AAV-SPL 2.0, a Modified Adeno-Associated Virus Gene Therapy Agent for the Treatment of Sphingosine Phosphate Lyase Insufficiency Syndrome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
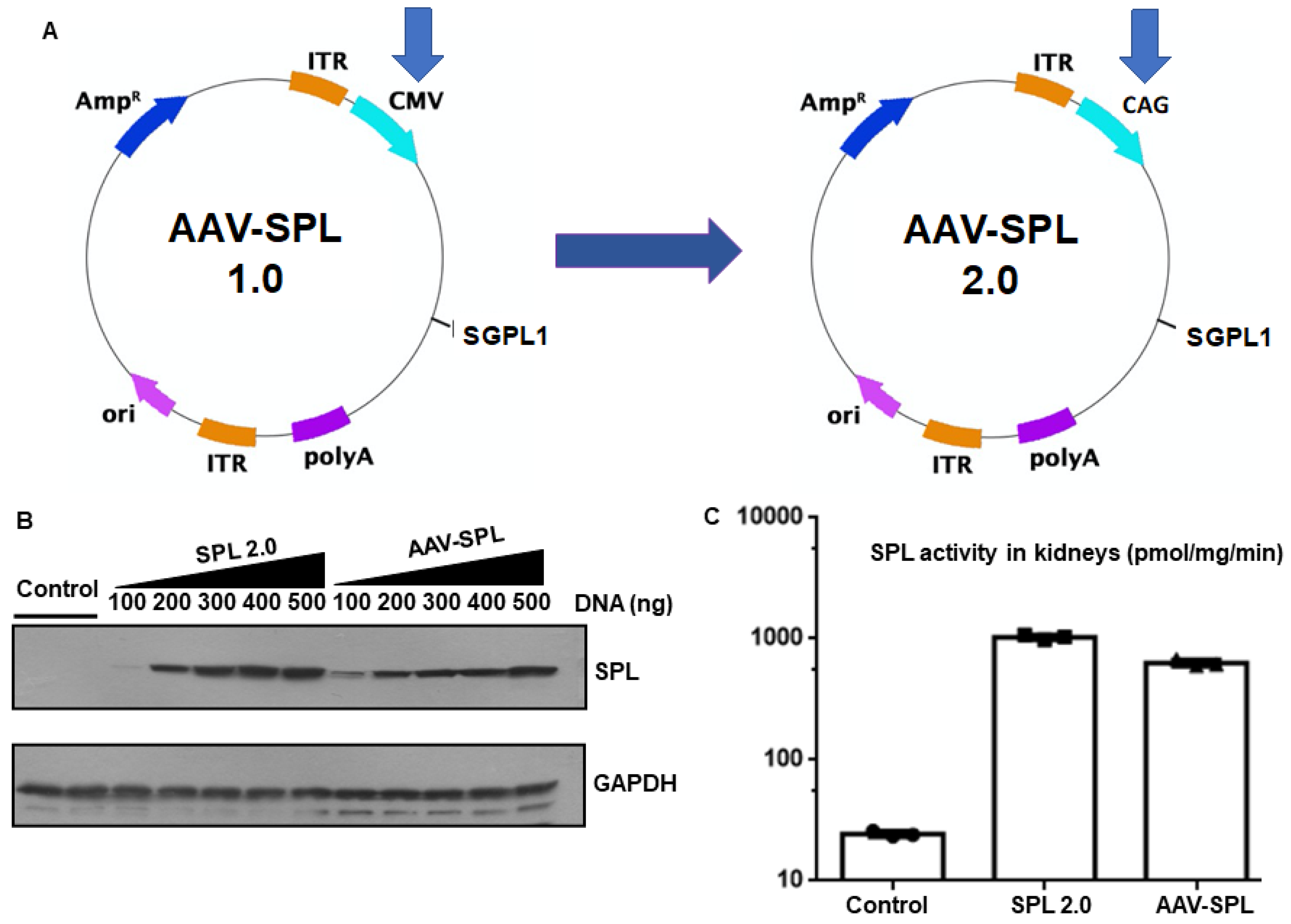
2.1. AAV-SPL 2.0 Results in Higher SPL Expression and Activity Than AAV-SPL after Infection of Human Kidney Cells
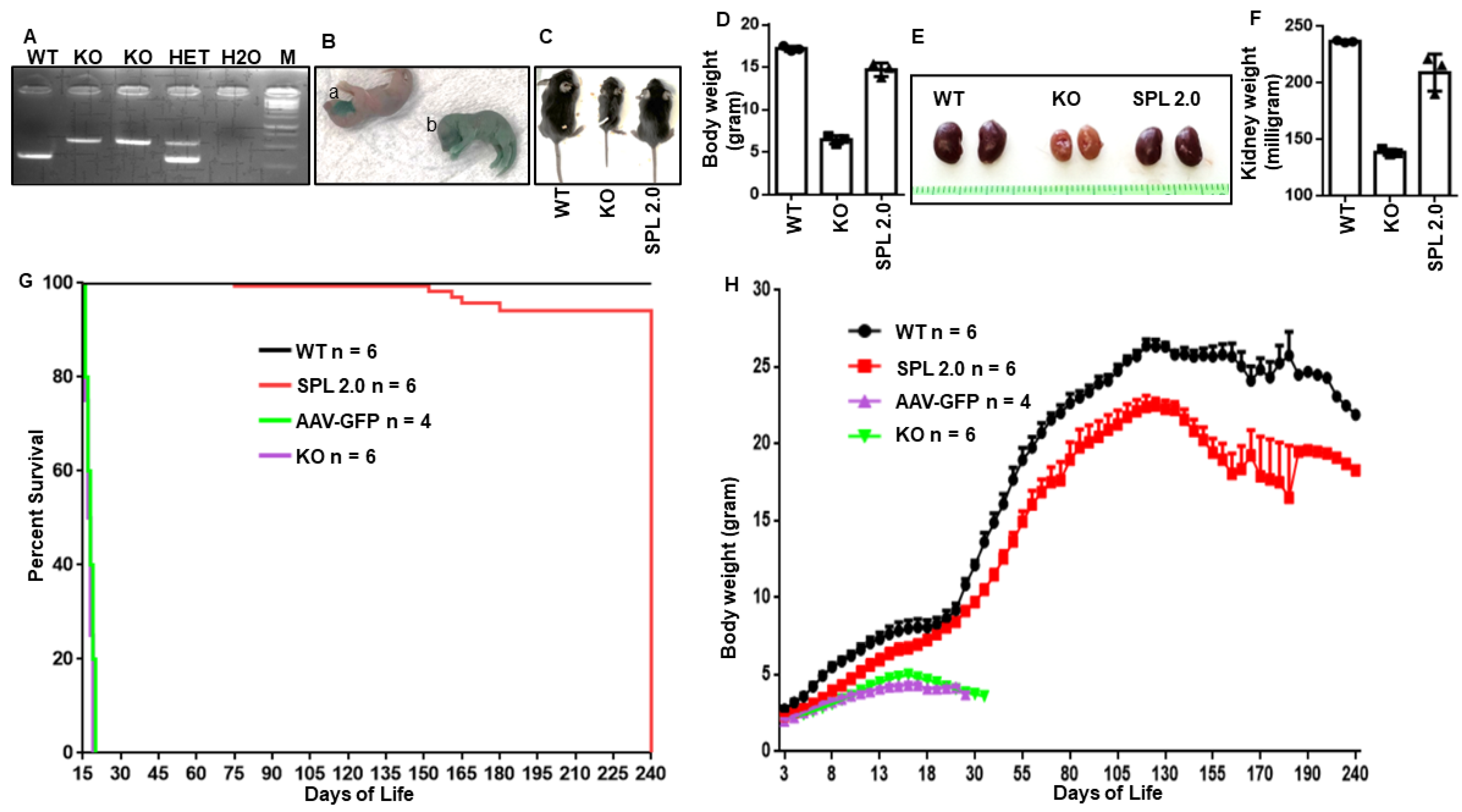
2.2. AAV-SPL 2.0 Promotes the Growth and Survival of Sgpl1 KO Mice
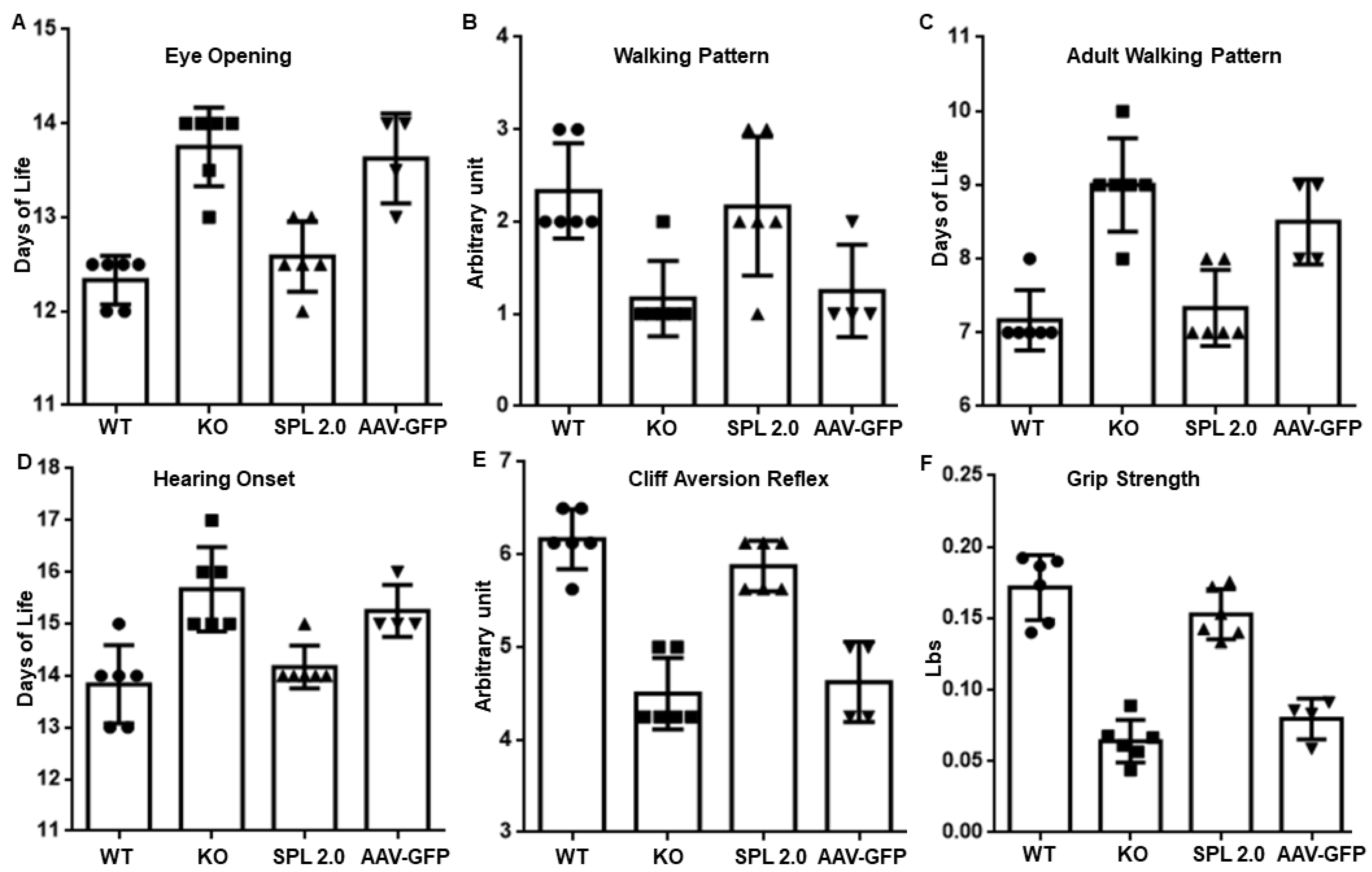
2.3. AAV-SPL 2.0 Prevents Neurodevelopmental Delay in Sgpl1 KO Mice
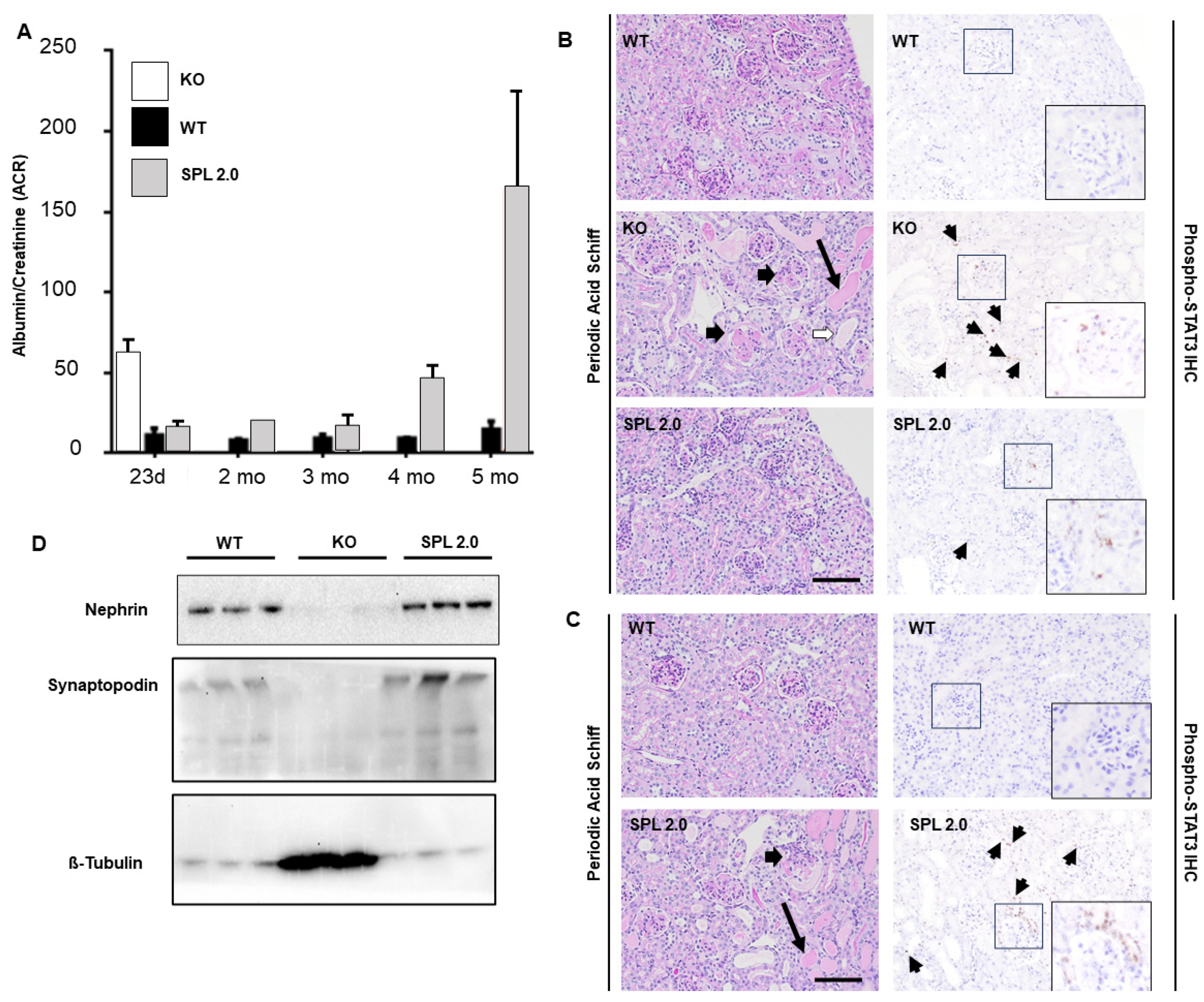
2.4. AAV-SPL 2.0 Delays Onset of Nephrotic Syndrome and Glomerulosclerosis in Sgpl1 KO Mice
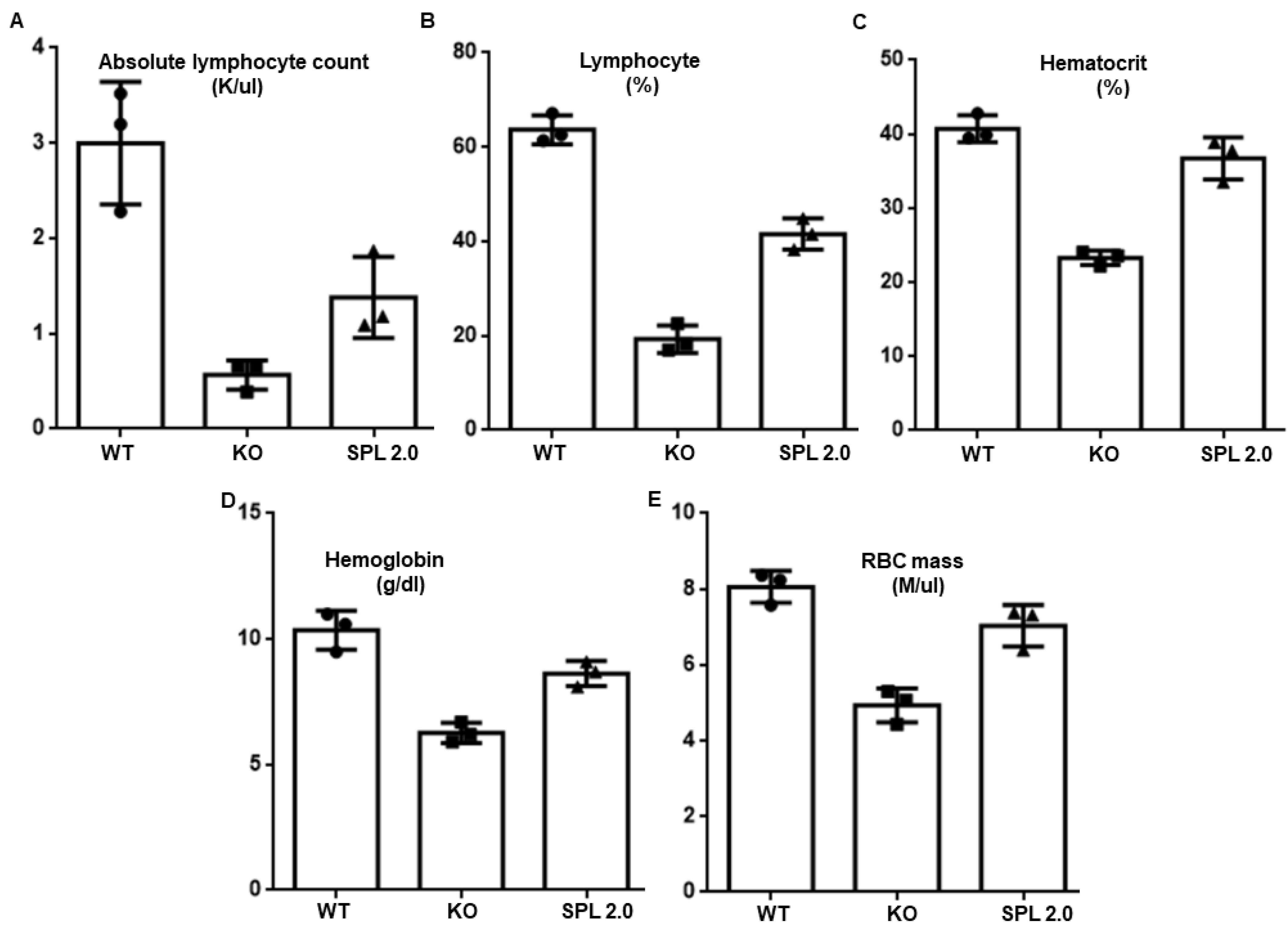
2.5. Other Features of SPL Insufficiency Are Improved by AAV-SPL 2.0 in Sgpl1 KO Mice
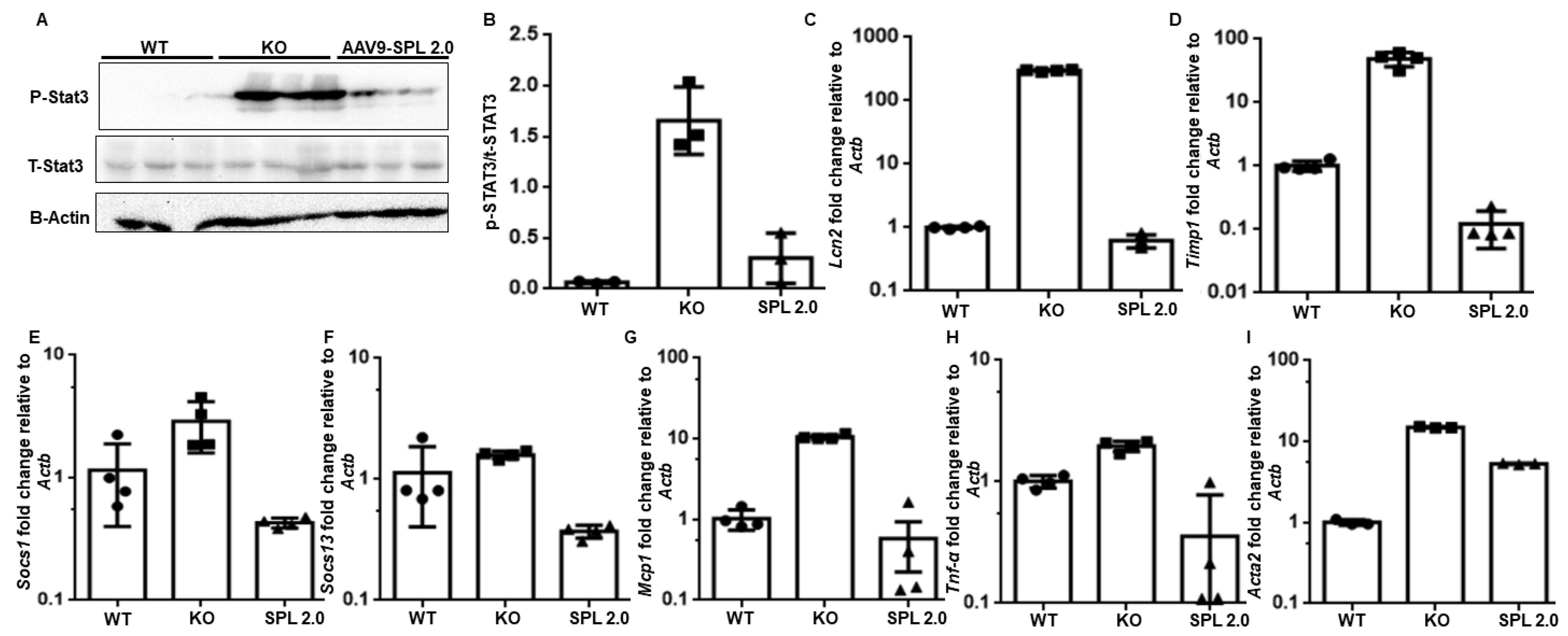
2.6. Pro-Inflammatory and Pro-Fibrogenic Signals Are Attenuated in Sgpl1 KO Mouse Kidneys by Treatment with AAV-SPL 2.0
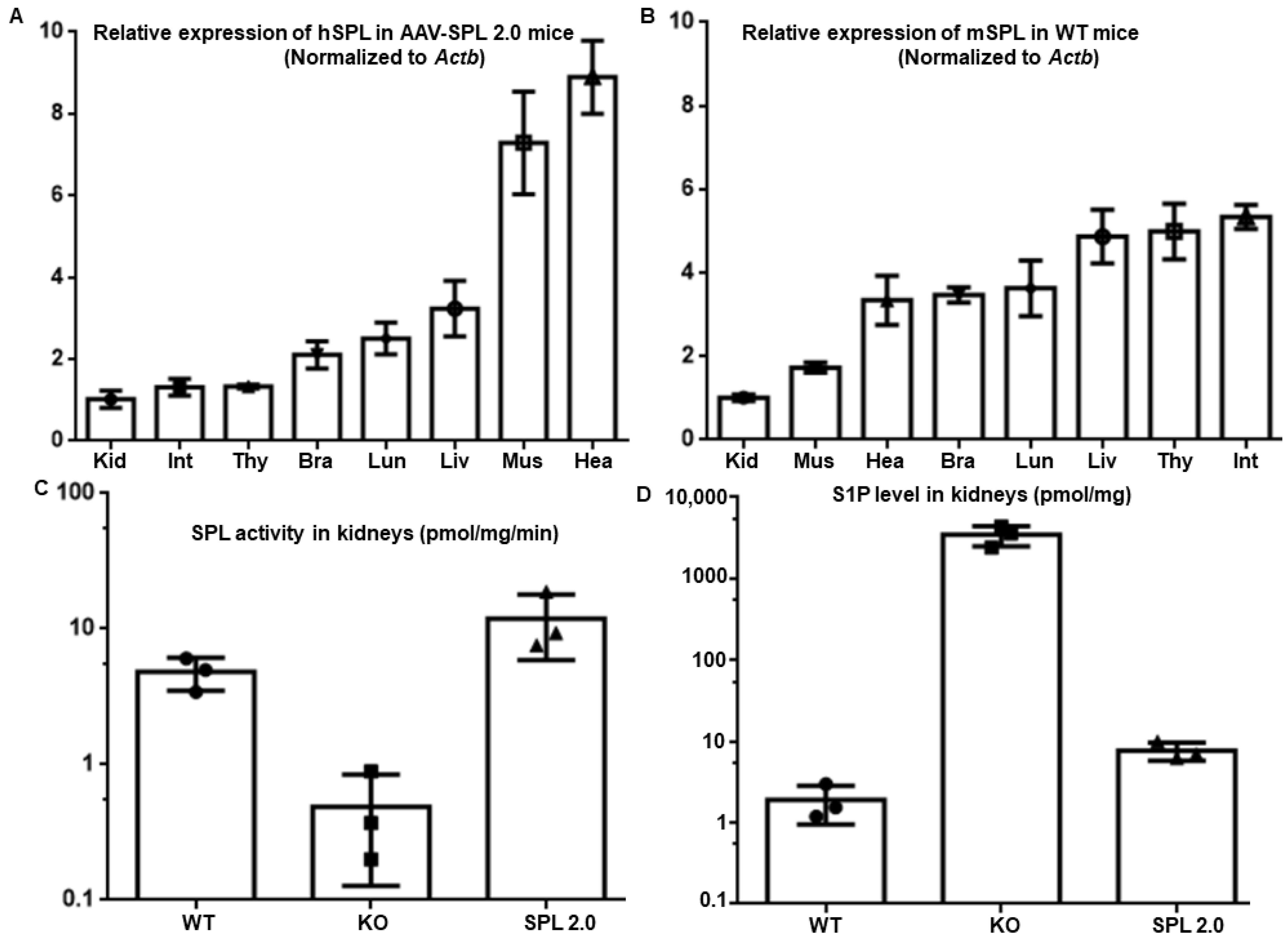
2.7. AAV-SPL 2.0 Treatment Restores SPL Expression and Activity in Tissues of Sgpl1 KO Mice
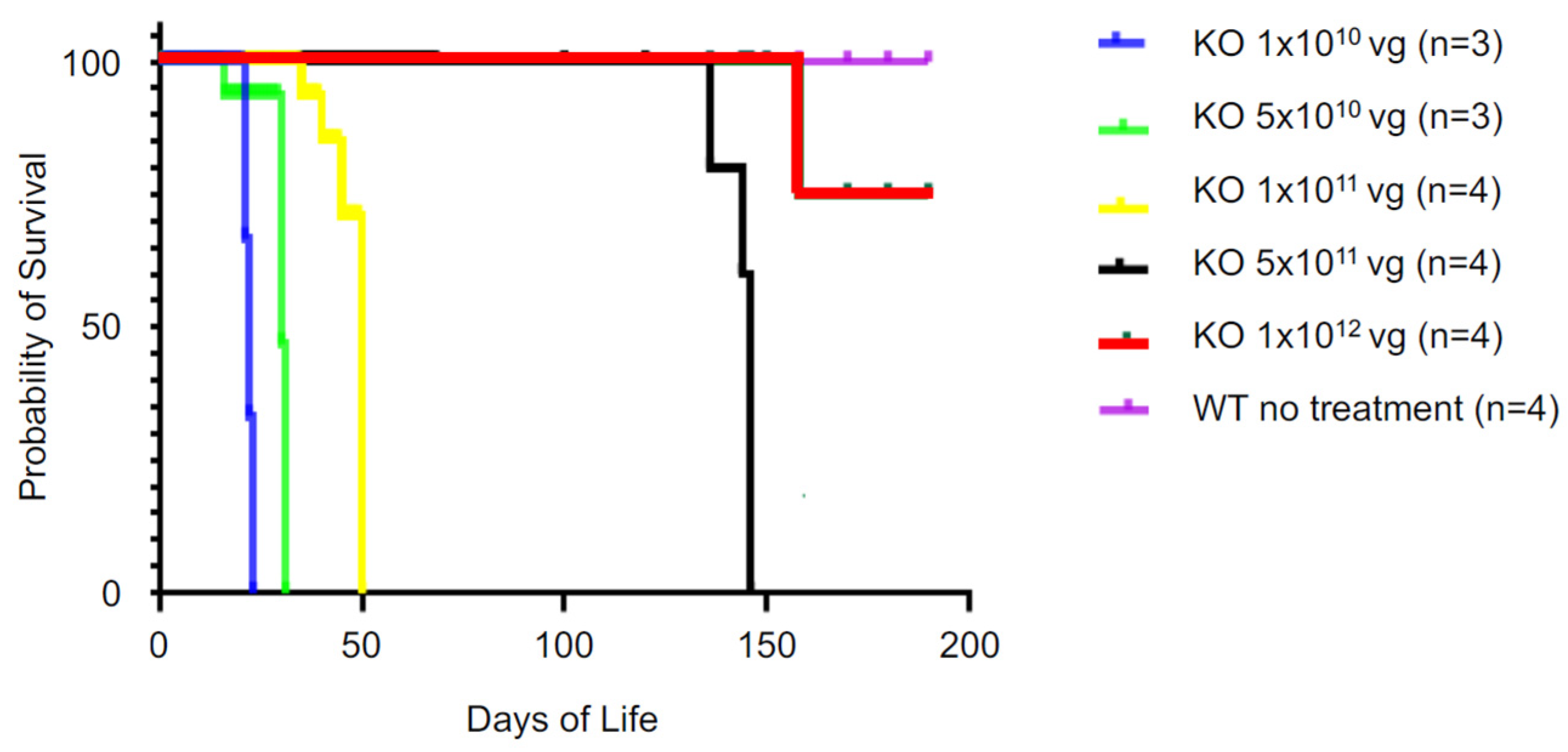
2.8. Efficacy of AAV-SPL 2.0 Is Lost upon Reduction in the Dose Lower than 5 × 1011 vg
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Virus Construct and Packaging
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Western Blotting and Image Quantification
