Comparative Efficacy of ALK Inhibitors for Treatment-Naïve ALK-Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Central Nervous System Metastasis: A Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Overview
1.2. ALK Inhibitors
1.2.1. Crizotinib
1.2.2. Ceritinib
1.2.3. Alectinib
1.2.4. Brigatinib
1.2.5. Ensartinib
1.2.6. Lorlatinib
1.3. Current Insights and Future Prospects on Treatment Strategies for ALK-p NSCLC with BM
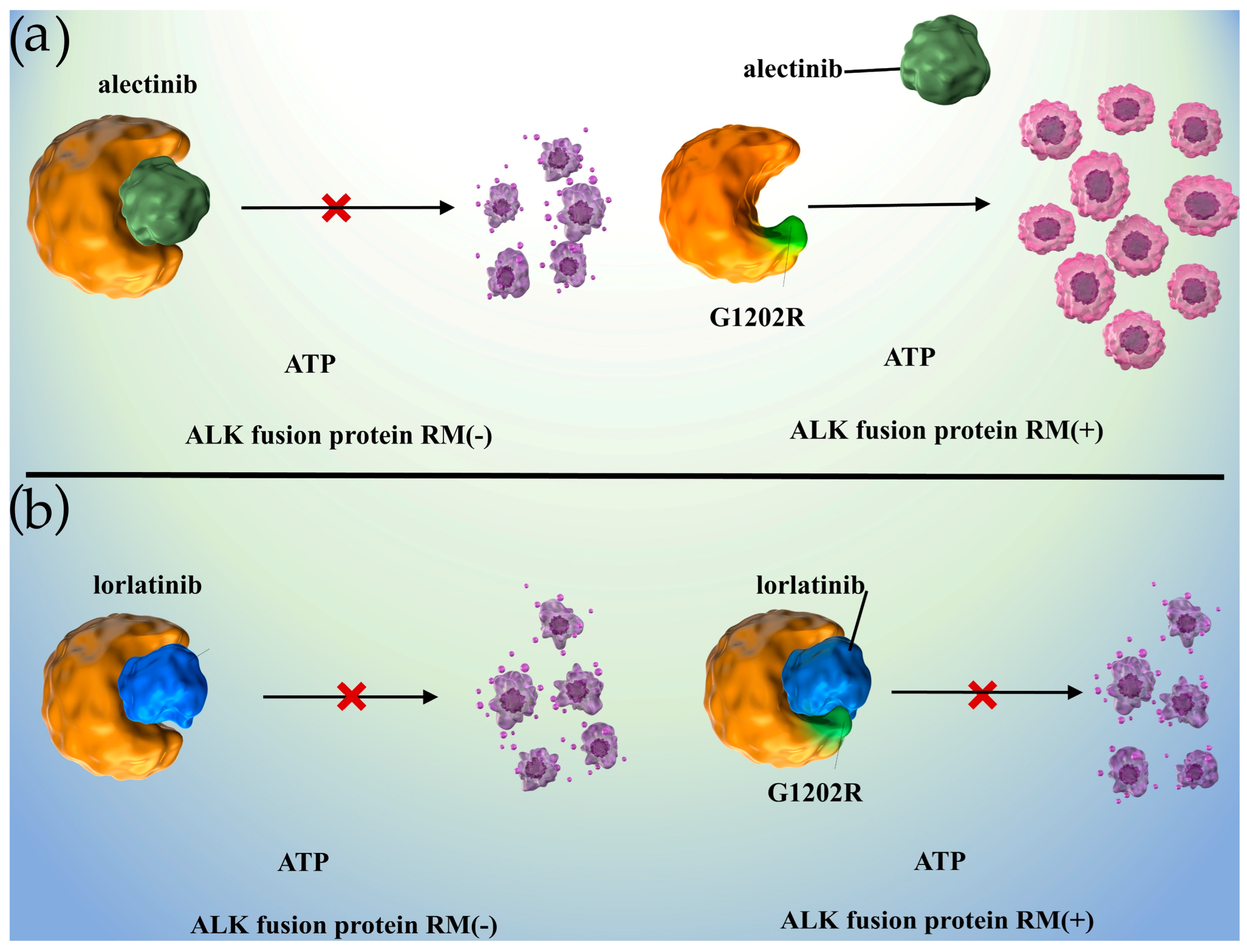
1.4. Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance to ALK Inhibitors and Prospects for Novel Strategies
1.5. Significance of the Present Meta-Analysis
2. Results
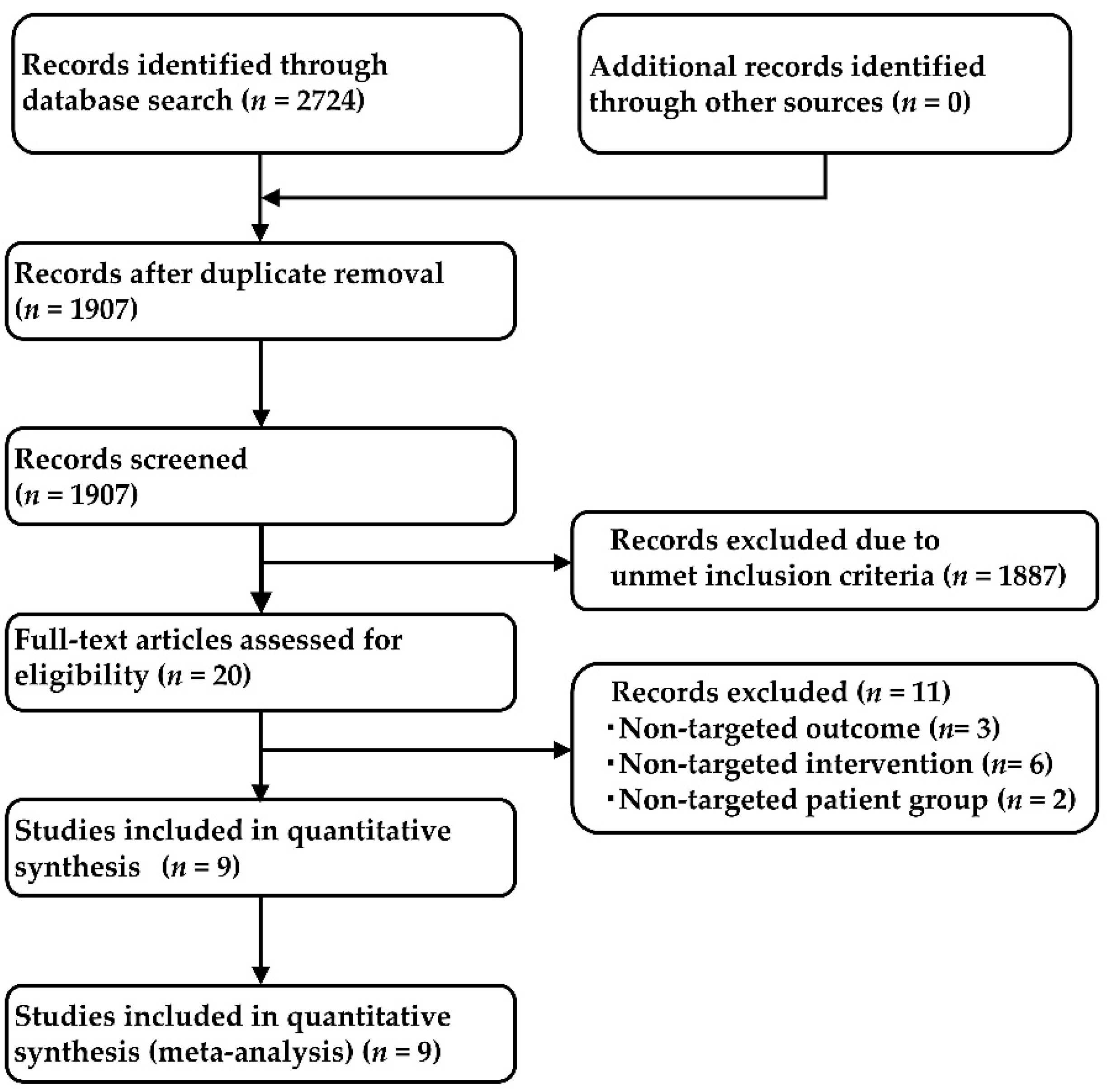
2.1. Systematic Review
2.2. Comparison of ALK Inhibitors by Generation
2.2.1. PFS in Overall Patients
2.2.2. PFS in a Subgroup of Patients with CNS Metastases
2.3. Comparison among ALK Inhibitors
2.3.1. PFS in Overall Patients
2.3.2. PFS in a Subgroup of Patients with CNS Metastases
2.3.3. PFS in Non-Asian Subgroup
2.3.4. PFS in Asian Subgroup
2.4. Evaluation of Bias
2.5. Sensitivity Analysis
2.6. Assessment of Study-to-Study Heterogeneity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Comprehensive Literature Search
4.2. Quality Assessment
4.3. Inclusion Criteria (Pre-Defined PICOS)
4.3.1. Patients
4.3.2. Intervention
4.3.3. Outcome
4.3.4. Study Design
4.4. Statistical Analysis
4.5. Sensitivity Analysis
4.6. Assessment for between-Study Heterogeneity
4.7. Ethical Aspects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Search Strategies in PubMed
| Search | Query | Results |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | (“Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer” OR “Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma” OR “Non Small Cell Lung Carcinoma” OR “Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma” OR “Non small Cell Lung Cancer” OR “Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinomas” OR “NSCLC”) | 95,433 |
| #2 | (“crizotinib” [ALL] OR (“crizotinib” [Supplementary Concept] OR “PF-02341066” [ALL] OR “PF 02341066” [ALL] OR “PF02341066” [ALL] OR “xalkori” [ALL] OR “ceritinib” [ALL] OR “ceritinib” [Supplementary Concept] OR “LDK-378” [ALL] OR “LDK 378” [ALL] OR “LDK378” [ALL] OR “zykadia” [ALL]) OR “alectinib” [ALL] OR (“alectinib” [Supplementary Concept] OR “CH-5424802” [ALL] OR “CH 5424802” [ALL] OR “CH5424802” [ALL] OR “RO-5424802” [ALL] OR “RO 5424802” [ALL] “RO5424802” [ALL] OR “alecensa” [ALL]) OR “brigatinib” [ALL] OR (“brigatinib” [Supplementary Concept] OR “AP-26113” [ALL] OR “AP 26113” [ALL] OR “AP26113” [ALL] OR “alunbrig” [ALL]) OR “lorlatinib” [ALL] OR (“lorlatinib” [Supplementary Concept] OR “PF-06463922” [ALL] OR “PF 06463922” [ALL] OR “PF06463922” [ALL] OR “lorbrena” [ALL]) OR “ensartinib” [ALL] OR (“ensartinib” [Supplementary Concept] OR “X-396” [ALL]) OR “cisplatin” [ALL] OR “cisplatin” [Supplementary Concept] OR “CDDP” [ALL] OR “carboplatin” [ALL] OR “carboplatin” [Supplementary Concept] OR “CBDCA” [ALL] OR “Platinum” [ALL]) | 141,836 |
| #3 | (“anaplastic lymphoma kinase” OR “ALK inhibitor” OR “ALK“ OR “ALKI”) | 14,355 |
| #4 | (“Randomized Controlled trial” [Title/Abstract] OR “Controlled clinical trial” [Title/Abstract] OR “Randomized” [Title/Abstract] OR “Placebo” [Title/Abstract] OR “Randomly” [Title/Abstract] OR “Trial” [Title/Abstract] OR “Drug Therapy” [Title/Abstract] OR ”Groups” [Title/Abstract]) | 3,510,441 |
| #5 | #1 AND #2 AND #3 AND #4 | 478 |
References
- The Japanese Lung Cancer Society Guideline. 2022. Available online: https://www.haigan.gr.jp/guideline/2022/ (accessed on 3 December 2022).
