Tween 20 and DMSO) as a control. There were six groups of seven rats of both strains: (1) aggressive treated with vehicle, (2) aggressive treated with 10 mg/kg of TC-2153, (3) aggressive treated with 20 mg/kg of TC-2153, (4) tame treated with vehicle, (5) tame treated with 10 mg/kg of TC-2153, and (6) tame treated with 20 mg/kg of TC-2153. Five hours after a single TC-2153 or vehicle injection the rats were decapitated; their brains were rapidly removed on ice; and the cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and midbrain were dissected, frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80 °C.
4.2. Real-Time PCR
Total RNA was extracted from the brain structures (cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and midbrain) using the TRIzol Reagent (Ambion, Austin, TX, USA) according to a previously described procedure [41]. The extracted RNA was treated with RNase-free DNase (Promega, Fitchburg, WI, USA) and diluted to 0.125 µg/µL with diethyl pyrocarbonate-treated water. The obtained total RNA was subjected to complementary DNA (cDNA) synthesis with a random hexanucleotide mixture (BioLab Mix, Novosibirsk, Russia). The primers employed to estimate the numbers of Bdnf exons’ and serotonin receptors’ cDNA copies are listed in Table 1. SYBR Green I fluorescence detection (R-402 Master mix, Syntol, Moscow, Russia) was performed. As external standards, we used genomic DNA (0.06, 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, and 64 ng/µL) extracted from the rat livers [79,80,81]. Gene expression was evaluated as the number of cDNA copies per 100 copies of a housekeeping gene: DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II (Polr2a). To control amplification specificity, we performed a melting curve analysis at the end of each run for each pair of primers.

Table 1.
The primer sequences, annealing temperatures, and amplicon lengths.
4.3. Statistical Analysis
The data from the assays of Bdnf exons’ and serotonin receptors’ mRNA expressions were checked for normality and equality of variance with Lilliefors’s test and Barlett’s test, respectively. These results are presented as means ± standard error of the means and were subjected to a two-way ANOVA with “genotype” (strain) and “treatment” as two independent factors that can interact. If any effect was significant, the difference between groups was assessed with a post hoc test (Fischer’s least significant difference test for pairwise comparisons). Statistical significance was set to p < 0.05. Dixon criteria were applied to identify outliers.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, in this study, for the first time, we demonstrated that acute administration of the novel antidepressant and antiaggressive drug TC-2153 upregulates the mRNA of Htr1b in the hypothalamus of rats selectively bred for either high aggression toward humans or its absence. Moreover, the drug significantly diminished the expressions of several Bdnf regulatory exons in the hypothalamus and midbrain of aggressive and tame rats. Furthermore, we noted an association between different Bdnf untranslated regulatory exons and genetically determined fear-induced aggression. In the hippocampus, all Bdnf regulatory exons except exon I proved to be downregulated in aggressive rats, while in the frontal cortex, hypothalamus, and midbrain, the aggressive rats had elevated levels of various Bdnf regulatory exons compared with the tame animals. These data shed new light on the research into the role of Bdnf gene structure and of its regulation in mechanisms of aggression.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms24020983/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: V.S.M., A.V.K., V.S.N. and E.A.K.; formal analysis: V.S.M. and E.A.K.; investigation: V.S.M., R.V.K. and E.A.K.; resources: R.V.K., T.M.K., K.P.V. and N.F.S.; visualization: V.S.M.; supervision: E.A.K.; writing—original draft preparation: V.S.M., A.V.K., V.S.N. and E.A.K.; writing—reviewing and editing: V.S.M., A.V.K., V.S.N. and E.A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, project number 21-15-00051. The animals’ maintenance was funded by a Basic Research Project for a Young Researcher, grant number FWNR-2022-0010.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All experimental procedures were in compliance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals approved by the Ministry of Public Health of Russia (Supplement to decree No. 267, 19 June 2003), with the National Institutes of Health “Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals” (NIH Publication No. 8023, revised in 1978), and the European Communities Council Directive 86/609/EES. All manipulations of the animals were approved by the Scientific Council 9 of the Institute of Cytology and Genetics, SB RAS, in accordance with Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and Council of 22 September 2010. All the experiments were approved by (and conducted in accordance with the guidelines of) the Ethics Committee on animal testing at the Institute of Cytology and Genetics, Novosibirsk, Russia (protocol #99 of 9 November 2021) (the decree of the Presidium of the Russian Academy of Sciences No. 12000-496 of 2 April 1980). Every effort was made to minimize the number of animals used and their suffering.