Involvement of Mast-Cell-Tryptase- and Protease-Activated Receptor 2—Mediated Signaling and Urothelial Barrier Dysfunction with Reduced Uroplakin II Expression in Bladder Hyperactivity Induced by Chronic Bladder Ischemia in the Rat
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
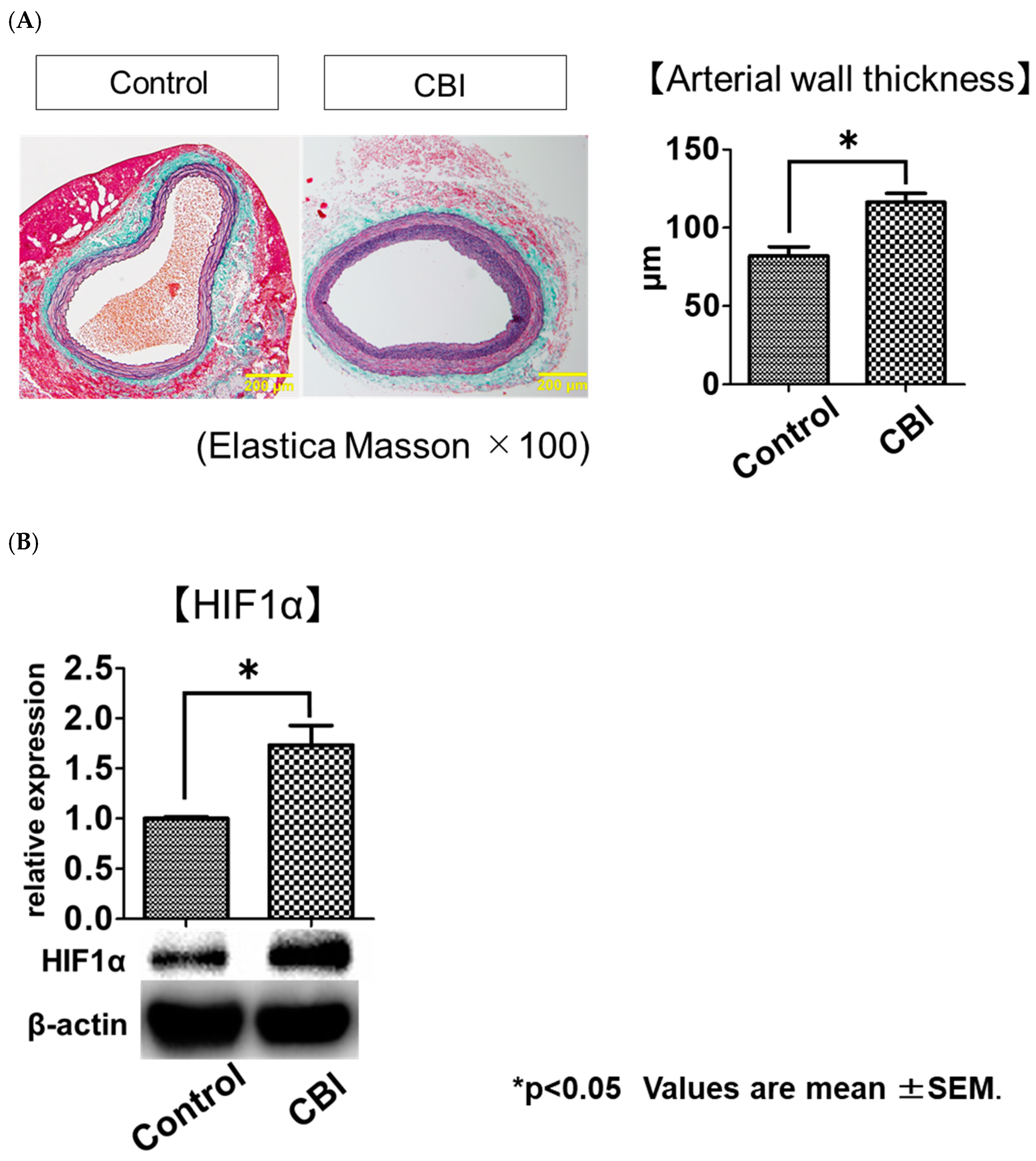
2.1. Arterial-Occlusion-Caused Bladder Hyperactivity Correlated with Chronic Ischemia
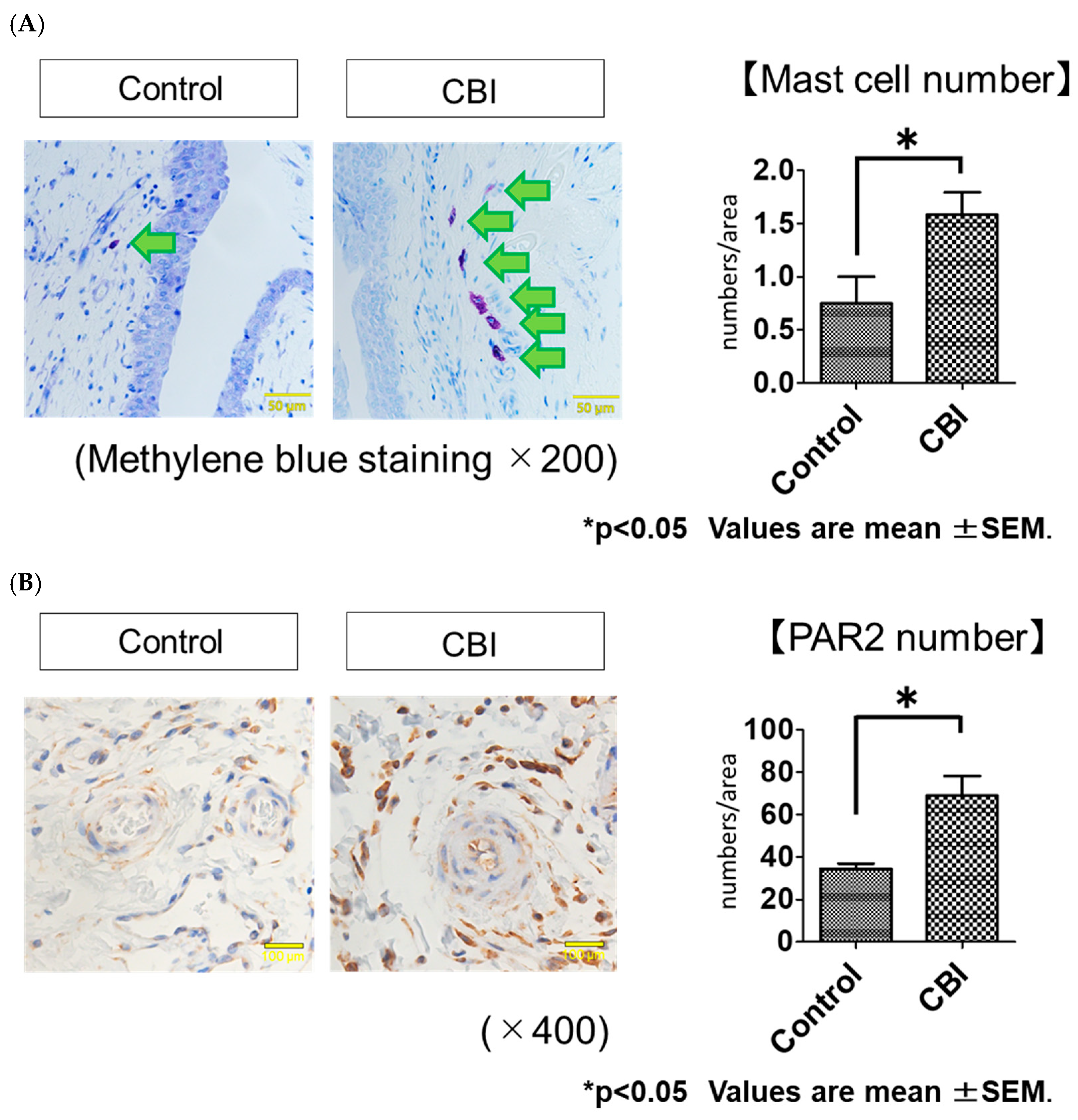
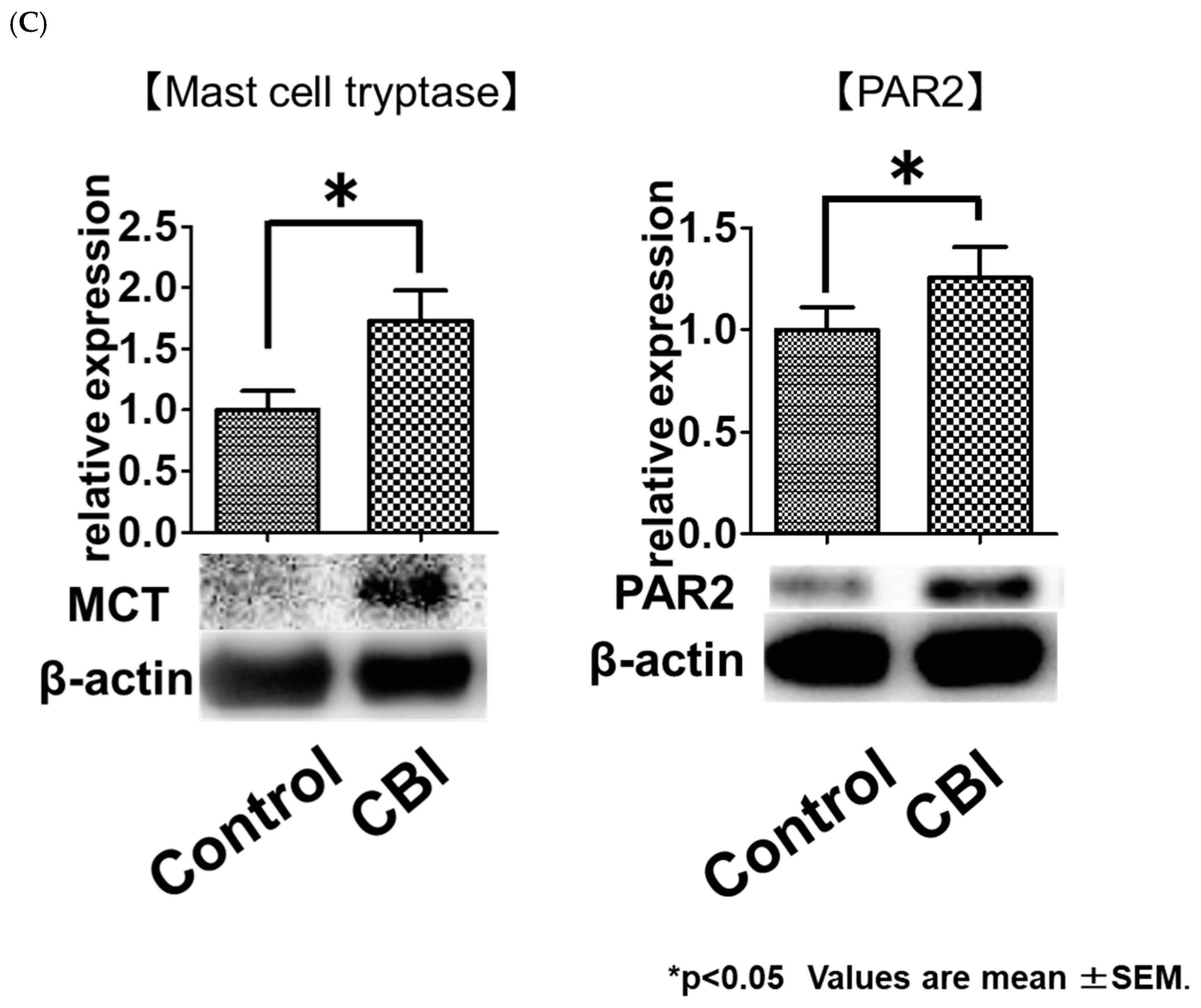
2.2. Increased Mast Cell Infiltration and PAR2 Expression in Rats with CBI
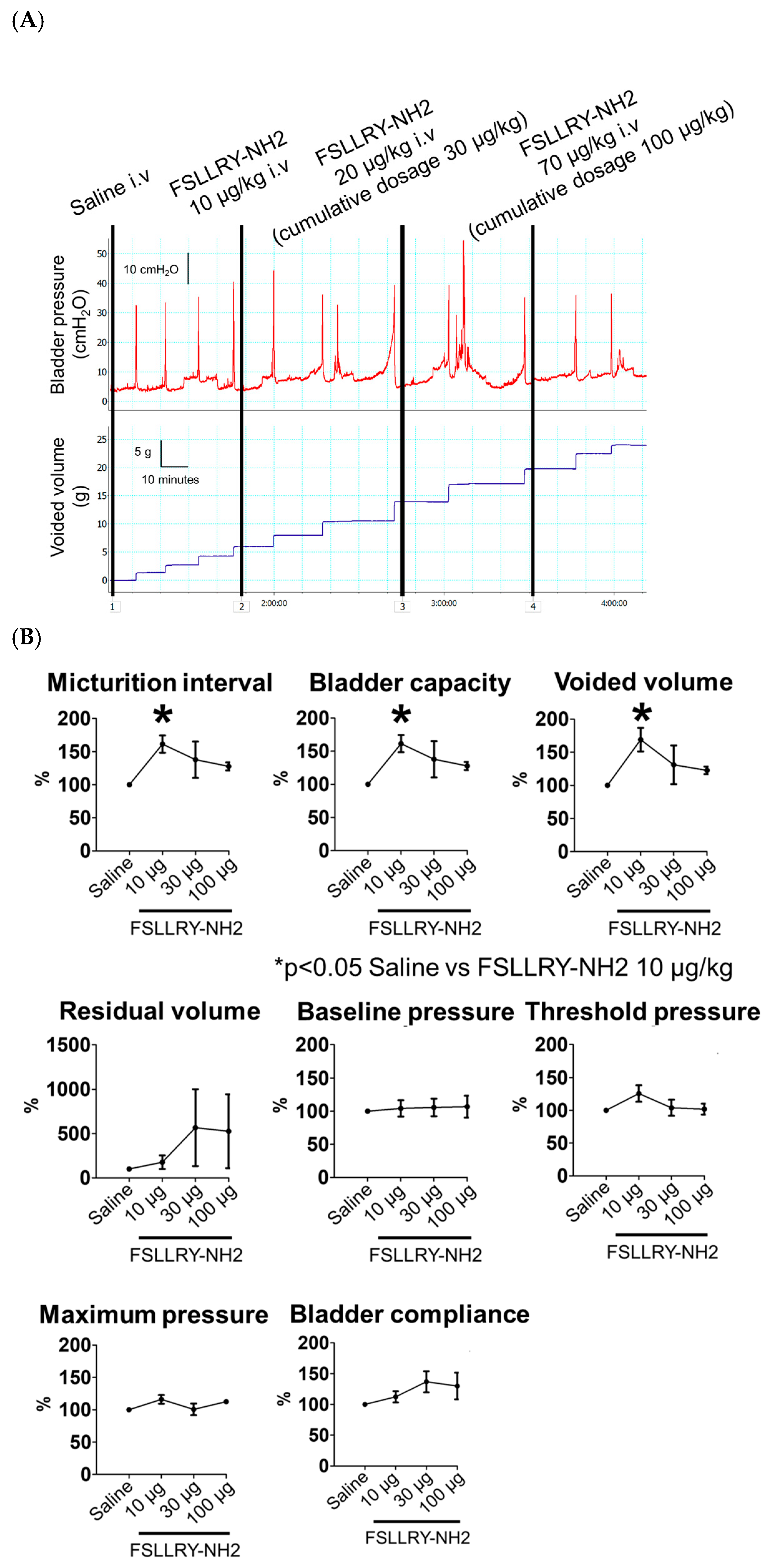
2.3. Effects of the PAR2 Antagonist on Bladder Function in CBI Rats
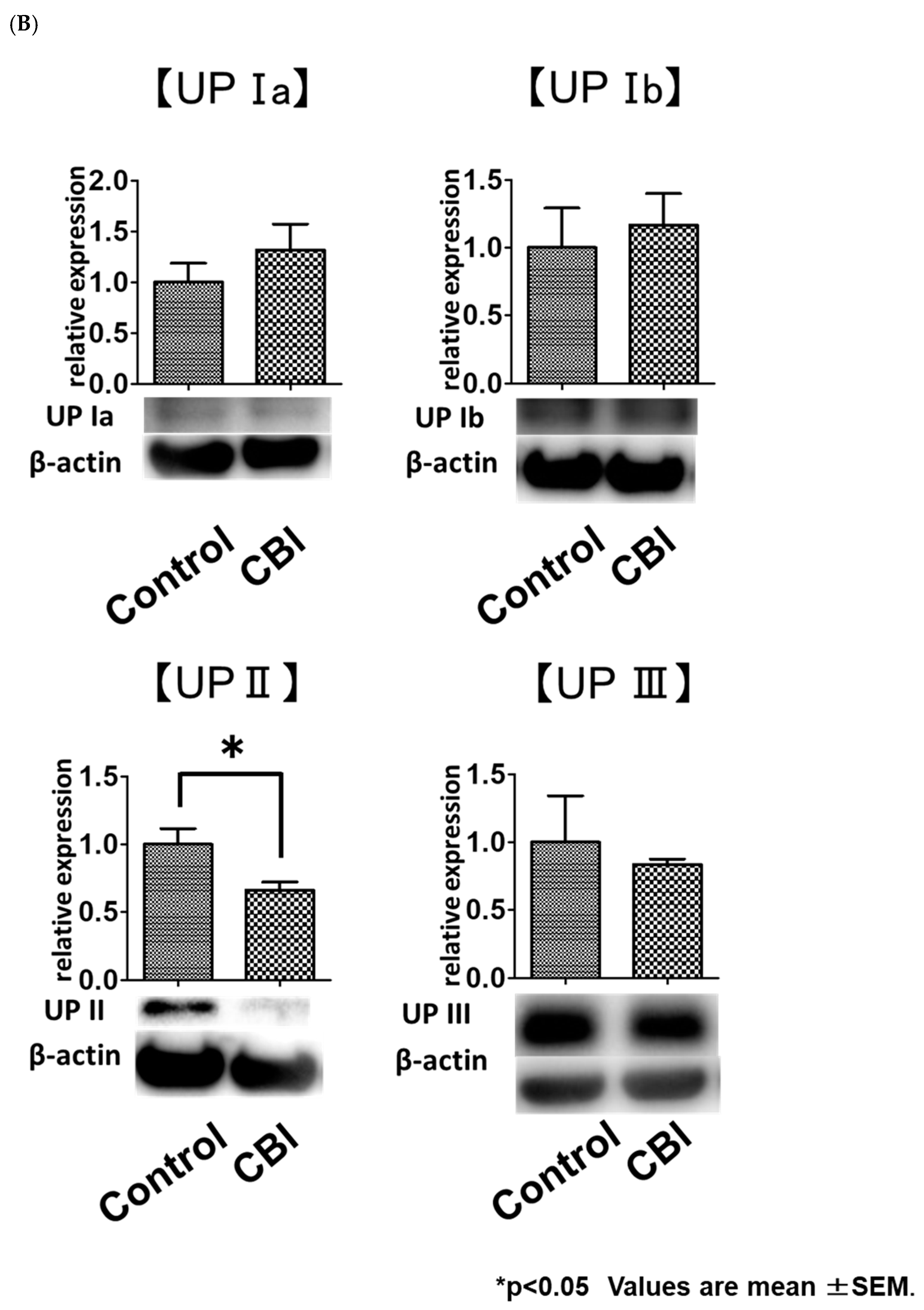
2.4. Reduced Uroplakin II Expression in the Bladder Urothelial Cells in CBI Rats
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design
4.2. Iliac Arterial Endothelial Injury
4.3. Metabolic Cage Studies
4.4. Histological Examination
4.5. Protein Extraction, SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
4.6. Cystometry in Conscious, Freely Moving Rats
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CBI | chronic bladder ischemia |
| DO | detrusor overactivity |
| LUTS | lower urinary tract symptom |
| LUTD | lower urinary tract dysfunction |
| MC | mast cell |
| MCT | mast cell tryptase |
| PAR2 | protease-activated receptor 2 |
References
- Irwin, D.E.; Milsom, I.; Hunskaar, S.; Reilly, K.; Kopp, Z.; Herschorn, S.; Coyne, K.; Kelleher, C.; Hampel, C.; Artibani, W.; et al. Population-based survey of urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, and other lower urinary tract symptoms in five countries: Results of the EPIC study. Eur. Urol. 2006, 50, 1306–1314, discussion 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapple, C.R.; Wein, A.J.; Abrams, P.; Dmochowski, R.R.; Giuliano, F.; Kaplan, S.A.; McVary, K.T.; Roehrborn, C.G. Lower