- Cognigni, V.; Pecci, F.; Lupi, A.; Pinterpe, G.; De Filippis, C.; Felicetti, C.; Cantini, L.; Berardi, R. The landscape of ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer: A comprehensive review of clinicopathologic, genomic characteristics, and therapeutic perspectives. Cancers 2022, 14, 4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duma, N.; Santana-Davila, R.; Molina, J.R. Non–small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, screening, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, T.; Kusumoto, S.; Ando, K.; Ohba, M.; Ohmori, T. Receptor tyrosine kinase-targeted cancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, M.; Sharma, G.G.; Manfroni, C.; Cortinovis, D.; Mologni, L. New advances in liquid biopsy technologies for anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)—Positive cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, D.; Nanni, I.; Ouafik, L.H.; Camilla, C.; Pellegrino, E.; Beaufils, N.; Greillier, L.; Dutau, H.; Astoul, P.; Kaspi, E.; et al. Comparison between immunocytochemistry, FISH and NGS for ALK and ROS1 rearrangement detection in cytological samples. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montella, M.; Ciani, G.; Granata, V.; Fusco, R.; Grassi, F.; Ronchi, A.; Cozzolino, I.; Franco, R.; Zito Marino, F.; Urraro, F.; et al. Preliminary experience of liquid biopsy in lung cancer compared to conventional assessment: Light and shadows. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jóri, B.; Falk, M.; Hövel, I.; Weist, P.; Tiemann, M.; Heukamp, L.C.; Griesinger, F. Acquired G2032R resistance mutation in ROS1 to lorlatinib therapy detected with liquid biopsy. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 6628–6634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanni, I.; Coco, S.; Truini, A.; Rusmini, M.; Dal Bello, M.G.; Alama, A.; Banelli, B.; Mora, M.; Rijavec, E.; Barletta, G.; et al. Next-generation sequencing workflow for NSCLC critical samples using a targeted sequencing approach by ion torrent PGM™ platform. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 28765–28782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Zhu, V.W.; Yoda, S.; Yeap, B.Y.; Schrock, A.B.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Jessop, N.A.; Jiang, G.Y.; Le, L.P.; Gowen, K.; et al. Impact of EML4-ALK variant on resistance mechanisms and clinical outcomes in ALK-positive lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, K.; Araki, M.; Sakashita, T.; Ma, B.; Kanada, R.; Yanagitani, N.; Horiike, A.; Koike, S.; Oh-Hara, T.; Watanabe, K.; et al. Prediction of ALK mutations mediating ALK-TKIs resistance and drug re-purposing to overcome the resistance. eBiomedicine 2019, 41, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, S.K.; Sharma, M.; Venur, V.A.; Schmitt, P.; Kotecha, R.; Chao, S.T.; Suh, J.H.; Angelov, L.; Mohammadi, A.M.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; et al. Impact of EGFR mutation and ALK rearrangement on the outcomes of non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastasis. Neurol. Oncol. 2020, 22, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gristina, V.; La Mantia, M.; Iacono, F.; Galvano, A.; Russo, A.; Bazan, V. The emerging therapeutic landscape of ALK inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, M.; Christopoulos, P. Therapeutic sequencing in ALK+ NSCLC. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán, T.; Quiroga, V.; Gil Mde, L.; Vilà, L.; Pardo, N.; Carcereny, E.; Capdevila, L.; Muñoz-Mármol, A.M.; Rosell, R. Targeting EML4-ALK driven non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2013, 2, 128–141. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Lei, Y.; Shi, X.; Wang, J. EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2022, 24, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, S.; Pashley, S.L.; O’Regan, L.; Khan, S.; Bayliss, R.; Fry, A.M. Alternative treatment options to ALK inhibitor monotherapy for EML4-ALK-driven lung cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chioureas, D.; Beck, J.; Baltatzis, G.; Vardaki, I.; Fonseca, P.; Tsesmetzis, N.; Vega, F.; Leventaki, V.; Eliopoulos, A.G.; Drakos, E.; et al. ALK+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL)-derived exosomes carry ALK signaling proteins and interact with tumor microenvironment. Cancers 2022, 14, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugrois, C.; Bessiere, C.; Dejean, S.; Anton-Leberre, V.; Commes, T.; Pyronnet, S.; Brousset, P.; Espinos, E.; Brugiere, L.; Meggetto, F.; et al. Gene expression signature associated with clinical outcome in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulf, A.M.; Moreno, M.M.; Paka, C.; Rampasekova, A.; Liu, K.J. Defining pathological activities of ALK in neuroblastoma, a neural crest-derived cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdura, S.; Encinar, J.A.