Inherently Antimicrobial P(MMA-ran-DMAEMA) Copolymers Sensitive to Photodynamic Therapy: A Double Bactericidal Effect for Active Wound Dressing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
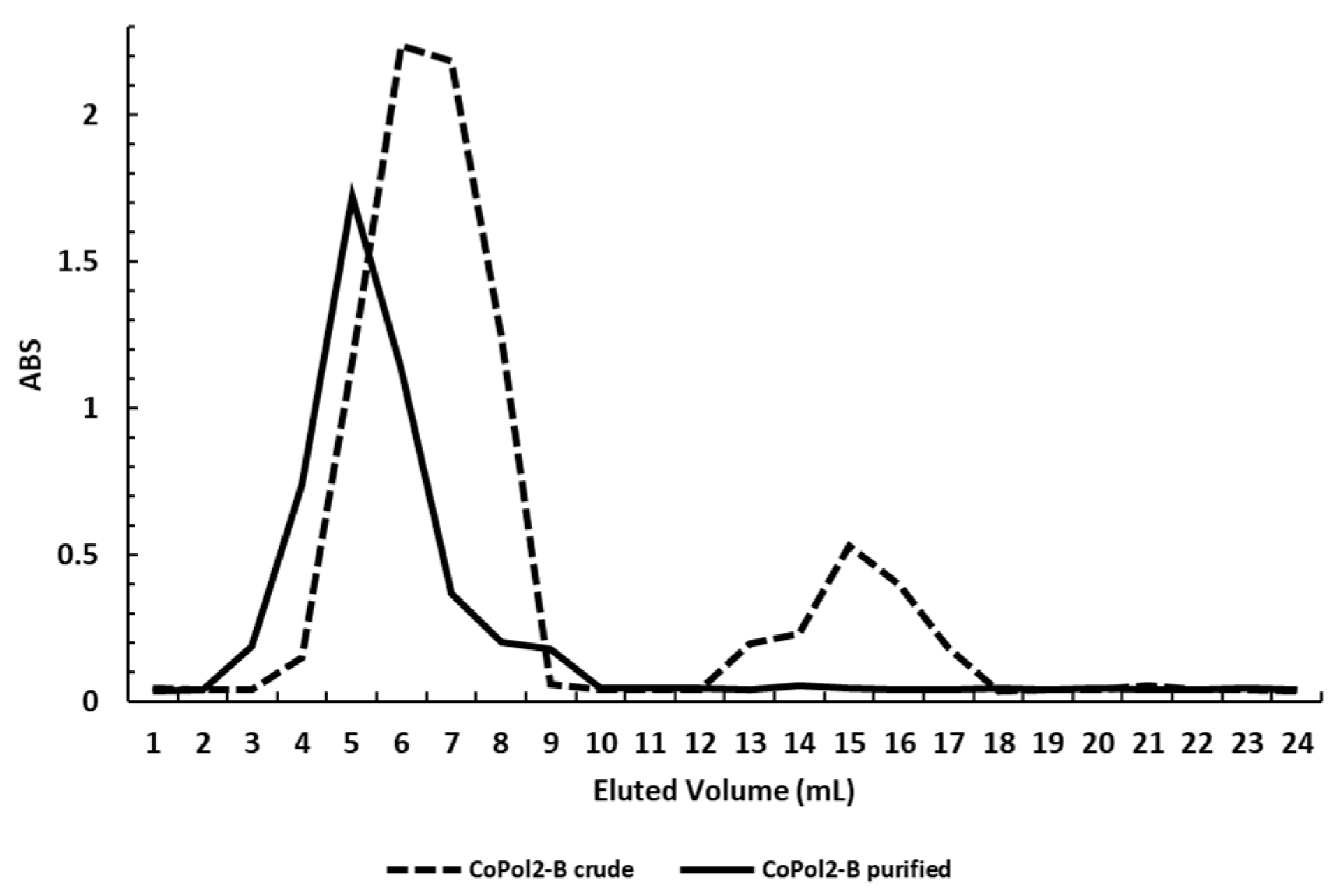
2.1. Synthesis of Copolymer Conjugated with Photosensitizers
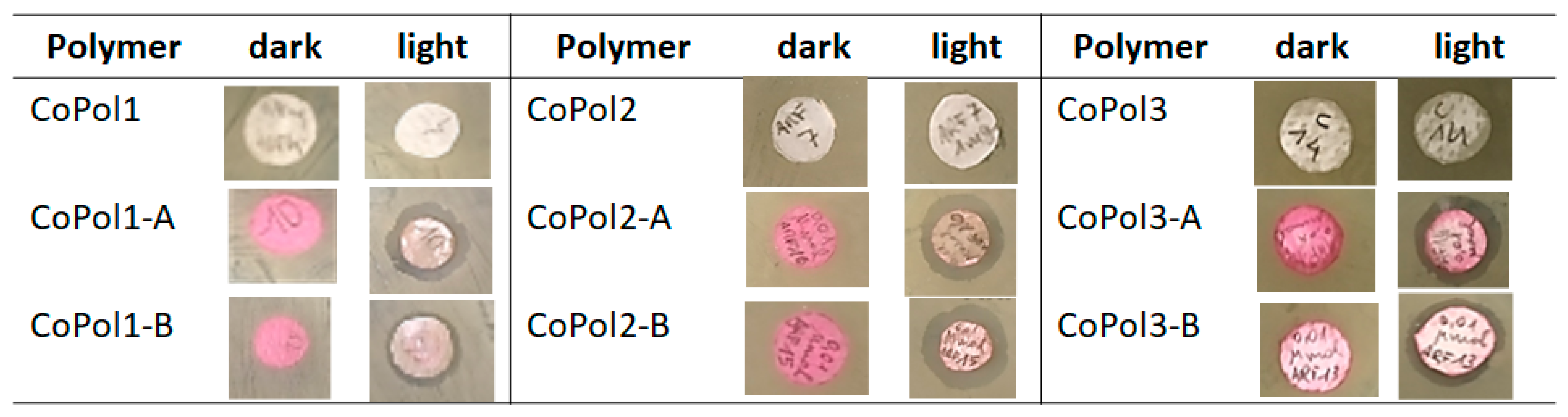
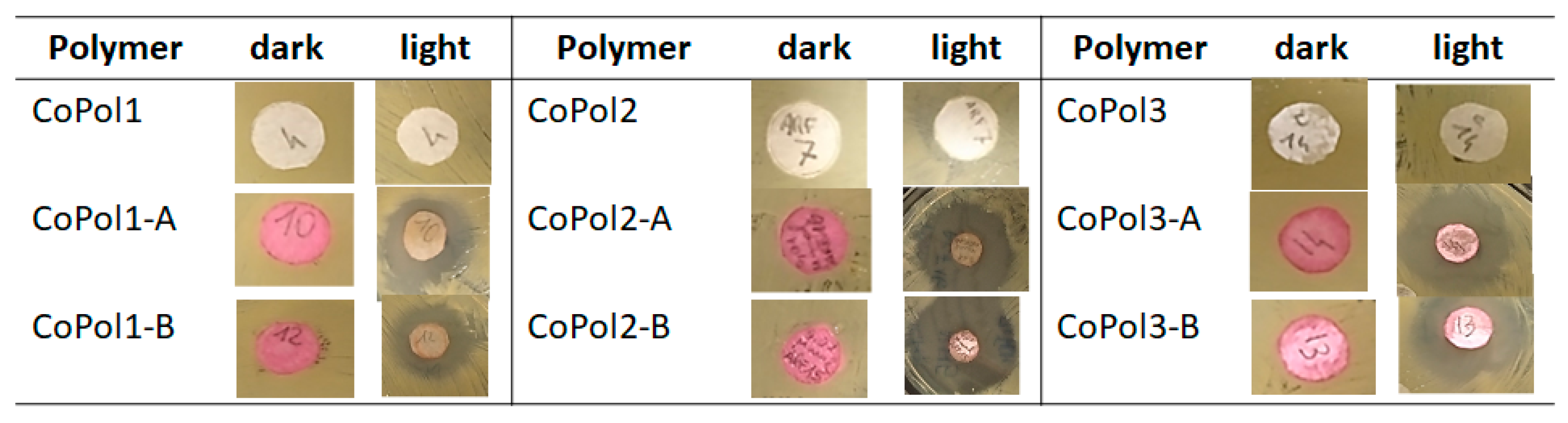
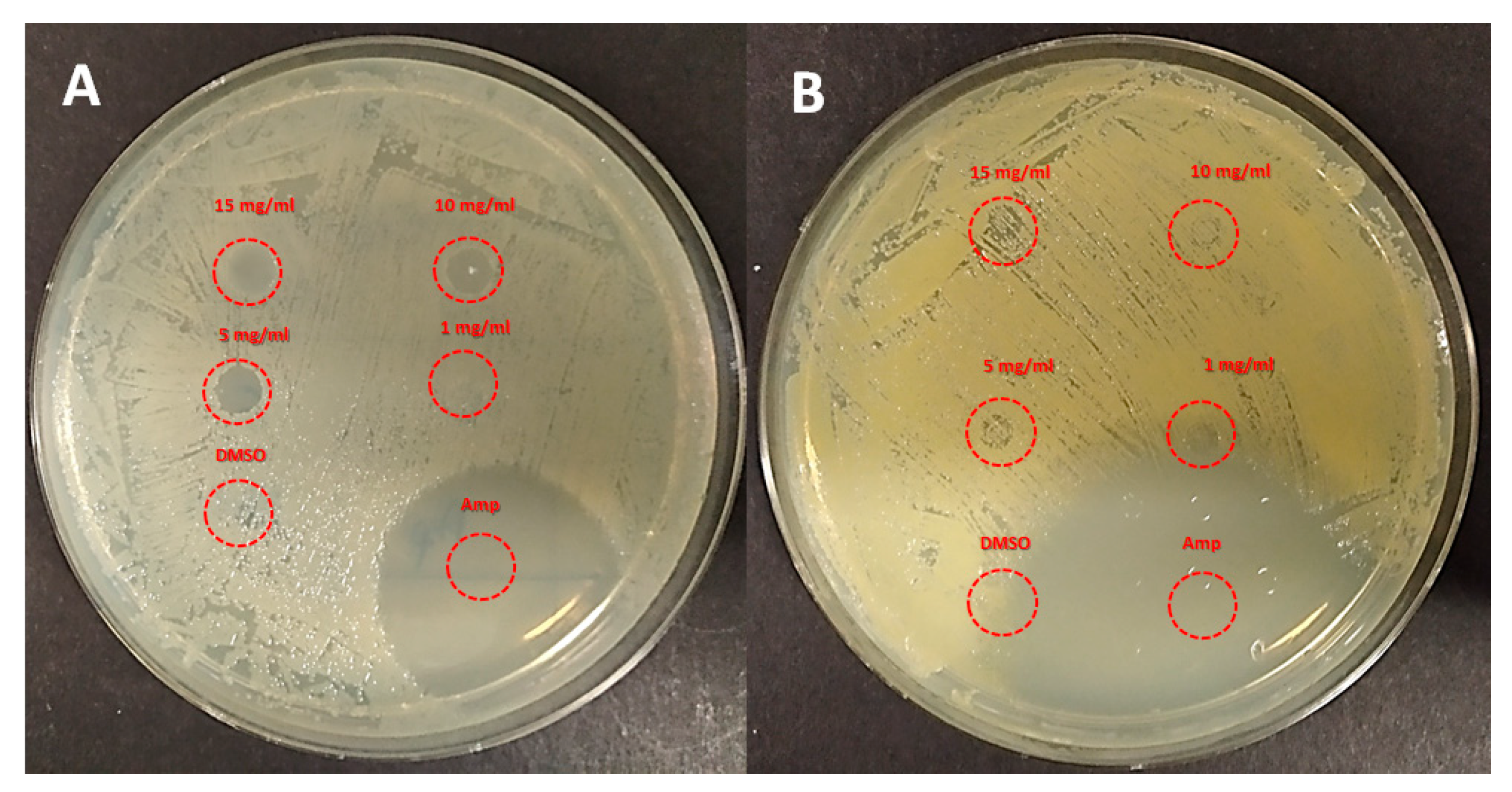
2.2. Antimicrobial Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of the BODIPYs
3.2. General Procedure for the Copolymerization of MMA and DMAEMA by ARGET-ATRP
χMMA = 1 − χDMAEMA
3.3. Binding of BODIPYs A and B to P(MMA-ran-DMAEMA) Copolymers
3.4. Preparation of Discs for Microbiological Assays
3.5. Antimicrobial Assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Note
- Templer, S.J.; Brito, M.O. Bacterial skin and soft tissue infections. Hospital Phys. 2009, 26, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Cardona, A.F.; Wilson, S.E. Skin and soft tissue infections: A critical review and the role of telavancin in their treatment. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, S69–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simoes, D.; Miguel, S.P.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Coutinho, P.; Mendoca, A.G.; Correia, I.J. Recent advances on antimicrobial wound dressing: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhivya, S.; Padma, V.V.; Santhini, E. Wound dressing—A review. BioMedicine 2015, 5, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigliotta, G.; Mella, M.; Rega, D.; Izzo, L. Modulating antimicrobial activity by synthesis: Dendritic copolymers based on nonquaternized 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate by Cu-mediated ATRP. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matrella, S.; Vitiello, C.; Mella, M.; Vigliotta, G.; Izzo, L. The Role of Charge Density and Hydrophobicity on the Biocidal Properties of Self-Protonable Polymeric Materials. Macromol. Biosci. 