Serum Mg Isotopic Composition Reveals That Mg Dyshomeostasis Remains in Type 1 Diabetes despite the Resolution of Hypomagnesemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
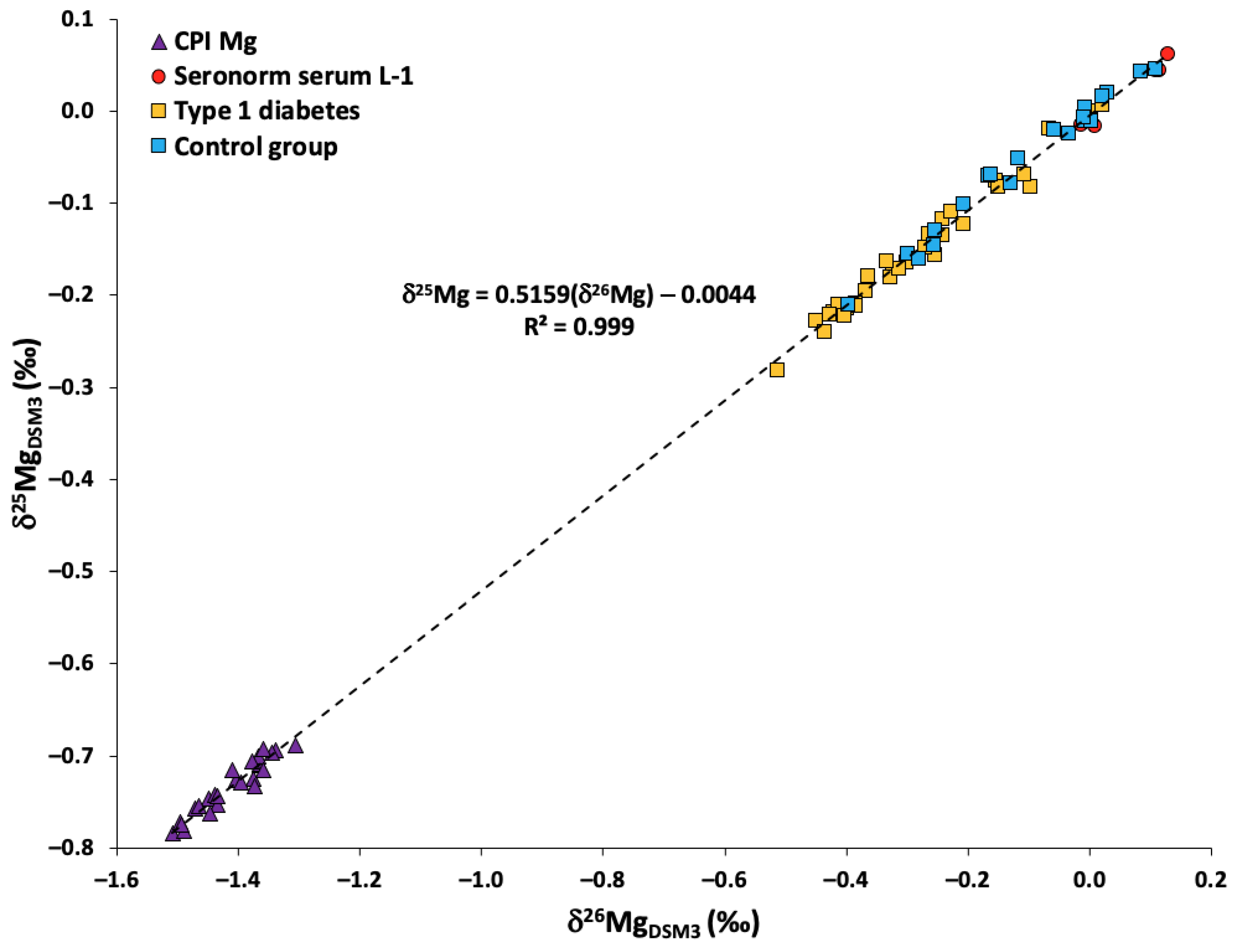
2.1. Quality Assurance/Quality Control
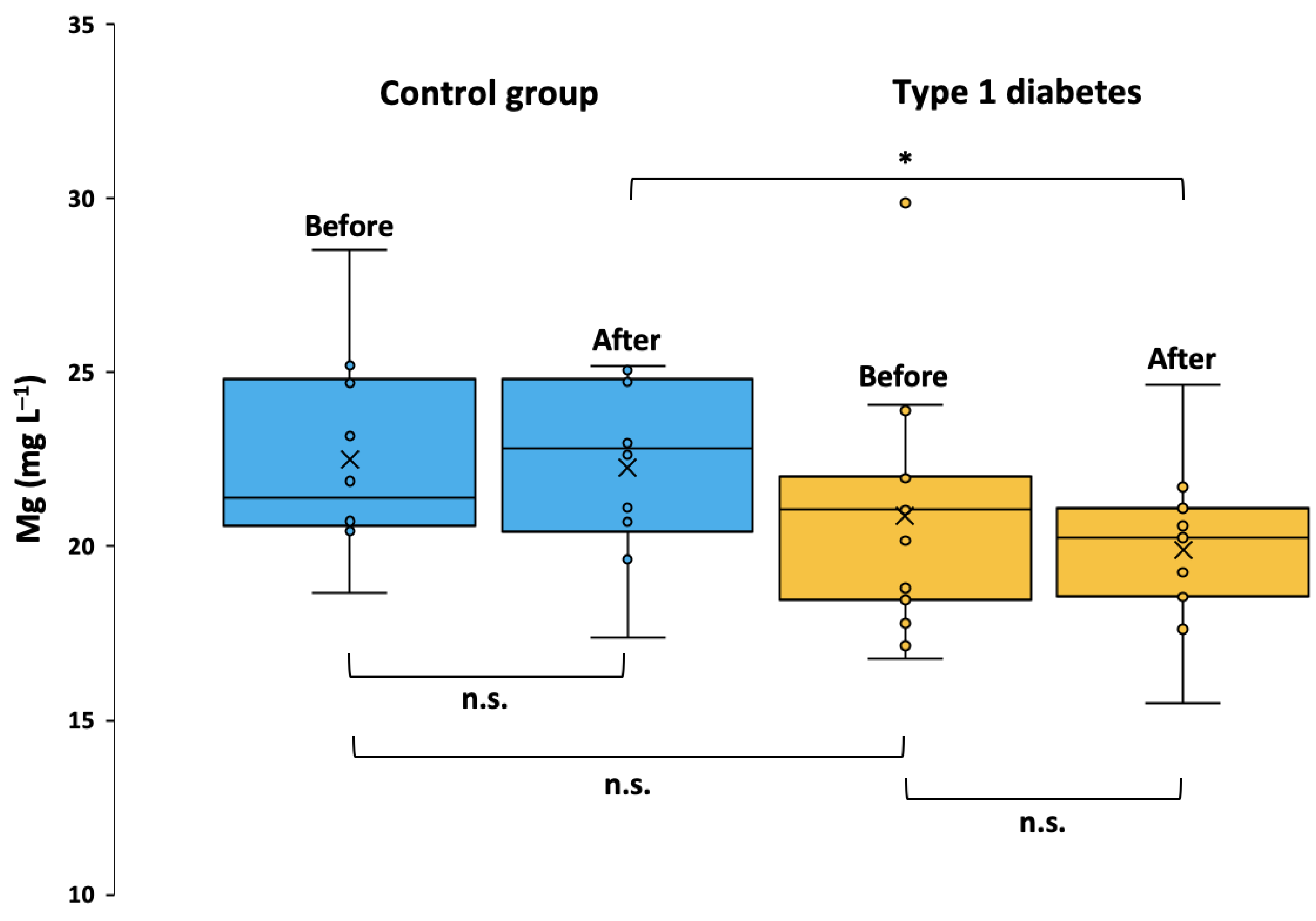
2.2. Serum Mg Concentration and Clinical Parameters
2.3. Serum Mg Isotopic Composition
3. Discussion
3.1. Potential Mechanisms behind Large Mg Isotopic Variations in T1DM
3.2. Insulin Resistance in T1DM
3.3. Contributions of Mg from Muscle and Bone
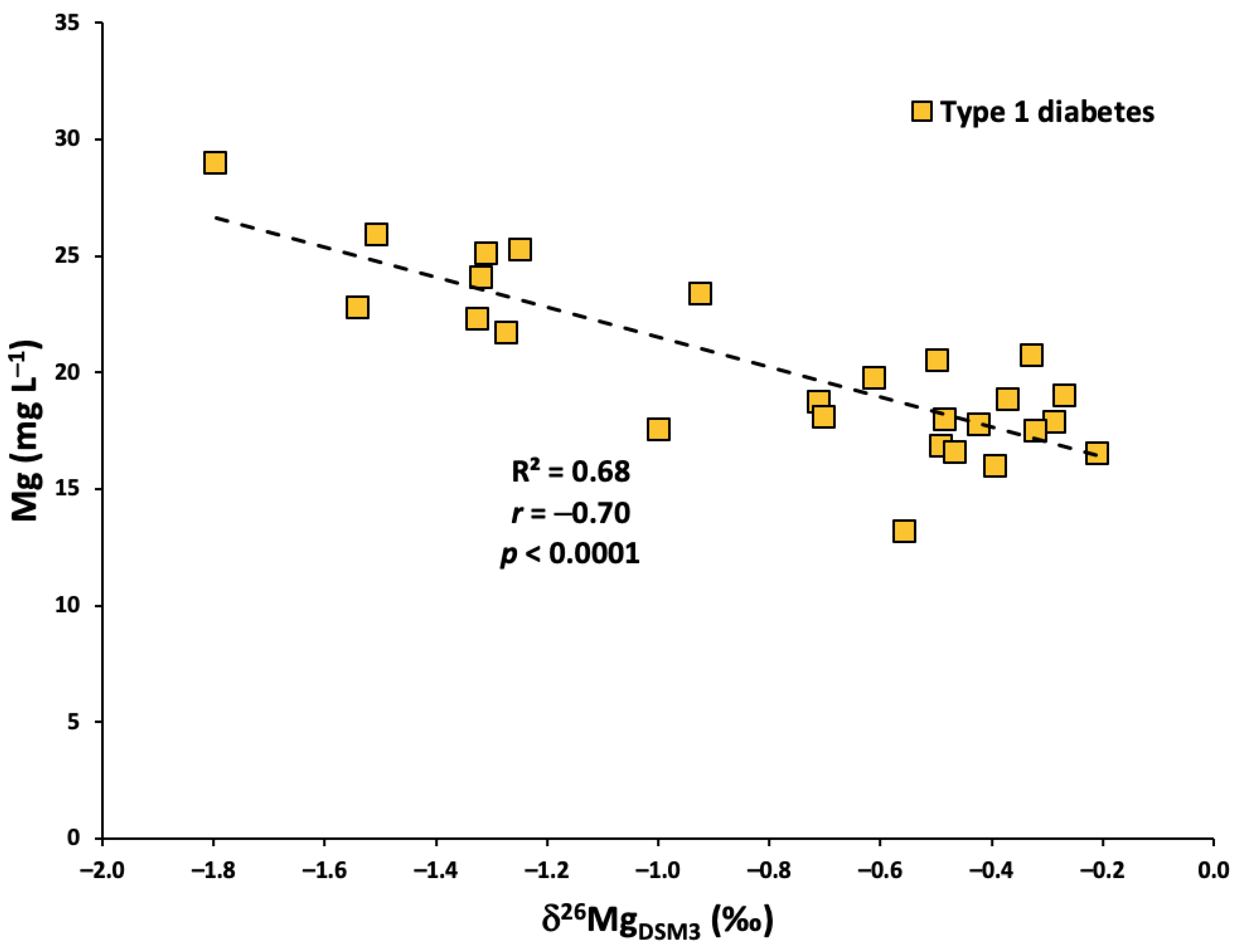
3.4. Correlation between Serum Mg Concentration and Isotopic Composition
3.5. Study Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Materials
4.2. Study Design
4.3. Sample Preparation
4.4. Instrumentation and Measurements
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Classification of Diabetes Mellitus; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. The Top 10 Causes of Death; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Paschou, S.A.; Petsiou, A.; Chatzigianni, K.; Tsatsoulis, A.; Papadopoulos, G.K. Type 1 Diabetes as an Autoimmune Disease: The Evidence. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 1500–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plowright, A.T. Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease: Scientific Discoveries and New Therapies. Edited by Philip Peplow, James Adams, Tim Young. ChemMedChem 2015, 10, 1933–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poretsky, L. Principles of Diabetes Mellitus, 2nd ed.; Springer Science & Business Media: Secaucus, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 21. [Google Scholar]
- Pickup, J.C. Hypomagnesaemia in IDDM Patients with Microalbuminuria and Clinical Proteinuria. Diabetologia 1994, 37, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNair, P.; Christensen, M.S.; Christiansen, C.; Madsbad, S.; Transbøl, I.B. Renal Hypomagnesaemia in Human Diabetes Mellitus: Its Relation to Glucose Homeostasis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1982, 12, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oost, L.J.; van Heck, J.I.; Tack, C.J.; de Baaij, J.H. The Association between Hypomagnesemia and Poor Glycaemic Control in Type 1 Diabetes Is Limited to Insulin Resistant Individuals. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium and Type 2 Diabetes. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delva, P.; Degan, M.; Trettene, M.; Lechi, A. Insulin and Glucose Mediate Opposite Intracellular Ionized Magnesium Variations in Human Lymphocytes. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 190, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, P.R.; Waanders, F.; Qiu, J.; de Boer, H.H.; Van Goor, H.; Bilo, H.J.G. Hypomagnesemia in Persons with Type 1 Diabetes: Associations with Clinical Parameters and Oxidative Stress. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 11, 2042018820980240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Mohammed, A. Magnesium: The Forgotten Electrolyte—A Review on Hypomagnesemia. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstl, E.-M.; Rabl, W.; Rosenbauer, J.; Gröbe, H.; Hofer, S.E.; Krause, U.; Holl, R.W. Metabolic Control as Reflectet by HbA1c in Children, Adolescents and Young Adults with Type-1 Diabetes Mellitus: Combined Longitudinal Analysis Including 27,035 Patients from 207 Centers in Germany and Austria during the Last Decade. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2008, 167, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.K.; Melo, A.E.; Domingueti, C.P. Association between Reduced Serum Levels of Magnesium and the Presence of Poor Glycemic Control and Complications in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2020, 14, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Workinger, J.L.; Doyle, R.P.; Bortz, J. Challenges in the Diagnosis of Magnesium Status. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, J.T.; Kumar, R. Atlas of Diseases of the Kidney: Divalent Cation: Magnesium; Current Medicine; Wiley-Blackwell: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick, L.L.; Jones, M.R.; Brautbar, N.; Lee, D.B. Site and Mechanism of Intestinal Magnesium Absorption. Miner. Electrolyte Metab. 1990, 16, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elin, R.J. Assessment of Magnesium Status. Clin. Chem. 1987, 33, 1965–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürlek, A.; Bayraktar, M.; Özaltin, N. Intracellular Magnesium Depletion Relates to Increased Urinary Magnesium Loss in Type I Diabetes. Horm. Metab. Res. 1998, 30, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNicolantonio, J.J.; O’Keefe, J.H.; Wilson, W. Subclinical Magnesium Deficiency: A Principal Driver of Cardiovascular Disease and a Public Health Crisis. Open Heart 2018, 5, e000668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ising, H.; Bertschat, F.; Günther, T.; Jeremias, E.; Jeremias, A. Measurement of Free Magnesium in Blood, Serum and Plasma with an Ion-Sensitive Electrode. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 1995, 33, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaine, J.; Chonchol, M.; Levi, M. Renal Control of Calcium, Phosphate, and Magnesium Homeostasis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, P.; Jacob, E.; Dong, S.; Khoo, O.T. Values for Tissue Magnesium as a Guide in Detecting Magnesium Deficiency. J. Clin. Pathol. 