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Numakawa, T.; Suzuki, S.; Kumamaru, E.; Adachi, N.; Richards, M.; Kunugi, H. BDNF function and intracellular signaling in neurons. Histol. Histopathol. 2010, 25, 237–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aid, T.; Kazantseva, A.; Piirsoo, M.; Palm, K.; Timmusk, T. Mouse and ratBDNF gene structure and expression revisited. J. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 85, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perovic, M.; Tesic, V.; Djordjevic, A.M.; Smiljanic, K.; Loncarevic-Vasiljkovic, N.; Ruzdijic, S.; Kanazir, S. BDNF transcripts, proBDNF and proNGF, in the cortex and hippocampus throughout the life span of the rat. AGE 2012, 35, 2057–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baj, G.; Leone, E.; Chao, M.V.; Tongiorgi, E. Spatial segregation of BDNF transcripts enables BDNF to differentially shape distinct dendritic compartments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16813–16818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Nagappan, G.; Lu, Y. BDNF and synaptic plasticity, cognitive function, and dysfunction. In Neurotrophic Factors; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 220, pp. 223–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, K.R.; Hobbs, J.W.; Sukumar, M.; Kardian, A.S.; Jimenez, D.V.; Schloesser, R.J.; Martinowich, K. Bdnf mRNA splice variants differentially impact CA1 and CA3 dendrite complexity and spine morphology in the hippocampus. Brain Struct. Funct. 2017, 222, 3295–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsankova, N.M.; Berton, O.; Renthal, W.; Kumar, A.; Neve, R.L.; Nestler, E.J. Sustained hippocampal chromatin regulation in a mouse model of depression and antidepressant action. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ieraci, A.; Mallei, A.; Popoli, M. Social Isolation Stress Induces Anxious-Depressive-Like Behavior and Alterations of Neuroplasticity-Related Genes in Adult Male Mice. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 6212983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CZuccato, C.; Ciammola, A.; Rigamonti, D.; Leavitt, B.R.; Goffredo, D.; Conti, L.; MacDonald, M.E.; Friedlander, R.M.; Silani, V.; Hayden, M.R.; et al. Loss of Huntingtin-Mediated BDNF Gene Transcription in Huntington’s Disease. Science 2001, 293, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, L.-C.; Gean, P.-W. Transcriptional Regulation of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in the Amygdala during Consolidation of Fear Memory. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 72, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattiner, L.M.; Davis, M.; Ressler, K.J. Differential regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor transcripts during the consolidation of fear learning. Learn. Mem. 2004, 11, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchikami, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Morinobu, S.; Takei, S.; Yamawaki, S. Epigenetic Regulation of BDNF Gene in Response to Stress. Psychiatry Investig. 2010, 7, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neeley, E.; Berger, R.; Koenig, J.; Leonard, S. Prenatal stress differentially alters brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression and signaling across rat strains. Neuroscience 2011, 187, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilchibaeva, T.V.; Tsybko, A.S.; Kozhemyakina, R.V.; Kondaurova, E.; Popova, N.K.; Naumenko, V.S. Genetically defined fear-induced aggression: Focus on BDNF and its receptors. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 343, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, U.E.; Günther, L.; Scheuch, K.; Klein, J.; Eckhart, S.; Hellweg, R.; Danker-Hopfe, H.; Oehler, J. Higher BDNF concentrations in the hippocampus and cortex of an aggressive mouse strain. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 197, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, W.E.; Mamounas, L.A.; Ricaurte, G.A.; Coppola, V.; Reid, S.W.; Bora, S.H.; Wihler, C.; Koliatsos, V.E.; Tessarollo, L. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-deficient mice develop aggressiveness and hyperphagia in conjunction with brain serotonergic abnormalities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 15239–15244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumenko, V.S.; Kondaurova, E.M.; Bazovkina, D.V.; Tsybko, A.S.; Il’Chibaeva, T.V.; Popova, N.K. On the role of 5-HT1Areceptor gene in behavioral effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J. Neurosci. Res. 2014, 92, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalletta, G.; Morris, D.; Angelucci, F.; Rubino, I.; Spoletini, I.; Bria, P.; Martinotti, G.; Siracusano, A.; Bonaviri, G.; Bernardini, S.; et al. BDNF Val66Met polymorphism is associated with aggressive behavior in schizophrenia. Eur. Psychiatry 2010, 25, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yochum, C.; Doherty-Lyon, S.; Hoffman, C.; Hossain, M.M.; Zelikoff, J.T.; Richardson, J.R. Prenatal cigarette smoke exposure causes hyperactivity and aggressive behavior: Role of altered catecholamines and BDNF. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 254, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, K.; Hill, J.; Calcaterra, N.E.; Palko, M.E.; Kardian, A.; Paredes, D.; Sukumar, M.; Adler, B.D.; Jimenez, D.V.; Schloesser, R.J.; et al. Functional Role of BDNF Production from Unique Promoters in Aggression and Serotonin Signaling. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 41, 1943–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, N.K. From genes to aggressive behavior: The role of serotonergic system. Bioessays 2006, 28, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilchibaeva, T.V.; Tsybko, A.S.; Kondaurova, E.M.; Kovetskaya, A.I.; Kozhemyakina, R.V.; Naumenko, V.S. Expression Patterns of Serotonin Receptors 1A and 7 in the Brain of Rats with Genetically Determined Fear-Induced Aggressive Behavior or the Lack of Aggression. Neurochem. J. 2020, 14, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, B.; van Oorschot, R. 5-HT1B receptors and aggression: A review. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 526, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, C.; Arnt, J.; Hyttel, J.; Moltzen, E.K. The role of serotonergic mechanisms in inhibition of isolation-induced aggression in male mice. Psychopharmacology 1993, 110, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Vegt, B.J.; Lieuwes, N.; van de Wall, E.H.E.M.; Kato, K.; Moya-Albiol, L.; Martínez-Sanchis, S.; de Boer, S.F.; Koolhaas, J.M. Activation of serotonergic neurotransmission during the performance of aggressive behavior in rats. Behav. Neurosci. 2003, 117, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumenko, V.; Kondaurova, E.; Bazovkina, D.; Tsybko, A.; Tikhonova, M.; Kulikov, A.; Popova, N. Effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on behavior and key members of the brain serotonin system in genetically predisposed to behavioral disorders mouse strains. Neuroscience 2012, 214, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumajogee, P.; Madeira, A.; Vergé, D.; Hamon, M.; Miquel, M.-C. Up-regulation of the neuronal serotoninergic phenotype in vitro: BDNF and cAMP share Trk B-dependent mechanisms. J. Neurochem. 2002, 83, 1525–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilchibaeva, T.; Tsybko, A.; Zeug, A.; Müller, F.E.; Guseva, D.; Bischoff, S.; Ponimaskin, E.; Naumenko, V. Serotonin Receptor 5-HT2A Regulates TrkB Receptor Function in Heteroreceptor Complexes. Cells 2022, 11, 2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsybko, A.S.; Ilchibaeva, T.V.; Filimonova, E.A.; Eremin, D.V.; Popova, N.K.; Naumenko, V.S. The Chronic Treatment With 5-HT2A Receptor Agonists Affects the Behavior and the BDNF System in Mice. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 3059–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, V.A.; Marek, G.J.; Aghajanian, G.K.; Duman, R.S. 5-HT2AReceptor-Mediated Regulation of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor mRNA in the Hippocampus and the Neocortex. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 2785–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumenko, V.S.; Kozhemjakina, R.V.; Plyusnina, I.Z.; Popova, N.K. Expression of serotonin transporter gene and startle response in rats with genetically determined fear-induced aggression. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2009, 147, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilchibaeva, T.V.; Tsybko, A.S.; Kozhemyakina, R.V.; Konoshenko, M.Y.; Popova, N.K.; Naumenko, V.S. The relationship between different types of genetically defined aggressive behavior. J. Ethol. 2016, 35, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, F.W.; Shchepina, O.; Winter, C.; Römpler, H.; Teupser, D.; Palme, R.; Ceglarek, U.; Kratzsch, J.; Sohr, R.; Trut, L.N.; et al. Phenotypic differences in behavior, physiology and neurochemistry between rats selected for tameness and for defensive aggression towards humans. Horm. Behav. 2008, 53, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliusnina, I.Z.; Shchepina, O.; Os’Kina, I.N.; Trut, L.N. Some features of learning in swimming Morris test in rats selected for behavior towards human. Zhurnal Vyss. Nervn. Deiatelnosti Im. IP Pavlov. 2007, 57, 344–351. [Google Scholar]
