The Regulation of Cyclins and Cyclin-Dependent Kinases in the Development of Gastric Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction to Gastric Cancer
1.1. General Epidemiology of Gastric Cancer
1.2. General Risk Factors for Gastric Cancer
1.3. Genetic Parameters Associated with Gastric Cancer
1.4. General Classification of Gastric Cancer
1.5. General Diagnosis and Therapies for Gastric Cancer
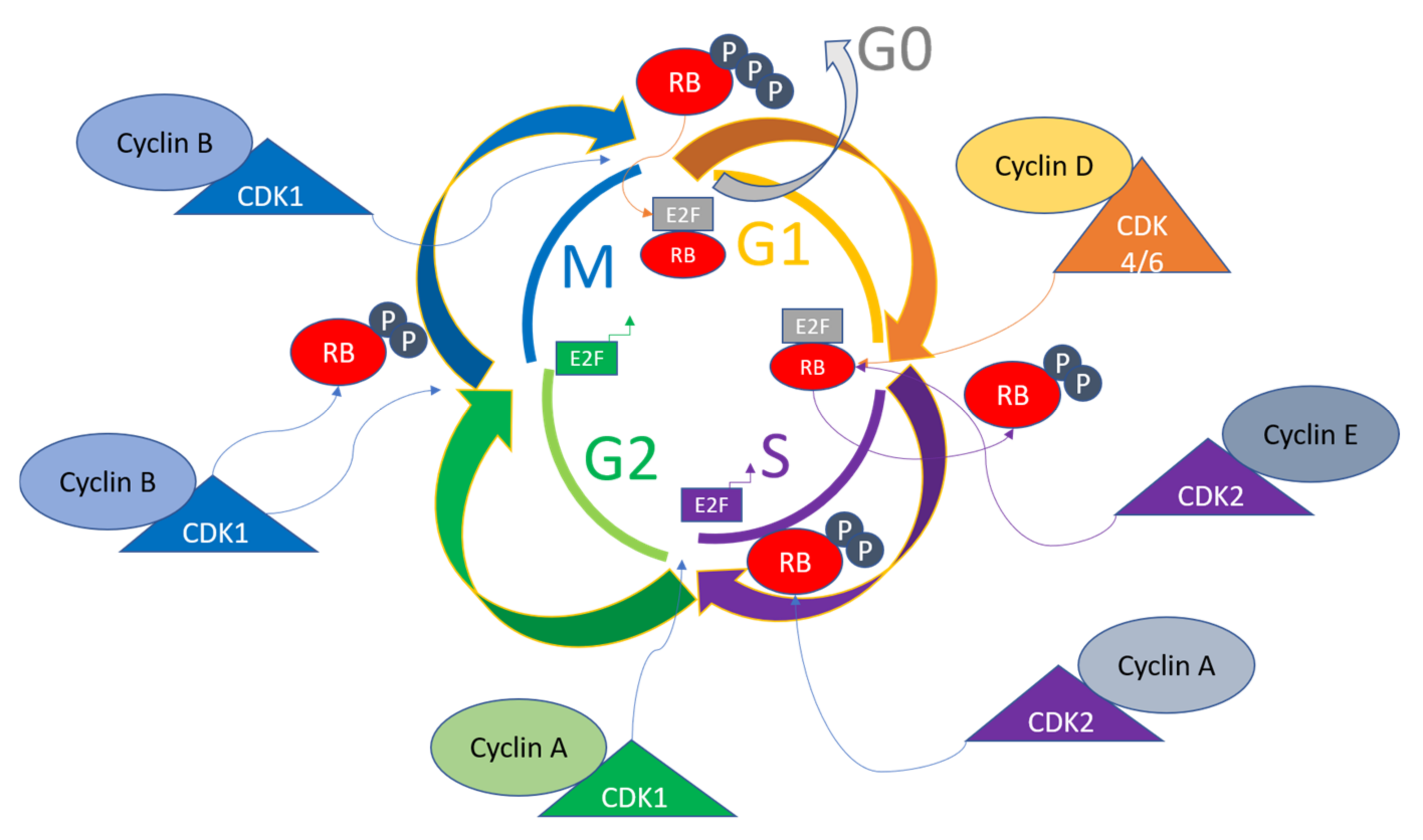
2. Overview of Cell Cycle Regulation
3. The Role of CDKs in Cell Cycle Control
4. The Regulation of Cyclins and CDKs in Gastric Cancer
4.1. The Regulation of Cyclin D1 in Gastric Cancer
4.1.1. Factors Downregulating Cyclin D1 in Gastric Cancer
4.1.2. Factors Upregulating Cyclin D1 in Gastric Cancer
4.2. The Regulation of CDK4/6 in Gastric Cancer
4.2.1. The Regulation of CDK4 in Gastric Cancer
4.2.2. The Regulation of CDK6 in Gastric Cancer
4.3. Cyclin E Regulation in Gastric Cancer
4.3.1. Cyclin E Expression Analyses in Gastric Cancer
4.3.2. Factors Regulating Cyclin E in Gastric Cancer Cells
4.4. Cyclin A and CDK2 Regulation in Gastric Cancer
4.4.1. Cyclin A Expression in Gastric Cancer
4.4.2. The Regulation of CDK2 in Gastric Cancer
4.5. The Regulation of Cyclin B/CDK1 Axis in Gastric Cancer
4.5.1. Cyclin B1 levels in Gastric Cancer
4.5.2. Cyclin B1 Regulation in Gastric Cancer
4.5.3. Regulation of CDK1 in Gastric Cancer
4.6. Natural Chemical Compounds against the Cyclin B/CDK1 axis in Gastric Cancer
4.7. Other Cyclins and CDKs Investigated in Gastric Cancer Cells
4.7.1. Other Cyclins in Gastric Cancer
4.7.2. Other CDKs in Gastric Cancer
5. Discussion and Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thrift, A.P.; El-Serag, H.B. Burden of Gastric Cancer. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamashima, C. The burden of gastric cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Shi, L.; He, X.; Luo, Y. Gastrointestinal cancers in China, the USA, and Europe. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2021, 9, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadri, Q.; Rasool, R.; Gulzar, G.M.; Naqash, S.; Shah, Z.A. H. pylori Infection, Inflammation and Gastric Cancer. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2014, 45, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentis, A.-F.A.; Boziki, M.; Grigoriadis, N.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric cancer biology: Tempering a double-edged sword. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 2477–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-Y.; Zhang, R.-G.; Duan, G.-C. Pathogenic mechanisms of the oncoprotein CagA in H. pylori-induced gastric cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 3087–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, M. Molecular Mechanism of Helicobacter pylori-Induced Gastric Cancer. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2021, 52, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, C.; Hu, J.; Su, R.; Zhang, J.; Han, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, Y. Molecular mechanism of Helicobacter pylori-induced autophagy in gastric cancer (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 6221–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Metz, D.C.; Ellenberg, S.; Kaplan, D.E.; Goldberg, D.S. Risk Factors and Incidence of Gastric Cancer After Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Large Cohort Study. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 527–536.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machlowska, J.; Baj, J.; Sitarz, M.; Maciejewski, R.; Sitarz, R. Gastric Cancer: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Classification, Genomic Characteristics and Treatment Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahid, F.; Davoodi, S.H. Nutritional Factors Involved in the Etiology of Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review. Nutr. Cancer 2021, 73, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.; Zakas, A.; Hause, J. Gastrointestinal disorders. In Handbook of Clinical Adult Genetics and Genomics: A Practice-Based Approach; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 185–211. ISBN 9780128173442. [Google Scholar]
- Hata, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kiyomatsu, T.; Tanaka, T.; Kazama, S.; Nozawa, H.; Kawai, K.; Tanaka, J.; Nishikawa, T.; Otani, K.; et al. Hereditary gastrointestinal cancer. Surg. Today 2016, 46, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurzu, S.; Jung, I.; Orlowska, J.; Sugimura, H.; Kadar, Z.; Turdean, S.; Bara, T. Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer—An overview. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2015, 211, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, H.T.; Lynch, J.F.; Shaw, T.G. Hereditary gastrointestinal cancer syndromes. Gastrointest. Cancer Res. 2011, 4, S9–S17. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, R.Y.C.; Ngeow, J. Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer: What the clinician should know. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2015, 7, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamble, L.A.; Heller, T.; Davis, J.L. Hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer Syndrome and the Role of CDH1: A Review. JAMA Surg. 2021, 156, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewski, I.J.; Kluijt, I.; Cats, A.; Scerri, T.S.; de Jong, D.; Kluin, R.J.C.; Hansford, S.; Hogervorst, F.B.L.; Bosma, A.J.; Hofland, I.; et al. An α-E-catenin (CTNNA1) mutation in hereditary diffuse gastric cancer. J. Pathol. 2013, 229, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taja-Chayeb, L.; Vidal-Millán, S.; Trejo-Becerril, C.; Pérez-Cárdenas, E.; Chávez-Blanco, A.; Domínguez-Gómez, G.; González-Fierro, A.; Romo-Pérez, A.; Dueñas-González, A. Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer (HDGC). An overview. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2022, 46, 101820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donner, I.; Kiviluoto, T.; Ristimäki, A.; Aaltonen, L.A.; Vahteristo, P. Exome sequencing reveals three novel candidate predisposition genes for diffuse gastric cancer. Fam. Cancer 2015, 14, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fewings, E.; Larionov, A.; Redman, J.; Goldgraben, M.A.; Scarth, J.; Richardson, S.; Brewer, C.; Davidson, R.; Ellis, I.; Evans, D.G.; et al. Germline pathogenic variants in PALB2 and other cancer-predisposing genes in families with hereditary diffuse gastric cancer without CDH1 mutation: A whole-exome sequencing study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Woods, S.L.; Healey, S.; Beesley, J.; Chen, X.; Lee, J.S.; Sivakumaran, H.; Wayte, N.; Nones, K.; Waterfall, J.J.; et al. Point Mutations in Exon 1B of APC Reveal Gastric Adenocarcinoma and Proximal Polyposis of the Stomach as a Familial Adenomatous Polyposis Variant. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 98, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Post, R.S.; Oliveira, C.; Guilford, P.; Carneiro, F. Hereditary gastric cancer: What’s new? Update 2013–2018. Fam. Cancer 2019, 18, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoda, K.; Watanabe, M.; Yamashita, K. Re-emerging role of macroscopic appearance in treatment strategy for gastric cancer. Ann. Gastroenterol. Surg. 2019, 3, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariette, C.; Carneiro, F.; Grabsch, H.I.; van der Post, R.S.; Allum, W.; de Manzoni, G.; on behalf of European Chapter of International Gastric Cancer Association. Consensus on the pathological definition and classification of poorly cohesive gastric carcinoma. Gastric Cancer 2019, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagtegaal, I.D.; Odze, R.D.; Klimstra, D.; Paradis, V.; Rugge, M.; Schirmacher, P.; Washington, K.M.; Carneiro, F.; Cree, I.A.; The WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. The 2019 WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. Histopathology 2020, 76, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Fang, W.-L.; Wang, R.-F.; Liu, C.-A.; Yang, M.-H.; Lo, S.-S.; Wu, C.-W.; Li, A.F.-Y.; Shyr, Y.-M.; Huang, K.-H. Clinicopathological Variation of Lauren Classification in Gastric Cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2016, 22, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoda, T.; Jung, H.-Y. Endoscopic resection (endoscopic mucosal resection/endoscopic submucosal dissection) for early gastric cancer. Dig. Endosc. 2013, 25, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necula, L.; Matei, L.; Dragu, D.; Neagu, A.I.; Mambet, C.; Nedeianu, S.; Bleotu, C.; Diaconu, C.C.; Chivu-Economescu, M. Recent advances in gastric cancer early diagnosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2029–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maconi, G.; Manes, G.; Porro, G.B. Role of symptoms in diagnosis and outcome of gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z. Recent Advances in the Surgical Treatment of Advanced Gastric Cancer: A Review. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 3537–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilson, D.H. Advances in the treatment of gastric cancer: 2019. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 35, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordick, F. Chemotherapy for resectable microsatellite instability-high gastric cancer? Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, F.M.; Beckman, M. Updates on Management of Gastric Cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 21, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irino, T.; Matsuda, S.; Wada, N.; Kawakubo, H.; Kitagawa, Y. Essential updates 2019/2020: Perioperative and surgical management of gastric cancer. Ann. Gastroenterol. Surg. 2021, 5, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro, K.; Van Cutsem, E.; Narita, Y.; Pentheroudakis, G.; Baba, E.; Li, J.; Ryu, M.