The N-Terminal Part of Drosophila CP190 Is a Platform for Interaction with Multiple Architectural Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
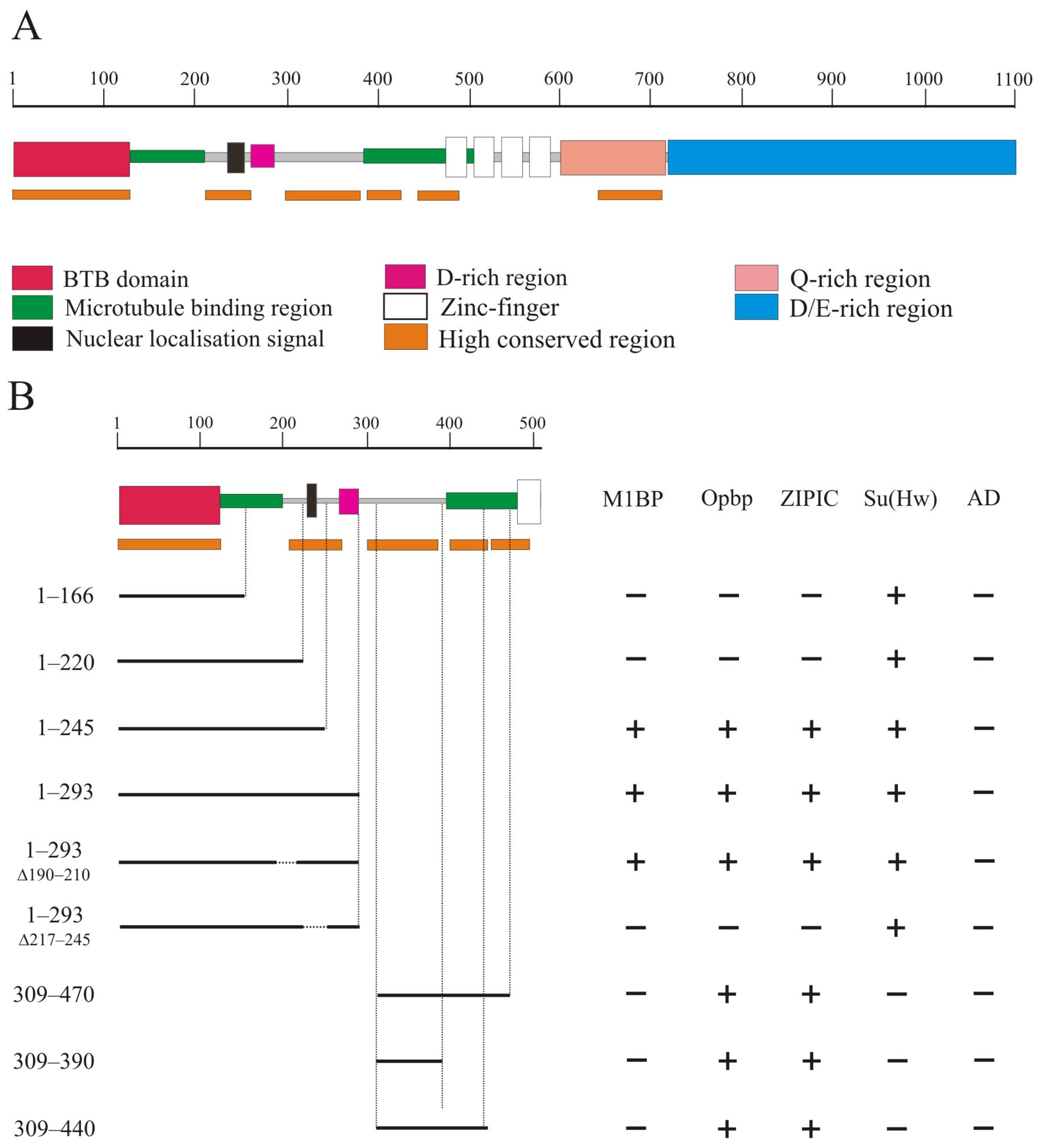
2.1. Mapping the Domains of CP190 Required for Interaction with Architectural Proteins
2.2. Testing the Functional Role of CP190 Domains Required for Interaction with the Architectural C2H2 Proteins
2.3. The Ability of CP190 Variants to Bind to Regulatory Elements
2.4. Identification of the CP190 Domain Required for the Formation of the Interband Region in Larval Polytene Chromosomes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plasmids and Cloning
4.1.1. Plasmids for Y2H Assay
4.1.2. Plasmids for Transgenic Lines Generation
4.2. Germ-Line Transformation, Genetic Crosses, and Phenotypic Analysis
4.3. Yeast Two-Hybrid Assay
4.4. Chromatin Preparation and ChIP Analysis
4.5. Antibodies
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Immunostaining of Polytene Chromosomes
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cavalheiro, G.R.; Pollex, T.; Furlong, E.E. To Loop or Not to Loop: What Is the Role of TADs in Enhancer Function and Gene Regulation? Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2021, 67, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlong, E.E.M.; Levine, M. Developmental Enhancers and Chromosome Topology. Science 2018, 361, 1341–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Dean, A. Enhancers Navigate the Three-Dimensional Genome to Direct Cell Fate Decisions. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2021, 71, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyrchanova, O.V.; Bylino, O.V.; Georgiev, P.G. Mechanisms of Enhancer-Promoter Communication and Chromosomal Architecture in Mammals and Drosophila. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1081088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Faryabi, R.B. Spatial promoter–enhancer hubs in cancer: Organization, regulation, and function. Trends Cancer 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa-Nunes, J.A.; Noordermeer, D. TADs: Dynamic structures to create stable regulatory functions. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2023, 81, 102622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyehara, C.M.; Apostolou, E. 3D enhancer-promoter interactions and multi-connected hubs: Organizational principles and functional roles. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, S.; Aljahani, A.; Karpinska, M.A.; Cao, T.B.N.; Velychko, T.; Cruz, J.N.; Lidschreiber, M.; Oudelaar, A.M. The Mediator complex regulates enhancer-promoter interactions. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2023, 30, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpinska, M.A.; Oudelaar, A.M. The role of loop extrusion in enhancer-mediated gene activation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2023, 79, 102022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo Ngoc, L.; Kassavetis, G.A.; Kadonaga, J.T. The RNA Polymerase II Core Promoter in Drosophila. Genetics 2019, 212, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serebreni, L.; Stark, A. Insights into Gene Regulation: From Regulatory Genomic Elements to DNA-Protein and Protein-Protein Interactions. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2021, 70, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzat, L.H.; Lei, E.P. Surviving an Identity Crisis: A Revised View of Chromatin Insulators in the Genomics Era. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1839, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Lei, E.P. Function and regulation of chromatin insulators in dynamic genome organization. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2019, 58, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, N.E.; White, R. Chromatin Architecture in the Fly: Living without CTCF/Cohesin Loop Extrusion?: Alternating Chromatin States Provide a Basis for Domain Architecture in Drosophila. Bioessays 2019, 41, e1900048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehingia, B.; Milewska, M.; Janowski, M.; Pękowska, A. CTCF shapes chromatin structure and gene expression in health and disease. Embo Rep. 2022, 23, e55146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneau, B.G. Dissecting CTCF site function in a tense HoxD locus. Minerva Anestesiol. 2021, 35, 1401–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, P.; Wang, L. Many facades of CTCF unified by its coding for three-dimensional genome architecture. J. Genet. Genom. 2020, 47, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikova, L.S.; Georgiev, P.G.; Golovnin, A.K. The Functions and Mechanisms of Action of Insulators in the Genomes of Higher Eukaryotes. Acta Naturae 2020, 12, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, V.S.; Cande, J.; Hong, J.-W.; Levine, M. Stalled Hox Promoters as Chromosomal Boundaries. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, M.; McKowen, J.K.; Hart, C.M. Overlapping but Distinct Sequences Play Roles in the Insulator and Promoter Activities of the Drosophila BEAF-Dependent Scs’ Insulator. Genetics 2020, 215, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuki, S.; Levine, M. GAGA Mediates the Enhancer Blocking Activity of the Eve Promoter in the Drosophila Embryo. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 3325–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cubeñas-Potts, C.; Rowley, M.J.; Lyu, X.; Li, G.; Lei, E.P.; Corces, V.G. Different Enhancer Classes in Drosophila Bind Distinct Architectural Proteins and Mediate Unique Chromatin Interactions and 3D Architecture. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 1714–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartkuhn, M.; Straub, T.; Herold, M.; Herrmann, M.; Rathke, C.; Saumweber, H.; Gilfillan, G.D.; Becker, P.B.; Renkawitz, R. Active Promoters and Insulators Are Marked by the Centrosomal Protein 190. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellogg, D.R.; Field, C.M.; Alberts, B.M. Identification of Microtubule-Associated Proteins in the Centrosome, Spindle, and Kinetochore of the Early Drosophila Embryo. J. Cell Biol. 1989, 109, 2977–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plevock, K.M.; Galletta, B.J.; Slep, K.C.; Rusan, N.M. Newly Characterized Region of CP190 Associates with Microtubules and Mediates Proper Spindle Morphology in Drosophila Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butcher, R.D.; Chodagam, S.; Basto, R.; Wakefield, J.G.; Henderson, D.S.; Raff, J.W.; Whitfield, W.G. The Drosophila Centrosome-Associated Protein CP190 Is Essential for Viability but Not for Cell Division. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, W.G.; Chaplin, M.A.; Oegema, K.; Parry, H.; Glover, D.M. The 190 kDa Centrosome-Associated Protein of Drosophila Melanogaster Contains Four Zinc Finger Motifs and Binds to Specific Sites on Polytene Chromosomes. J. Cell Sci. 1995, 108 Pt 11, 3377–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, D.; Sheehan, B.; South, H.; Akbari, O.; Pai, C.Y. The Chromosomal Association/Dissociation of the Chromatin Insulator Protein Cp190 of Drosophila Melanogaster Is Mediated by the BTB/POZ Domain and Two Acidic Regions. BMC Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stogios, P.J.; Downs, G.S.; Jauhal, J.J.S.; Nandra, S.K.; Privé, G.G. Sequence and Structural Analysis of BTB Domain Proteins. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, R82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelmann, J.; Le Gall, A.; Dejardin, S.; Allemand, F.; Gamot, A.; Labesse, G.; Cuvier, O.; Negre, N.; Cohen-Gonsaud, M.; Margeat, E.; et al. Chromatin Insulator Factors Involved in Long-Range DNA Interactions and Their Role in the Folding of the Drosophila Genome. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabirov, M.; Popovich, A.; Boyko, K.; Nikolaeva, A.; Kyrchanova, O.; Maksimenko, O.; Popov, V.; Georgiev, P.; Bonchuk, A. Mechanisms of CP190 Interaction with Architectural Proteins in Drosophila Melanogaster. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaharbakhshi, E.; Jemc, J.C. Broad-Complex, Tramtrack, and Bric-à-Brac (BTB) Proteins: Critical Regulators of Development. Genesis 2016, 54, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonchuk, A.; Balagurov, K.; Georgiev, P. BTB Domains: A Structural View of Evolution, Multimerization, and Protein-Protein Interactions. Bioessays 2023, 45, e2200179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melnick, A.; Carlile, G.; Ahmad, K.F.; Kiang, C.-L.; Corcoran, C.; Bardwell, V.; Prive, G.G.; Licht, J.D. Critical Residues within the BTB Domain of PLZF and Bcl-6 Modulate Interaction with Corepressors. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 22, 1804–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lopez-Guisa, J.M.; Ninan, N.; Weiner, E.J.; Rauscher, F.J.; Marmorstein, R. Overexpression, Purification, Characterization, and Crystallization of the BTB/POZ Domain from the PLZF Oncoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 27324–27329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, K.F.; Engel, C.K.; Privé, G.G. Crystal Structure of the BTB Domain from PLZF. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 12123–12128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuartero, S.; Fresan, U.; Reina, O.; Planet, E.; Espinas, M.L. Ibf1 and Ibf2 Are Novel CP190-Interacting Proteins Required for Insulator Function. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, C.Y.; Lei, E.P.; Ghosh, D.; Corces, V.G. The Centrosomal Protein CP190 Is a Component of the Gypsy Chromatin Insulator. Mol. Cell 2004, 16, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimenko, O.; Bartkuhn, M.; Stakhov, V.; Herold, M.; Zolotarev, N.; Jox, T.; Buxa, M.K.; Kirsch, R.; Bonchuk, A.; Fedotova, A.; et al. Two New Insulator Proteins, Pita and ZIPIC, Target CP190 to Chromatin. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, I.; Dale, R.K.; Palmer, C.; Lei, E.P. The Zinc-Finger Protein CLAMP Promotes Gypsy Chromatin Insulator Function in Drosophila. J. Cell Sci. 2019, 132, jcs226092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, J.F.; Parida, M.; Long, A.; Wankum, J.; Lilienthal, A.J.; Nukala, K.M.; Manak, J.R. The Dm-Myb Oncoprotein Contributes to Insulator Function and Stabilizes Repressive H3K27me3 PcG Domains. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 3218–3228.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, K.F.; Melnick, A.; Lax, S.; Bouchard, D.; Liu, J.; Kiang, C.-L.; Mayer, S.; Takahashi, S.; Licht, J.D.; Privé, G.G. Mechanism of SMRT Corepressor Recruitment by the BCL6 BTB Domain. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 1551–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzi, K.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, C.; Garrett-Bakelman, F.; Gearhart, M.D.; Giannopoulou, E.G.; Zumbo, P.; Kirouac, K.; Bhaskara, S.; Polo, J.M.; et al. A Hybrid Mechanism of Action for BCL6 in B Cells Defined by Formation of Functionally Distinct Complexes at Enhancers and Promoters. Cell Rep. 2013, 4, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghetu, A.F.; Corcoran, C.M.; Cerchietti, L.; Bardwell, V.J.; Melnick, A.; Privé, G.G. Structure of a BCOR Corepressor Peptide in Complex with the BCL6 BTB Domain Dimer. Mol. Cell 2008, 29, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabirov, M.; Kyrchanova, O.; Pokholkova, G.V.; Bonchuk, A.; Klimenko, N.; Belova, E.; Zhimulev, I.F.; Maksimenko, O.; Georgiev, P. Mechanism and Functional Role of the Interaction between CP190 and the Architectural Protein Pita in Drosophila Melanogaster. Epigenet. Chromatin 2021, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrchanova, O.; Klimenko, N.; Postika, N.; Bonchuk, A.; Zolotarev, N.; Maksimenko, O.; Georgiev, P. Drosophila Architectural Protein CTCF Is Not Essential for Fly Survival and Is Able to Function Independently of CP190. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2021, 1864, 194733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikova, L.; Kostyuchenko, M.; Molodina, V.; Parshikov, A.; Georgiev, P.; Golovnin, A. Interactions between BTB Domain of CP190 and Two Adjacent Regions in Su(Hw) Are Required for the Insulator Complex Formation. Chromosoma 2018, 127, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotarev, N.; Maksimenko, O.; Kyrchanova, O.; Sokolinskaya, E.; Osadchiy, I.; Girardot, C.; Bonchuk, A.; Ciglar, L.; Furlong, E.E.M.; Georgiev, P. Opbp Is a New Architectural/Insulator Protein Required for Ribosomal Gene Expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 12285–12300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahanger, S.H.; Günther, K.; Weth, O.; Bartkuhn, M.; Bhonde, R.R.; Shouche, Y.S.; Renkawitz, R. Ectopically Tethered CP190 Induces Large-Scale Chromatin Decondensation. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, I.; Chen, S.; Rosin, L.F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.-Y.; Yu, G.-Y.; Lei, E.P. M1BP Cooperates with CP190 to Activate Transcription at TAD Borders and Promote Chromatin Insulator Activity. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, Q.; Czajkowsky, D.M.; Shao, Z. Sub-Kb Hi-C in D. Melanogaster Reveals Conserved Characteristics of TADs between Insect and Mammalian Cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohla, D.; Herold, M.; Panzer, I.; Buxa, M.K.; Ali, T.; Demmers, J.; Krüger, M.; Scharfe, M.; Jarek, M.; Bartkuhn, M.; et al. A Functional Insulator Screen Identifies NURF and dREAM Components to Be Required for Enhancer-Blocking. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.Y.; Grisan, V.; Jang, B.; Herbert, J.; Badenhorst, P. Genome-Wide Mapping Targets of the Metazoan Chromatin Remodeling Factor NURF Reveals Nucleosome Remodeling at Enhancers, Core Promoters and Gene Insulators. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.; Krüger, M.; Bhuju, S.; Jarek, M.; Bartkuhn, M.; Renkawitz, R. Chromatin Binding of Gcn5 in Drosophila Is Largely Mediated by CP190. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 2384–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Rosin, L.F.; Pegoraro, G.; Moshkovich, N.; Murphy, P.J.; Yu, G.; Lei, E.P. NURF301 Contributes to Gypsy Chromatin Insulator-Mediated Nuclear Organization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 7906–7924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahanger, S.H.; Shouche, Y.S.; Mishra, R.K. Functional Sub-Division of the Drosophila Genome via Chromatin Looping: The Emerging Importance of CP190. Nucleus 2013, 4, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savitsky, M.; Kim, M.; Kravchuk, O.; Schwartz, Y.B. Distinct Roles of Chromatin Insulator Proteins in Control of the Drosophila Bithorax Complex. Genetics 2016, 202, 601–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, S.K.; Deaton, A.M.; Domingues, H.; Wang, P.I.; Sadreyev, R.I.; Kingston, R.E.; Bender, W. H3K27 Modifications Define Segmental Regulatory Domains in the Drosophila Bithorax Complex. Elife 2014, 3, e02833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, R.K.; Karch, F. The Open for Business Model of the Bithorax Complex in Drosophila. Chromosoma 2015, 124, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajirnis, N.; Mishra, R.K. Homeotic Genes: Clustering, Modularity, and Diversity. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 718308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, A.; Mishra, R.K. Lessons on Gene Regulation Learnt from the Drosophila Melanogaster Bithorax Complex. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2020, 64, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumlauf, R. Hox Genes, Clusters and Collinearity. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2018, 62, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyrchanova, O.; Maksimenko, O.; Ibragimov, A.; Sokolov, V.; Postika, N.; Lukyanova, M.; Schedl, P.; Georgiev, P. The Insulator Functions of the Drosophila Polydactyl C2H2 Zinc Finger Protein CTCF: Necessity versus Sufficiency. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, T.G.; Savitsky, M.; Kuong, C.; Jacquier, C.; Cavalli, G.; Chang, J.-M.; Schwartz, Y.B. Topological Screen Identifies Hundreds of Cp190- and CTCF-Dependent Drosophila Chromatin Insulator Elements. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade0090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalheiro, G.R.; Girardot, C.; Viales, R.R.; Pollex, T.; Cao, T.B.N.; Lacour, P.; Feng, S.; Rabinowitz, A.; Furlong, E.E.M. CTCF, BEAF-32, and CP190 Are Not Required for the Establishment of TADs in Early Drosophila Embryos but Have Locus-Specific Roles. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobanova, Y.; Filonova, G.; Kaplun, D.; Zhigalova, N.; Prokhortchouk, E.; Zhenilo, S. TRIM28 Regulates Transcriptional Activity of Methyl-DNA Binding Protein Kaiso by SUMOylation. Biochimie 2023, 206, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokhortchouk, A.; Hendrich, B.; Jørgensen, H.; Ruzov, A.; Wilm, M.; Georgiev, G.; Bird, A.; Prokhortchouk, E. The P120 Catenin Partner Kaiso Is a DNA Methylation-Dependent Transcriptional Repressor. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 1613–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischof, J.; Maeda, R.K.; Hediger, M.; Karch, F.; Basler, K. An Optimized Transgenesis System for Drosophila Using Germ-Line-Specific phiC31 Integrases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3312–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatolina, T.Y.; Boldyreva, L.V.; Demakova, O.V.; Demakov, S.A.; Kokoza, E.B.; Semeshin, V.F.; Babenko, V.N.; Goncharov, F.P.; Belyaeva, E.S.; Zhimulev, I.F. Identical Functional Organization of Nonpolytene and Polytene Chromosomes in Drosophila Melanogaster. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, M.; Bartkuhn, M.; Herold, M.; Philippen, A.; Heinl, N.; Bardenhagen, I.; Leers, J.; White, R.A.; Renkawitz-Pohl, R.; Saumweber, H.; et al. The Drosophila Insulator Proteins CTCF and CP190 Link Enhancer Blocking to Body Patterning. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 4203–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, T.J.; Kuhn, E.J.; Gilmore, B.L.; Helou, C.; Wold, M.S.; Geyer, P.K. Identification of Genomic Sites That Bind the Drosophila Suppressor of Hairy-Wing Insulator Protein. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 5983–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnell, T.J.; Viering, M.M.; Skjesol, A.; Helou, C.; Kuhn, E.J.; Geyer, P.K. An Endogenous Suppressor of Hairy-Wing Insulator Separates Regulatory Domains in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13436–13441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyer, P.K.; Corces, V.G. DNA Position-Specific Repression of Transcription by a Drosophila Zinc Finger Protein. Genes Dev. 1992, 6, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdridge, C.; Dorsett, D. Repression of Hsp70 Heat Shock Gene Transcription by the Suppressor of Hairy-Wing Protein of Drosophila Melanogaster. Mol. Cell Biol. 1991, 11, 1894–1900. [Google Scholar]
- Kyrchanova, O.; Sokolov, V.; Georgiev, P. Mechanisms of Interaction between Enhancers and Promoters in Three Drosophila Model Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zykova, T.Y.; Levitsky, V.G.; Belyaeva, E.S.; Zhimulev, I.F. Polytene Chromosomes—A Portrait of Functional Organization of the Drosophila Genome. Curr. Genom. 2018, 19, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokholkova, G.V.; Demakov, S.A.; Andreenkov, O.V.; Andreenkova, N.G.; Volkova, E.I.; Belyaeva, E.S.; Zhimulev, I.F. Tethering of CHROMATOR and dCTCF Proteins Results in Decompaction of Condensed Bands in the Drosophila Melanogaster Polytene Chromosomes but Does Not Affect Their Transcription and Replication Timing. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplun, D.; Starshin, A.; Sharko, F.; Gainova, K.; Filonova, G.; Zhigalova, N.; Mazur, A.; Prokhortchouk, E.; Zhenilo, S. Kaiso Regulates DNA Methylation Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhenilo, S.; Deyev, I.; Litvinova, E.; Zhigalova, N.; Kaplun, D.; Sokolov, A.; Mazur, A.; Prokhortchouk, E. DeSUMOylation switches Kaiso from activator to repressor upon hyperosmotic stress. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1938–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T. Regulation of hematopoietic development by ZBTB transcription factors. Int. J. Hematol. 2016, 104, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Maeda, T. POK/ZBTB proteins: An emerging family of proteins that regulate lymphoid development and function. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 247, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suliman, B.A.; Xu, D.; Williams, B.R.G. The Promyelocytic Leukemia Zinc Finger Protein: Two Decades of Molecular Oncology. Front. Oncol. 2012, 2, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; He, J.; Li, Y.; Mi, D.; Guan, T.; Guo, W.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y. B-Cell Lymphoma 6 Inhibitors: Current Advances and Prospects of Drug Development for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 15559–15583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamura, S.; Nomura, A.; Kubo, M. BCL6 fine-tunes long-term tumor control. Sci. Immunol. 2023, 8, eadj6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-Ochoa, J.L.; Kazemian, M.; Afzali, B. The role of transcription factors in shaping regulatory T cell identity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louwen, F.; Kreis, N.-N.; Ritter, A.; Friemel, A.; Solbach, C.; Yuan, J. BCL6, a key oncogene, in the placenta, pre-eclampsia and endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. Updat. 2022, 28, 890–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ouyang, C. BTB protein family and human breast cancer: Signaling pathways and clinical progress. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 16213–16229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikova, E.A.; Kulikov, A.V. Kaiso Protein in the Regulation of Brain and Behavior. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2018, 19, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Roy, F.M.; McCrea, P.D. A role for Kaiso–p120ctn complexes in cancer? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeman-Neill, R.J.; Bhagat, G. BCL6 as a Therapeutic Target for Lymphoma. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, C.C.; Hercules, S.M.; Yates, C.; Daniel, J.M. Dancing from Bottoms up—Roles of the POZ-ZF Transcription Factor Kaiso in Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2019, 1871, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhu, Q. SPOP in Cancer: Phenomena, Mechanisms and Its Role in Therapeutic Implications. Genes 2022, 13, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, M.; Guo, W.; Zhu, S.; Li, S.; Lv, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Xing, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. A small molecule BCL6 inhibitor as chemosensitizers in acute myeloid leukemia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 166, 115358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Hwang, L.; MacKerell, A.D.; Melnick, A.; Xue, F. Progress toward B-Cell Lymphoma 6 BTB Domain Inhibitors for the Treatment of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Beyond. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 4333–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Linhares, B.M.; Yu, W.; Cardenas, M.G.; Ai, Y.; Jiang, W.; Winkler, A.; Cohen, S.; Melnick, A.; MacKerell, A.; et al. Identification of Thiourea-Based Inhibitors of the B-Cell Lymphoma 6 BTB Domain via NMR-Based Fragment Screening and Computer-Aided Drug Design. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 7573–7588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenas, M.G.; Oswald, E.; Yu, W.; Xue, F.; MacKerell, A.D.; Melnick, A.M. The Expanding Role of the BCL6 Oncoprotein as a Cancer Therapeutic Target. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.R.; Liu, S.; Xiang, M.; Nicolais, M.; Hatzi, K.; Giannopoulou, E.; Elemento, O.; Cerchietti, L.; Melnick, A.; Frank, D.A. The transcriptional modulator BCL6 as a molecular target for breast cancer therapy. Oncogene 2014, 34, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, F.; Bhardwaj, V.; Arrigoni, L.; Lam, K.C.; Grüning, B.A.; Villaveces, J.; Habermann, B.; Akhtar, A.; Manke, T. High-Resolution TADs Reveal DNA Sequences Underlying Genome Organization in Flies. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, K.; Forcato, M.; Jost, D.; Sexton, T.; Vaillant, C.; Salviato, E.; Mazza, E.M.C.; Lugli, E.; Cavalli, G.; Ferrari, F. Global Chromatin Conformation Differences in the Drosophila Dosage Compensated Chromosome X. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, O.; Raynal, F.; Gurgo, J.; Fiche, J.-B.; Pancaldi, V.; Nollmann, M. 3D chromatin interactions involving Drosophila insulators are infrequent but preferential and arise before TADs and transcription. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochman, H.; Gerber, A.S.; Hartl, D.L. Genetic Applications of an Inverse Polymerase Chain Reaction. Genetics 1988, 120, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedotova, A.A.; Georgiev, P.G.; Bonchuk, A.N. Study of the in Vivo Functional Role of Mutations in the BTB Domain of the CP190 Protein of Drosophila Melanogaster. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2023, 509, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golovnin, A.; Volkov, I.; Georgiev, P. SUMO Conjugation Is Required for the Assembly of Drosophila Su(Hw) and Mod(Mdg4) into Insulator Bodies That Facilitate Insulator Complex Formation. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 2064–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melnikova, L.; Molodina, V.; Erokhin, M.; Georgiev, P.; Golovnin, A. HIPP1 Stabilizes the Interaction between CP190 and Su(Hw) in the Drosophila Insulator Complex. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towbin, H.; Staehelin, T.; Gordon, J. Electrophoretic Transfer of Proteins from Polyacrylamide Gels to Nitrocellulose Sheets: Procedure and Some Applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 4350–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murawska, M.; Brehm, A. Immunostaining of Drosophila Polytene Chromosomes to Investigate Recruitment of Chromatin-Binding Proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 809, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Golovnin, A.; Melnikova, L.; Babosha, V.; Pokholkova, G.V.; Slovohotov, I.; Umnova, A.; Maksimenko, O.; Zhimulev, I.F.; Georgiev, P. The N-Terminal Part of Drosophila CP190 Is a Platform for Interaction with Multiple Architectural Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115917
Golovnin A, Melnikova L, Babosha V, Pokholkova GV, Slovohotov I, Umnova A, Maksimenko O, Zhimulev IF, Georgiev P. The N-Terminal Part of Drosophila CP190 Is a Platform for Interaction with Multiple Architectural Proteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(21):15917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115917
Chicago/Turabian StyleGolovnin, Anton, Larisa Melnikova, Valentin Babosha, Galina V. Pokholkova, Ivan Slovohotov, Anastasia Umnova, Oksana Maksimenko, Igor F. Zhimulev, and Pavel Georgiev. 2023. "The N-Terminal Part of Drosophila CP190 Is a Platform for Interaction with Multiple Architectural Proteins" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 21: 15917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115917
APA StyleGolovnin, A., Melnikova, L., Babosha, V., Pokholkova, G. V., Slovohotov, I., Umnova, A., Maksimenko, O., Zhimulev, I. F., & Georgiev, P. (2023). The N-Terminal Part of Drosophila CP190 Is a Platform for Interaction with Multiple Architectural Proteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(21), 15917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242115917