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Joven, J.; Cuyàs, E.; Bosch-Barrera, J.; Menendez, J.A. Silibinin suppresses the hyperlipidemic effects of the ALK-tyrosine kinase inhibitor lorlatinib in hepatic cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, S.; Takahashi, K.; Iwakawa, R.; Matsuno, Y.; Nakanishi, Y.; Kohno, T.; Shimizu, E.; Yokota, J. Frequent EGFR mutations in brain metastases of lung adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 1491–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Xing, P.; Hao, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Shan, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Ma, K.; Dong, G.; et al. Intracranial efficacy of alectinib in ALK-positive NSCLC patients with CNS metastases-a multicenter retrospective study. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, F.; Lazzari, C.; Ardito, R.; Borgonovo, K.; Bulotta, A.; Conti, B.; Cabiddu, M.; Capitanio, J.F.; Brighenti, M.; Ghilardi, M.; et al. Efficacy of ALK inhibitors on NSCLC brain metastases: A systematic review and pooled analysis of 21 studies. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducray, S.P.; Natarajan, K.; Garland, G.D.; Turner, S.D.; Egger, G. The transcriptional roles of ALK fusion proteins in tumorigenesis. Cancers 2019, 11, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Mok, T.; Kim, D.W.; Wu, Y.L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; et al. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Lu, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Shi, Y.K.; Sriuranpong, V.; Ho, J.C.M.; Ong, C.K.; Tsai, C.M.; Chung, C.H.; et al. Results of PROFILE 1029, a Phase III Comparison of first-Line crizotinib versus Chemotherapy in East Asian Patients with ALK-Positive Advanced non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Koivunen, J.; Ogino, A.; Yanagita, M.; Nikiforow, S.; Zheng, W.; Lathan, C.; Marcoux, J.P.; Du, J.; Okuda, K.; et al. A novel ALK secondary mutation and EGFR signaling cause resistance to ALK kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6051–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, R.; Shaw, A.T.; Khan, T.M.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Solomon, B.J.; Halmos, B.; Jessop, N.A.; Wain, J.C.; Yeo, A.T.; Benes, C.; et al. Mechanisms of acquired crizotinib resistance in ALK-rearranged lung Cancers. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 120ra17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, T.; Tsukaguchi, T.; Yoshida, M.; Kondoh, O.; Sakamoto, H. Selective ALK inhibitor alectinib with potent antitumor activity in models of crizotinib resistance. Cancer Lett. 2014, 351, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Bauer, T.M.; de Marinis, F.; Felip, E.; Goto, Y.; Liu, G.; Mazieres, J.; Kim, D.W.; Mok, T.; Polli, A.; et al. First-line lorlatinib or crizotinib in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2018–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kim, H.R.; Ahn, M.J.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Han, J.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Hochmair, M.J.; Li, J.Y.; Chang, G.C.; Lee, K.H.; et al. Brigatinib versus crizotinib in ALK-Positive non–small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.W.; Ou, S.I.; Pérol, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in untreated ALK-positive non–small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.C.; Tan, D.S.W.; Chiari, R.; Wu, Y.L.; Paz-Ares, L.; Wolf, J.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Cortinovis, D.; Yu, C.J.; et al. First-line ceritinib versus platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (ASCEND-4): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2017, 389, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hida, T.; Nokihara, H.; Kondo, M.; Kim, Y.H.; Azuma, K.; Seto, T.; Takiguchi, Y.; Nishio, M.; Yoshioka, H.; Imamura, F.; et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (J-ALEX): An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Kim, S.W.