An Emerging Role for Anti-DNA Antibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Generation of Anti-DNA Antibodies
3. Penetration of Anti-DNA Antibodies into Live Cells (Figure 1)
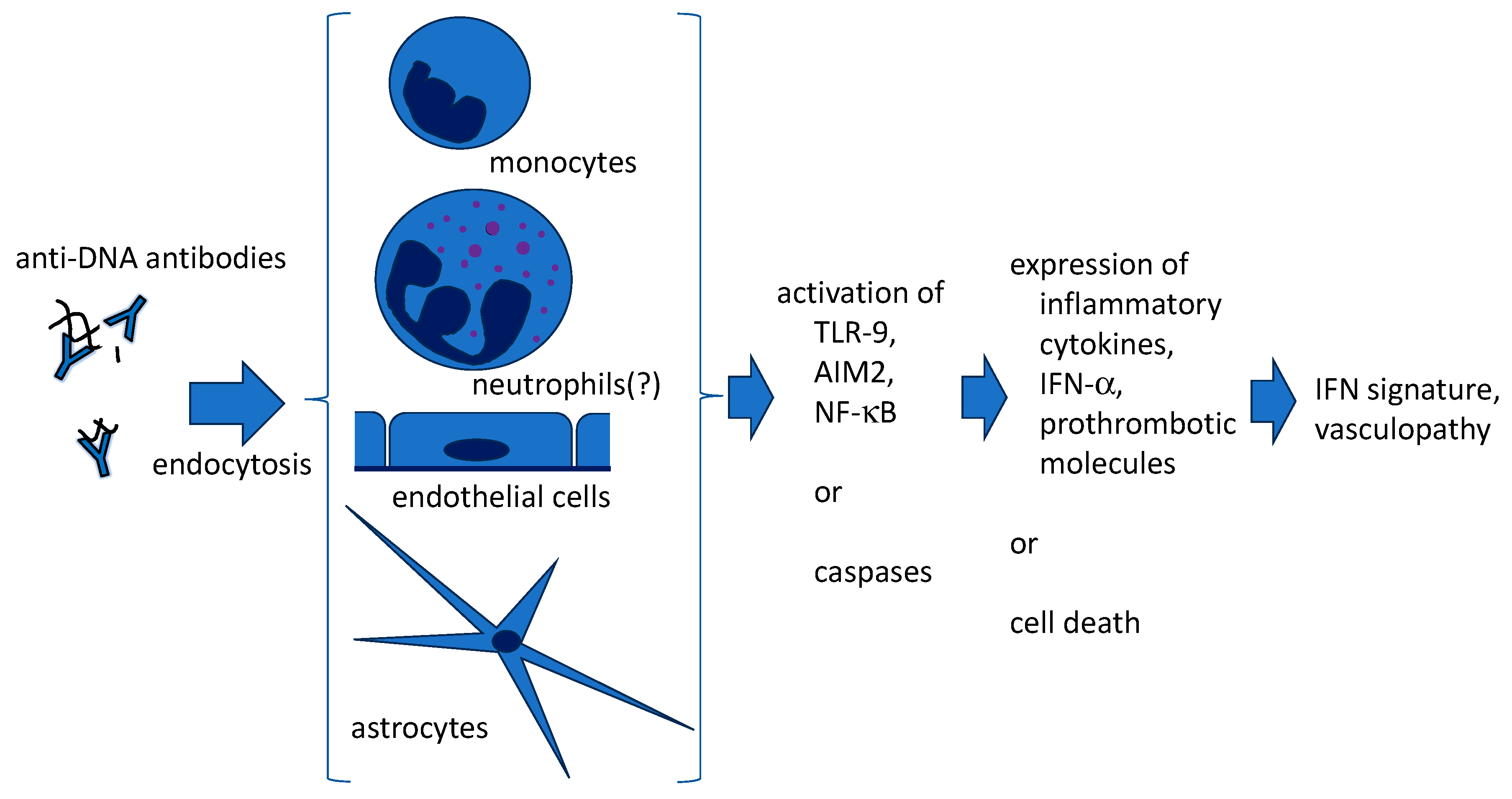
4. Anti-DNA Antibodies and NETs
4.1. What Are NETs?
4.2. NETs in Autoimmune Diseasses
4.2.1. SLE
4.2.2. APS
4.2.3. AAV
4.3. Quantification of NETs
4.4. Anti-NET Antibodies
4.5. Amplification of SLE Disease Activity by Anti-DNA Antibodies and NETs (Figure 2)
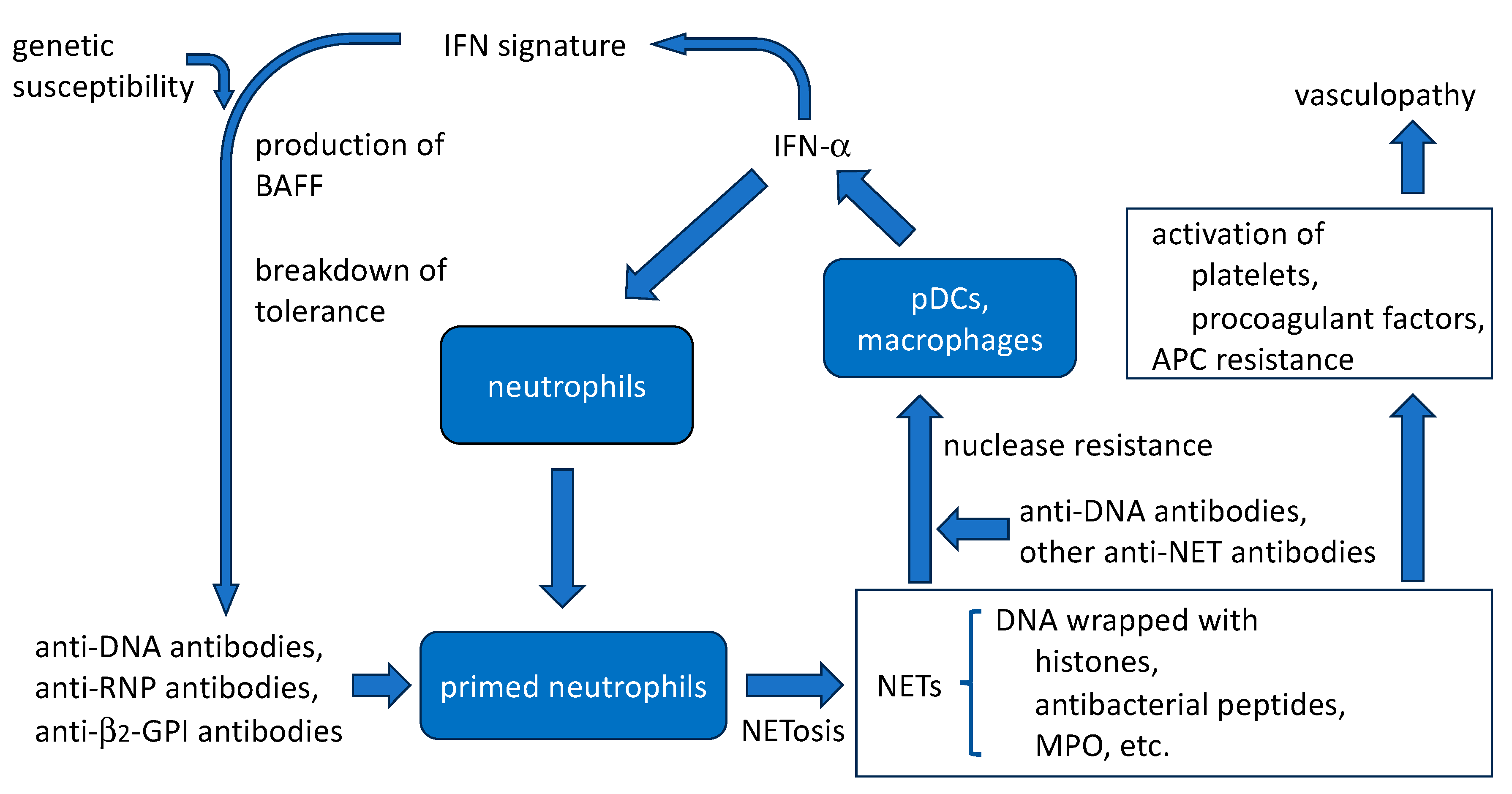
4.5.1. Aggravation of IFN Signature
4.5.2. Protection of NETs from Nucleases by Anti-DNA Antibodies
4.5.3. Thrombogenic Properties
4.5.4. Induction of NET Release by Anti-DNA Antibodies
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaul, A.; Gordon, C.; Crow, M.K.; Touma, Z.; Urowitz, M.B.; van Vollenhoven, R.; Ruiz-Irastorza, G.; Hughes, G. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameer, M.A.; Chaudhry, H.; Mushtaq, J.; Khan, O.S.; Babar, M.; Hashim, T.; Zeb, S.; Tariq, M.A.; Patlolla, S.R.; Ali, J.; et al. An overview of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) pathogenesis, classification, and management. Cureus 2022, 14, e30330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisetsky, D.S.; Lipsky, P.E. New insights into the role of antinuclear antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsokos, G.C.; Lo, M.S.; Reis, P.C.; Sullivan, K.E. New insights into the immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 716–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aringer, M.; Costenbader, K.; Daikh, D.; Brinks, R.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Smolen, J.S.; Wofsy, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuckle, M.R.; McClain, M.T.; Rubertone, M.V.; Scofield, R.H.; Dennis, G.J.; James, J.A.; Harley, J.B. Development of autoantibodies before the clinical onset of systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekvig, O.P. The anti-DNA antibody: Origin and impact, dogmas and controversies. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Ohmura, K.; Jin, H.; Naito, R.; Arase, N.; Kohyama, M.; Suenaga, T.; Sakakibara, S.; Kochi, Y.; Okada, Y.; et al. Anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies recognize DNA presented on HLA class II molecules of systemic lupus erythematosus risk alleles. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, C.; Chida, A.S.; Adlowitz, D.; Silver, L.; Fox, E.; Jenks, S.A.; Palmer, E.; Wang, Y.; Heimburg-Molinaro, J.; Li, Q.Z.; et al. Molecular basis of 9G4 B cell autoreactivity in human systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4926–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Bañuelos, E.; Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Cashman, K.S.; Paz, M.; Trejo-Zambrano, M.I.; Bugrovsky, R.; Wang, Y.; Chida, A.S.; Sherman-Baust, C.A.; et al. Affinity maturation generates pathogenic antibodies with dual reactivity to DNase1L3 and dsDNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uprety, L.P.; Park, Y.H.; Jang, Y.J. Autoantigen spermatid nuclear transition protein I enhances pro-inflammatory cytokine production stimulated by anti-DNA autoantibodies in macrophages. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2022, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcon-Segovia, D.; Ruiz-Arguelles, A.; Fishbein, E. Antibody to nuclear ribonucleoprotein penetrates live human mononuclear cells through Fc receptors. Nature 1978, 271, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcón-Segovia, D.; Llorente, L.; Fishbein, E.; Díaz-Jouanen, E. Abnormalities in the content of nucleic acids of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Relationship to DNA antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1982, 23, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlahakos, D.; Foster, M.H.; Ucci, A.A.; Barrett, K.J.; Datta, S.K.; Madaio, M.P. Murine monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies penetrate cells, bind to nuclei, and induce glomerular proliferation and proteinuria in vivo. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1992, 2, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zannikou, M.; Bellou, S.; Eliades, P.; Hatzioannou, A.; Mantzaris, M.D.; Carayanniotis, G.; Avrameas, S.; Lymberi, P. DNA-histone complexes as ligands amplify cell penetration and nuclear targeting of anti-DNA antibodies via energy-independent mechanisms. Immunology 2015, 147, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Kim, M.; Seo, Y.; Ham, Y.; Cho, M.Y.; Kwon, M.H. Cytosolic internalization of anti-DNA antibodies by human monocytes induces production of pro-inflammatory cytokines independently of the tripartite motif-containing 21 (TRIM21)-mediated pathway. Front. Immunol. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.Y.; Jeong, J.G.; Jun, H.R.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Kwon, M.H. A nucleic acid-hydrolyzing antibody penetrates into cells via caveolae-mediated endocytosis, localizes in the cytosol and exhibits cytotoxicity. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 1985–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.R.; Im, S.W.; Chung, H.Y.; Pravinsagar, P.; Jang, Y.J. Cell- and nuclear-penetrating anti-dsDNA autoantibodies have multiple arginines in CDR3 of VH and increase cellular level of pERK and Bcl-2 in mesangial cells. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 67, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, K.A.; Tømmerås, B.; Marion, T.N.; Rekvig, O.P. Pure anti-dsDNA mAbs need chromatin structures to promote glomerular mesangial deposits in BALB/c mice. Autoimmunity 2010, 43, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Makino, Y.; Inoue, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Hoshi, O.; Kubota, T. Anti-DNA antibodies cross-reactive with β2-glycoprotein I induce monocyte tissue factor through the TLR9 pathway. Immunol. Med. 2021, 44, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leadbetter, E.A.; Rifkin, I.R.; Hohlbaum, A.M.; Beaudette, B.C.; Shlomchik, M.J.; Marshak-Rothstein, A. Chromatin-IgG complexes activate B cells by dual engagement of IgM and Toll-like receptors. Nature 2002, 416, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillatreau, S.; Manfroi, B.; Dörner, T. Toll-like receptor signalling in B cells during systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Ishizawa, M.; Kubota, T. Monoclonal anti-dsDNA antibody 2C10 escorts DNA to intracellular DNA sensors in normal mononuclear cells and stimulates secretion of multiple cytokines implicated in lupus pathogenesis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 199, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virachith, S.; Saito, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Inoue, K.; Hoshi, O.; Kubota, T. Anti-β2-glycoprotein I antibody with DNA binding activity enters living monocytes via cell surface DNA and induces tissue factor expression. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 195, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Yan, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhou, B.; Wen, H.; Guo, D.; Zhou, F.; Wang, H. Toll-like receptor (TLR)-4 mediates anti-β2GPI/β2GPI-induced tissue factor expression in THP-1 cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 163, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, M.; Nii, T.; Trimova, G.; Miura, S.; Umezawa, K.; Kubota, T. The NF-κB specific inhibitor DHMEQ prevents thrombus formation in a mouse model of antiphospholipid syndrome. J. Nephropathol. 2013, 2, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, N.; Stock, A.D.; Putterman, C. Neuropsychiatric lupus: New mechanistic insights and future treatment directions. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, E. Autoantibodies in neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus (NPSLE): Can they be used as biomarkers for the differential diagnosis of this disease? Clin. Rev. Allerg. Immunol. 2022, 63, 194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamou, M.; Grodzki, A.C.; van Oostrum, M.; Wollscheid, B.; Lein, P.J. Fc gamma receptors are expressed in the developing rat brain and activate downstream signaling molecules upon cross-linking with immune complex. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Hoshi, O.; Kubota, T. Internalization of anti-DNA antibodies by rat brain cells: A possible pathogenetic mechanism of neuropsychiatric lupus. Med. Res. Arch. 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, A.O. Astrocytes imagined. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2022, 21, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R.E.; Nemeth, J.F.; Singh, S.; Lingham, R.B.; Grewal, I.S. Harnessing SLE autoantibodies for intracellular delivery of biologic therapeutics. Trends. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattray, Z.; Deng, G.; Zhang, S.; Shirali, A.; May, C.K.; Chen, X.; Cuffari, B.J.; Liu, J.; Zou, P.; Rattray, N.J.W.; et al. ENT2 facilitates brain endothelial cell penetration and blood-brain barrier transport by a tumor-targeting anti-DNA autoantibody. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e145875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruano-Salguero, J.S.; Lee, K.H. Antibody transcytosis across brain endothelial-like cells occurs nonspecifically and independent of FcRn. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takei, H.; Araki, A.; Watanabe, H.; Ichinose, A.; Sendo, F. Rapid killing of human neutrophils by the potent activator phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) accompanied by changes different from typical apoptosis or necrosis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1996, 59, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, T.A.; Abed, U.; Goosmann, C.; Hurwitz, R.; Schulze, I.; Wahn, V.; Weinrauch, Y.; Brinkmann, V.; Zychlinsky, A. Novel cell death program leads to neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 176, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Köckritz-Blickwede, M.; Goldmann, O.; Thulin, P.; Heinemann, K.; Norrby-Teglund, A.; Rohde, M.; Medina, E. Phagocytosis-independent antimicrobial activity of mast cells by means of extracellular trap formation. Blood 2008, 111, 3070–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, S.; Gold, J.A.; Andina, N.; Lee, J.J.; Kelly, A.M.; Kozlowski, E.; Schmid, I.; Straumann, A.; Reichenbach, J.; Gleich, G.J.; et al. Catapult-like release of mitochondrial DNA by eosinophils contributes to antibacterial defense. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, E.A.; He, X.Y.; Denorme, F.; Campbell, R.A.; Ng, D.; Salvatore, S.P.; Mostyka, M.; Baxter-Stolzfus, A.; Borczuk, A.C.; Loda, M.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to immmunothrombosis in COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome. Blood 2020, 136, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandpur, R.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; Vivekanandan-Giri, A.; Gizinski, A.; Yalavarthi, S.; Knight, J.S.; Friday, S.; Li, S.; Patel, R.M.; Subramanian, V.; et al. NETs are a source of citrullinated autoantigens and stimulate inflammatory responses in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 178ra40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lande, R.; Ganguly, D.; Facchinetti, V.; Frasca, L.; Conrad, C.; Gregorio, J.; Meller, S.; Chamilos, G.; Sebasigari, R.; Riccieri, V.; et al. Neutrophils activate plasmacytoid dendritic cells by releasing self-DNA–peptide complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 73ra19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Romo, G.S.; Caielli, S.; Vega, B.; Connolly, J.; Allantaz, F.; Xu, Z.; Punaro, M.; Baisch, J.; Guiducci, C.; Coffman, R.L.; et al. Netting neutrophils are major inducers of type I IFN production in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 73ra20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Avondt, K.; Fritsch-Stork, R.; Derksen, R.H.W.M.; Meyaard, L. Ligation of signal inhibitory receptor on leukocytes-1 suppresses the release of neutrophil extracellular traps in systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bont, C.M.; Boelens, W.C.; Pruijn, G.J.M. NETosis, complement, and coagulation: A triangular relationship. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foret, T.; Dufrost, V.; du Mont, L.S.; Costa, P.; Lakomy, C.; Lagrange, J.; Lacolley, P.; Regnault, V.; Zuily, S.; Wahl, D. A new pro-thrombotic mechanism of neutrophil extracellular traps in antiphospholipid syndrome: Impact on activated protein C resistance. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 2993–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünlü, O.; Zuily, S.; Erkan, D. The clinical significance of antiphospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 3, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalavarthi, S.; Gould, T.J.; Rao, A.N.; Mazza, L.F.; Morris, A.E.; Núñez-Álvarez, C.; Hernández-Ramírez, D.; Bockenstedt, P.L.; Liaw, P.C.; Cabral, A.R.; et al. Release on neutrophil extracellular traps by neutrophils