Tyrosine Metabolism Pathway Is Downregulated in Dopaminergic Neurons with LRRK2 Overexpression in Drosophila
Abstract
:1. Introduction
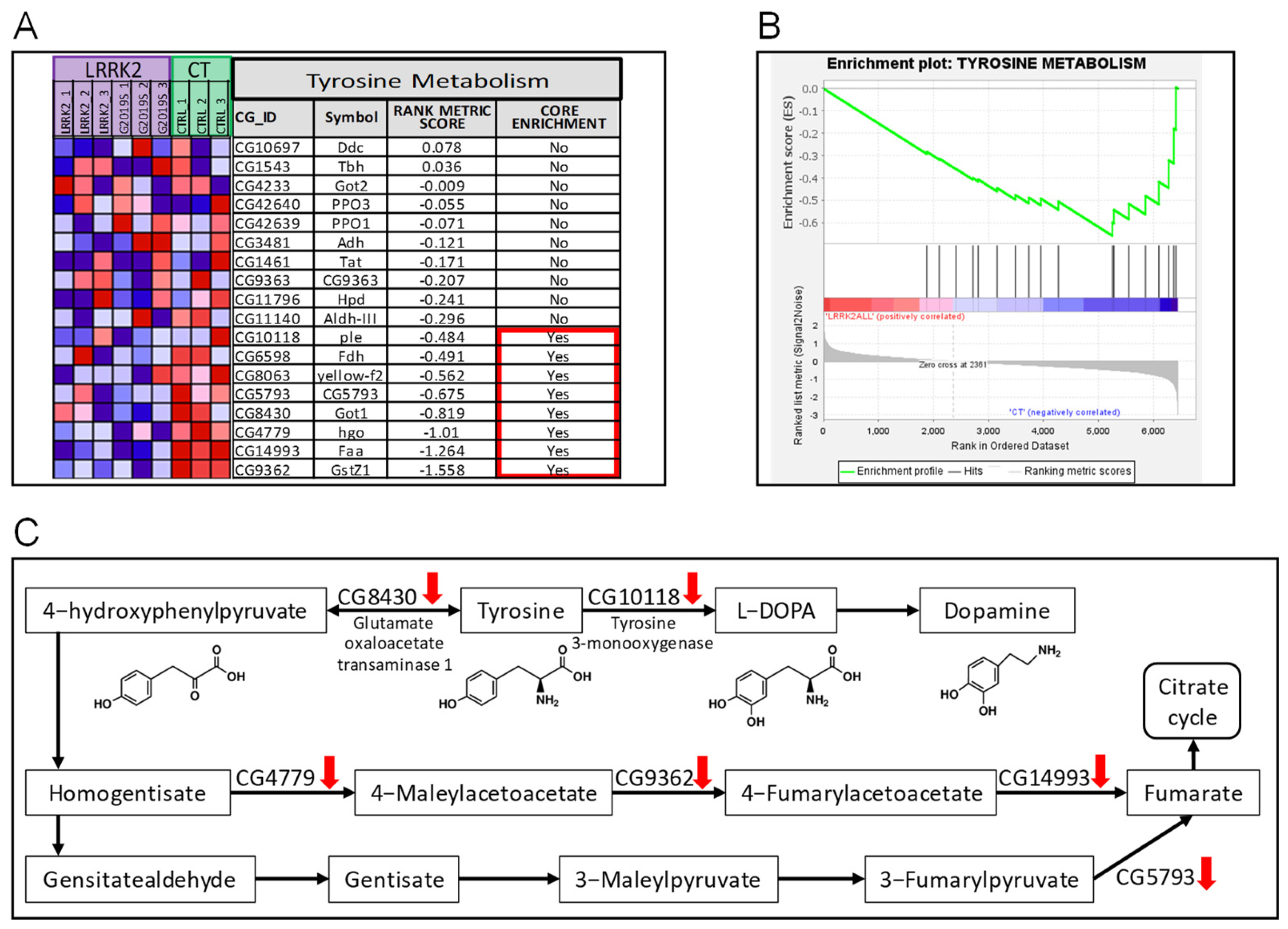
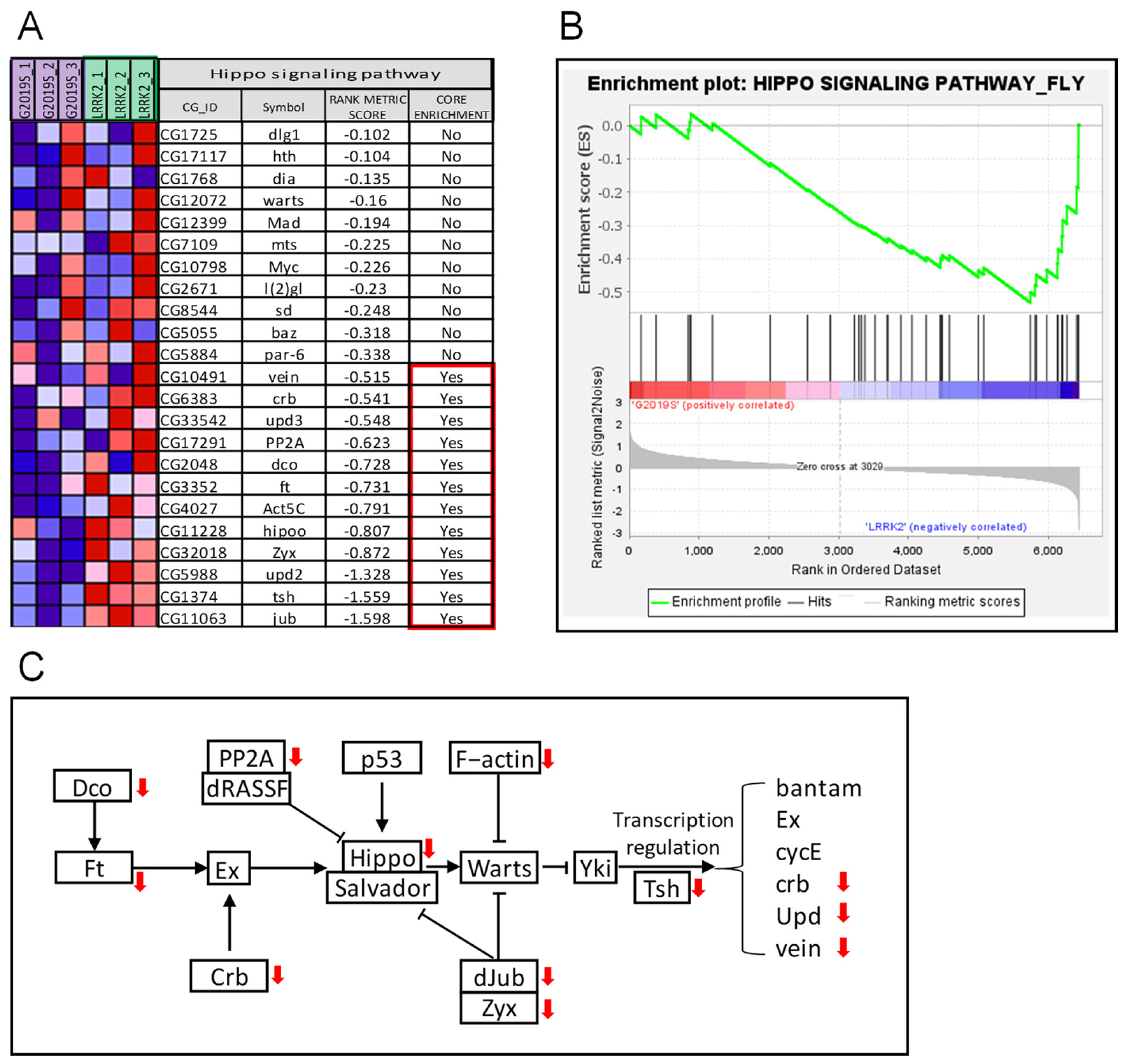
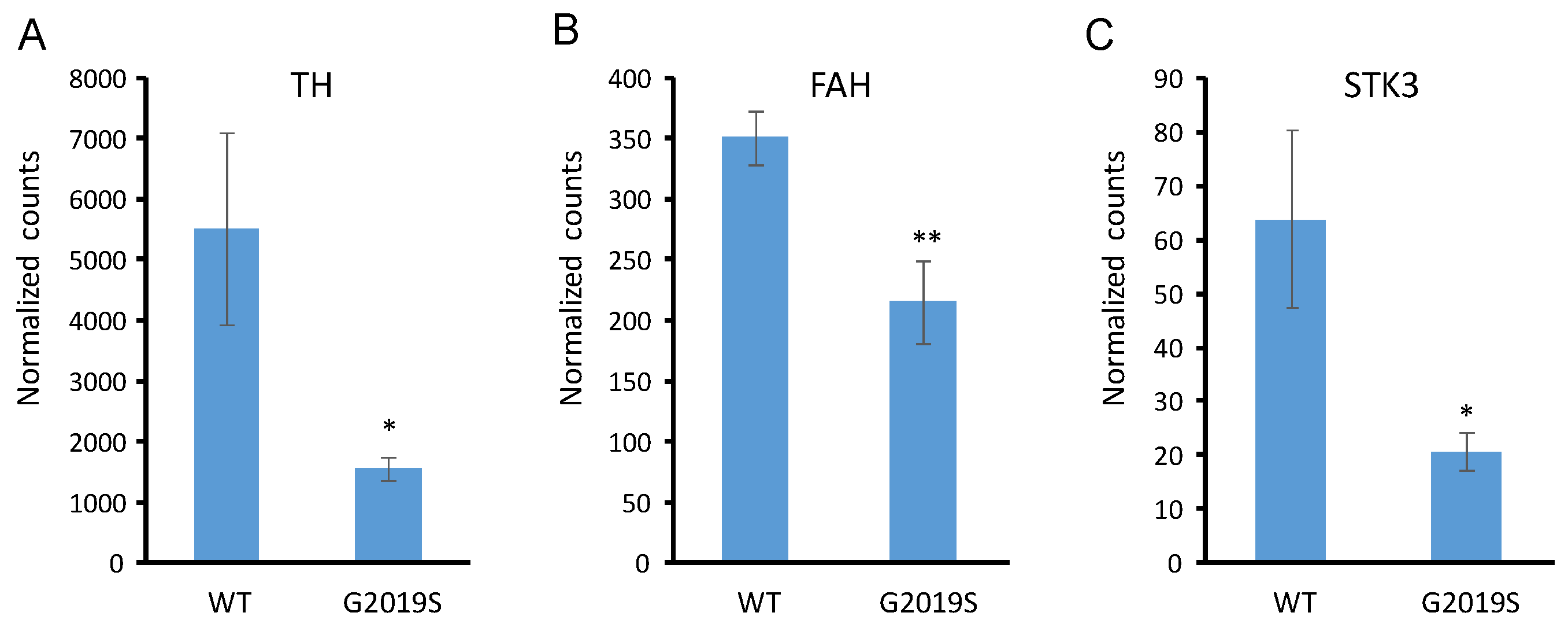
2. Results
3. Discussion
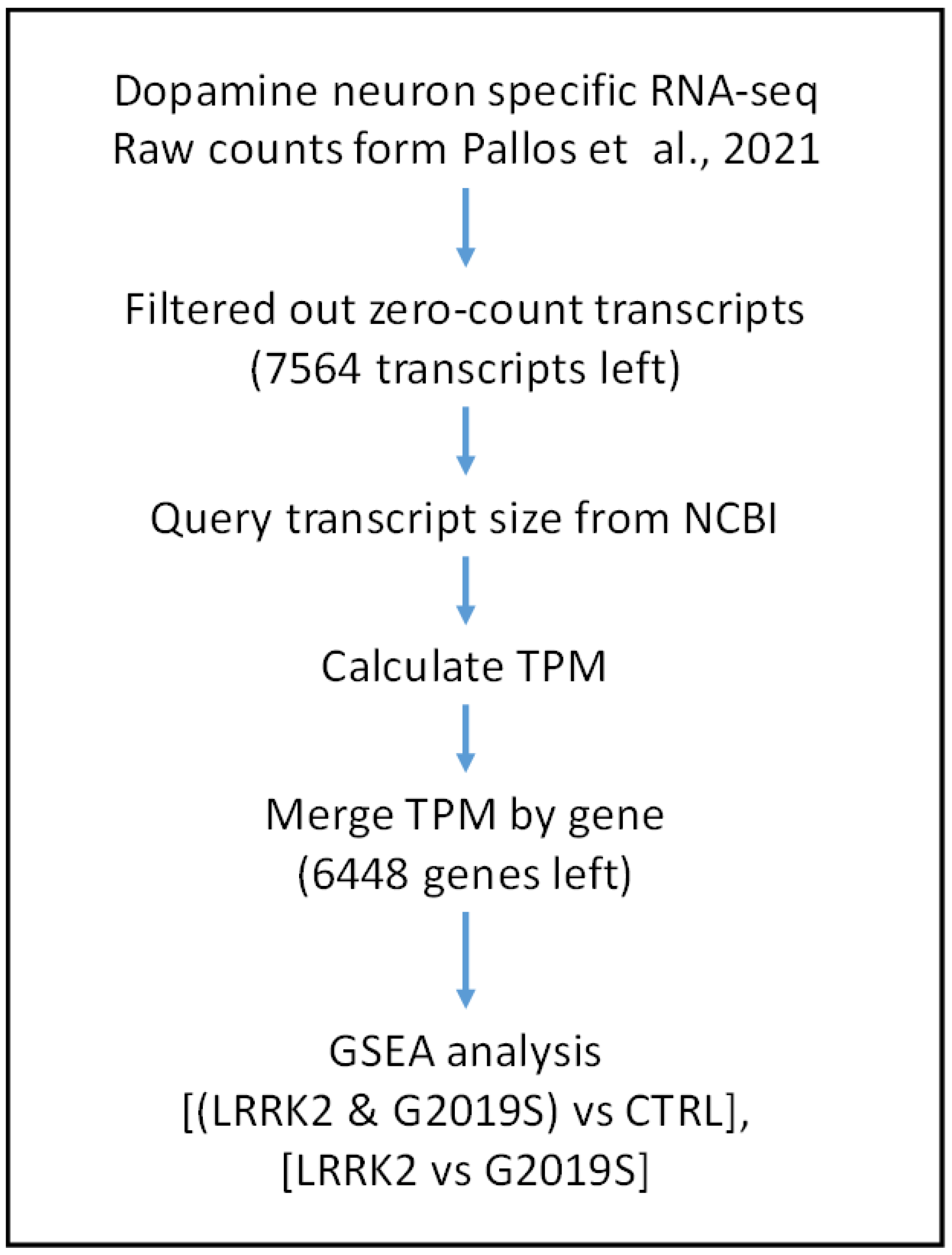
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Source
4.2. TPM Calculation
4.3. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalia, L.V.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2015, 386, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloem, B.R.; Okun, M.S.; Klein, C. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2284–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deuschl, G.; Beghi, E.; Fazekas, F.; Varga, T.; Christoforidi, K.A.; Sipido, E.; Bassetti, C.L.; Vos, T.; Feigin, V.L. The burden of neurological diseases in Europe: An analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Public Health 2020, 5, e551–e567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarthing, K.; Rafaloff, G.; Baptista, M.; Mursaleen, L.; Fuest, R.; Wyse, R.K.; Stott, S.R. Parkinson’s disease drug therapies in the clinical trial pipeline: 2022 update. J. Park. Dis. 2022, 12, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, B.S.; Lang, A.E. Pharmacological treatment of Parkinson disease: A review. JAMA 2014, 311, 1670–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandres-Ciga, S.; Diez-Fairen, M.; Kim, J.J.; Singleton, A.B. Genetics of Parkinson’s disease: An introspection of its journey towards precision medicine. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 137, 104782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turski, P.; Chaberska, I.; Szukało, P.; Pyska, P.; Milanowski, Ł.; Szlufik, S.; Figura, M.; Hoffman-Zacharska, D.; Siuda, J.; Koziorowski, D. Review of the epidemiology and variability of LRRK2 non-p. Gly2019Ser pathogenic mutations in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 971270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolosa, E.; Vila, M.; Klein, C.; Rascol, O. LRRK2 in Parkinson disease: Challenges of clinical trials. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimprich, A.; Biskup, S.; Leitner, P.; Lichtner, P.; Farrer, M.; Lincoln, S.; Kachergus, J.; Hulihan, M.; Uitti, R.J.; Calne, D.B. Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron 2004, 44, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Zhang, S.; Bustos, D.; Kleinheinz, T.; Le Pichon, C.E.; Dominguez, S.L.; Solanoy, H.O.; Drummond, J.; Zhang, X.; Ding, X. Ser1292 autophosphorylation is an indicator of LRRK2 kinase activity and contributes to the cellular effects of PD mutations. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 164ra161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steger, M.; Tonelli, F.; Ito, G.; Davies, P.; Trost, M.; Vetter, M.; Wachter, S.; Lorentzen, E.; Duddy, G.; Wilson, S. Phosphoproteomics reveals that Parkinson’s disease kinase LRRK2 regulates a subset of Rab GTPases. eLife 2016, 5, e12813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-L.; Wu, R.-M. LRRK 2 gene mutations in the pathophysiology of the ROCO domain and therapeutic targets for Parkinson’s disease: A review. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berwick, D.C.; Heaton, G.R.; Azeggagh, S.; Harvey, K. LRRK2 Biology from structure to dysfunction: Research progresses, but the themes remain the same. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, D.L.; Matikainen-Ankney, B.A.; Hussein, A.; Huntley, G.W. Functional and behavioral consequences of Parkinson’s disease-associated LRRK2-G2019S mutation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018, 46, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikonova, E.V.; Xiong, Y.; Tanis, K.Q.; Dawson, V.L.; Vogel, R.L.; Finney, E.M.; Stone, D.J.; Reynolds, I.J.; Kern, J.T.; Dawson, T.M. Transcriptional responses to loss or gain of function of the leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) gene uncover biological processes modulated by LRRK2 activity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta-Orfila, T.; Sànchez-Pla, A.; Fernández, M.; Carmona, F.; Ezquerra, M.; Tolosa, E. Brain transcriptomic profiling in idiopathic and LRRK2-associated Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. 2012, 1466, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallos, J.; Jeng, S.; McWeeney, S.; Martin, I. Dopamine neuron-specific LRRK2 G2019S effects on gene expression revealed by translatome profiling. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 155, 105390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björklund, A.; Dunnett, S.B. Dopamine neuron systems in the brain: An update. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haavik, J.; Toska, K. Tyrosine hydroxylase and Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 1998, 16, 285–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubner, S.C.; Le, T.; Wang, S. Tyrosine hydroxylase and regulation of dopamine synthesis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 508, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.B.; Kim, W.; Lee, S.; Chung, J. Loss of LRRK2/PARK8 induces degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in Drosophila. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 358, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, T.; Jiang, H.; Ren, Q.; Jiao, Y.; Sawa, A.; Moran, T. A Drosophila model for LRRK2-linked parkinsonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2693–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.D.; Saw, W.T.; Ho, P.G.H.; Zhang, Z.W.; Zeng, L.; Chang, Y.Y.; Sun, A.X.Y.; Ma, D.R.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhou, L. The role of tyrosine hydroxylase–dopamine pathway in Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, S.; Cox, M.; Lugon, M.; Hodkinson, M.; Tomkins, A. Increased energy expenditure in Parkinson’s disease. BMJ Br. Med. J. 1990, 301, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, H.; Cox, M.; Tomkins, A. Raised resting energy expenditure in Parkinson’s disease and its relationship to muscle rigidity. Clin. Sci. 1992, 83, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delikanaki-Skaribas, E.; Trail, M.; Wong, W.W.L.; Lai, E.C. Daily energy expenditure, physical activity, and weight loss in Parkinson’s disease patients. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2009, 24, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weindel, C.G.; Bell, S.L.; Vail, K.J.; West, K.O.; Patrick, K.L.; Watson, R.O. LRRK2 maintains mitochondrial homeostasis and regulates innate immune responses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. eLife 2020, 9, e51071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D. The hippo signaling pathway in development and cancer. Dev. Cell 2010, 19, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, M.R.; Mondal, A.C. The emerging role of Hippo signaling in neurodegeneration. J. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 98, 796–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, S.; Dong, Y.; Yuan, Z. The role and regulatory mechanism of hippo signaling components in the neuronal system. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; He, J.; Huang, B.; Liu, S.; Zhu, H.; Xu, T. Emerging role of the Hippo pathway in autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wu, M.; Yue, Z. Autophagy and Parkinson’s disease. In Autophagy: Biology and Diseases: Clinical Science; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 21–51. [Google Scholar]
- Jennings, D.; Huntwork-Rodriguez, S.; Henry, A.G.; Sasaki, J.C.; Meisner, R.; Diaz, D.; Solanoy, H.; Wang, X.; Negrou, E.; Bondar, V.V. Preclinical and clinical evaluation of the LRRK2 inhibitor DNL201 for Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabj2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, N.A.; Wright, M.W.; Brister, J.R.; Ciufo, S.; Haddad, D.; McVeigh, R.; Rajput, B.; Robbertse, B.; Smith-White, B.; Ako-Adjei, D. Reference sequence (RefSeq) database at NCBI: Current status, taxonomic expansion, and functional annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D733–D745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B.A.