urinary tract symptoms revisited: A broader clinical perspective. Eur. Urol. 2008, 54, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K.E. Storage and voiding symptoms: Pathophysiologic aspects. Urology 2003, 62, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, O.; Nomiya, M.; Andersson, K.E. Functional consequences of chronic bladder ischemia. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2014, 33, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponholzer, A.; Temml, C.; Wehrberger, C.; Marszalek, M.; Madersbacher, S. The association between vascular risk factors and lower urinary tract symptoms in both sexes. Eur. Urol. 2006, 50, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinggera, G.M.; Mitterberger, M.; Steiner, E.; Pallwein, L.; Frauscher, F.; Aigner, F.; Bartsch, G.; Strasser, H. Association of lower urinary tract symptoms and chronic ischaemia of the lower urinary tract in elderly women and men: Assessment using colour Doppler ultrasonography. BJU Int. 2008, 102, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, N.; Shishido, K.; Sato, Y.; Ogawa, S.; Oguro, T.; Kataoka, M.; Shiomi, H.; Uchida, H.; Haga, N.; Hosoi, T.; et al. The Association between Severity of Atherosclerosis and Lower Urinary Tract Function in Male Patients with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. Lower Urin. Tract Symptoms 2012, 4, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Gao, G.; Peterson, B.Z.; Ouyang, A. TRPA1 in mast cell activation-induced long-lasting mechanical hypersensitivity of vagal afferent C-fibers in guinea pig esophagus. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2009, 297, G34–G42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.T.; Shie, J.H.; Chen, S.H.; Wang, Y.S.; Kuo, H.C. Differences in mast cell infiltration, E-cadherin, and zonula occludens-1 expression between patients with overactive bladder and interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Urology 2012, 80, 225.e13–225.