Dynamic Up-Regulation of PD-L1 in the Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Cohort
2.2. Expression of PD-L1 in Primary Tumors
2.3. Expression of PD-L1 in Recurrent Tumors
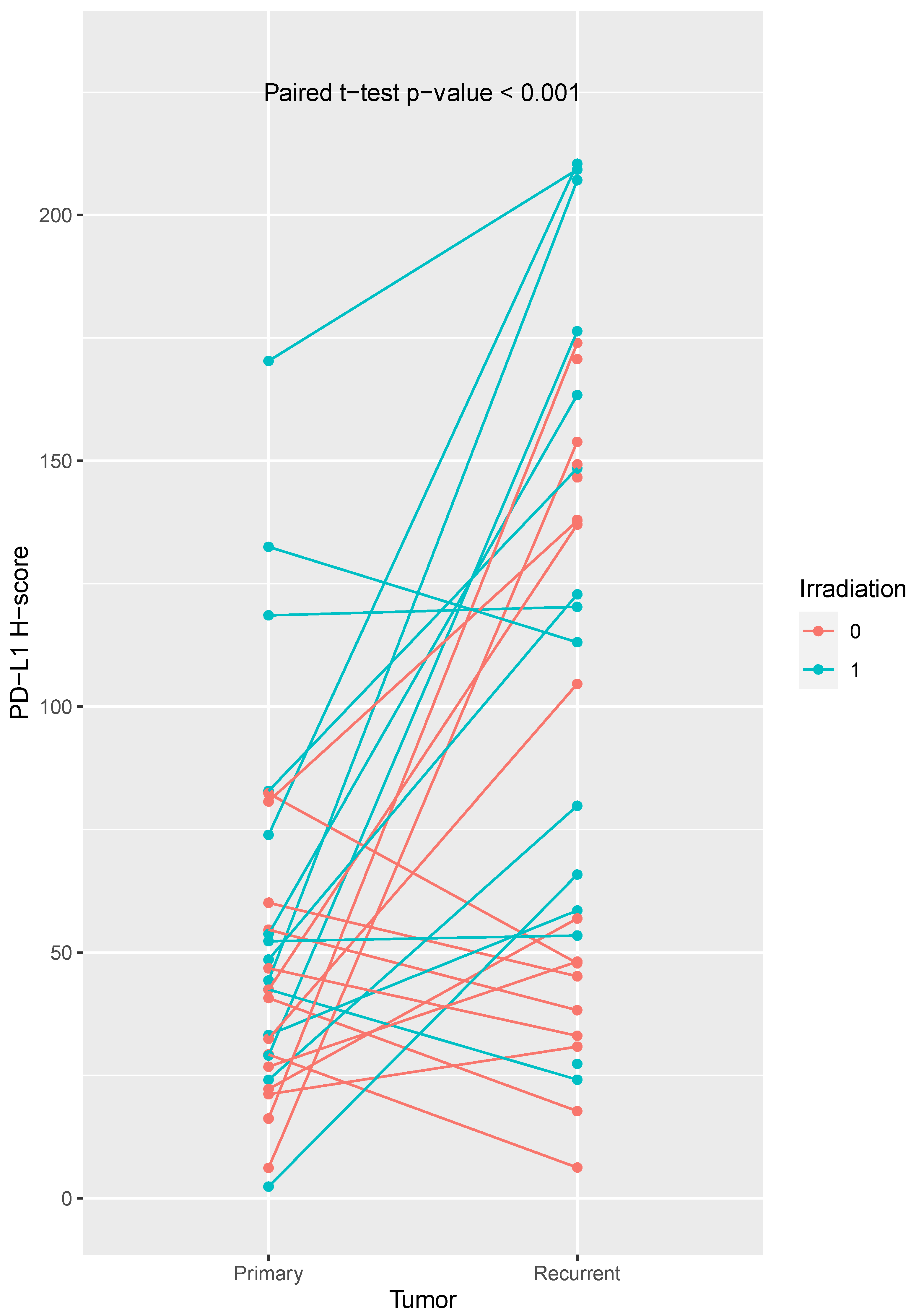
2.4. Comparison of PD-L1 Expression in Primary and Recurrent Tumors
2.5. Overall and Progression Free Survival
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Patients and Samples
3.2. Tissue Microarray and Histological Slices
3.3. Immunohistochemistry and Digital Pathology Scoring
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mody, M.D.; Rocco, J.W.; Yom, S.S.; Haddad, R.I.; Saba, N.F. Head and neck cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 2289–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Cruz, A.K.; Vaish, R.; Kapre, N.; Dandekar, M.; Gupta, S.; Hawaldar, R.; Agarwal, J.P.; Pantvaidya, G.; Chaukar, D.; Deshmukh, A.; et al. Elective versus Therapeutic Neck Dissection in Node-Negative Oral Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kligerman, J.; Lima, R.A.; Soares, J.R.; Prado, L.; Dias, F.L.; Freitas, E.Q.; Olivatto, L.O. Supraomohyoid neck dissection in the treatment of T1/T2 squamous cell carcinoma of oral cavity. Am. J. Surg. 1994, 168, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, S.; Ikram, M.; Ghaffar, S. Neck involvement in early carcinoma of tongue. Is elective neck dissection warranted? J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2007, 57, 305–307. [Google Scholar]
- Pignon, J.P.; le Maitre, A.; Maillard, E.; Bourhis, J.; Group, M.-N.C. Meta-analysis of chemotherapy in head and neck cancer (MACH-NC): An update on 93 randomised trials and 17,346 patients. Radiother. Oncol. 2009, 92, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forastiere, A.; Koch, W.; Trotti, A.; Sidransky, D. Head and neck cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 1890–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, L.Q.M. Head and Neck Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argiris, A.; Harrington, K.J.; Tahara, M.; Schulten, J.; Chomette, P.; Ferreira Castro, A.; Licitra, L. Evidence-Based Treatment Options in Recurrent and/or Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, K.J.; Burtness, B.; Greil, R.; Soulières, D.; Tahara, M.; de Castro, G., Jr.; Psyrri, A.; Brana, I.; Basté, N.; Neupane, P.; et al. Pembrolizumab with or without Chemotherapy in Recurrent or Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Updated Results of the Phase III KEYNOTE-048 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology—Head and Neck Cancers; Version 1.2021; National Comprehensive Cancer Network: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ferris, R.L.; Blumenschein, G., Jr.; Fayette, J.; Guigay, J.; Colevas, A.D.; Licitra, L.; Harrington, K.; Kasper, S.; Vokes, E.E.; Even, C.; et al. Nivolumab for Recurrent Squamous-Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferris, R.L.; Blumenschein, G., Jr.; Fayette, J.; Guigay, J.; Colevas, A.D.; Licitra, L.; Harrington, K.J.; Kasper, S.; Vokes, E.E.; Even, C.; et al. Nivolumab vs investigator’s choice in recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: 2-year long-term survival update of CheckMate 141 with analyses by tumor PD-L1 expression. Oral Oncol. 