Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Aging Kidneys and Future Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
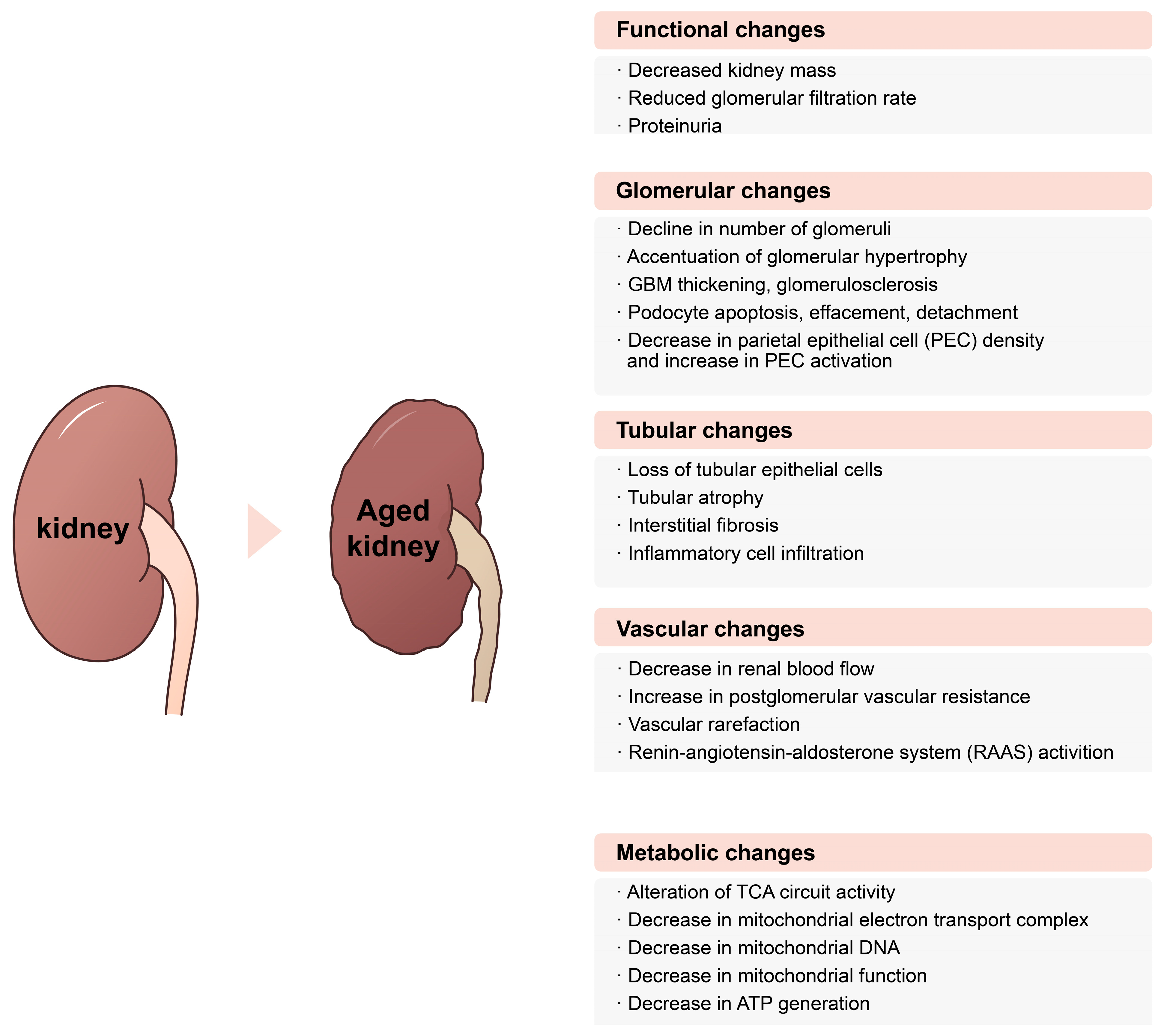
2. Functional Changes in Aging Kidneys and Measuring Kidney Function in Elderly People
Aging and Decline of Kidney Functions
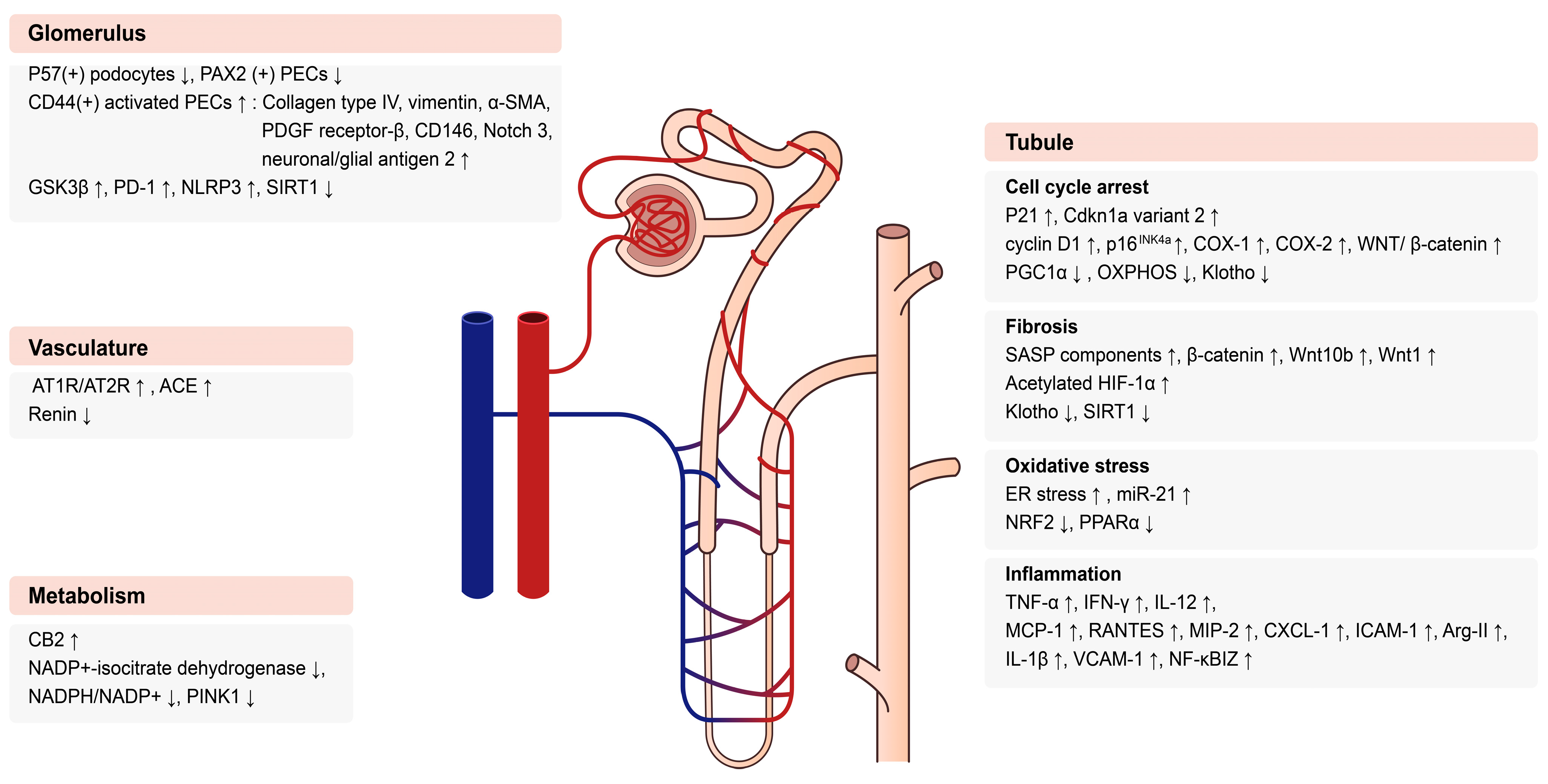
3. Molecular Mechanisms in Aging Kidneys
3.1. Glomerular Changes in Aging Kidneys
3.2. Tubular Changes in Aging Kidneys
3.2.1. Cell Cycle
3.2.2. Pro-Fibrotic Pathway
3.2.3. Oxidative Stress
3.2.4. Inflammation
3.3. Vascular Changes with Age
4. Metabolic Changes in Aging Kidney
5. Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harman, D. The Aging Process. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 7124–7128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, L.P. Epidemiology of Aging. Epidemiol. Rev. 2000, 22, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knickman, J.R.; Snell, E.K. The 2030 Problem: Caring for Aging Baby Boomers. Health Serv. Res. 2002, 37, 849–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puelles, V.G.; Huber, T.B. Kidneys Control Inter-Organ Homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 18, 207–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Yanagita, M. Renal Anemia: From Incurable to Curable. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2013, 305, F1239–F1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauchi, H.; Tsuboi, K.; Okutomi, J. Age Changes in the Human Kidney of the Different Races. Gerontology 1971, 17, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denic, A.; Lieske, J.C.; Chakkera, H.A.; Poggio, E.D.; Alexander, M.P.; Singh, P.; Kremers, W.K.; Lerman, L.O.; Rule, A.D. The Substantial Loss of Nephrons in Healthy Human Kidneys with Aging. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.F.; Shock, N.W. Age Changes in Glomerular Filtration Rate, Effective Renal Plasma Flow, and Tubular Excretory Capacity in Adult Males. J. Clin. Investig. 1950, 29, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bonventre, J.V.; Parrish, A.R. The Aging Kidney: Increased Susceptibility to Nephrotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 15358–15376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Chronic Kidney Disease (Ckd) Surveillance System. CDC. Available online: https://nccd.cdc.gov/ckd/default.aspx (accessed on 4 October 2023).
- Hill, N.R.; Fatoba, S.T.; Oke, J.L.; Hirst, J.A.; O’Callaghan, C.A.; Lasserson, D.S.; Hobbs, F.D.R. Global Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.A.; Ban, T.H.; Kang, C.Y.; Hwang, S.D.; Choi, S.R.; Lee, H.; Jung, H.Y.; Kim, K.; Kwon, Y.E.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Trends in Epidemiologic Characteristics of End-Stage Renal Disease from 2019 Korean Renal Data System (Kords). Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 40, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnak, M.J.; Levey, A.S.; Schoolwerth, A.C.; Coresh, J.; Culleton, B.; Hamm, L.L.; McCullough, P.A.; Kasiske, B.L.; Kelepouris, E. Kidney Disease as a Risk Factor for Development of Cardiovascular Disease: A Statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology; Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation 2003, 108, 2154–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, L.A.; Li, S.; Wang, C.; Huang, C.; Becker, B.N.; Bomback, A.S.; Brown, W.W.; Burrows, N.R.; Jurkovitz, C.T.; McFarlane, S.I. Prevalence of Ckd and Comorbid Illness in Elderly Patients in the United States: Results from the Kidney Early Evaluation Program (Keep). Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 55, S23–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nicola, L.; Donfrancesco, C.; Minutolo, R.; Noce, C.L.; Palmieri, L.; De Curtis, A.; Iacoviello, L.; Zoccali, C.; Gesualdo, L.; Conte, G. Prevalence and Cardiovascular Risk Profile of Chronic Kidney Disease in Italy: Results of the 2008–12 National Health Examination Survey. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, N.; Jakob, O.; Gaedeke, J.; Van Der Giet, M.; Kuhlmann, M.K.; Martus, P.; Mielke, N.; Schuchardt, M.; Tölle, M.; Wenning, V. Prevalence of Reduced Kidney Function and Albuminuria in Older Adults: The Berlin Initiative Study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brück, K.; Stel, V.S.; Gambaro, G.; Hallan, S.; Völzke, H.; Ärnlöv, J.; Kastarinen, M.; Guessous, I.; Vinhas, J.; Stengel, B. Ckd Prevalence Varies across the European General Population. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 2135–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, P.; Jalal, K.; Gupta, A.; Carter, R.L.; Lohr, J.W. Progression of Kidney Disease in Elderly Stage 3 and 4 Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2017, 49, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polkinghorne, K.R.; Wolfe, R.; Jachno, K.M.; Wetmore, J.B.; Woods, R.L.; McNeil, J.J.; Nelson, M.R.; Reid, C.M.; Murray, A.M.; ASPREE Investigator Group. Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease in the Elderly Using the Aspirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly Study Cohort. Nephrology 2019, 24, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Kibria, G.M.; Crispen, R. Prevalence and Trends of Chronic Kidney Disease and Its Risk Factors among Us Adults: An Analysis of Nhanes 2003–2018. Prev. Med. Rep. 2020, 20, 101193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Nishi, H.; Inoue, R.; Ueda, S.; Nangaku, M. Chronic Kidney Disease Prevalence and Awareness in Middle Age and Young Old: Regional Comparative Study in Japan. Nephrology 2023, 28, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cognuck, S.Q.; de Almeida, L.F.; Reis, W.L.; Silva, M.S.; Almeida-Pereira, G.; Zorro, S.V.; Mecawi, A.S.; Coimbra, T.M.; Elias, L.L.K.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J. Alterations in Kidney Structures Caused by Age Vary According to Sex and Dehydration Condition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dybiec, J.; Szlagor, M.; Młynarska, E.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. Structural and Functional Changes in Aging Kidneys. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallappallil, M.; Friedman, E.A.; Delano, B.G.; McFarlane, S.I.; Salifu, M.O. Chronic Kidney Disease in the Elderly: Evaluation and Management. Clin. Pract. 2014, 11, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, M.J.; Kim, J.E.; Bae, S.Y.; Cho, E.; Ahn, S.Y.; Kwon, Y.J.; Ko, G.-J. Impaired Nrf2 Inhibits Recovery from Ischemic Reperfusion Injury in the Aging Kidney. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greka, A.; Mundel, P. Cell Biology and Pathology of Podocytes. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2012, 74, 299–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeder, S.S.; Stefanska, A.; Eng, D.G.; Kaverina, N.; Sunseri, M.W.; McNicholas, B.A.; Rabinovitch, P.; Engel, F.B.; Daniel, C.; Amann, K.; et al. Changes in Glomerular Parietal Epithelial Cells in Mouse Kidneys with Advanced Age. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2015, 309, F164–F178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiggins, J.E. Aging in the Glomerulus. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2012, 67, 1358–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Chen, B.; Liu, Z.; Gong, A.Y.; Gunning, W.T.; Ge, Y.; Malhotra, D.; Gohara, A.F.; Dworkin, L.D.; Gong, R. Age-Related Gsk3 Β Overexpression Drives Podocyte Senescence and Glomerular Aging. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e141848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beurel, E.; Grieco, S.F.; Jope, R.S. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (Gsk3): Regulation, Actions, and Diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 148, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, P.Y.; Cai, W.; Li, X.; Fang, L.; Xu, J.; Yacoub, R.; He, J.C.; Lee, K. Reduction in Podocyte Sirt1 Accelerates Kidney Injury in Aging Mice. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2017, 313, F621–F628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pippin, J.W.; Kaverina, N.; Wang, Y.; Eng, D.G.; Zeng, Y.; Tran, U.; Loretz, C.J.; Chang, A.; Akilesh, S.; Poudel, C. Upregulated Pd-1 Signaling Antagonizes Glomerular Health in Aged Kidneys and Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e156250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaverina, N.; Schweickart, R.A.; Chan, G.C.; Maggiore, J.C.; Eng, D.G.; Zeng, Y.; McKinzie, S.R.; Perry, H.S.; Ali, A.; O’Connor, C. Inhibiting Nlrp3 Signaling in Aging Podocytes Improves Their Life-and Health-Span. Aging 2023, 15, 6658–6689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, F.; Yu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. C/Ebpalpha Deficiency in Podocytes Aggravates Podocyte Senescence and Kidney Injury in Aging Mice. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Hickson, L.J.; Eirin, A.; Kirkland, J.L.; Lerman, L.O. Cellular Senescence: The Good, the Bad and the Unknown. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 18, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herranz, N.; Gil, J. Mechanisms and Functions of Cellular Senescence. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.C.; Zager, R.A. Plasma and Urinary P21: Potential Biomarkers of Aki and Renal Aging. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2018, 315, F1329–F1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Domínguez, J.A.; Rodríguez-López, S.; Ahumada-Castro, U.; Desprez, P.-Y.; Konovalenko, M.; Laberge, R.-M.; Cárdenas, C.; Villalba, J.M.; Campisi, J. Cdkn1a Transcript Variant 2 Is a Marker of Aging and Cellular Senescence. Aging 2021, 13, 13380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkenkamp, B.; Susnik, N.; Baisantry, A.; Kuznetsova, I.; Jacobi, C.; Sörensen-Zender, I.; Broecker, V.; Haller, H.; Melk, A.; Schmitt, R. In Vivo and in Vitro Analysis of Age-Associated Changes and Somatic Cellular Senescence in Renal Epithelial Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melk, A.; Schmidt, B.M.W.; Takeuchi, O.; Sawitzki, B.; Rayner, D.C.; Halloran, P.F. Expression of P16ink4a and Other Cell Cycle Regulator and Senescence Associated Genes in Aging Human Kidney. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melk, A.; Kittikowit, W.; Sandhu, I.; Halloran, K.M.; Grimm, P.; Schmidt, B.M.W.; Halloran, P.F. Cell Senescence in Rat Kidneys in Vivo Increases with Growth and Age Despite Lack of Telomere Shortening. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 2134–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Liu, J.; Niu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, W.; Luo, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Yang, P. Wnt/Β-Catenin/Ras Signaling Mediates Age-Related Renal Fibrosis and Is Associated with Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e13004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Tao, J.; Gu, X.; Yu, Z.; Wang, R.; Zuo, G.; Li, Q.; Lv, X.; Miao, D. P16 Ink4a Deletion Ameliorated Renal Tubulointerstitial Injury in a Stress-Induced Premature Senescence Model of Bmi-1 Deficiency. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Y. Cellular Senescence in Kidney Fibrosis: Pathologic Significance and Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 601325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erben, R.G.; Andrukhova, O. Fgf23-Klotho Signaling Axis in the Kidney. Bone 2017, 100, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, H.; Doi, S.; Nakashima, A.; Ike, T.; Maeoka, Y.; Sasaki, K.; Doi, T.; Masaki, T. Klotho Overexpression Protects against Renal Aging Along with Suppression of Transforming Growth Factor-Β1 Signaling Pathways. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2021, 321, F799–F811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, D.R.; Yu, M.R.; Kong, K.H.; Kim, H.; Kwon, S.H.; Jeon, J.S.; Han, D.C.; Noh, H. Sirt1–Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Interaction Is a Key Mediator of Tubulointerstitial Damage in the Aged Kidney. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, I.; Russo, G.; Curcio, F.; Bulli, G.; Aran, L.; Della-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Testa, G.; Cacciatore, F.; Bonaduce, D.; et al. Oxidative Stress, Aging, and Diseases. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Murakami, S.; Matsumaru, D.; Kawauchi, T.; Nabeshima, Y.-I.; Motohashi, H. Nrf2 Pathway Activation Attenuates Ageing-Related Renal Phenotypes Due to A-Klotho Deficiency. J. Biochem. 2022, 171, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez-Exposito, L.; Tejedor-Santamaria, L.; Valentijn, F.A.; Tejera-Muñoz, A.; Rayego-Mateos, S.; Marchant, V.; Rodrigues-Diez, R.R.; Rubio-Soto, I.; Knoppert, S.N.; Ortiz, A. Oxidative Stress and Cellular Senescence Are Involved in the Aging Kidney. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, D.; Liu, D.; Sun, X.; Feng, Z.; Chen, X. The Transcription Factor Nrf2 Might Be Involved in the Process of Renal Aging. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 12, 5405–5411. [Google Scholar]