- Ilchibaeva, T.V.; Kondaurova, E.M.; Tsybko, A.S.; Kozhemyakina, R.V.; Popova, N.K.; Naumenko, V.S. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and its precursor (proBDNF) in genetically defined fear-induced aggression. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 290, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondaurova, E.M.; Ilchibaeva, T.V.; Tsybko, A.S.; Kozhemyakina, R.V.; Popova, N.K.; Naumenko, V.S. 5-HT1A receptor gene silencers Freud-1 and Freud-2 are differently expressed in the brain of rats with genetically determined high level of fear-induced aggression or its absence. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 310, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumenko, V.S.; Kozhemyakina, R.V.; Plyusnina, I.F.; Kulikov, A.V.; Popova, N.K. Serotonin 5-HT1A receptor in infancy-onset aggression: Comparison with genetically defined aggression in adult rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 243, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, N.K.; Naumenko, V.S.; Plyusnina, I.Z.; Kulikov, A.V. Reduction in 5-HT1A receptor density, 5-HT1A mRNA expression, and functional correlates for 5-HT1A receptors in genetically defined aggressive rats. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 80, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popova, N.K.; Kulikov, A.V.; Nikulina, E.M.; Kozlachkova, E.Y.; Maslova, G.B. Serotonin metabolism and 5-HT receptors in Norway rats selected for low aggressiveness to man. Aggr. Behav. 1991, 17, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voĭtenko, N.N.; Kolpakov, V.G. Brain monoamine oxidase and the predisposition for catalepsy in tame and aggressive Norway rats. Zhurnal Vyss. Nervn. Deiatelnosti Im. IP Pavlov. 1993, 43, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Moskaliuk, V.S.; Kozhemyakina, R.V.; Bazovkina, D.V.; Terenina, E.; Khomenko, T.M.; Volcho, K.P.; Salakhutdinov, N.F.; Kulikov, A.V.; Naumenko, V.S.; Kulikova, E. On an association between fear-induced aggression and striatal-enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase (STEP) in the brain of Norway rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 147, 112667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulikov, A.V.; Tikhonova, M.A.; Kulikova, E.A.; Volcho, K.P.; Khomenko, T.M.; Salakhutdinov, N.F.; Popova, N.K. A new synthetic varacin analogue, 8-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2,3,4,5-benzopentathiepin-6-amine hydrochloride (TC-2153), decreased hereditary catalepsy and increased the BDNF gene expression in the hippocampus in mice. Psychopharmacology 2011, 221, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikov, A.V.; Tikhonova, M.A.; Kulikova, E.A.; Khomenko, T.M.; Korchagina, D.V.; Volcho, K.P.; Salakhutdinov, N.F.; Popova, N.K. Effect of new potential psychotropic drug, 8-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2,3,4,5-benzopentathiepin-6-amine hydrochloride, on the expression of serotonin-related genes in mouse brain. Mol. Biol. 2011, 45, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikova, E.; Kulikov, A.; Kulikov, E.K.A.A. Striatal-enriched Tyrosine Protein Phosphatase (STEP) in the Mechanisms of Depressive Disorders. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2017, 18, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikova, E.; Khotskin, N.; Illarionova, N.; Sorokin, I.; Bazhenova, E.; Kondaurova, E.; Volcho, K.; Khomenko, T.; Salakhutdinov, N.; Ponimaskin, E.; et al. Inhibitor of Striatal-Enriched Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase, 8-(Trifluoromethyl)-1,2,3,4,5-Benzopentathiepin-6-Amine hydrochloride (TC-2153), Produces Antidepressant-Like Effect and Decreases Functional Activity and Protein Level of 5-HT2A Receptor in the Brain. Neuroscience 2018, 394, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikova, E.A.; Volcho, K.P.; Salakhutdinov, N.F.; Kulikov, A.V. Benzopentathiepine Derivative, 8-(Trifluoromethyl)-1,2,3,4,5-Benzopentathiepin- 6-Amine Hydrochloride (TC-2153), as a Promising Antidepressant of New Generation. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2017, 14, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, B.G. Differential regulation of Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor transcripts by antidepressant treatments in the adult rat brain. Neuropharmacology 2003, 45, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.-J.; Pei, L.; Li, Y.-N.; Zheng, H.; Yang, S.; Wan, Y.; Mao, L.; Xia, Y.-P.; He, Q.