Molecular Mapping of Putative Genomic Regions Controlling Fruit and Seed Morphology of Watermelon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of Genetic Characteristics of Phenotypes
2.1.1. Peel Color (PC, Scoring)
2.1.2. Fruit Weight (FW, kg)
2.1.3. Peel Thickness (PT, mm)
2.1.4. Seed Length (SL, mm)
2.1.5. Seed Width (SWi, mm)
2.1.6. Seed Shape Index (SSi, SL/SWi)
2.1.7. Seed Weight (SW, g)
2.2. Analysis of Phenotypic Correlation
2.3. Construction of Genetic Linkage Map
2.4. Mapping of QTLs
2.4.1. QTLs of PC
2.4.2. QTLs of FW
2.4.3. QTLs of PT
2.4.4. QTLs of SL
2.4.5. QTLs of SWi
2.4.6. QTLs of SSi
2.4.7. QTLs of SW
2.5. Analysis of Putative Genes Underlying Major QTLs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experiment Materials and Mapping Populations
4.2. Phenotyping of Fruit and Seed Traits
4.3. Whole Genome Resequencing (WGRS)
4.4. Development of CAPS Markers
4.5. Genetic Mapping and QTL Analysis
4.6. Predictions of Putative Candidate Genes
4.7. Statistical Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sandlin, K.; Prothro, J.; Heesacker, A.; Khalilian, N.; Okashah, R.; Xiang, W.; Bachlava, E.; Caldwell, D.G.; Taylor, C.A.; Seymour, D.K.; et al. Comparative mapping in watermelon [Citrullus lanatus (Thunb.) Matsum. et Nakai]. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 125, 1603–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renner, S.S.; Wu, S.; Pérez-Escobar, O.A.; Silber, M.V.; Fei, Z.; Chomicki, G. A chromosome-level genome of a Kordofan melon illuminates the origin of domesticated watermelons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2101486118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grumet, R.; McCreight, J.D.; McGregor, C.; Weng, Y.; Mazourek, M.; Reitsma, K.; Labate, J.; Davis, A.; Fei, Z. Genetic Resources and Vulnerabilities of Major Cucurbit Crops. Genes 2021, 12, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; McGregor, C.; Liu, S.; Luan, F.; Gao, M.; Weng, Y. Genetic architecture of fruit size and shape variation in cucurbits: A comparative perspective. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 133, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, J.; Sun, H.; Salse, J.; Lucas, W.J.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Mao, L.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. The draft genome of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) and resequencing of 20 diverse accessions. Nat. Genet. 2012, 45, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.; Zhao, S.; Yang, D.; Lu, X.; Anees, M.; He, N.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, W. Genome-wide association analysis provides molecular insights into natural variation in watermelon seed size. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhab074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Luan, F.; Wang, X.; Gao, P.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, S.; Baloch, A.M.; Zhang, Y. Construction of a genetic linkage map of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) using CAPS and SSR markers and QTL analysis for fruit quality traits. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 202, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Gao, M.; Amanullah, S.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, C.; Luan, F. Identification of QTLs linked with watermelon fruit and seed traits using GBS-based high-resolution genetic mapping. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 303, 111237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Lu, X.; Zhu, H.; Anees, M.; He, N.; Liu, W. Genome-wide association study provides genetic insights into natural variation in watermelon rind thickness and single fruit weight. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1074145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Amanullah, S.; Pan, J.; Chen, G.; Liu, S.; Ma, S.; Wang, J.; Gao, P.; Wang, X. Identification of putative genetic regions for watermelon rind hardness and related traits by BSA-seq and QTL mapping. Euphytica 2021, 217, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, P.; Pan, J.; Amanullah, S.; Luan, F.; Han, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, X. Genome-Wide Analysis of the Peroxidase Gene Family and Verification of Lignin Synthesis-Related Genes in Watermelon. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amanullah, S.; Li, S.; Osae, B.A.; Yang, T.; Abbas, F.; Gao, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Gao, P.; Luan, F. Primary mapping of quantitative trait loci regulating multivariate horticultural phenotypes of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1034952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weetman, L.M. Inheritance and correlation of shape, size, and color in watermelon, Citrullus Vulgaris Schrad. Iowa Agric. Exp. Stn. Annu. Bull. 1937, 228, 224–256. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Wehner, T.C. Quantitative Analysis of Generations for Inheritance of Fruit Yield in Watermelon. HortScience 2013, 48, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.; Lu, X.; Ali, A.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; He, N.; Liu, W. Genetic mapping reveals a marker for yellow skin in watermelon (Citrullus lanatus L.). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Shang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, D.; Li, N.; Ma, S. Fine mapping and discovery of candidate genes for seed size in watermelon by genome survey sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, E.; Tzuri, G.; Vexler, L.; Dafna, A.; Meir, A.; Faigenboim, A.; Kenigswald, M.; Portnoy, V.; Schaffer, A.A.; Levi, A.; et al. The multi-allelic APRR2 gene is associated with fruit pigment accumulation in melon and watermelon. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 3781–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jang, G.; Choi, Y.; Park, G.; Park, S.; Kwon, G.; Je, B.; Park, Y. Identification of Candidate Genes for Rind Color and Bloom Formation in Watermelon Fruits Based on a Quantitative Trait Locus-Seq. Plants 2022, 11, 2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Gao, M.; Liang, X.; Xu, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Qu, S.; et al. Quantitative Trait Loci for Seed Size Variation in Cucurbits—A Review. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, C.F.; Grimball, P.C.; Porter, D.R. Inheritance of seed characters in watermelon. J. Agric. Res. 1941, 66, 433–456. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.F.; Zhang, J.N. Inheritance of seed size in watermelon. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2011, 39, 216–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, J.; Li, X.; Chu, X.; Xu, B.; Tian, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, B.; et al. A telomere-to-telomere gap-free reference genome of watermelon and its mutation library provide important resources for gene discovery and breeding. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 1268–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wu, S.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Tang, X.; Guo, S.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, S.; Xu, Y.; Weng, Y.; et al. CuGenDBv2: An updated database for cucurbit genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 51, D1457–D1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Wang, X.; Reddy, U.; Sun, H.; Bao, K.; Gao, L.; Mao, L.; Patel, T.; Ortiz, C.; Abburi, V.L.; et al. Genome of ‘Charleston Gray’, the principal American watermelon cultivar, and genetic characterization of 1,365 accessions in the U.S. National Plant Germplasm System watermelon collection. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 2246–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qiao, A.; Fang, X.; Sun, L.; Gao, P.; Davis, A.R.; Liu, S.; Luan, F. Fine Mapping of Lycopene Content and Flesh Color Related Gene and Development of Molecular Marker–Assisted Selection for Flesh Color in Watermelon (Citrullus lanatus). Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Luan, F.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, S. Quantitative trait loci and candidate genes responsible for pale green flesh colour in watermelon (Citrullus lanatus). Plant Breed. 2021, 140, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, S.; Qu, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, S.; Song, Z.; Xia, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; et al. BSA-seq and quantitative trait locus mapping reveals a major effective QTL for carpel number in watermelon (Citrullus lanatus ). Plant Breed. 2022, 141, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osae, B.A.; Amanullah, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Saroj, A.; Zhang, C.; Liu, T.; Gao, P.; Luan, F. CAPS marker-base genetic linkage mapping and QTL analysis for watermelon ovary, fruit and seed-related traits. Euphytica 2022, 218, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Gao, Z.; Wang, X.; Luan, F.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q. Nucleotide variation in the phytoene synthase (ClPsy1) gene contributes to golden flesh in watermelon (Citrullus lanatus L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 135, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shang, L.; Zhu, Q.-H.; Fan, L.; Guo, L. Twenty years of plant genome sequencing: Achievements and challenges. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 27, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-H.; Yang, H.-J.; Jung, K.-H.; Yoo, S.-C.; Paek, N.-C. Quantitative Trait Locus Mapping and Candidate Gene Analysis for Plant Architecture Traits Using Whole Genome Re-Sequencing in Rice. Mol. Cells 2014, 37, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Zhao, S.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Lin, T.; Ren, Y.; Gao, L.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Resequencing of 414 cultivated and wild watermelon accessions identifies selection for fruit quality traits. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1616–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ren, H.Z.; Kang, G.B.; Wang, Y.J. QTL mapping and genetic effect analysis of watermelon fruit traits. Acta Genet. Sin. 2000, 27, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Van Houten, J.; Gonzalez, G.; Xiao, H.; van der Knaap, E. Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of SUN, OFP and YABBY gene family in tomato. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2013, 288, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, C.F. Genetics of Cultivated Cucurbits. J. Hered. 1944, 35, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, B.; Keyhaninejad, N.; Rodríguez, G.R.; Kim, H.J.; Chakrabarti, M.; Illa-Berenguer, E.; Taitano, N.K.; Gonzalo, M.J.; Díaz, A.; et al. A common genetic mechanism underlies morphological diversity in fruits and other plant organs. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, B.; Dane, F. Gene list for watermelon. Cucurbit Genet. Cooperative Rep. 1999, 22, 61–77. [Google Scholar]
- Guner, N.; Wehner, T.C. The Genes of Watermelon. HortScience 2004, 39, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-W.; Kim, K.-T.; Kang, S.-C.; Yang, H.-B. Rapid and practical molecular marker development for rind traits in watermelon. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2016, 57, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.E.; Buckley, B. A Genetic Study of Rind Color Patterns in Watermelon. HortScience 1991, 26, 496d–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-B.; Park, S.-W.; Park, Y.; Lee, G.P.; Kang, S.-C.; Kim, Y.K. Linkage Analysis of the Three Loci Determining Rind Color and Stripe Pattern in Watermelon. Korean J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2015, 33, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Hwang, J.-H.; Han, D.-Y.; Park, M.; Kim, S.; Choi, D.; Kim, Y.; Lee, G.P.; Kim, S.-T.; Park, Y.-H. Major Quantitative Trait Loci and Putative Candidate Genes for Powdery Mildew Resistance and Fruit-Related Traits Revealed by an Intraspecific Genetic Map for Watermelon (Citrullus lanatus var. lanatus). PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0145665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zhao, S.; Dou, J.; Ali, A.; Gebremeskel, H.; Gao, L.; He, N.; Lu, X.; Liu, W. Genetic mapping and development of molecular markers for a candidate gene locus controlling rind color in watermelon. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 2741–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, N.; Hu, Z.; Li, Y.; Hao, J.; Chen, S.; Xue, Q.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, K.; Mahmoud, A.; Ali, A.; et al. Ethylene-responsive factor 4 is associated with the desirable rind hardness trait conferring cracking resistance in fresh fruits of watermelon. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 18, 1066–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xue, J.; Jin, F.; Bai, Y. Relationship between crack and peel structure of eggplant and its heterosis. North China Agric. J. 2007, 3, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Prothro, J.; Sandlin, K.; Abdel-Haleem, H.; Bachlava, E.; White, V.; Knapp, S.; McGregor, C. Main and Epistatic Quantitative Trait Loci Associated with Seed Size in Watermelon. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2012, 137, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prothro, J.; Sandlin, K.; Gill, R.; Bachlava, E.; White, V.; Knapp, S.J.; McGregor, C. Mapping of the Egusi Seed Trait Locus (eg) and Quantitative Trait Loci Associated with Seed Oil Percentage in Watermelon. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2012, 137, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.W.; Lu, B.Y.; Ma, H.Y.; Gao, P.; Luan, F.S.; Gao, Q.F.; Qi, G.A. QTL mapping of watermelon seed traits. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2016, 43, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meru, G.; McGregor, C. Genetic Mapping of Seed Traits Correlated with Seed Oil Percentage in Watermelon. HortScience 2013, 48, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meru, G.; Fu, Y.; Leyva, D.; Sarnoski, P.; Yagiz, Y. Phenotypic relationships among oil, protein, fatty acid composition and seed size traits in Cucurbita pepo. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 233, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, F.; Fan, C.; Sun, L.; Cui, H.; Amanullah, S.; Tang, L.; Gao, P. Genetic mapping reveals a candidate gene for egusi seed in watermelon. Euphytica 2019, 215, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Kong, S.; Zhou, D.; Shang, J.; Wang, J.; Li, N.; Liu, L.; Ma, S. A 13.96-kb chromosomal deletion of two genes is responsible for the tomato seed size in watermelon (Citrullus lanatus). Plant Breed. 2021, 140, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Inheritance of seed size from diverse crosses in watermelon. Cucurbit Genet. Coop. Rep. 1996, 19, 67–69. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, T.; Wimol, S.; Mizutani, T. Inheritance of Fruit Shape and Seed Size of Watermelon. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1995, 64, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kensler, T.; Barham, W. The inheritance of seed size in watermelon. Proc. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 1958, 71, 480–484. [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa, K.; Kurinami, S.; Oki, K.; Abe, Y.; Ando, T.; Kono, I.; Yano, M.; Kitano, H.; Iwasaki, Y. A Novel Kinesin 13 Protein Regulating Rice Seed Length. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 1315–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.-N.; Gu, S.-L.; Zhu, F.-G.; Ma, Z.-Y.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Tan, X.-L. Long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 2 is involved in seed oil production in Brassica napus. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawahir, V.; Zolman, B.K. Long chain acyl CoA synthetase 4 catalyzes the first step in peroxisomal indole-3-butyric acid to IAA conversion. Plant Physiol. 2020, 185, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S. A seed-specific AP2-domain transcription factor from soybean plays a certain role in regulation of seed germination. Sci. China Life Sci. 2008, 51, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irish, V. The ABC model of floral development. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R887–R890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohto, M.-A.; Floyd, S.K.; Fischer, R.L.; Goldberg, R.B.; Harada, J.J. Effects of APETALA2 on embryo, endosperm, and seed coat development determine seed size in Arabidopsis. Sex. Plant Reprod. 2009, 22, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Ma, X.; Zhao, S.; Tang, Y.; Liu, F.; Gu, P.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Cai, H.; Sun, C.; et al. The APETALA2-Like Transcription Factor SUPERNUMERARY BRACT Controls Rice Seed Shattering and Seed Size. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shi, C.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Yu, C.; Li, Z.; et al. SOAPnuke: A MapReduce acceleration-supported software for integrated quality control and preprocessing of high-throughput sequencing data. GigaScience 2017, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows—Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, T.; Kota, R.; Grosse, I.; Stein, N.; Graner, A. SNP2CAPS: A SNP and INDEL analysis tool for CAPS marker development. Nucleic Acids Res 2004, 32, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. QTL IciMapping: Integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop J. 2015, 3, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
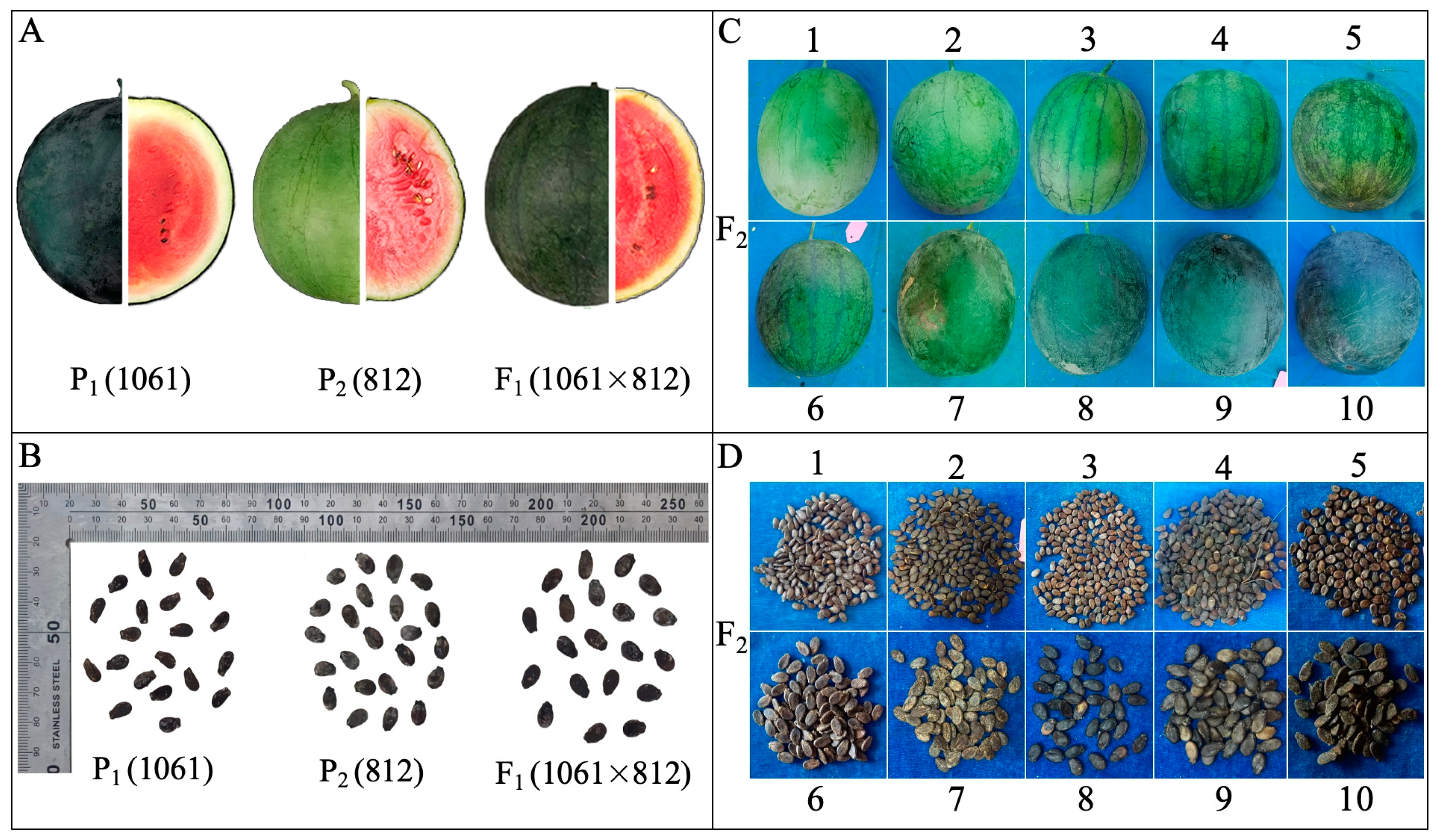




| Phenotypes | P1 (1061) | P2 (812) | F1 (Hybrid) | F2 Population in 2020 | F2 Population in 2021 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Low | High | Mean ± SD | Low | High | |
| FW (kg) | 3.45 ± 0.23 a | 2.65 ± 0.06 b | 3.74 ± 0.24 a | 2.79 ± 0.99 | 0.90 | 7.18 | 1.85 ± 0.99 | 0.12 | 5.26 |
| PT (mm) | 11.44 ± 0.02 a | 5.89 ± 0.11 c | 10.64 ± 0.03 b | 11.21 ± 3.42 | 4.73 | 21.13 | 8.33 ± 3.53 | 2.26 | 18.35 |
| SL (mm) | 9.52 ± 0.07 a | 8.9 ± 0.08 b | 9.62 ± 0.14 a | 9.32 ± 1.20 | 6.40 | 12.30 | 9.61 ± 1.30 | 4.60 | 12.8 |
| SWi (mm) | 4.58 ± 0.16 b | 5.69 ± 0.25 a | 5.9 ± 0.08 a | 5.74 ± 0.84 | 3.80 | 10.10 | 5.92 ± 0.80 | 3.90 | 9.10 |
| SSi (SL/SWi) | 2.08 ± 0.09 a | 1.57 ± 0.08 b | 1.63 ± 0.03 b | 1.63 ± 0.12 | 1.38 | 1.99 | 1.63 ± 0.18 | 0.50 | 2.14 |
| 1000-SW (g) | 47.07 ± 1.61 b | 48.23 ± 0.86 b | 62.90 ± 1.61 a | 74.62 ± 34.53 | 27.33 | 209.33 | 61.02 ± 18.49 | 20 | 117 |
| Chromosomes | Linkage Map of F2 Mapping Population in 2020 | Linkage Map of F2 Mapping Population in 2021 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAPS Markers | Genetic Length (cM) | Average Distance (cM) | CAPS Markers | Genetic Length (cM) | Average Distance (cM) | |
| Cla97Chr01 | 14 | 432.38 | 30.88 | 14 | 320.84 | 22.92 |
| Cla97Chr02 | 11 | 264.08 | 24.01 | 8 | 256.36 | 32.05 |
| Cla97Chr03 | 9 | 209.09 | 23.23 | 6 | 128.60 | 21.43 |
| Cla97Chr04 | 9 | 131.48 | 14.61 | 9 | 138.82 | 15.42 |
| Cla97Chr05 | 16 | 300.94 | 18.81 | 14 | 342.66 | 24.48 |
| Cla97Chr06 | 11 | 216.11 | 19.65 | 11 | 274.01 | 24.91 |
| Cla97Chr07 | 10 | 174.98 | 17.50 | 9 | 225.34 | 25.04 |
| Cla97Chr08 | 13 | 254.20 | 19.55 | 12 | 239.92 | 19.99 |
| Cla97Chr09 | 14 | 301.13 | 21.51 | 14 | 275.66 | 19.69 |
| Cla97Ch10 | 17 | 303.61 | 17.86 | 11 | 281.17 | 25.56 |
| Cla97Chr11 | 12 | 246.28 | 20.52 | 11 | 238.07 | 21.64 |
| Total | 136 | 2834.28 | 20.84 | 119 | 2721.45 | 22.87 |
| QTL | Adjacent Markers | LOD | PVE (%) | Add Effect | Dom Effect | Left CI | Right CI | Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC-2-1 | CL2_26969934 | CL2_28759532 | 9.18 | 10.00 | 0.33 | 0.23 | 209.50 | 217.50 | (2021) |
| PC-2-2 | CL2_28759532 | CL2_31952769 | 7.24 | 8.50 | −0.47 | 0.26 | 221.50 | 233.50 | (2020) |
| PC-8-1 | CL8_24317747 | CL8_25038923 | 22.28 | 28.29 | 0.57 | 0.48 | 238.50 | 239.00 | (2021) |
| CL8_24317747 | CL8_25038923 | 23.34 | 38.98 | −0.83 | 0.63 | 238.50 | 249.50 | (2020) | |
| PC-9-1 | CL9_2643032 | CL9_4916844 | 5.08 | 8.97 | 0.32 | 0.27 | 30.50 | 49.50 | (2021) |
| PC-11-1 | CL11_2619817 | CL11_3559898 | 3.43 | 4.01 | −1.39 | −4.24 | 20.50 | 36.50 | (2020) |
| FW-2-1 | CL2_1147879 | CL2_9962482 | 3.12 | 6.92 | 0.60 | −0.84 | 30.50 | 62.50 | (2021) |
