Autologous Platelet and Extracellular Vesicle-Rich Plasma as Therapeutic Fluid: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Composition of Plasma Rich with Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles
2.1. Platelets
2.2. Leukocytes
2.3. Molecules
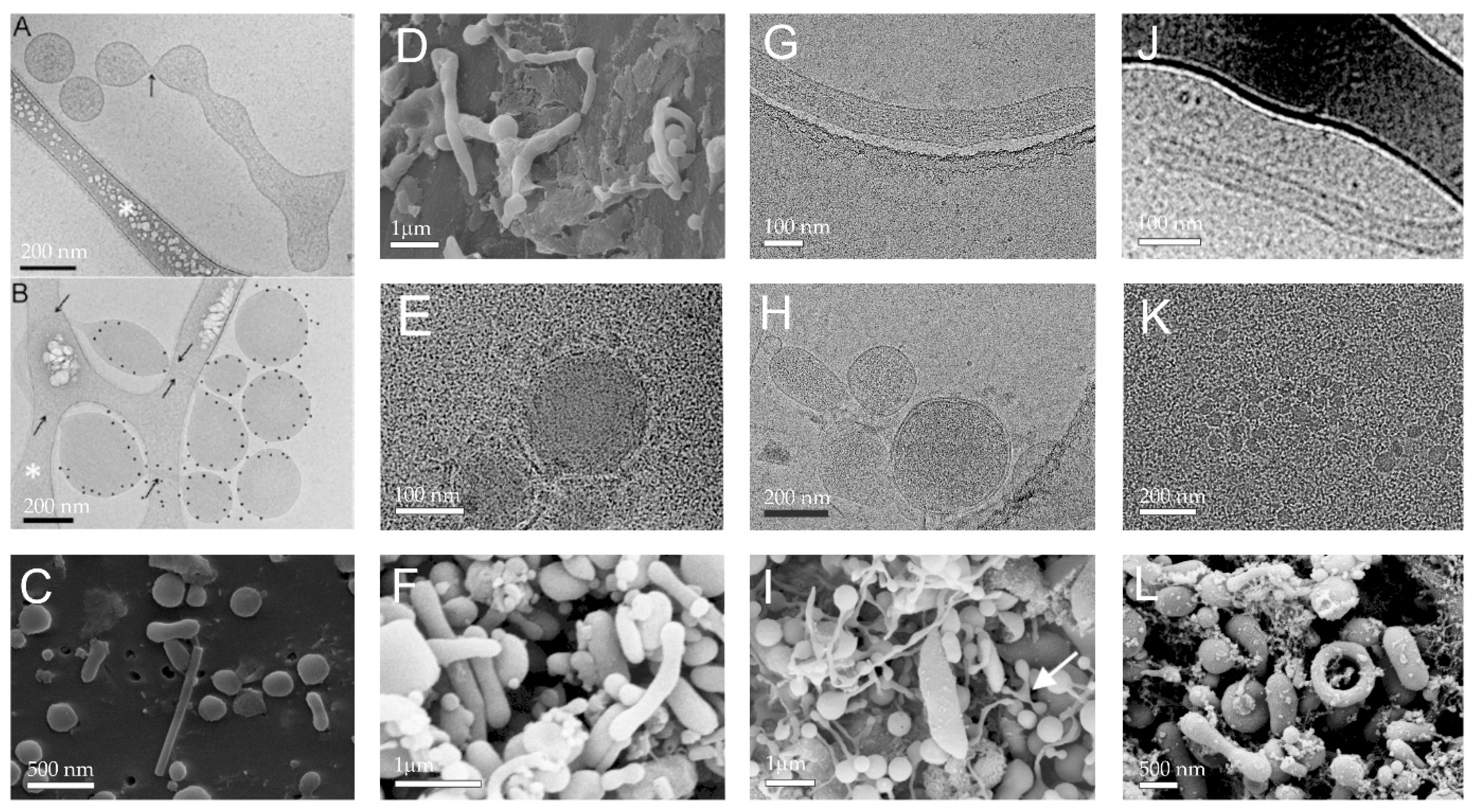
2.4. Extracellular Vesicles
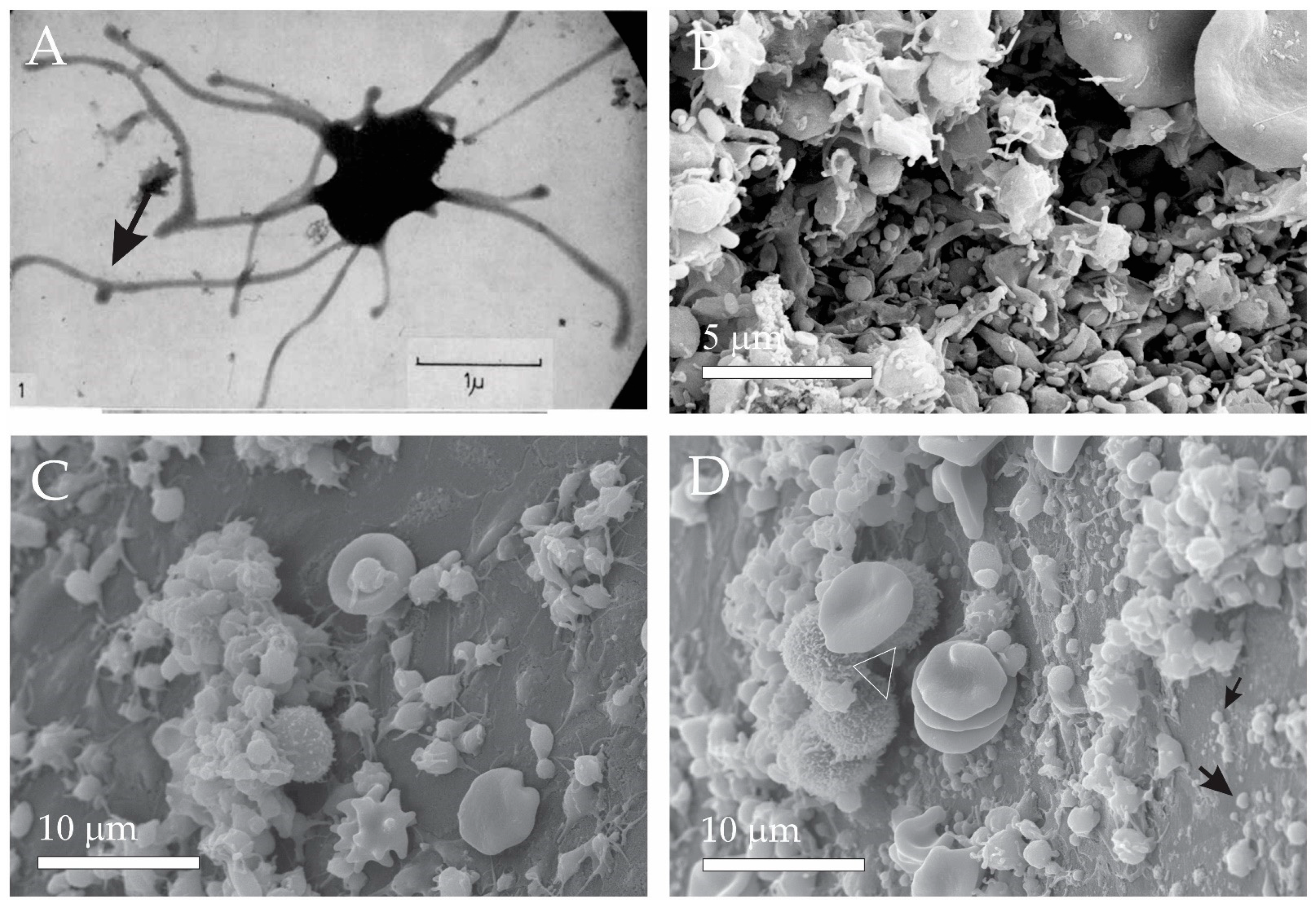
2.5. Influence of Different Physiological and Pathophysiological Conditions on Plasma Rich with Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles
3. Preparation of Platelet and Extracellular Vesicle-Rich Plasma
4. Characterization of PVRP Composition and Methodological Approaches
4.1. Assessment of Chemical Composition
4.2. Assessment of the Quantity and Size of EVs
4.2.1. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
4.2.2. Interferometric Light Microscopy (ILM)
5. Storage of PVRP
6. Use of Plasma Rich with Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles in Human Medicine
6.1. Use of Plasma Rich with Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles in Treatment of Ligament and Tendon Injuries
6.2. Use of Plasma Rich with Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles in Treatment of Chronic Wounds
6.3. Use of Plasma Rich with Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles in Treatment of Burns
6.4. Regenerative Effects of Plasma Rich with Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles in Maxillofacial Surgery, Dental Medicine and Bone and Joint Disorders
6.5. Use of Plasma Rich with Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles in Treatment of Ocular Surface Disorders
6.6. Use of Plasma Rich with Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles in Scar Revision
6.7. Use of Plasma Rich with Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles in Treatment of Alopecia
6.8. Skin Rejuvenating Effects of Plasma Rich with Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles
6.9. Use of Plasma Rich with Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles in Otorhinolaryngology
7. Use of Plasma Rich with Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles in Veterinary Medicine
7.1. Use of Plasma Rich with Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles in Treatment of Ligament and Tendon Injuries
7.2. Use of Plasma Rich with Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles in Treatment of Arthritis
7.3. Use of Plasma Rich with Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles in Wound Healing
7.4. Use of Plasma Rich with Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles in Treatment of Burns
7.5. Use of Plasma Rich with Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles in Treatment of Corneal Disorders
8. Use of Plasma Rich with Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles and Stem Cells for Regeneration
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knighton, D.R.; Ciresi, K.F.; Fiegel, V.D.; Austin, L.L.; Butler, E.L. Classification and Treatment of Chronic Nonhealing Wounds. Successful Treatment with Autologous Platelet-Derived Wound Healing Factors (PDWHF). Ann. Surg. 1986, 204, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etulain, J. Platelets in Wound Healing and Regenerative Medicine. Platelets 2018, 29, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everts, P.; Onishi, K.; Jayaram, P.; Lana, J.F.; Mautner, K. Platelet-Rich Plasma: New Performance Understandings and Therapeutic Considerations in 2020. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šuštar, V.; Bedina-Zavec, A.; Štukelj, R.; Frank, M.; Bobojević, G.; Janša, R.; Ogorevc, E.; Kruljc, P.; Mam, K.; Šimunič, B.; et al. Nanoparticles Isolated from Blood: A Reflection of Vesiculability of Blood Cells during the Isolation Process. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 2737–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.H.; Cui, C.; Zhou, X.X.; Zeng, Y.X.; Jia, W.H. Centrifugation: An Important Pre-Analytic Procedure That Influences Plasma MicroRNA Quantification during Blood Processing. Chin. J. Cancer 2013, 32, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.-C.; Guo, S.-C.; Zhang, C.-Q. Platelet-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: An Emerging Therapeutic Approach. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štukelj, R.; Schara, K.; Bedina-Zavec, A.; Šuštar, V.; Pajnič, M.; Pađen, L.; Krek, J.L.; Kralj-Iglič, V.; Mrvar-Brečko, A.; Janša, R. Effect of Shear Stress in the Flow through the Sampling Needle on Concentration of Nanovesicles Isolated from Blood. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 98, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božič, D.; Vozel, D.; Hočevar, M.; Jeran, M.; Jan, Z.; Pajnič, M.; Pađen, L.; Iglič, A.; Battelino, S.; Kralj-Iglič, V. Enrichment of Plasma in Platelets and Extracellular Vesicles by the Counterflow to Erythrocyte Settling. Platelets 2022, 33, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.-M.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological Properties of Extracellular Vesicles and Their Physiological Functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fais, S.; O’Driscoll, L.; Borras, F.E.; Buzas, E.; Camussi, G.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; Cordeiro da Silva, A.; Del Portillo, H.; El Andaloussi, S.; et al. Evidence-Based Clinical Use of Nanoscale Extracellular Vesicles in Nanomedicine. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 3886–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozel, D.; Božič, D.; Jeran, M.; Jan, Z.; Pajnič, M.; Pađen, L.; Uršič, B.; Iglič, A.; Kralj-Iglič, V.; Battelino, S. Treatment with Platelet- and Extracellular Vesicle-Rich Plasma in Otorhinolaryngology—A Review and Future Perspectives. In Advances in Biomembranes and Lipid Self-Assembly; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 33, pp. 119–153. ISBN 978-0-12-824608-5. [Google Scholar]
- Božič, D.; Hočevar, M.; Kisovec, M.; Pajnič, M.; Pađen, L.; Jeran, M.; Bedina Zavec, A.; Podobnik, M.; Kogej, K.; Iglič, A.; et al. Stability of Erythrocyte-Derived Nanovesicles Assessed by Light Scattering and Electron Microscopy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozel, D.; Uršič, B.; Krek, J.L.; Štukelj, R.; Kralj-Iglič, V. Applicability of Extracellular Vesicles in Clinical Studies. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2017, 47, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pascale, M.R.; Sommese, L.; Casamassimi, A.; Napoli, C. Platelet Derivatives in Regenerative Medicine: An Update. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2015, 29, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarzadeh, S.; McKenzie, M.B.; Rahman, M.M.; Cleland, H. Allogeneic Platelet-Rich Plasma: Is It Safe and Effective for Wound Repair? Eur. Surg. Res. 2021, 62, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenič, D.; Cirman, T.; Rožman, P.; Smrke, D.M. Regeneration of Chronic Wounds with Allogenic Platelet Gel versus Hydrogel Treament: A Prospective Study. Acta Clin. Croat. 2018, 57, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, E.; Flückiger, L.; Fujioka-Kobayashi, M.; Sawada, K.; Sculean, A.; Schaller, B.; Miron, R.J. Comparative Release of Growth Factors from PRP, PRF, and Advanced-PRF. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 20, 2353–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Hogan, M.V.; Wang, J.H.-C. The Differential Effects of Leukocyte-Containing and Pure Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) on Tendon Stem/Progenitor Cells—Implications of PRP Application for the Clinical Treatment of Tendon Injuries. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mescher, A.L. Junqueira’s Basic Histology Text & Atlas, 14th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-0-07-184270-9. MHID: 0-07-184270-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kierszenbaum, A.; Tres, L. Histology and Cell Biology: An Introduction to Pathology, 5th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN1 9780323673211. ISBN2 9780323683784. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzucco, L.; Balbo, V.; Cattana, E.; Guaschino, R.; Borzini, P. Not Every PRP-Gel Is Born Equal. Evaluation of Growth Factor Availability for Tissues through Four PRP-Gel Preparations: Fibrinet, RegenPRP-Kit, Plateltex and One Manual Procedure. Vox Sang. 2009, 97, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, L.S. On the Germinal Matterof the Blood, with Remarksupon the Formationof Fibrin. Trans. Microsc. Soc. J. 1864, 12, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koupenova, M.; Clancy, L.; Corkrey, H.A.; Freedman, J.E. Circulating Platelets as Mediators of Immunity, Inflammation, and Thrombosis. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.A.; Wuescher, L.M.; Worth, R.G. Platelets: Essential Components of the Immune System. Curr. Trends Immunol. 2015, 16, 65–78. [Google Scholar]
