Quercetin Ameliorates Deoxynivalenol-Induced Intestinal Injury and Barrier Dysfunction Associated with Inhibiting Necroptosis Signaling Pathway in Weaned Pigs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
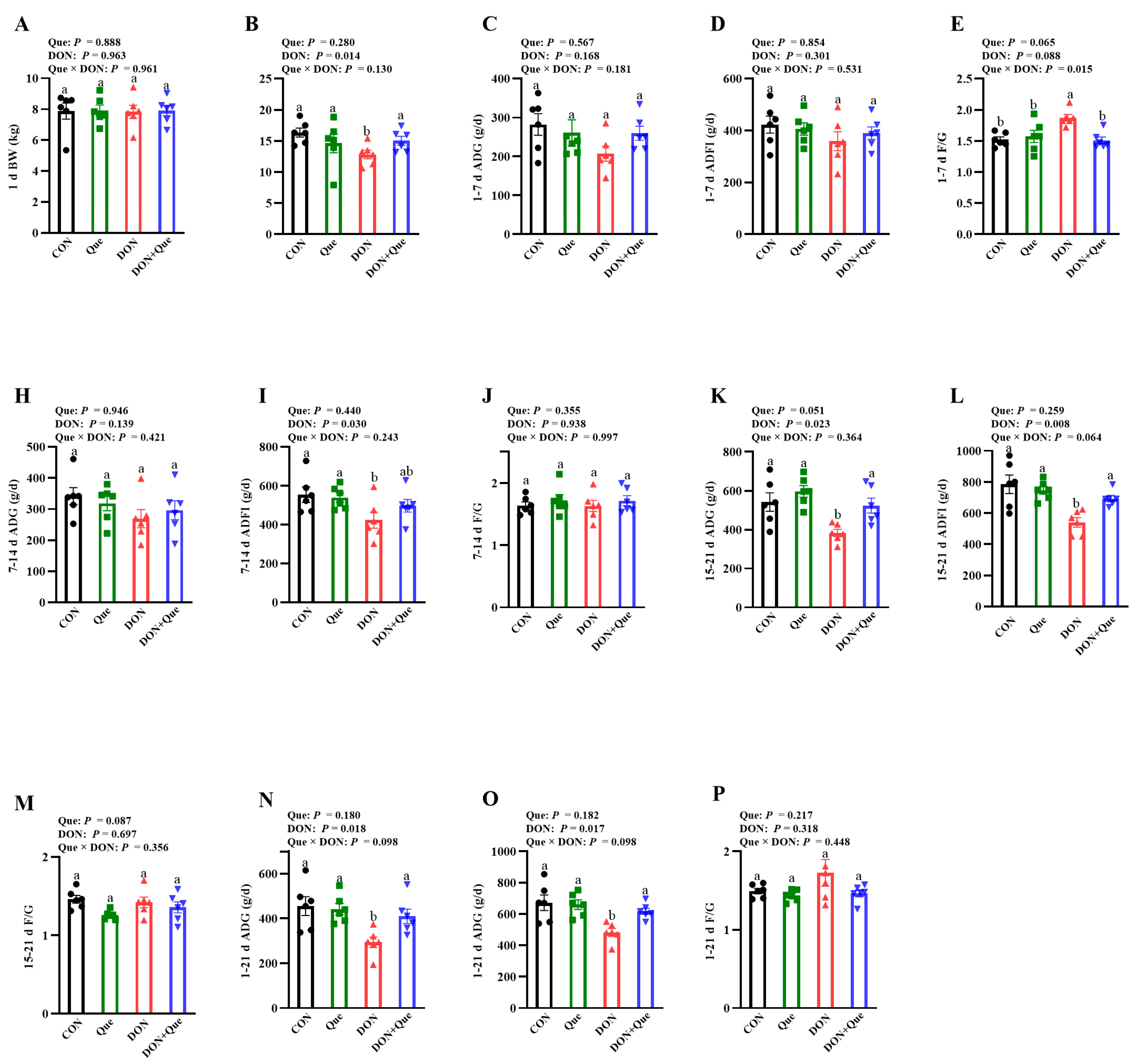
2.1. Effects of Dietary Que on Growth Performance in Weaned Piglets after DON Exposure
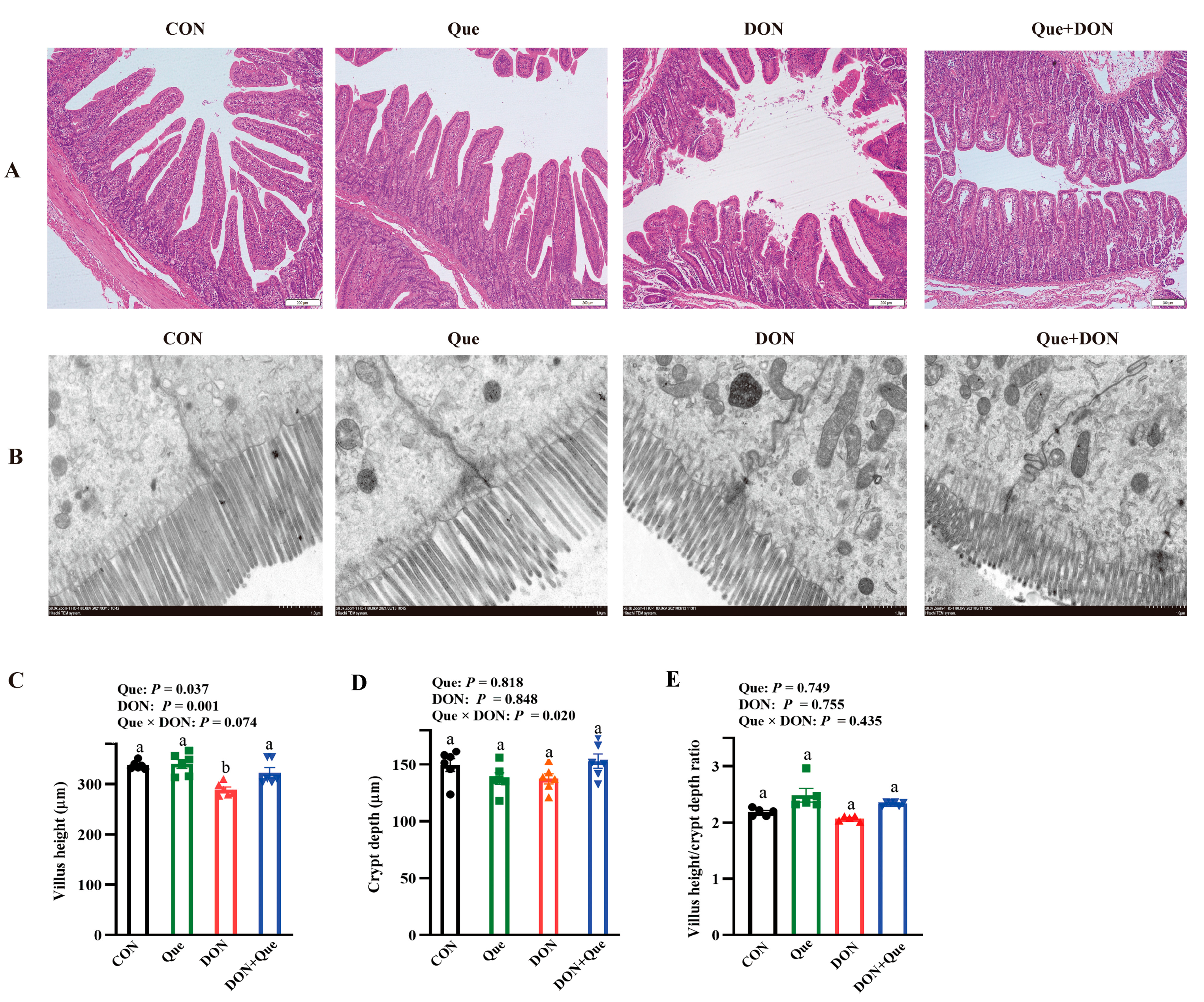
2.2. Effects of Dietary Que on Intestinal Morphology in Weaned Piglets after DON Exposure
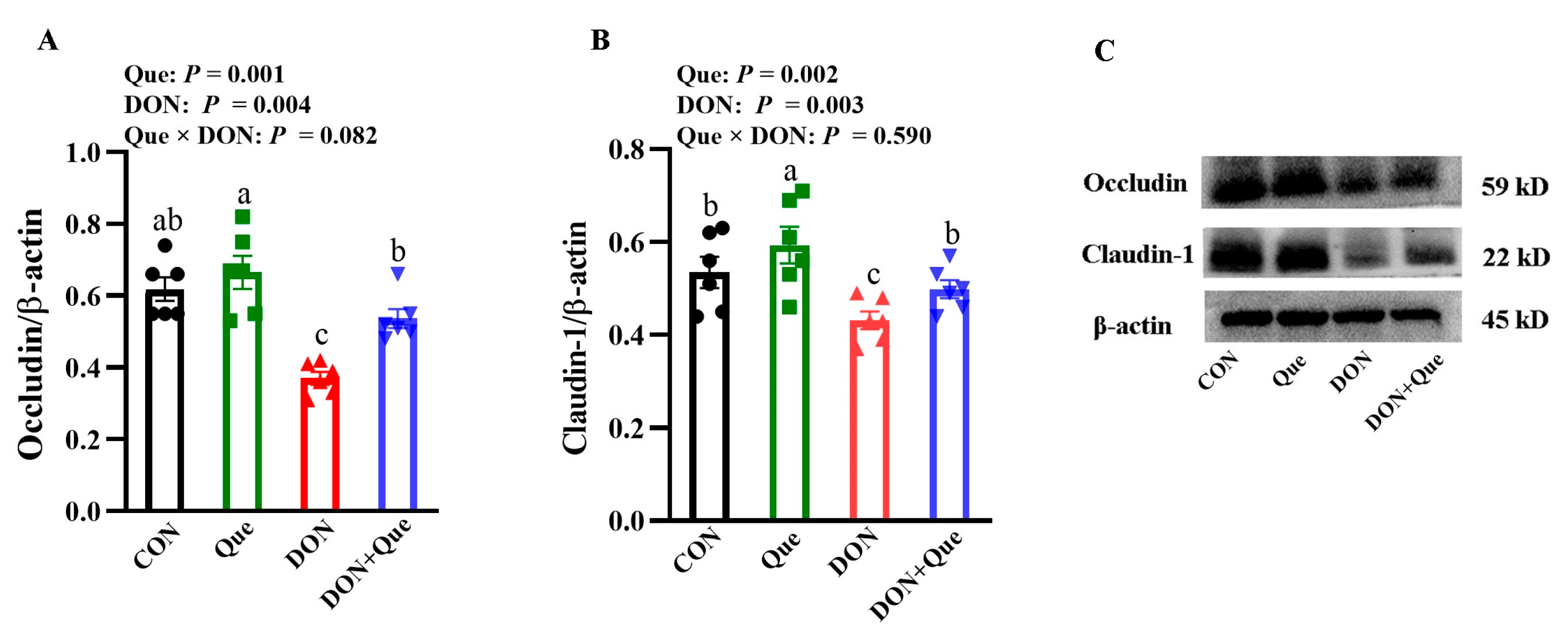
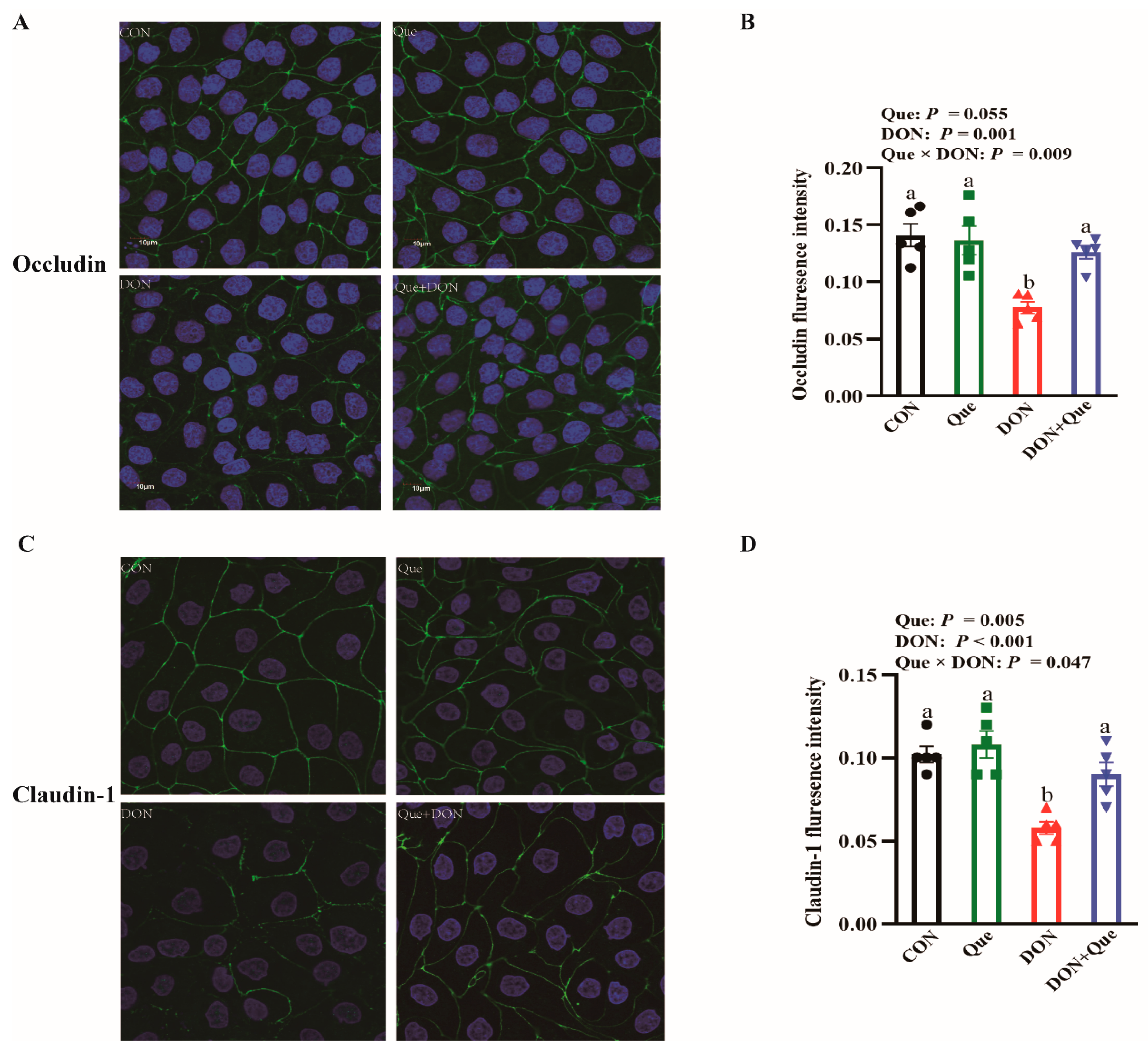
2.3. Effects of Dietary Que on Intestinal Tight Junction Protein Expression in Weaned Piglets after DON Exposure
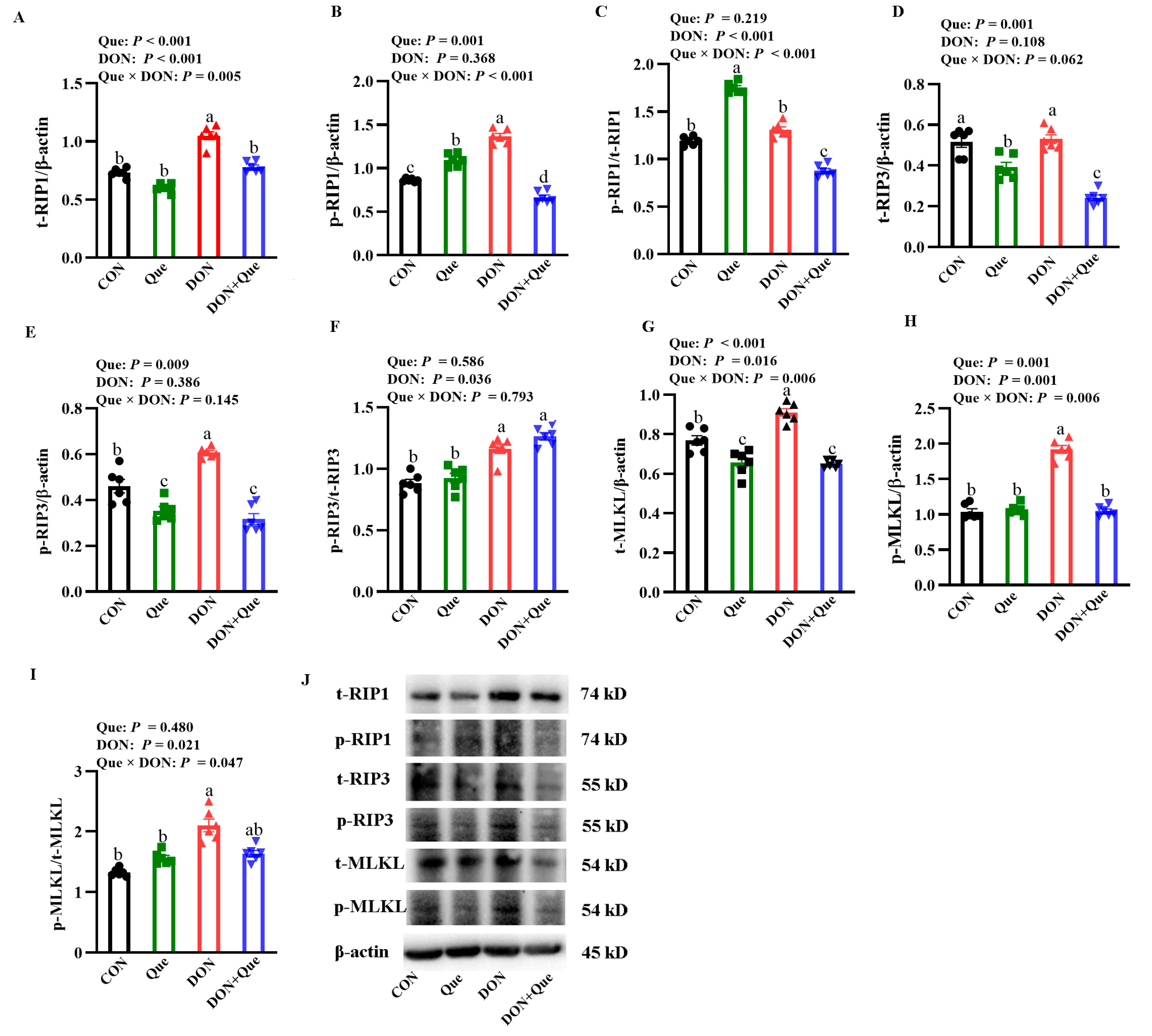
2.4. Effects of Dietary Que on Intestinal Necroptosis Protein Expression in Weaned Piglets after DON Exposure
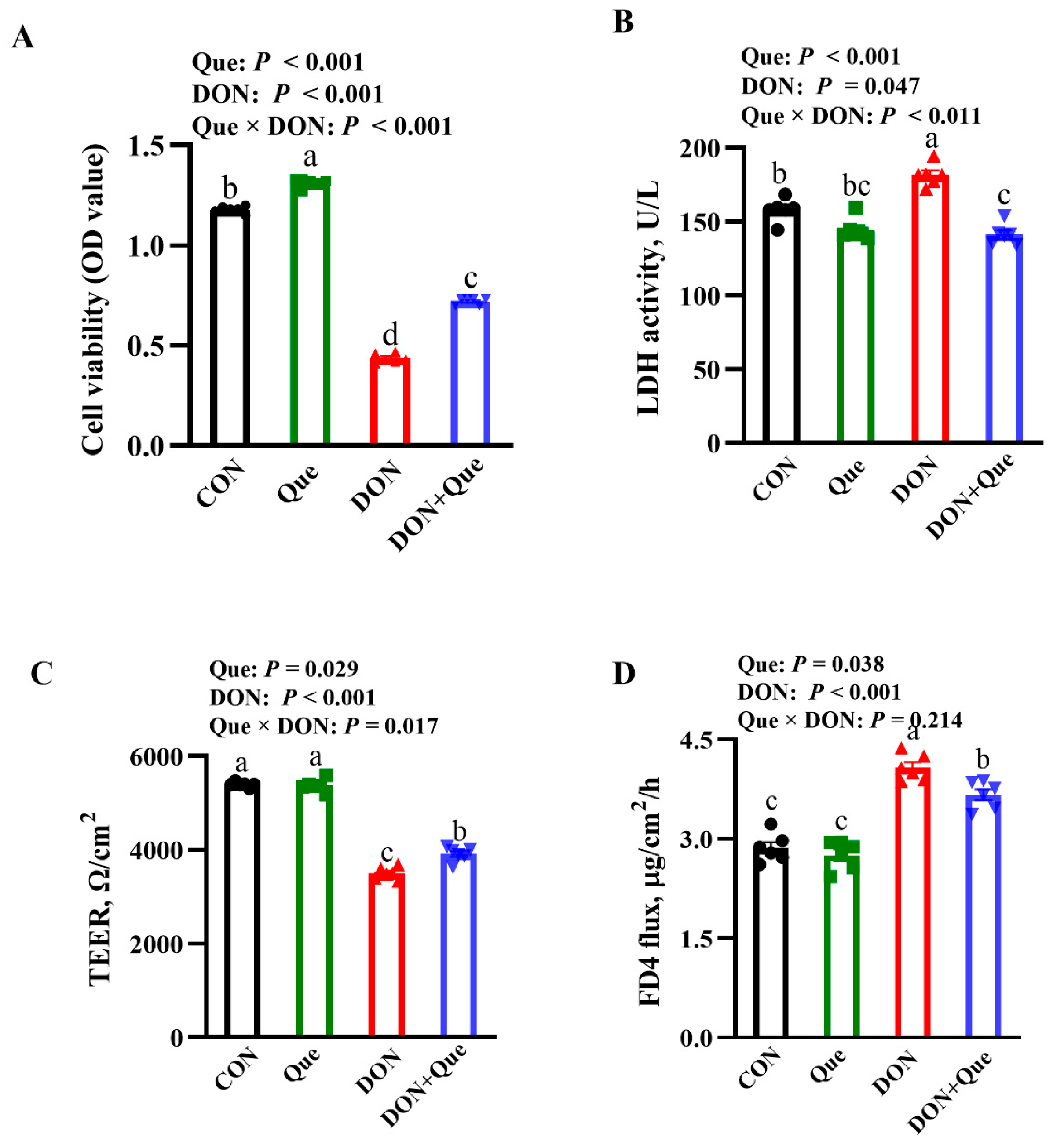
2.5. Effects of Que on Cell Viability and Lactate Dehydrogenases (LDH) Activity in IPEC-1 Cell after DON Challenge
2.6. Effects of Que on Cell Barrier Integrity in IPEC-1 Cells after DON Challenge
2.7. Effects of Que on Tight Junction Protein Distribution in IPEC-1 Cells after DON Challenge
2.8. Effects of Que on Necroptosis Protein Expression in IPEC-1 Cells after DON Challenge
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Experimental Design
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Intestinal Histology
4.4. Intestinal Ultrastructure
4.5. Cell Viability
4.6. Cell Supernatant Lactate Dehydrogenases (LDH)
4.7. Cell Barrier Function
4.8. Tight Junction Protein Distribution
4.9. Protein Expression by Western Blotting