-H.; Wan Zamaniah, W.I.; Yong, W.-P.; Yeh, K.-H.; et al. Pan-Asian adapted ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic gastric cancer: A JSMO–ESMO initiative endorsed by CSCO, KSMO, MOS, SSO and TOS. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.D.; Syn, N.L.X.; Moehler, M.; Grothe, W.; Yong, W.P.; Tai, B.-C.; Ho, J.; Unverzagt, S. Chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 8, CD004064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, R.; Chen, B.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Pan, T.; et al. Efficacy and safety of elemene combined with chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancerr: A Meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, 19481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallaert, W.; Kedziora, K.M.; Taylor, C.D.; Zikry, T.M.; Ranek, J.S.; Sobon, H.K.; Taylor, S.R.; Young, C.L.; Cook, J.G.; Purvis, J.E. The structure of the human cell cycle. Cell Syst. 2022, 13, 230–240.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, J.G.; Jones, H.; Eggert, U.S. Membrane and organelle dynamics during cell division. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Salem, S.; Venkadakrishnan, V.B.; Heemers, H.V. Novel insights in cell cycle dysregulation during prostate cancer progression. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2021, 28, R141–R155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satyanarayana, A.; Kaldis, P. Mammalian cell-cycle regulation: Several Cdks, numerous cyclins and diverse compensatory mechanisms. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2925–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacinti, C.; Giordano, A. RB and cell cycle progression. Oncogene 2006, 25, 5220–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Kaldis, P. Cdks, cyclins and CKIs: Roles beyond cell cycle regulation. Development 2013, 140, 3079–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekholm, S.V.; Reed, S.I. Regulation of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases in the mammalian cell cycle. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2000, 12, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, J.; Miller, I.; Carter, D.; Spencer, S.L. Control of the Restriction Point by Rb and p21. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8219–E8227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suski, J.M.; Braun, M.; Strmiska, V.; Sicinski, P. Targeting cell-cycle machinery in cancer. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 759–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malumbres, M.; Barbacid, M. To cycle or not to cycle: A critical decision in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2001, 1, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G. Cell cycle regulation and anticancer drug discovery. Cancer Biol. Med. 2017, 14, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Rollins, B.J. Cyclin C/Cdk3 Promotes Rb-Dependent G0 Exit. Cell 2004, 117, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.-H.; Osley, M.A. Chromatin structure restricts origin utilization when quiescent cells re-enter the cell cycle. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 864–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, U.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; Turner, N.C.; Knudsen, E.S. The history and future of targeting cyclin-dependent kinases in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visconti, R.; Della Monica, R.; Grieco, D. Cell cycle checkpoint in cancer: A therapeutically targetable double-edged sword. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditano, J.P.; Sakurikar, N.; Eastman, A. Activation of CDC25A phosphatase is limited by CDK2/cyclin A-mediated feedback inhibition. Cell Cycle 2021, 20, 1308–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Carter, J.H.; Swanger, J.; Mazin, A.V.; Moritz, R.L.; Clurman, B.E. A novel landscape of nuclear human CDK2 substrates revealed by in situ phosphorylation. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz9899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Cao, J.; Lin, W.; Chen, H.; Xiong, X.; Ao, H.; Yu, M.; Lin, J.; Cui, Q. The Roles of Cyclin-Dependent Kinases in Cell-Cycle Progression and Therapeutic Strategies in Human Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, K.T.; Rosner, M.R.; Minella, A.C. An integrated view of cyclin E function and regulation. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavet, O.; Pines, J. Progressive Activation of CyclinB1-Cdk1 Coordinates Entry to Mitosis. Dev. Cell 2010, 18, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, J.E.; Weaver, J.; Jones, K.T. Spatial regulation of APCCdh1-induced cyclin B1 degradation maintains G2 arrest in mouse oocytes. Development 2010, 137, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaría, D.; Barrière, C.; Cerqueira, A.; Hunt, S.; Tardy, C.; Newton, K.; Cáceres, J.F.; Dubus, P.; Malumbres, M.; Barbacid, M. Cdk1 is sufficient to drive the mammalian cell cycle. Nature 2007, 448, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapova, T.A.; Daum, J.R.; Byrd, K.S.; Gorbsky, G.J. Fine Tuning the Cell Cycle: Activation of the Cdk1 Inhibitory Phosphorylation Pathway during Mitotic Exit. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 1737–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunada, S.; Saito, H.; Zhang, D.; Xu, Z.; Miki, Y. CDK1 inhibitor controls G2/M phase transition and reverses DNA damage sensitivity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 550, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensimon, A.; Aebersold, R.; Shiloh, Y. Beyond ATM: The protein kinase landscape of the DNA damage response. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 1625–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Piwnica-Worms, H. ATR-Mediated Checkpoint Pathways Regulate Phosphorylation and Activation of Human Chk1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 4129–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustofa, M.K.; Tanoue, Y.; Tateishi, C.; Vaziri, C.; Tateishi, S. Roles of Chk2/CHEK2 in guarding against environmentally induced DNA damage and replication-stress. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2020, 61, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bačević, K.; Lossaint, G.; Achour, T.N.; Georget, V.; Fisher, D.; Dulić, V. Cdk2 strengthens the intra-S checkpoint and counteracts cell cycle exit induced by DNA damage. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Siddik, Z.H.; Huang, Z.; Wang, R.; Koomen, J.; Kobayashi, R.; Khokhar, A.R.; Kuang, J. Induction of p21 by p53 following DNA damage inhibits both Cdk4 and Cdk2 activities. Oncogene 2005, 24, 2929–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, T.; Sicinski, P. Cell cycle proteins as promising targets in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Rohe, A.; Platzer, C.; Najjar, A.; Erdmann, F.; Sippl, W. Regulation of G2/M Transition by Inhibition of WEE1 and PKMYT1 Kinases. Molecules 2017, 22, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musacchio, A. The Molecular Biology of Spindle Assembly Checkpoint Signaling Dynamics. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, R1002–R1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafim, R.A.M.; Da Silva Santiago, A.; Schwalm, M.P.; Hu, Z.; dos Reis, C.V.; Takarada, J.E.; Mezzomo, P.; Massirer, K.B.; Kudolo, M.; Gerstenecker, S.; et al. Development of the First Covalent Monopolar Spindle Kinase 1 (MPS1/TTK) Inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 3173–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, K.L.; Soria-Bretones, I.; Mak, T.W.; Cescon, D.W. Targeting the cell cycle in breast cancer: Towards the next phase. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 1871–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatskevich, S.; Kroonen, J.S.; Alfieri, C.; Tischer, T.; Howes, A.C.; Clijsters, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, K.; Vertegaal, A.C.O.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of APC/C release from spindle assembly checkpoint inhibition by APC/C SUMOylation. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, S.; Moulder, S.; Keyomarsi, K.; Layman, R.M. Inhibiting CDK in Cancer Therapy: Current Evidence and Future Directions. Target. Oncol. 2018, 13, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Hei, R.; Li, X.; Cai, H.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Q.; Cai, C. CDK inhibitors in cancer therapy, an overview of recent development. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 1913–1935. [Google Scholar]
