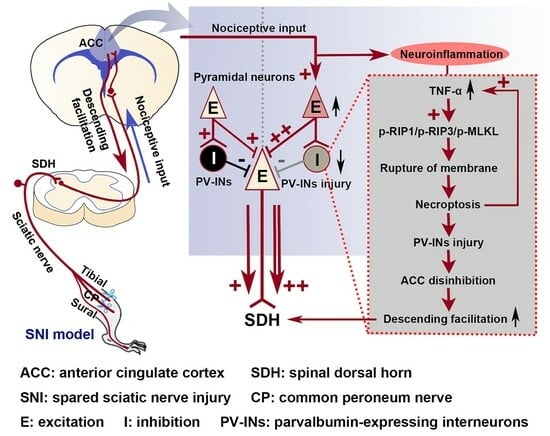
Activation of the TNF-α-Necroptosis Pathway in Parvalbumin-Expressing Interneurons of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex Contributes to Neuropathic Pain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
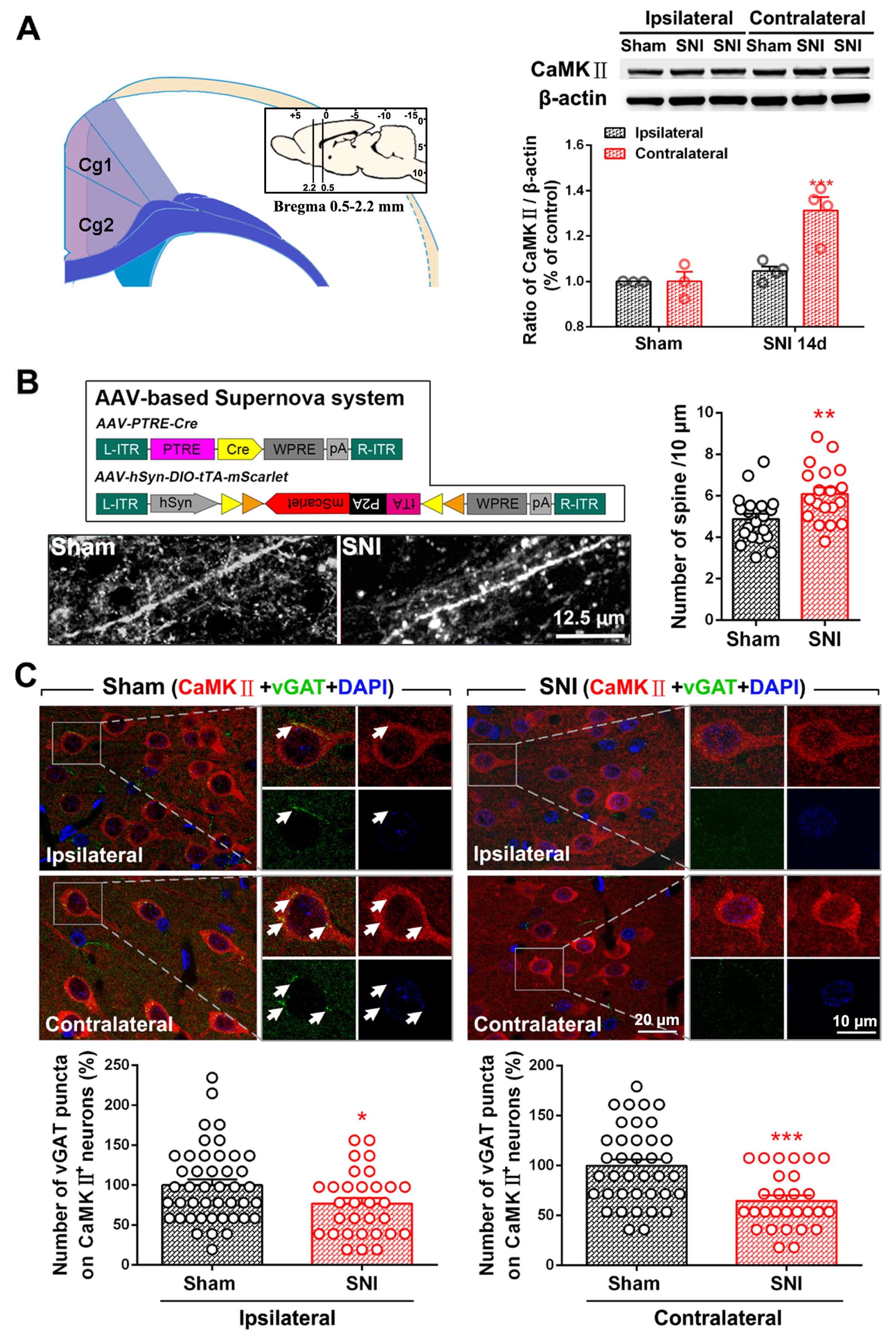
2.1. SNI Induces Excitation/Inhibition (E/I) Imbalance in ACC
2.2. The Activation of the TNF-α-Necroptosis Pathway in ACC PV-INs Following SNI Surgery
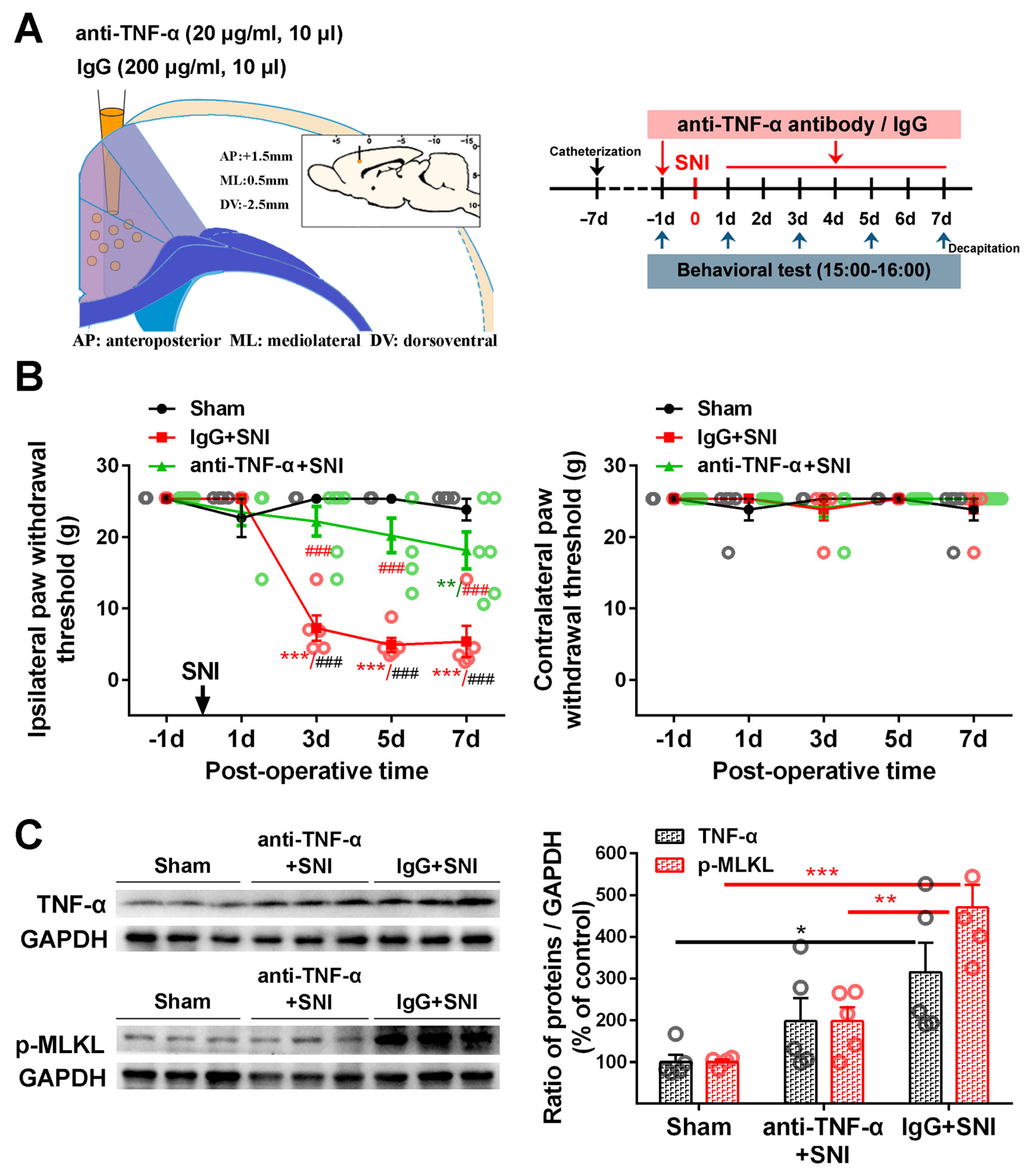
2.3. Inhibition of the ACC TNF-α-Necroptosis Pathway Reduces Neuroinflammation in the ACC and Alleviates SNI-Induced Mechanical Allodynia
3. Discussion
3.1. ACC Hyper-Excitability Induces Pain Hypersensitivity and Pain-Related Emotional Disorders
3.2. Dysfunction of ACC Inhibitory Interneurons in Chronic Pain Promotes E/I Imbalance in the ACC
3.3. The Role of the TNF-α-Necroptosis Pathway in ACC Disinhibition Following Peripheral Nerve Injury
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Spared Nerve Injury (SNI)
4.3. Fifty Percent Paw Withdrawal Threshold Test
4.4. Immunohistochemistry and Immunofluorescence
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Bioinformatic Tools
4.7. Intra-ACC Drug Application
4.8. Transfection of siRNA In Vivo
4.9. Supernova
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lançon, K.; Qu, C.; Navratilova, E.; Porreca, F.; Séguéla, P. Decreased dopaminergic inhibition of pyramidal neurons in anterior cingulate cortex maintains chronic neuropathic pain. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 109933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.L.; Asada, N.; Malenka, R.C. Anterior cingulate inputs to nucleus accumbens control the social transfer of pain and analgesia. Science 2021, 371, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Taniguchi, W.; Chen, Q.Y.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Song, Q.; Liu, R.H.; Koga, K.; Matsuda, T.; Kaito-Sugimura, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Top-down descending facilitation of spinal sensory excitatory transmission from the anterior cingulate cortex. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Koga, K.; Descalzi, G.; Qiu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.S.; Zhang, Z.J.; He, X.B.; Qin, X.; Xu, F.Q.; et al. Postsynaptic potentiation of corticospinal projecting neurons in the anterior cingulate cortex after nerve injury. Mol. Pain 2014, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.Y.; Chen, S.X.; Liu, J.Y.; Yao, P.W.; Duan, Y.W.; Li, Y.Y.; Zang, Y. Neuroinflammation in the anterior cingulate cortex: The potential supraspinal mechanism underlying the mirror-image pain following motor fiber injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, P.W.; Wang, S.K.; Chen, S.X.; Xin, W.J.; Liu, X.G.; Zang, Y. Upregulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the anterior cingulate cortex contributes to neuropathic pain and pain-associated aversion. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 130, 104456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meda, K.S.; Patel, T.; Braz, J.M.; Malik, R.; Turner, M.L.; Seifikar, H.; Basbaum, A.I.; Sohal, V.S. Microcircuit Mechanisms through which Mediodorsal Thalamic Input to Anterior Cingulate Cortex Exacerbates Pain-Related Aversion. Neuron 2019, 102, 944–959.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, M. A synaptic model for pain: Long-term potentiation in the anterior cingulate cortex. Mol. Cells 2007, 23, 259–271. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura, H.; Iwata, K.; Tsuboi, Y.; Toda, K.; Kitajima, K.; Shimizu, N.; Nomura, H.; Hibiya, J.; Fujita, S.; Sumino, R. Morphological and electrophysiological properties of ACCx nociceptive neurons in rats. Brain Res. 1996, 735, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, S.M.; Pfister, J.P.; Santello, M.; Senn, W.; Nevian, T. Nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain causes disinhibition of the anterior cingulate cortex. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 5754–5764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.H.; Wen, H.Z.; Shen, L.L.; Zhao, Y.D.; Ruan, H.Z. Activation of mGluR1 contributes to neuronal hyperexcitability in the rat anterior cingulate cortex via inhibition of HCN channels. Neuropharmacology 2016, 105, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.H.; Shen, L.L.; Wen, H.Z.; Zhao, Y.D.; Chen, P.H.; Ruan, H.Z. The projections from the anterior cingulate cortex to the nucleus accumbens and ventral tegmental area contribute to neuropathic pain-evoked aversion in rats. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 140, 104862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.; Fang, J.; Qiu, M.; Wang, S.; Xi, D.; Shao, X.; He, X.; Du, J. Electroacupuncture Ameliorates Chronic Inflammatory Pain-Related Anxiety by Activating PV Interneurons in the Anterior Cingulate Cortex. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 691931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.J.; Kwak, C.; Lee, J.; Sim, S.E.; Shim, J.; Choi, T.; Collingridge, G.L.; Zhuo, M.; Kaang, B.K. Bidirectional modulation of hyperalgesia via the specific control of excitatory and inhibitory neuronal activity in the ACC. Mol. Brain 2015, 8, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.Y.; Duan, Y.W.; Zhou, Y.H.; Chen, S.X.; Li, Y.Y.; Zang, Y. NLRP3-Mediated Piezo1 Upregulation in ACC Inhibitory Parvalbumin-Expressing Interneurons Is Involved in Pain Processing after Peripheral Nerve Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.X.; Liao, G.J.; Yao, P.W.; Wang, S.K.; Li, Y.Y.; Zeng, W.A.; Liu, X.G.; Zang, Y. Calpain-2 Regulates TNF-alpha Expression Associated with Neuropathic Pain Following Motor Nerve