1969, 22, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, M.; Hubert, J.; Mazur, A. Methods of Assessment of Magnesium Status in Humans: A Systematic Review. Magnes. Res. 2011, 24, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoryan, R.; Costas-Rodríguez, M.; Van Laecke, S.; Speeckaert, M.; Lapauw, B.; Vanhaecke, F. Multi-Collector ICP-Mass Spectrometry Reveals Changes in the Serum Mg Isotopic Composition in Diabetes Type I Patients. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2019, 34, 1514–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, W.A.; Coplen, T.B.; Vogl, J.; Rosner, M.; Prohaska, T. Assessment of International Reference Materials for Isotope-Ratio Analysis (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2014, 86, 425–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastuti, A.A.M.B.; Costas-Rodríguez, M.; Matsunaga, A.; Ichinose, T.; Hagiwara, S.; Shimura, M.; Vanhaecke, F. Cu and Zn Isotope Ratio Variations in Plasma for Survival Prediction in Hematological Malignancy Cases. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Goff, S.; Godin, J.-P.; Albalat, E.; Nieves, J.M.R.; Balter, V. Magnesium Stable Isotope Composition, but Not Concentration, Responds to Obesity and Early Insulin-Resistant Conditions in Minipig. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Goff, S.; Albalat, E.; Dosseto, A.; Godin, J.-P.; Balter, V. Determination of Magnesium Isotopic Ratios of Biological Reference Materials via Multi-Collector Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 35, e9074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoryan, R.; Costas-Rodríguez, M.; Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Vanhaecke, F. High-Precision Isotopic Analysis of Mg and Ca in Biological Samples Using Multi-Collector ICP-Mass Spectrometry after Their Sequential Chromatographic Isolation—Application to the Characterization of the Body Distribution of Mg and Ca Isotopes in Mice. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1130, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vega, C.G.; Chernonozhkin, S.M.; Grigoryan, R.; Costas-Rodríguez, M.; Vanhaecke, F. Characterization of the new isotopic reference materials IRMM-524A and ERM-AE143 for Fe and Mg isotopic analysis of geological and biological samples. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2020, 35, 2517–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, J.; Brandt, B.; Noordmann, J.; Rienitz, O.; Malinovskiy, D. Characterization of a Series of Absolute Isotope Reference Materials for Magnesium: Ab Initio Calibration of the Mass Spectrometers, and Determination of Isotopic Compositions and Relative Atomic Weights. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2016, 31, 1440–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, T.M.; Matthews, D.R. The Assessment of Insulin Resistance in Man. Diabet. Med. 2002, 19, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickup, J.; Williams, G. Textbook of Diabetes; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gragossian, A.; Bashir, K.; Bhutta, B.S.; Friede, R. Hypomagnesemia; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Odusan, O.O.; Familoni, O.B.; Odewabi, A.O.; Idowu, A.O.; Adekolade, A.S. Patterns and Correlates of Serum Magnesium Levels in Subsets of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in Nigeria. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 21, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, K.; Moore, R.E.T.; Rehkämper, M.; Layton-Matthews, D.; Leybourne, M.I.; Puxty, J.; Kyser, T.K. Postprandial Zinc Stable Isotope Response in Human Blood Serum. Metallomics 2020, 9, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauwens, S.; Costas-Rodríguez, M.; Van Vlierberghe, H.; Vanhaecke, F. High-Precision Isotopic Analysis of Cu in Blood Serum via Multi-Collector ICP-Mass Spectrometry for Clinical Investigation: Steps towards Improved Robustness and Higher Sample Throughput. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2017, 32, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, K.V.; Moore, R.E.T.; Vanhaecke, F. The Influence of Physiological and Lifestyle Factors on Essential Mineral Element Isotopic Compositions in the Human Body: Implications for the Design of Isotope Metallomics Research. Metallomics 2023, 15, mfad012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolisek, M.; Sponder, G.; Pilchova, I.; Cibulka, M.; Tatarkova, Z.; Werner, T.; Racay, P. Magnesium Extravaganza: A Critical Compendium of Current Research into Cellular Mg2+ Transporters Other than TRPM6/7. In Reviews of Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology 176; de Tombe, P., Gudermann, T., Jahn, R., Lill, R., Eds.; Reviews of Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 176, pp. 65–105. ISBN 978-3-030-14027-4. [Google Scholar]
- Mastrototaro, L.; Tietjen, U.; Sponder, G.; Vormann, J.; Aschenbach, J.R.; Kolisek, M. Insulin Modulates the Na+/Mg2+ Exchanger SLC41A1 and Influences Mg2+ Efflux from Intracellular Stores in Transgenic HEK293 Cells. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 2440–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, G.; Kalra, S. A Review of Insulin Resistance in Type 1 Diabetes: Is There a Place for Adjunctive Metformin? Diabetes Ther. 2018, 9, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, K.; Apostolopoulou, M.; Roden, M. Insulin Resistance in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Metabolism 2015, 64, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruschitz, R.; Wallner-Liebmann, S.J.; Hamlin, M.J.; Moser, M.; Ludvik, B.; Schnedl, W.J.; Tafeit, E. Detecting Body Fat–A Weighty Problem BMI versus Subcutaneous Fat Patterns in Athletes and Non-Athletes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, D.