- Ettl, T.; Schulz, D.; Bauer, R.J. The Renaissance of Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitors. Cancers 2022, 14, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Wei, W. Cell cycle on the crossroad of tumorigenesis and cancer therapy. Trends Cell Biol. 2022, 32, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauklin, S.; Madrigal, P.; Bertero, A.; Vallier, L. Initiation of stem cell differentiation involves cell cycle-dependent regulation of developmental genes by Cyclin D. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Leone, G.W.; Wang, H. Cyclin D-CDK4/6 functions in cancer. In Advances in Cancer Research; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; ISBN 9780128203279. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, H.M.; AbdElbary, A.M.; Mohamed, S.Y.; Elwan, A.; Abdelhamid, M.I.; Ibrahim, A. Prognostic Value of Cyclin D1 and CD44 Expression in Gastric Adenocarcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2019, 50, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, P.; Xu, Y.; Huang, C. CHREBP suppresses gastric cancer progression via the cyclin D1-Rb-E2F1 pathway. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Peng, Y.; Dong, N.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, M.; Li, J. RN181 is a tumour suppressor in gastric cancer by regulation of the ERK/MAPK–cyclin D1/CDK4 pathway. J. Pathol. 2019, 248, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Ge, Q.; Lin, Z.; Shen, W.; Lin, R.; Wu, J.; Wang, B.; Lu, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; et al. MiR-129-5p induces cell cycle arrest through modulating HOXC10/Cyclin D1 to inhibit gastric cancer progression. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 8544–8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, X. Curcumin Promoted miR-34a Expression and Suppressed Proliferation of Gastric Cancer Cells. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2019, 34, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Yang, W.; Bian, W.; Yang, H.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Feng, W.; Liu, X. MicroRNA-623 Targets Cyclin D1 to Inhibit Cell Proliferation and Enhance the Chemosensitivity of Cells to 5-Fluorouracil in Gastric Cancer. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2018, 27, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Xue, Z.; Luo, Q. Leukemia inhibitory factor inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer by inducing G1-phase arrest. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 3613–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Long, Z.; Cai, H.; Yu, S.; Wu, J. TRIM58 suppresses the tumor growth in gastric cancer by inactivation of β-catenin signaling via ubiquitination. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2020, 21, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ge, X.; Qu, H.; Wang, N.; Zhou, J.; Xu, W.; Xie, J.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, L.; Qin, Z.; et al. Glycyrrhizic Acid Inhibits Proliferation of Gastric Cancer Cells by Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 2853–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.-N.; Zhu, M.-Y.; Peng, S.-Q.; Zhu, J.-S.; Zhang, J.; Qu, G.-Q. Dihydroartemisinin inhibits the growth and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating cyclin D1-CDK4-Rb signaling. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, X.; Deng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Li, Q.; Zeng, X.; Ju, J.; et al. AURKB promotes gastric cancer progression via activation of CCND1 expression. Aging 2020, 12, 1304–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, Y.; Gong, J.; Kou, F.; Zhang, M.; Tian, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; et al. Pyrotinib combined with CDK4/6 inhibitor in HER2-positive metastatic gastric cancer: A promising strategy from AVATAR mouse to patients. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, e148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, X.; Sun, F.; Tong, X.; Bai, Y.; Jin, K.; Liu, L.; Dai, F.; Li, N. HP-CagA+ Regulates the Expression of CDK4/CyclinD1 via reg3 to Change Cell Cycle and Promote Cell Proliferation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Qian, X.-K.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Sun, X.-G.; Shi, X.-J.; Gao, Y.-S. KLF5 promotes proliferation in gastric cancer via regulating p21 and CDK4. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 4224–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-K.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Wang, C.-M.; Li, B.; Zhang, T.-Z.; Zhou, W.-J.; Cheng, L.-J.; Huo, M.-Y.; Zhang, C.-H.; He, Y.-L. METTL16 promotes cell proliferation by up-regulating cyclin D1 expression in gastric cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 6602–6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiech, T.; Nikolopoulos, E.; Lassman, S.; Heidt, T.; Schöpflin, A.; Sarbia, M.; Werner, M.; Shimizu, Y.; Sakka, E.; Ooka, T.; et al. Cyclin D1 expression is induced by viral BARF1 and is overexpressed in EBV-associated gastric cancer. Virchows Arch. 2008, 452, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-X.; Xie, X.-S.; Weng, X.-F.; Qiu, S.-L.; Xie, J.-W.; Wang, J.-B.; Lu, J.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Cao, L.-L.; Lin, M.; et al. Overexpression of IC53d promotes the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by activating the AKT/GSK3β/cyclin D1 signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 2739–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Guo, F.; Liu, M. Up-regulated WDR5 promotes gastric cancer formation by induced cyclin D1 expression. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 3304–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.-P.; Qiang, L.; Zhang, J.-L. Transcription activated p73-modulated cyclin D1 expression leads to doxorubicin resistance in gastric cancer. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 1831–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Jin, P.; Sun, X.; Jiao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, M. SIX1 is upregulated in gastric cancer and regulates proliferation and invasion by targeting the ERK pathway and promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2018, 36, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Deng, H.-B.; Wang, Y.-H.; Guo, J.-J. Resveratrol inhibits the growth of gastric cancer via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 1579–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Liu, J.; Jiang, W.; Wang, P.; Sun, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H. METTL3 promotes the proliferation and mobility of gastric cancer cells. Open Med. 2019, 14, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, K.; Ran, M.-J.; Zou, F.-W.; Yang, T.-W.; He, F. Long non-coding RNA LINC00857 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and predicts poor patient survival. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, W.L.; Jiang, J.T.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Q.C.; Li, J.; Gu, W.D.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.T. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000467 Promotes the Development of Gastric Cancer by Competitively Binding to MicroRNA miR-326-3p. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 4030826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Tan, S.; Zhu, T.; Ding, K. CORO1C expression is associated with poor survival rates in gastric cancer and promotes metastasis in vitro. FEBS Open Bio 2019, 9, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Li, H.; Xiang, H.; Gao, M.; Yin, C.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Xiong, M. Long Chain Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA) HOTAIR Knockdown Increases miR-454-3p to Suppress Gastric Cancer Growth by Targeting STAT3/Cyclin D1. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 1537–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCartney, A.; Migliaccio, I.; Bonechi, M.; Biagioni, C.; Romagnoli, D.; De Luca, F.; Galardi, F.; Risi, E.; De Santo, I.; Benelli, M.; et al. Mechanisms of Resistance to CDK4/6 Inhibitors: Potential Implications and Biomarkers for Clinical Practice. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.; An, H.J.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, S.A.; Kim, S.; Lim, S.M.; Kim, G.M.; Sohn, J.; Moon, Y.W. Molecular mechanisms of resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer: A review. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Fernández, M.; Malumbres, M. Mechanisms of Sensitivity and Resistance to CDK4/6 Inhibition. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 514–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Guo, X.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, Q. The application and prospect of CDK4/6 inhibitors in malignant solid tumors. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, C.; Zhou, X.; You, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, C.; Yao, F.; Li, S. Double amplifications of CDK4 and MDM2 in a gastric inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor mimicking cancer with local invasion of the spleen and diaphragm. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2018, 19, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Hou, G.; Han, X.; Song, W. PAK1 silencing is synthetic lethal with CDK4/6 inhibition in gastric cancer cells via regulating PDK1 expression. Hum. Cell 2020, 33, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Liang, X.; Li, S.; Li, T.; Zheng, L.; Shao, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Ma, L.; Jia, J. Orphan nuclear receptor Nurr1 promotes Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric carcinogenesis by directly enhancing CDK4 expression. eBioMedicine 2020, 53, 102672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Han, L.; Pan, L.; Li, X.; Kong, Q.; Wang, G.; Su, X. Clinical implications of progranulin in gastric cancer and its regulation via a positive feedback loop involving AKT and ERK signaling pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 9685–9691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Guo, H.; He, Y.; Pang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Ao, X.; Li, P.; Wang, J. Long noncoding RNA gastric cancer-related lncRNA1 mediates gastric malignancy through miRNA-885-3p and cyclin-dependent kinase 4. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isinger-Ekstrand, A.; Johansson, J.; Ohlsson, M.; Francis, P.; Staaf, J.; Jönsson, M.; Borg, Å.; Nilbert, M. Genetic profiles of gastroesophageal cancer: Combined analysis using expression array and tiling array–comparative genomic hybridization. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2010, 200, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Ye, H.; Guo, W.; Dong, X.; Wu, N.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Z. CDK4/6 inhibitor suppresses gastric cancer with CDKN2A mutation. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 11692–11700. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.-P.; Wu, W.-J.; Sun, D.-Y.; Xie, Z.-Y.; Ma, Y.-C.; Zhao, Y.