Injury. Neuroscience 2018, 376, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.H.; Zang, Y.; Chen, X.; Pang, R.P.; Xu, J.T.; Zhou, X.; Wei, X.H.; Li, Y.Y.; Xin, W.J.; Qin, Z.H.; et al. TNF-alpha contributes to up-regulation of Nav1.3 and Nav1.8 in DRG neurons following motor fiber injury. Pain 2010, 151, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.H.; Zang, Y.; Wu, C.Y.; Xu, J.T.; Xin, W.J.; Liu, X.G. Peri-sciatic administration of recombinant rat TNF-alpha induces mechanical allodynia via upregulation of TNF-alpha in dorsal root ganglia and in spinal dorsal horn: The role of NF-kappa B pathway. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 205, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Na, X.; Zang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Xin, W.; Pang, R.; Zhou, L.; Wei, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. Upregulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in nucleus accumbens attenuates morphine-induced rewarding in a neuropathic pain model. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 449, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Aaronson, S.A.; Abrams, J.M.; Adam, D.; Agostinis, P.; Alnemri, E.S.; Altucci, L.; Amelio, I.; Andrews, D.W.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 486–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.W.; Chen, S.X.; Li, Q.Y.; Zang, Y. Neuroimmune Mechanisms Underlying Neuropathic Pain: The Potential Role of TNF-alpha-Necroptosis Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhuriya, Y.K.; Sharma, D. Necroptosis: A regulated inflammatory mode of cell death. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; McQuade, T.; Siemer, A.B.; Napetschnig, J.; Moriwaki, K.; Hsiao, Y.S.; Damko, E.; Moquin, D.; Walz, T.; McDermott, A.; et al. The RIP1/RIP3 necrosome forms a functional amyloid signaling complex required for programmed necrosis. Cell 2012, 150, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degterev, A.; Huang, Z.; Boyce, M.; Li, Y.; Jagtap, P.; Mizushima, N.; Cuny, G.D.; Mitchison, T.J.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Yuan, J. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, S.; Li, S.; Xu, Y.; Wu, J.; Lv, Y.; Du, D. Role of receptor-interacting protein 1/receptor-interacting protein 3 in inflammation and necrosis following chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve. Neuroreport 2018, 29, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, D.I.; Devi, B.I.; Bharti, K.; Panda, R. Cortical plasticity after brachial plexus injury and repair: A resting-state functional MRI study. Neurosurg. Focus 2017, 42, E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.; Kambi, N.; Raghunathan, P.; Khushu, S.; Jain, N. Large-scale reorganization of the somatosensory cortex of adult macaque monkeys revealed by fMRI. Brain Struct. Funct. 