Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) represents the most prevalent type of dementia in elderly people, primarily characterized by brain accumulation of beta-amyloid (Aβ) peptides, derived from Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP), in the extracellular space (amyloid plaques) and intracellular deposits of the hyperphosphorylated form of the protein tau (p-tau; tangles or neurofibrillary aggregates). The Nerve growth factor receptor (NGFR/p75NTR) represents a low-affinity receptor for all known mammalians neurotrophins (i.e., proNGF, NGF, BDNF, NT-3 e NT-4/5) and it is involved in pathways that determine both survival and death of neurons. Interestingly, also Aβ peptides can blind to NGFR/p75NTR making it the “ideal” candidate in mediating Aβ-induced neuropathology. In addition to pathogenesis and neuropathology, several data indicated that NGFR/p75NTR could play a key role in AD also from a genetic perspective. Other studies suggested that NGFR/p75NTR could represent a good diagnostic tool, as well as a promising therapeutic target for AD. Here, we comprehensively summarize and review the current experimental evidence on this topic.
1. Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) represents the most prevalent type of dementia in elderly people [1], primarily characterized by brain accumulation of beta-amyloid (Aβ) peptide in the extracellular space (amyloid plaques) and intracellular deposits of paired helical filaments (PHF), mainly formed by the hyperphosphorylated form of the protein tau (p-tau) (tangles or neurofibrillary aggregates) [2,3]. The main clinical feature of AD consists of increasing cognitive decline over time, often anticipated, or accompanied by a set of behavioral disturbances [4,5,6]. Two major forms of the disease exist: sporadic (sAD), the causes of which are not yet completely understood and can be related to several hypotheses, and familial (fAD), inherited within families from generation to generation even with a clear autosomal dominant transmission of mutations in Presenilin 1 (PSEN1), 2 (PSEN2) or Amyloid Precursors Protein (APP) genes [7,8,9]. In both forms, amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles are accompanied by neuronal and synaptic loss [10], microgliosis [11], astrogliosis [12], and neuroinflammation [13].
Amyloid plaques originate from the APP, which is a membrane glycoprotein with a large N-terminal glycosylated domain on the extracellular side and a C-terminal domain on the intracellular side of the cell membrane [14]. Under physiological conditions, APP is processed by two distinct pathways, one non-amyloidogenic (α-secretases pathway, e.g., ADAM10 and ADAM17) and one amyloidogenic (β-secretase pathway), the latter of which leads to the production of Aβ peptides (e.g., Aβ1−42 and Aβ25−35) [15]. Specifically, BACE1 is the β-secretase enzyme that cleaves the transmembrane APP and, together with γ-secretase, generates Aβ species that form increasingly large and conformationally complex soluble aggregates [15,16,17,18]. Over the years, several hypotheses have been formulated to explain how the neuropathological features of AD are causally related to each other, underpinning its pathogenesis. Among these, the most debated in scientific communities is the “amyloid cascade hypothesis” which posed that the progressive accumulation of Aβ in the brain triggers a complex cascade of events that result in the tau hyperphosphorylation, loss of synapses, glial activations, progressive deficiency of neurotransmitters, and neural death [19,20]. However, this hypothesis has been subject to several criticisms or alternative interpretation because of lack of a strong link that can explain how Aβ can cause all these neuropathological phenotypes [21]. One of the most fascinating alternative hypotheses is the “deficient neurotrophic hypothesis”, according to which the loss of trophic support to the cholinergic neurons due to an imbalance of neurotrophins and their receptors underlies the pathogenesis of AD [22,23]. Within this hypothesis, an increasing body of evidence indicates that the nerve growth factor receptor (NGFR), also known as p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR), could represent the “missing piece” to elucidate the neuropathological mechanism underpinning both fAD and sAD.
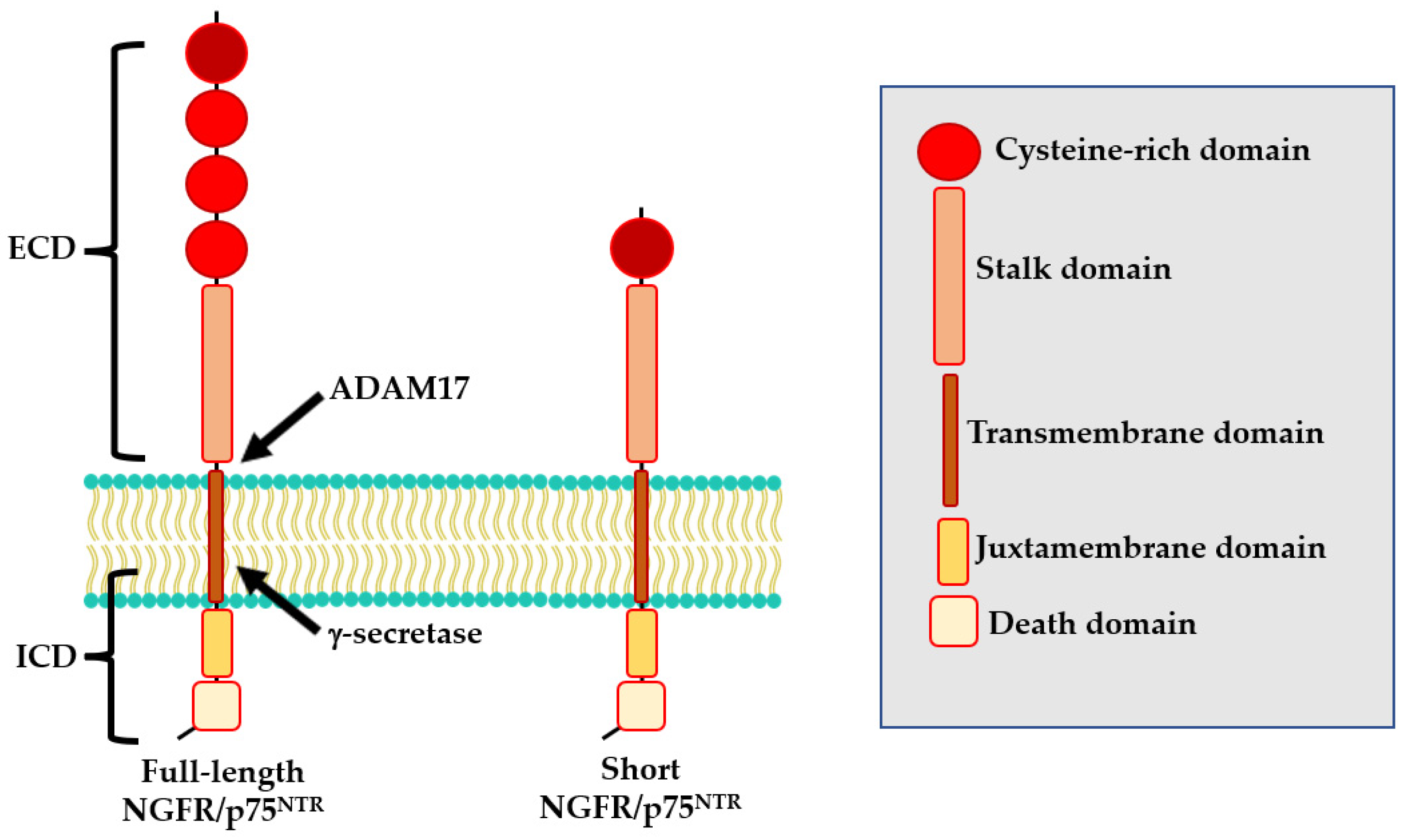
The NGFR/p75NTR protein is encoded by the NGFR/p75NTR gene, located on the long arm of chromosome 17 (17q21.33). At least two isoforms of NGFR/p75NTR exist: a full-length isoform and a shorts isoform (s-NGFR/p75NTR) both of which are expressed in nerve cells [24]. The full-length isoform includes six exons and five introns [25]. The resulting protein comprises an extracellular domain that contains four cysteine-rich motifs (CDR1-CRD4), a transmembrane domain, and an intra-cellular domain formed by a juxtamembrane domain (Chopper) and a death domain (Figure 1) [26,27]. The s-NGFR/p75NTR isoform results from alternative splicing of exon III of the NGFR/p75NTR locus which encodes for the CDR 2–4 [28] and consequently lacks the neurotrophin-binding site. For this reason, while the full-length isoform can bind all known neurotrophins, the s-NGFR/p75NTR isoform does not interact with several molecules including Nogo, sortilin and Trk (Figure 1) [29,30]. Sabry and colleagues also reported a human NGFR/p75NTR 36 kD isoform, not yet fully characterized [30].