-G. miR-449a and CDK6 in gastric carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 8, 1533–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y. miR-107 targets cyclin-dependent kinase 6 expression, induces cell cycle G1 arrest and inhibits invasion in gastric cancer cells. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Sun, Y.; Li, W.; Ye, F.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, D.Y.; Suo, J. Antiproliferative effects of the CDK6 inhibitor PD0332991 and its effect on signaling networks in gastric cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 2473–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, L.; Huang, L.; Yao, S.; Lin, N.; Li, P.; Xu, H.; Wu, X.; Xu, J.; Lu, Y.; et al. Oncogenic PAX6 elicits CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance by epigenetically inactivating the LATS2-Hippo signaling pathway. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tao, X.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, Q. CDC37L1 acts as a suppressor of migration and proliferation in gastric cancer by down-regulating CDK6. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 3145–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhao, L.-M.; Bai, H.-Y.; Zhang, C.; Dai, S.-L.; Lv, H.-L.; Shan, B.-E. The tumor-suppressive function of miR-1296-5p by targeting EGFR and CDK6 in gastric cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, N.J.; Hou, H.H.; Li, F.; Guo, S.T.; Wang, Y. miRNA-191-5p represses cell growth by targeting CDK6 in gastric cancer. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2020, 100, 3689–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, Z.-N.; Cheng, X.-H.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Dai, X.; Bao, G.-M.; Zhou, L.-B. MiR-29c suppresses cell invasion and migration by directly targeting CDK6 in gastric carcinoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 7920–7928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Chai, F.; Jiang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Wan, Y.; et al. Regional hyperthermia combined with chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer. Open Med. 2019, 14, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhao, H.; Ding, Q.; Li, H.; Liu, T.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y. CDK6 is stimulated by hyperthermia and protects gastric cancer cells from hyperthermia-induced damage. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, W.; Cai, G.; Liao, G. Identification of UAP1L1 as tumor promotor in gastric cancer through regulation of CDK6. Aging 2020, 12, 6904–6927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Tian, Y.; He, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, R.; Zhu, W.-J.; Gao, P. Linc01133 contributes to gastric cancer growth by enhancing YES1-dependent YAP1 nuclear translocation via sponging miR-145-5p. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liang, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Shen, M.; Han, C.; Ren, C. The prognostic value of circRNAs for gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 9096–9106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Li, G.; Fang, X.; Wang, L.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, Q. hsa_circ_0081143 promotes cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer by targeting miR-646/CDK6 pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wei, N.; Shao, G.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L. circZNF609 promotes the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer by sponging miR-483-3p and regulating CDK6. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 8197–8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Ji, F.; Wen, X.; Jin, Z. Circular RNA circ_ASAP2 promotes cell viability, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating the miR-770-5p/CDK6 axis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 13, 2806–2819. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Yin, Y.; Qian, A.; Guo, R.; Qi, J. LncRNA LINC00974 Upregulates CDK6 to Promote Cell Cycle Progression in Gastric Carcinoma. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2019, 34, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bani-Hani, K.E.; Almasri, N.M.; Khader, Y.S.; Sheyab, F.M.; Karam, H.N. Combined Evaluation of Expressions of Cyclin E and p53 Proteins as Prognostic Factors for Patients with Gastric Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akama, Y.; Yasui, W.; Yokozaki, H.; Kuniyasu, H.; Kitahara, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Tahara, E. Frequent Amplification of the Cyclin E Gene in Human Gastric Carcinomas. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1995, 86, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsina, M.; Landolfi, S.; Aura, C.; Caci, K.; Jimenez, J.; Prudkin, L.; Castro, S.; Moreno, D.; Navalpotro, B.; Tabernero, J.; et al. Cyclin E amplification/overexpression is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 438–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, Q.; Gu, J.; Chen, S.; Li, Q.; Ying, L. Down-regulation of CCNE1 expression suppresses cell proliferation and sensitizes gastric carcinoma cells to Cisplatin. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, K.; Koufuji, K.; Yang, S.; Murakami, N.; Terasaki, Y.; Yamasaki, Y.; Takeda, J.; Tanaka, M.; Shirouzu, K. Immunohistochemical Study on the Expression of Cyclin D1 and E in Gastric Cancer. Kurume Med. J. 2000, 47, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.J.; Kim, B.H.; Jang, S.J.; Hong, E.K.; Lee, W.M.; Baik, H.K.; Park, H.K.; Lee, C.B.; Ki, M. Expression of cyclin D1 and cyclin E in human gastric carcinoma and its clinicopathologic significance. J. Korean Med. Sci. 1998, 13, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-J.; Kou, Y.-W.; Wang, Q. Expression of P27 and cyclin D1 and E expression in gastric cancer. World Chin. J. Dig. 2007, 15, 3809–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiaqing, L.; Hokita, S.; Xiangming, C.; Natsugoe, S.; Tanabe, G.; Baba, M.; Takao, S.; Aikou, T. Role of cyclin E and p53 expression in progression of early gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 1998, 1, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.-J.; Park, Y.-W.; Park, M.-H.; Lee, J.-D.; Lee, Y.-Y.; Jung, T.-J.; Kim, I.-S.; Choi, I.-Y.; Ki, M.; Choi, B.-Y.; et al. Expression of cell-cycle regulators, cyclin E and p21WAF1/CIP1, potential prognostic markers for gastric cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. (EJSO) 1999, 25, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, J.B.Y.; Samarasinge, K.; Raju, G.C.; Moochhala, S.M.; Ti, T.-K. Expression of Cell-Cycle Regulators p27 and Cyclin E Correlates with Survival in Gastric Carcinoma Patients. J. Surg. Res. 2000, 94, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, A.N.A.; Carvalho, R.; Jansen, M.; Kranenbarg, E.M.-K.; Van De Velde, C.J.H.; Morsink, F.M.; Musler, A.R.; Weterman, M.A.J.; Offerhaus, G.J.A. Cyclin E low molecular weight isoforms occur commonly in early-onset gastric cancer and independently predict survival. J. Clin. Pathol. 2008, 61, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, S.; Puneet; Prasad, S.B.; Yadav, S.S.; Kumari, S.; Kumar, M.; Khanna, A.; Dixit, V.K.; Nath, G.; Singh, S.; et al. Cyclin D1 and cyclin E2 are differentially expressed in gastric cancer. Med. Oncol. 2016, 33, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouraklis, G.; Katsoulis, I.E.; Theocharis, S.; Tsourouflis, G.; Xipolitas, N.; Glinavou, A.; Sioka, C.; Kostakis, A. Does the Expression of Cyclin E, pRb, and p21 Correlate with Prognosis in Gastric Adenocarcinoma? Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Ren, F.; Tang, R.; Feng, Z.; Chen, G. Prognostic Value of Expression of Cyclin E in Gastrointestinal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 15, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Shin, H.C.; Heo, Y.J.; Ha, S.Y.; Jang, K.-T.; Kim, S.T.; Kang, W.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.-M. CCNE1 amplification is associated with liver metastasis in gastric carcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.-L.; Xu, B.; Song, Y.-G.; Zhang, W.-D. Overexpression of cyclin E in Mongolian gerbil with Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric precancerosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 8, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, A.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lim, J.M.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, K.-H.; Kim, T.-Y.; Oh, D.-Y.; Bang, Y.-J.; et al. Cyclin E overexpression confers resistance to the CDK4/6 specific inhibitor palbociclib in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2018, 430, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, K.; Shen, Y.; Chiang, Y.; Liu, P.; Huang, C.; Cheng, A. Preferential chemosensitivity to gemcitabine by cyclin E overexpression in human gastric cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 21020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagundes, R.; Teixeira, L.K. Cyclin E/CDK2: DNA Replication, Replication Stress and Genomic Instability. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 774845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shen, M.; Zhou, G. Upregulation of CDCA5 promotes gastric cancer malignant progression via influencing cyclin E1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. β-carotene Inhibits Expression of c-Myc and Cyclin E in Helicobacter pylori-infected Gastric Epithelial Cells. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 24, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yan, Z.; Wan, Y.; Wei, S.; Bi, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Liao, D.J.; Huang, H. Knockdown of long noncoding RNA GHET1 inhibits cell-cycle progression and invasion of gastric cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 3375–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Nie, Y.; Wang, J.; Song, J.; Jin, H.; He, L.; Gao, L.; Qiao, L.; et al. Ribosomal protein L6 promotes growth and cell cycle progression through upregulating cyclin E in gastric cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 393, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, L.; Li, D.; Mu, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, B.; Lyu, H.; Han, L.; Nie, C.; Yang, C.; Wang, L.; et al. Analysis of cyclin E co-expression genes reveals nuclear transcription factor Y subunit alpha is an oncogene in gastric cancer. Chronic Dis. Transl. Med. 2019, 5, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Yan, L.; Gu, H.; Mu, Y.; Tong, G.; Zhang, G. 14-3-3ɛ functions as an oncogene in SGC7901 gastric cancer cells through involvement of cyclin E and p27kip1. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 3145–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Song, Y.S.; Yoon, J.S.; Song, K.W.; Lee, Y.Y. Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 expression is associated with tumor cell proliferation and metastasis in gastric cancer. Apmis 2010, 118, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dong, Z.; Shi, P.; Tan, L.; Xu, J.; Huang, P.; Wang, Z.; Cui, H.; Yang, L. Bruceine D inhibits Cell Proliferation Through Downregulating LINC01667/MicroRNA-138-5p/Cyclin E1 Axis in Gastric Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 584960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam, C.H.; Fung, T.K.; Poon, R.Y.C. Cyclin A in cell cycle control and cancer. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, I.; Dynlacht, B.D. New insights into cyclins, CDKs, and cell cycle control. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005, 16, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrena, J.; Wiksten, J.-P.; Kokkola, A.; Nordling, S.; Haglund, C.; Ristimäki, A. Prognostic significance of cyclin A in gastric cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 1897–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadesse, S.; Anshabo, A.T.; Portman, N.; Lim, E.; Tilley, W.; Caldon, C.E.; Wang, S. Targeting CDK2 in cancer: Challenges and opportunities for therapy. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; He, Z.; Kitazato, K.; Wang, Y. Selective Autophagy Regulates Cell Cycle in Cancer Therapy. Theranostics 2019, 9, 104–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neganova, I.; Vilella, F.; Atkinson, S.P.; Lloret, M.; Passos, J.F.; von Zglinicki, T.; O’Connor, J.-E.; Burks, D.; Jones, R.; Armstrong, L.; et al. An Important Role for CDK2 in G1 to S Checkpoint Activation and DNA Damage Response in Human Embryonic Stem Cells. STEM CELLS 2011, 29, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, R.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, H. Silencing LINC01021 inhibits gastric cancer through upregulation of KISS1 expression by blocking CDK2-dependent phosphorylation of CDX2. Mol. Ther.—Nucleic Acids 2021, 24, 832–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lei, J.; Zheng, Q.; Tan, S.; Ding, K.; Yu, C. Poly(rC) binding protein 2 (PCBP2) promotes the viability of human gastric cancer cells by regulating CDK2. FEBS Open Bio 2018, 8, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wu, N.; Han, Y.; Hou, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Xie, X.; Chen, F. DDX21 promotes gastric cancer proliferation by regulating cell cycle. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 505, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Li, L.; Tang, Y.; Xie, D.; Wu, K.; Wei, W.; Xiao, Q. CDK2 positively regulates aerobic glycolysis by suppressing SIRT5 in gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2590–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-T.; Liu, S.; Liu, L.; Ma, R.-R.; Gao, P. EGR1-Mediated Transcription of lncRNA-HNF1A-AS1 Promotes Cell-Cycle Progression in Gastric Cancer. Cancer Res 2018, 78, 5877–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Dong, N.; Su, X.; Duan, M.; Wei, Y.; Wei, J.; Liu, G.; Peng, Q.; Zhao, Y. Sulforaphane induces S-phase arrest and apoptosis via p53-dependent manner in gastric cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Kim, S.N.; Jong, H.-S.; Kim, N.K.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, S.-J.; Bang, Y.-J. Caspase-mediated Cdk2 activation is a critical step to execute transforming growth factor-β1-induced apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells. Oncogene 2001, 20, 1254–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-N.; Ma, J.-Q.; Zheng, Q.; Zhai, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liao, Z.-J.; Yao, Y. MICRORNA-638 INHIBITED CELL PROLIFERATION BY TARGETING CDK2. Acta Medica Mediterr. 2020, 36, 2839–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.-Y.; Wang, L.-P.; Wang, Q.; Han, P.; Zhuang, W.-P.; Li, M.-J.; Yuan, H. miR-302b regulates cell cycles by targeting CDK 2 via ERK signaling pathway in gastric cancer. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 2302–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, V.; Place, R.F.; Portnoy, V.; Wang, J.; Qi, Z.; Jia, Z.; Yu, A.; Shuman, M.; Yu, J.; Li, L.-C. Upregulation of Cyclin B1 by miRNA and its implications in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 1695–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H. Prognostic Implications of Cyclin B1, p34cdc2, p27Kip1and p53 Expression in Gastric Cancer. Yonsei Med. J. 2007, 48, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, M.; Takesue, F.; Inutsuka, S.; Honda, M.; Nozoe, T.; Korenaga, D. Overexpression of cyclin B1 in gastric cancer and its clinicopathological significance: An immunohistological study. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 128, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-P.; Li, S.-Y.; Wang, J.-P.; Jun, L. Clinical significance and biological roles of cyclins in gastric cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 6673–6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begnami, M.D.; Fregnani, J.H.T.G.; Nonogaki, S.; Soares, F.A. Evaluation of cell cycle protein expression in gastric cancer: Cyclin B1 expression and its prognostic implication. Hum. Pathol. 2010, 41, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Wang, S.; Jiang, N.; Li, J.J. Cyclin B1/CDK1-regulated mitochondrial bioenergetics in cell cycle progression and tumor resistance. Cancer Lett. 2019, 443, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Yang, L.; He, Y.; Zhu, B.; Ren, F.; Fan, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Kuang, Y.; et al. CREPT/RPRD1B associates with Aurora B to regulate Cyclin B1 expression for accelerating the G2/M transition in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Cai, X.; Du, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, F. Downregulation of P21-Activated Kinase-1 Inhibits the Growth of Gastric Cancer Cells Involving Cyclin B1. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 2511–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Hu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, L.; Peng, L.; Yu, L.; Sun, L.; Liu, J.; Yang, Z.; Ran, Y. Tumor-suppressive mir-663 gene induces mitotic catastrophe growth arrest in human gastric cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 24, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Ni, X.; Lei, M.; Xia, Q.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W. Phosphorylation of islet-1 serine 269 by CDK1 increases its transcriptional activity and promotes cell proliferation in gastric cancer. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, S.; Nikkhoo, A.; Hojat-Farsangi, M.; Namdar, A.; Azizi, G.; Mohammadi, H.; Yousefi, M.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F. CDK1 in Breast Cancer: Implications for Theranostic Potential. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, H.; Zou, Q.; Wu, J. Analysis of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 1 as an Independent Prognostic Factor for Gastric Cancer Based on Statistical Methods. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 620164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najar, M.A.; Aravind, A.; Dagamajalu, S.; Sidransky, D.; Ashktorab, H.; Smoot, D.T.; Gowda, H.; Prasad, T.S.K.; Modi, P.K.; Chatterjee, A. Hyperactivation of MEK/ERK pathway by Ca 2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 promotes cellular proliferation by activating cyclin-dependent kinases and minichromosome maintenance protein in gastric cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2021, 60, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-L.; Huang, H.-C.; Juan, H.-F. Revealing the Molecular Mechanism of Gastric Cancer Marker Annexin A4 in Cancer Cell Proliferation Using Exon Arrays. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Kang, W.; Lu, X.; Ma, S.; Dong, L.; Zou, B. LncRNA CASC11 promoted gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro by regulating cell cycle pathway. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 1886–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.-N.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Li, O.; Liu, S.-L.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Pan, L.-J.; Zhao, C.; Gong, W.; Shu, Y.-J.; Dong, P. ESRRA promotes gastric cancer development by regulating the CDC25C/CDK1/CyclinB1 pathway via DSN1. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 1909–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi Ch, N.P.; Sivagnanam, A.; Raja, S.; Mahalingam, S. Molecular basis for RASSF10/NPM/RNF2 feedback cascade–mediated regulation of gastric cancer cell proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 100935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Du, K.; Zhu, X.; Chang, S.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Sun, J.; Luo, X.; Deng, S.; et al. Circ_CEA promotes the interaction between the p53 and cyclin-dependent kinases 1 as a scaffold to inhibit the apoptosis of gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-J.; Lee, H.