Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Basic Research and Clinical Applications
Abstract
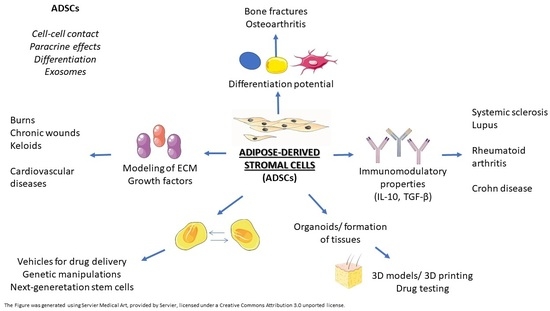
:1. Introduction
2. Flow Cytometry Characteristic
3. Immunomodulatory Effects of AD-MSCs
4. Differentiating Potential
5. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (AD-MSCs) Versus Bone-Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (BM-MSCs)
| S | AD-MSCs | BM-MSCs | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD13 | ++ | ++ | [16] |
| CD 14 | [39,40,43,46] | ||
| CD29 | + | + | [42] |
| CD 34 | ++ | − | [39,40,46] |
| CD 44 | + | [42] | |
| CD 45 | − | + | [16] |
| CD 49d | ++ | + | [39] |
| CD 73 | +++ | +++ | [39] |
| CD90 | +++ | +++ | [39] |
| CD105 | +++ | +++ | [39,42] |
| CD106 | ± | ++ | [16,42] |
| CD 133 | − | + | [39,40,43,46] |
| CD 144 | − | + | [39,40,43,46] |
| HLA-DR | − | − | [46] |
| Stro-1 | + | ++ | [39] |
| AD-MSCs | BM-MSCs | References | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proliferation |
|
| [39] |
| Adipogenic differentiation capacity |
|
| [39,42] |
| Osteogenic differentiation capacity |
|
| [42,46] |
| Chondrogenic differentiation capacity |
|
| [39] |
6. Metabolism of Adipocytes and AD-MSCs
7. Therapeutic Potential of Exosomes
8. Clinical Applications
9. Safety Issues and Side Effects of AD-MSCs Application
10. The Role of miRNAs in the Modulation of Immune Response
11. Bioengineered AD-MSCs in Regenerative Medicine
12. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mazini, L.; Rochette, L.; Amine, M.; Malka, G. Regenerative Capacity of Adipose Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs), Comparison with Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mieczkowska, A.; Schumacher, A.; Filipowicz, N.; Wardowska, A.; Zieliński, M.; Madanecki, P.; Nowicka, E.; Langa, P.; Deptuła, M.; Zieliński, J.; et al. Immunophenotyping and Transcriptional Profiling of in Vitro Cultured Human Adipose Tissue Derived Stem Cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: Current Applications and Future Directions in the Regeneration of Multiple Tissues. Stem Cells Int. 2020, 2020, e8810813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luck, J.; Weil, B.D.; Lowdell, M.; Mosahebi, A. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells for Regenerative Wound Healing Applications: Understanding the Clinical and Regulatory Environment. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2020, 40, 784–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, A.; Cichorek, M.; Pikuła, M. Komórki Macierzyste Tkanki Tłuszczowej w Inżynierii Tkankowej i Terapii Trudno Gojących Się Ran. Postępy Hig. I Med. Doświadczalnej 2018, 72, 806–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, M.; Dompe, C.; Sibiak, R.; Wąsiatycz, G.; Mozdziak, P.; Jaśkowski, J.M.; Antosik, P.; Kempisty, B.; Dyszkiewicz-Konwińska, M. In Vitro Cultures of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: An Overview of Methods, Molecular Analyses, and Clinical Applications. Cells 2020, 9, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanshahi, A.; Hassanshahi, M.; Khabbazi, S.; Hosseini-Khah, Z.; Peymanfar, Y.; Ghalamkari, S.; Su, Y.-W.; Xian, C.J. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells for Wound Healing. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 7903–7914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazini, L.; Rochette, L.; Admou, B.; Amal, S.; Malka, G. Hopes and Limits of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs) and Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) in Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deptuła, M.; Brzezicka, A.; Skoniecka, A.; Zieliński, J.; Pikuła, M. Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells for Nonhealing Wounds: Emerging Opportunities and Challenges. Med. Res. Rev. 2021, 41, 2130–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, J.; Griffin, M.; Mosahebi, A.; Butler, P. Systematic Review of Patient Factors Affecting Adipose Stem Cell Viability and Function: Implications for Regenerative Therapy. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuk, P.A.; Zhu, M.; Mizuno, H.; Huang, J.; Futrell, J.W.; Katz, A.J.; Benhaim, P.; Lorenz, H.P.; Hedrick, M.H. Multilineage Cells from Human Adipose Tissue: Implications for Cell-Based Therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001, 7, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, S.; Sun, H.M.; Hwang, K.-C.; Kim, S.-W. Adipose-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction Cells: Update on Clinical Utility and Efficacy. CRE 2015, 25, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sharma, A.K.; Wolfrum, C. Novel Insights into Adipose Tissue Heterogeneity. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabol, R.A.; Bowles, A.C.; Côté, A.; Wise, R.; Pashos, N.; Bunnell, B.A. Therapeutic Potential of Adipose Stem Cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1341, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikuła, M.; Marek-Trzonkowska, N.; Wardowska, A.; Renkielska, A.; Trzonkowski, P. Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells in Clinical Applications. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2013, 13, 1357–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourin, P.; Bunnell, B.A.; Casteilla, L.; Dominici, M.; Katz, A.J.; March, K.L.; Redl, H.; Rubin, J.P.; Yoshimura, K.; Gimble, J.M. Stromal Cells from the Adipose Tissue-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction and Culture Expanded Adipose Tissue-Derived Stromal/Stem Cells: A Joint Statement of the International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science (IFATS) and the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT). Cytotherapy 2013, 15, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Markov, A.; Thangavelu, L.; Aravindhan, S.; Zekiy, A.O.; Jarahian, M.; Chartrand, M.S.; Pathak, Y.; Marofi, F.; Shamlou, S.; Hassanzadeh, A. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells as a Valuable Source for the Treatment of Immune-Mediated Disorders. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccarelli, S.; Pontecorvi, P.; Anastasiadou, E.; Napoli, C.; Marchese, C. Immunomodulatory Effect of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: The Cutting Edge of Clinical Application. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, C.H.; Kang, M.-I.; Shin, Y.D.; Kim, Y.; Park, Y.-B. The Expression of Immunomodulation-Related Cytokines and Genes of Adipose- and Bone Marrow-Derived Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Early to Late Passages. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 15, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiori, A.; Uhlig, S.; Klüter, H.; Bieback, K. Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Inhibit CD4+ T Cell Proliferation and Induce Regulatory T Cells as Well as CD127 Expression on CD4+CD25+ T Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawagishi-Hotta, M.; Hasegawa, S.; Igarashi, T.; Yamada, T.; Takahashi, M.; Numata, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Iwata, Y.; Arima, M.; Yamamoto, N.; et al. Enhancement of Individual Differences in Proliferation and Differentiation Potentials of Aged Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Regen. Ther. 2017, 6, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grotheer, V.; Skrynecki, N.; Oezel, L.; Windolf, J.; Grassmann, J. Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Fibroblasts Differs Depending on Tissue Origin and Replicative Senescence. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohiuddin, O.A.; O’Donnell, B.T.; Poche, J.N.; Iftikhar, R.; Wise, R.M.; Motherwell, J.M.; Campbell, B.; Savkovic, S.D.; Bunnell, B.A.; Hayes, D.J.; et al. Human Adipose-Derived Hydrogel Characterization Based on In Vitro ASC Biocompatibility and Differentiation. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 9276398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zampar, A.G.; Farina Junior, J.A.; Orellana, M.D.; Caruso, S.R.; Fernandes, T.R.; Gomes, R.; Aragon, D.C.; De Santis, G.C.; Covas, D.T. Analysis of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells from Different Donor Areas and Their Influence on Fibroblasts In Vitro. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2020, 44, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedenstein, A.J.; Petrakova, K.V.; Kurolesova, A.I.; Frolova, G.P. Heterotopic of Bone Marrow. Analysis of Precursor Cells for Osteogenic and Hematopoietic Tissues. Transplantation 1968, 6, 230–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, P.; Robey, P.G.; Simmons, P.J. Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Revisiting History, Concepts, and Assays. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 2, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Triffitt, J.T. JTT A Brief History of the Development of Stromal Stem Cells (Stem Cells of the Skeleton). Biomater. Transl. 2021, 2, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, C.; Kang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Hui, Y. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: Sources, Potency, and Implications for Regenerative Therapies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 114, 108765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, W.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Sugii, S. Adipose Tissue: Understanding the Heterogeneity of Stem Cells for Regenerative Medicine. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, M.; Jing, X.; Guo, W.; Hao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, S.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; et al. Bone Marrow- and Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Characterization, Differentiation, and Applications in Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2018, 28, 285–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, M.; Windsor, J.; Dunbar, P.R. Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: Isolation, Characterization and Applications in Surgery. ANZ J. Surg. 2009, 79, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.; Shin, T.-H.; Kim, H.-S. Current Strategies to Enhance Adipose Stem Cell Function: An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strioga, M.; Viswanathan, S.; Darinskas, A.; Slaby, O.; Michalek, J. Same or Not the Same? Comparison of Adipose Tissue-Derived versus Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem and Stromal Cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21, 2724–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izadpanah, R.; Trygg, C.; Patel, B.; Kriedt, C.; Dufour, J.; Gimble, J.M.; Bunnell, B.A. Biologic Properties of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived From Bone Marrow and Adipose Tissue. J Cell Biochem 2006, 99, 1285–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oryan, A.; Kamali, A.; Moshiri, A.; Baghaban Eslaminejad, M. Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Bone Regenerative Medicine: What Is the Evidence? Cells Tissues Organs 2017, 204, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Francesco, F.; Ricci, G.; D’Andrea, F.; Nicoletti, G.F.; Ferraro, G.A. Human Adipose Stem Cells: From Bench to Bedside. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2015, 21, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klar, A.S.; Zimoch, J.; Biedermann, T. Skin Tissue Engineering: Application of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9747010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bajek, A.; Gurtowska, N.; Olkowska, J.; Kazmierski, L.; Maj, M.; Drewa, T. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells as a Tool in Cell-Based Therapies. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2016, 64, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohamed-Ahmed, S.; Fristad, I.; Lie, S.A.; Suliman, S.; Mustafa, K.; Vindenes, H.; Idris, S.B. Adipose-Derived and Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Donor-Matched Comparison. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.B.; McIntosh, K.; Zvonic, S.; Garrett, S.; Floyd, Z.E.; Kloster, A.; Di Halvorsen, Y.; Storms, R.W.; Goh, B.; Kilroy, G.; et al. Immunophenotype of Human Adipose-Derived Cells: Temporal Changes in Stromal-Associated and Stem Cell–Associated Markers. Stem Cells 2006, 24, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, G.-I. Bone Marrow-Derived Stem/Stromal Cells and Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem/Stromal Cells: Their Comparative Efficacies and Synergistic Effects. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2017, 105, 2640–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, S.; Eichler, H.; Stoeve, J.; Klüter, H.; Bieback, K. Comparative Analysis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Bone Marrow, Umbilical Cord Blood, or Adipose Tissue. Stem Cells 2006, 24, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldner, M.; Zhang, W.; James, I.B.; Allbright, K.; Havis, E.; Bliley, J.M.; Almadori, A.; Schweizer, R.; Plock, J.A.; Washington, K.M.; et al. Characteristics and Immunomodulating Functions of Adipose-Derived and Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Across Defined Human Leukocyte Antigen Barriers. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baptista, L.S. Adipose Stromal/Stem Cells in Regenerative Medicine: Potentials and Limitations. World J. Stem Cells 2020, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Lin, J.; Zhao, K.; Jin, K.; He, Q.; Hu, Y.; Feng, G.; Cai, Y.; Xia, C.; Liu, H.; et al. Single-Cell Profiles and Clinically Useful Properties of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells of Adipose and Bone Marrow Origin. Am. J. Sports Med. 2019, 47, 1722–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed-Ahmed, S.; Yassin, M.A.; Rashad, A.; Espedal, H.; Idris, S.B.; Finne-Wistrand, A.; Mustafa, K.; Vindenes, H.; Fristad, I. Comparison of Bone Regenerative Capacity of Donor-Matched Human Adipose–Derived and Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2021, 383, 1061–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; El-Sabbagh, A.S.; Lukas, B.E.; Tanneberger, S.J.; Jiang, Y. Adipose Stem Cells in Obesity: Challenges and Opportunities. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20194076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, A.; Frontini, A.; Cinti, S. Convertible Visceral Fat as a Therapeutic Target to Curb Obesity. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skubis-Sikora, A.; Sikora, B.; Witkowska, A.; Mazurek, U.; Gola, J. Osteogenesis of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells from Patients with Glucose Metabolism Disorders. Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yin, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, F.; Jin, P. Inhibition of Autophagy Promoted High Glucose/ROS-Mediated Apoptosis in ADSCs. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shree, N.; Venkategowda, S.; Venkatranganna, M.V.; Datta, I.; Bhonde, R.R. Human Adipose Tissue Mesenchymal Stem Cells as a Novel Treatment Modality for Correcting Obesity Induced Metabolic Dysregulation. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 2107–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conley, S.M.; Hickson, L.J.; Kellogg, T.A.; McKenzie, T.; Heimbach, J.K.; Taner, T.; Tang, H.; Jordan, K.L.; Saadiq, I.M.; Woollard, J.R.; et al. Human Obesity Induces Dysfunction and Early Senescence in Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lv, M.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, B.; Cao, S.; Dong, Y.; Cao, L.; Guo, S. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Regulate Metabolic Homeostasis and Delay Aging by Promoting Mitophagy. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Kim, Y.; Ha, S.; Sheller-Miller, S.; Yoo, J.; Choi, C.; Park, C.H. The Emerging Role of Exosomes as Novel Therapeutics: Biology, Technologies, Clinical Applications, and the Next. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2021, 85, e13329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradetti, B.; Gonzalez, D.; Mendes Pinto, I.; Conlan, R.S. Editorial: Exosomes as Therapeutic Systems. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 714743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlan, R.S.; Pisano, S.; Oliveira, M.I.; Ferrari, M.; Mendes Pinto, I. Exosomes as Reconfigurable Therapeutic Systems. Trends Mol. Med. 2017, 23, 636–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, G.; Song, X.; Yang, F.; Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y. Exosomes Derived from MiR-122-Modified Adipose Tissue-Derived MSCs Increase Chemosensitivity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ju, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yang, P.; Xie, X.; Fang, B. Extracellular Vesicle-Loaded Hydrogels for Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Mater. Today Bio. 2023, 18, 100522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Niazi, V.; Hussen, B.M.; Omrani, M.D.; Taheri, M.; Basiri, A. The Emerging Role of Exosomes in the Treatment of Human Disorders With a Special Focus on Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 653296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, G.; Yang, Y.; Liu, F.; Ye, B.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, M.; Liu, Y. MiR-122 Modification Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells against Liver Fibrosis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 2963–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Han, S.; Wan, L.; Sun, X.; Chen, H. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Extracellular Vesicles Confer Antitumor Activity in Preclinical Treatment of Breast Cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 157, 104843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Bajo, M.J.; Rovira, J.; Lazo-Rodriguez, M.; Banon-Maneus, E.; Tubita, V.; Moya-Rull, D.; Hierro-Garcia, N.; Ventura-Aguiar, P.; Oppenheimer, F.; Campistol, J.M.; et al. Impact of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Their Extracellular Vesicles in a Rat Model of Kidney Rejection. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, B.S.; Kim, J.O.; Ha, D.H.; Yi, Y.W. Exosomes Derived from Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Atopic Dermatitis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, K.-O.; Ha, D.H.; Kim, J.O.; Crumrine, D.A.; Meyer, J.M.; Wakefield, J.S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; et al. Exosomes from Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Epidermal Barrier Repair by Inducing de Novo Synthesis of Ceramides in Atopic Dermatitis. Cells 2020, 9, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.-Z.; Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.-H.; Wu, S.; Yi, Y.-Y. Extracellular Vesicles Derived From Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Prevent the Formation of Hypertrophic Scar in a Rabbit Model. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2020, 84, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yu, R.; Huang, F.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L. Exosomes Derived from Human Adipose Mensenchymal Stem Cells Accelerates Cutaneous Wound Healing via Optimizing the Characteristics of Fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szwedowicz, U.; Łapińska, Z.; Gajewska-Naryniecka, A.; Choromańska, A. Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles with High Therapeutic Potential: Their Applications in Oncology, Neurology, and Dermatology. Molecules 2022, 27, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, J.; Feghhi, M.; Etemadi, T. A Review on Exosomes Application in Clinical Trials: Perspective, Questions, and Challenges. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueyama, H.; Okano, T.; Orita, K.; Mamoto, K.; Ii, M.; Sobajima, S.; Iwaguro, H.; Nakamura, H. Local Transplantation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Has a Significant Therapeutic Effect in a Mouse Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maria, A.T.J.; Maumus, M.; Le Quellec, A.; Jorgensen, C.; Noël, D.; Guilpain, P. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Autoimmune Disorders: State of the Art and Perspectives for Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 52, 234–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, X.; Shi, G.; Lei, X.; Huang, Y.; Bai, L.; Qin, C. Effectiveness and Mechanisms of Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Therapy in Animal Models of Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Transl. Neurodegener. 2021, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carstens, M.; Haq, I.; Martinez-Cerrato, J.; Dos-Anjos, S.; Bertram, K.; Correa, D. Sustained Clinical Improvement of Parkinson’s Disease in Two Patients with Facially-Transplanted Adipose-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction Cells. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 81, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pers, Y.-M.; Jorgensen, C. Adipose Derived Stem Cells for Regenerative Therapy in Osteoarticular Diseases. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2016, 28, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huri, P.Y.; Hamsici, S.; Ergene, E.; Huri, G.; Doral, M.N. Infrapatellar Fat Pad-Derived Stem Cell-Based Regenerative Strategies in Orthopedic Surgery. Knee Surg. Relat. Res. 2018, 30, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, C.-J.; Lin, C.-H.; Tsai, C.-H.; Yang, I.-C.; Ma, H. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells-Induced Burn Wound Healing and Regeneration of Skin Appendages in a Novel Skin Island Rat Model. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2019, 82, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharl, M.; Rogler, G. Pathophysiology of Fistula Formation in Crohn’s Disease. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2014, 5, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, L.J. Darvadstrocel: A Review in Treatment-Refractory Complex Perianal Fistulas in Crohn’s Disease. BioDrugs 2018, 32, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimbrel, E.A.; Lanza, R. Next-Generation Stem Cells-Ushering in a New Era of Cell-Based Therapies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 463–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bos, J.; Ouaamari, Y.E.; Wouters, K.; Cools, N.; Wens, I. Are Cell-Based Therapies Safe and Effective in the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases? A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghadban, S.; Artiles, M.; Bunnell, B.A. Adipose Stem Cells in Regenerative Medicine: Looking Forward. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 9, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prockop, D.J.; Brenner, M.; Fibbe, W.E.; Horwitz, E.; Le Blanc, K.; Phinney, D.G.; Simmons, P.J.; Sensebe, L.; Keating, A. Defining the Risks of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy. Cytotherapy 2010, 12, 576–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalu, M.M.; McIntyre, L.; Pugliese, C.; Fergusson, D.; Winston, B.W.; Marshall, J.C.; Granton, J.; Stewart, D.J. Safety of Cell Therapy with Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (SafeCell): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosanya, C.H.; Isaacs, J.D. Tolerising Cellular Therapies: What Is Their Promise for Autoimmune Disease? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caplan, H.; Olson, S.D.; Kumar, A.; George, M.; Prabhakara, K.S.; Wenzel, P.; Bedi, S.; Toledano-Furman, N.E.; Triolo, F.; Kamhieh-Milz, J.; et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapeutic Delivery: Translational Challenges to Clinical Application. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, G.; Elsallab, M.; Abou-El-Enein, M. Concise Review: A Comprehensive Analysis of Reported Adverse Events in Patients Receiving Unproven Stem Cell-Based Interventions. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2018, 7, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuriyan, A.E.; Albini, T.A.; Townsend, J.H.; Rodriguez, M.; Pandya, H.K.; Leonard, R.E.; Parrott, M.B.; Rosenfeld, P.J.; Flynn, H.W.; Goldberg, J.L. Vision Loss after Intravitreal Injection of Autologous “Stem Cells” for AMD. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- YMJ: Yonsei Medical Journal. Available online: https://eymj.org/DOIx.php?id=10.3349/ymj.2013.54.5.1293 (accessed on 6 January 2023).