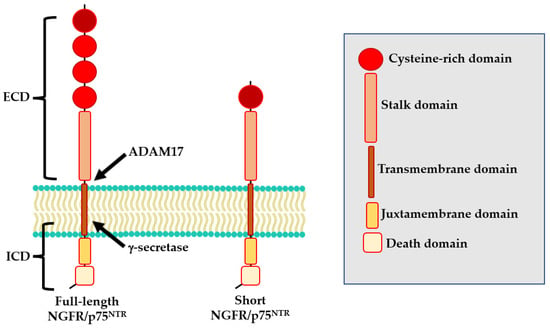
Figure 1.
Structure of NGFR/p75NTR isoforms.
NGFR/p75NTR represents a similar-affinity receptor for all known mammalian neurotrophins—i.e., nerve growth factor (NGF), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), NT-3, and NT4/5 [31]-and a higher affinity receptor for their immature forms (i.e., proNGF, pro-BDNF) [32,33]. The ligand binding to NGFR/p75NTR mainly causes the activation of apoptosis signaling pathways [9,34]. However, these neurotrophins can also bind other receptors—i.e., NGF to TrkA, BDNF and NT-4/5 to TrkB, whereas NT-3 to TrkC, promoting downstream signaling involved in neuronal survival and differentiation [35]. Other findings also showed that NGFR/p75NTR can regulate axonal growth, cell cycle, and synaptic plasticity [36]. The specificity of the signaling pathways to be activated (i.e., death vs. survivor) is reached through the formation of NGFR/p75NTR molecular complexes with different co-receptors, such as Trk family, sortilin and Nogo receptors [37]. In particular, the NGFR/p75NTR interaction with Trk receptors induces neuronal survival and differentiation [38,39], the cooperation with sortilin causes the trigger of pro-neutrotrophins-induced cell death [39] whereas the binding with Nogo receptors is involved in the suppression of axonal growth (for a review see [40]).
Moreover, preliminary data indicated that NGFR/p75NTR can also undergo epigenetic modifications such as methylation and histone acetylation. For example, it has been shown that ibuprofen can increase the mRNA and protein levels of NGFR/p75NTR by inducing its promoter hypomethylation and by increasing N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-NGFR/p75NTR expression in cancer cell lines [41].
Interestingly, NGFR/p75NTR could also undergo to a three-step proteolytic cleavage that could modify its functional properties [42,43]. During the first step, the extracellular domain (ECD) of NGFR/p75NTR is cleaved by ADAM17, generating a membrane-bound C-terminal fragment (CTF). Then, CTF undergoes to a second cleavage by the PSEN-dependent γ-secretase, releasing the intracellular domain (ICD) into the cytoplasm [31].
Given the multiple functions and implications of NGFR/p75NTR in the central nervous system (CNS), this review will explore the genetic and molecular evidence surrounding its relationship with AD, the experimental evidence around NGFR/p75NTR-driven AD neuropathology, as well as the relevance of this protein as a prognostic–diagnostic tool and therapeutic target for AD.
2. Expression and Signaling Pathways of NGFR/p75NTR in AD
NGFR/p75NTR receptors are highly expressed of both neurons and glial cells during the CNS development [44] and after brain injury [45], whereas in the normal adulthood are present only in specific brain regions such as neurons and astrocytes of hippocampal cornus ammon 1 (CA1) [46] and especially in the cholinergic neurons (CNs) of the basal forebrain, of which antibodies against these receptors represent the most used immunohistochemical marker [47,48,49]. The CNs of the basal forebrain send long projections to several cortical areas, including the entorhinal cortex and visual cortex, as well as the amygdala, resulting in several cholinergic circuits involved in the regulations of working memory, visual discrimination, and attention [50].
It has long been known that the CNs of the basal forebrain play a critical role in AD for different reasons: (i) the AD neurodegeneration could originate in these neurons and only then may affect other brain regions; (ii) CNs represent the type of neurons most affected in AD; (iii) CNs degeneration predicts the cortical spread of AD neuropathology [51]. Interestingly, TrkA expression is reduced in early and late stages of AD [52,53,54] whereas the NGFR/p75NTR expression is not affected or is increased in AD-damaged CNs of the basal forebrain [54,55,56]. Besides the basal forebrain, AD patients showed higher levels of NGFR/p75NTR receptors also in cortical neurons [57,58], entorhinal cortex [59] and hippocampi [60,61]. Since NGFR/p75NTR mediates apoptotic signaling in the absence of TrkA [45,62] the imbalance ratio of NGFR/p75NTR and TrkA may result in an increased programmed cell death. Sáez and collegues [56] demonstrated that the Aβ25−35 exerts an indirect neurotoxic effect by stimulating the astrocytes synthesis of NGF that in turn causes tau hyperphosphorylation and hippocampal neuron death through NGFR/p75NTR [63]. Therefore, NGFR/p75NTR and TrkA receptors differentially regulate APP processing, promoting the non-amyloidogenic and amyloidogenic pathways, respectively. In particular, the binding of NGF to NGFR/p75NTR leads to the activation of the second messenger ceramide and then to the β-secretase cleavage of APP [64].
Interestingly, an increasing amount of evidence indicates the pivotal role of NGFR7p75NTR in amyloidogenesis and in Aβ-induced neurotoxicity due to the binding of Aβ to these receptors. In particular, Devarajan and Sharmila [58] demonstrated that Aβ1-42 specifically recognizes CRD1 and CRD2 domains of the NGFR/p75NTR receptor and forms a “cap” like structure at the N-terminal that is stabilized by a network of hydrogen bonds [65].