- Naghibi, N.; Sadeghi, A.; Movahedinia, S.; Naiini, M.R.; Rajizadeh, M.A.; Bahri, F.; Nazari-Robati, M. Ellagic Acid Ameliorates Aging-Induced Renal Oxidative Damage through Upregulating Sirt1 and Nrf2. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Chang, Z.-Y.; Tsai, F.-J.; Chen, S.-Y. Resveratrol Pretreatment Ameliorates Concanavalin a-Induced Advanced Renal Glomerulosclerosis in Aged Mice through Upregulation of Sirtuin 1-Mediated Klotho Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Lan, R.S.; Huang, R.; Feng, H.; Kumar, R.; Dayal, S.; Chan, K.-S.; Dai, D.-F. Glutathione Peroxidase-1 Overexpression Reduces Oxidative Stress, and Improves Pathology and Proteome Remodeling in the Kidneys of Old Mice. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Cao, T.; Chen, E.; Li, Y.; Lei, W.; Hu, Y.; He, B.; Liu, S. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Oxidative Stress in Inflammatory Diseases. DNA Cell Biol. 2022, 41, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, R.; Huang, L.; Zheng, Z.; Vlassara, H.; Striker, G.; Zhang, X.; Guan, Y.; Zheng, F. Excessive Oxidative Stress Contributes to Increased Acute Er Stress Kidney Injury in Aged Mice. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 2746521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.W.; Lee, E.K.; Lee, M.K.; Oh, G.T.; Yu, B.P.; Chung, H.Y. Impairment of Pparα and the Fatty Acid Oxidation Pathway Aggravates Renal Fibrosis During Aging. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 1223–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, J.; Sousa-Victor, P. Regulation of Inflammation as an Anti-Aging Intervention. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M.; Tian, Z.; Ma, K.; Li, Y.; Wang, L. Moussa Ide Nasser, and Chi Liu. The Diseased Kidney: Aging and Senescent Immunology. Immun. Ageing 2022, 19, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooman, J.P.; Dekker, M.J.; Usvyat, L.A.; Kotanko, P.; van der Sande, F.M.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; Shiels, P.G.; Stenvinkel, P. Inflammation and Premature Aging in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2017, 313, F938–F950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-G.; Yang, J.; Ko, Y.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Oh, S.W.; Cho, W.Y.; Jo, S.-K. Impact of Aging on Transition of Acute Kidney Injury to Chronic Kidney Disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, R.; Torreggiani, M.; Ting, A.; Xiong, H.; Striker, G.E.; Vlassara, H.; Zheng, F. Induction of Diabetes in Aged C57b6 Mice Results in Severe Nephropathy: An Association with Oxidative Stress, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Inflammation. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 2163–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Liang, X.; Ladeiras, D.; Fellay, B.; Ming, X.F.; Yang, Z. Role of Tubular Epithelial Arginase-Ii in Renal Inflammaging. Npj Aging Mech. Dis. 2021, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.W.; Jeong, H.O.; Lee, B.; Park, D.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, E.K.; Kim, K.M.; Park, J.W.; Yu, B.P. Involvement of Nf-Κbiz and Related Cytokines in Age-Associated Renal Fibrosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, L.; JaIacovoni, S.; Martini, H.; Bellière, J.; Maggiorani, D.; Dutaur, M.; Marsal, D.J.; Decaunes, P.; Pizzinat, N.; Mialet-Perez, J. Kidney Inflammaging Is Promoted by Ccr2+ Macrophages and Tissue-Derived Micro-Environmental Factors. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 3485–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Gao, X.; Deng, H. Ap-1 Is a Regulatory Transcription Factor of Inflammaging in the Murine Kidney and Liver. Aging Cell 2023, 22, e13858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindeman, R.D. Renal and Urinary Tract Function. In Encyclopedia of Gerontology, 2nd ed.; Birren, J.E., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 424–433. [Google Scholar]