2018, 81, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, K.J.; Ferris, R.L.; Blumenschein, G., Jr.; Colevas, A.D.; Fayette, J.; Licitra, L.; Kasper, S.; Even, C.; Vokes, E.E.; Worden, F.; et al. Nivolumab versus standard, single-agent therapy of investigator’s choice in recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (CheckMate 141): Health-related quality-of-life results from a randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burtness, B.; Harrington, K.J.; Greil, R.; Soulieres, D.; Tahara, M.; de Castro, G., Jr.; Psyrri, A.; Baste, N.; Neupane, P.; Bratland, A.; et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2019, 394, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiwert, T.Y.; Burtness, B.; Mehra, R.; Weiss, J.; Berger, R.; Eder, J.P.; Heath, K.; McClanahan, T.; Lunceford, J.; Gause, C.; et al. Safety and clinical activity of pembrolizumab for treatment of recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-012): An open-label, multicentre, phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Wehrhan, F.; Baran, C.; Agaimy, A.; Buttner-Herold, M.; Preidl, R.; Neukam, F.W.; Ries, J. PD-L1 expression in tumor tissue and peripheral blood of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 112584–112597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, A.H.; Pauken, K.E. The diverse functions of the PD1 inhibitory pathway. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moratin, J.; Metzger, K.; Safaltin, A.; Herpel, E.; Hoffmann, J.; Freier, K.; Hess, J.; Horn, D. Upregulation of PD-L1 and PD-L2 in neck node metastases of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2019, 41, 2484–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.M.; Sung, W.W.; Hsieh, M.J.; Tsai, S.C.; Lai, H.W.; Yang, S.M.; Shen, K.H.; Chen, M.K.; Lee, H.; Yeh, K.T.; et al. High PD-L1 Expression Correlates with Metastasis and Poor Prognosis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruse, Y.; Kawano, S.; Jinno, T.; Matsubara, R.; Goto, Y.; Kaneko, N.; Sakamoto, T.; Hashiguchi, Y.; Moriyama, M.; Toyoshima, T.; et al. Significant association of increased PD-L1 and PD-1 expression with nodal metastasis and a poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 47, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtness, B.; Rischin, D.; Greil, R.; Soulieres, D.; Tahara, M.; de Castro, G., Jr.; Psyrri, A.; Brana, I.; Baste, N.; Neupane, P.; et al. Pembrolizumab Alone or with Chemotherapy for Recurrent/Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma in KEYNOTE-048: Subgroup Analysis by Programmed Death Ligand-1 Combined Positive Score. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2321–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freier, K.; Joos, S.; Flechtenmacher, C.; Devens, F.; Benner, A.; Bosch, F.X.; Lichter, P.; Hofele, C. Tissue microarray analysis reveals site-specific prevalence of oncogene amplifications in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bankhead, P.; Loughrey, M.B.; Fernandez, J.A.; Dombrowski, Y.; McArt, D.G.; Dunne, P.D.; McQuaid, S.; Gray, R.T.; Murray, L.J.; Coleman, H.G.; et al. QuPath: Open source software for digital