- Coller, B.S. Historical Perspective and Future Directions in Platelet Research. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 374–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmo, C.; Bajwa, T.; Burns, B. Physiology, Clotting Mechanism. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430685/ (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Marx, R.E. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): What Is PRP and What Is Not PRP? Implant. Dent. 2001, 10, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; Andia, I.; Ardanza, B.; Nurden, P.; Nurden, A.T. Autologous Platelets as a Source of Proteins for Healing and Tissue Regeneration. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 91, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolidakis, D.; Jansen, J.A. The Biology of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Its Application in Oral Surgery: Literature Review. Tissue Eng. Part. B Rev. 2008, 14, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, T.E.; Puskas, B.L.; Mandelbaum, B.R.; Gerhardt, M.B.; Rodeo, S.A. Platelet-Rich Plasma: From Basic Science to Clinical Applications. Am. J. Sports Med. 2009, 37, 2259–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, J.M.; Russell, R.P.; Mazzocca, A.D. Platelet-Rich Plasma: The PAW Classification System. Arthroscopy 2012, 28, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrotniak, M.; Bielecki, T.; Gaździk, T.S. Current Opinion about Using the Platelet-Rich Gel in Orthopaedics and Trauma Surgery. Ortop. Traumatol. Rehabil 2007, 9, 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Assirelli, E.; Filardo, G.; Mariani, E.; Kon, E.; Roffi, A.; Vaccaro, F.; Marcacci, M.; Facchini, A.; Pulsatelli, L. Effect of Two Different Preparations of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Synoviocytes. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2015, 23, 2690–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Park, Y.-B.; Ha, C.-W.; Roh, Y.J.; Park, J.-G. Adverse Reactions and Clinical Outcomes for Leukocyte-Poor Versus Leukocyte-Rich Platelet-Rich Plasma in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2021, 9, 23259671211011948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, K.L.; Begley, L.A.; Mor-Vaknin, N.; Markovitz, D.M.; Macoska, J.A. Leukocytic Promotion of Prostate Cellular Proliferation. Prostate 2010, 70, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, J.T.; Ramalingam, T.R.; Mentink-Kane, M.M.; Wilson, M.S.; El Kasmi, K.C.; Smith, A.M.; Thompson, R.W.; Cheever, A.W.; Murray, P.J.; Wynn, T.A. Arginase-1-Expressing Macrophages Suppress Th2 Cytokine-Driven Inflammation and Fibrosis. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lana, J.F.; Huber, S.C.; Purita, J.; Tambeli, C.H.; Santos, G.S.; Paulus, C.; Annichino-Bizzacchi, J.M. Leukocyte-Rich PRP versus Leukocyte-Poor PRP—The Role of Monocyte/Macrophage Function in the Healing Cascade. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2019, 10, S7–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moojen, D.J.F.; Everts, P.A.M.; Schure, R.-M.; Overdevest, E.P.; van Zundert, A.; Knape, J.T.A.; Castelein, R.M.; Creemers, L.B.; Dhert, W.J.A. Antimicrobial Activity of Platelet-Leukocyte Gel against Staphylococcus Aureus. J. Orthop. Res. 2008, 26, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boswell, S.G.; Cole, B.J.; Sundman, E.A.; Karas, V.; Fortier, L.A. Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Milieu of Bioactive Factors. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2012, 28, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andia, I.; Maffulli, N. Platelet-Rich Plasma for Managing Pain and Inflammation in Osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niessen, F.B.; Andriessen, M.P.; Schalkwijk, J.; Visser, L.; Timens, W. Keratinocyte-Derived Growth Factors Play a Role in the Formation of Hypertrophic Scars. J. Pathol. 2001, 194, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrell, C.N.; Aggrey, A.A.; Chapman, L.M.; Modjeski, K.L. Emerging Roles for Platelets as Immune and Inflammatory Cells. Blood 2014, 123, 2759–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwertz, H.; Rowley, J.W.; Tolley, N.D.; Campbell, R.A.; Weyrich, A.S. Assessing Protein Synthesis by Platelets. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 788, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andia, I.; Abate, M. Platelet-Rich Plasma: Underlying Biology and Clinical Correlates. Regen. Med. 2013, 8, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Lingampalli, N.; Koltsov, J.C.B.; Leung, L.L.; Bhutani, N.; Robinson, W.H.; Chu, C.R. Men and Women Differ in the Biochemical Composition of Platelet-Rich Plasma. Am. J. Sports Med. 2018, 46, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, P. The Nature and Significance of Platelet Products in Human Plasma. Br. J. Haematol. 1967, 13, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romolo, A.; Jan, Z.; Bedina Zavec, A.; Kisovec, M.; Arrigler, V.; Spasovski, V.; Podobnik, M.; Iglič, A.; Pocsfalvi, G.; Kogej, K.; et al. Assessment of Small Cellular Particles from Four Different Natural Sources and Liposomes by Interferometric Light Microscopy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hargett, L.A.; Bauer, N.N. On the Origin of Microparticles: From “Platelet Dust” to Mediators of Intercellular Communication. Pulm. Circ. 2013, 3, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding Light on the Cell Biology of Extracellular Vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abels, E.R.; Breakefield, X.O. Introduction to Extracellular Vesicles: Biogenesis, RNA Cargo Selection, Content, Release, and Uptake. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular Vesicles: Exosomes, Microvesicles, and Friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.; Wildman, D.E. Extracellular Vesicles and the Promise of Continuous Liquid Biopsies. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2018, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A Position Statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and Update of the MISEV2014 Guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogorevc, E.; Hudoklin, S.; Veranič, P.; Kralj-Iglič, V. Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Transfer of Membranous Components from the Highly Malignant T24 Urinary Carcinoma Cell Line to the Non-Malignant RT4 Urinary Papilloma Cell Line. Protoplasma 2014, 251, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijnen, H.F.; Schiel, A.E.; Fijnheer, R.; Geuze, H.J.; Sixma, J.J. Activated Platelets Release Two Types of Membrane Vesicles: Microvesicles by Surface Shedding and Exosomes Derived from Exocytosis of Multivesicular Bodies and Alpha-Granules. Blood 1999, 94, 3791–3799. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, E.W.; Omenn, G.S.; Sun, Z.; Maes, M.; Pernemalm, M.; Palaniappan, K.K.; Letunica, N.; Vandenbrouck, Y.; Brun, V.; Tao, S.; et al. Advances and Utility of the Human Plasma Proteome. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 5241–5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocozza, F.; Grisard, E.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Mathieu, M.; Théry, C. SnapShot: Extracellular Vesicles. Cell 2020, 182, 262–262.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brečko, A.; Šuštar, V.; Janša, V.; Štukelj, R.; Janša, R.; Mujagić, E.; Kruljc, P.; Hägerstrand, H.; Kralj-Iglic, V. Isolated Microvesicles from Peripheral Blood and Body Fluids as Observed by Scanning Electron Microscope. BCMD 2010, 44, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arraud, N.; Linares, R.; Tan, S.; Gounou, C.; Pasquet, J.-M.; Mornet, S.; Brisson, A.R. Extracellular Vesicles from Blood Plasma: Determination of Their Morphology, Size, Phenotype and Concentration. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuana, Y.; Koning, R.I.; Kuil, M.E.; Rensen, P.C.; Koster, A.J.; Bertina, R.M.; Osanto, S. Cryo-electron microscopy of extracellular vesicles in fresh plasma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 21494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, M.; Ort, M.; Lauterbach, L.; Streitz, M.; Wilhelm, A.; Grütz, G.; Fleckenstein, F.N.; Graef, F.; Blankenstein, A.; Reinke, S.; et al. Individual Immune Cell and Cytokine Profiles Determine Platelet-Rich Plasma Composition. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanson, J.R.; Guyton, M.K.; Oliver, D.L.; Hire, J.M.; Topolski, R.L.; Zumbrun, S.D.; McPherson, J.C.; Bojescul, J.A. Gender and Age Differences in Growth Factor Concentrations from Platelet-Rich Plasma in Adults. Mil. Med. 2014, 179, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, S.P.; Burke, E.E.; Holmes, S.P. The Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Osseous Healing in Dogs Undergoing High Tibial Osteotomy. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovtun, A.; Bergdolt, S.; Wiegner, R.; Radermacher, P.; Huber-Lang, M.; Ignatius, A. The Crucial Role of Neutrophil Granulocytes in Bone Fracture Healing. Eur. Cell Mater. 2016, 32, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Greer, J.M.; Hull, R.; O’Sullivan, J.D.; Henderson, R.D.; Read, S.J.; McCombe, P.A. The Effect of Ageing on Human Lymphocyte Subsets: Comparison of Males and Females. Immun. Ageing 2010, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, M.P.; DiCostanzo, A.C.; Wheatley, C.M.; Kim, C.