- Long, D.A.; Mu, W.; Price, K.L.; Johnson, R.J. Blood Vessels and the Aging Kidney. Nephron Exp. Nephrol. 2005, 101, e95–e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.; Rennke, H.G.; Zatz, R. Glomerular Adaptations with Normal Aging and with Long-Term Converting Enzyme Inhibition in Rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 267 Pt 2, F35–F43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.E.; Choi, B.S. The Renin-Angiotensin System and Aging in the Kidney. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2014, 29, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamatani, H.; Eng, D.G.; Kaverina, N.V.; Gross, K.W.; Freedman, B.S.; Pippin, J.W.; Shankland, S.J. Lineage Tracing Aged Mouse Kidneys Shows Lower Number of Cells of Renin Lineage and Reduced Responsiveness to Raas Inhibition. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2018, 315, F97–F109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, F.F.; Kennefick, T.M.; Ingelfinger, J.R.; Vora, J.P.; Anderson, S. Down-Regulation of the Intrarenal Renin-Angiotensin System in the Aging Rat. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1995, 5, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, I.H.; Zhou, M.-S.; Treuer, A.V.; Chadipiralla, K.; Hare, J.M.; Raij, L. Altered Renal Expression of Angiotensin Ii Receptors, Renin Receptor, and Ace-2 Precede the Development of Renal Fibrosis in Aging Rats. Am. J. Nephrol. 2010, 32, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, Q.N.; Drummond, G.R.; Kemp-Harper, B.K.; Diep, H.; De Silva, T.M.; Kim, H.A.; Vinh, A.; Robertson, A.A.B.; Cooper, M.A.; Mansell, A. Pressor Response to Angiotensin Ii Is Enhanced in Aged Mice and Associated with Inflammation, Vasoconstriction and Oxidative Stress. Aging 2017, 9, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, I.-A.; Kim, E.N.; Lim, J.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Ban, T.H.; Yoon, H.E.; Park, C.W.; Chang, Y.S.; Choi, B.S. Effects of Resveratrol on the Renin-Angiotensin System in the Aging Kidney. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogi, M. Effect of Renin–Angiotensin System on Senescence. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2020, 20, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, E.; Lee, J.; Han, J.; Lee, S.-M.; Kwon, K.-S.; Hwang, G.-S. Glutathione Is an Aging-Related Metabolic Signature in the Mouse Kidney. Aging 2021, 13, 21009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.; Qi, L.; Hu, L.; Hu, D.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhao, C.; Wu, H. Changes in Aging-Induced Kidney Dysfunction in Mice Based on a Metabolomics Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 959311. [Google Scholar]
