Contribution of Retrotransposons to the Pathogenesis of Type 1 Diabetes and Challenges in Analysis Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Reported Relationship between the Occurrence of T1D and Viral Infections
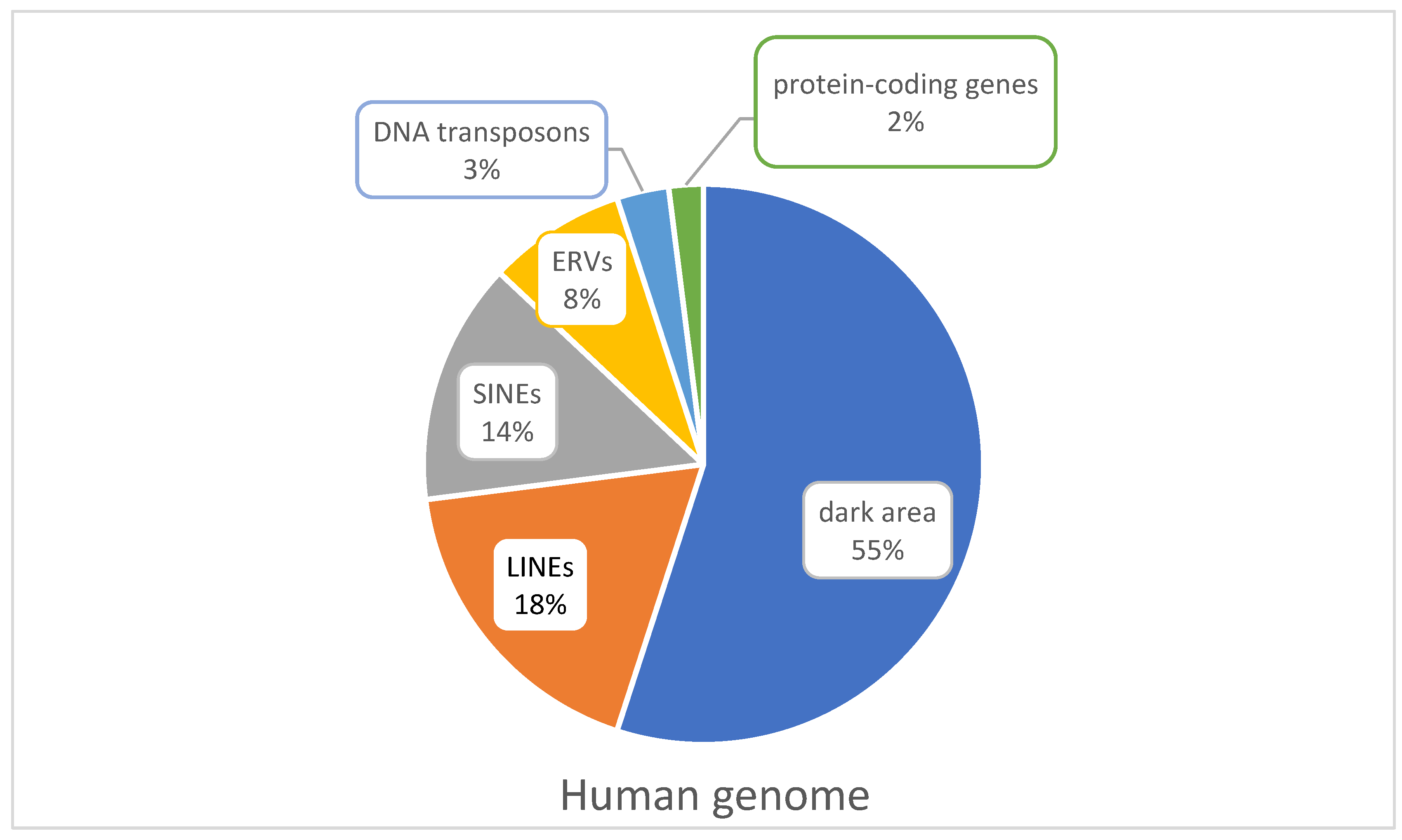
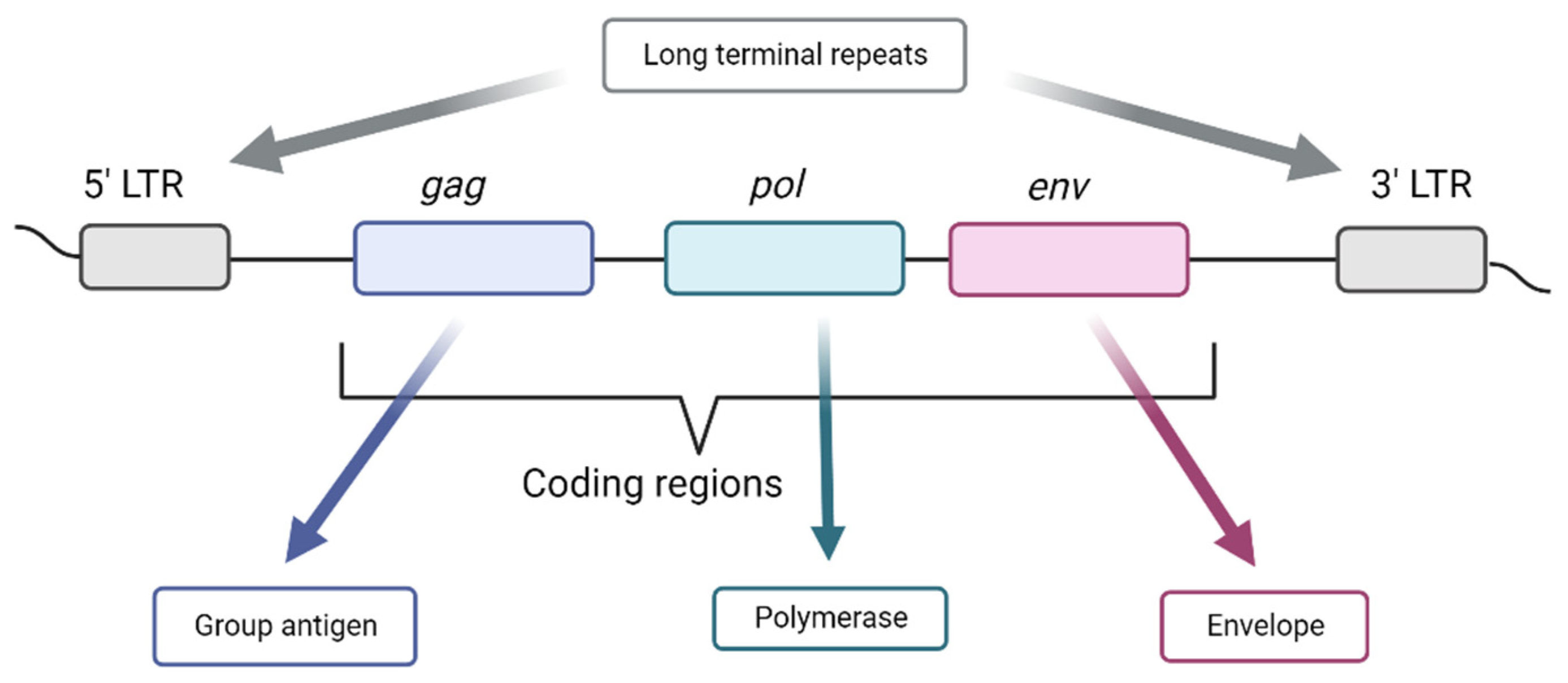
3. Endogenous Viral Elements
4. The Influence of Retrotransposons on Diseases
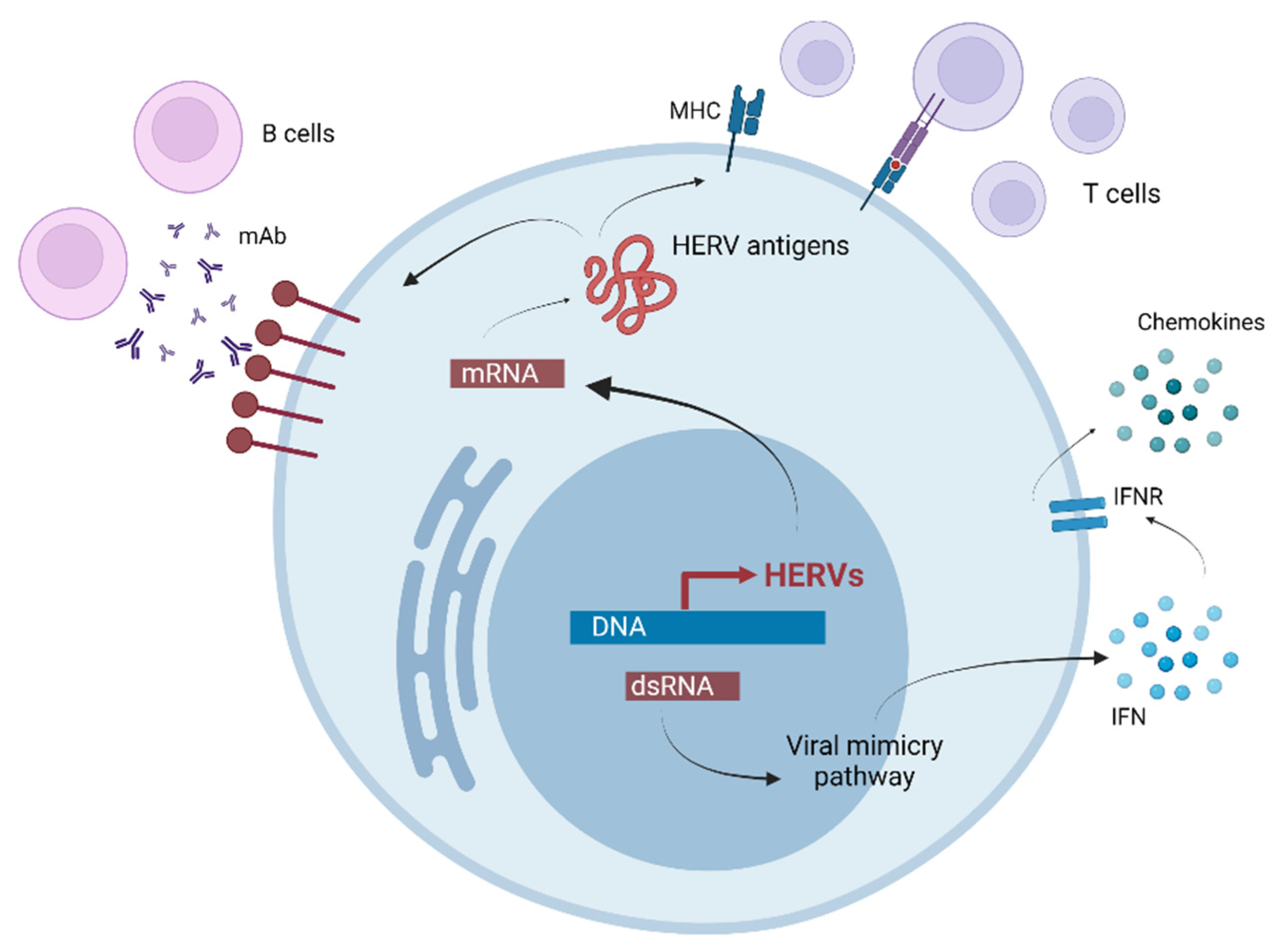
5. The Influence of Retrotransposons on T1D
6. Technologies for the Study of Retrotransposons
7. Best Practices for Analysis of Genomic Regions including Retrotransposons
8. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atkinson, M.A.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; Michels, A.W. Type 1 Diabetes. Lancet 2014, 383, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Differences between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes, Diabetes UK. Available online: https://www.diabetes.org.uk/diabetes-the-basics/differences-between-type-1-and-type-2-diabetes (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, S17–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorena, K.; Michalska, M.; Kurpas, M.; Jaskulak, M.; Murawska, A.; Rostami, S. Environmental Factors and the Risk of Developing Type 1 Diabetes—Old Disease and New Data. Biology 2022, 11, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, G.A.; Robinson, T.I.G.; Linklater, S.E.; Wang, F.; Colagiuri, S.; de Beaufort, C.; Donaghue, K.C.; International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas Type 1 Diabetes in Adults Special Interest Group; Magliano, D.J.; Maniam, J.; et al. Global incidence, prevalence, and mortality of type 1 diabetes in 2021 with projection to 2040: A modelling study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 741–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, C.C.; Karuranga, S.; Salpea, P.; Saeedi, P.; Dahlquist, G.; Soltesz, G.; Ogle, G.D. Worldwide Estimates of Incidence, Prevalence and Mortality of Type 1 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maahs, D.M.; West, N.A.; Lawrence, J.M.; Mayer-Davis, E.J. Epidemiology of Type 1 Diabetes. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 2010, 39, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottesman, B.L.; Yu, J.; Tanaka, C.; Longhurst, C.A.; Kim, J.J. Incidence of New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes Among US Children During the COVID-19 Global Pandemic. JAMA Pediatr. 2022, 176, 414–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilonen, J.; Lempainen, J.; Veijola, R. The Heterogeneous Pathogenesis of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noli, M.; Meloni, G.; Manca, P.; Cossu, D.; Palermo, M.; Sechi, L.A. HERV-W and Mycobacteriumavium Subspecies Paratuberculosis Are at Play in Pediatric Patients at Onset of Type 1 Diabetes. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abela, A.G.; Fava, S. Prenatal and Early Life Factors and Type 1 Diabetes. Endocrine 2022, 77, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulski, J.K.; Suzuki, S.; Shiina, T. SNP-Density Crossover Maps of Polymorphic Transposable Elements and HLA Genes Within MHC Class I Haplotype Blocks and Junction. Front. Genet. 2021, 11, 594318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, M.; Molvig, J. The Susceptibility to Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Is Associated with C4 Allotypes Independently of the Association with HLA-DQ Alleles in HLA-DR3, 4 heterozygotes. Immunogenetics 1988, 28, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colli, M.L.; Ramos-Rodríguez, M.; Nakayasu, E.S.; Alvelos, M.I.; Lopes, M.; Hill, J.L.E.; Turatsinze, J.-V.; Coomans de Brachène, A.; Russell, M.A.; Raurell-Vila, H.; et al. An Integrated Multi-Omics Approach Identifies the Landscape of Interferon-α-Mediated Responses of Human Pancreatic Beta Cells. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzourakis, A.; Gifford, R.J. Endogenous Viral Elements in Animal Genomes. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuong, E.B.; Elde, N.C.; Feschotte, C. Regulatory Activities of Transposable Elements: From Conflicts to Benefits. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancks, D.C.; Kazazian, H.H. Roles for Retrotransposon Insertions in Human Disease. Mob. DNA 2016, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, B.F. SARS-CoV-2 and Human Retroelements: A Case for Molecular Mimicry. BMC Genom. Data 2022, 23, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feschotte, C.; Gilbert, C. Endogenous Viruses: Insights into Viral Evolution and Impact on Host Biology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechaumes, A.; Bertin, A.; Sane, F.; Levet, S.; Varghese, J.; Charvet, B.; Gmyr, V.; Kerr-Conte, J.; Pierquin, J.; Arunkumar, G.; et al. Coxsackievirus-B4 Infection Can Induce the Expression of Human Endogenous Retrovirus W in Primary Cells. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Liu, X.; He, X.; Zhou, L. Exogenous Coronavirus Interacts With Endogenous Retrotransposon in Human Cells. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 609160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R.M.; Tate, J.E.; Jiang, B.; Parashar, U.D. Rotavirus and Type 1 Diabetes—Is There a Connection? A Synthesis of the Evidence. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanz, J.M.; Clarke, C.L.; Xu, S.; Daley, M.F.; Shoup, J.A.; Schroeder, E.B.; Lewin, B.J.; McClure, D.L.; Kharbanda, E.; Klein, N.P.; et al. Association Between Rotavirus Vaccination and Type 1 Diabetes in Children. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labombarde, J.G.; Pillai, M.R.; Wehenkel, M.; Lin, C.