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Yang, J.J.; Cheng, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Bu, L.; et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in untreated Asian patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ALESIA): A randomised phase 3 study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, K.; Manabe, R.; Kishino, Y.; Kusumoto, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Tanaka, A.; Ohmori, T.; Sagara, H. Comparative efficacy and safety of lorlatinib and alectinib for ALK-rearrangement positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer in Asian and non-Asian patients: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, K.; Akimoto, K.; Sato, H.; Manabe, R.; Kishino, Y.; Homma, T.; Kusumoto, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Tanaka, A.; Ohmori, T.; et al. Brigatinib and alectinib for ALK rearrangement-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer with or without central nervous system metastasis: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Cancers 2020, 12, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, L.; Wang, Z.; Wu, G.; Poddubskaya, E.; Mok, T.; Reck, M.; Wakelee, H.; Chiappori, A.A.; Lee, D.H.; Breder, V.; et al. Ensartinib vs crizotinib for patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small cell lung cancer: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1617–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgeel, S.; Peters, S.; Mok, T.; Shaw, A.T.; Kim, D.W.; Ou, S.I.; Pérol, M.; Wrona, A.; Novello, S.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus crizotinib in treatment-naive anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive (ALK+) non-small-cell lung cancer: CNS efficacy results from the ALEX study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2214–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishio, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Mitsudomi, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Tanaka, T.; Kuriki, H.; Zeaiter, A.; Tamura, T. Analysis of central nervous system efficacy in the J-ALEX study of alectinib versus crizotinib in ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2018, 121, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.W.; Richardson, P.F.; Bailey, S.; Brooun, A.; Burke, B.J.; Collins, M.R.; Cui, J.J.; Deal, J.G.; Deng, Y.L.; Dinh, D.; et al. Discovery of (10R)-7-amino-12-fluoro-2,10,16-trimethyl-15-oxo-10,15,16,17-tetrahydro-2H-8,4-(metheno)pyrazolo[4,3-h][2,5,11]-benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile (PF-06463922), a macrocyclic inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and c-ros oncogene 1 (ROS1) with preclinical brain exposure and broad-spectrum potency against ALK-resistant mutations. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4720–4744. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gadgeel, S.M.; Shaw, A.T.; Govindan, R.; Gandhi, L.; Socinski, M.A.; Camidge, D.R.; De Petris, L.; Kim, D.W.; Chiappori, A.; Moro-Sibilot, D.L.; et al. Pooled analysis of CNS response to alectinib in two studies of pretreated patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4079–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, E.; Odé, Z.; Derieppe, M.P.P.; Groenink, L.; Heymans, M.W.; Otten, R.; Lequin, M.H.; Janssens, G.O.R.; Hoving, E.W.; van Vuurden, D.G. Blood-brain barrier permeability following conventional photon radiotherapy—A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical and preclinical studies. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 35, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okawa, S.; Shibayama, T.; Shimonishi, A.; Nishimura, J.; Ozeki, T.; Takada, K.; Kayatani, H.; Minami, D.; Sato, K.; Fujiwara, K.; et al. Success of crizotinib combined with whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases in a patient with anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearrangement-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Case Rep. Oncol. 