-W.; Baek, J.-H.; Cho, Y.-H.; Kang, H.G.; Jeong, J.S.; Song, J.; Park, H.-S.; Chun, K.-H. Activation of nuclear PTEN by inhibition of Notch signaling induces G2/M cell cycle arrest in gastric cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Du, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Z.; Ouyang, P. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 1 (CDK1) is Co-Expressed with CDCA5: Their Functions in Gastric Cancer Cell Line MGC-803. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e923664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yue, Y.; Pan, M.; Sun, J.; Chu, J.; Lin, X.; Xu, W.; Feng, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, D.; et al. Histone deacetylase 3 inhibits new tumor suppressor gene DTWD1 in gastric cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 663–673. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, A.; Malagraba, G.; Yarmohammadi, M.; Perelló-Reus, C.M.; Barceló, C.; Rubio-Tomás, T. Therapeutic Potential of Mitotic Kinases’ Inhibitors in Cancers of the Gastrointestinal System. Futur. Pharmacol. 2022, 2, 214–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-H.; Park, K.-I.; Park, H.-S.; Kang, S.-R.; Nagappan, A.; Kim, J.-A.; Kim, E.-H.; Lee, W.-S.; Hah, Y.-S.; Chung, H.-J.; et al. Flavonoids Isolated from Korea Citrus aurantium L. Induce G2/M Phase Arrest and Apoptosis in Human Gastric Cancer AGS Cells. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 515901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Bao, J.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Y.; Mao, X.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Xue, Y. Kaempferol inhibits gastric cancer tumor growth: An in vitro and in vivo study. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, R.; Valiveti, C.K.; Kumar, D.R.; Van Slambrouck, S.; Kesharwani, S.S.; Seefeldt, T.; Scaria, J.; Tummala, H.; Bhat, G.J. The Flavonoid Metabolite 2,4,6-Trihydroxybenzoic Acid Is a CDK Inhibitor and an Anti-Proliferative Agent: A Potential Role in Cancer Prevention. Cancers 2019, 11, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Cho, Y.; Kim, D.H.; Woo, H.J.; Yang, J.Y.; Kwon, H.J.; Yeon, M.J.; Park, M.; Kim, S.H.; Moon, C.; et al. Menadione induces G2/M arrest in gastric cancer cells by down-regulation of CDC25C and proteasome mediated degradation of CDK1 and cyclin B1. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 5246–5255. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, W.; Zhu, J. Anti-proliferative and chemosensitizing effects of luteolin on human gastric cancer AGS cell line. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 313, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Song, G.; Yu, Y.; Ma, H.; Ma, L.; Jin, Y.; Jiang, M. Apoptosis and G2/M arrest induced by Allium ursinum (ramson) watery extract in an AGS gastric cancer cell line. OncoTargets Ther. 2013, 6, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.-Y.; Li, J.; Qu, X.-Y.; Zhu, N.; Ji, Y.-B. Downregulation of Cdk1 and CyclinB1 Expression Contributes to Oridonin-induced Cell Cycle Arrest at G2/M Phase and Growth Inhibition in SGC-7901 Gastric Cancer Cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 6437–6441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.-Y.; Hao, M.; Yang, X.-Y.; Ba, Q.; Li, M.; Ni, S.-J.; Wang, L.-S.; Du, X. Licochalcone A inhibits growth of gastric cancer cells by arresting cell cycle progression and inducing apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2011, 302, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Cai, H.; Jiang, G.; Zhou, T.-B.; Wu, H. Silibinin Inhibits Proliferation, Induces Apoptosis and Causes Cell Cycle Arrest in Human Gastric Cancer MGC803 Cells Via STAT3 Pathway Inhibition. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 6791–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Zhou, X.; Gu, M.; Jiao, W.; Yu, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.; Ji, F. Resveratrol synergizes with cisplatin in antineoplastic effects against AGS gastric cancer cells by inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis and G2/M phase arrest. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 1605–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, T.; Liu, W.; Tao, K.; Wu, C. A Review of Research Progress in Multidrug-Resistance Mechanisms in Gastric Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 1797–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Zeng, X.; Gao, H. Ubiquitylation of cyclin C by HACE1 regulates cisplatin-associated sensitivity in gastric cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Jin, X.; Zhou, C.; Gong, Z. Cyclin C: A new responser for chemosensitivity in cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.-G.; Noh, J.H.; An, J.Y.; Hong, S.K.; Park, S.B.; Baik, Y.H.; Kim, K.-M.; Sohn, T.S.; Kim, S. Expression Levels of Cyclin G2, But Not Cyclin E, Correlate with Gastric Cancer Progression. J. Surg. Res. 2009, 157, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhao, C.; Liu, Q.; Hou, X.; Li, S.; Xing, X.; Yang, C.; Luo, Y. Cyclin G2 suppresses Wnt/β-catenin signaling and inhibits gastric cancer cell growth and migration through Dapper1. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Zhou, H.; Xue, Y.; Yao, B.; Zhao, W. MicroRNA-340 promotes the tumor growth of human gastric cancer by inhibiting cyclin G2. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Luo, Y. Mutation analysis of the negative regulator cyclin G2 in gastric cancer. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 14618–14624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Kwiatkowski, N.; Abraham, B.J.; Lee, T.I.; Xie, S.; Yuzugullu, H.; Von, T.; Li, H.; Lin, Z.; et al. CDK7-Dependent Transcriptional Addiction in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cell 2015, 163, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peissert, S.; Schlosser, A.; Kendel, R.; Kuper, J.; Kisker, C. Structural basis for CDK7 activation by MAT1 and Cyclin H. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 26739–26748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-R.; Qin, W.-M.; Wang, K.; Fu, D.-R.; Zhang, W.-J.; Jiang, Q.-W.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, M.-L.; Xing, Z.-H.; Wei, M.-N.; et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase 7 inhibitor THZ2 inhibits the growth of human gastric cancer in vitro and in vivo. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 3664–3676. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.-L.; Huang, D.-Z.; Deng, T.; Zhou, L.-K.; Wang, X.; Bai, M.; Ba, Y. Overexpression of Cyclin L2 Inhibits Growth and Enhances Chemosensitivity in Human Gastric Cancer Cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 1425–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Song, Q.; Chen, Z. MicroRNA-216b regulates cell proliferation, invasion and cycle progression via interaction with cyclin T2 in gastric cancer. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2020, 31, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzi, Z.A.; Tai, I.T. CDK10 in Gastrointestinal Cancers: Dual Roles as a Tumor Suppressor and Oncogene. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 655479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kciuk, M.; Gielecińska, A.; Mujwar, S.; Mojzych, M.; Kontek, R. Cyclin-dependent kinases in DNA damage response. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-Q.; Xie, J.-W.; Xie, H.-T.; Chen, P.-C.; Zhang, X.-L.; Zheng, C.-H.; Li, P.; Wang, J.-B.; Lin, J.-X.; Cao, L.-L.; et al. Expression of CRM1 and CDK5 shows high prognostic accuracy for gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 2012–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.; Yang, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, H.; Luo, M.; Yu, Q.; Lin, G.; et al. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 5 Decreases in Gastric Cancer and Its Nuclear Accumulation Suppresses Gastric Tumorigenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Lin, J.-X.; Zhang, P.-Y.; Sun, Y.-Q.; Li, P.; Xie, J.-W.; Wang, J.-B.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Cao, L.-L.; Lin, Y.; et al. CDK5 suppresses the metastasis of gastric cancer cells by interacting with and regulating PP2A. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.-Y.; Liu, Q.-Y.; Cao, J.; Chen, J.-W.; Liu, Z.-S. Selective CDK7 inhibition with BS-181 suppresses cell proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseh, G.; Mohammadifard, M.; Mohammadifard, M. Upregulation of cyclin-dependent kinase 7 and matrix metalloproteinase-14 expression contribute to metastatic properties of gastric cancer. IUBMB Life 2016, 68, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-Q.; Ma, X.-H.; Ma, G.-L.; Lin, B.; Liu, C.; Deng, Q.-J.; Lv, W.-P. MicroRNA-107 promotes proliferation of gastric cancer cells by targeting cyclin dependent kinase 8. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 9, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-Y.; Han, S.I.; Lim, S.-C. Roles of cyclin-dependent kinase 8 and?-catenin in the oncogenesis and progression of gastric adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 38, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, W. MicroRNA-613 inhibits the progression of gastric cancer by targeting CDK9. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.-W.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.-F.; Xiang, J.; Zhou, Z.-W.; Peng, J.-S.; Chen, Y.-B. Low Expression of CDK10 Correlates with Adverse Prognosis in Gastric Carcinoma. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 2907–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Bai, F.