-Y.; Keating, R.; Brown, S.A.; Crawford, J.C.; Brice, D.C.; Castellaw, A.H.; Mandarano, A.H.; et al. Induction of broadly reactive influenza antibodies increases susceptibility to autoimmunity. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekhlabi, N.; Haoudar, A.; Echcharii, N.; Ettair, S.; Dini, N. New-Onset Diabetes with Ketoacidosis Precipitated by COVID-19 in Children: A Report of Two Cases. Case Rep. Pediatr. 2021, 2021, 5545258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Huneidi, W.; Hamad, M.; Taneera, J. Expression of SARS-CoV-2 Receptor “ACE2” in Human Pancreatic β Cells: To Be or Not to Be! Islets 2021, 13, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, J.N.; Feschotte, C. A Field Guide to Eukaryotic Transposable Elements. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2020, 54, 539–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebollo, R.; Romanish, M.T.; Mager, D.L. Transposable Elements: An Abundant and Natural Source of Regulatory Sequences for Host Genes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2012, 46, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, X.G.; Barra, V. Losing DNA Methylation at Repetitive Elements and Breaking Bad. Epigenetics Chromatin 2021, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourque, G.; Burns, K.H.; Gehring, M.; Gorbunova, V.; Seluanov, A.; Hammell, M.; Imbeault, M.; Izsvák, Z.; Levin, H.L.; Macfarlan, T.S.; et al. Ten Things You Should Know about Transposable Elements. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurka, J.; Kapitonov, V.V. Sectorial Mutagenesis by Transposable Elements. In Transposable Elements and Genome Evolution; McDonald, J.F., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 1, pp. 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinov, V.M.; Zverev, V.V.; Krasnov, G.S.; Filatov, F.P.; Shargunov, A.V. Viral Component of the Human Genome. Mol. Biol. 2017, 51, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geis, F.K.; Goff, S.P. Silencing and Transcriptional Regulation of Endogenous Retroviruses: An Overview. Viruses 2020, 12, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Liu, M.; Yang, C.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Han, J.; Zhai, X.; Wang, X.; Li, T.; Li, J.; et al. Comprehensive Identification and Characterization of the HERV-K (HML-9) Group in the Human Genome. Retrovirology 2022, 19, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cong, Y.-S. Human Endogenous Retroviruses in Development and Disease. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 5978–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swergold, G.D. Identification, Characterization, and Cell Specificity of a Human LINE-1 Promoter. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1990, 10, 6718–6729. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Faulkner, G.J.; Garcia-Perez, J.L. L1 Mosaicism in Mammals: Extent, Effects, and Evolution. Trends Genet. 2017, 33, 802–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, A.F.A.; Tóth, G.; Riggs, A.D.; Jurka, J. Ancestral, Mammalian-Wide Subfamilies of LINE-1 Repetitive Sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 246, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Du, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhao, K. BST2 Suppresses LINE-1 Retrotransposition by Reducing the Promoter Activity of LINE-1 5′ UTR. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e01610-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewing, A.D. Transposable Element Detection from Whole Genome Sequence Data. Mob. DNA 2015, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Sternberg, R.M.; Novick, G.E.; Gao, G.-P.; Herrera, R.J. Genome Canalization: The Coevolution of Transposable and Interspersed Repetitive Elements with Single Copy DNA. Genetica 1992, 86, 215–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandi, N.; Tramontano, E. Type W Human Endogenous Retrovirus (HERV-W) Integrations and Their Mobilization by L1 Machinery: Contribution to the Human Transcriptome and Impact on the Host Physiopathology. Viruses 2017, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.; Perron, H.; Feschotte, C. Variation in Proviral Content among Human Genomes Mediated by LTR Recombination. Mob. DNA 2018, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandi, N.; Tramontano, E. HERV Envelope Proteins: Physiological Role and Pathogenic Potential in Cancer and Autoimmunity. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongyoo, P.; Avihingsanon, Y.; Prom-On, S.; Mutirangura, A.; Mhuantong, W.; Hirankarn, N. EnHERV: Enrichment Analysis of Specific Human Endogenous Retrovirus Patterns and Their Neighboring Genes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monde, K.; Satou, Y.; Goto, M.; Uchiyama, Y.; Ito, J.; Kaitsuka, T.; Terasawa, H.; Monde, N.; Yamaga, S.; Matsusako, T.; et al. Movements of Ancient Human Endogenous Retroviruses Detected in SOX2-Expressing Cells. J. Virol. 2020, 96, 202135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Human hg38 hla Class 1 UCSC Genome Browser v435. Available online: https://genome-euro.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgTracks?hgsid=290034057_wP8VzIyVszc26kOb26XSLCCasPrB&org=Human&db=hg38&position=hla+class+1&pix=1883 (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- Kent, W.J.; Sugnet, C.W.; Furey, T.S.; Roskin, K.M.; Pringle, T.H.; Zahler, A.M.; Haussler, D. The Human Genome Browser at UCSC. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, A.F.A.; Hubley, R.; Green, P. RepeatMasker. Available online: https://www.repeatmasker.org/webrepeatmaskerhelp.html (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- Ali, A.; Han, K.; Liang, P. Role of Transposable Elements in Gene Regulation in the Human Genome. Life 2021, 11, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iouranova, A.; Grun, D.; Rossy, T.; Duc, J.; Coudray, A.; Imbeault, M.; de Tribolet-Hardy, J.; Turelli, P.; Persat, A.; Trono, D. KRAB Zinc Finger Protein ZNF676 Controls the Transcriptional Influence of LTR12-Related Endogenous Retrovirus Sequences. Mob. DNA 2022, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, S.I.; Tse, H.M. Innate Viral Sensor MDA5 and Coxsackievirus Interplay in Type 1 Diabetes Development. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küry, P.; Nath, A.; Créange, A.; Dolei, A.; Marche, P.; Gold, J.; Giovannoni, G.; Hartung, H.-P.; Perron, H. Human Endogenous Retroviruses in Neurological Diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Precechtelova, J.; Borsanyiova, M.; Sarmirova, S.; Bopegamage, S. Type I Diabetes Mellitus: Genetic Factors and Presumptive Enteroviral Etiology or Protection. J. Pathog. 2014, 2014, 738512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovo, P.-A.; Rabbone, I.; Tinti, D.; Galliano, I.; Trada, M.; Daprà, V.; Cerutti, F.; Bergallo, M. Enhanced Expression of Human Endogenous Retroviruses in New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes: Potential Pathogenetic and Therapeutic Implications. Autoimmunity 2020, 53, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, Y.; Marguerat, S. Interferon-α-Induced Endogenous Superantigen: A Model Linking Environment and Autoimmunity. Immunity 2001, 15, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niegowska, M.; Wajda-Cuszlag, M.; Stępień-Ptak, G.; Trojanek, J.; Michałkiewicz, J.; Szalecki, M.; Sechi, L.A. Anti-HERV-WEnv Antibodies Are Correlated with Seroreactivity against Mycobacterium Avium Subsp. Paratuberculosis in Children and Youths at T1D Risk. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levet, S.; Charvet, B.; Bertin, A.; Deschaumes, A.; Perron, H.; Hober, D. Human Endogenous Retroviruses and Type 1 Diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2019, 19, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolei, A. Endogenous Retroviruses and Human Disease. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 2, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diebold, M.; Derfuss, T. The Monoclonal Antibody GNbAC1: Targeting Human Endogenous Retroviruses in Multiple Sclerosis. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2019, 12, 1756286419833574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marguerat, S.; Wang, W.; Todd, J.; Conrad, B. Association of Human Endogenous Retrovirus K-18 Polymorphisms with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2004, 53, 852–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrad, B.; Weissmahr, R.N.; Böni, J.; Arcari, R.; Schüpbach, J.; Mach, B. A Human Endogenous Retroviral Superantigen as Candidate Autoimmune Gene in Type I Diabetes. Cell 1997, 90, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchins, A.P. Single Cells and Transposable Element Heterogeneity in Stem Cells and Development. Cell Regen. 