Recent Advances of Microfluidic Platform for Cell Based Non-Invasive Prenatal Diagnosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Progress of Prenatal Screening Test for Fetal Aneuploidies
3. Cell Based NIPD
4. Microfluidics Technologies for NIPD
4.1. Immunoaffinity Based Microfluidic Technique
4.2. Size-Based Microfluidic Technology
5. Isolation of Fetal Cells
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morris, J.K.; Mutton, D.E.; Alberman, E. Revised estimates of the maternal age specific live birth prevalence of Down’s syndrome. J. Med. Screen. 2002, 9, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ACOG Committee on Practice Bulletins. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 77: Screening for fetal chromosomal abnormalities. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 109, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaides, K.H.; Azar, G.; Byrne, D.; Mansur, C.; Marks, K. Fetal nuchal translucency: Ultrasound screening for chromosomal defects in first trimester of pregnancy. Br. Med. J. 1992, 304, 867–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santorum, M.; Wright, D.; Syngelaki, A.; Karagioti, N.; Nicolaides, K.H. Accuracy of first-trimester combined test in screening for trisomies 21, 18 and 13. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 49, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, Y.M.; Corbetta, N.; Chamberlain, P.F.; Rai, V.; Sargent, I.L.; Redman, C.W.; Wainscoat, J.S. Presence of fetal DNA in maternal plasma and serum. Lancet 1997, 350, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomaki, G.E.; Kloza, E.M.; Lambert-Messerlian, G.M.; Haddow, J.E.; Neveux, L.M.; Ehrich, M.; van den Boom, D.; Bombard, A.T.; Deciu, C.; Grody, W.W.; et al. DNA sequencing of maternal plasma to detect down syndrome: An international clinical validation study. Genet. Med. 2011, 13, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, F.L.; Hemming, K.; Allen, S.; Morris, R.K.; Kilby, M.D. The accuracy of cell-free fetal DNA-based non-invasive prenatal testing in singleton pregnancies: A systematic review and bivariate meta-analysis. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2017, 124, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pös, O.; Budiš, J.; Szemes, T. Recent trends in prenatal genetic screening and testing. F1000Research 2019, 8, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walknowska, J.; Conte, F.; Grumbach, M. Practical and theoretical implications of fetal/maternal lymphocyte transfer. Lancet 1969, 293, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbatinelli, G.; Fantasia, D.; Palka, C.; Morizio, E.; Alfonsi, M.; Calabrese, G. Isolation and Enrichment of Circulating Fetal Cells for NIPD: An Overview. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudejans, C.B.M.; Tjoa, M.L.; Westerman, B.A.; Mulders, M.A.M.; Van Wijk, I.J.; Van Vugt, J.M.G. Circulating trophoblast in maternal blood. Prenat. Diagn. 2003, 23, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvestiti, F.; Agrati, C.; Grimi, B.; Pompilii, E.; Izzi, C.; Martinoni, L.; Gaetani, E.; Liuti, M.R.; Trotta, A.; Maggi, F.; et al. Interpreting mosaicism in chorionic villi: Results of a monocentric series of 1001 mosaics in chorionic villi with follow-up amniocentesis. Prenat. Diagn. 