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, N.; Yao, L.; Tang, Y.; Li, X. Downregulated CDK10 expression in gastric cancer: Association with tumor progression and poor prognosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 6812–6818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Fan, H.; Li, T.; Sihong, L.; Qiao, S.; Bi, J. Low expression of CDK12 in gastric cancer is correlated with advanced stage and poor outcome. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Shin, S.H.; Chen, H.; Liu, T.; Li, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, C.; Kim, D.J.; Liu, K.; et al. CDK12 and PAK2 as novel therapeutic targets for human gastric cancer. Theranostics 2020, 10, 6201–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, F.; Wang, F.; Jia, J.; Feng, Z.; Huo, X.; Yang, J.; Jin, W.; Sa, R.; et al. CDK13-Mediated Cell Cycle Disorder Promotes Tumorigenesis of High HMGA2 Expression Gastric Cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 707295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhu, J.; Huang, H.; Yang, Q.; Cai, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Shao, M.; Xiao, J.; Cao, J.; et al. PFTK1 Promotes Gastric Cancer Progression by Regulating Proliferation, Migration and Invasion. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Ge, D.; Li, P.; Hu, F.; Chu, J.; Chen, X.; Song, W.; Wang, A.; Tian, G.; Gu, X. CXXC finger protein 4 inhibits the CDK18-ERK1/2 axis to suppress the immune escape of gastric cancer cells with involvement of ELK1/MIR100HG pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 10151–10165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.-Q.; Li, X.-N.; Fu, L.-P.; Zhang, N.; Cai, J.-H. ISOC1 promotes the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by positively regulating CDK19. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 11602–11609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, C.E.; Oh, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, H.S. Pharmacogenomic Analysis Reveals CCNA2 as a Predictive Biomarker of Sensitivity to Polo-Like Kinase I Inhibitor in Gastric Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; He, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Song, P. Identifying of biomarkers associated with gastric cancer based on 11 topological analysis methods of CytoHubba. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.S.; Hsu, H.P.; Lai, M.D.; Hung, Y.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Yen, M.C.; Chen, Y.L. Cyclin D1 overexpression correlates with poor tumor differentiation and prognosis in gastric cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 4517–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feakins, R.M.; Nickols, C.D.; Bidd, H.; Walton, S.-J. Abnormal expression of pRb, p16, and cyclin D1 in gastric adenocarcinoma and its lymph node metastases: Relationship with pathological features and survival. Hum. Pathol. 2003, 34, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenderenda, M. A study on the prognostic value of cyclins D1 and E expression levels in resectable gastric cancer and on some correlations between cyclins expression, histoclinical parameters and selected protein products of cell-cycle regulatory genes. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 24, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takano, Y.; Kato, Y.; van Diest, P.J.; Masuda, M.; Mitomi, H.; Okayasu, I. Cyclin D2 Overexpression and Lack of p27 Correlate Positively and Cyclin E Inversely with a Poor Prognosis in Gastric Cancer Cases. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, Y.; Kato, Y.; Masuda, M.; Ohshima, Y.; Okayasu, I. Cyclin D2, but not cyclin D1, overexpression closely correlates with gastric cancer progression and prognosis. J. Pathol. 1999, 189, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, T.; Watanabe, A.; Sawada, H.; Yamada, Y.; Yamashita, J.; Matsuda, M.; Nakajima, M.; Miwa, T.; Hirao, T.; Nakano, H. Prognostic value of cyclin E and p53 expression in gastric carcinoma. Cancer 1998, 82, 1238–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiangming, C.; Natsugoe, S.; Takao, S.; Hokita, S.; Tanabe, G.; Baba, M.; Kuroshima, K.; Aikou, T. The cooperative role of p27 with cyclin E in the prognosis of advanced gastric carcinoma. Cancer 2000, 89, 1214–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.-A.; Inoue, H.; Nishida, K.; Sonoda, H.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Kakeji, Y.; Utsunomiya, T.; Mori, M. Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 gene expression is associated with poor prognosis in gastric carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 5693–5698. [Google Scholar]
- Ihle, M.A.; Huss, S.; Jeske, W.; Hartmann, W.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S.; Schildhaus, H.-U.; Büttner, R.; Sihto, H.; Hall, K.S.; Eriksson, M.; et al. Expression of cell cycle regulators and frequency of TP53 mutations in high risk gastrointestinal stromal tumors prior to adjuvant imatinib treatment. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J. Identification of Potentially Functional CircRNA-miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network in Gastric Carcinoma using Bioinformatics Analysis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 8777–8796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Huang, J.; Ke, J.; Ding, H.; Xiao, J.; Shan, X.; Liu, Q.; et al. Upregulation of CDK7 in gastric cancer cell promotes tumor cell proliferation and predicts poor prognosis. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2016, 100, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Zhou, C.; Wu, J.; Cai, Q.; Shi, M.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, J. Expression pattern of CDK12 protein in gastric cancer and its positive correlation with CD8+ cell density and CCL12 expression. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 16, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, S. CDH1 (E-Cadherin) Mutation and Gastric Cancer: Genetics, Molecular Mechanisms and Guidelines for Management. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 10477–10486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, T.; Shibata, T.; Nakamura, M.; Yamashita, H.; Yoshioka, D.; Okubo, M.; Yonemura, J.; Maeda, Y.; Maruyama, N.; Kamano, T.; et al. Association Between Cyclin D1 Polymorphism with CpG Island Promoter Methylation Status of Tumor Suppressor Genes in Gastric Cancer. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 3449–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Chen, C.; Geng, J.; Han, D.; Wang, T.; Xie, T.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Lei, Z.; et al. Targeting KDM1A attenuates Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to eliminate sorafenib-resistant stem-like cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2017, 398, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Huang, W.; Tian, T.; Zang, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Lai, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Gao, J.; et al. Characterization and validation of potential therapeutic targets based on the molecular signature of patient-derived xenografts in gastric cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, C.A.; Vargas, L.; Martinez, V.; Bravo, S.; Brown, N.E. Palbociclib-induced autophagy and senescence in gastric cancer cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 360, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honma, K.; Nakanishi, R.; Nakanoko, T.; Ando, K.; Saeki, H.; Oki, E.; Iimori, M.; Kitao, H.; Kakeji, Y.; Maehara, Y. Contribution of Aurora-A and -B expression to DNA aneuploidy in gastric cancers. Surg. Today 2014, 44, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Wang, G.-H.; Zhou, Y.-M.; Deng, J.-P.; Feng, Y.; Chen, J.-Q.; Tian, L. AURKB Promotes the Metastasis of Gastric Cancer, Possibly by Inducing EMT. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 6947–6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhao, G.; Wang, Z. Aurora kinase B inhibitor barasertib (AZD1152) inhibits glucose metabolism in gastric cancer cells. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2019, 30, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Liu, W.; Lu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Antitumor activity of a novel Aurora A/B kinases inhibitor TY-011 against gastric cancer by inducing DNA damage. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2020, 31, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Vafaee, R.; Shoorei, H.; Taheri, M. MicroRNAs in gastric cancer: Biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Gene 2020, 757, 144937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Lin, Z.; Pang, X.; Tariq, M.A.; Ao, X.; Li, P.; Wang, J. Epigenetic regulation of long non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 19443–19458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; An, Y.; Liu, B. Long non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer: New emerging biological functions and therapeutic implications. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8880–8902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Sun, J.; Zhang, N.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Lv, L.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Yang, M. Noncoding RNAs in gastric cancer: Implications for drug resistance. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasic, T.B.; O’Hara, M.H.; Teitelbaum, U.R.; Damjanov, N.; Giantonio, B.J.; D’Entremont, T.S.; Gallagher, M.; Zhang, P.J.; O’Dwyer, P.J. Phase II Trial of Palbociclib in Patients with Advanced Esophageal or Gastric Cancer. Oncologist 2020, 25, e1864–e1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagraba, G.; Yarmohammadi, M.; Javed, A.; Barceló, C.; Rubio-Tomás, T. The Role of LSD1 and LSD2 in Cancers of the Gastrointestinal System: An Update. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Regulator Molecule | Cyclin/CDK | Mode of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| CHREBP | Cyclin D1 | Negative 242 modulation of the Cyclin D1-Rb-E2F1 signaling mechanism | [82] |