-H.; Bornschlegl, S.; Gastineau, D.A.; Johnson, B.D.; Dietz, A.B. A Systems Biology Approach to Investigating the Influence of Exercise and Fitness on the Composition of Leukocytes in Peripheral Blood. J. Immunother. Cancer 2017, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verboket, R.D.; Anbar, B.; Söhling, N.; Kontradowitz, K.; Marzi, I.; Ghanaati, S.; Henrich, D. Changes in Platelet-Rich Fibrin Composition after Trauma and Surgical Intervention. Platelets 2020, 31, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyluk, K.; Jarosz, A.; Balcerzyk-Matić, A.; Iwanicka, J.; Iwanicki, T.; Nowak, T.; Gierek, M.; Negru, M.; Kalita, M.; Górczyńska-Kosiorz, S.; et al. Polymorphic Variants of the PDGFRB Gene Influence Efficacy of PRP Therapy in Treating Tennis Elbow: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, N.; Vozel, D.; Urbančič, J.; Božič, D.; Kralj-Iglič, V.; Battelino, S. Clinical Implementation of Platelet- and Extracellular Vesicle-Rich Product Preparation Protocols. Tissue Eng. Part A 2022, 28, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.I. The Physics of Continuous Flow Centrifugal Cell Separation. Artif. Organs 1989, 13, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsousou, J.; Thompson, M.; Hulley, P.; Noble, A.; Willett, K. The Biology of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Its Application in Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery: A Review of the Literature. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2009, 91, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocca, A.D.; McCarthy, M.B.R.; Chowaniec, D.M.; Cote, M.P.; Romeo, A.A.; Bradley, J.P.; Arciero, R.A.; Beitzel, K. Platelet-Rich Plasma Differs According to Preparation Method and Human Variability. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2012, 94, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.K.; Versteeg, S.G.; Rapaport, J.; Hausauer, A.K.; Shear, N.H.; Piguet, V. The Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Field of Hair Restoration and Facial Aesthetics—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2019, 23, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozel, D.; Božič, D.; Jeran, M.; Jan, Z.; Pajnič, M.; Pađen, L.; Steiner, N.; Kralj-Iglič, V.; Battelino, S. Autologous Platelet- and Extracellular Vesicle-Rich Plasma Is an Effective Treatment Modality for Chronic Postoperative Temporal Bone Cavity Inflammation: Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 677541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fufa, D.; Shealy, B.; Jacobson, M.; Kevy, S.; Murray, M.M. Activaton of Platelet- Rich Plasma Using Solubile Tyoe I Collagen. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 66, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Delaney, M.K.; O’Brien, K.A.; Du, X. Signaling During Platelet Adhesion and Activation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 2341–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kita, R.; Takahashi, A.; Kaibara, M.; Kubota, K. Formation of Fibrin Gel in Fibrinogen-Thrombin System: Static and Dynamic Light Scattering Study. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andia, I.; Maffulli, N. A Contemporary View of Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapies: Moving toward Refined Clinical Protocols and Precise Indications. Regen. Med. 2018, 13, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Zapata, M.J.; Martí-Carvajal, A.J.; Solà, I.; Expósito, J.A.; Bolíbar, I.; Rodríguez, L.; Garcia, J.; Zaror, C. Autologous Platelet-rich Plasma for Treating Chronic Wounds. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 2016, CD006899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Andia, I.; Zumstein, M.A.; Zhang, C.Q.; Pinto, N.R.; Bielecki, T. Classification of Platelet Concentrates (Platelet-Rich Plasma-PRP, Platelet-Rich Fibrin-PRF) for Topical and Infiltrative Use in Orthopedic and Sports Medicine: Current Consensus, Clinical Implications and Perspectives. MLTJ 2014, 4, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, K.; Shope, B. Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Dentistry and Oral Surgery: Introduction and Review of the Literature. J. Vet. Dent. 2019, 36, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choukroun, J.; Miron, R.J. Platelet Rich Fibrin: A Second-Generation Platelet Concentrate. In Platelet Rich Fibrin in Regenerative Dentistry: Biological Background and Clinical Indications; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–14. ISBN 978-1-119-40679-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hosnuter, M.; Aslan, C.; Isik, D.; Caliskan, G.; Arslan, B.; Durgun, M. Functional Assessment of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) after Long-Term Storage at -20 °C without Any Preservation Agent. J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2017, 51, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solakoglu, Ö.; Heydecke, G.; Amiri, N.; Anitua, E. The Use of Plasma Rich in Growth Factors (PRGF) in Guided Tissue Regeneration and Guided Bone Regeneration. A Review of Histological, Immunohistochemical, Histomorphometrical, Radiological and Clinical Results in Humans. Ann. Anat. 2020, 231, 151528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervelli, V.; Nicoli, F.; Spallone, D.; Verardi, S.; Sorge, R.; Nicoli, M.; Balzani, A. Treatment of Traumatic Scars Using Fat Grafts Mixed with Platelet-Rich Plasma, and Resurfacing of Skin with the 1540 Nm Nonablative Laser. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 37, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mautner, K.; Malanga, G.A.; Smith, J.; Shiple, B.; Ibrahim, V.; Sampson, S.; Bowen, J.E. A Call for a Standard Classification System for Future Biologic Research: The Rationale for New PRP Nomenclature. PM&R 2015, 7, S53–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohan, D.M.; Choukroun, J.; Diss, A.; Dohan, S.L.; Dohan, A.J.J.; Mouhyi, J.; Gogly, B. Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF): A Second-Generation Platelet Concentrate. Part I: Technological Concepts and Evolution. Oral Surg Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2006, 101, e37–e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Fabbro, M.; Bortolin, M.; Taschieri, S. Is Autologous Platelet Concentrate Beneficial for Post-Extraction Socket Healing? A Systematic Review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 40, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisiday, J.D.; McIlwraith, C.W.; Rodkey, W.G.; Frisbie, D.D.; Steadman, J.R. Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma Composition on Anabolic and Catabolic Activities in Equine Cartilage and Meniscal Explants. Cartilage 2012, 3, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahla, J.; Cinque, M.E.; Piuzzi, N.S.; Mannava, S.; Geeslin, A.G.; Murray, I.R.; Dornan, G.J.; Muschler, G.F.; LaPrade, R.F. A Call for Standardization in Platelet-Rich Plasma Preparation Protocols and Composition Reporting: A Systematic Review of the Clinical Orthopaedic Literature. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2017, 99, 1769–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, R.M.; Bernard, J.A.; Oliver, K.S.; Dines, J.S. Commercial Separation Systems Designed for Preparation of Platelet-Rich Plasma Yield Differences in Cellular Composition. HSS J. 2017, 13, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardos, D.; Simon, M.; Vácz, G.; Hinsenkamp, A.; Holczer, T.; Cseh, D.; Sárközi, A.; Szenthe, K.; Bánáti, F.; Szathmary, S.; et al. The Composition of Hyperacute Serum and Platelet-Rich Plasma Is Markedly Different despite the Similar Production Method. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugaya, H.; Yoshioka, T.; Kato, T.; Taniguchi, Y.; Kumagai, H.; Hyodo, K.; Ohneda, O.; Yamazaki, M.; Mishima, H. Comparative Analysis of Cellular and Growth Factor Composition in Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate and Platelet-Rich Plasma. Bone Marrow Res. 2018, 2018, 1549826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalon, J.; Bausset, O.; Serratrice, N.; Giraudo, L.; Aboudou, H.; Veran, J.; Magalon, G.; Dignat-Georges, F.; Sabatier, F. Characterization and Comparison of 5 Platelet-Rich Plasma Preparations in a Single-Donor Model. Arthroscopy 2014, 30, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundman, E.A.; Cole, B.J.; Fortier, L.A. Growth Factor and Catabolic Cytokine Concentrations Are Influenced by the Cellular Composition of Platelet-Rich Plasma. Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 2135–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakayama, T.; Saita, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Nishio, H.; Uchino, S.; Fukusato, S.; Ikeda, H.; Kaneko, K. Quality Comparison between Two Different Types of Platelet-Rich Plasma for Knee Osteoarthritis. Regen Med. Res. 2020, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Kwon, O.H.; Kim, T.K.; Cho, Y.K.; Choi, K.Y.; Chung, H.Y.; Cho, B.C.; Yang, J.D.; Shin, J.H. Platelet-Rich Plasma: Quantitative Assessment of Growth Factor Levels and Comparative Analysis of Activated and Inactivated Groups. Arch. Plast Surg. 2013, 40, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Castro Pochini, A.; Antonioli, E.; Bucci, D.Z.; Sardinha, L.R.; Andreoli, C.V.; Ferretti, M.; Ejnisman, B.; Goldberg, A.C.; Cohen, M. Analysis of Cytokine Profile and Growth Factors in Platelet-Rich Plasma Obtained by Open Systems and Commercial Columns. Einstein (Sao Paulo) 2016, 14, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.H.; Kim, W.; Park, K.U.; Roh, Y.H. Comparison of the Cellular Composition and Cytokine-Release Kinetics of Various Platelet-Rich Plasma Preparations. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015, 43, 3062–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, P.G.; Ortiz, G.A.; Martinez, L.T.; Emilio, J.; Barbero, F.; O’Valle, F.; Wang, H.-L. Composition of Platelet-Rich Plasma Gel: A Western Blot Analysis. J. Oral Sci. Rehabil. 2016, 2, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Lewenstam, A. Clinical Analysis of Blood Gases and Electrolytes by Ion-Selective Sensors. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2007, 49, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hamed, F.S.; Abu-Nada, L.; Rodan, R.; Sarrigiannidis, S.; Ramirez-Garcialuna, J.L.; Moussa, H.; Elkashty, O.; Gao, Q.; Basiri, T.; Baca, L.; et al. Differences in Platelet-Rich Plasma Composition Influence Bone Healing. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2021, 48, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-M.; Kannan, K. Determination of 19 Steroid Hormones in Human Serum and Urine Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Toxics 2022, 10, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matysik, S.; Schmitz, G. Determination of Steroid Hormones in Human Plasma by GC-Triple Quadrupole MS. Steroids 2015, 99, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Spirito, M.; Brunelli, R.; Mei, G.; Bertani, F.R.; Ciasca, G.; Greco, G.; Papi, M.; Arcovito, G.; Ursini, F.; Parasassi, T. Low Density Lipoprotein Aged in Plasma Forms Clusters Resembling Subendothelial Droplets: Aggregation via Surface Sites. Biophys. J. 2006, 90, 4239–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, R.; Mellis, B.; Garza, K.; Hameed, S.A.; Jurica, J.M.; Hernandez, A.V.; Nguyen, M.N.; Mittal, C.K. Remnant Lipoprotein Size Distribution Profiling via Dynamic Light Scattering Analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 462, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauch, O.; Schubert, R.; Savin, G.; Burchard, W. Structure of Artificial Cytoskeleton Containing Liposomes in Aqueous Solution Studied by Static and Dynamic Light Scattering. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božič, D.; Hočevar, M.; Kononenko, V.; Jeran, M.; Štibler, U.; Fiume, I.; Pajnič, M.; Pađen, L.; Kogej, K.; Drobne, D.; et al. Pursuing Mechanisms of Extracellular Vesicle Formation. Effects of Sample Processing. In Advances in Biomembranes and Lipid Self-Assembly; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 32, pp. 113–155. ISBN 978-0-12-820968-4. [Google Scholar]
- Chaikov, L.L.; Kirichenko, M.N.; Krivokhizha, S.V.; Zaritskiy, A.R. Dynamics of Statistically Confident Particle Sizes and Concentrations in Blood Plasma Obtained by the Dynamic Light Scattering Method. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 57003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitar, S.; Kejžar, A.; Pahovnik, D.; Kogej, K.; Tušek-Žnidarič, M.; Lenassi, M.; Žagar, E. Size Characterization and Quantification of Exosomes by Asymmetrical-Flow Field-Flow Fractionation. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9225–9233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božič, D.; Sitar, S.; Junkar, I.; Štukelj, R.; Pajnič, M.; Žagar, E.; Kralj-Iglič, V.; Kogej, K. Viscosity of Plasma as a Key Factor in Assessment of Extracellular Vesicles by Light Scattering. Cells 2019, 8, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogej, K.; Božič, D.; Kobal, B.; Herzog, M.; Černe, K. Application of Dynamic and Static Light Scattering for Size and Shape Characterization of Small Extracellular Nanoparticles in Plasma and Ascites of Ovarian Cancer Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarassova, E.; Aseyev, V.; Filippov, A.; Tenhu, H. Structure of Poly(Vinyl Pyrrolidone)-C70 Complexes in Aqueous Solutions. Polymer 2007, 48, 4503–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schartl, W. Light Scattering from Polymer Solutions and Nanoparticle Dispersions; Springer Laboratory; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; ISBN 978-3-540-71950-2. [Google Scholar]
- Roose-Amsaleg, C.; Fedala, Y.; Vénien-Bryan, C.; Garnier, J.; Boccara, A.-C.; Boccara, M. Utilization of Interferometric Light Microscopy for the Rapid Analysis of Virus Abundance in a River. Res. Microbiol. 2017, 168, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkki, V.; Alppila, E.; Ylä-Herttuala, S.; Lesch, H.P. Experimental Evaluation of an Interferometric Light Microscopy Particle Counter for Titering and Characterization of Virus Preparations. Viruses 2021, 13, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, Q.; André-Grégoire, G.; Alves-Nicolau, C.; Dupont, A.; Bidère, N.; Jouglar, E.; Guével, L.; Frénel, J.-S.; Gavard, J. The von Willebrand Factor Stamps Plasmatic Extracellular Vesicles from Glioblastoma Patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddoch, K.M.; Pidcoke, H.F.; Montgomery, R.K.; Fedyk, C.G.; Aden, J.K.; Ramasubramanian, A.K.; Cap, A.P. Hemostatic Function of Apheresis Platelets Stored at 4 °C and 22 °C. Shock 2014, 41, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, G.A.; Tuccelli, M.; Kunicki, T.; Chalos, M.K.; Aster, R.H. Studies of Platelet Concentrates Stored at 22 C Nad 4 C. Transfusion 1973, 13, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeri, C.R. Circulation and Hemostatic Effectiveness of Platelets Stored at 4 C or 22 C: Studies in Aspirin-Treated Normal Volunteers. Transfusion 1976, 16, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, S.; Gardner, F.H. Platelet Storage at 22°C; Metabolic, Morphologic, and Functional Studies. J. Clin. Investig. 1971, 50, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, S.; Gardner, F.H. Effect of Storage Temperature on Maintenance of Platelet Viability--Deleterious Effect of Refrigerated Storage. N. Engl. J. Med. 1969, 280, 1094–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bausset, O.; Giraudo, L.; Veran, J.; Magalon, J.; Coudreuse, J.-M.; Magalon, G.; Dubois, C.; Serratrice, N.; Dignat-George, F.; Sabatier, F. Formulation and Storage of Platelet-Rich Plasma Homemade Product. BioResearch Open Access 2012, 1, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.H.; Cole, B.J.; Goodale, M.B.; Fortier, L.A. Short-Term Storage of Platelet-Rich Plasma at Room Temperature Does Not Affect Growth Factor or Catabolic Cytokine Concentration. Am. J. Orthop. 2018, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.W.; Maloney, J.C.; Archer, R.A.; Brown, K.L.; Mayger, K.; Bromidge, E.S.; Najafi, M.F. Platelet-Rich Plasma for Tissue Regeneration Can Be Stored at Room Temperature for at Least Five Days. Br. J. Biomed. Sci 2017, 74, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.-H.; Lin, W.-Y.; Lin, C.-J.; Sun, Y.-C.; Chang, P.-Y.; Wang, H.-Y.; Lu, J.-J.; Yeh, W.-L.; Chiueh, T.-S. Sustained or Higher Levels of Growth Factors in Platelet-Rich Plasma during 7-Day Storage. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 483, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-García, J.S.; García-Lozano, I.; Rivas, L.; Ramírez, N.; Méndez, M.T.; Raposo, R. Stability of Growth Factors in Autologous Serum Eyedrops After Long-Term Storage. Curr. Eye Res. 2016, 41, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiga, Y.; Orita, S.; Kubota, G.; Kamoda, H.; Yamashita, M.; Matsuura, Y.; Yamauchi, K.; Eguchi, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Inage, K.; et al. Freeze-Dried Platelet-Rich Plasma Accelerates Bone Union with Adequate Rigidity in Posterolateral Lumbar Fusion Surgery Model in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.I.; Bae, H.C.; Park, H.J.; Lee, M.C.; Han, H.S. Effect of Storage Conditions and Activation on Growth Factor Concentration in Platelet-Rich Plasma. J. Orthop. Res. 2020, 38, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, T.; Nakatani, Y.; Ohba, S.; Hara, M.; Sumita, Y.; Nagai, K.; Asahina, I. Clinical Safety Assessment of Autologous Freeze-Drying Platelet-Rich Plasma for Bone Regeneration in Maxillary Sinus Floor Augmentation: A Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMello, V.; Chen, G.; Wakshlag, J.; Mason, D. Evaluation of Platelet and Leukocyte Counts in Canine Platelet-Rich Plasma Obtained After Successive Blood Collections From the Same Patient and the Effects of Freezing on the Concentration of Growth Factors Present in It. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 838481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, T.; Wang, Y.; Murrell, G. The Roles of Growth Factors in Tendon and Ligament Healing. Sports Med. 2003, 33, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Pavelko, T. Treatment of Chronic Elbow Tendinosis with Buffered Platelet-Rich Plasma. Am. J. Sports Med. 2006, 34, 1774–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.; Anitua, E.; Azofra, J.; Andía, I.; Padilla, S.; Mujika, I. Comparison of Surgically Repaired Achilles Tendon Tears Using Platelet-Rich Fibrin Matrices. Am. J. Sports Med. 2007, 35, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanasas, C.; Papadimitriou, G.; Charalambidis, C.; Paraskevopoulos, I.; Papanikolaou, A. Platelet-Rich Plasma versus Autologous Whole Blood for the Treatment of Chronic Lateral Elbow Epicondylitis: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 2130–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaweda, K.; Tarczynska, M.; Krzyzanowski, W. Treatment of Achilles Tendinopathy with Platelet-Rich Plasma. Int J. Sports Med. 2010, 31, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alviti, F.; Gurzì, M.; Santilli, V.; Paoloni, M.; Padua, R.; Bernetti, A.; Bernardi, M.; Mangone, M. Achilles Tendon Open Surgical Treatment With Platelet-Rich Fibrin Matrix Augmentation: Biomechanical Evaluation. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2017, 56, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, R.J.; Weir, A.; van Schie, H.T.M.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.A.; Verhaar, J.A.N.; Weinans, H.; Tol, J.L. Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection for Chronic Achilles Tendinopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. JAMA 2010, 303, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepull, T.; Kvist, J.; Norrman, H.; Trinks, M.; Berlin, G.; Aspenberg, P. Autologous Platelets Have No Effect on the Healing of Human Achilles Tendon Ruptures: A Randomized Single-Blind Study. Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boesen, A.P.; Boesen, M.I.; Hansen, R.; Barfod, K.W.; Lenskjold, A.; Malliaras, P.; Langberg, H. Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Nonsurgically Treated Acute Achilles Tendon Ruptures: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Prospective Study. Am. J. Sports Med. 2020, 48, 2268–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filardo, G.; Di Matteo, B.; Kon, E.; Merli, G.; Marcacci, M. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Tendon-Related Disorders: Results and Indications. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2018, 26, 1984–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsousou, J.; Keene, D.J.; Harrison, P.; Hulley, P.; Wagland, S.; Thompson, J.Y.; Parsons, S.R.; Byrne, C.; Schlüssel, M.M.; O’Connor, H.M.; et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection for Adults with Acute Achilles Tendon Rupture: The PATH-2 RCT; Efficacy and Mechanism Evaluation; NIHR Journals Library: Southampton, UK, 2019. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551288/ (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Keene, D.J.; Alsousou, J.; Harrison, P.; O’Connor, H.M.; Wagland, S.; Dutton, S.J.; Hulley, P.; Lamb, S.E.; Willett, K. PATH-2 Trial group Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection for Acute Achilles Tendon Rupture: Two-Year Follow-up of the PATH-2 Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Superiority Trial. Bone Joint J. 2022, 104-B, 1256–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.; Ceilley, R. Chronic Wound Healing: A Review of Current Management and Treatments. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieślik-Bielecka, A.; Glik, J.; Skowroński, R.; Bielecki, T. Benefit of Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Plasma in Operative Wound Closure in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 7649206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupski, W.C.; Reilly, L.M.; Perez, S.; Moss, K.M.; Crombleholme, P.A.; Rapp, J.H. A Prospective Randomized Trial of Autologous Platelet-Derived Wound Healing Factors for Treatment of Chronic Nonhealing Wounds: A Preliminary Report. J. Vasc. Surg. 1991, 14, 526–532; discussion 532–536. [Google Scholar]
- Margolis, D.J.; Kantor, J.; Santanna, J.; Strom, B.L.; Berlin, J.A. Effectiveness of Platelet Releasate for the Treatment of Diabetic Neuropathic Foot Ulcers. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, R.; Holmstrøm, K.; Clausen, C.; Jørgensen, B.; Karlsmark, T. Characteristics of an Autologous Leukocyte and Platelet-Rich Fibrin Patch Intended for the Treatment of Recalcitrant Wounds. Wound Repair Regen 2013, 21, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, V.; Afradi, H.; Gohardani, H.Z.; Nasseri, F.; Azarafza, M.; Teimourian, S. Management of Chronic Diabetic Foot Ulcers Using Platelet-Rich Plasma. J. Wound Care 2017, 26, 784–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieslik-Bielecka, A.; Skowroński, R.; Jędrusik-Pawłowska, M.; Pierchała, M. The Application of L-PRP in AIDS Patients with Crural Chronic Ulcers: A Pilot Study. Adv. Med. Sci. 2018, 63, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, M.J.; Fylling, C.P.; Parnell, L.K.S. Use of Platelet Rich Plasma Gel on Wound Healing: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eplasty 2011, 11, e38. [Google Scholar]
- Crovetti, G.; Martinelli, G.; Issi, M.; Barone, M.; Guizzardi, M.; Campanati, B.; Moroni, M.; Carabelli, A. Platelet Gel for Healing Cutaneous Chronic Wounds. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2004, 30, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, N.; Long, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ran, X. Study on the mechanism of autologous platelet-rich gel to treat the refractory diabetic dermal ulcers. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2009, 40, 292–294. [Google Scholar]
- McAleer, J.P.; Kaplan, E.; Persich, G. Efficacy of Concentrated Autologous Platelet-Derived Growth Factors in Chronic Lower-Extremity Wounds. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2006, 96, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z. Effectiveness of Platelet Rich Plasma in Burn Wound Healing: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2022, 33, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marck, R.E.; Middelkoop, E.; Breederveld, R.S. Considerations on the Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma, Specifically for Burn Treatment. J. Burn. Care Res. 2014, 35, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakos, K.; Lyras, D.N.; Verettas, D.; Tilkeridis, K.; Tryfonidis, M. The Use of Autologous PRP Gel as an Aid in the Management of Acute Trauma Wounds. Injury 2009, 40, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, N.G.; Marques, R.G.; dos Santos, J.S.; Monte-Alto-Costa, A. Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Deep Second- and Third-Degree Burns. Burns 2016, 42, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.L.; Cupp, C.L.; Ross, E.V.; Shick, P.C.; Keefe, M.A.; Wester, D.C.; Hannon, T.; McConnell, D. The Effects of Autologous Platelet Gel on Wound Healing. Ear Nose Throat J. 2003, 82, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marx, R.E.; Carlson, E.R.; Eichstaedt, R.M.; Schimmele, S.R.; Strauss, J.E.; Georgeff, K.R. Platelet-Rich Plasma: Growth Factor Enhancement for Bone Grafts. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 1998, 85, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, G.; Yang, S. Application of Platelet-Rich Plasma with Stem Cells in Bone and Periodontal Tissue Engineering. Bone Res. 2016, 4, 16036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswamy Reddy, S.H.; Reddy, R.; Babu, N.C.; Ashok, G.N. Stem-Cell Therapy and Platelet-Rich Plasma in Regenerative Medicines: A Review on Pros and Cons of the Technologies. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2018, 22, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daif, E.T. Effect of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma on Bone Regeneration in Mandibular Fractures. Dent. Traumatol. 2013, 29, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, A.; Licata, M.E.; Polizzi, B.; Campisi, G. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) in Dental and Oral Surgery: From the Wound Healing to Bone Regeneration. Immun. Ageing 2013, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amable, P.R.; Carias, R.B.V.; Teixeira, M.V.T.; da Cruz Pacheco, Í.; Corrêa do Amaral, R.J.F.; Granjeiro, J.M.; Borojevic, R. Platelet-Rich Plasma Preparation for Regenerative Medicine: Optimization and Quantification of Cytokines and Growth Factors. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2013, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kon, E.; Buda, R.; Filardo, G.; Di Martino, A.; Timoncini, A.; Cenacchi, A.; Fornasari, P.M.; Giannini, S.; Marcacci, M. Platelet-Rich Plasma: Intra-Articular Knee Injections Produced Favorable Results on Degenerative Cartilage Lesions. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2010, 18, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowery, G.L.; Kulkarni, S.; Pennisi, A.E. Use of Autologous Growth Factors in Lumbar Spinal Fusion. Bone 1999, 25, 47S–50S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielecki, T.; Gazdzik, T.S.; Szczepanski, T. Benefit of Percutaneous Injection of Autologous Platelet-Leukocyte-Rich Gel in Patients with Delayed Union and Nonunion. Eur. Surg. Res. 2008, 40, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belk, J.W.; Kraeutler, M.J.; Houck, D.A.; Goodrich, J.A.; Dragoo, J.L.; McCarty, E.C. Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Hyaluronic Acid for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Sports Med. 2021, 49, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berney, M.; McCarroll, P.; Glynn, L.; Lenehan, B. Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections for Hip Osteoarthritis: A Review of the Evidence. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 190, 1021–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitua, E.; Muruzabal, F.; Pino, A.; Merayo-Lloves, J.; Orive, G. Biological Stability of Plasma Rich in Growth Factors Eye Drops After Storage of 3 Months. Cornea 2013, 32, 1380–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Nakagawa, S.; Nishida, T. Stimulatory Effects of Fibronectin and EGF on Migration of Corneal Epithelial Cells. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci 1987, 28, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barton, K.; Nava, A.; Monroy, D.C.; Pflugfelder, S.C. Cytokines and Tear Function in Ocular Surface Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1998, 438, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannaccare, G.; Versura, P.; Buzzi, M.; Primavera, L.; Pellegrini, M.; Campos, E.C. Blood Derived Eye Drops for the Treatment of Cornea and Ocular Surface Diseases. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2017, 56, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oneto, P.; Etulain, J. PRP in Wound Healing Applications. Platelets 2021, 32, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, V.; Andollo, N.; Etxebarria, J.; Durán, J.A.; Morales, M.-C. In Vitro Effects of Three Blood Derivatives on Human Corneal Epithelial Cells. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 5571–5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyol-Salman, I. Effects of Autologous Serum Eye Drops on Corneal Wound Healing after Superficial Keratectomy in Rabbits. Cornea 2006, 25, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.M.; Shin, Y.-T.; Kim, H.K. Effect of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma on Persistent Corneal Epithelial Defect after Infectious Keratitis. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 56, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Hu, F.-R.; Huang, J.-Y.; Shen, E.P.; Tsai, T.-Y.; Chen, W.-L. The Effect of Topical Autologous Serum on Graft Re-Epithelialization after Penetrating Keratoplasty. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 150, 352–359.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekhanont, K.; Jongkhajornpong, P.; Choubtum, L.; Chuckpaiwong, V. Topical 100% Serum Eye Drops for Treating Corneal Epithelial Defect after Ocular Surgery. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 521315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Dogru, M.; Goto, E.; Ohashi, Y.; Kojima, T.; Ishida, R.; Tsubota, K. Autologous Serum Application in the Treatment of Neurotrophic Keratopathy. Ophthalmology 2004, 111, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-García, J.S.; Rivas, L.; García-Lozano, I.; Murube, J. Autologous Serum Eyedrops in the Treatment of Aniridic Keratopathy. Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralph, R.A.; Doane, M.G.; Dohlman, C.H. Clinical Experience with a Mobile Ocular Perfusion Pump. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1975, 93, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, R.I.; Chan, R.; Michelson, J.B.; Belmont, J.B.; Michelson, P.E. Beneficial Effect of Artificial Tears Made with Autologous Serum in Patients with Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca. Arthritis Rheum. 1984, 27, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tananuvat, N.; Daniell, M.; Sullivan, L.J.; Yi, Q.; McKelvie, P.; McCarty, D.J.; Taylor, H.R. Controlled Study of the Use of Autologous Serum in Dry Eye Patients. Cornea 2001, 20, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Angelina, A.; Marrone, M.; Stark, W.J.; Akpek, E.K. Autologous Serum Eye Drops for Dry Eye. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017, 2, CD009327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alio, J.L.; Colecha, J.R.; Pastor, S.; Rodriguez, A.; Artola, A. Symptomatic Dry Eye Treatment with Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma. Ophthalmic Res. 2007, 39, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alio, J.L.; Abad, M.; Artola, A.; Rodriguez-Prats, J.L.; Pastor, S.; Ruiz-Colecha, J. Use of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Dormant Corneal Ulcers. Ophthalmology 2007, 114, 1286–1293.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alio, J.L.; Rodriguez, A.E.; Martinez, L.M.; Rio, A.L. Autologous Fibrin Membrane Combined with Solid Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Management of Perforated Corneal Ulcers: A Pilot Study. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2013, 131, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, A.; Jain, M.; Vanathi, M.; Velpandian, T.; Khokhar, S.; Dada, T. Topical Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Eyedrops for Acute Corneal Chemical Injury. Cornea 2012, 31, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merolle, L.; Iotti, B.; Berni, P.; Bedeschi, E.; Boito, K.; Maurizi, E.; Gavioli, G.; Razzoli, A.; Baricchi, R.; Marraccini, C.; et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma Lysate for Treatment of Eye Surface Diseases. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, 186, e63772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, M.S.; Kumar, A.S.; Kirit, R.; Konathan, R.; Sivamani, R.K. Systematic Review of the Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Aesthetic Dermatology. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2015, 14, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzena, B.; Mazzoleni, F.; Abatangelo, G.; Zavan, B.; Vindigni, V. Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma as an Adipocyte in Vivo Delivery System: Case Report. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2008, 32, 155–158; discussion 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majani, U.; Majani, A. Correction of Scars by Autologous Fat Graft and Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP). Acta Med. Mediterr. 2012, 28, 99–100. [Google Scholar]
- Gentile, P.; De Angelis, B.; Pasin, M.; Cervelli, G.; Curcio, C.B.; Floris, M.; Di Pasquali, C.; Bocchini, I.; Balzani, A.; Nicoli, F.; et al. Adipose-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction Cells and Platelet-Rich Plasma: Basic and Clinical Evaluation for Cell-Based Therapies in Patients with Scars on the Face. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2014, 25, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-T.; Xuan, M.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Liu, H.-W.; Cai, J.-H.; Wu, Y.-H.; Xiang, X.-F.; Shan, G.-Q.; Cheng, B. The Efficacy of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma Combined with Erbium Fractional Laser Therapy for Facial Acne Scars or Acne. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 8, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, M.N.; Mun, S.K. The Efficacy of Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma Combined with Ablative Carbon Dioxide Fractional Resurfacing for Acne Scars: A Simultaneous Split-Face Trial. Dermatol. Surg 2011, 37, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawdat, H.I.; Hegazy, R.A.; Fawzy, M.M.; Fathy, M. Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma: Topical versus Intradermal after Fractional Ablative Carbon Dioxide Laser Treatment of Atrophic Acne Scars. Dermatol. Surg. 2014, 40, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, J.I.; Choi, J.W.; Choi, H.R.; Jeong, J.B.; Park, K.C.; Youn, S.W.; Huh, C.H. Rapid Healing and Reduced Erythema after Ablative Fractional Carbon Dioxide Laser Resurfacing Combined with the Application of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma. Dermatol. Surg. 2011, 37, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Kanodia, S.; Singh, K. Combined Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma with Microneedling Verses Microneedling with Distilled Water in the Treatment of Atrophic Acne Scars: A Concurrent Split-Face Study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2016, 15, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Domyati, M.; Abdel-Wahab, H.; Hossam, A. Combining Microneedling with Other Minimally Invasive Procedures for Facial Rejuvenation: A Split-Face Comparative Study. Int. J. Dermatol. 2018, 57, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, S. Split Face Comparative Study of Microneedling with PRP Versus Microneedling with Vitamin C in Treating Atrophic Post Acne Scars. J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg. 2014, 7, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.K.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Salem, A.M. Skin Microneedling plus Platelet-Rich Plasma versus Skin Microneedling Alone in the Treatment of Atrophic Post Acne Scars: A Split Face Comparative Study. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2018, 29, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellomo, R.; Rapaport, J. Incorporating Platelet-Rich Plasma for Hair Restoration Into Your Practice. Dermatologist, 2017. Available online: https://www.hmpgloballearningnetwork.com/site/thederm/issue-content/incorporating-platelet-rich-plasma-hair-restoration-your-practice (accessed on 6 December 2022).