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Janik, E.; Niemcewicz, M.; Ceremuga, M.; Stela, M.; Saluk-Bijak, J.; Siadkowski, A.; Bijak, M. Molecular aspects of mycotoxins—A serious problem for human health. Int. J. Mol. 2020, 21, 8187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinton, P.; Accensi, F.; Beauchamp, E.; Cossalter, A.; Callu, P.; Grosjean, F.; Oswald, I. Ingestion of deoxynivalenol (DON) contaminated feed alters the pig vaccinal immune responses. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 177, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, E.; Horn, N.; Ajuwon, K. Mechanisms of deoxynivalenol-induced endocytosis and degradation of tight junction proteins in jejunal IPEC-J2 cells involve selective activation of the MAPK pathways. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 2065–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, D.; Yang, P.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, K.; Qi, D.; Wang, S. Deoxynivalenol triggers porcine intestinal tight junction disorder through hijacking SLC5A1 and PGC1α-mediated mitochondrial function. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 163, 112921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Gonzalez, G.; Vandenabeele, P.; Krysko, D.V. Necroptosis: A novel cell death modality and its potential relevance for critical care medicine. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasparakis, M.; Vandenabeele, P. Necroptosis and its role in inflammation. Nature 2015, 517, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, M.; Gupta, K.; Franco, S.; Liu, B. Necroptosis in the Pathophysiology of Disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liang, T.; Xiao, K. Necroptosis is active and contributes to intestinal injury in a piglet model with lipopolysaccharide challenge. Cell. Death Dis. 2021, 12, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addi, M.; Elbouzidi, A.; Abid, M.; Tungmunnithum, D.; Elamrani, A.; Hano, C. An overview of bioactive flavonoids from citrus fruits. Applied Sci. 2022, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, L.; Zeng, X.; Yang, J.; Tian, M.; Liu, H.; Yang, B. Identification of a flavonoid C-glycoside as potent antioxidant. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 110, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.M.; Murphy, E.A.; Carmichael, M.D. Effects of the dietary flavonoid quercetin upon performance and health. Curr. Sport. Med. Rep. 2009, 8, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yao, J.; Han, C.; Yang, J.; Chaudhry, M.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y. Quercetin, inflammation and immunity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Wei, H.; Xiang, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, J. Protective effect of quercetin on pig intestinal integrity after transport stress is associated with regulation oxidative status and inflammation. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2016, 78, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinton, P.; Nougayrède, J.; Del Rio, J.; Moreno, C.; Marin, D.; Ferrier, L.; Bracarense, A.; Kolf-Clauw, M.; Oswald, I.P. The food contaminant deoxynivalenol, decreases intestinal barrier permeability and reduces claudin expression. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 237, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinton, P.; Braicu, C.; Nougayrede, J.; Laffitte, J.; Taranu, I.; Oswald, I. Deoxynivalenol impairs porcine intestinal barrier function and decreases the protein expression of claudin-4 through a mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent mechanism. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1956–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierron, A.; Alassane-Kpembi, I.; Oswald, I. Impact of two mycotoxins deoxynivalenol and fumonisin on pig intestinal health. Porc. Health Manag. 2016, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahle, M.; Buerge, I.; Hauser, A.; Müller, M.; Poiger, T. Azole fungicides: Occurrence and fate in wastewater and surface waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7193–7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, E.; Lopes, I.; Pardal, M. Occurrence, fate and effects of azoxystrobin in aquatic ecosystems: A review. Environ. Int. 2013, 53, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepika; Maurya, P. Health benefits of quercetin in age-related diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, S.; Pevny, S.; Ziegenhagen, R.; Bakhiya, N.; Schäfer, B.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.; Lampen, A. Safety aspects of the use of quercetin as a dietary supplement. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulusoy, H.; Sanlier, N. A minireview of quercetin: From its metabolism to possible mechanisms of its biological activities. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3290–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellington, M.; Bosompem, M.; Petracek, R.; Nagl, V.; Columbus, D.J. Effect of long-term feeding of graded levels of deoxynivalenol (DON) on growth performance, nutrient utilization, and organ health in finishing pigs and DON content in biological samples. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Sureshkumar, S.; Kim, I. Influences of dietary flavonoid (quercetin) supplementation on growth performance and immune response of growing pigs challenged with Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2020, 62, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Hu, L.; Suo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jin, F.; Feng, X.; Teng, N.; Li, Y. Effects of dietary supplementation