4.4. SPL Enzyme Activity
4.5. Animals
4.6. Tissue Collection and Histology
4.7. Hematological Testing
4.8. Urine ACR Analyses
4.9. Quantitative RT-PCR
4.10. Sphingolipid Quantitation
4.11. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lovric, S.; Goncalves, S.; Gee, H.Y.; Oskouian, B.; Srinivas, H.; Choi, W.I.; Shril, S.; Ashraf, S.; Tan, W.; Rao, J.; et al. Mutations in sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase cause nephrosis with ichthyosis and adrenal insufficiency. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 912–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, R.; Hadjidemetriou, I.; Maharaj, A.; Meimaridou, E.; Buonocore, F.; Saleem, M.; Hurcombe, J.; Bierzynska, A.; Barbagelata, E.; Bergada, I.; et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase mutations cause primary adrenal insufficiency and steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 942–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, D.; Okuniewska, M.; Schwab, S.R. Secrets and lyase: Control of sphingosine 1-phosphate distribution. Immunol. Rev. 2019, 289, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Veldhoven, P.P. Sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase. Methods Enzymol. 2000, 311, 244–254. [Google Scholar]
- Pournasiri, Z.; Madani, A.; Nazarpack, F.; Sayer, J.A.; Chavoshzadeh, Z.; Nili, F.; Tran, P.; Saba, J.D.; Jamee, M. Sphingosine phosphate lyase insufficiency syndrome: A systematic review. World J. Pediatr. 2023, 19, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tastemel Ozturk, T.; Canpolat, N.; Saygili, S.; Bayrakci, U.S.; Soylemezoglu, O.; Ozaltin, F.; Topaloglu, R. A rare cause of nephrotic syndrome-sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase (SGPL1) deficiency: 6 cases and a review of the literature. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2023, 38, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garris, C.S.; Blaho, V.A.; Hla, T.; Han, M.H. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 signalling in T cells: Trafficking and beyond. Immunology 2014, 142, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipuk, J.E.; McStay, G.P.; Bharti, A.; Kuwana, T.; Clarke, C.J.; Siskind, L.J.; Obeid, L.M.; Green, D.R. Sphingolipid metabolism cooperates with BAK and BAX to promote the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Cell 2012, 148, 988–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeler, A.M.; Flotte, T.R. Recombinant adeno-associated virus gene therapy in light of Luxturna (and Zolgensma and Glybera): Where are we, and how did we get here? Annu. Rev. Virol. 2019, 6, 601–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tai, P.W.L.; Gao, G. Adeno-associated virus vector as a platform for gene therapy delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 358–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daya, S.; Berns, K.I. Gene therapy using adeno-associated virus vectors. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nidetz, N.F.; McGee, M.C.; Tse, L.V.; Li, C.; Cong, L.; Li, Y.; Huang, W. Adeno-associated viral vector-mediated immune responses: Understanding barriers to gene delivery. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 207, 107453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungar, L. Deaths in US gene therapy study sparks search for answers. U.S. News & World Report, 4 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Tassew, G.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Oskouian, B.; Munoz, D.P.; Hodgin, J.B.; Watson, G.L.; Tang, F.; Wang, J.Y.; Luo, J.; et al. Efficacy of AAV9-mediated SGPL1 gene transfer in a mouse model of S1P lyase insufficiency syndrome. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e145936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippidis, A. Fourth Boy Dies in Clinical Trial of Astellas’ AT132. Hum. Gene Ther. 2021, 32, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippidis, A. After Third Death, Audentes’ AT132 Remains on Clinical Hold. Hum. Gene Ther. 2020, 31, 908–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.K.; Majumdar, S.S.; Alam, P.; Gulati, N.; Brahmachari, V. Epigenetic regulation of cytomegalovirus major immediate-early promoter activity in transgenic mice. Gene 2009, 428, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montano-Samaniego, M.; Bravo-Estupinan, D.M.; Mendez-Guerrero, O.; Alarcon-Hernandez, E.; Ibanez-Hernandez, M. Strategies for Targeting Gene Therapy in Cancer Cells With Tumor-Specific Promoters. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 605380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, J.; Takaki, S.; Araki, K.; Tashiro, F.; Tominaga, A.; Takatsu, K.; Yamamura, K. Expression vector system based on the chicken beta-actin promoter directs efficient production of interleukin-5. Gene 1989, 79, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- Niwa, H.; Yamamura, K.; Miyazaki, J. Efficient selection for high-expression transfectants with a novel eukaryotic vector. Gene 1991, 108, 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Schmahl, J.; Raymond, C.S.; Soriano, P. PDGF signaling specificity is mediated through multiple immediate early genes. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merscher, S.; Fornoni, A. Podocyte pathology and nephropathy—Sphingolipids in glomerular diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogo, A.B. Causes and pathogenesis of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Deng, J.; Kujawski, M.; Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Herrmann, A.; Kortylewski, M.; Horne, D.; Somlo, G.; Forman, S.; et al. STAT3-induced S1PR1 expression is crucial for persistent STAT3 activation in tumors. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosius, F.C., 3rd; He, J.C. JAK inhibition and progressive kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2015, 24, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Mariani, L.; Eddy, S.; Maecker, H.; Kambham, N.; Mehta, K.; Hartman, J.; Wang, W.; Kretzler, M.; Lafayette, R.A. JAK-STAT activity in peripheral blood cells and kidney tissue in IgA nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, J.; Paladugu, P.; Das, B.; He, J.C.; Mallipattu, S.K. Targeting STAT3 signaling in kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2019, 316, F1151–F1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, Y. Expression of JAKs/STATs pathway molecules in rat model of rapid focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2009, 24, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Zhou, J.; Gauchat, J.F.; Sharma, R.; McCarthy, E.T.; Srivastava, T.; Savin, V.J. Janus kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 inhibitors attenuate the effect of cardiotrophin-like cytokine factor 1 and human focal segmental glomerulosclerosis serum on glomerular filtration barrier. Transl. Res. 2015, 166, 384–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukashchuk, V.; Lewis, K.E.; Coldicott, I.; Grierson, A.J.; Azzouz, M. AAV9-mediated central nervous system-targeted gene delivery via cisterna magna route in mice. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2016, 3, 15055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.H.; Eltanawy, A.; Rangan, A.; Saba, J.D. A facile stable-isotope dilution method for determination of sphingosine phosphate lyase activity. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2016, 194, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.H.; Saba, J.D. Sphingosine-1-phosphate in inflammatory bowel disease and colitis-associated colon cancer: The fat’s in the fire. Transl. Cancer Res. 2015, 4, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Primer Name | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| h-SGPL1-F | CAAGACCAAGGATGATATTAGC |
| h-SGPL1-R | CAGAAGGCGTCCATAGAG |
| m-Sgpl1-F | TTTCCTCATGGTGTGATGGA |
| m-Sgpl1-R | CCCCAGACAAGCATCCAC |
| mMCP1-F | TTAAAAACCTGGATCGGAACCAA |
| mMCP1-R | GCATTAGCTTCAGATTTACGGGT |
| mLcn2-F | TGGCCCTGAGTGTCATGTG |
| mLcn2-R | CTCTTGTAGCTCATAGATGGTGC |
| mSocs1-F | CTGCGGCTTCTATTGGGGAC |
| mSocs1-R | AAAAGGCAGTCGAAGGTCTCG |
| mSocs3-F | CCCTTGCAGTTCTAAGTTCAACA |
| mSocs3-R | ACCTTTGACAAGCGGACTCTC |
| mTimp1-F | GCAACTCGGACCTGGTCATAA |
| mTimp1-R | CGGCCCGTGATGAGAAACT |
| mTnf-α-F | CAGGCGGTGCCTATGTCTC |
| mTnf-α-R | CGATCACCCCGAAGTTCAGTAG |
| mActa2-F | GCATCCACGAAACCACCTAT |
| mActa2-R | ATCTCCTTCTGCATCCTGTC |
| m-B-Actin-F | GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG |
| m-B-Actin-R | CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, R.; Oskouian, B.; Lee, J.Y.; Hodgin, J.B.; Yang, Y.; Tassew, G.; Saba, J.D. AAV-SPL 2.0, a Modified Adeno-Associated Virus Gene Therapy Agent for the Treatment of Sphingosine Phosphate Lyase Insufficiency Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115560
Khan R, Oskouian B, Lee JY, Hodgin JB, Yang Y, Tassew G, Saba JD. AAV-SPL 2.0, a Modified Adeno-Associated Virus Gene Therapy Agent for the Treatment of Sphingosine Phosphate Lyase Insufficiency Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(21):15560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115560
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Ranjha, Babak Oskouian, Joanna Y. Lee, Jeffrey B. Hodgin, Yingbao Yang, Gizachew Tassew, and Julie D. Saba. 2023. "AAV-SPL 2.0, a Modified Adeno-Associated Virus Gene Therapy Agent for the Treatment of Sphingosine Phosphate Lyase Insufficiency Syndrome" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 21: 15560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115560
APA StyleKhan, R., Oskouian, B., Lee, J. Y., Hodgin, J. B., Yang, Y., Tassew, G., & Saba, J. D. (2023). AAV-SPL 2.0, a Modified Adeno-Associated Virus Gene Therapy Agent for the Treatment of Sphingosine Phosphate Lyase Insufficiency Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(21), 15560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115560