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Heo, M.; Jebb, S.A.; Murgatroyd, P.R.; Sakamoto, Y. Healthy Percentage Body Fat Ranges: An Approach for Developing Guidelines Based on Body Mass Index. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, C.; Srivastava, P.S.; Hawke, T.J.; Kalaitzoglou, E. Diabetic Bone Disease and Diabetic Myopathy: Manifestations of the Impaired Muscle-Bone Unit in Type 1 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 2022, e2650342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoryan, R.; Costas-Rodríguez, M.; Van Wonterghem, E.; Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Vanhaecke, F. Effect of Endotoxemia Induced by Intraperitoneal Injection of Lipopolysaccharide on the Mg Isotopic Composition of Biofluids and Tissues in Mice. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 664666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, T. Dietary Factors Influencing Magnesium Absorption in Humans. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2008, 4, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp Schuchardt, J.; Hahn, A. Intestinal Absorption and Factors Influencing Bioavailability of Magnesium-an Update. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2017, 13, 260–278. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, R.; Walker, G.; Linz, M.D.; MacKellar, I. Metabolic Responses of Adolescent Boys to Two Levels of Dietary Magnesium and Protein. I. Magnesium and Nitrogen Retention. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1973, 26, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohn, T.; Davidsson, L.; Walczyk, T.; Hurrell, R.F. Phytic Acid Added to White-Wheat Bread Inhibits Fractional Apparent Magnesium Absorption in Humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.E.; Vance, D.; Balter, V. Magnesium Stable Isotope Ecology Using Mammal Tooth Enamel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.E.; Vance, D.; Balter, V. Natural Variation of Magnesium Isotopes in Mammal Bones and Teeth from Two South African Trophic Chains. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 2014, 130, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, L.K.; Duchon, K.K.; Lesaja, S.; Robison, V.A.; Presson, S.M. Adjusted Fluoride Concentrations and Control Ranges in 34 States: 2006–2010 and 2015. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2017, 109, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machoy-Mokrzynska, A. Fluoride-Magnesium Interaction. Fluoride 1995, 28, 175. [Google Scholar]