- Uebel, C.O.; da Silva, J.B.; Cantarelli, D.; Martins, P. The Role of Platelet Plasma Growth Factors in Male Pattern Baldness Surgery. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 118, 1458–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, F.; Hersant, B.; Niddam, J.; Meningaud, J.-P. Injections of Platelet-Rich Plasma for Androgenic Alopecia: A Systematic Review. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 118, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiyeh, B.; Oneisi, A.; Ghieh, F. Platelet-Rich Plasma Facial Rejuvenation: Myth or Reality? Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2021, 45, 2928–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Justicz, N.; Lee, L.N. Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Androgenic Alopecia: A Systematic Review. Facial Plast. Surg. 2018, 34, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Mays, R.R.; Dotzert, M.S.; Versteeg, S.G.; Shear, N.H.; Piguet, V. Efficacy of Non-Surgical Treatments for Androgenetic Alopecia: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, 2112–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuaf, O.K.; Yildiz, H.; Baloglu, H.; Bilgili, M.E.; Simsek, H.A.; Dogan, B. Histologic Evidence of New Collagen Formulation Using Platelet Rich Plasma in Skin Rejuvenation: A Prospective Controlled Clinical Study. Ann. Dermatol. 2016, 28, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hersant, B.; SidAhmed-Mezi, M.; Aboud, C.; Niddam, J.; Levy, S.; Mernier, T.; La Padula, S.; Meningaud, J.-P. Synergistic Effects of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma and Hyaluronic Acid Injections on Facial Skin Rejuvenation. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2021, 41, NP854–NP865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnehrawy, N.Y.; Ibrahim, Z.A.; Eltoukhy, A.M.; Nagy, H.M. Assessment of the Efficacy and Safety of Single Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection on Different Types and Grades of Facial Wrinkles. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2017, 16, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Ley, B.; Cuevast, J.; Alonso-Castro, L.; Calvo, M.I.; Ríos-Buceta, L.; Orive, G.; Anitua, E.; Jaén, P. Benefits of Plasma Rich in Growth Factors (PRGF) in Skin Photodamage: Clinical Response and Histological Assessment. Dermatol. Ther. 2015, 28, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sclafani, A.P. Platelet-Rich Fibrin Matrix for Improvement of Deep Nasolabial Folds. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2010, 9, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehryan, P.; Zartab, H.; Rajabi, A.; Pazhoohi, N.; Firooz, A. Assessment of Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) on Infraorbital Dark Circles and Crow’s Feet Wrinkles. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2014, 13, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neinaa, Y.; Hodeib, A.; Morquos, M.; Elgarhy, L. Platelet Poor Plasma Gel versus Platelet Rich Plasma for Infraorbital Rejuvenation: A Clinical and Dermoscopic Comparative Study. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e14255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Hughart, R.; Champlain, A.; Geisler, A.; Paghdal, K.; Whiting, D.; Hammel, J.A.; Maisel, A.; Rapcan, M.J.; West, D.P.; et al. Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection for Rejuvenation of Photoaged Facial Skin. JAMA Dermatol. 2018, 154, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemsen, J.C.N.; van der Lei, B.; Vermeulen, K.M.; Stevens, H.P.J.D. The Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Recovery Time and Aesthetic Outcome in Facial Rejuvenation: Preliminary Retrospective Observations. Aesthetic. Plast. Surg. 2014, 38, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araco, A. A Prospective Study Comparing Topic Platelet-Rich Plasma vs. Placebo on Reducing Superficial Perioral Wrinkles and Restore Dermal Matrix. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2019, 21, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, M.-K.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, N.-I. Platelet-Rich Plasma Combined with Fractional Laser Therapy for Skin Rejuvenation. Dermatol. Surg. 2012, 38, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuksel, E.P.; Sahin, G.; Aydin, F.; Senturk, N.; Turanli, A.Y. Evaluation of Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Human Facial Skin. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2014, 16, 206–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, S.H.; Kim, J.P.; Park, J.J.; Chung, P.S.; Lee, S.H.; Jeong, H.S. Autologous Platelet-Poor Plasma Gel for Injection Laryngoplasty. Yonsei Med. J. 2013, 54, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, N.K.; Gao, W.Z.; Timmons Sund, L.; Castro, M.E.; O’Dell, K.; Johns, M.M. Platelet-Rich Plasma for Vocal Fold Scar: A Preliminary Report of Concept. J. Voice, 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.; Murry, T. Short-Term Voice Improvement after Repeated Office-Based Platelet-Rich Plasma PRP Injection in Patients with Vocal Fold Scar, Sulcus, and Atrophy. J. Voice, 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, A.; Balouch, B.; Martha, V.V.; Sataoff, R.T. Laryngeal Applications of Platelet Rich Plasma and Platelet Poor Plasma: A Systematic Review. J. Voice, 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.X.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Saim, A.B.; Idrus, R.B.H. Platelet-Rich Plasma with Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts Enhance Healing of Full-Thickness Wounds. J. Tissue Viability 2017, 26, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandour, M.F.; Elsheikh, M.N.; Khalil, M.F. Platelet-Rich Plasma Fat Graft versus Cartilage Perichondrium for Repair of Medium-Size Tympanic Membrane Perforations. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 160, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Shi, Y.; Wu, L.; Lv, C.; Hu, Y.; Shen, Y. Comparative Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma Applied in Myringoplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Anwar, M.W.; El-Ahl, M.A.S.; Zidan, A.A.; Yacoup, M.A.-R.A.-S. Topical Use of Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma in Myringoplasty. Auris Nasus Larynx 2015, 42, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete Álvaro, M.L.; Ortiz, N.; Rodriguez, L.; Boemo, R.; Fuentes, J.F.; Mateo, A.; Ortiz, P. Pilot Study on the Efficiency of the Biostimulation with Autologous Plasma Rich in Platelet Growth Factors in Otorhinolaryngology: Otologic Surgery (Tympanoplasty Type I). ISRN Surg. 2011, 2011, 451020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankaranarayanan, G.; Prithiviraj, V.; Kumar, V. A Study on Efficacy of Autologous Platelet Rich Plasma in Myringoplasty. Otolaryngol. Online J. 2013, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Habesoglu, M.; Oysu, C.; Sahin, S.; Sahin-Yilmaz, A.; Korkmaz, D.; Tosun, A.; Karaaslan, A. Platelet-Rich Fibrin Plays a Role on Healing of Acute-Traumatic Ear Drum Perforation. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2014, 25, 2056–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbary, M.E.S.A.; Nasr, W.F.; Sorour, S.S. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Reconstruction of Posterior Meatal Wall after Canal Wall Down Mastoidectomy. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 22, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Lim, Y.M.; Lew, D.H.; Song, S.Y. Salvage of Unilateral Complete Ear Amputation with Continuous Local Hyperbaric Oxygen, Platelet-Rich Plasma and Polydeoxyribonucleotide without Micro-Revascularization. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2017, 44, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friji, M.T.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Verma, S.K.; Parida, P.K.; Mohapatra, D.P. New Regenerative Approach to Atrophic Rhinitis Using Autologous Lipoaspirate Transfer and Platelet-Rich Plasma in Five Patients: Our Experience. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2014, 39, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, J.; Song, E.A.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.W. Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection in Patients with Atrophic Rhinitis. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2021, 83, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomerantz, J.; Dutton, J.M. Platelet Gel for Endoscopic Sinus Surgery. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2005, 114, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldin, A.; Hussein, A. Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Nasal Mucociliary Clearance after Submucous Diathermy of Inferior Turbinate. Egypt. J. Ear Nose Throat Allied Sci. 2012, 13, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzucu, I.; Beriat, G.K.; Ezerarslan, H.; Ozdemir, S.; Kocaturk, S. Effects of the Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma in Nasal Pack on Postoperative Quality of Life. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2017, 28, e299–e302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldatova, L.; Campbell, R.G.; Elkhatib, A.H.; Schmidt, T.W.; Pinto, N.R.; Pinto, J.M.; Prevedello, D.M.; Ditzel Filho, L.F.; Otto, B.A.; Carrau, R.L. Role of Leukocyte–Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Endoscopic Endonasal Skull Base Surgery Defect Reconstruction. J. Neurol. Surg. B Skull Base 2017, 78, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khafagy, Y.W.; Abd Elfattah, A.M.; Moneir, W.; Salem, E.H. Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin: A New Graft Material in Endoscopic Repair of Spontaneous CSF Leaks. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 275, 2245–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredes, F.; Pinto, J.; Pinto, N.; Rojas, P.; Prevedello, D.M.; Carrau, R.L.; Schmidt, T. Potential Effect of Leukocyte-Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Bone Healing of Skull Base: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Otolaryngol. 2017, 2017, 1231870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, J.; Ruggeri, C.; Ciraolo, C.; Baccanelli, M.; Yampolsky, C.; Ajler, P. Application of Fibrin Rich in Leukocytes and Platelets in the Reconstruction of Endoscopic Approaches to the Skull Base. World Neurosurg. 2018, 118, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constanzo, F.; Pinto, J.; Ledermann, C.; Schmidt, T. Leukocyte-Rich and Platelet-Rich Fibrin for Skull Base Reconstruction After Endoscopic Endonasal Skull Base Surgery. Neurosurgery 2022, 78, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrogeni, P.; Kanakopoulos, A.; Maihoub, S.; Krasznai, M.; Szirmai, A. Anosmia Treatment by Platelet Rich Plasma Injection. Int. Tinnitus J. 2017, 20, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechien, J.R.; Saussez, S. Injection of Platelet Rich Plasma in the Olfactory Cleft for COVID-19 Patients with Persistent Olfactory Dysfunction: Description of the Technique. Ear Nose Throat J. 2022, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffens, Y.; Le Bon, S.-D.; Lechien, J.; Prunier, L.; Rodriguez, A.; Saussez, S.; Horoi, M. Effectiveness and Safety of PRP on Persistent Olfactory Dysfunction Related to COVID-19. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 279, 5951–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidman, J.D.; Lander, T.A.; Finkelstein, M. Platelet-Rich Plasma for Pediatric Tonsillectomy Patients. Laryngoscope 2008, 118, 1765–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanditha, S.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Karthikeyan, P.; Singh Bakshi, S. Efficacy of Topical Application of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma in Adult Tonsillectomy Patients: A Randomised Control Study. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2021, 135, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waselau, M.; Sutter, W.W.; Genovese, R.L.; Bertone, A.L. Intralesional Injection of Platelet-Rich Plasma Followed by Controlled Exercise for Treatment of Midbody Suspensory Ligament Desmitis in Standardbred Racehorses. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2008, 232, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giunta, K.; Donnell, J.R.; Donnell, A.D.; Frisbie, D.D. Prospective Randomized Comparison of Platelet Rich Plasma to Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Treatment of Proximal Suspensory Pain in Western Performance Horses. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 126, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geburek, F.; Gaus, M.; van Schie, H.T.M.; Rohn, K.; Stadler, P.M. Effect of Intralesional Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Treatment on Clinical and Ultrasonographic Parameters in Equine Naturally Occurring Superficial Digital Flexor Tendinopathies—A Randomized Prospective Controlled Clinical Trial. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, M.; Mereu, P.; Spagnolo, F.; Massa, M.; Barla, A.; Mosci, S.; Forno, G.; Ingenito, A.; Strada, P. The Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma Gel in Patients with Mixed Tumour Undergoing Superficial Parotidectomy: A Randomized Study. In Vivo 2014, 28, 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Montano, C.; Auletta, L.; Greco, A.; Costanza, D.; Coluccia, P.; Del Prete, C.; Meomartino, L.; Pasolini, M.P. The Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma for Treatment of Tenodesmic Lesions in Horses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical and Experimental Data. Animals 2021, 11, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brossi, P.M.; Moreira, J.J.; Machado, T.S.L.; Baccarin, R.Y.A. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Orthopedic Therapy: A Comparative Systematic Review of Clinical and Experimental Data in Equine and Human Musculoskeletal Lesions. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbin, L.C.; Olver, C.S. Platelet-Rich Products and Their Application to Osteoarthritis. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2020, 86, 102820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.H.; Bommala, P.; Richbourg, H.A.; Rademacher, N.; Kearney, M.T.; Lopez, M.J. Gait Changes Vary among Horses with Naturally Occurring Osteoarthritis Following Intra-Articular Administration of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma. Front. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrnenopoulou, P.; Diakakis, N.; Karayannopoulou, M.; Savvas, I.; Koliakos, G. Evaluation of Intra-Articular Injection of Autologous Platelet Lysate (PL) in Horses with Osteoarthritis of the Distal Interphalangeal Joint. Vet. Q 2016, 36, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, C.A.; Jolly, D.G.; Worden, C.E.; Hendren, D.G.; Kane, C.J.M. Platelet-Rich Plasma Gel Promotes Differentiation and Regeneration during Equine Wound Healing. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2003, 74, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, R.C.d.F.; De La Côrte, F.D.; Brass, K.E.; da Silva Azevedo, M.; Gallio, M.; Cantarelli, C.; Dau, S.L.; Cezar, A.S.; Inkelmann, M.A. Evaluation of Three Methods of Platelet-Rich Plasma for Treatment of Equine Distal Limb Skin Wounds. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2019, 72, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.O.; Lepage, O.M.; Theoret, C.L. Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma on the Repair of Wounds on the Distal Aspect of the Forelimb in Horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2009, 70, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciel, F.B.; DeRossi, R.; Módolo, T.J.C.; Pagliosa, R.C.; Leal, C.R.J.; Delben, A.A.S.T. Scanning Electron Microscopy and Microbiological Evaluation of Equine Burn Wound Repair after Platelet-Rich Plasma Gel Treatment. Burns 2012, 38, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushton, J.O.; Kammergruber, E.; Tichy, A.; Egerbacher, M.; Nell, B.; Gabner, S. Effects of Three Blood Derived Products on Equine Corneal Cells, an in Vitro Study. Equine Vet. J. 2018, 50, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancarrow-Lei, R.; Mafi, P.; Mafi, R.; Khan, W. A Systemic Review of Adult Mesenchymal Stem Cell Sources and Their Multilineage Differentiation Potential Relevant to Musculoskeletal Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 12, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.; Krause, D.; Deans, R.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.; Horwitz, E. Minimal Criteria for Defining Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy Position Statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andia, I.; Martin, J.I.; Maffulli, N. Platelet-Rich Plasma and Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Exciting, But … Are We There Yet? Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 2018, 26, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Huang, C.; Zhao, M.; Li, P.; Gao, X.; Kong, J.; Niu, Y.; Huang, R.; Quan, J.; Wei, J.; et al. Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Platelet-Rich Plasma on the Bone Healing of Ovariectomized Rats. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 9458396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, N.; Wang, Y.; Ding, L.; Yuan, J.; Du, L.; Zhu, Z.; Pan, M.; Xue, F.; Xiao, H. Platelet-Rich Plasma Enhances the Repair Capacity of Muscle-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Large Humeral Bone Defect in Rabbits. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tandulwadkar, S.; Selva Karthick, M. Combined Use of Autologous Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cells and Platelet-Rich Plasma for Ovarian Rejuvenation in Poor Responders. J. Hum. Reprod. Sci. 2020, 13, 184–190. Available online: https://www.jhrsonline.org/article.asp?issn=0974-1208;year=2020;volume=13;issue=3;spage=184;epage=190;aulast=Tandulwadkar (accessed on 10 December 2022). [PubMed]
- Van Pham, P.; Bui, K.H.-T.; Ngo, D.Q.; Vu, N.B.; Truong, N.H.; Phan, N.L.-C.; Le, D.M.; Duong, T.D.; Nguyen, T.D.; Le, V.T.; et al. Activated Platelet-Rich Plasma Improves Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Transplantation Efficiency in Injured Articular Cartilage. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2013, 4, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atashi, F.; Jaconi, M.E.E.; Pittet-Cuénod, B.; Modarressi, A. Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Biological Supplement to Enhance Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Expansion. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2015, 21, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.; Kakudo, N.; Morimoto, N.; Taketani, S.; Hara, T.; Ogawa, T.; Kusumoto, K. Platelet-Rich Plasma Enhances the Proliferation of Human Adipose Stem Cells through Multiple Signaling Pathways. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasovski, D.; Spasovski, V.; Baščarević, Z.; Stojiljković, M.; Vreća, M.; Anđelković, M.; Pavlović, S. Intra-Articular Injection of Autologous Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. J. Gene Med. 2018, 20, e3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuz, P.C.; Krüger, J.P.; Metzlaff, S.; Freymann, U.; Endres, M.; Pruss, A.; Petersen, W.; Kaps, C. Platelet-Rich Plasma Preparation Types Show Impact on Chondrogenic Differentiation, Migration, and Proliferation of Human Subchondral Mesenchymal Progenitor Cells. Arthroscopy 2015, 31, 1951–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalowiec, J.M.; D’Este, M.; Bara, J.J.; Denom, J.; Menzel, U.; Alini, M.; Verrier, S.; Herrmann, M. An In Vitro Investigation of Platelet-Rich Plasma-Gel as a Cell and Growth Factor Delivery Vehicle for Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2016, 22, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Biocactive Molecule | Suggested Healing Mechanism |
|---|---|
| Molecules originating from α-granules | |
| PF4 | Chemokine: monocyte, recruitment of neutrophils and lymphocytes, differentiation of helper T-cells |
| PPBP | Chemokine: recruitment and activation of neutrophils; activation of macrophages |
| CCL5 or RANTES | Chemokine: recruitment of immune cells |
| P-selectin | Adhesion transmembrane protein: mediation of the adhesion of leukocytes; activation of complement |
| CD40L | A TNF receptor superfamily: provision of activation signals in antigen-presenting cells such as B cells, macrophages and dendritic cells |
| TGF-β | Cytokine: promotion of T lymphocyte proliferation; involvement in regulation of B lymphocytes and macrophage proliferation |
| PDGF | Growth factor: influence on growth and differentiation of monocytes and macrophages; enhancement of cell migration and proliferation; improving cell survival associated with crosstalk with extracellular matrix components and receptors |
| vWF | Glycoprotein: mediation of the adhesion of platelets; extravasation of neutrophils |
| FGF | Growth factor: promotion of growth, differentiation and motility of cells; mediation of angiogenesis by interaction with heparin, heparan sulfat and proteoglicans to induce action of heparan sulfate-degrading enzymes |
| VEGF | Growth factor in the family of pdgfs: induction of angiogenesis; permeabilization of vessels; recruitment of inflammatory cells; expression of adhesion molecules |
| IGF-1 | Growth factor: promotion of migration of stromal cells into the fibrin clot; stimulation of proliferation of fibroblasts and endothelial cells; modulation of cell apoptosis |
| Thrombospondin | Matricellular glycoprotein: regulation of cell migration, cellular attachment and invasion |
| MIP-1α | Cytokine: activation of neutrophils and eosinophils; formation of immunoglobulins |
| MMP-2, MMP-9 | Proteases: degradation of extracellular matrix; formation of platelet and leukocyte clusters |
| cyclophiline A | Smooth muscle growth factor |
| Molecules originating from δ granules | |
| Serotonine | Biogenic amine: regulation of dendrite cells and lymphocytes T, vasoconstriction and increase of capillary permeability |
| Glutamate | Amino acid, neurotransmitter: regulation of lymphocytes T |
| ADP | Adenine nucleotide: activation of platelets, leukocytes and endothelial cells |
| Histamine | Biogenic amine: degranulation, increasing vascular permeability, involvement in pro- and anti-inflammatory effects |
| Molecules not originating from granules | |
| IL-1β | Cytokine: involvement in acute inflammation phase, activation of leukocytes and endothelial cells |
| Thromboxane | Eikosanoid: activation of monocytes, differentiation of lymphocytes |
| nitrous oxide | Reactive oxygen species: involvement in anti-inflammatory and anti-trombotic effects |
| GPIbα | Adhesion molecule: binding to von Willebrand factor and to leukocytes |
| Platelet-Rich Preparation | Description and Preparation Method | Notable Points Regarding Its Use, the Main Advantages and Disadvantages of Its Use |
|---|---|---|
| P-PVRP/LP-PVRP |
|
|
| L-PVRP/LR-PVRP |
|
|
| L-PVRF |
|
|
| P-PVRF |
|
|
| Author, Year | Type of Storage | Temperature, Storage Duration | Study Design, Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| López-García, 2016 [127] | frozen PRP |
|
|
| Shiga et al., 2016 [128] | three types of storage:
|
|
|
| Hosnuter et al., 2017 [83] | frozen PVRP | −20 °C, analyzed on the 0th, 7th and 14th day of storage |
|
| Kim et al., 2020 [129] | cold-storage leukocyte-rich PVRP and frozen leukocyte-rich PVRP |
|
|
| Koga et al., 2021 [130] | freeze-dried PVRP | −20 °C for up to 1 month |
|
| DeMello et al., 2022 [131] | frozen PVRP | −20 °C for 6 months |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Troha, K.; Vozel, D.; Arko, M.; Bedina Zavec, A.; Dolinar, D.; Hočevar, M.; Jan, Z.; Kisovec, M.; Kocjančič, B.; Pađen, L.; et al. Autologous Platelet and Extracellular Vesicle-Rich Plasma as Therapeutic Fluid: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043420
Troha K, Vozel D, Arko M, Bedina Zavec A, Dolinar D, Hočevar M, Jan Z, Kisovec M, Kocjančič B, Pađen L, et al. Autologous Platelet and Extracellular Vesicle-Rich Plasma as Therapeutic Fluid: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(4):3420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043420
Chicago/Turabian StyleTroha, Kaja, Domen Vozel, Matevž Arko, Apolonija Bedina Zavec, Drago Dolinar, Matej Hočevar, Zala Jan, Matic Kisovec, Boštjan Kocjančič, Ljubiša Pađen, and et al. 2023. "Autologous Platelet and Extracellular Vesicle-Rich Plasma as Therapeutic Fluid: A Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 4: 3420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043420
APA StyleTroha, K., Vozel, D., Arko, M., Bedina Zavec, A., Dolinar, D., Hočevar, M., Jan, Z., Kisovec, M., Kocjančič, B., Pađen, L., Pajnič, M., Penič, S., Romolo, A., Repar, N., Spasovski, V., Steiner, N., Šuštar, V., Iglič, A., Drobne, D., ... Kralj-Iglič, V. (2023). Autologous Platelet and Extracellular Vesicle-Rich Plasma as Therapeutic Fluid: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(4), 3420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043420