| RN181 | Cyclin D1/CDK4 | E3 ubiquitin ligase regulates Cyclin 245 D1-CDK4 activity via inhibition of ERK/MAPK | [83] |
| Circumin | Cyclin D1/CDK4 | Stabilization of miR-34a, which inhibits Cyclin D1 and CDK4 | [85] |
| LIF | Cyclin D1 | Downregulates Cyclin D1 and upregulates p21 | [87] |
| TRIM58 | Cyclin D1 | Reduction of survivin, Cyclin D1, c-myc, and β-catenin via degradation | [88] |
| Glycyrrhizic acid | Cyclin D1 | An anti-tumor compound induces apoptosis along with reduction of Cyclin D1, D2, D3, E1, and E2 | [89] |
| DHA | Cyclin D1/ CDK4 | Anti-tumor activities through inhibition of CDK4 activity and targets Cyclin D1 negatively | [90] |
| AZD1152 | Cyclin D1 | Specifically inhibits Aurora B also reduces Cyclin D1 for inhibiting tumorigenesis | [91] |
| SHR6390 | Cyclin D1/ CDK4/6 | Reduces refraction from Pyrotinib and increases efficacy against gastric cancer | [92] |
| Regulator Molecule | Mode of Action on Cyclin D1 | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| KLF5 | Correlated with Cyclin D1 and higher expression showed worse prognosis | [94] |
| CagA | Assists in formation of Cyclin D1-CDK4 complex formation | [93] |
| Aurora B | Phosphorylates H3 and induces Cyclin D1 transcription | [91] |
| METTL16 | Upregulates Cyclin D1 transcription through its methyltransferase activity | [95] |
| BARF1 | Stabilizes and interacts with Cyclin D1 | [96] |
| IC53d | Promotes GSK3b/Akt signaling and induces Cyclin D1 | [97] |
| WDR5 | Induces H3K4me3 and Cyclin D1 for the progression of the cell cycle | [98] |
| p73 | Regulates activator protein 1 (AP-1) for promoting Cyclin D1 | [99] |
| SIX1 | Stabilizes p-ERK and MMP2 for upregulating Cyclin D1 | [100] |
| METTL3 | Modifying mRNA via N6-methyladenosine to upregulate Cyclin D1 and activates the Akt signaling pathway | [102] |
| CORO1C | Assembles F-actin via actin-dependent processes to promote Cyclin D1 and Vimentin | [105] |
| Regulator Molecule | Cyclin/CDK | Effect on Cyclin/CDK | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| SHR6390 | CDK4/6 | Reduces refraction from Pyrotinib and increases efficacy against gastric cancer | [92] |
| PAK1 | CDK4/6 | PAK1 silenced cells sensitizes gastric cancer cells ina PDK1-AKT1 dependent pathway to CDK4/6 inhibition | [112] |
| Nurr1 | CDK4 | Binds to CDK4 promoter to induce transcription and activation of CDK4 | [113] |
| PD0332991 | CDK6 | Direct inhibition of CDK6 and reduction of Rb-phosphorylation to induce cell cycle arrest | [120] |
| PAX6 | CDK4/6 | Upregulates CDK4/6 and induces chemoresistance in gastric cancer cells against Palbociclib | [121] |
| CDC37L1 | CDK6 | Inhibits the activity and expression of CDK6 in gastric cancer cells | [122] |
| UAP1L1 | CDK6 | CDK6 regulates UAP1L1-mediated phenotypes (UAP1L1 is a downstream regulator of CDK6) | [128] |
| PD-0332991 | CDK4/6 | Direct inhibition of CDK4/6 and induction of apoptosis | [117] |
| Non-Coding RNA | Category | Cyclin/CDK | Effect on Cyclin/CDK | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-129-5p | MicroRNA | Cyclin D1 | Downregulation | [84] |
| miR-34a | MicroRNA | Cyclin D1 CDK4 | Downregulation | [85] |
| miR-623 | MicroRNA | Cyclin D1 | Downregulation | [86] |
| LINC0857 | Long Non-coding RNA | Cyclin D1 | Upregulation | [103] |
| Hsa_circ00000647 | Circular RNA | Cyclin D1 | Upregulation | [104] |
| HOTAIR | Long Non-coding RNA | Cyclin D1 | Upregulation | [106] |
| GCRL1 | Long Non-coding RNA | CDK4 | Downregulation | [115] |
| miR-885-3p | MicroRNA | CDK4 | Upregulation | [115] |
| miR-449a | MicroRNA | CDK6 | Downregulation | [118] |
| miR-107 | MicroRNA | CDK6 | Downregulation | [119] |
| miR1296-5p | MicroRNA | CDK6 | Downregulation | [123] |
| miR-191-5p | MicroRNA | CDK6 | Downregulation | [124] |
| miR-29c | MicroRNA | CDK6 | Downregulation | [125] |
| LINC01133 | Long Non-coding RNA | Cyclin D1-CDK4/6 | Upregulation | [129] |
| circZNF609 | Circular RNA | CDK6 | Upregulation | [132] |
| circ_ASAP2 | Circular RNA | CDK6 | Upregulation | [133] |
| LINC00974 | Long Non-coding RNA | CDK6 | Upregulation | [134] |
| circ-0081143 | Circular RNA | CDK6 | Upregulation | [131] |
| Regulator Molecule | Cyclin/CDK | Effect on Cyclin/CDK | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CDCA5 | Cyclin E | Induces proliferative phenotype via Cyclin E activation upregulation | [154] |
| β-carotene | Cyclin E | Inhibits cell proliferation and downregulates Cyclin E in H. pylori infected gastric cells | [155] |
| RPL6 | Cyclin E | Upregulates Cyclin E, confers multi-drug resistance and progresses cells from G1 to S-phase | [157] |
| NF-YA | Cyclin E | Coexpressed with Cyclin E and increases its transcription | [158] |
| 14-3-3ε | Cyclin E | An upstream factor of Cyclin E, acts as oncogene in gastric cancer | [159] |
| EZH2 | Cyclin E | A polycomb protein upregulates Cyclin E and its inhibition leads to Cyclin D1 and Cyclin E downregulation | [160] |
| PCBP2 | CDK2 | Interacts with CDK2 and directly activates it, higher expression is associated with poor prognosis | [169] |
| DDX21 | CDK2 | An ATP-dependent RNA helicase directly upregulates Cyclin D1 and CDK2 | [170] |
| EGR1 | CDK2 | Activates CDK2 and leads to inhibition of p21 | [172] |
| SFN | CDK2 | Downregulates CDK2 and induces apoptosis via p53 mediated pathway | [173] |
| TGF-b1 | CDK2 | Activates caspase mediated apoptosis and CDK2 | [174] |
| Non-Coding RNA | Category | Cyclin/CDK | Effect on Cyclin/CDK | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LINC0857 | Long Non-coding RNA | Cyclin E1 | Upregulation | [103] |
| GHET1 | Long Non-coding RNA | Cyclin E1/CDK2 | Upregulation | [156] |
| LINC01667 | Long Non-coding RNA | Cyclin E1 | Upregulation | [161] |
| miR-138-p | MicroRNA | Cyclin E1 | Downregulation | [161] |
| LINC01021 | Long Non-coding RNA | CDK2 | Upregulation | [168] |
| HNF1A-AS1 | Long Non-coding RNA | CDK2 | Upregulation | [172] |
| miR-638 | MicroRNA | CDK2 | Downregulation | [175] |
| miR-302b | MicroRNA | CDK2 | Downregulation | [176] |
| Non-Coding RNA | Category | Cyclin/CDK | Effect on Cyclin/CDK | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-663 | MicroRNA | Cyclin B1 | Downregulation | [185] |
| miR-340-p | MicroRNA | CDK1 | Downregulation | [191] |
| CASC11 | Long Non-coding RNA | CDK1 | Upregulation | [191] |
| CirC_CEA | Circular RNA | CDK1 | Upregulation | [194] |
| Regulator Molecule | Cyclin/CDK | Effect on Cyclin/CDK | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| NFkB | Cyclin B1 | Recruited to promoter of Cyclin B1 via Pak1 activity for upregulation of Cyclin B1 | [184] |
| E2F4, NFYA, SIN3A, FOXM1 | Cyclin B1 | Increase the transcription of Cyclin B1 via transcription factor activity | [180] |
| Aurora B | Cyclin B1 | Interacts with and phosphorylates CREPT/RPRD1B to upregulate transcription of Cyclin B1 | [183] |
| ISL-1 | Cyclin B1 | CDK1 stabilizes ISL-1, which binds to Cyclin B1 promoter and upregulates its transcription | [186] |
| CAMKK2 | CDK1 | Works in MEK/ERK1 signaling cascade and activates CDK1 | [189] |
| Annexin A4 | CDK1 | Functions as an intracellular Ca2+ regulator and upregulates the transcription of CDK1 | [190] |
| ESRRA | Cyclin B1/CDK1 | Targets DSN1 and increases cell viability via CDC25/Cyclin B1/CDK1 pathway | [192] |
| RASSF10 | Cyclin B1/CDK1 | Promotes the GADD45a nuclear accumulation and inhibits Cyclin B1/CDK1 complex formation | [193] |
| GSI/PTEN | Cyclin B1/CDK1 | GSI dephosphorylates PTEN, which causes nuclear accumulation of Cyclin B1/CDK1 and induces apoptosis | [195] |
| CDCA5 | CDK1 | Coexpressed with CDK1 and also stabilizes it in gastric cancer cells | [196] |
| DTWD1 | Cyclin B1 | Histone deacetylase 3 inhibits DTWD1 which further inhibits Cyclin B1 in gastric cancer | [197] |
| Cyclin/CDK | Expression in Cancer vs. Normal Cells/Tissues | References |
|---|---|---|
| Cyclin A | Upregulated | [164,239] |
| Cyclin B1 | Upregulated | [178,179,181,240] |
| Cyclin C | Downregulated | [210] |
| Cyclin D1 | Upregulated | [81,241,242,243] |
| Cyclin D2 | Upregulated | [244,245] |
| Cyclin E | Upregulated | [135,147,243,246,247] |
| Cyclin G2 | Downregulated | [212,213,214,215] |
| Cyclin L2 | Downregulated | [219] |
| Cyclin T2 | Upregulated | [220] |
| CDK1 | Upregulated | [186,188,196,240,248] |
| CDK4 | Upregulated | [83,249] |
| CDK5 | Downregulated | [224] |
| CDK6 | Upregulated | [250] |
| CDK7 | Upregulated | [218,251] |
| CDK8 | Upregulated | [229] |
| CDK9 | Upregulated | [230] |
| CDK10 | Downregulated | [231,232] |
| CDK12 | Upregulated/Downregulated | [233,234,252] |
| CDK13 | Upregulated | [235] |
| CDK14 | Upregulated | [236] |
| CDK18 | Upregulated | [237] |
| CDK19 | Upregulated | [238] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Javed, A.; Yarmohammadi, M.; Korkmaz, K.S.; Rubio-Tomás, T. The Regulation of Cyclins and Cyclin-Dependent Kinases in the Development of Gastric Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032848
Javed A, Yarmohammadi M, Korkmaz KS, Rubio-Tomás T. The Regulation of Cyclins and Cyclin-Dependent Kinases in the Development of Gastric Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(3):2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032848
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaved, Aadil, Mahdieh Yarmohammadi, Kemal Sami Korkmaz, and Teresa Rubio-Tomás. 2023. "The Regulation of Cyclins and Cyclin-Dependent Kinases in the Development of Gastric Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 3: 2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032848
APA StyleJaved, A., Yarmohammadi, M., Korkmaz, K. S., & Rubio-Tomás, T. (2023). The Regulation of Cyclins and Cyclin-Dependent Kinases in the Development of Gastric Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(3), 2848. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032848