| FW-5-1 | CL5_25539634 | CL5_30784074 | 6.18 | 9.94 | −0.97 | −0.46 | 228.50 | 258.50 | (2021) |
| FW-9-1 | CL9_29718594 | CL9_31049233 | 6.29 | 20.12 | 0.43 | 0.75 | 251.50 | 264.50 | (2020) |
| PT-2-1 | CL2_26969934 | CL2_28759532 | 3.57 | 7.69 | 1.56 | −0.21 | 200.50 | 230.50 | (2021) |
| PT-2-2 | CL2_28759532 | CL2_31952769 | 5.25 | 17.04 | −0.22 | 0.08 | 217.50 | 238.50 | (2020) |
| SL-6-1 | CL6_683495 | CL6_6716713 | 6.66 | 15.16 | 0.85 | −0.56 | 0.00 | 20.50 | (2021) |
| SL-6-2 | CL6_6716713 | CL6_6893470 | 6.93 | 11.27 | −0.08 | −0.02 | 63.50 | 72.50 | (2020) |
| SL-9-1 | CL9_29718594 | CL9_31049233 | 11.59 | 18.78 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 250.50 | 255.50 | (2020) |
| CL9_29718594 | CL9_31049233 | 11.66 | 18.93 | −0.94 | 0.86 | 242.50 | 250.50 | (2021) | |
| SWi-6-1 | CL6_683495 | CL6_6716713 | 4.70 | 10.68 | 0.62 | −0.33 | 0.00 | 23.50 | (2021) |
| SWi-6-2 | CL6_6716713 | CL6_6893470 | 4.31 | 9.67 | −0.04 | −0.02 | 65.50 | 82.50 | (2020) |
| SWi-9-1 | CL9_29718594 | CL9_31049233 | 12.91 | 34.81 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 250.50 | 258.50 | (2020) |
| CL9_29718594 | CL9_31049233 | 2.67 | 3.77 | −0.33 | 0.39 | 236.50 | 249.50 | (2021) | |
| SWi-9-2 | CL9_31049233 | CL9_34338129 | 8.42 | 11.27 | −0.62 | 0.50 | 255.50 | 271.50 | (2021) |
| SSi-9-1 | CL9_280180 | CL9_2643032 | 7.72 | 23.14 | −0.09 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 15.50 | (2020) |
| CL9_280180 | CL9_2643032 | 7.21 | 12.06 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 10.50 | 26.50 | (2021) | |
| SW-1-1 | CL1_6772635 | CL1_13517768 | 3.35 | 6.15 | 0.76 | −1.38 | 159.50 | 179.50 | (2020) |
| SW-1-2 | CL1_15842725 | CL1_21916657 | 3.68 | 7.40 | −0.97 | −1.34 | 240.50 | 256.50 | (2020) |
| SW-6-1 | CL6_683495 | CL6_6716713 | 4.64 | 5.33 | −1.13 | −1.26 | 31.50 | 55.50 | (2020) |
| CL6_683495 | CL6_6716713 | 4.21 | 13.30 | 0.12 | −0.08 | 0.00 | 26.50 | (2021) | |
| SW-9-1 | CL9_31049233 | CL9_34338129 | 8.75 | 15.08 | −0.13 | 0.10 | 251.50 | 269.50 | (2021) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, T.; Amanullah, S.; Li, S.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, H.; Luan, F.; Wang, X. Molecular Mapping of Putative Genomic Regions Controlling Fruit and Seed Morphology of Watermelon. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115755
Yang T, Amanullah S, Li S, Cheng R, Zhang C, Zhao Z, Liu H, Luan F, Wang X. Molecular Mapping of Putative Genomic Regions Controlling Fruit and Seed Morphology of Watermelon. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(21):15755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115755
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Tiantian, Sikandar Amanullah, Shenglong Li, Rui Cheng, Chen Zhang, Zhengxiang Zhao, Hongyu Liu, Feishi Luan, and Xuezheng Wang. 2023. "Molecular Mapping of Putative Genomic Regions Controlling Fruit and Seed Morphology of Watermelon" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 21: 15755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115755
APA StyleYang, T., Amanullah, S., Li, S., Cheng, R., Zhang, C., Zhao, Z., Liu, H., Luan, F., & Wang, X. (2023). Molecular Mapping of Putative Genomic Regions Controlling Fruit and Seed Morphology of Watermelon. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(21), 15755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115755