2014, 219, 1305–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.M.; Chen, L.; Mao, Y.; Wu, J.S.; Tang, W.J.; Hu, S.N.; Zhou, L.F.; Gu, Y.D. Sensorimotor cortical changes assessed with resting-state fMRI following total brachial plexus root avulsion. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2014, 85, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.B.; Regenbogen, C.; Ohse, M.C.; Frasnelli, J.; Freiherr, J.; Lundstrom, J.N. Brain activations during pain: A neuroimaging meta-analysis of patients with pain and healthy controls. Pain 2016, 157, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Tan, Q.; Cheng, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Gu, E.W.; Fang, W.; Lu, X.; Liu, X. The Changes of Intrinsic Excitability of Pyramidal Neurons in Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Neuropathic Pain. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2018, 12, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; O’Den, G.; Song, Q.; Koga, K.; Zhang, M.M.; Zhuo, M. Adenylyl cyclase subtype 1 is essential for late-phase long term potentiation and spatial propagation of synaptic responses in the anterior cingulate cortex of adult mice. Mol. Pain 2014, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, M. Cortical LTP: A Synaptic Model for Chronic Pain. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1099, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Koga, K.; Descalzi, G.; Chen, T.; Ko, H.G.; Lu, J.; Li, S.; Son, J.; Kim, T.; Kwak, C.; Huganir, R.L.; et al. Coexistence of two forms of LTP in ACC provides a synaptic mechanism for the interactions between anxiety and chronic pain. Neuron 2015, 85, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Li, X.H.; Zhuo, M. NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity in the anterior cingulate cortex. Neuropharmacology 2021, 197, 108749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchatta, O.; Aby, F.; Sifeddine, W.; Bouali-Benazzouz, R.; Brochoire, L.; Manouze, H.; Fossat, P.; Ba M’Hamed, S.; Bennis, M.; Landry, M. Pain hypersensitivity in a pharmacological mouse model of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2114094119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, H. State-dependent opioid control of pain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeker, T.J.; Schmid, A.C.; Keaser, M.L.; Khan, S.A.; Gullapalli, R.P.; Dorsey, S.G.; Greenspan, J.D.; Seminowicz, D.A. Tonic pain alters functional connectivity of the descending pain modulatory network involving amygdala, periaqueductal gray, parabrachial nucleus and anterior cingulate cortex. Neuroimage 2022, 256, 119278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calejesan, A.A.; Kim, S.J.; Zhuo, M. Descending facilitatory modulation of a behavioral nociceptive response by stimulation in the adult rat anterior cingulate cortex. Eur. J. Pain 2000, 4, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillinger, C.; Yalcin, I.; Barrot, M.; Veinante, P. Efferents of anterior cingulate areas 24a and 24b and midcingulate areas 24a ‘ and 24b ‘ in the mouse. Brain Struct. Funct. 