- Ersoy, I.H.; Koroglu, B.K.; Varol, S.; Ersoy, S.; Varol, E.; Aylak, F.; Tamer, M.N. Serum Copper, Zinc, and Magnesium Levels in Patients with Chronic Fluorosis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2011, 143, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylander, R.; Megevand, Y.; Lasserre, B.; Amstutz, W.; Granbom, S. Moderate Alcohol Consumption and Urinary Excretion of Magnesium and Calcium. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. 2001, 61, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kynast-Gales, S.A.; Massey, L.K. Effect of Caffeine on Circadian Excretion of Urinary Calcium and Magnesium. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1994, 13, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- William, J.H.; Danziger, J. Magnesium Deficiency and Proton-Pump Inhibitor Use: A Clinical Review. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 56, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begley, J.; Smith, T.; Barnett, K.; Strike, P.; Azim, A.; Spake, C.; Richardson, T. Proton Pump Inhibitor Associated Hypomagnasaemia-a Cause for Concern? Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 81, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polk, R.E. Drug-Drug Interactions with Ciprofloxacin and Other Fluoroquinolones. Am. J. Med. 1989, 87, S76–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dante, G.; Vaiarelli, A.; Facchinetti, F. Vitamin and Mineral Needs during the Oral Contraceptive Therapy: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Reprod. Contracept. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinloye, O.; Adebayo, T.O.; Oguntibeju, O.O.; Oparinde, D.P.; Ogunyemi, E.O. Effects of Contraceptives on Serum Trace Elements, Calcium and Phosphorus Levels. West Indian Med. J. 2011, 60, 308–315. [Google Scholar]
- Dørup, I. Magnesium and Potassium Deficiency. Its Diagnosis, Occurrence and Treatment in Diuretic Therapy and Its Consequences for Growth, Protein Synthesis and Growth Factors. Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl. 1994, 618, 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, P.; Jacob, E. Magnesium Deficiency in Patients on Long-Term Diuretic Therapy for Heart Failure. Br. Med. J. 1972, 3, 620–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bîcu, M.L.; Bîcu, D.; Vladu, M.I.; Clenciu, D.; Chirila, A.M.C.; Vîlvoi, D.; Sandu, M.; Panduru, N.M.; Moța, E.; Moța, M. Insulin Resistance Markers in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Rom. J. Diabetes Nutr. Metab. Dis. 2015, 22, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bolea-Fernandez, E.; Rua-Ibarz, A.; Resano, M.; Vanhaecke, F. To Shift, or Not to Shift: Adequate Selection of an Internal Standard in Mass-Shift Approaches Using Tandem ICP-Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS). J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2021, 36, 