- Yarian, C.S.; Toroser, D.; Sohal, R.S. Aconitase Is the Main Functional Target of Aging in the Citric Acid Cycle of Kidney Mitochondria from Mice. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2006, 127, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, J.B.; Haigis, M.C. The Multifaceted Contributions of Mitochondria to Cellular Metabolism. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liu, C.; Jiang, N.; Liu, Y.; Luo, S.; Li, C.; Zhao, H.; Han, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, L. Mitochondrial Homeostasis: A Potential Target for Delaying Renal Aging. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1191517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choksi, K.B.; Nuss, J.E.; Boylston, W.H.; Rabek, J.P.; Papaconstantinou, J. Age-Related Increases in Oxidatively Damaged Proteins of Mouse Kidney Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain Complexes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 1423–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averina, O.A.; Permyakov, O.A.; Emelianova, M.A.; Guseva, E.A.; Grigoryeva, O.O.; Lovat, M.L.; Egorova, A.E.; Grinchenko, A.V.; Kumeiko, V.V.; Marey, M.V. Kidney-Related Function of Mitochondrial Protein Mitoregulin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, M.H.; Kim, M.S.; An, H.-J.; Sung, M.-J.; Lee, Y.H.; Yang, D.-H.; Jung, S.H.; Baek, J.; Choi, Y.; Taylor, D.M. Pten-Induced Kinase 1 Is Associated with Renal Aging, Via the Cgas-Sting Pathway. Aging Cell 2023, 22, e13865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Ling, X.; Meng, P.; Liang, Y.; Shen, K.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y. Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Plays a Central Role in Renal Tubular Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Kidney Ageing. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 8957–8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.M.-W.; He, J.C. Aged Glomeruli: A Link between Pd-1 and Podocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e162330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinning, J.; Funk, N.D.; Soerensen-Zender, I.; Wulfmeyer, V.C.; Liao, C.M.; Haller, H.; Hinze, C.; Schmidt-Ott, K.M.; Melk, A.; Schmitt, R. The Aging Kidney Is Characterized by Tubuloinflammaging, a Phenotype Associated with Mhc-Ii Gene Expression. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1222339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, D.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, C.; Lin, Y.; Sun, L.; Zheng, Y. Assessing the Effects of Aging on the Renal Endothelial Cell Landscape Using Single-Cell Rna Sequencing. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1175716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No | Author (Study Year) | Region | Cohort | Elderly Population (≥65 Years)/Total Population | Age of Participants (Years) | CKD Definition | CKD Prevalence | Correlation with Aging | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Stevens et al. [14] (2010) | US | KEEP (2000–2008) NHANES (1999–2006) Medicare 5% sample (2006) | KEEP: 27,017/107,309 NHANES: 5538/41,474 Medicare 5% 2006: 1,236,946/1,479,818 | ≥65 | KEEP, NHANES: eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (MDRD)oralbuminuria (ACR ≥ 30 mg/g) Medicare 5% sample: ICD-9-CM CKD | KEEP: 43.6% NHANES: 44.2% Medicare 5%: 6.5% | age (y) | KEEP | NHANES | Medicare |
| 65–74 (%) | 61.9 | 55.0 | 50.8 | ||||||||
| 75–59 (%) | 20.9 | 20.4 | 20.7 | ||||||||
| ≥ 80 (%) | 17.1 | 24.6 | 28.5 | ||||||||