2021, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Babarinde, I.A.; Sun, L.; Xu, S.; Chen, R.; Shi, J.; Wei, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, G.; Zhuang, Q.; et al. Identifying Transposable Element Expression Dynamics and Heterogeneity during Development at the Single-Cell Level with a Processing Pipeline ScTE. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodzic, E. Single-Cell Analysis: Advances and Future Perspectives. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2016, 16, 313–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, S.J.; Tatovic, D.; Thayer, T.C.; Dayan, C.M. Insights From Single Cell RNA Sequencing Into the Immunology of Type 1 Diabetes- Cell Phenotypes and Antigen Specificity. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 751701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchi, E.; Jones, M.; Klenerman, P.; Frater, J.; Magiorkinis, G.; Belshaw, R. BreakAlign: A Perl Program to Align Chimaeric (Split) Genomic NGS Reads and Allow Visual Confirmation of Novel Retroviral Integrations. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yandell, M.; Ence, D. A Beginner’s Guide to Eukaryotic Genome Annotation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storer, J.M.; Hubley, R.; Rosen, J.; Smit, A.F.A. Methodologies for the De Novo Discovery of Transposable Element Families. Genes 2022, 13, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storer, J.M.; Hubley, R.; Rosen, J.; Smit, A.F.A. Curation Guidelines for de Novo Generated Transposable Element Families. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, C.M.; Quesneville, H. Discovering and Detecting Transposable Elements in Genome Sequences. Brief. Bioinform. 2007, 8, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TE Hub. Available online: https://tehub.org/ (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- dbRIP—Home. Available online: https://dbrip.brocku.ca/index.html (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- Wang, J.; Song, L.; Grover, D.; Azrak, S.; Batzer, M.A.; Liang, P. DbRIP: A Highly Integrated Database of Retrotransposon Insertion Polymorphisms in Humans. Hum. Mutat. 2006, 27, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genetic Information Research Institute. Available online: https://www.girinst.org/ (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- Bao, W.; Kojima, K.K.; Kohany, O. Repbase Update, a Database of Repetitive Elements in Eukaryotic Genomes. Mob. DNA 2015, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pačes, J.; Pavlíček, A.; Pačes, V. HERVd: Database of Human Endogenous Retroviruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 205–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurka, J. Repbase Update: A Database and an Electronic Journal of Repetitive Elements. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HERVd. Available online: https://herv.img.cas.cz/ (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Pačes, J.; Pavlíček, A.; Zika, R.; Kapitonov, V.V.; Jurka, J.; Pačes, V. HERVd: The Human Endogenous RetroViruses Database: Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EnHERV. Available online: http://sysbio.chula.ac.th/enherv/ (accessed on 19 August 2022).
- Autio, M.I.; Bin Amin, T.; Perrin, A.; Wong, J.Y.; Foo, R.S.-Y.; Prabhakar, S. Transposable Elements That Have Recently Been Mobile in the Human Genome. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweiger, D.S. Recent Advances in Immune-Based Therapies for Type 1 Diabetes. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| HLA Locus | Alu Family | LINE-1 Family | ERV Family |
|---|---|---|---|
| DQA1 | AluJr, AluJo | MER51A, MER51B | |
| DQB1 | AluYh3 | LTR13 | |
| DRB1 | AluYa5, AluJb, AluSc8, AluSq2, AluSg, AluSx | L1PA3, L1PA4, L1P1, L1M5 | LTR12 |
| B | AluJr, AluJb, AluSq2, FLAM_A, FLAM_C | L1M4a1, L1M4a2, L1M5, L1ME1, L1MEf, L1MD, L1PA8A, L1PA13, HAL1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Štangar, A.; Kovač, J.; Šket, R.; Tesovnik, T.; Zajec, A.; Čugalj Kern, B.; Jenko Bizjan, B.; Battelino, T.; Dovč, K. Contribution of Retrotransposons to the Pathogenesis of Type 1 Diabetes and Challenges in Analysis Methods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043104
Štangar A, Kovač J, Šket R, Tesovnik T, Zajec A, Čugalj Kern B, Jenko Bizjan B, Battelino T, Dovč K. Contribution of Retrotransposons to the Pathogenesis of Type 1 Diabetes and Challenges in Analysis Methods. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(4):3104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043104
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠtangar, Anja, Jernej Kovač, Robert Šket, Tine Tesovnik, Ana Zajec, Barbara Čugalj Kern, Barbara Jenko Bizjan, Tadej Battelino, and Klemen Dovč. 2023. "Contribution of Retrotransposons to the Pathogenesis of Type 1 Diabetes and Challenges in Analysis Methods" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 4: 3104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043104
APA StyleŠtangar, A., Kovač, J., Šket, R., Tesovnik, T., Zajec, A., Čugalj Kern, B., Jenko Bizjan, B., Battelino, T., & Dovč, K. (2023). Contribution of Retrotransposons to the Pathogenesis of Type 1 Diabetes and Challenges in Analysis Methods. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(4), 3104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043104