pathology image analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moratin, J.; Mock, A.; Obradovic, S.; Metzger, K.; Flechtenmacher, C.; Zaoui, K.; Fröhling, S.; Jäger, D.; Krauss, J.; Hoffmann, J.; et al. Digital Pathology Scoring of Immunohistochemical Staining Reliably Identifies Prognostic Markers and Anatomical Associations in a Large Cohort of Oral Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 712944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabajakian, A.; Bouaoud, J.; Michon, L.; Kamal, M.; Crozes, C.; Zrounba, P.; Auclair-Perossier, J.; Gadot, N.; Attignon, V.; Le Tourneau, C.; et al. Longitudinal assessment of PD-L1 expression and gene expression profiles in patients with head and neck cancer reveals temporal heterogeneity. Oral Oncol. 2021, 119, 105368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blatt, S.; Kruger, M.; Rump, C.; Zimmer, S.; Sagheb, K.; Kunzel, J. Differences in PD-L1 Expression between oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, S.; Kadletz, L.; Wiebringhaus, R.; Kenner, L.; Selzer, E.; Fureder, T.; Rajky, O.; Berghoff, A.S.; Preusser, M.; Heiduschka, G. PD-1 and PD-L1 expression in HNSCC primary cancer and related lymph node metastasis—Impact on clinical outcome. Histopathology 2018, 73, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, M.; Drecoll, E.; Pfarr, N.; Weichert, W.; Langer, R.; Hapfelmeier, A.; Gotz, C.; Wolff, K.D.; Kolk, A.; Specht, K. CD274/PD-L1 gene amplification and PD-L1 protein expression are common events in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 12024–12034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournel, L.; Wu, Z.; Stadler, N.; Damotte, D.; Lococo, F.; Boulle, G.; Segal-Bendirdjian, E.; Bobbio, A.; Icard, P.; Tredaniel, J.; et al. Cisplatin increases PD-L1 expression and optimizes immune check-point blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 464, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.J.; Mattox, A.K.; Clayburgh, D.; Patel, M.; Bell, R.B.; Yueh, B.; Leidner, R.; Xiao, H.; Couey, M.; Li, S.; et al. Chemoradiation therapy alters the PD-L1 score in locoregional recurrent squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Oral Oncol. 2022, 135, 106183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Joung, J.G.; Min, Y.W.; Nam, J.Y.; Ryu, D.; Oh, D.; Park, W.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, Y.; Ahn, J.S.; et al. Paired whole exome and transcriptome analyses for the Immunogenomic changes during concurrent chemoradiotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affolter, A.; Liebel, K.; Tengler, L.; Seiz, E.; Tiedtke, M.; Azhakesan, A.; Schutz, J.; Theodoraki, M.N.; Kern, J.; Ruder, A.M.; et al. Modulation of PD-L1 expression by standard therapy in head and neck cancer cell lines and exosomes. Int. J. Oncol. 2023, 63, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulose, J.V.; Kainickal, C.T. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review of phase-3 clinical trials. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 13, 388–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satgunaseelan, L.; Gupta, R.; Madore, J.; Chia, N.; Lum, T.; Palme, C.E.; Boyer, M.; Scolyer, R.A.; Clark, J.R. Programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma is associated with an inflammatory phenotype. Pathology 2016, 48, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Chen, X.F.; Xu, M.G.; Zhao, J. Relationship of programmed death ligand-1 expression with clinicopathological features and prognosis in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Arch. Oral Biol. 2020, 114, 104717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocini, R.; Vianini, M.; Girolami, I.; Calabrese, L.; Scarpa, A.; Martini, M.; Morbini, P.; Marletta, S.; Brunelli, M.; Molteni, G.; et al. PD-L1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma: A key biomarker from the laboratory to the bedside. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2022, 8, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenouvel, D.; Gonzalez-Moles, M.A.; Ruiz-Avila, I.; Gonzalez-Ruiz, L.; Gonzalez-Ruiz, I.; Ramos-Garcia, P. Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of PD-L1 overexpression in oral squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and comprehensive meta-analysis. Oral Oncol. 2020, 106, 104722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, J.H.; Lelkaitis, G.; Hakansson, K.; Vogelius, I.R.; Johannesen, H.H.; Fischer, B.M.; Bentzen, S.M.; Specht, L.; Kristensen, C.A.; von Buchwald, C.; et al. Intratumor heterogeneity of PD-L1 expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 1003–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Number of Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Female | 85 (38.3) |
| Male | 137 (61.7) |
| Age | |
| <65 years | 112 (50.5) |
| >65 years | 110 (49.5) |
| T Stadium | |
| T1 | 82 (36.9) |
| T2 | 72 (32.4) |
| T3 | 8 (3.6) |
| T4 | 60 (27.1) |
| N Stadium | |
| 0 | 147 (66.2) |
| 1 | 27 (12.2) |
| 2a | 1 (0.5) |
| 2b | 28 (12.5) |
| 2c | 18 (8.1) |
| 3 | 1 (0.5) |
| M Stadium | |
| 0 | 222 (100) |
| 1 | 0 (0) |
| UICC | |
| 1 | 69 (31.1) |
| 2 | 44 (19.8) |
| 3 | 23 (10.4) |
| 4 | 86 (38.7) |
| Grading | |
| 1 | 17 (7.7) |
| 2 | 153 (68.9) |
| 3 | 46 (20.7) |
| Missing | 6 (2.7) |
| Resection margin | |
| R0 | 210 (94.6) |
| R1 | 10 (4.5) |
| Rx | 2 (0.9) |
| Localization | |
| Floor of the mouth | 64 (28.8) |
| Tongue | 52 (23.4) |
| Mandible | 70 (31.5) |
| Maxilla | 5 (2.3) |
| Oropharynx | 16 (7.2) |
| Buccal Plane | 14 (6.3) |
| Lower lip | 1 (0.5) |
| Disease recurrence | |
| yes | 47 (21.2) |
| no | 175 (78.8) |
| Type of recurrence | |
| Local recurrence | 27 (69.2) |
| Cervical metastases | 11 (28.2) |
| Distant metastases | 1 (2.6) |
| Adjuvant therapy | |
| No adjuvant therapy | 133 (59.9) |
| Adjuvant radiotherapy | 54 (24.3) |
| Adjuvant chemoradiotherapy | 31 (14.0) |
| Adjuvant radioimmunotherapy | 4 (1.8) |
| Average | Median | Minimum | Maximum | Standard Deviation | N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary tumors | 47.065 | 40.175 | 2.38 | 170.33 | 31.398 | 194 |
| with recurrence | 49.676 | 42.465 | 2.38 | 170.33 | 34.822 | 40 |
| without recurrence | 46.386 | 39.532 | 4.16 | 152.57 | 30.532 | 154 |
| Recurrent tumors | 103.526 | 113.08 | 6.26 | 210.44 | 62.779 | 33 |
| Low PD-L1 | High PD-L1 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary tumors | |||