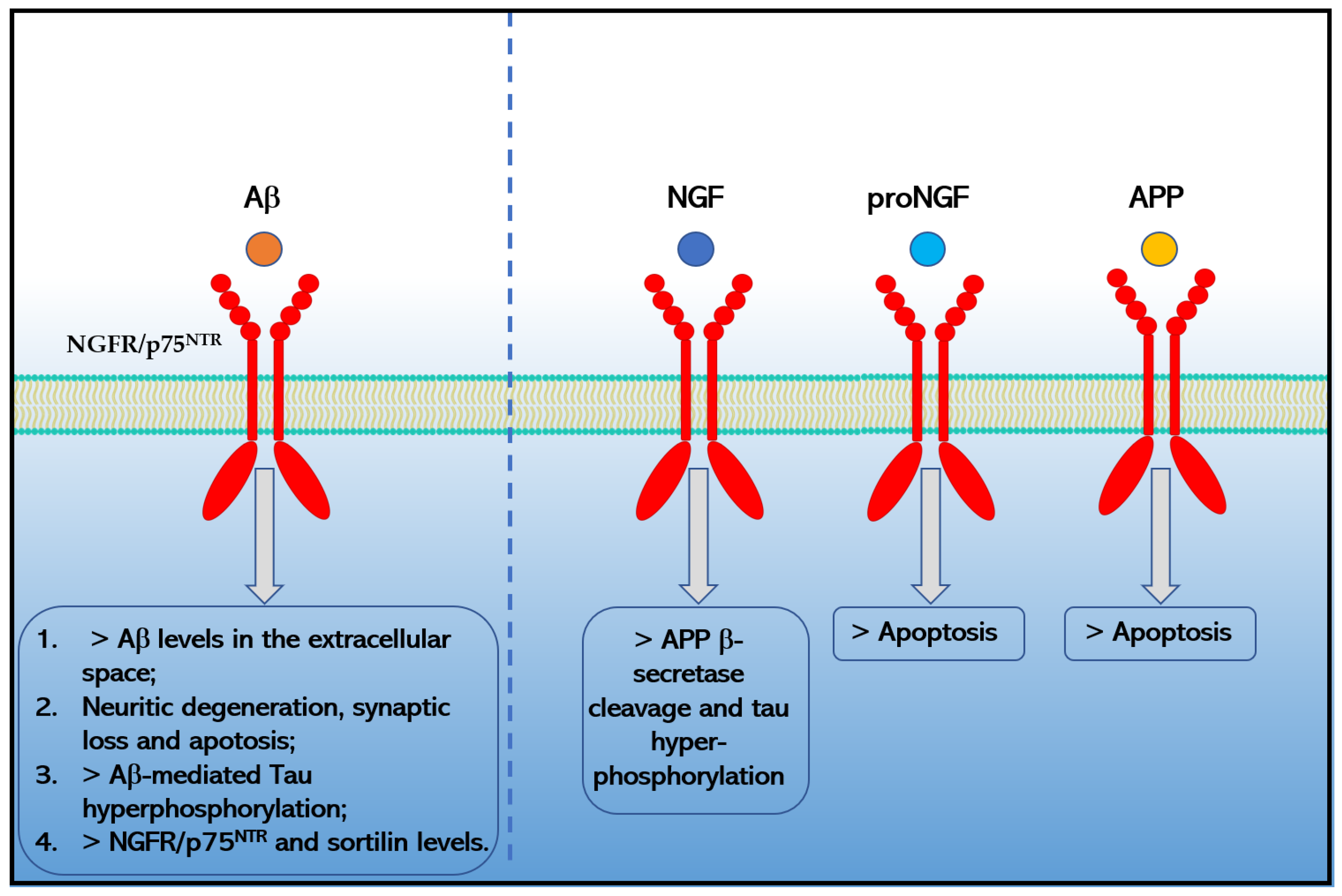
Moreover, the binding of Aβ1−42 to NGFR/p75NTR increases the extracellular levels of Aβ1−42 [66], causes neurotoxicity [62] by signaling pathways that involve JNK, NADPH oxidase, and caspases-9/3, as well as by an alternative PLAIDD pathway [67,68,69], mediates Aβ-induced tau hyperphosphorylation and neurodegeneration (i.e., synaptic disorder and neuronal loss) through the calpain/CDK5 and AKT/GSK3β pathways [70] and increases the expression of another pro-apoptotic neurotrophin receptor, sortilin via the RhoA pathway [58] that in turn could interact with NGFR/p75NTR to induce neuronal apoptosis [71]. Chakravarthy and colleagues suggested that Aβ accumulation in turn upregulates the expression of membrane-associated NGFR/p75NTR through insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) phosphorylation [61,72]. Moreover, Hu and colleagues reported in 2013 that the death receptor 6 (DR6) forms a receptor complex with NGFR/p75NTR that mediates Aβ-induced neurotoxicity in cortical neurons [73]. Finally, preliminary data also indicated that APP and proNGF could directly interact with NGFR/p75NTR increasing apoptosis in AD [59,74,75] (Figure 2). Moreover, preliminary data indicated that NGFR/p75NTR could facilitate the effects of soluble Aβ oligomers on dendritic spine density and structure in non-apoptotic hippocampal neurons [76].
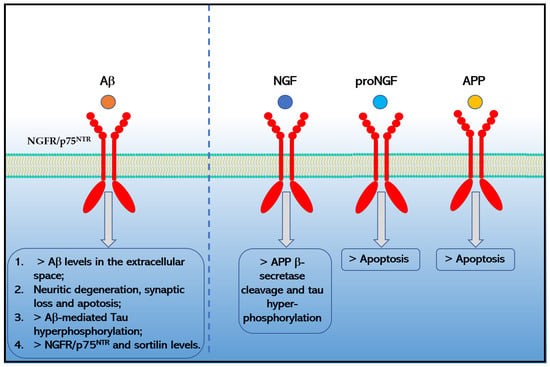
Figure 2.
Effects caused by the binding of Aβ1−42, NGF, proNGF and APP to NGFR/p75NTR in Alzheimer’s disease.
Interestingly, several data indicated that NGFR/p75NTR ECD, derived from the proteolytic cleavage by ADAM-17 followed by regulated-intramembranous proteolysis by γ-secretase, represents a protective factor against AD-neuropathology [77]. This effect is probable due to the fact that the NGFR/p75NTR ECD contains the binding sites for Aβ—i.e., CRD1 and CRD2 domains—and for other ligands that can induce apoptosis through the activation of these receptors [78]. Thus, the impaired NGFR/p75NTR ECD shedding and the imbalanced levels of NGFR/p75NTR and NGFR/p75NTR ECD could play an important role in regulating the production and clearance of Aβ [79]. Moreover, the PSEN1 M146V mutation increases γ-secretase cutting of NGFR/p75NTR in vitro and potentially exacerbates the pathogenic outcomes observed in fAD [80]. He and colleagues also reported an overproduction of naturally occurring autoantibodies against NGFR/p75NTR ECD in AD patients, strengthening the role of the immune system and immunosenescence in the AD pathogenesis [79].
Further evidence about the involvement of NGFR/p75NTR in AD derives from inactivation and ablation studies. Indeed, the 5xFAD mice, which expresses a signaling-deficient variant of the NGFR/p75NTR, shows a greater neuroprotection from AD neuropathology than animals lacking this receptor [81]. In the same manner, the ablation of NGFR/p75NTR signaling protects the hippocampal network against pathophysiological changes observed in AD (e.g., Aβ-induced degradation of gamma oscillations and gamma–theta interaction) in vitro [82].