-W.; Li, M.; et al. Alleviative effects of fluoxetine on depressive-like behaviors by epigenetic regulation of BDNF gene transcription in mouse model of post-stroke depression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, M.; Amendola, T.; Triaca, V.; Tirassa, P.; Alleva, E.; Aloe, L. Agonistic encounters in aged male mouse potentiate the expression of endogenous brain NGF and BDNF: Possible implication for brain progenitor cells’ activation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 1455–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chan, J.; Unger, T.; Byrnes, J.; Rios, M. Examination of behavioral deficits triggered by targeting BDNF in fetal or postnatal brains of mice. Neuroscience 2006, 142, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, W.; Chehab, M.; Thakur, S.; Li, J.; Morozov, A. BDNF-restricted knockout mice as an animal model for aggression. Genes Brain Behav. 2011, 10, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, B.L.; Azmitia, E. Structure and function of the brain serotonin system. Physiol. Rev. 1992, 72, 165–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, M.J.; Staley, J.K.; Globus, M.Y.-T.; Whittemore, S.R. Developmental Regulation of Early Serotonergic Neuronal Differentiation: The Role of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Membrane Depolarization. Dev. Biol. 1995, 170, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, C.; Hyman, C.; Studer, L.; Egli, M.; Evtouchenko, L.; Jackson, C.; Dahl-Jørgensen, A.; Lindsay, R.M.; Seiler, R.W. Effect of BDNF on Dopaminergic, Serotonergic, and GABAergic Neurons in Cultures of Human Fetal Ventral Mesencephalon. Exp. Neurol. 1995, 133, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, N.K.; Naumenko, V.S. Neuronal and behavioral plasticity: The role of serotonin and BDNF systems tandem. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2019, 23, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, S.F.; Lesourd, M.; Mocaer, E.; Koolhaas, J.M. Selective antiaggressive effects of alnespirone in resident-intruder test are mediated via 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptors: A comparative pharmacological study with 8-hydroxy-2-dipropylaminotetralin, ipsapirone, buspirone, eltoprazine, and WAY-100635. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 288, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Heisler, L.K.; Chu, H.-M.; Brennan, T.J.; Danao, J.A.; Bajwa, P.; Parsons, L.H.; Tecott, L.H. Elevated anxiety and antidepressant-like responses in serotonin 5-HT 1A receptor mutant mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 15049–15054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renner, U.; Zeug, A.; Woehler, A.; Niebert, M.; Dityatev, A.; Dityateva, G.; Gorinski, N.; Guseva, D.; Abdel-Galil, D.; Fröhlich, M.; et al. Heterodimerization of serotonin receptors 5-HT1A and 5-HT7 differentially regulates receptor signalling and trafficking. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 2486–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guscott, M.; Bristow, L.; Hadingham, K.; Rosahl, T.; Beer, M.; Stanton, J.; Bromidge, F.; Owens, A.; Huscroft, I.; Myers, J.; et al. Genetic knockout and pharmacological blockade studies of the 5-HT7 receptor suggest therapeutic potential in depression. Neuropharmacology 2005, 48, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesołowska, A.; Nikiforuk, A.; Stachowicz, K.; Tatarczyńska, E. Effect of the selective 5-HT7 receptor antagonist SB 269970 in animal models of anxiety and depression. Neuropharmacology 2006, 51, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiedl, O.; Pappa, E.; Konradsson-Geuken, Å.; Ögren, S.O. The role of the serotonin receptor subtypes 5-HT1A and 5-HT7 and its interaction in emotional learning and memory. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Almeida, R.M.M.; Miczek, K.A. Aggression Escalated by Social Instigation or by Discontinuation of Reinforcement (“Frustration”) in Mice Inhibition by Anpirtoline: A 5-HT1B Receptor Agonist. Neuropsychopharmacology 2002, 27, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saudou, F.; Amara, D.A.; Dierich, A.; LeMeur, M.; Ramboz, S.; Segu, L.; Buhot, M.-C.; Hen, R. Enhanced Aggressive Behavior in Mice Lacking 5-HT 1B Receptor. Science 1994, 265, 1875–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muehlenkamp, F.; Lucion, A.; Vogel, W. Effects of selective serotonergic agonists on aggressive behavior in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1995, 50, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaue, M.; Ago, Y.; Sowa, C.; Sakamoto, Y.; Nishihara, B.; Koyama, Y.; Baba, A.; Matsuda, T. Modulation by 5-HT2A Receptors of Aggressive Behavior in Isolated Mice. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 89, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, S.C.; Garcia-Garcia, A.L.; Leonardo, E.D.; Andrews, A.M. Rethinking 5-HT1AReceptors: Emerging Modes of Inhibitory Feedback of Relevance to Emotion-Related Behavior. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raote, I.; Bhattacharya, A.; Panicker, M.M. Serotonin 2A (5-HT2A) Receptor Function: Ligand-Dependent Mechanisms and Pathways. In Serotonin Receptors in Neurobiology; Chattopadhyay, A., Ed.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1853/ (accessed on 8 October 2022).