stimulated with antiphospholipid antibodies. A newly identified mechanism of thrombosis in the antiphospholipid syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2990–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Yalavarthi, S.; Kanthi, Y.; Mazza, L.F.; Elfline, M.A.; Luke, C.E.; Pinsky, D.J.; Henke, P.K.; Knight, J.S. In vivo role of neutrophil extracellular traps in antiphospholipid antibody-mediated venous thrombosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Linden, M.; van den Hoogen, L.L.; Westerlaken, G.H.A.; Fritsch-Stork, R.D.E.; van Roon, J.A.G.; Radstake, T.R.D.J.; Meyaard, L. Neutrophil extracellular trap release is associated with antinuclear antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus and anti-phospholipid syndrome. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorch, S.K.; Kubes, P. An emerging role for neutrophil extracellular traps in noninfectious disease. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dam, L.S.; Kraaij, T.; Kamerling, S.W.A.; Bakker, J.A.; Scherer, U.H.; Rabelink, T.J.; van Kooten, C.; Teng, Y.K.O. Intrinsically distinct role of neutrophil extracellular trap formation in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis compared to systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 2047–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, H.; Ibrahim, N.; Klopf, J.; Zagrapan, B.; Mauracher, L.M.; Hell, L.; Hofbauer, T.M.; Ondracek, A.S.; Schoergenhofer, C.; Jilma, B.; et al. ELISA detection of MPO-DNA complexes in human plasma is error-prone and yields limited information on neutrophil extracellular traps formed in vivo. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matta, B.; Battaglia, J.; Barnes, B.J. Detection of neutrophil extracellular traps in patient plasma: Method development and validation in systemic lupus erythematosus and healthy donors that carry IRF5 genetic risk. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 951254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends, E.J.; van Dam, L.S.; Kraaij, T.; Kamerling, S.W.A.; Rabelink, T.J.; van Kooten, C.; Teng, Y.K.O. A high-throughput assay to assess and quantify neutrophil extracellular trap fprmation. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 143, e59150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeremic, I.; Djuric, O.; Nikolic, M.; Vlajnic, M.; Nikolic, A.; Radojkovic, D.; Bonaci-Nikolic, B. Neutrophil extracellular traps-associated markers are elevated in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol. Int. 2019, 39, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattanda, F.; Nakazawa, D.; Watanabe-Kusunoki, K.; Kusunoki, Y.; Shida, H.; Masuda, S.; Nishio, S.; Tomaru, U.; Atsumi, T.; Ishizu, A. The presence of anti-neutrophil extracellular trap antibody in patients with microscopic polyangiitis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Yalavarthi, S.; Gockman, K.; Madison, J.A.