1135–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Tong, S.; Zhou, L.; Hu, Z.; Mester, Z.; Meija, J. A Critical Review on Isotopic Fractionation Correction Methods for Accurate Isotope Amount Ratio Measurements by MC-ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2018, 33, 1849–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Material | n (m) | Mg ± 1SD (mg L−1) | n (m) | Measured δ26MgDSM3 ± 2SD (‰) | Measured δ25MgDSM3 ± 2SD (‰) | Reported δ26MgDSM3 ± 2SD (‰) | Reported δ25MgDSM3 ± 2SD (‰) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPI Mg | - | 25 | −1.41 ± 0.11 | −0.73 ± 0.06 | −1.39 ± 0.08 | −0.73 ± 0.04 | [30] | |
| Seronorm serum L-1 | 2(2) | 20.1 ± 0.4 | 5(2) | 0.08 ± 0.10 | 0.03 ± 0.05 | 0.12 ± 0.11 | 0.06 ± 0.06 | [30] |
| 0.13 ± 0.11 | 0.06 ± 0.06 | [31] | ||||||
| 0.08 ± 0.06 | 0.04 ± 0.05 | [25] | ||||||
| Control Group | Type 1 Diabetes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg (mg L−1) | ΔMg (mg L−1) | Mg (mg L−1) | ΔMg (mg L−1) | ||||
| Sample ID | Before | After | After—Before | Sample ID | Before | After | After—Before |
| MgG-1 | 25.2 | 25.1 | −0.1 | MgD-1 | 21.0 | 20.3 | −0.7 |
| MgG-2 | 21.9 | 24.7 | 2.8 | MgD-2 | 18.5 | 17.6 | −0.8 |
| MgG-3 | 24.7 | 22.6 | −2.1 | MgD-3 | 17.1 | 21.1 | 4.0 |
| MgG-4 | 28.5 | 23.1 | −5.5 | MgD-4 | 29.9 | 20.6 | −9.3 |
| MgG-5 | 20.7 | 20.7 | 0.0 | MgD-5 | 21.9 | 21.1 | −0.8 |
| MgG-6 | 20.9 | 25.2 | 4.3 | MgD-6 | 22.0 | 21.7 | −0.3 |
| MgG-7 | 23.2 | 23.0 | −0.2 | MgD-7 | 20.2 | 20.3 | 0.1 |
| MgG-8 | 18.6 | 17.4 | −1.3 | MgD-8 | 21.2 | 21.8 | 0.6 |
| MgG-9 | 20.4 | 19.6 | −0.8 | MgD-9 | 24.1 | 24.6 | 0.6 |
| MgG-10 | 20.7 | 21.1 | 0.4 | MgD-10 | 23.9 | 18.5 | −5.3 |
| MgD-11 | 21.2 | 19.5 | −1.7 | ||||
| MgD-12 | 16.8 | 15.5 | −1.3 | ||||
| MgD-13 | 17.8 | 19.3 | 1.5 | ||||
| MgD-14 | 18.8 | 18.7 | −0.1 | ||||
| MgD-15 | 18.6 | 17.7 | −0.9 | ||||
| Mean | 22.5 | 22.2 | −0.2 | Mean | 20.9 | 19.9 | −1.0 |
| 1SD | 2.9 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 1SD | 3.4 | 2.2 | 3.0 |
| n | 10 | 10 | n | 15 | 15 | ||
| 1SE | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1SE | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.8 |
| Median | 21.4 | 22.8 | −0.2 | Median | 21.0 | 20.3 | −0.7 |
| Minimum | 18.6 | 17.4 | −5.5 | Minimum | 16.8 | 15.5 | −9.3 |
| Maximum | 28.5 | 25.2 | 4.3 | Maximum | 29.9 | 24.6 | 4.0 |
| Control Group | Type 1 Diabetes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ26MgDSM3 (‰) | Δ26Mg (‰) | δ26MgDSM3 (‰) | Δ26Mg (‰) | ||||
| Sample ID | Before | After | After—Before | Sample ID | Before | After | After—Before |
| MgG-1 | −0.21 | −0.26 | −0.05 | MgD-1 | −0.40 | −0.39 | 0.00 |
| MgG-2 | −0.06 | −0.03 | 0.03 | MgD-2 | −0.20 | −0.10 | 0.10 |
| MgG-3 | −0.30 | −0.25 | 0.05 | MgD-3 | −0.27 | −0.23 | 0.04 |