of quercetin on performance, egg quality, cecal microflora populations, and antioxidant status in laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, P.; Braber, S.; Varasteh, S.; Alizadeh, A.; Garssen, J.; Fink-Gremmels, J. The intestinal barrier as an emerging target in the toxicological assessment of mycotoxins. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 1007–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blikslager, A.; Moeser, A.; Gookin, J.; Jones, S.; Odle, J. Restoration of barrier function in injured intestinal mucosa. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 545–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhotnik, I.; Moati, D.; Shaoul, R.; Loberman, B.; Pollak, Y.; Schwartz, B. Quercetin prevents small intestinal damage and enhances intestinal recovery during methotrexate-induced intestinal mucositis of rats. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 62, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Huang, L.; Wang, P.; Wu, Z.; Li, F.; Wang, C. The Effect of low and high dose deoxynivalenol on intestinal morphology, distribution, and expression of inflammatory cytokines of weaning rabbits. Toxins 2019, 11, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Yu, H.; Yang, Z.; Hu, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wei, H.; Peng, J. Gly-Pro-Ala peptide and FGSHF3 exert protective effects in DON-induced toxicity and intestinal damage via decreasing oxidative stress. Food Res. Int. 2021, 139, 109840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Zhang, Y.; Si, X.; Jin, Y.; Jiang, D.; Dai, Z.; Wu, Z. Quercetin alleviates oxidative damage by activating nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 signaling in porcine enterocytes. Nutrients 2021, 13, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.; Odenwald, M.; Turner, J.; Zuo, L. Tight