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L.; Wold, B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, G.P.; Kin, K.; Lynch, V.J. Measurement of mRNA abundance using RNA-seq data: RPKM measure is inconsistent among samples. Theory Biosci. 2012, 131, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Hsu, L.-F.; Juan, Y.-H.; Liu, H.-P.; Lin, W.-Y. Pathway-targeting gene matrix for Drosophila gene set enrichment analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, J.; Wu, B.-T.; Liu, H.-P.; Lin, W.-Y. Tyrosine Metabolism Pathway Is Downregulated in Dopaminergic Neurons with LRRK2 Overexpression in Drosophila. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115587
Cheng J, Wu B-T, Liu H-P, Lin W-Y. Tyrosine Metabolism Pathway Is Downregulated in Dopaminergic Neurons with LRRK2 Overexpression in Drosophila. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(21):15587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115587
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Jack, Bor-Tsang Wu, Hsin-Ping Liu, and Wei-Yong Lin. 2023. "Tyrosine Metabolism Pathway Is Downregulated in Dopaminergic Neurons with LRRK2 Overexpression in Drosophila" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 21: 15587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115587
APA StyleCheng, J., Wu, B.-T., Liu, H.-P., & Lin, W.-Y. (2023). Tyrosine Metabolism Pathway Is Downregulated in Dopaminergic Neurons with LRRK2 Overexpression in Drosophila. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(21), 15587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115587