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.Z.; Ma, L.; Jun, C.; Guo, Y.X.; Yuan, H.Q. Changes in mast cell infiltration: A possible mechanism in detrusor overactivity induced by visceral hypersensitivity. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2016, 42, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dery, O.; Corvera, C.U.; Steinhoff, M.; Bunnett, N.W. Proteinase-activated receptors: Novel mechanisms of signaling by serine proteases. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 1998, 274, C1429–C1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, P.G.; Aston, D.; Sarkar, D.; Ahluwalia, A. Protease-activated receptor-2 activation causes EDHF-like coronary vasodilation: Selective preservation in ischemia/reperfusion injury: Involvement of lipoxygenase products, VR1 receptors, and C-fibers. Circ. Res. 2002, 90, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Diest, S.A.; Stanisor, O.I.; Boeckxstaens, G.E.; de Jonge, W.J.; van den Wijngaard, R.M. Relevance of mast cell-nerve interactions in intestinal nociception. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2012, 1822, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Ni, B.; Xi, Y.; Chu, X.; Zhang, R.; You, H. Protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR-2) antagonist AZ3451 as a novel therapeutic agent for osteoarthritis. Aging 2019, 11, 12532–12545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenac, N.; Garcia-Villar, R.; Ferrier, L.; Larauche, M.; Vergnolle, N.; Bunnett, N.W.; Coelho, A.M.; Fioramonti, J.; Bueno, L. Proteinase-activated receptor-2-induced colonic inflammation in mice: Possible involvement of afferent neurons, nitric oxide, and paracellular permeability. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 4296–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dattilio, A.; Vizzard, M.A. Up-regulation of protease activated receptors in bladder after cyclophosphamide induced cystitis and colocalization with capsaicin receptor (VR1) in bladder nerve fibers. J. Urol. 2005, 173, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetinel, S.; Canillioglu, Y.E.; Cikler, E.; Sener, G.; Ercan, F. Leukotriene D4 receptor antagonist montelukast alleviates protamine sulphate-induced changes in rat urinary bladder. BJU Int. 2011, 107, 1320–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, N.; Nishino, M.; Fujii, A.; Hashizume, K.; Nakamura, J.; Kondo, H.; Ohuchi, A.; Hase, T.; Murase, T. Perilla extract improves frequent urination in spontaneously hypertensive rats with enhancement of the urothelial presence and anti-inflammatory effects. Int. J. Urol. 2018, 25, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, P.; Meyers, S.; Liang, F.X.; Deng, F.M.; Kachar, B.; Zeidel, M.L.; Sun, T.T. Role of membrane proteins in permeability barrier function: Uroplakin ablation elevates urothelial permeability. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2002, 283, F1200–F1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, X.T.; Deng, F.M.; Hu, P.; Liang, F.X.; Zhou, G.; Auerbach, A.B.; Genieser, N.; Nelson, P.K.; Robbins, E.S.; Shapiro, E.; et al. Roles of uroplakins in plaque formation, umbrella cell enlargement, and urinary tract diseases. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 167, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.A. Everything you wanted to know about the bladder epithelium but were afraid to ask. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2000, 278, F867–F874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavelle, J.P.; Apodaca, G.; Meyers, S.A.; Ruiz, W.G.; Zeidel, M.L. Disruption of guinea pig urinary bladder permeability barrier in noninfectious cystitis. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 1998, 274, F205–F214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavelle, J.P.; Meyers, S.A.; Ruiz, W.G.; Buffington, C.A.; Zeidel, M.L.; Apodaca, G. Urothelial pathophysiological changes in feline interstitial cystitis: A human model. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2000, 278, F540–F553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, P.H.; Chun, S.Y.; Chung, J.W.; Kim, Y.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, J.N.; Ha, Y.S.; Yoo, E.S.; Kwon, T.G.; Kim, J.; et al. Comparison of 5 Different Rat Models to Establish a Standard Animal Model for Research Into Interstitial Cystitis. Int. Neurourol. J. 2017, 21, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nomiya, M.; Yamaguchi, O.; Andersson, K.E.; Sagawa, K.; Aikawa, K.; Shishido, K.; Yanagida, T.; Kushida, N.; Yazaki, J.; Takahashi, N. The effect of atherosclerosis-induced chronic bladder ischemia on bladder function in the rat. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2012, 31, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keith, I.M.; Jin, J.; Saban, R. Nerve-mast cell interaction in normal guinea pig urinary bladder. J. Comp. Neurol. 1995, 363, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrozkova, P.; Palecek, J.; Spicarova, D. The role of protease-activated receptor type 2 in nociceptive signaling and pain. Physiol. Res. 2016, 65, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanai, A.; Wyndaele, J.J.; Andersson, K.E.; Fry, C.; Ikeda, Y.; Zabbarova, I.; De Wachter, S. Researching bladder afferents-determining the effects of beta(3) -adrenergic receptor agonists and botulinum toxin type-A. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2011, 30, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baldi, E.; Bucherelli, C. The inverted “u-shaped” dose-effect relationships in learning and memory: Modulation of arousal and consolidation. Nonlinearity Biol. Toxicol. Med. 2005, 3, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuardi, A.W.; Rodrigues, N.P.; Silva, A.L.; Bernardo, S.A.; Hallak, J.E.C.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Crippa, J.A.S. Inverted U-Shaped Dose-Response Curve of the Anxiolytic Effect of Cannabidiol during Public Speaking in Real Life. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monte-Silva, K.; Kuo, M.F.; Thirugnanasambandam, N.; Liebetanz, D.; Paulus, W.; Nitsche, M.A. Dose-dependent inverted U-shaped effect of dopamine (D2-like) receptor activation on focal and nonfocal plasticity in humans. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 6124–6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Andrea, M.R.; Saban, M.R.; Nguyen, N.B.; Andrade-Gordon, P.; Saban, R. Expression of protease-activated receptor-1, -2, -3, and -4 in control and experimentally inflamed mouse bladder. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 907–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshimura, N.; Seki, S.; Chancellor, M.B.; de Groat, W.C.; Ueda, T. Targeting afferent hyperexcitability for therapy of the painful bladder syndrome. Urology 2002, 59, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamper, M.; Viereck, V.; Eberhard, J.; Binder, J.; Moll, C.; Welter, J.; Moser, R. Local immune response in bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis ESSIC type 3C. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2013, 24, 2049–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, S.D.; Liu, H.T.; Lin, H.; Kuo, H.C. Elevation of serum c-reactive protein in patients with OAB and IC/BPS implies chronic inflammation in the urinary bladder. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2011, 30, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboushwareb, T.; Zhou, G.; Deng, F.M.; Turner, C.; Andersson, K.E.; Tar, M.; Zhao, W.; Melman, A.; D’Agostino, R., Jr.; Sun, T.T.; et al. Alterations in bladder function associated with urothelial defects in uroplakin II and IIIa knockout mice. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2009, 28, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akaihata, H.; Hata, J.; Tanji, R.; Honda-Takinami, R.; Matsuoka, K.; Sato, Y.; Kataoka, M.; Ogawa, S.; Kojima, Y. Tetrahydrobiopterin prevents chronic ischemia-related lower urinary tract dysfunction through the maintenance of nitric oxide bioavailability. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaihata, H.; Nomiya, M.; Matsuoka, K.; Koguchi, T.; Hata, J.; Haga, N.; Kushida, N.; Ishibashi, K.; Aikawa, K.; Kojima, Y. Protective Effect of a Rho-kinase Inhibitor on Bladder Dysfunction in a Rat Model of Chronic Bladder Ischemia. Urology 2018, 111, 238.e7–238.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaihata, H.; Nomiya, M.; Hata, J.; Yabe, M.; Takahashi, N.; Haga, N.; Kushida, N.; Ishibashi, K.; Aikawa, K.; Yamaguchi, O.; et al. Pelvic arterial occlusive disease affects the RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway in bladder smooth muscle. J. Urol. 2015, 193, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Control (n = 10) | CBI (n = 10) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean void volume (mL) | 1.46 ± 0.33 | 1.01 ± 0.21 | p < 0.01 |
| Maximum void volume (mL) | 2.62 ± 0.60 | 2.01 ± 0.41 | p = 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akaihata, H.; Matsuoka, K.; Hata, J.; Harigane, Y.; Yaginuma, K.; Endo, Y.; Imai, H.; Matsuoka, Y.; Onagi, A.; Tanji, R.; et al. Involvement of Mast-Cell-Tryptase- and Protease-Activated Receptor 2—Mediated Signaling and Urothelial Barrier Dysfunction with Reduced Uroplakin II Expression in Bladder Hyperactivity Induced by Chronic Bladder Ischemia in the Rat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3982. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043982