- Coppin, L.; Sokal, E.; Stéphenne, X. Thrombogenic Risk Induced by Intravascular Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Cells 2019, 27, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toyserkani, N.M.; Jørgensen, M.G.; Tabatabaeifar, S.; Jensen, C.H.; Sheikh, S.P.; Sørensen, J.A. Concise Review: A Safety Assessment of Adipose-Derived Cell Therapy in Clinical Trials: A Systematic Review of Reported Adverse Events. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1786–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Yi, H.; Song, Y. The Safety of MSC Therapy over the Past 15 Years: A Meta-Analysis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wei, Y. Modulators of MicroRNA Function in the Immune System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pers, Y.-M.; Maumus, M.; Bony, C.; Jorgensen, C.; Noël, D. Contribution of MicroRNAs to the Immunosuppressive Function of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Biochimie 2018, 155, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bier, A.; Berenstein, P.; Kronfeld, N.; Morgoulis, D.; Ziv-Av, A.; Goldstein, H.; Kazimirsky, G.; Cazacu, S.; Meir, R.; Popovtzer, R.; et al. Placenta-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Their Exosomes Exert Therapeutic Effects in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Biomaterials 2018, 174, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.-B.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Wang, C.; He, B.-X.; Liu, X.-Q.; Meng, X.-C.; Peng, Y.-Q.; Xu, Z.-B.; Fan, X.-L.; Wu, Z.-J.; et al. Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Prevent Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell-Dominant Allergic Airway Inflammation through Delivery of MiR-146a-5p. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1723260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, Z.; Qiao, S.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Wei, Z.; Dai, Q.; Kang, L.; Xu, B. MiRNA-181a over-Expression in Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Influenced Inflammatory Response after Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Life Sci. 2019, 232, 116632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, M.; Mavin, E.; Nicholson, L.; Green, K.; Dickinson, A.M.; Wang, X. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Attenuate Dendritic Cell Maturation and Function. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujii, S.; Miura, Y.; Fujishiro, A.; Shindo, T.; Shimazu, Y.; Hirai, H.; Tahara, H.; Takaori-Kondo, A.; Ichinohe, T.; Maekawa, T. Graft-Versus-Host Disease Amelioration by Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Is Associated with Peripheral Preservation of Naive T Cell Populations. Stem Cells 2018, 36, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, S.; Chu, J.; Wu, L.-C.; Mao, H.; Peng, Y.; Alvarez-Breckenridge, C.A.; Hughes, T.; Wei, M.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, S.; et al. MicroRNAs Activate Natural Killer Cells through Toll-like Receptor Signaling. Blood 2013, 121, 4663–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Lv, T.; Lin, J.; Zhou, L. Inflammatory Stimuli Significantly Change the MiRNA Profile of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 1340341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Qin, Y.-R.; Di, G.-H.; Lei, Y.-H.; Liu, H.-X.; Li, Y.-Q.; Wu, C.; Hu, X.-W.; et al. Short-Term Memory of Danger Signals or Environmental Stimuli in Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Implications for Therapeutic Potential. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, W.; Pu, G.; Wu, J.; Qin, F. Exosomes Derived from MiR-338-3p-Modified Adipose Stem Cells Inhibited Inflammation Injury of Chondrocytes via Targeting RUNX2 in Osteoarthritis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2022, 17, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashor, C.J.; Hilton, I.B.; Bandukwala, H.; Smith, D.M.; Veiseh, O. Engineering the next Generation of Cell-Based Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 655–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verisqa, F.; Cha, J.-R.; Nguyen, L.; Kim, H.-W.; Knowles, J.C. Digital Light Processing 3D Printing of Gyroid Scaffold with Isosorbide-Based Photopolymer for Bone Tissue Engineering. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mörö, A.; Samanta, S.; Honkamäki, L.; Rangasami, V.K.; Puistola, P.; Kauppila, M.; Narkilahti, S.; Miettinen, S.; Oommen, O.; Skottman, H. Hyaluronic Acid Based next Generation Bioink for 3D Bioprinting of Human Stem Cell Derived Corneal Stromal Model with Innervation. Biofabrication 2022, 15, 015020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, C.; Parson, J.; Meyer, G.A. Harnessing Adipose Stem Cell Diversity in Regenerative Medicine. APL Bioeng. 