- Aleyasin, H.; Flanigan, M.E.; Russo, S.J. Neurocircuitry of aggression and aggression seeking behavior: Nose poking into brain circuitry controlling aggression. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2018, 49, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, F.; Luoni, A.; Guidotti, G.; Racagni, G.; Fumagalli, F.; Riva, M.A. Modulation of neuronal plasticity following chronic concomitant administration of the novel antipsychotic lurasidone with the mood stabilizer valproic acid. Psychopharmacology 2012, 226, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Chatterjee, M.; Baguley, T.D.; Brouillette, J.; Kurup, P.; Ghosh, D.; Kanyo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Seyb, K.; Ononenyi, C.; et al. Inhibitor of the Tyrosine Phosphatase STEP Reverses Cognitive Deficits in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, e1001923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Kurup, P.; Baguley, T.D.; Foscue, E.; Ellman, J.A.; Nairn, A.C.; Lombroso, P.J. Inhibition of the tyrosine phosphatase STEP61 restores BDNF expression and reverses motor and cognitive deficits in phencyclidine-treated mice. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casarotto, P.C.; Girych, M.; Fred, S.M.; Kovaleva, V.; Moliner, R.; Enkavi, G.; Biojone, C.; Cannarozzo, C.; Sahu, M.P.; Kaurinkoski, K.; et al. Antidepressant drugs act by directly binding to TRKB neurotrophin receptors. Cell 2021, 184, 1299–1313.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikov, A.V.; Sinyakova, N.A.; Kulikova, E.A.; Khomenko, T.M.; Salakhutdinov, N.F.; Kulikov, V.A.; Volcho, K.P. Effects of Acute and Chronic Treatment of Novel Psychotropic Drug, 8- (Trifluoromethyl)-1, 2, 3, 4, 5-benzopentathiepin-6-amine Hydrochloride (TC-2153), on the Behavior of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio): A Comparison with Fluoxetine. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2019, 16, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikov, A.V.; Tikhonova, M.; Kulikova, E.A.; Volcho, K.P.; Khomenko, T.M.; Salakhutdinov, N.F.; Popova, N.K. Antidepressant Activity of 8-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2,3,4,5-benzopentathiepin- 6-amine hydrochloride (TC-2153): Comparison with Classical Antidepressants. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2013, 11, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikova, E.A.; Tikhonova, M.A.; Volcho, K.P.; Khomenko, T.M.; Salakhutdinov, N.F.; Kulikov, A.V.; Popova, N.K. Comparison of behavioral effects of fluoxetine, imipramine and new psychotropic drug TC-2153 on mice with hereditary predisposition to catalepsy. Zhurnal Vyss. Nervn. Deiatelnosti Im. IP Pavlov. 2015, 65, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroteaux, L.; Saudou, F.; Amlaiky, N.; Boschert, U.; Plassat, J.L.; Hen, R. Mouse 5HT1B serotonin receptor: Cloning, functional expression, and localization in motor control centers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 3020–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumenko, E.; Popova, N.; Nikulina, E.; Dygalo, N.; Shishkina, G.; Borodin, P.; Markel, A. Behavior, adrenocortical activity, and brain monoamines in Norway rats selected for reduced aggressiveness towards man. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1989, 33, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plyusnina, I.; Oskina, I. Behavioral and Adrenocortical Responses to Open-Field Test in Rats Selected for Reduced Aggressiveness Toward Humans. Physiol. Behav. 1997, 61, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikov, A.V.; Naumenko, V.S.; Voronova, I.P.; Tikhonova, M.A.; Popova, N.K. Quantitative RT-PCR assay of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A serotonin receptor mRNAs using genomic DNA as an external standard. J. Neurosci. Methods 2005, 141, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumenko, V.S.; Osipova, D.V.; Kostina, E.V.; Kulikov, A.V. Utilization of a two-standard system in real-time PCR for quantification of gene expression in the brain. J. Neurosci. Methods 2008, 170, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumenko, V.S.; Kulikov, A.V. Quantitative assay of 5-HT(1A) serotonin receptor gene expression in the brain. Mol. Biol. 2006, 40, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).