junction proteins occludin and ZO-1 as regulators of epithelial proliferation and survival. Ann. N. Y Acad. Sci. 2022, 1514, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Hara, H.J.T.J. Quercetin enhances intestinal barrier function through the assembly of zonula [corrected] occludens-2, occludin, and claudin-1 and the expression of claudin-4 in Caco-2 cells. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Xu, H.; Huang, C.; Fan, J.; Mei, Q.; Lu, Y.; Lou, L.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Y. Quercetin protects against intestinal barrier disruption and inflammation in acute necrotizing pancreatitis through TLR4/MyD88/p38 MAPK and ERS inhibition. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 742–752. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, K.; Zhou, M.; Lv, Q.; He, P.; Qin, X.; Wang, D.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y. Protocatechuic acid and quercetin attenuate ETEC-caused IPEC-1 cell inflammation and injury associated with inhibition of necroptosis and pyroptosis signaling pathways. J. Anim. Sci. Biotech. 2023, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.; Geng, H.; Tan, X. Cell death of intestinal epithelial cells in intestinal diseases. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2020, 72, 308–324. [Google Scholar]
- Vanlangenakker, N.; Vanden Berghe, T.; Vandenabeele, P. Many stimuli pull the necrotic trigger, an overview. Cell. Death Differ. 2012, 19, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, J.; Tanzer, M.; Lucet, I.; Young, S.; Spall, S.; Sharma, P.; Pierotti, C.; Garnier, J.; Dobson, R.; Webb, A.; et al. Activation of the pseudokinase MLKL unleashes the four-helix bundle domain to induce membrane localization and necroptotic cell