2018, 11, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Grinsven, E.E.; Nagtegaal, S.H.J.; Verhoeff, J.J.C.; van Zandvoort, M.J.E. The impact of stereotactic or whole brain radiotherapy on neurocognitive functioning in adult patients with brain metastases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2021, 44, 622–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, C.N.; Nowsheen, S.; Bonner, J.A.; Yang, E.S. Emerging roles of glycogen synthase kinase 3 in the treatment of brain tumors. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Okada, K.; Adachi, J.; Abe, Y.; Narumi, R.; Uchibori, K.; Yanagitani, N.; Koike, S.; Takagi, S.; Nishio, M.; et al. GSK3 inhibition circumvents and overcomes acquired lorlatinib resistance in ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.W.; Zhai, D.; Deng, W.; Zhang, X.; Ung, J.; Nguyen, V.; Zhang, H.; Barrera, M.; Parra, A.; Cowell, J.; et al. TPX-0131, a potent CNS-penetrant, next-generation inhibitor of wild-type ALK and ALK-resistant mutations. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.I.; Nagasaka, M.; Brazel, D.; Hou, Y.; Zhu, V.W. Will the clinical development of 4th-generation “double mutant active” ALK TKIs (TPX-0131 and NVL-655) change the future treatment paradigm of ALK+ NSCLC? Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanidou, O.; Landi, L.; Cappuzzo, F.; Califano, R. Overcoming resistance to first/second generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors and ALK inhibitors in oncogene-addicted advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2016, 8, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, M.M.; Shaw, A.T. ALK inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: Crizotinib and beyond. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 12, 429–439. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.J.; Riely, G.J.; Shaw, A.T. Targeting ALK: Precision medicine takes on drug resistance. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, X.; Niu, X.; Chang, L.; Chen, R.; Ou, S.I.; Lu, S. Next generation sequencing reveals a novel ALK G1128A mutation resistant to crizotinib in an ALK-Rearranged NSCLC patient. Lung Cancer 2018, 123, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, D.W.; Go, H.; Keam, B.; Lee, S.H.; Ku, J.L.; Chung, D.H.; Heo, D.S. Heterogeneity of genetic changes associated with acquired crizotinib resistance in ALK-rearranged lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagitani, N.; Uchibori, K.; Koike, S.; Tsukahara, M.; Kitazono, S.; Yoshizawa, T.; Horiike, A.; Ohyanagi, F.; Tambo, Y.; Nishikawa, S.; et al. Drug resistance mechanisms in Japanese anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small cell lung cancer and the clinical responses based on the resistant mechanisms. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friboulet, L.; Li, N.; Katayama, R.; Lee, C.C.; Gainor, J.F.; Crystal, A.S.; Michellys, P.Y.; Awad, M.M.; Yanagitani, N.; Kim, S.; et al. The ALK inhibitor ceritinib overcomes crizotinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, H.; Tsukaguchi, T.; Hiroshima, S.; Kodama, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Fukami, T.A.; Oikawa, N.; Tsukuda, T.; Ishii, N.; Aoki, Y. CH5424802, a selective ALK inhibitor capable of blocking the resistant gatekeeper mutant. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Anjum, R.; Squillace, R.; Nadworny, S.; Zhou, T.; Keats, J.; Ning, Y.; Wardwell, S.D.; Miller, D.; Song, Y.; et al. The potent ALK inhibitor brigatinib (AP26113) overcomes mechanisms of resistance to first- and second-generation ALK inhibitors in preclinical models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5527–5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Shaw, A.T. Emerging paradigms in the development of resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3987–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, R.; Lovly, C.M.; Shaw, A.T. Therapeutic targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in lung cancer: A paradigm for precision cancer medicine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gainor, J.F.; Dardaei, L.; Yoda, S.; Friboulet, L.; Leshchiner, I.; Katayama, R.