| 2 | Nicola et al. [15] (2015) | Italy | OEC/HES-CARHES | -/7552 | 35–79 | Early stages CKD G1/G2 A2–3 Advanced stage CKD (≥G3): eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (CKD EPI) | G1 & G2: 4.16% G3a-G5: 2.89% | CKD prevalence across age strata: 35–49 years: 2.7% 50–59 years: 3.4% 60–69 years: 8.7% 70–79 years: 17.0% | |||
| 3 | Ebert et al. [16] (2016) | Germany | BIS with AOK-Nordost sample | 2069/2069 (≥70 years of age) | ≥70 | eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (CKD-EPI) | 39.3% | eGFR(CKD EPI) < 60 in each age group: 70–74 years: 16.6% 75–79 years: 28.3% 80–84 years: 47.3% 85–89 years: 57.9% ≥90 years: 76.2% | |||
| 4 | Bruck et al. [17] (2016) | Europe | 19 general population-based studies from 13 European countries | 64,137/189,171 | 20–74 | eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (CKD EPI) | 1.0–5.9% | CKD 3–5 prevalence in each age group: 20–44 years: 0.1–0.6% 45–64 years: 0.8–6.4% 65–74 years: 4.1–25.5% | |||
| 5 | Arora et al. [18] (2017) | USA | US Department of Veterans Affairs, VISN 2 | 9212/180,533 | ≥20 | eGFR 15–59 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 9.9% | CKD stage | Predicted progression rate | ||
| <1% | 1–4% | >4% | |||||||||
| 3a | 49.4% | 48.3% | 2.3% | ||||||||
| 3b | 61.8% | 37.7% | 0.5% | ||||||||
| 4 | 69.4% | 30.6% | 0 | ||||||||
| 6 | Polkinghorne et al. [19] (2019) | USA Australia | ASPREE | 17,762/17,762 | ≥65 | eGFR < 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2 (CKDEPI,BIS1) or UACR ≥ 3 mg/mmolwitheGFR ≥ 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 27% | CKD prevalence by age groups: 65–69 years: 3% 70–74 years: 44% 75–79 years: 28% 80–84 years: 19% ≥85 years: 7% | |||
| 7 | Kibria, Crispen [20] (2020) | USA | NHANES (2003–2018) | -/39,569 | ≥20 | eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (CKD EPI) or UACR ≥ 30 mg/g | 18% | Age with CKD Prevalence (OR) 20–39 years: reference 40–59 years: 1.5 ≥60 years: 5.9 | |||
| 8 | Li et al. [21] (2023) | Japan | 6th NDB Open Data Japan 2019 database | -/approximately 29.4 million | 40–74 | eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2,dipstickproteinuria ≥ 1+ | CKD G3-G5: 11.1% Proteinuria ≥ 1+: 3.72% | Age was positively correlated with prevalence of lower eGFR (r = 0.716, p < 0.0001) Correlation coefficient between age and prevalence of proteinuria was very low (r = 0.196, p < 0.001) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jo, M.-J.; Lee, J.-K.; Kim, J.-E.; Ko, G.-J. Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Aging Kidneys and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316912
Jo M-J, Lee J-K, Kim J-E, Ko G-J. Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Aging Kidneys and Future Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(23):16912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316912
Chicago/Turabian StyleJo, Min-Jee, Joo-Kyung Lee, Ji-Eun Kim, and Gang-Jee Ko. 2023. "Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Aging Kidneys and Future Perspectives" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 23: 16912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316912
APA StyleJo, M.-J., Lee, J.-K., Kim, J.-E., & Ko, G.-J. (2023). Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Aging Kidneys and Future Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(23), 16912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316912