2021, 5, 021501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, F.; Aghaee Bakhtiari, S.H.; Pasdar, A.; Saburi, E. Evaluation of Osteogenic Induction Potency of MiR-27a-3p in Adipose Tissue-Derived Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells (AD-HMSCs). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 50, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, H.; Moriyama, M.; Ozawa, T.; Tsuruta, D.; Hayakawa, T. Differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells into Insulin-Producing Cells with A Single Tet-Off Lentiviral Vector System. Cell J. 2022, 24, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Wu, T.; Wang, K.; Xia, K.; Yin, L.; Chen, C. Polydopamine-Modified Decellularized Intestinal Scaffolds Loaded with Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Promote Intestinal Regeneration. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 11, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.-L.; Zhu, J.-W.; Gao, X.-M. Netrin-1 Promotes the Vasculogenic Capacity of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Cell Tissue Bank. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yang, J.; Ji, X.; Wang, Z.; Dai, C.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, J.; et al. Clinical Application of a Double-Modified Sulfated Bacterial Cellulose Scaffold Material Loaded with FGFR2-Modified Adipose-Derived Stem Cells in Urethral Reconstruction. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Fu, X.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Han, W.; Wang, Y. Modification of Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles with Fibrin-Targeting Peptide CREKA for Enhanced Bone Repair. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 20, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eke, G.; Mangir, N.; Hasirci, N.; MacNeil, S.; Hasirci, V. Development of a UV Crosslinked Biodegradable Hydrogel Containing Adipose Derived Stem Cells to Promote Vascularization for Skin Wounds and Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2017, 129, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, N.; Zhang, D.; Wu, M.; Yang, H.; Liu, X.; Song, J. Enhancing Therapeutic Effects and in Vivo Tracking of Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Liver Injury Using Bioorthogonal Click Chemistry. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2022. Available online: https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/chemistry/2022/press-release/ (accessed on 8 January 2023).
| Surface Marker | Gene | Name | Function | AD-MSCs Expression |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD10 | MME | membrane metalloendopeptidase |
| positive |
| CD105 | ENG | endoglin |
| positive |
| CD13 | ANPEP | Alanyl aminopeptidase, membrane |
| positive |
| CD26 | DPP4 | dipeptidyl peptidase 4 |
| positive |
| CD29 | ITGB1 | integrin subunit beta 1 |
| positive |
| CD36 | CD36 | CD36 molecule |
| positive |
| CD44 | CD44 | CD44 molecule |
| positive |
| CD49d | ITGA4 | integrin subunit alpha 4 |
| positive |
| CD49e | ITGA5 | integrin subunit alpha 5 |
| positive |
| CD59 | CD59 | CD59 molecule |
| positive |
| CD73 | NT5E | 5′-nucleotidase ecto |
| positive |
| CD90 | THY1 | Thy-1 cell surface antigen |
| positive |
| CD106 | VCAM1 | vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| positive |
| CD11b | ITGAM | integrin subunit alpha M |
| negative |
| CD14 | CD14 | CD14 molecule |
| negative |
| CD79A | CD79A | CD79a molecule |
| negative |
| CD19 | CD19 | CD19 molecule |
| negative |
| CD253a | GYPA | glycophorin A |
| negative |
| CD31 | PECAM1 | platelet and endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| negative |
| CD34 | CD34 | CD34 molecule |
| variable expression |
| CD45 | PTPRC | protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type C |
| negative |
| CD49f | ITGA6 | integrin subunit alpha 6 |
| negative |
| CD56 | NCAM1 | neural cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| negative |
| CD62 | SELP | selectin P |
| negative |
| HLA-DRA | HLA-DRA | major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR alpha |
| negative |
| HLA-DRB1 | HLA-DRB1 | major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 1 |
| negative |
| HLA-DRB3 | HLA-DRB3 | major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 3 |
| negative |
| HLA-DRB4 | HLA-DRB4 | major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 4 |