2015, 35, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleihauer, E.; Braun, H.; Betke, K. Demonstration von fetalem Hämoglobin in den Erythrocyten Eines Blutausstrichs. Klin. Wochenschr. 1957, 35, 637–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gänshirt, D.; Garritsen, H.; Miny, P.; Holzgreve, W. Fetal cells in maternal circulation throughout gestation. Lancet 1994, 343, 1038–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, D.; Kersaudy-Kerhoas, M.; Dhariwal, R.; Desmulliez, M. Current and emerging techniques of fetal cell separation from maternal blood. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 1905–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, H.A. Life-span of the fetal red blood cell. J. Pediatr. 1967, 70, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gänshirt-Ahlert, D.; Pohlschmidt, M.; Gal, A.; Miny, P.; Horst, J.; Holzgreve, W. Ratio of fetal to maternal DNA is less than 1 in 5000 at different gestational ages in maternal blood. Clin. Genet. 1990, 38, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.O.; Elias, S.; Wachtel, S.S.; Klinger, K.; Dockter, M.; Tharapel, A.; Shulman, L.P.; Phillips, O.P.; Meyers, C.M.; Shook, D.; et al. Prenatal diagnosis with fetal cells isolated from maternal blood by multiparameter flow cytometry. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1991, 165, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Guo, F.; Feng, C.; Cai, B.; Lata, J.P.; He, R.; Huang, Q.; Yu, X.; Rao, L.; Liu, H.; et al. Fetal nucleated red blood cell analysis for non-invasive prenatal diagnostics using a nanostructure microchip. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Chen, J.-F.; Song, M.; Zhu, Y.; Jan, Y.J.; Chen, S.H.; Weng, T.-H.; Ling, D.-A.; Chen, S.-F.; Ro, T.; et al. Imprinted NanoVelcro microchips for isolation and characterization of circulating fetal trophoblasts: Toward noninvasive prenatal diagnostics. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 8167–8177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-E.; Ma, G.-C.; Jou, H.-J.; Lin, W.-H.; Lee, D.-J.; Lin, Y.-S.; Ginsberg, N.A.; Chen, H.-F.; Chang, F.M.-C.; Chen, M. Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy by circulating fetal nucleated red blood cells and extravillous trophoblasts using silicon-based nanostructured microfluidics. Mol. Cytogenet. 2017, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; He, Z.; Cai, B.; Peng, J.; Song, J.; Yu, X.; Sun, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y. Non-invasive prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal aneuploidies and microdeletion syndrome using fetal nucleated red blood cells isolated by nanostructure microchips. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.-C.; Lin, W.-H.; Huang, C.-E.; Chang, T.-Y.; Liu, J.-Y.; Yang, Y.-J.; Lee, M.-H.; Wu, W.-J.; Chang, Y.-S.; Chen, M. A silicon-based coral-like nanostructured microfluidics to isolate rare cells in human circulation: Validation by SK-BR-3 cancer cell line and its utility in circulating fetal nucleated red blood cells. Micromachines 2019, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonek, J.; Muller, R.; Muller-Cohn, J.; Dickerson, J.; Lopez, B.G.; Barber-Singh, J.; Dufek, D.; Hiett, A.K.; Buchanan, P. Identification of fetal aneuploidy with dual-probe fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis in circulating trophoblasts after enrichment using a high-sensitivity microfluidic platform. Prenat. Diagn. 