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Gadgeel, S.; Schultz, K.; Singh, M.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of resistance to first- and second-generation ALK inhibitors in ALK-rearranged lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignatius Ou, S.H.; Azada, M.; Hsiang, D.J.; Herman, J.M.; Kain, T.S.; Siwak-Tapp, C.; Casey, C.; He, J.; Ali, S.M.; Klempner, S.J.; et al. Next-generation sequencing reveals a Novel NSCLC ALK F1174V mutation and confirms ALK G1202R mutation confers high-level resistance to alectinib (CH5424802/RO5424802) in ALK-rearranged NSCLC patients who progressed on crizotinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Makimoto, G.; Ohashi, K.; Tomida, S.; Nishii, K.; Matsubara, T.; Kayatani, H.; Higo, H.; Ninomiya, K.; Sato, A.; Watanabe, H.; et al. Rapid acquisition of alectinib resistance in ALK-positive lung cancer with high tumor mutation burden. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 2009–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehlman, C.; Chaabane, N.; Lacave, R.; Kerrou, K.; Ruppert, A.M.; Cadranel, J.; Fallet, V. Ceritinib ALK T1151R resistance mutation in lung cancer with initial response to brigatinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, e95–e96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, V.W.; Cui, J.J.; Fernandez-Rocha, M.; Schrock, A.B.; Ali, S.M.; Ou, S.I. Identification of a novel T1151K ALK mutation in a patient with ALK-rearranged NSCLC with prior exposure to crizotinib and ceritinib. Lung Cancer 2017, 110, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Rooney, M.; Lin, J.J.; Nagy, R.J.; Yeap, B.Y.; Hubbeling, H.; Chin, E.; Ackil, J.; Farago, A.F.; Hata, A.N.; et al. Treatment with next-generation ALK inhibitors fuels plasma ALK mutation diversity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6662–6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabari, J.K.; Santini, F.C.; Schram, A.M.; Bergagnini, I.; Chen, R.; Mrad, C.; Lai, W.V.; Arbour, K.C.; Drilon, A. The activity, safety, and evolving role of brigatinib in patients with ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancers. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recondo, G.; Mezquita, L.; Facchinetti, F.; Planchard, D.; Gazzah, A.; Bigot, L.; Rizvi, A.Z.; Frias, R.L.; Thiery, J.P.; Scoazec, J.Y.; et al. Diverse resistance mechanisms to the third-generation ALK inhibitor lorlatinib in ALK-rearranged lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyawaki, M.; Yasuda, H.; Tani, T.; Hamamoto, J.; Arai, D.; Ishioka, K.; Ohgino, K.; Nukaga, S.; Hirano, T.; Kawada, I.; et al. Overcoming EGFR bypass signal-induced acquired resistance to ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors in ALK-translocated lung cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouji, T.; Takashi, S.; Mitsuhiro, T.; Yukito, I. Crizotinib can overcome acquired resistance to CH5424802: Is amplification of the MET gene a key factor? J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, e27–e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Filho, S.N.M.; Li, M.; Fares, A.; Weiss, J.; Pham, N.A.; Ludkovski, O.; Raghavan, V.; Li, Q.; Ravi, D.; et al. BRAF V600E mutation and MET amplification as resistance pathways of the second-generation anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitor alectinib in lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2020, 146, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, T.; Ozasa, H.; Aoki, W.; Aburaya, S.; Funazo, T.; Furugaki, K.; Yoshimura, Y.; Ajimizu, H.; Okutani, R.; Yasuda, Y.; et al. Alectinib resistance in ALK-rearranged lung cancer by dual salvage signaling in a clinically paired resistance model. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovly, C.M.; McDonald, N.T.; Chen, H.; Ortiz-Cuaran, S.; Heukamp, L.C.; Yan, Y.; Florin, A.; Ozretić, L.; Lim, D.; Wang, L.; et al. Rationale for co-targeting IGF-1R and ALK in ALK fusion-positive lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lin, C.; Peng, T.; Hu, C.; Lu, C.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Han, R.; Feng, M.; Sun, F.; et al. Metformin reduces HGF-induced resistance to alectinib via the inhibition of Gab1. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesman, M.M.; Fojo, T.; Bates, S.E. Multidrug resistance in cancer: Role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuki, S.; Terasaki, T. Contribution of carrier-mediated transport systems to the blood-brain barrier as a supporting and protecting interface for the brain; importance for CNS drug discovery and development. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1745–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, I.; Zaorsky, N.G.; Palmer, J.D.; Mehra, R.; Lu, B. Targeting brain metastases in ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e510–e521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kort, A.; Sparidans, R.W.; Wagenaar, E.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schinkel, A.H. Brain accumulation of the EML4-ALK inhibitor ceritinib is restricted by P-glycoprotein (P-GP/ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2). Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 102, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, R.; Sakashita, T.; Yanagitani, N.; Ninomiya, H.; Horiike, A.; Friboulet, L.; Gainor, J.F.; Motoi, N.; Dobashi, A.; Sakata, S.; et al. P-glycoprotein mediates ceritinib resistance in anaplastic lymphoma kinase-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. eBiomedicine 2016, 3, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Gregg, J.P.; Ma, W.; Yoneda, K.; Moore, E.H.; Daly, M.E.; Zhang, Y.; Williams, M.J.; Li, T. Squamous cell transformation of primary lung adenocarcinoma in a patient with EML4-ALK fusion variant 5 refractory to ALK inhibitors. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2019, 17, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oya, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Uemura, T.; Murakami, Y.; Inaba, Y.; Hida, T. Serum ProGRP and NSE levels predicting small cell lung cancer transformation in a patient with ALK rearrangement-positive non-small cell lung cancer: A case report. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 4219–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Han, J.; Sun, J.M. Histologic transformation of ALK-rearranged adenocarcinoma to squamous cell carcinoma after treatment with ALK inhibitor. Lung Cancer 2019, 127, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Liao, X.H.; Wang, W.X.; Xu, C.W.; Zhuang, W.; Zhong, L.H.; Du, K.Q.; Chen, Y.P.; Chen, G.; Fang, M.Y. Patients harboring ALK rearrangement adenocarcinoma after acquired resistance to crizotinib and transformation to small-cell lung cancer: A case report. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 3187–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequist, L.V.; Waltman, B.A.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Digumarthy, S.; Turke, A.B.; Fidias, P.; Bergethon, K.; Shaw, A.T.; Gettinger, S.; Cosper, A.K.; et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 75ra26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederst, M.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Poirier, J.T.; Mermel, C.H.; Lockerman, E.L.; Garcia, A.R.; Katayama, R.; Costa, C.; Ross, K.N.; Moran, T.; et al. RB loss in resistant EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinomas that transform to small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 3 December 2022).
- Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials [CENTRAL]. Available online: https://www.cochranelibrary.com/ (accessed on 3 December 2022).
- Embase. Available online: https://www.embase.com/login (accessed on 3 December 2022).
- Scopus. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/home.uri (accessed on 3 December 2022).
- Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Copas, J.; Shi, J.Q. Meta-analysis, funnel plots and sensitivity analysis. Biostatistics 2000, 1, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chootrakool, H.; Shi, J.Q.; Yue, R. Meta-analysis and sensitivity analysis for multi-arm trials with selection bias. Stat. Med. 2011, 30, 1183–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Fong, T.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, J.; Luo, P. The efficacy and safety of ALK inhibitors in the treatment of ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer: A network meta-analysis. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 4993–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Hsieh, C.C.; Lee, Y.L.; Li, C.Y. Which should be used first for ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Chemotherapy or targeted therapy? A meta-analysis of five randomized trials. Medicina 2019, 55, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, H.; Lu, Y.; Hao, W.; Han, L. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: A meta-analysis. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, J.; Bai, Z.; Hsieh, S.C.; Kelly, S.E.; Chen, L.; Skidmore, B.; Yousef, S.; Zheng, C.; Stewart, D.J.; Wells, G.A. ALK inhibitors for non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, T.; Myung, S.K.; Pham, T.T.; Park, B. Efficacy of crizotinib, ceritinib, and alectinib in ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer treatment: A meta-analysis of clinical trials. Cancers 2020, 12, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.H.; Chen, H.L.; Chang, H.M.; Tsai, Y.C.; Wu, K.L.; Chen, I.H.; Chen, K.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, C.L.; et al. Systematic review and network meta-analysis of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitors for treatment-naïve ALK-positive lung cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.L.; Chen, H.L.; Tsai, Y.M.; Lee, T.H.; Chang, H.M.; Tsai, Y.C.; Chuang, C.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Tu, Y.K.; Yang, C.J.; et al. First-line anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitors for ALK-positive lung cancer in Asian populations: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sheng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Song, J.; Teng, L.; Liu, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, B.; Li, B. Comparison of lorlatinib, alectinib and brigatinib in ALK inhibitor–naive/untreated ALK-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. J. Chemother. 2022, 34, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.; Ioannidis, J. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate interventions: Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P.; et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: Checklist and explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salanti, G.; Ades, A.E.; Ioannidis, J.P. Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: An overview and tutorial. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoaglin, D.C.; Hawkins, N.; Jansen, J.P.; Scott, D.A.; Itzler, R.; Cappelleri, J.C.; Boersma, C.; Thompson, D.; Larholt, K.M.; Diaz, M.; et al. Conducting indirect-treatment-comparison and network-meta-analysis studies: Report of the ISPOR Task Force on Indirect Treatment Comparisons Good Research Practices: Part 2. Value Health 2011, 14, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, J.P.; Fleurence, R.; Devine, B.; Itzler, R.; Barrett, A.; Hawkins, N.; Lee, K.; Boersma, C.; Annemans, L.; Cappelleri, J.C. Interpreting indirect treatment comparisons and network meta-analysis for health-care decision making: Report of the ISPOR Task Force on Indirect Treatment Comparisons Good Research Practices: Part 1. Value Health 2011, 14, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ades, A.E.; Cliffe, S. Markov chain Monte Carlo estimation of a multiparameter decision model: Consistency of evidence and the accurate assessment of uncertainty. Med. Decis. Mak. 2002, 22, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Ades, A.E. Combination of direct and indirect evidence in mixed treatment comparisons. Stat. Med. 2004, 23, 3105–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, S.P.; Gelman, A. General methods for monitoring convergence of iterative simulations. J. Comp. Graph. Stat. 1998, 7, 434–455. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, S.P.; Roberts, G.O. Convergence assessment techniques for Markov chain Monte Carlo. Stat. Comput. 1998, 8, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ando, K.; Manabe, R.; Kishino, Y.; Kusumoto, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Tanaka, A.; Ohmori, T.; Sagara, H. Comparative Efficacy of ALK Inhibitors for Treatment-Naïve ALK-Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Central Nervous System Metastasis: A Network Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032242
Ando K, Manabe R, Kishino Y, Kusumoto S, Yamaoka T, Tanaka A, Ohmori T, Sagara H. Comparative Efficacy of ALK Inhibitors for Treatment-Naïve ALK-Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Central Nervous System Metastasis: A Network Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(3):2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032242
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndo, Koichi, Ryo Manabe, Yasunari Kishino, Sojiro Kusumoto, Toshimitsu Yamaoka, Akihiko Tanaka, Tohru Ohmori, and Hironori Sagara. 2023. "Comparative Efficacy of ALK Inhibitors for Treatment-Naïve ALK-Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Central Nervous System Metastasis: A Network Meta-Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 3: 2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032242
APA StyleAndo, K., Manabe, R., Kishino, Y., Kusumoto, S., Yamaoka, T., Tanaka, A., Ohmori, T., & Sagara, H. (2023). Comparative Efficacy of ALK Inhibitors for Treatment-Naïve ALK-Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Central Nervous System Metastasis: A Network Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(3), 2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032242







