Biological Evaluation of 8-Methoxy-2,5-dimethyl-5H-indolo[2,3-b] Quinoline as a Potential Antitumor Agent via PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
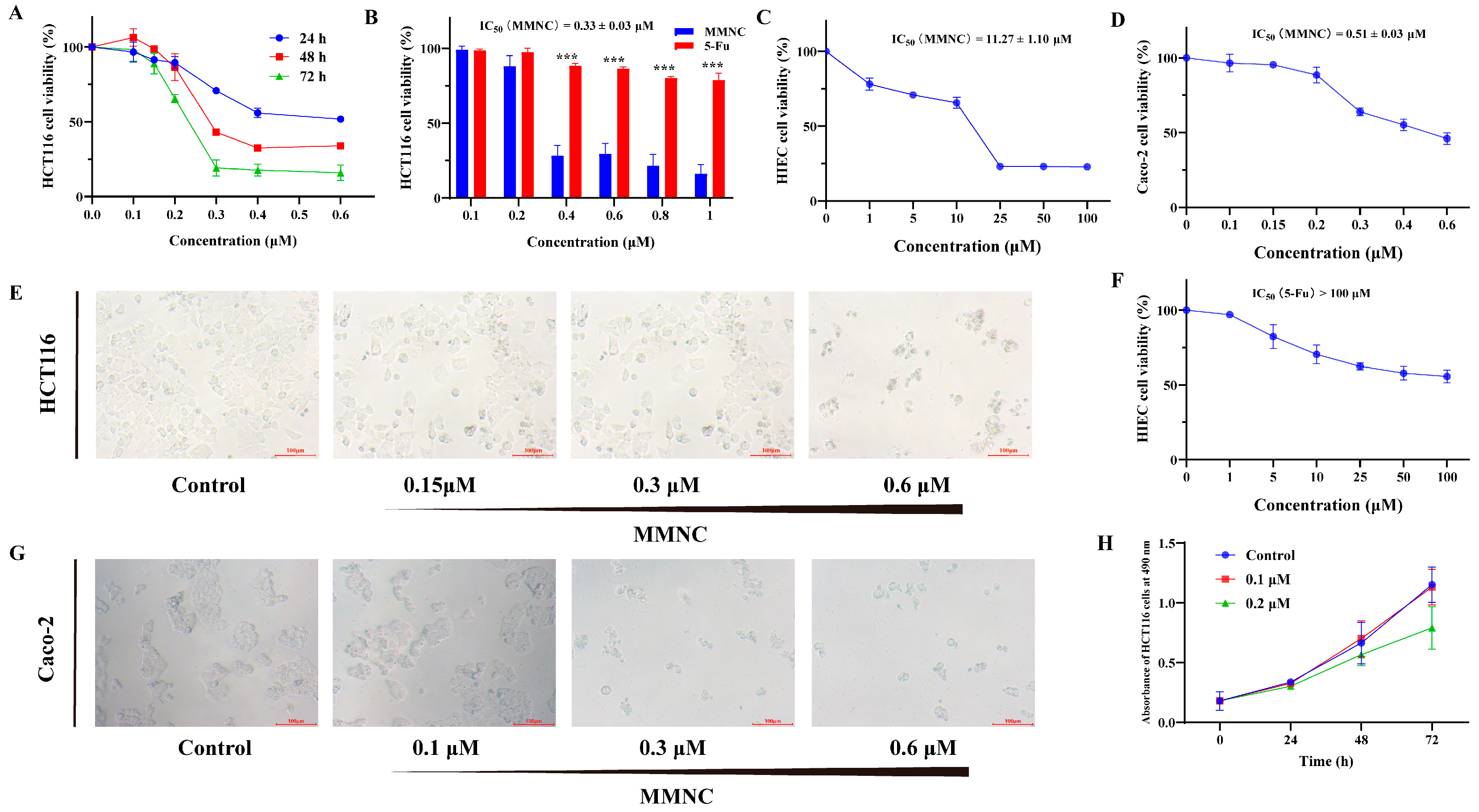
2.2. MMNC Displays Potent Cytotoxic Ability in the Colorectal Cell Line
2.3. MMNC Inhibited the Colony Formation of HCT116 and Caco-2 Cells
2.4. MMNC Arrested the HCT116 and Caco-2 Cells Cycle in the G2/M Stage
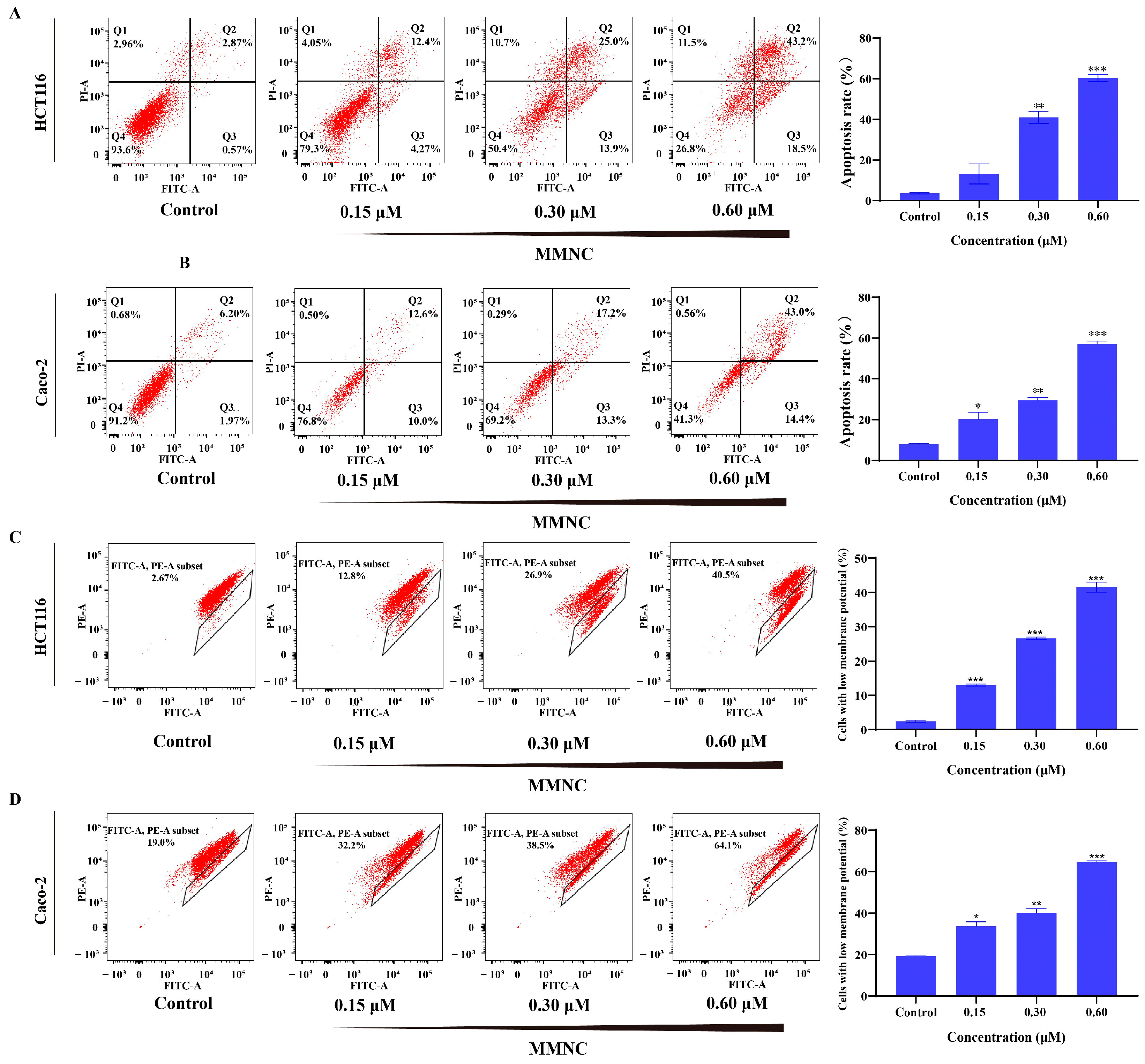
2.5. MMNC Can Induce Apoptosis of HCT116 Cells
2.6. MMNC Reduced Cellular Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
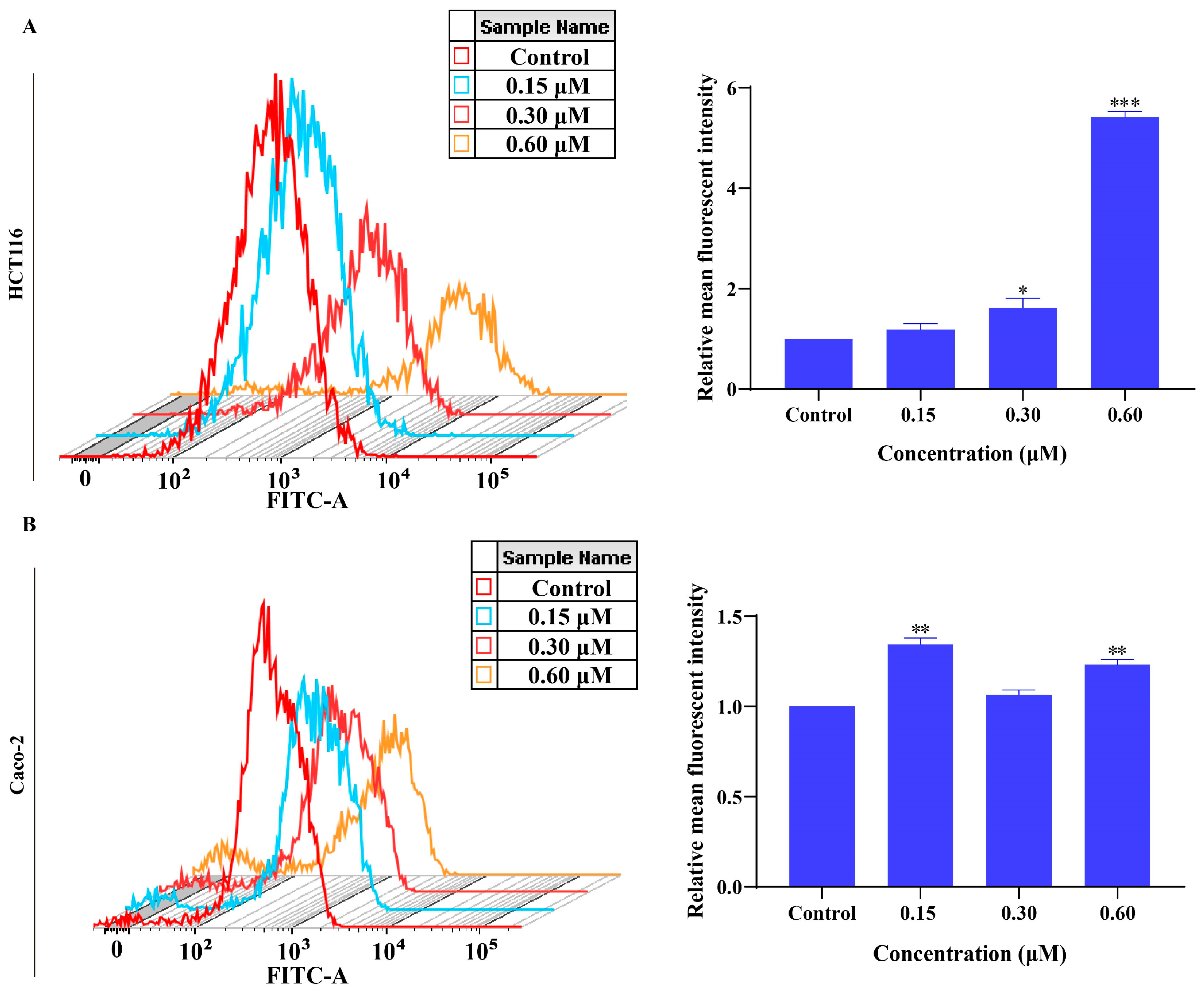
2.7. MMNC Can Promote the Production of Reactive Oxygen Species in HCT116 and Caco-2 Cells
2.8. MMNC Could Regulate the Expression of Proteins Related to Cells Cycle and the PI3K/AKT Cell Signaling Pathway in the HCT116 and Caco-2
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Synthesis
3.2. Cell Culture
3.3. Cytotoxicity Test
3.4. Colony Formation Assay
3.5. Analysis of Cell Cycle Arrest
3.6. Analysis of Cell Apoptosis
3.7. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Analysis
3.8. ROS Analysis
3.9. Molecular Docking Analysis
3.10. Western Blotting Assay
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, R.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Fei, J.; Hao, X.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Tagitinin C induces ferroptosis through PERK-Nrf2-HO-1 signaling pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 2703–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauriello, D.V.F.; Calon, A.; Lonardo, E.; Batlle, E. Determinants of metastatic competency in colorectal cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 97–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Shi, L.; He, X.; Luo, Y. Gastrointestinal cancers in China, the USA, and Europe. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2021, 9, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitz, J.; Koch, M.; Debus, J.; Höhler, T.; Galle, P.R.; Büchler, M.W. Colorectal cancer. Lancet 2005, 365, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johdi, N.A.; Sukor, N.F. Colorectal Cancer Immunotherapy: Options and Strategies. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xu, H.; Huang, T.; Zhang, C.; Wu, J.; Luo, S. Simultaneous delivery of anti-miRNA and docetaxel with supramolecular self-assembled “chitosome” for improving chemosensitivity of triple negative breast cancer cells. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, E.C.; Kumar, R.; Davis, R.A. The use of isolated natural products as scaffolds for the generation of chemically diverse screening libraries for drug discovery. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.L.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Quinn, R.J. The re-emergence of natural products for drug discovery in the genomics era. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidoryk, K.; Jaromin, A.; Edward, J.A.; Świtalska, M.; Stefańska, J.; Cmoch, P.; Zagrodzka, J.; Szczepek, W.; Peczyńska-Czoch, W.; Wietrzyk, J.; et al. Searching for new derivatives of neocryptolepine: Synthesis, antiproliferative, antimicrobial and antifungal activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 78, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.K.; Gao, J.M.; Yang, C.J.; Shang, X.F.; Zhao, Z.M.; Lawoe, R.K.; Zhou, R.; Sun, Y.; Yin, X.D.; Liu, Y.Q. Design, Synthesis, and Antifungal Evaluation of Neocryptolepine Derivatives against Phytopathogenic Fungi. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2020, 68, 2306–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, A.S. PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors in cancer: At the bench and bedside. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 59, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulda, S. Modulation of mitochondrial apoptosis by PI3K inhibitors. Mitochondrion 2013, 13, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Sun, M.M.; Zhang, G.G.; Yang, J.; Chen, K.S.; Xu, W.W.; Li, B. Targeting PI3K/Akt signal transduction for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Nie, J.; Ma, X.; Wei, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wei, X. Targeting PI3K in cancer: Mechanisms and advances in clinical trials. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, F.; He, X.; Zeng, N. Tetrandrine: A review of its anticancer potentials, clinical settings, pharmacokinetics and drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 1491–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkachairin, B.; Rodphon, W.; Reamtong, O.; Mungthin, M.; Tummatorn, J.; Thongsornkleeb, C.; Ruchirawat, S. Synthesis of neocryptolepines and carbocycle-fused quinolines and evaluation of their anticancer and antiplasmodial activities. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 98, 103732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassonneville, L.; Lansiaux, A.; Wattelet, A.; Wattez, N.; Mahieu, C.; Van Miert, S.; Pieters, L.; Bailly, C. Cytotoxicity and cell cycle effects of the plant alkaloids cryptolepine and neocryptolepine: Relation to drug-induced apoptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 409, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altwaijry, N.; El-Ghlban, S.; El Sayed, I.E.; El-Bahnsawye, M.; Bayomi, A.I.; Samaka, R.M.; Shaban, E.; Elmongy, E.I.; El-Masry, T.A.; Ahmed, H.M.A.; et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Antitumor Activity of Indolo[2,3-b] Quinolines, Natural Product Analogs from Neocryptolepine Alkaloid. Molecules 2021, 26, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, S.; Du, K.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Lu, J.; Niu, Y.; Tu, L.; et al. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Neocryptolepine Derivatives as Potential Anti-Gastric Cancer Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Tian, Y.; Du, K.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Lu, J.; Niu, Y.; Tu, L.; et al. CFNC, a neocryptolepine derivative, inhibited the growth of gastric cancer AGS cells by inhibiting PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 938, 175408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhl, E.; Wolff, F.; Mangal, S.; Dube, H.; Zanin, E. Light-Controlled Cell-Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Tyagi, A.K. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and cancer: Role of antioxidative nutraceuticals. Cancer Lett. 2017, 387, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattahi, S.; Amjadi-Moheb, F.; Tabaripour, R.; Ashrafi, G.H.; Akhavan-Niaki, H. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in gastric cancer: Epigenetics and beyond. Life Sci. 2020, 262, 118513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, R.; Du, K.; Syed, A.; et al. IPM712, a vanillin derivative as potential antitumor agents, displays better antitumor activity in colorectal cancers cell lines. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 152, 105464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunnery, S.E.; Mayer, I.A. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Hormone-Positive Breast Cancer. Drugs 2020, 80, 1685–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Samuels, Y.; Li, Q.; Krokowski, D.; Guan, B.-J.; Wang, C.; Jin, Z.; Dong, B.; Cao, B.; Feng, X.; et al. Oncogenic PIK3CA mutations reprogram glutamine metabolism in colorectal cancer. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arafeh, R.; Samuels, Y. PIK3CA in cancer: The past 30 years. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 59, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, A.K.; Munirajan, A.K.; Tsuchida, N. Genetic deregulation of the PIK3CA oncogene in oral cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 338, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Vogt, P.K. Class I PI3K in oncogenic cellular transformation. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5486–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| IC50 (μM) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | HCT116 | Caco-2 | AGS | PANC-1 | SMMC-7721 | HIEC |
| MMNC | 0.33 | 0.51 | 3.6 | 18.4 | 9.7 | 11.3 |
| Neocryptolepine | 6.26 | 13.54 | 5.81 | >50 | 19.31 | 31.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, M.; Tu, L.; Lu, J.; et al. Biological Evaluation of 8-Methoxy-2,5-dimethyl-5H-indolo[2,3-b] Quinoline as a Potential Antitumor Agent via PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015142
Ma Y, Zhu H, Jiang X, Zhou Z, Zhou Y, Tian Y, Zhang H, Sun M, Tu L, Lu J, et al. Biological Evaluation of 8-Methoxy-2,5-dimethyl-5H-indolo[2,3-b] Quinoline as a Potential Antitumor Agent via PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(20):15142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015142
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yunhao, Hongmei Zhu, Xinrong Jiang, Zhongkun Zhou, Yong Zhou, Yanan Tian, Hao Zhang, Mengze Sun, Lixue Tu, Juan Lu, and et al. 2023. "Biological Evaluation of 8-Methoxy-2,5-dimethyl-5H-indolo[2,3-b] Quinoline as a Potential Antitumor Agent via PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 20: 15142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015142
APA StyleMa, Y., Zhu, H., Jiang, X., Zhou, Z., Zhou, Y., Tian, Y., Zhang, H., Sun, M., Tu, L., Lu, J., Niu, Y., Liu, H., Liu, Y., & Chen, P. (2023). Biological Evaluation of 8-Methoxy-2,5-dimethyl-5H-indolo[2,3-b] Quinoline as a Potential Antitumor Agent via PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(20), 15142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015142