Thus, the involvement of NGFR/p75NTR in the AD-associated brain alterations appears to be multifactorial and encompasses several ligands, including Aβ, NGF, proNGF and APP, as well as the activity of ADAM17 and γ-secretases, although the complete set of elements needed by the neurons to enter the apoptotic program in response to these interactions remains to be determined.
3. NGFR/p75NTR Genetic Variants and AD
The first evidence of a genetic involvement of NGFR/p75NTR in AD emerged from a study of Cozza and colleagues [83]. The authors analyzed the genetic variability of four functional NGFR/p75NTR polymorphisms (i.e., rs2072445 and rs2072446 located in exon 4, rs741072 located in exon 6, rs734194 located in the 3′-UTR) and the risk of developing AD in an Italian sample consisting of 151 sAD patients, 100 fAD patients, and 97 healthy subjects. fAD was defined as those patients with at least two first-degree relatives in two generations affected by AD in absence of mutations in PSEN1, PSEN2 and APP genes. From the results of this study emerged a significant association between the rs2072446 variant and the risk of fAD. Since the polymorphism is located near the genetic region that codes for the cleavage region recognized by ADAM17, its variability may affect the cleavage efficiency of NGFR/p75NTR and, thus, the release of NGFR/p75NTR ECD [79]. However, this association did not remain significant after correction for multiple comparisons. In a second study, Cheng and colleagues [84] examined the genetic variability of the four SNPs previously analyzed by Cozza and collaborators [83] together with the rs741073 variant, located on 3′-UTR, and the risk of developing AD in a Chinese sample consisting of 264 sAD patients and 389 healthy controls the authors found that the rs734194 variant was significantly associated with a decreased risk of AD. However, also in this case, this association did not remain significant after correction for multiple comparisons. Moreover, Matyi and colleagues [85] analyzed the association between the rs2072446 variant and the risk of AD in a population sample of older adults from the Cache County Study on Memory in Aging (CCSMA) of Utah, consisting of 396 AD and 3272 controls. They found a significant association between the genetic variability of the rs2072446 polymorphism and the risk of developing AD only in females. In particular, they found that compared to male non-carriers, female carriers of the minor T allele of rs2072446 showed a 60% higher risk of developing AD in contrast with the finding previously reported by Cozza [83]. Through the analysis of an Australian sample consisting of 258 cases and 247 controls, Vacher and colleagues [86] found a significant association between the variant rs9908234, located in the intron 1 of the NGFR/p75NTR gene, and the brain accumulation of Aβ. More recently, He and collaborators [87] conducted a case–control association study (366 sAD patients and 390 age-and sex-matched controls) in a Chinese Han population. By analyzing the variability of twelve tag-SNPs within the NGFR/p75NTR gene located in the promoter region (rs603769 and rs2584665), in intron 1 (rs9908234 and rs3785931), in intron 3 (rs2537706 and rs534561), in exon 4 (rs2072446) and in exon 6 (rs7219709, rs1804011, rs734194, rs741072, and rs741073), they found that the rs2072446-T allele was significantly associated with an increased risk of sAD (OR = 1.79). Interestingly, by analyzing another cohort (279 cognitive normal, 480 MCI, and 47 AD) from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) database it has also been shown that T allele at the rs2072446 variant was also associated with the heavier Aβ burden, which further contributed to an increased risk of AD progression in APOE ε4 non-carrier. Probably the heterogeneity of these results might be due to the presence of sex- and population-specific associations that might be also modified by socio-economic and lifestyle factors and epistatic genetic effects that could be more efficiently captured in large population samples with more accurate and detailed clinical data. Thus, other studies are needed to better understand the role of NGFR/p75NTR variants in different populations and selecting a set of more informative SNPs to capture most of the genetic variations of the entire gene.
4. NGFR/p75NTR as a Biomarker of AD
The evidence that NGFR/p75NTR could represent a specific biomarker for AD emerged in 2015 from a study of Yao and colleagues [77], who reported a significant reduction of NGFR/p75NTR ECD levels in cerebrospinal fluid (CFS) and in the brains of AD patients and of APP/PSEN1 double-transgenic mice, due to the Aβ-induced reduction in the expression and activity of ADAM17 (Table 1). In the same period, Jiao and collaborators [88] reported a distinct and typical NGFR/p75NTR ECD profile in AD patients, characterized by a decreased CFS and an increased serum levels, compared to other diseases (i.e., Parkinson’s disease, stroke) as well as to the control group (elderly people without neurological disorders). The serum and CFS levels of NGFR/p75NTR ECD also correlated with the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores in AD patients and, therefore, its detection could represent a good tool for differential diagnosis of these diseases. In addition, the combination of CSF Aβ1-42, CSF Aβ42-40, CSF ptau181 or CSF ptau181/Aβ1-42 with CSF NGFR/p75NTR ECD improves diagnostic accuracy (Table 1). More recently, He and colleagues [79] investigated the presence and alterations of naturally occurring autoantibodies against NGFR/p75NTR ECD in AD patients, as well as their effects on AD pathology. From the results of this study emerged an increased level of these naturally occurring antibodies in the CFS and a negative association between these and the CFS levels of NGFR/p75NTR ECD in AD patients (Table 1). Interestingly, transgenic AD mice actively immunized with NGFR/p75NTR ECD showed a lower level of NGFR/p75NTR ECD and a more severe AD pathology in the brain and worse cognitive functions compared to two different control groups immunized with the reverse sequence of NGFR/p75NTR ECD and phosphate-buffered saline, respectively. Moreover, Crispoltoni and collaborators [89] examined the relationship between the plasma levels of NGF as well as the expression levels of TrkA and NGFR/p75NTR in monocytes of patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), mild and severe AD. The authors reported an increased concentration of plasma NGF accompanied by a higher expression of TrkA, but not of NGFR/p75NTR, in monocytes from patients with MCI and mild AD. Conversely, in patients with severe AD it has been reported a decreased NGF plasma concentration whereas in the monocytes, the expression of TrkA and NGFR/p75NTR were decreased and increased, respectively, and were associated with caspase 3-mediated apoptosis (Table 1). Therefore, this study reported a plasmatic-NGF and monocytic TrkA and NGFR/p75NTR variation during the progression from MCI to severe AD. However, as far as we know, these studies did not carry out a genetic screening on AD patients to verify the presence of mutations in the PS1, PS2 and APP genes or have included patients with no family history of dementia. Further studies are needed to understand whether these findings can be applied to both sporadic and genetic AD patients, taking into account gender differences as well.

Table 1.
Summary of the main studies reporting NGFR/p75NTR as a biomarker for AD.
5. NGFR/p75NTR as a Therapeutic Target for AD
Given the results discussed so far regarding the involvement of NGFR/p75NTR in the neuropathology of AD, since the mid-2000s, several research groups have tested in vivo and in vitro the effect of several molecules capable of blocking or altering the expression of these receptor for the treatment of this currently incurable disease [90]. These include LM11A-31 [91], CATDIKGAEC [92,93] and sulforaphane [94] (Table 2). Furthermore, other researchers have experimented the efficacy of the administration of NGFR/p75NTR ECD in counteracting AD phenotype [70,95].