| negative |
| HLA- DRB5 | HLA-DRB5 | major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 5 |
| negative |
| NA | PODXL | podocalyxin like |
| negative |
| Medical Conditions | Source of AD-MSCs | Phase Study | Research Model | NCT Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skin diseases | Keloids | Autologous AD-MSCs | Phase 2 | 8 participants; Lipoaspirate was collected from each patient and stromal vascular fraction was infiltrated into the keloid tissue | NCT04553159 |
| Burn | Allogenic AD-MSC | Phase 1 | 5 participants; Patients with wounds resulting from second-degree burns were applied with an ALLO-AD-MSC-DFU dressing containing AD-MSCs | NCT02394873 | |
| Chronic wounds associated with diabetes, venous and pressure ulcers | Autologous AD-MSCs | Phase 2 | 25 participants; Injection around and within the wound of AD-MSCs obtained from lipoaspirate | NCT02092870 | |
| Orthopedic diseases | Knee osteoarthritis | Allogenic AD-MSCs | Phases 1 and 2 | 57 participants; Administration of allogeneic AD-MSCs in three amounts—1.6 × 107; 3.2 × 107; 6.4 × 107 cells | NCT02784964 |
| Rotator cuff tear | Allogenic AD-MSCs | Phase 2 | 24 participants; Patients were administered allogeneic AD-MSCs in scaffolds of fibrin glue | NCT02298023 | |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Autologous AD-MSCs | Phases 1 and 2 | 15 participants; Administer a single dose of stem cells as an intravenous infusion | NCT03691909 | |
| Cardiovascular diseases | Peripheral arterial disease | Autologous AD-MSCs | Phase 1 | 10 participants; Single administration of AD-MSC or pretreatment of patients with ultrasound therapy | NCT02756884 |
| Cardiovascular disorders, including myocardial infarction, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease | Autologous AD-MSCs | Phase 1 | 14 participants; Collection of lipoaspirate followed by administration of adipose-tissue-derived stem cells | NCT00442806 | |
| Heart failure | Allogenic AD-MSCs | Phase 2 | 138 participants; Direct injection of AD-MSCs from the Cardiology Stem Cell Center into the heart muscle | NCT02673164 | |
| Autoimmune diseases | Systemic sclerosis | Autologous stromal vascular fraction (SVF) | Phase 1 | 20 participants; Injection of SVF obtained from lipoaspirate using automated methods | NCT03060551 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Allogenic AD-MSCs | Phases 1 and 2 | 53 participants; Intravenous infusion of AD-MSCs with simultaneous treatment with a non-biological drug that modifies the disease | NCT01663116 | |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Autologous AD-MSCs | Phases 1 and 2 | 15 participants; A single intravenous infusion of AD-MSCs obtained from patients with rheumatoid arthritis | NCT03691909 | |
| Other diseases | Liver cirrhosis | Autologous AD-MSCs | Phase 1 | 6 participants; Hepatic injection of autologous AD-MSCs in patients with cirrhosis of the liver | NCT02297867 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | Autologous AD-MSCs | Phases 1 and 2 | 26 participants; Provision of AD-MSC along with SVF obtained by liposuction | NCT02216630 | |
| Crohn’s fistula | Autologous AD-MSCs | Phase 2 | 40 participants; Injection of AD-MSCs in the form of a preparation called ADIPOPLUS | NCT01011244 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czerwiec, K.; Zawrzykraj, M.; Deptuła, M.; Skoniecka, A.; Tymińska, A.; Zieliński, J.; Kosiński, A.; Pikuła, M. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Basic Research and Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043888
Czerwiec K, Zawrzykraj M, Deptuła M, Skoniecka A, Tymińska A, Zieliński J, Kosiński A, Pikuła M. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Basic Research and Clinical Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(4):3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043888
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzerwiec, Katarzyna, Małgorzata Zawrzykraj, Milena Deptuła, Aneta Skoniecka, Agata Tymińska, Jacek Zieliński, Adam Kosiński, and Michał Pikuła. 2023. "Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Basic Research and Clinical Applications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 4: 3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043888
APA StyleCzerwiec, K., Zawrzykraj, M., Deptuła, M., Skoniecka, A., Tymińska, A., Zieliński, J., Kosiński, A., & Pikuła, M. (2023). Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Basic Research and Clinical Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(4), 3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043888