death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15072–15077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinlich, R.; Oberst, A.; Beere, H.; Green, D. Necroptosis in development, inflammation and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2017, 18, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Xu, X.; Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Lu, Z. RIP3 knockdown inhibits necroptosis of human intestinal epithelial cells via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling and ameliorates murine colitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Liu, C.; Qin, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Odle, J.; Lin, X.; Hu, C.; Liu, Y. EPA and DHA attenuate deoxynivalenol-induced intestinal porcine epithelial cell injury and protect barrier function integrity by inhibiting necroptosis signaling pathway. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 2483–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Tang, H.; Shan, L.; Liu, S.; Huang, D.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Yang, M.; Yin, X.; Yang, H.; et al. Quercetin prevents necroptosis of oligodendrocytes by inhibiting macrophages/microglia polarization to M1 phenotype after spinal cord injury in rats. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Qiao, X. The alleviative effects of quercetin on cadmium-induced necroptosis via inhibition ROS/iNOS/NF-κB pathway in the chicken brain. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 1584–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, B.; Wu, K.; Yang, A.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Rajput, S.; Zhang, N.; et al. Deoxynivalenol impairs porcine intestinal host defense peptide expression in weaned piglets and IPEC-J2 cells. Toxins 2018, 10, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, F.; Odle, J.; Lin, X.; Jacobi, S.; Zhu, H.; Wu, Z.; Hou, Y. Fish oil enhances intestinal integrity and inhibits TLR4 and NOD2 signaling pathways in weaned pigs after LPS challenge. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Zhou, M.; Xu, Q.; Lv, Q.; Guo, J.; Qin, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, S.; Zhao, J.; Xiao, K.; et al. Quercetin Ameliorates Deoxynivalenol-Induced Intestinal Injury and Barrier Dysfunction Associated with Inhibiting Necroptosis Signaling Pathway in Weaned Pigs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015172
Liu J, Zhou M, Xu Q, Lv Q, Guo J, Qin X, Xu X, Chen S, Zhao J, Xiao K, et al. Quercetin Ameliorates Deoxynivalenol-Induced Intestinal Injury and Barrier Dysfunction Associated with Inhibiting Necroptosis Signaling Pathway in Weaned Pigs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(20):15172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015172
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jiahao, Mohan Zhou, Qilong Xu, Qingqing Lv, Junjie Guo, Xu Qin, Xiaoye Xu, Shaokui Chen, Jiangchao Zhao, Kan Xiao, and et al. 2023. "Quercetin Ameliorates Deoxynivalenol-Induced Intestinal Injury and Barrier Dysfunction Associated with Inhibiting Necroptosis Signaling Pathway in Weaned Pigs" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 20: 15172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015172
APA StyleLiu, J., Zhou, M., Xu, Q., Lv, Q., Guo, J., Qin, X., Xu, X., Chen, S., Zhao, J., Xiao, K., & Liu, Y. (2023). Quercetin Ameliorates Deoxynivalenol-Induced Intestinal Injury and Barrier Dysfunction Associated with Inhibiting Necroptosis Signaling Pathway in Weaned Pigs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(20), 15172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015172