Table 2.
Summary of the main studies reporting NGFR/p75NTR as a therapeutic target for AD.
LM11A-31 is a small non-peptide NGFR/p75NTR ligand able to selectively activate survival signaling and simultaneously inhibit pro-apoptosis pathways [96]. Several animal data indicated that this molecule is able to inhibit Aβ-induced neural death and neuritic degeneration, as well as to prevent tau phosphorylation and misfolding, loss of cholinergic neurites, microglia and astrocyte activation, and cognitive decline and to reverse synaptic function [91,97,98,99,100]. These encouraging results have prompted the researchers to test its effects in humans as well. Indeed, a phase II clinical trial is currently underway on mild–moderate AD patients (ClinicalTrials.gov accession number NCT03069014; Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03069014?term=LM11A-31-BHS&draw=2&rank=1 accessed on 22 December 2022).
In 2007, Yaar and colleagues [92,93] tested the efficacy of CATDIKGAEC heterocyclic peptide, homologous to amino acids 28–36 of NGF, in counteracting the AD phenotype. Preliminary data showed that also this molecule is able to interfere with Ab1-40 signaling and rescue neurons from Aβ1–40-induced toxicity in vitro. In addition, the in vivo injections of Aβ together with CATDIKGAEC into the cerebral cortex of B57BL/6 mice significantly decreased the Aβ-induced brain inflammation compared to the injection of Aβ and a control peptide. However, as far as we know, this line of research was no longer pursued. Moreover, in 2017, Zhang and colleagues [94] tested the efficacy of sulforaphane (SFN), a secondary metabolite found in edible cruciferous vegetables, in the treatment of AD. Interestingly, the administration of this molecule to APP/PSEN1 double-transgenic mice, ameliorated the cognitive dysfunction and protected against the Increment of amyloid plaques. These effects may be associated with an up-regulation of NGFR/p75NTR expression which is mediated, at least partly, by SFN-induced reduction in the expression of histone deacetylases (i.e., HDAC1 and HDAC3) that regulates the NGFR/p75NTR transcription. Other studies are needed to better characterize the effects of this molecule in the attenuation of the AD-phenotype, as well as the underlying molecular mechanisms in which NGFR/p75NTR could be implicated.
Finally, as mentioned above, several data indicated that NGFR/p75NTR ECD could have a protective effect on Aβ-induced neuropathology and has been proposed as a good candidate AD biomarker [77]. Interestingly, it has also been shown that the restoration of NGFR/p75NTR levels thought the intracerebroventricular injection of a soluble NGFR/p75NTR ECD-fusion construct protected Tau P301L mice against pathological tau modifications [70] whereas the intramuscular delivery of an AAV-NGFR/p75NTR ECD vector in APP/PSEN1 double-transgenic mice ameliorates spatial learning and memory, a reduced Aβ accumulation in the brain and blood and reduced neurite degeneration, neuronal death, microgliosis, inflammation, and tau phosphorylation [95]. Therefore, also the use of a NGFR/p75NTR-based peripheral approach represents a promising direction to develop novel therapies for AD.
6. Conclusions
The evidence here reported, underline the pivotal role of NGFR/p75NTR in all neuropathological changes observed in AD. In the adult brain, these receptors are highly expressed by the cholinergic neurons CNs of the basal forebrain which represent the type of neurons firstly and most affected in AD. Indeed, the binding of Aβ to these receptors increases the extracellular levels of Aβ1–42, causes neurotoxicity, synaptic disorder, and neuronal loss, mediates Aβ-induced tau hyperphosphorylation and increases the expression of membrane-associated NGFR/p75NTR as well as of its “death” co-receptors sortilin. The presence of reduced NGFR/p75NTR ECD levels in CFS and in the brains of AD patients, which has a protective effect in AD-like pathology since it prevents the binding of Aβ NGFR/p75NTR, not only pushes to consider it as an AD powerful biomarker but opens new avenues for understanding why impaired NGFR/p75NTR signaling occurs in this disease. The genome-wide association studies (GWAS) carried out so far indicate that, only in part, it can be explained by the variability of polymorphisms in the NGFR/p75NTR gene—currently “only” the rs9908234 and rs2072446 were significantly associated with the brain accumulation of Aβ—although more extensive and large-scale studies are needed in this topic to detect rare NGFR/p75NTR variants and possible epistatic effects with other genetic variants able to modulate the disease susceptibility. For instance, since NGFR/p75NTR ECD is derived from the proteolytic cleavage by ADAM17, further studies are also needed to investigate the role of this biological and functional interaction in the pathogenesis and neuropathology of AD. Moreover, since it has been shown that NGFR promoter is subject to epigenetic regulation, it is also important to clarify the role of the gene expression regulation on the AD susceptibility. Nevertheless, the analysis of the epigenetic variability in relation to the AD onset is still poorly investigated. Finally, the use of NGFR/p75NTR antagonist molecules or the administration of NGFR/p75NTR ECD appear to be promising therapeutic approaches for AD; a phase II clinical trial is currently underway on mild–moderate AD patients with the use of the small NGFR/p75NTR ligand LM11A-31.