| Sex | |||
| Female | 89 | 28 | 0.192 |
| Male | 52 | 25 | |
| Age | |||
| <65 years | 69 | 24 | 0.650 |
| >65 years | 72 | 29 | |
| pT Stadium | |||
| T1/T2 | 104 | 29 | 0.011 |
| T3/T4 | 37 | 24 | |
| pN Stadium | |||
| pN− | 98 | 34 | 0.476 |
| pN+ | 43 | 19 | |
| Stage | |||
| I/II | 79 | 21 | 0.042 |
| III/IV | 62 | 32 | |
| Grading | |||
| G1 | 12 | 3 | 0.786 |
| G2 | 96 | 36 | |
| G3 | 29 | 12 | |
| Recurrent tumors | |||
| Sex | |||
| Female | 5 | 7 | 0.840 |
| Male | 8 | 13 | |
| Age | |||
| <65 years | 8 | 9 | 0.353 |
| >65 years | 5 | 11 | |
| pT Stadium | |||
| T1/T2 | 11 | 9 | 0.023 |
| T3/T4 | 2 | 11 | |
| pN Stadium | |||
| pN− | 9 | 4 | 0.005 |
| pN+ | 4 | 16 | |
| Stage | |||
| I/II | 8 | 2 | 0.002 |
| III/IV | 5 | 18 | |
| Grading | |||
| G1 | 1 | 0 | 0.222 |
| G2 | 8 | 17 | |
| G3 | 3 | 2 |
| Parameter | Number of Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| No adjuvant therapy | 23 (50.0) |
| Adjuvant radiotherapy | 19 (41.3) |
| Adjuvant chemoradiotherapy | 3 (6.5) |
| Adjuvant radioimmunotherapy | 1 (2.2) |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value |
| PD-L1 expression | 1.97 (1.01–3.86) | 0.048 | 1.86 (0.93–3.72) | 0.078 |
| T Classification | 2.34 (1.30–4.21) | 0.004 | 2.27 (0.95–5.46) | 0.066 |
| N Classification | 3.57 (1.99–6.40) | <0.001 | 3.93 (1.34–11.50) | 0.013 |
| UICC stage | 3.13 (1.66–5.87) | <0.001 | 0.70 (0.19–2.67) | 0.603 |
| Age | 1.057 (0.6–1.88) | 0.849 | 1.09 (0.54–2.17) | 0.813 |
| Sex | 0.86 (0.47–1.57) | 0.615 | 0.87 (0.43–1.75) | 0.687 |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value |
| PD-L1 expression | 1.06 (0.51–2.19) | 0.879 | 0.97 (0.46–2.03) | 0.926 |
| T Classification | 1.89 (1.04–3.43) | 0.038 | 2.04 (0.87–4.80) | 0.102 |
| N Classification | 3.66 (2.04–6.59) | <0.001 | 4.28 (1.36–13.56) | 0.013 |
| UICC stage | 2.90 (1.55–5.41) | 0.001 | 0.59 (0.15–2.36) | 0.459 |
| Age | 0.91 (0.51–1.60) | 0.735 | 1.00 (0.51–1.95) | 0.997 |
| Sex | 0.72 (0.39–1.13) | 0.294 | 0.90 (0.45–1.78) | 0.763 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Steen, S.; Semmelmayer, K.; Flechtenmacher, C.; Hoffmann, J.; Freier, K.; Horn, D.; Hess, J.; Freudlsperger, C.; Moratin, J. Dynamic Up-Regulation of PD-L1 in the Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216386
Steen S, Semmelmayer K, Flechtenmacher C, Hoffmann J, Freier K, Horn D, Hess J, Freudlsperger C, Moratin J. Dynamic Up-Regulation of PD-L1 in the Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(22):16386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216386
Chicago/Turabian StyleSteen, Sonja, Karl Semmelmayer, Christa Flechtenmacher, Jürgen Hoffmann, Kolja Freier, Dominik Horn, Jochen Hess, Christian Freudlsperger, and Julius Moratin. 2023. "Dynamic Up-Regulation of PD-L1 in the Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 22: 16386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216386
APA StyleSteen, S., Semmelmayer, K., Flechtenmacher, C., Hoffmann, J., Freier, K., Horn, D., Hess, J., Freudlsperger, C., & Moratin, J. (2023). Dynamic Up-Regulation of PD-L1 in the Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(22), 16386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216386