2021, 41, 1701–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayrefourcq, L.; Vincent, M.-C.; Pierredon, S.; Moutou, C.; Imbert-Bouteille, M.; Haquet, E.; Puechberty, J.; Willems, M.; Liautard-Haag, C.; Molinari, N.; et al. Single circulating fetal trophoblastic cells eligible for non invasive prenatal diagnosis: The exception rather than the rule. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yu, S.; Chao, S.; Wu, L.; Tao, M.; Situ, B.; Ye, X.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, S.; Chen, W.; et al. Isolation of circulating fetal trophoblasts by a four-stage inertial microfluidic device for single-cell analysis and noninvasive prenatal testing. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 4342–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiddler, M. Fetal Cell Based Prenatal Diagnosis: Perspectives on the Present and Future. J. Clin. Med. 2014, 3, 972–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Hatt, L.; Ravn, K.; Vogel, I.; Petersen, O.B.; Uldbjerg, N.; Schelde, P. Fetal cells in maternal blood for prenatal diagnosis: A love story rekindled. Biomark. Med. 2017, 11, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, D.; Simpson, J.; Jackson, L. National Institute of Child Health and Development Fetal Cell Isolation Study. Fetal gender and aneuploidy detection using fetal cells in maternal blood: Analysis of NIFTY I data. Prenat. Diagn. 2002, 22, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, M.P.; Thendral, V.; Uthappa, U.T.; Lee, K.-H.; Kigga, M.; Altalhi, T.; Kurkuri, M.D.; Kant, K. Recent Advances in Microfluidic Platform for Physical and Immunological Detection and Capture of Circulating Tumor Cells. Biosensors 2022, 12, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cheng, L.; Wei, X.; Cai, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, L.; Zhao, X.-Z. High-throughput isolation of fetal nucleated red blood cells by multifunctional microsphere-assisted inertial microfluidics. Biomed. Microdevices 2020, 22, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Mao, H.; Huang, C. Nanotechnology-assisted isolation and analysis of circulating tumor cells on microfluidic devices. Micromachines 2020, 11, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, L.; Guo, S. Nanomaterial-Based Immunocapture Platforms for the Recognition, Isolation, and Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 850241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dundas, C.M.; Demonte, D.; Park, S. Streptavidin–biotin technology: Improvements and innovations in chemical and biological applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9343–9353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stayton, P.S.; Freitag, S.; Klumb, A.L.; Chilkoti, A.; Chu, V.; Penzotti, E.J.; To, R.; Hyre, D.; Le Trong, I.; Lybrand, T.P.; et al. Streptavidin–biotin binding energetics. Biomol. Eng. 1999, 16, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, T.R.; Cotner, K.L.; Li, B.; Sohn, L.L. Developments in label-free microfluidic methods for single-cell analysis and sorting. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 11, e1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.; Zamarchi, R. Single-cell analysis of circulating tumor cells: How far have we come in the -omics era? Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Lu, Y.-T.; Li, F.; Wu, K.; Hou, S.; Yu, J.; Shen, Q.; Wu, D.; Song, M.; Ouyang, W.-H.; et al. High-purity prostate circulating tumor cell isolation by a polymer nanofiber-embedded microchip for whole exome sequencing. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2897–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmert-Buck, M.R.; Bonner, R.F.; Smith, P.D.; Chuaqui, R.F.; Zhuang, Z.; Goldstein, S.R.; Weiss, R.A.; Liotta, L.A. Laser capture microdissection. Science 1996, 274, 998–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 : antibody;
: antibody;  : biotin;
: biotin;  : streptavidin; LCM: laser capture microdissection.
: streptavidin; LCM: laser capture microdissection.
 : antibody;
: antibody;  : biotin;
: biotin;  : streptavidin; LCM: laser capture microdissection.
: streptavidin; LCM: laser capture microdissection.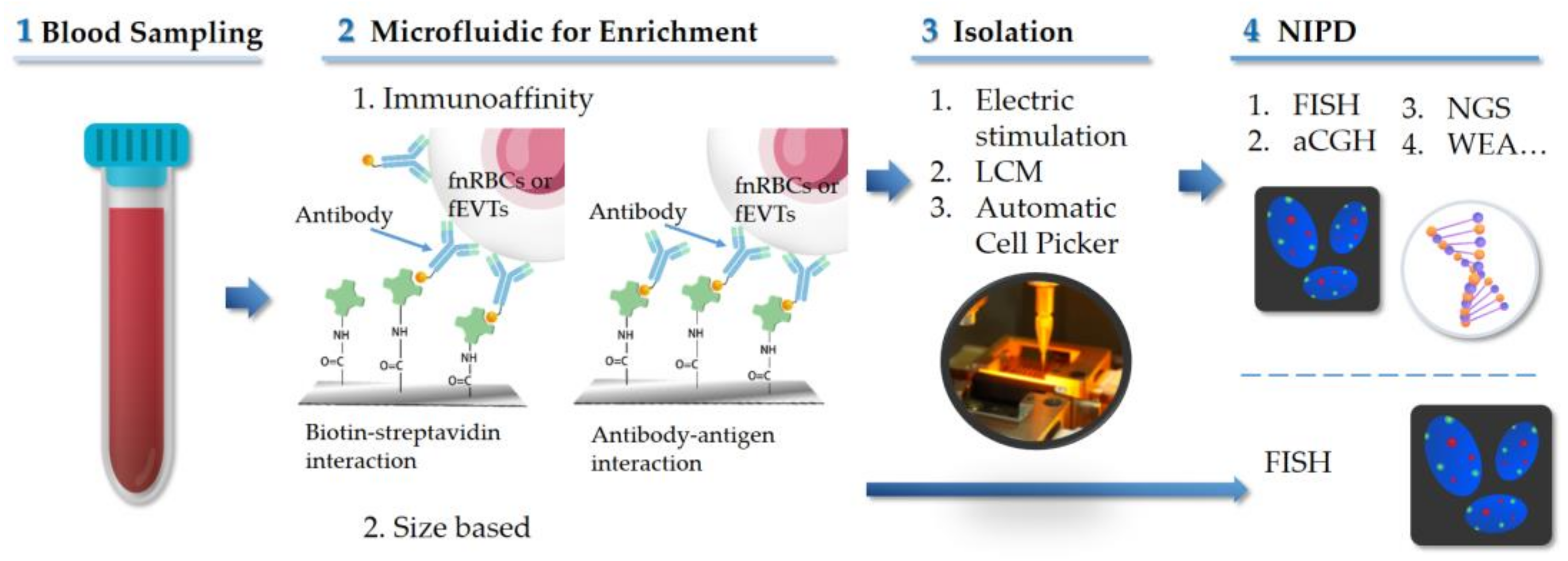
| Authors/Year/Ref. | Case No. | GA | Cell Type | Microfluidic Platform | Markers for Enrichment | Immuno-Staining | Cell No. | Down-Stream Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immunoaffinity | ||||||||
| He (2017) [19] | 48 | 10–30 | fnRBCs | HA/CTS NPs | CD147 | ε-HbF+/CD71+/DAPI+ | 3–71/mL | FISH |
| Hou (2017) [20] | 15 | 8–23 | EVTs | NanoVelcro Microchip | EpCAM | Hoechst+/CK7+/HLA-G+/CD45− | 3–6/2mL * 5–15/2 mL ** | aCGH, STR |
| Huang CE (2017) [21] | 24 | 11–13 | EVTs | Cell Reveal with PicoBioChip | EpCAM | CK7+/ HLA-G+/CD45−/DAPI+ | 1–44/4mL | FISH, aCGH, STR, NGS |
| fnRBCs | Cell RevealTM system with PicoBioChip | CD71 | CD71+/GPA+/ CD45−/DAPI+ | 14–22/4mL | FISH, aCGH, STR, NGS | |||
| Feng (2018) [22] | 13 | ~18 | fnRBCs | Biotin-doped Ppy microchip | CD147 | ε-HbF+/CD71+/DAPI+ | NA | FISH, WEA |
| Ma (2019) [23] | 14 | 13–27 | fnRBCs | Cell RevealTM system with Coral Chip | CD71 | CD71+/GPA+/CD45−/Hoechst+ | 2–71/2 mL | FISH, aCGH, STR, NGS |
| Sonek (2021) [24] | 9 | 12–35 | EVTs | LiquidScan® | EpCAM | None | 1.28/mL | FISH |
| 6 | 12–35 | EVTs | LiquidScan® | mixture | None | 2.67/mL | FISH | |
| Size-based (Label free) | ||||||||
| Cayrefourcq (2020) [25] | 16 | 10–16 | EVTs | Pasotix system | None | CD105+/ panCK+/ β-hCG+/CD45− | Only 5 fetal cells obtained | WGA |
| Huang Y (2020) [26] | 30 | NA | EVTs | CelutriateChip 1 | None | CK7+/CD45−/DAPI+ | 1–3/2mL in 26/30 cases | WGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jou, H.-J.; Lo, P.-H.; Ling, P.-Y. Recent Advances of Microfluidic Platform for Cell Based Non-Invasive Prenatal Diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24020991
Jou H-J, Lo P-H, Ling P-Y. Recent Advances of Microfluidic Platform for Cell Based Non-Invasive Prenatal Diagnosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(2):991. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24020991
Chicago/Turabian StyleJou, Hei-Jen, Pei-Hsuan Lo, and Pei-Ying Ling. 2023. "Recent Advances of Microfluidic Platform for Cell Based Non-Invasive Prenatal Diagnosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 2: 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24020991
APA StyleJou, H.-J., Lo, P.-H., & Ling, P.-Y. (2023). Recent Advances of Microfluidic Platform for Cell Based Non-Invasive Prenatal Diagnosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(2), 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24020991