Author Contributions
F.B. conceptualized the manuscript. F.B., P.A. and A.M. wrote the manuscript. F.B. created the figures. D.L., A.C.B. and R.M. reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by funds granted by the Italian Ministry of Health—Ricerca Finalizzata–Starting Grant 2018: SG-2018-12366233.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G.; Cairns, N.J.; Crowther, R.A. Tau proteins of Alzheimer paired helical filaments: Abnormal phosphorylation of all six brain isoforms. Neuron 1992, 8, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaper, S.D. Alzheimer’s disease and amyloid: Culprit or coincidence? Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2012, 102, 277–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeboom, J.; Weinstein, H. Neuropsychology of cognitive ageing, minimal cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular cognitive impairment. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 490, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomari, N.; Bruno, F.; Laganà, V.; Smirne, N.; Colao, R.; Curcio, S.; Di Lorenzo, R.; Frangipane, F.; Maletta, R.; Puccio, G.; et al. A Comparison of Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia (BPSD) and BPSD Sub-Syndromes in Early-Onset and Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 85, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laganà, V.; Bruno, F.; Altomari, N.; Bruni, G.; Smirne, N.; Curcio, S.; Mirabelli, M.; Colao, R.; Puccio, G.; Frangipane, F.; et al. Neuropsychiatric or Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia (BPSD): Focus on Prevalence and Natural History in Alzheimer’s Disease and Frontotemporal Dementia. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 832199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abondio, P.; Sarno, S.; Giuliani, C.; Laganà, V.; Maletta, R.; Bernardi, L.; Bruno, F.; Colao, R.; Puccio, G.; Frangipane, F.; et al. Amyloid Precursor Protein A713T Mutation in Calabrian Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease: A Population Genomics Approach to Estimate Inheritance from a Common Ancestor. Biomedicines 2021, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, F.; Laganà, V.; Di Lorenzo, R.; Bruni, A.C.; Maletta, R. Calabria as a Genetic Isolate: A Model for the Study of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, F.; Malvaso, A.; Canterini, S.; Bruni, A.C. Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs) in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Implications for Diagnosis and Treatment. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeTure, M.A.; Dickson, D.W. The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, D.V.; Hanson, J.E.; Sheng, M. Microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Cell. Biol. 2018, 217, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.; Wadhwa, P.K.; Jadhav, H.R. Reactive Astrogliosis: Role in Alzheimer’s Disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2015, 14, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heneka, M.T.; Carson, M.J.; Khoury, J.E.; Landreth, G.E.; Brosseron, F.; Feinstein, D.L.; Jacobs, A.H.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Vitorica, J.; Ransohoff, R.M.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, U.C.; Deller, T.; Korte, M. Not just amyloid: Physiological functions of the amyloid precursor protein family. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojro, E.; Fahrenholz, F. The non-amyloidogenic pathway: Structure and function of alpha-secretases. Subcell. Biochem. 2005, 38, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalivaeva, N.N.; Turner, A.J. Targeting amyloid clearance in Alzheimer’s disease as a therapeutic strategy. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 3447–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Xia, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C. Targeting Amyloidogenic Processing of APP in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Hardy, J.; Blennow, K.; Chen, C.; Perry, G.; Kim, S.H.; Villemagne, V.L.; Aisen, P.; Vendruscolo, M.; Iwatsubo, T.; et al. The Amyloid-β Pathway in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5481–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, J.; Vöglein, J.; Quiroz, Y.T.; Bateman, R.J.; Ghisays, V.; Lopera, F.; McDade, E.; Reiman, E.; Tariot, P.N.; Morris, J.C. Testing the amyloid cascade hypothesis: Prevention trials in autosomal dominant Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022, 18, 2687–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Lin, D.; Cheng, Y.; Jiang, S.; Riaz, M.W.; Fu, N.; Mou, C.; Ye, M.; Zheng, Y. Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: Progress and Challenges. Aging Dis. 2022, 13, 1745–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancu, I.-C.; Vasconcelos, B.; Terwel, D.; Dewachter, I. Models of β-amyloid induced Tau-pathology: The long and “folded” road to understand the mechanism. Mol. Neurodegener. 2014, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-Q.; Sawa, M.; Mobley, W.C. Dysregulation of neurotrophin signaling in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease and of Alzheimer disease in Down syndrome. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 114, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-Q.; Mobley, W.C. Exploring the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer Disease in Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Neurons: Converging Insights from Alternative Hypotheses. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Schack, D.; Casademunt, E.; Schweigreiter, R.; Meyer, M.; Bibel, M.; Dechant, G. Complete ablation of the neurotrophin receptor p75NTR causes defects both in the nervous and the vascular system. Nat. Neurosci. 2001, 4, 977–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-T.; Lu, X.-M.; Shu, Y.-H.; Xiao, L.; Chen, K.-T. Selection of human p75NTR tag SNPs and its biological significance for clinical association studies. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 2014, 24, 3833–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underwood, C.K.; Coulson, E.J. The p75 neurotrophin receptor. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 1664–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeldal, S.; Matusica, D.; Nykjaer, A.; Coulson, E.J. Proteolytic processing of the p75 neurotrophin receptor: A prerequisite for signalling? Neuronal life, growth and death signalling are crucially regulated by intra-membrane proteolysis and trafficking of p75(NTR). Bioessays 2011, 33, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaccia-Bonnefil, P.; Gu, C.; Khursigara, G.; Chao, M.V. p75 neurotrophin receptor as a modulator of survival and death decisions. Microsc. Res. Technol. 1999, 45, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeker, R.; Williams, K. The p75 neurotrophin receptor: At the crossroad of neural repair and death. Neural. Regen. Res. 2015, 10, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabry, M.A.; Fares, M.; Folkesson, R.; Al-Ramadan, M.; Alabkal, J.; Al-Kafaji, G.; Hassan, M. Commentary: Impact of a deletion of the full-length and short isoform of p75NTR on cholinergic innervation and the population of postmitotic doublecortin positive cells in the dentate gyrus. Front. Neuroanat. 2016, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, R.D.; Duarte, C.B. p75NTR Processing and Signaling: Functional Role. In Handbook of Neurotoxicity; Kostrzewa, R.M., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1899–1923. ISBN 978-1-4614-5835-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ibáñez, C.F. Jekyll-Hyde neurotrophins: The story of proNGF. Trends Neurosci. 2002, 25, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.K.; Teng, K.K.; Lee, R.; Wright, S.; Tevar, S.; Almeida, R.D.; Kermani, P.; Torkin, R.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Lee, F.S.; et al. ProBDNF induces neuronal apoptosis via activation of a receptor complex of p75NTR and sortilin. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 5455–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.-H.; Lu, X.-M.; Wei, J.-X.; Xiao, L.; Wang, Y.-T. Update on the role of p75NTR in neurological disorders: A novel therapeutic target. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 76, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Pang, P.T.; Woo, N.H. The yin and yang of neurotrophin action. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibáñez, C.F.; Simi, A. p75 neurotrophin receptor signaling in nervous system injury and degeneration: Paradox and opportunity. Trends Neurosci. 2012, 35, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blöchl, A.; Blöchl, R. A cell-biological model of p75NTR signaling. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M.V. Neurotrophins and their receptors: A convergence point for many signalling pathways. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasia, A.; Barker, P.A.; Chao, M.V.; Hempstead, B.L. Detection of p75NTR Trimers: Implications for Receptor Stoichiometry and Activation. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 11911–11920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeker, R.; Williams, K. Dynamic Nature of the p75 Neurotrophin Receptor in Response to Injury and Disease. J. Neuroimmune Pharm. 2014, 9, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Wu, Z.; Tan, B.; Liu, Z.; Zu, Z.; Wu, X.; Bi, Y.; Hu, X. Ibuprofen promotes p75 neurotrophin receptor expression through modifying promoter methylation and N6-methyladenosine-RNA-methylation in human gastric cancer cells. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 14595–14604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicario, A.; Kisiswa, L.; Tann, J.Y.; Kelly, C.E.; Ibáñez, C.F. Neuron-type-specific signaling by the p75NTR death receptor regulated by differential proteolytic cleavage. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Shi, J.; Xie, F.; Liu, Z.; Yu, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Q. Proteolytic Release of the p75NTR Intracellular Domain by ADAM10 Promotes Metastasis and Resistance to Anoikis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2262–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragnolini, A.B.; Friedman, W.J. The function of p75NTR in glia. Trends Neurosci. 2008, 31, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nykjaer, A.; Willnow, T.E.; Petersen, C.M. p75NTR--live or let die. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2005, 15, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, L.-W.; Chong, Y.S.; Lin, W.; Kisiswa, L.; Sim, E.; Ibáñez, C.F.; Sajikumar, S. Age-related changes in hippocampal-dependent synaptic plasticity and memory mediated by p75 neurotrophin receptor. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, A.G.; Long, D.H.; Gu, H.G.; Yang, D.D.; Hong, L.P.; Leng, S.L. BDNF improves the effects of neural stem cells on the rat model of Alzheimer’s disease with unilateral lesion of fimbria-fornix. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 440, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, A.G.; Luo, M.; Ji, W.D.; Long, D.H. Effects of engrafted neural stem cells in Alzheimer’s disease rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 450, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiernan, C.T.; Mufson, E.J.; Kanaan, N.M.; Counts, S.E. Tau Oligomer Pathology in Nucleus Basalis Neurons During the Progression of Alzheimer Disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 77, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cade, S.; Zhou, X.-F.; Bobrovskaya, L. The role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and the neurotrophin receptor p75NTR in age-related brain atrophy and the transition to Alzheimer’s disease. Rev. Neurosci. 2022, 33, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, T.W.; Nathan Spreng, R. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative Basal forebrain degeneration precedes and predicts the cortical spread of Alzheimer’s pathology. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissiere, F.; Faucheux, B.; Ruberg, M.; Agid, Y.; Hirsch, E.C. Decreased TrkA gene expression in cholinergic neurons of the striatum and basal forebrain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 1997, 145, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mufson, E.J.; Lavine, N.; Jaffar, S.; Kordower, J.H.; Quirion, R.; Saragovi, H.U. Reduction in p140-TrkA receptor protein within the nucleus basalis and cortex in Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 1997, 146, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsberg, S.D.; Che, S.; Wuu, J.; Counts, S.E.; Mufson, E.J. Down regulation of trk but not p75NTR gene expression in single cholinergic basal forebrain neurons mark the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2006, 97, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedert, M.; Fine, A.; Dawbarn, D.; Wilcock, G.K.; Chao, M.V. Nerve growth factor receptor mRNA distribution in human brain: Normal levels in basal forebrain in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1989, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernfors, P.; Lindefors, N.; Chan-Palay, V.; Persson, H. Cholinergic Neurons of the Nucleus basalis Express Elevated Levels of Nerve Growth Factor Receptor mRNA in Senile Dementia of the Alzheimer Type. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 1990, 1, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mufson, E.J.; Kordower, J.H. Cortical neurons express nerve growth factor receptors in advanced age and Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadipour, K.; Yang, M.; Lim, Y.; Georgiou, K.; Sun, Y.; Keating, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.-R.; Gai, W.-P.; Zhong, J.-H.; et al. Amyloid beta1–42 (Aβ42) up-regulates the expression of sortilin via the p75(NTR)/RhoA signaling pathway. J. Neurochem. 2013, 127, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlesniy, P.; Kichev, A.; Pedraza, C.; Saurat, J.; Encinas, M.; Perez, B.; Ferrer, I.; Espinet, C. Pro-NGF from Alzheimer’s disease and normal human brain displays distinctive abilities to induce processing and nuclear translocation of intracellular domain of p75NTR and apoptosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-Y.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Qin, S.; Xu, H.; Swaab, D.F.; Zhou, J.-N. Increased p75(NTR) expression in hippocampal neurons containing hyperphosphorylated tau in Alzheimer patients. Exp. Neurol. 2002, 178, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthy, B.; Ménard, M.; Ito, S.; Gaudet, C.; Dal Prà, I.; Armato, U.; Whitfield, J. Hippocampal membrane-associated p75NTR levels are increased in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2012, 30, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabizadeh, S.; Bitler, C.M.; Butcher, L.L.; Bredesen, D.E. Expression of the low-affinity nerve growth factor receptor enhances beta-amyloid peptide toxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 10703–10706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sáez, E.T.; Pehar, M.; Vargas, M.R.; Barbeito, L.; Maccioni, R.B. Production of nerve growth factor by beta-amyloid-stimulated astrocytes induces p75NTR-dependent tau hyperphosphorylation in cultured hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 84, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, C.; Weindruch, R.; Della Valle, G.; Puglielli, L. A TrkA-to-p75NTR molecular switch activates amyloid beta-peptide generation during aging. Biochem. J. 2005, 391, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devarajan, S.; Sharmila, J.S. Computational Studies of Beta Amyloid (Aβ42) with p75NTR Receptor: A Novel Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer’s Disease. Adv. Bioinform. 2014, 2014, 736378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaar, M.; Zhai, S.; Pilch, P.F.; Doyle, S.M.; Eisenhauer, P.B.; Fine, R.E.; Gilchrest, B.A. Binding of beta-amyloid to the p75 neurotrophin receptor induces apoptosis. A possible mechanism for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 2333–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, E.; Hashimoto, Y.; Kanekura, K.; Niikura, T.; Aiso, S.; Nishimoto, I. Characterization of the toxic mechanism triggered by Alzheimer’s amyloid-beta peptides via p75 neurotrophin receptor in neuronal hybrid cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 2003, 73, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Kaneko, Y.; Tsukamoto, E.; Frankowski, H.; Kouyama, K.; Kita, Y.; Niikura, T.; Aiso, S.; Bredesen, D.E.; Matsuoka, M.; et al. Molecular characterization of neurohybrid cell death induced by Alzheimer’s amyloid-beta peptides via p75NTR/PLAIDD. J. Neurochem. 2004, 90, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotthibundhu, A.; Sykes, A.M.; Fox, B.; Underwood, C.K.; Thangnipon, W.; Coulson, E.J. Beta-amyloid(1-42) induces neuronal death through the p75 neurotrophin receptor. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3941–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.-L.; Li, W.-W.; Xu, Y.-L.; Gao, S.-H.; Xu, M.-Y.; Bu, X.-L.; Liu, Y.-H.; Wang, J.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, F.; et al. Neurotrophin receptor p75 mediates amyloid β-induced tau pathology. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 132, 104567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeldal, S.; Sykes, A.M.; Glerup, S.; Matusica, D.; Palstra, N.; Autio, H.; Boskovic, Z.; Madsen, P.; Castrén, E.; Nykjaer, A.; et al. Mapping of the interaction site between sortilin and the p75 neurotrophin receptor reveals a regulatory role for the sortilin intracellular domain in p75 neurotrophin receptor shedding and apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 43798–43809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthy, B.; Gaudet, C.; Ménard, M.; Atkinson, T.; Brown, L.; Laferla, F.M.; Armato, U.; Whitfield, J. Amyloid-beta peptides stimulate the expression of the p75(NTR) neurotrophin receptor in SHSY5Y human neuroblastoma cells and AD transgenic mice. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 19, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Lee, X.; Shao, Z.; Apicco, D.; Huang, G.; Gong, B.J.; Pepinsky, R.B.; Mi, S. A DR6/p75(NTR) complex is responsible for β-amyloid-induced cortical neuron death. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedraza, C.E.; Podlesniy, P.; Vidal, N.; Arévalo, J.C.; Lee, R.; Hempstead, B.; Ferrer, I.; Iglesias, M.; Espinet, C. Pro-NGF isolated from the human brain affected by Alzheimer’s disease induces neuronal apoptosis mediated by p75NTR. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fombonne, J.; Rabizadeh, S.; Banwait, S.; Mehlen, P.; Bredesen, D.E. Selective vulnerability in Alzheimer’s disease: Amyloid precursor protein and p75(NTR) interaction. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 65, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, A.; Zagrebelsky, M.; Korte, M.; Holz, A. Signaling via the p75 neurotrophin receptor facilitates amyloid-β-induced dendritic spine pathology. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.-Q.; Jiao, S.-S.; Saadipour, K.; Zeng, F.; Wang, Q.-H.; Zhu, C.; Shen, L.-L.; Zeng, G.-H.; Liang, C.-R.; Wang, J.; et al. p75NTR ectodomain is a physiological neuroprotective molecule against amyloid-beta toxicity in the brain of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-F.; Wang, Y.-J. The p75NTR extracellular domain: A potential molecule regulating the solubility and removal of amyloid-β. Prion 2011, 5, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.-Y.; Tian, D.-Y.; Chen, S.-H.; Jin, W.-S.; Cheng, Y.; Xin, J.-Y.; Li, W.-W.; Zeng, G.-H.; Tan, C.-R.; Jian, J.-M.; et al. Elevated Levels of Naturally-Occurring Autoantibodies Against the Extracellular Domain of p75NTR Aggravate the Pathology of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurosci. Bull. 2022, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatchett, C.S.; Tyler, S.; Armstrong, D.; Dawbarn, D.; Allen, S.J. Familial Alzheimer’s disease presenilin 1 mutation M146V increases gamma secretase cutting of p75NTR in vitro. Brain Res. 2007, 1147, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Goh, K.Y.; Wong, L.-W.; Ramanujan, A.; Tanaka, K.; Sajikumar, S.; Ibáñez, C.F. Inactive variants of death receptor p75NTR reduce Alzheimer’s neuropathology by interfering with APP internalization. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e104450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Talavera, Y.; Balleza-Tapia, H.; Dolz-Gaitón, P.; Chen, G.; Johansson, J.; Fisahn, A. Ablation of p75NTR signaling strengthens gamma-theta rhythm interaction and counteracts Aβ-induced degradation of neuronal dynamics in mouse hippocampus in vitro. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozza, A.; Melissari, E.; Iacopetti, P.; Mariotti, V.; Tedde, A.; Nacmias, B.; Conte, A.; Sorbi, S.; Pellegrini, S. SNPs in neurotrophin system genes and Alzheimer’s disease in an Italian population. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2008, 15, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-C.; Sun, Y.; Lai, L.-C.; Chen, S.-Y.; Lee, W.-C.; Chen, J.-H.; Chen, T.-F.; Chen, H.-H.; Wen, L.-L.; Yip, P.-K.; et al. Genetic polymorphisms of nerve growth factor receptor (NGFR) and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Negat. Results Biomed. 2012, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matyi, J.; Tschanz, J.T.; Rattinger, G.B.; Sanders, C.; Vernon, E.K.; Corcoran, C.; Kauwe, J.S.K.; Buhusi, M. Sex Differences in Risk for Alzheimer’s Disease Related to Neurotrophin Gene Polymorphisms: The Cache County Memory Study. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2017, 72, 1607–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacher, M.; Porter, T.; Villemagne, V.L.; Milicic, L.; Peretti, M.; Fowler, C.; Martins, R.; Rainey-Smith, S.; Ames, D.; Masters, C.L.; et al. Validation of a priori candidate Alzheimer’s disease SNPs with brain amyloid-beta deposition. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.-Y.; Wang, Z.-T.; Shen, Y.-Y.; Shi, A.-Y.; Li, H.-Y.; Chen, D.-W.; Zeng, G.-H.; Tan, C.-R.; Yu, J.-T.; Zeng, F.; et al. Association of rs2072446 in the NGFR gene with the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and amyloid-β deposition in the brain. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2022, 28, 2218–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, S.-S.; Bu, X.-L.; Liu, Y.-H.; Wang, Q.-H.; Liu, C.-H.; Yao, X.-Q.; Zhou, X.-F.; Wang, Y.-J. Differential levels of p75NTR ectodomain in CSF and blood in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: A novel diagnostic marker. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispoltoni, L.; Stabile, A.M.; Pistilli, A.; Venturelli, M.; Cerulli, G.; Fonte, C.; Smania, N.; Schena, F.; Rende, M. Changes in Plasma β-NGF and Its Receptors Expression on Peripheral Blood Monocytes During Alzheimer’s Disease Progression. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 55, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, A.M.; Meeker, R.B. The new wave of p75 neurotrophin receptor targeted therapies. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Knowles, J.K.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Arancio, O.; Moore, L.A.; Chang, T.; Wang, Q.; Andreasson, K.; Rajadas, J.; et al. Small molecule, non-peptide p75 ligands inhibit Abeta-induced neurodegeneration and synaptic impairment. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaar, M.; Zhai, S.; Panova, I.; Fine, R.E.; Eisenhauer, P.B.; Blusztajn, J.K.; Lopez-Coviella, I.; Gilchrest, B.A. A cyclic peptide that binds p75(NTR) protects neurones from beta amyloid (1-40)-induced cell death. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2007, 33, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaar, M.; Arble, B.L.; Stewart, K.B.; Qureshi, N.H.; Kowall, N.W.; Gilchrest, B.A. p75NTR antagonistic cyclic peptide decreases the size of beta amyloid-induced brain inflammation. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2008, 28, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhan, Z.; Li, X.; Zhou, F.; Xing, A.; Jiang, C.; Chen, Y.; An, L. Beneficial Effects of Sulforaphane Treatment in Alzheimer’s Disease May Be Mediated through Reduced HDAC1/3 and Increased P75NTR Expression. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.-H.; Wang, Y.-R.; Zhang, T.; Jiao, S.-S.; Liu, Y.-H.; Zeng, F.; Li, J.; Yao, X.-Q.; Zhou, H.-D.; Zhou, X.-F.; et al. Intramuscular delivery of p75NTR ectodomain by an AAV vector attenuates cognitive deficits and Alzheimer’s disease-like pathologies in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. J. Neurochem. 2016, 138, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, S.M.; Xie, Y.; Yang, T.; Harrington, A.W.; Kim, M.L.; Yoon, S.O.; Kraemer, R.; Moore, L.A.; Hempstead, B.L.; Longo, F.M. Small, nonpeptide p75NTR ligands induce survival signaling and inhibit proNGF-induced death. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 5288–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, J.K.; Simmons, D.A.; Nguyen, T.-V.V.; Vander Griend, L.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, T.; Pollak, J.; Chang, T.; Arancio, O.; et al. Small molecule p75NTR ligand prevents cognitive deficits and neurite degeneration in an Alzheimer’s mouse model. Neurobiol. Aging 2013, 34, 2052–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, D.A.; Knowles, J.K.; Belichenko, N.P.; Banerjee, G.; Finkle, C.; Massa, S.M.; Longo, F.M. A small molecule p75NTR ligand, LM11A-31, reverses cholinergic neurite dystrophy in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models with mid- to late-stage disease progression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Tran, K.C.; Zeng, A.Y.; Massa, S.M.; Longo, F.M. Small molecule modulation of the p75 neurotrophin receptor inhibits multiple amyloid beta-induced tau pathologies. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Liu, H.; Tran, K.C.; Leng, A.; Massa, S.M.; Longo, F.M. Small-molecule modulation of the p75 neurotrophin receptor inhibits a wide range of tau molecular pathologies and their sequelae in P301S tauopathy mice. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).