Akaihata H, Matsuoka K, Hata J, Harigane Y, Yaginuma K, Endo Y, Imai H, Matsuoka Y, Onagi A, Tanji R, et al. Involvement of Mast-Cell-Tryptase- and Protease-Activated Receptor 2—Mediated Signaling and Urothelial Barrier Dysfunction with Reduced Uroplakin II Expression in Bladder Hyperactivity Induced by Chronic Bladder Ischemia in the Rat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(4):3982. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043982
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkaihata, Hidenori, Kanako Matsuoka, Junya Hata, Yuki Harigane, Kei Yaginuma, Yu Endo, Hitomi Imai, Yuta Matsuoka, Akifumi Onagi, Ryo Tanji, and et al. 2023. "Involvement of Mast-Cell-Tryptase- and Protease-Activated Receptor 2—Mediated Signaling and Urothelial Barrier Dysfunction with Reduced Uroplakin II Expression in Bladder Hyperactivity Induced by Chronic Bladder Ischemia in the Rat" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 4: 3982. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043982
APA StyleAkaihata, H., Matsuoka, K., Hata, J., Harigane, Y., Yaginuma, K., Endo, Y., Imai, H., Matsuoka, Y., Onagi, A., Tanji, R., Honda-Takinami, R., Hoshi, S., Koguchi, T., Sato, Y., Kataoka, M., Uemura, M., Igawa, Y., & Kojima, Y. (2023). Involvement of Mast-Cell-Tryptase- and Protease-Activated Receptor 2—Mediated Signaling and Urothelial Barrier Dysfunction with Reduced Uroplakin II Expression in Bladder Hyperactivity Induced by Chronic Bladder Ischemia in the Rat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(4), 3982. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043982