| MgG-4 | −0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | MgD-4 | −0.30 | 0.00 | 0.30 |
| MgG-5 | −0.40 | −0.28 | 0.12 | MgD-5 | −0.51 | −0.24 | 0.27 |
| MgG-6 | −0.13 | −0.17 | −0.04 | MgD-6 | −0.45 | −0.43 | 0.02 |
| MgG-7 | −0.16 | −0.01 | 0.16 | MgD-7 | −0.36 | −0.25 | 0.11 |
| MgG-8 | 0.11 | 0.02 | −0.09 | MgD-8 | 0.00 | −0.07 | −0.07 |
| MgG-9 | 0.08 | 0.03 | −0.05 | MgD-9 | −0.15 | −0.21 | −0.06 |
| MgG-10 | −0.12 | −0.01 | 0.11 | MgD-10 | −0.32 | −0.38 | −0.06 |
| MgD-11 | −0.38 | −0.33 | 0.06 | ||||
| MgD-12 | −0.27 | −0.41 | −0.14 | ||||
| MgD-13 | −0.11 | 0.02 | 0.13 | ||||
| MgD-14 | −0.40 | −0.31 | 0.09 | ||||
| MgD-15 | −0.33 | −0.43 | −0.09 | ||||
| Mean | −0.12 | −0.10 | 0.02 | Mean | −0.30 | −0.25 | 0.05 |
| 1SD | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 1SD | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.13 |
| n | 10 | 10 | n | 15 | 15 | ||
| 1SE | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 1SE | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 |
| Median | −0.12 | −0.02 | 0.02 | Median | −0.32 | −0.25 | 0.04 |
| Minimum | −0.40 | −0.28 | −0.09 | Minimum | −0.51 | −0.43 | −0.14 |
| Maximum | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.16 | Maximum | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sullivan, K.V.; Assantuh, Y.; Grigoryan, R.; Costas-Rodríguez, M.; Bolea-Fernandez, E.; Lapauw, B.; Van Laecke, S.; Vanhaecke, F. Serum Mg Isotopic Composition Reveals That Mg Dyshomeostasis Remains in Type 1 Diabetes despite the Resolution of Hypomagnesemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115683
Sullivan KV, Assantuh Y, Grigoryan R, Costas-Rodríguez M, Bolea-Fernandez E, Lapauw B, Van Laecke S, Vanhaecke F. Serum Mg Isotopic Composition Reveals That Mg Dyshomeostasis Remains in Type 1 Diabetes despite the Resolution of Hypomagnesemia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(21):15683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115683
Chicago/Turabian StyleSullivan, Kaj Vaughan, Yasmina Assantuh, Rosa Grigoryan, Marta Costas-Rodríguez, Eduardo Bolea-Fernandez, Bruno Lapauw, Steven Van Laecke, and Frank Vanhaecke. 2023. "Serum Mg Isotopic Composition Reveals That Mg Dyshomeostasis Remains in Type 1 Diabetes despite the Resolution of Hypomagnesemia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 21: 15683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115683
APA StyleSullivan, K. V., Assantuh, Y., Grigoryan, R., Costas-Rodríguez, M., Bolea-Fernandez, E., Lapauw, B., Van Laecke, S., & Vanhaecke, F. (2023). Serum Mg Isotopic Composition Reveals That Mg Dyshomeostasis Remains in Type 1 Diabetes despite the Resolution of Hypomagnesemia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(21), 15683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115683