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Kahlenberg, J.M.; McCune, W.J.; Bockenstedt, P.L.; Karp, D.R.; Knight, J.S. Anti-neutrophil extracellular trap antibodies and impaired neutrophil extracellular trap degradation in antiphospholipid syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 2130–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Navaz, S.; Tsodikov, A.; Kmetova, K.; Kluge, L.; Ambati, A.; Hoy, C.K.; Yalavarthi, S.; de Andrade, D.; Tektonidou, M.G.; et al. Anti-neutrophil extracellular trap antibodies in antiphospholipid antibody-positive patients: Results from the Antiphospholipid Syndrome Alliance for Clinical Trials and InternatiOnal Networking clinical database and repository. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023, 75, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, M.; Wang, Z.; Bao, H.; Di, C.; Xia, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. Antibodies against neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) potentiate clinical performance of anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 249, 109297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antiochos, B.; Trejo-Zambrano, D.; Fenaroli, P.; Rosenberg, A.; Baer, A.; Garg, A.; Sohn, J.; Li, J.; Petri, M.; Goldman, D.W.; et al. The DNA sensors AIM2 and IFI16 are SLE autoantigens that bind neutrophil extracellular traps. eLife 2022, 11, e72103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, H.; Klopf, J.; Ibrahim, N.; Knöbl, V.; Sotir, A.; Mekis, R.; Nowikovsky, K.; Eilenberg, W.; Neumayer, C.; Brostjan, C. Quantitation of oxidized nuclear and mitochondrial DNA in plasma samples of patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 206, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, M.S.; Mistry, N.; Wood, C.; Herbert, K.E.; Lunec, J. Immunogenicity of DNA damaged by reactive oxygen species—Implications for anti-DNA antibodies in lupus. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 22, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, F.; Andreeva, L.; Knackstedt, L.S.; Streeck, R.; Frese, C.K.; Goosmann, C.; Hopfner, K.P.; Zychlinsky, A. The cytosolic DNA sensor cGAS recognizes neutrophil extracellular traps. Sci. Signal. 2021, 14, eaax7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, H.; Wojciak-Stothard, B.; Ruseva, M.M.; Cook, H.T.; Kelleher, P.; Pickering, M.C.; Mongkolsapaya, J.; Screaton, G.R.; Xu, X. Autoantibody-dependent amplification of inflammation in SLE. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patiño-Trives, A.M.; Pérez-Sánchez, C.; Pérez-Sánchez, L.; Luque-Tévar, M.; Ábalos-Aguilera, M.C.; Alcaide-Ruggiero, L.; Arias-de la Rosa, I.; Román-Rodríguez, C.; Seguí, P.; Espinosa, M.; et al. Anti-dsDNA antibodies increase the cardiovascular risk in systemic lupus erythematosus promoting a distinctive immune and vascular activation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 2417–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kubota, T. An Emerging Role for Anti-DNA Antibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216499
Kubota T. An Emerging Role for Anti-DNA Antibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(22):16499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216499
Chicago/Turabian StyleKubota, Tetsuo. 2023. "An Emerging Role for Anti-DNA Antibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 22: 16499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216499
APA StyleKubota, T. (2023). An Emerging Role for Anti-DNA Antibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(22), 16499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216499