2018, 223, 1747–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamm, C.; Decety, J.; Singer, T. Meta-analytic evidence for common and distinct neural networks associated with directly experienced pain and empathy for pain. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Matsuura, T.; Xue, M.; Chen, Q.Y.; Liu, R.H.; Lu, J.S.; Shi, W.; Fan, K.; Zhou, Z.; Miao, Z.; et al. Oxytocin in the anterior cingulate cortex attenuates neuropathic pain and emotional anxiety by inhibiting presynaptic long-term potentiation. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Zhang, Y.Q. A new perspective on the anterior cingulate cortex and affective pain. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 90, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, K.; Shimoyama, S.; Yamada, A.; Furukawa, T.; Nikaido, Y.; Furue, H.; Nakamura, K.; Ueno, S. Chronic inflammatory pain induced GABAergic synaptic plasticity in the adult mouse anterior cingulate cortex. Mol. Pain 2018, 14, 1744806918783478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peek, A.L.; Leaver, A.M.; Foster, S.; Puts, N.A.; Oeltzschner, G.; Henderson, L.; Galloway, G.; Ng, K.; Refshauge, K.; Rebbeck, T. Increase in ACC GABA+ levels correlate with decrease in migraine frequency, intensity and disability over time. J. Headache Pain 2021, 22, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, N.T.; Austin, P.J. Peripheral Nerve Injury Triggers Neuroinflammation in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex and Ventral Hippocampus in a Subgroup of Rats with Coincident Affective Behavioural Changes. Neuroscience 2019, 416, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.J.; Lu, Y.C.; Hua, X.Y.; Ma, S.J.; Xu, J.G. A Longitudinal Mapping Study on Cortical Plasticity of Peripheral Nerve Injury Treated by Direct Anastomosis and Electroacupuncture in Rats. World Neurosurg. 2018, 114, e267–e282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, A.L.; Zheng, M.X.; Hua, X.Y.; Huo, B.B.; Shen, J.; Xu, J.G. Electroacupuncture-Related Metabolic Brain Connectivity in Neuropathic Pain due to Brachial Plexus Avulsion Injury in Rats. Front. Neural Circuits 2020, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiers, S.; Pradhan, G.; Mwirigi, J.; Mejia, G.; Ahmad, A.; Kroener, S.; Price, T. Neuropathic pain creates an enduring prefrontal cortex dysfunction corrected by the type II diabetic drug metformin but not by gabapentin. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 7337–7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, J.F.; Williams, J.P.; Yan, Y.N.; Xiao, X.L.; Shi, W.R.; Qian, X.Y.; An, J.X. Neuropathic Pain Creates Systemic Ultrastructural Changes in the Nervous System Corrected by Electroacupuncture but Not by Pregabalin. J. Pain Res. 2021, 14, 2893–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; He, X.H.; Xin, W.J.; Pang, R.P.; Wei, X.H.; Zhou, L.J.; Li, Y.Y.; Liu, X.G. Inhibition of NF-kappaB prevents mechanical allodynia induced by spinal ventral root transection and suppresses the re-expression of Nav1.3 in DRG neurons in vivo and in vitro. Brain Res. 2010, 1363, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, J.K.; Ji, R.R. Cytokine mechanisms of central sensitization: Distinct and overlapping role of interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in regulating synaptic and neuronal activity in the superficial spinal cord. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 5189–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Zhou, L.J.; Hu, N.W.; Xu, J.T.; Wu, C.Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.Y.; Liu, X.G. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces long-term potentiation of C-fiber evoked field potentials in spinal dorsal horn in rats with nerve injury: The role of NF-kappa B, JNK and p38 MAPK. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Guo, W.; Zou, S.; Ren, K.; Dubner, R. Supraspinal glial-neuronal interactions contribute to descending pain facilitation. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 10482–10495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Nei, H.; Dougherty, P.M. A p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent mechanism of disinhibition in spinal synaptic transmission induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 12844–12855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhao, H.; Gao, H.; Liu, D.; Li, J. Participation of pro-inflammatory cytokines in neuropathic pain evoked by chemotherapeutic oxaliplatin via central GABAergic pathway. Mol. Pain 2018, 14, 1744806918783535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holler, N.; Zaru, R.; Micheau, O.; Thome, M.; Attinger, A.; Valitutti, S.; Bodmer, J.L.; Schneider, P.; Seed, B.; Tschopp, J. Fas triggers an alternative, caspase-8-independent cell death pathway using the kinase RIP as effector molecule. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 1, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, B.; Pan, H.; Najafov, A.; Yuan, J. Necroptosis in development and diseases. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jitkaew, S.; Cai, Z.Y.; Choksi, S.; Li, Q.N.; Luo, J.; Liu, Z.G. Mixed lineage kinase domain-like is a key receptor interacting protein 3 downstream component of TNF-induced necrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5322–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasparakis, M.; Vandenabeele, P. Necroptosis and its role in inflammation. Nature 2015, 517, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, R.; Zhong, J.; Ying, Y.; Wang, W.; Cao, Y.; Cai, H.; Li, X.; Shuai, J.; Han, J. Mosaic composition of RIP1-RIP3 signalling hub and its role in regulating cell death. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dondelinger, Y.; Declercq, W.; Montessuit, S.; Roelandt, R.; Goncalves, A.; Bruggeman, I.; Hulpiau, P.; Weber, K.; Sehon, C.A.; Marquis, R.W.; et al. MLKL Compromises Plasma Membrane Integrity by Binding to Phosphatidylinositol Phosphates. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Sun, L.M.; Su, L.J.; Rizo, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.F.; Wang, F.S.; Wang, X.D. Mixed Lineage Kinase Domain-like Protein MLKL Causes Necrotic Membrane Disruption upon Phosphorylation by RIP3. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabal, M.; Muller, N.; Adler, H.; Knies, N.; Gross, C.J.; Damgaard, R.B.; Kanegane, H.; Ringelhan, M.; Kaufmann, T.; Heikenwalder, M.; et al. XIAP restricts TNF- and RIP3-dependent cell death and inflammasome activation. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Yang, C.; Huang, W.; Du, S.; Mai, H.; Xiao, J.; Lu, T. Sulforaphane attenuates microglia-mediated neuronal necroptosis through down-regulation of MAPK/NF-kappaB signaling pathways in LPS-activated BV-2 microglia. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 133, 218–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallach, D.; Kang, T.B.; Dillon, C.P.; Green, D.R. Programmed necrosis in inflammation: Toward identification of the effector molecules. Science 2016, 352, aaf2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, H.; Cotsmire, S.; Langland, J.; Kibler, K.V.; Kalman, D.; Upton, J.W.; Mocarski, E.S.; Jacobs, B.L. Inhibition of DAI-dependent necroptosis by the Z-DNA binding domain of the vaccinia virus innate immune evasion protein, E3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11506–11511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, K.; Manning, G. Necroptosis and Inflammation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2016, 85, 743–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Cao, J.; Wang, X. RIP3/MLKL pathway-regulated necroptosis: A new mechanism of paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Cao, J.; Wang, G.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, S. Macrophage Infiltration Initiates RIP3/MLKL-Dependent Necroptosis in Paclitaxel-Induced Neuropathic Pain. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 1567210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.X.; Wang, N.N.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Juan, Z.D.; Zhang, C. Necrostatin-1 Ameliorates Peripheral Nerve Injury-Induced Neuropathic Pain by Inhibiting the RIP1/RIP3 Pathway. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Sun, G.Q.; Wang, J.Y. RIP3-mediated necroptosis increases neuropathic pain via microglia activation: Necrostatin-1 has therapeutic potential. FEBS Open Bio 2021, 11, 2858–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Li, L.; Sun, Y.; Shao, J.; Ren, X.; Zang, W.; Cao, J. Role of spinal RIP3 in inflammatory pain and electroacupuncture-mediated analgesic effect in mice. Life Sci. 2022, 306, 120839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurabe, M.; Sasaki, M.; Furutani, K.; Furue, H.; Kamiya, Y.; Baba, H. Structural and functional properties of spinal dorsal horn neurons after peripheral nerve injury change overtime via astrocyte activation. iScience 2022, 25, 105555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannini, S.; Coraci, D.; Brau, F.; Galluzzo, V.; Loreti, C.; Caliandro, P.; Padua, L.; Maccauro, G.; Biscotti, L.; Bernabei, R. Neuropathic Pain in the Elderly. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

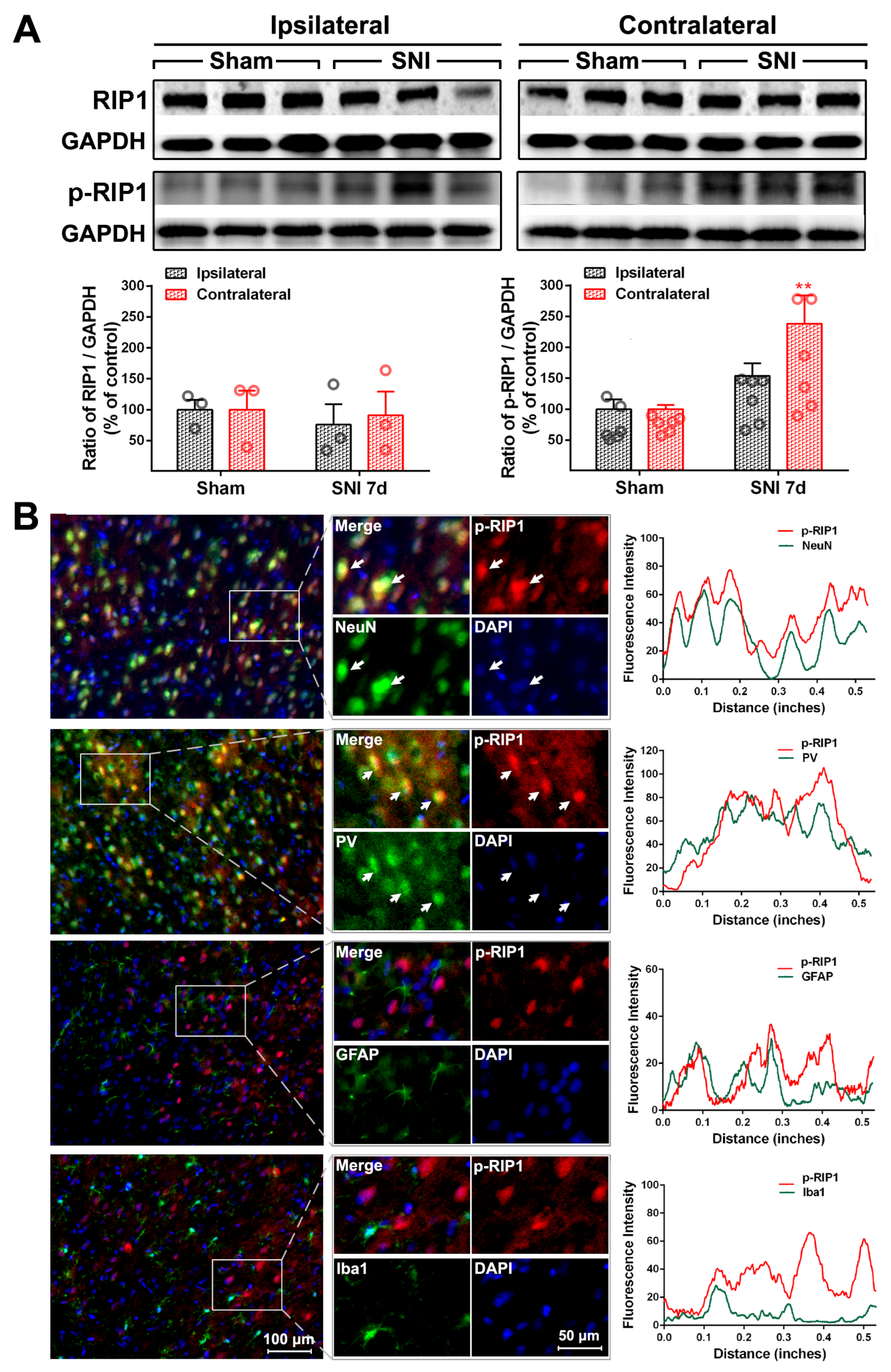
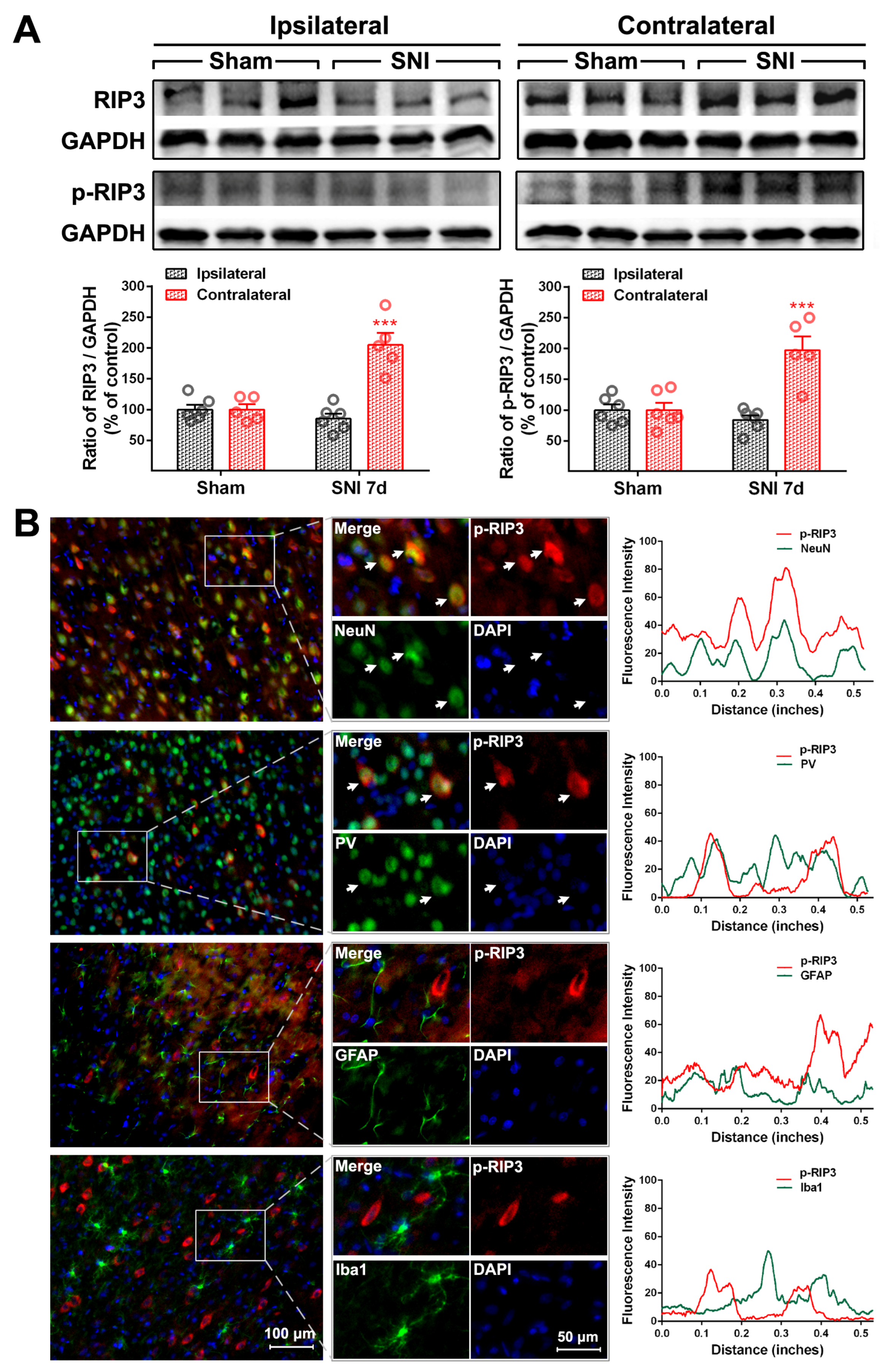
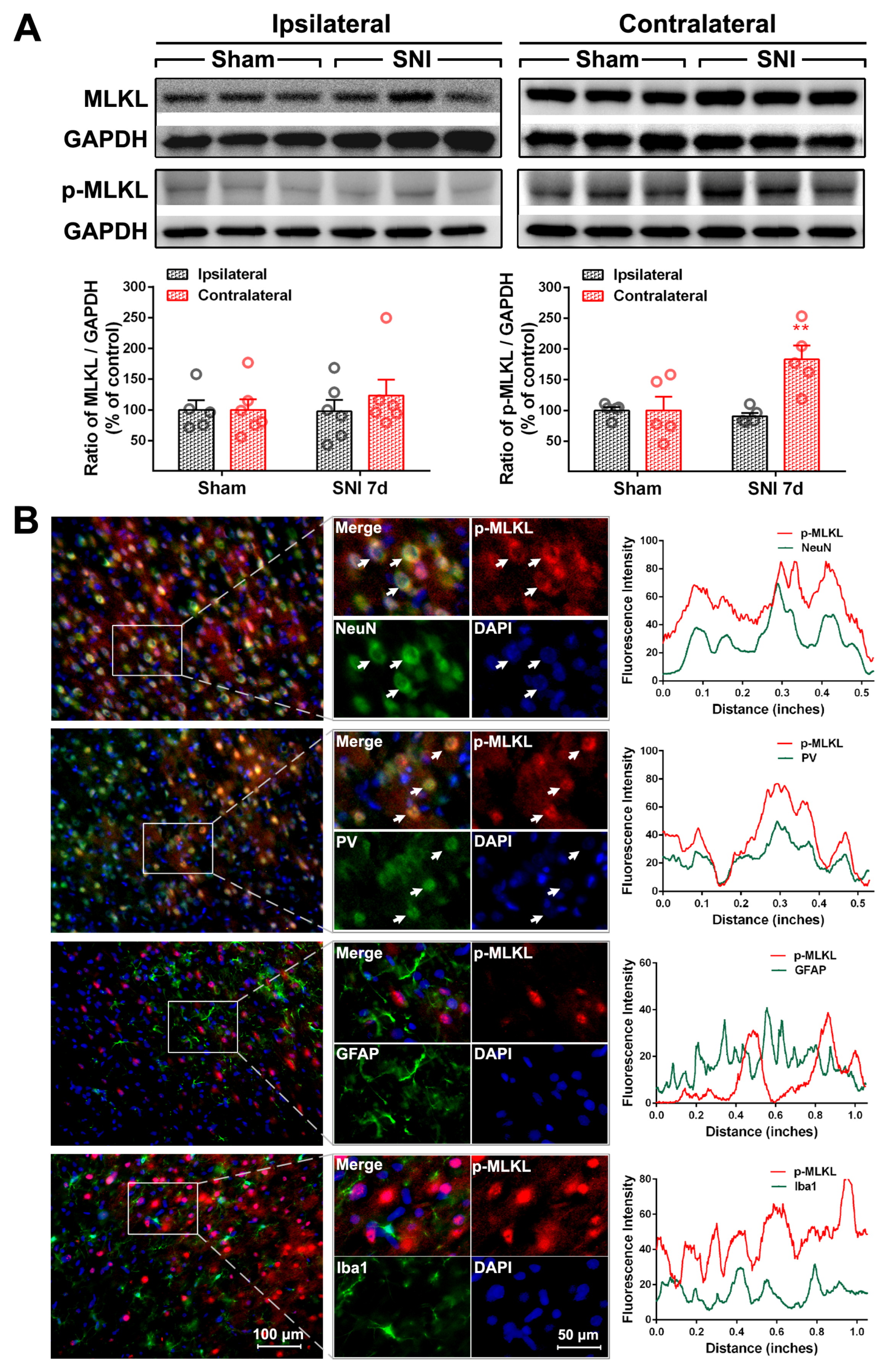

| Cell Markers Proteins | NeuN | PV | GFAP | Iba1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RIP1 | 20.30 ± 1.64% | 17.69 ± 2.87% | 76.17 ± 1.89% | 13.69 ± 1.71% |
| P-RIP1 | 79.48 ± 3.48% | 70.54 ± 3.15% | 12.71 ± 3.65% | 15.25 ± 2.35% |
| RIP3 | 84.32 ± 3.63% | 82.42 ± 2.22% | 14.64 ± 1.85% | 7.17 ± 0.74% |
| P-RIP3 | 83.60 ± 1.24% | 73.92 ± 5.58% | 29.26 ± 2.40% | 8.17 ± 0.91% |
| MLKL | 85.36 ± 2.84% | 79.62 ± 0.87% | 11.8 ± 1.6% | 6.71 ± 0.27% |
| P-MLKL | 93.58 ± 0.36% | 84.83 ± 5.51% | 5.61 ± 0.41% | 4.71 ± 0.48% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Zang, Y. Activation of the TNF-α-Necroptosis Pathway in Parvalbumin-Expressing Interneurons of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex Contributes to Neuropathic Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015454
Duan Y, Li Q, Zhou Y, Chen S, Li Y, Zang Y. Activation of the TNF-α-Necroptosis Pathway in Parvalbumin-Expressing Interneurons of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex Contributes to Neuropathic Pain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(20):15454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015454
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Yiwen, Qiaoyun Li, Yaohui Zhou, Shaoxia Chen, Yongyong Li, and Ying Zang. 2023. "Activation of the TNF-α-Necroptosis Pathway in Parvalbumin-Expressing Interneurons of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex Contributes to Neuropathic Pain" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 20: 15454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015454
APA StyleDuan, Y., Li, Q., Zhou, Y., Chen, S., Li, Y., & Zang, Y. (2023). Activation of the TNF-α-Necroptosis Pathway in Parvalbumin-Expressing Interneurons of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex Contributes to Neuropathic Pain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(20), 15454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015454