2015, 15, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliabue, A.; Izzo, L.; Mella, M. Out of Equilibrium Self-Assembly of Janus Nanoparticles: Steering It from Disordered Amorphous to 2D Patterned Aggregates. Langmuir 2016, 32, 12934–12946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mella, M.; Izzo, L. Structural properties of hydrophilic polymeric chains bearing covalently-linked hydrophobic substituents: Exploring the effects of chain length, fractional loading and hydrophobic interaction strength with coarse grained potentials and Monte Carlo simulations. Polymer 2010, 51, 3582–3589. [Google Scholar]
- Mella, M.; Tagliabue, A.; Mollica, L.; Izzo, L. Monte Carlo study of the effects of macroion charge distribution on the ionization and adsorption of weak polyelectrolytes and concurrent counterion release. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 560, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliabue, A.; Izzo, L.; Mella, M. Absorbed weak polyelectrolytes: Impact of confinement, topology, and chemically specific interactions on ionization, conformation free energy, counterion condensation, and absorption equilibrium. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2019, 57, 491–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mella, M.; Izzo, L. Modulation of ionization and structural properties of weak polyelectrolytes due to 1D, 2D, and 3D confinement. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2017, 55, 1088–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mella, M.; Mollica, L.; Izzo, L. Influence of charged intramolecular hydrogen bonds in weak polyelectrolytes: A Monte Carlo study of flexible and extendible polymeric chains in solution and near charged spheres. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2015, 53, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, M.; Vigliotta, G.; Soriente, A.; Capaccio, V.; Gorrasi, G.; Adami, R.; Reverchon, E.; Mella, M.; Izzo, L. “Leaching or not leaching”: An alternative approach to antimicrobial materials via copolymers containing crown ethers as active groups. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izzo, L.; Matrella, S.; Mella, M.; Benvenuto, G.; Vigliotta, G. Escherichia coli as a Model for the Description of the Antimicrobial Mechanism of a Cationic Polymer Surface: Cellular Target and Bacterial Contrast Response. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 15332–15343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarheed, O.; Ahmed, A.; Shouqair, D.; Boateng, J. Antimicrobial Dressings for Improving Wound Healing. In Wound Healing—New Insights into Ancient Challenges; Alexandrescu, V.A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; pp. 373–398. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, R. Photosensitized generation of singlet oxygen. Photochem. Photobiol. 2007, 82, 1161–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foote, C.S. Mechanisms of photosensitized oxidation. There are several different types of photosensitized oxidation which may be important in biological systems. Science 1968, 162, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeRosa, M.; Crutchley, R.J. Photosensitized singlet oxygen and its applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2002, 233–235, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, S.L.; Suleman, L.; Vuotto, C.; Donelli, G. Healthcare-Associated infections, medical devices and biofilms: Risk, tolerance and control. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yogo, T.; Urano, Y.; Ishitsuka, Y.; Maniwa, F.; Nagano, T. Highly Efficient and Photostable Photosensitizer Based on BODIPY Chromophore. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12162–12163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, M.E.; Durantini, J.E.; Reynoso, E.; Alvarez, M.G.; Milanesio, M.E.; Durantini, E.N. Porphyrin–Schiff Base Conjugates Bearing Basic Amino Groups as Antimicrobial Phototherapeutic Agents. Molecules 2021, 26, 5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, V.T.; Martegani, E.; Bolognese, F.; Caruso, E. Searching for antimicrobial photosensitizers among a panel of BODIPYs. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2022, 21, 1233–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintauer, T.; Matyjaszewski, K. Atom transfer radical addition and polymerization reactions catalyzed by ppm amounts of copper complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowski, W.; Matyjaszewski, K. Activators regenerated by electron transfer for atom-transfer radical polymerization of (meth)acrylates and related block copolymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 4482–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowski, W.; Min, K.; Matyjaszewski, K. Activators Regenerated by Electron Transfer for Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization of Styrene. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.; Gao, H.; Matyjaszewski, K. Use of Ascorbic Acid as Reducing Agent for Synthesis of Well-Defined Polymers by ARGET ATRP. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 1789–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, E.; Malacarne, M.C.; Marras, E.; Papa, E.; Bertato, L.; Banfi, S.; Gariboldi, M.B. New BODIPYs for photodynamic therapy (PDT): Synthesis and activity on human cancer cell lines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115737–115745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausen, M.; Ucuncu, M.; Bradley, M. Design of photosensitizing agents for targeter antimicrobial photodynamic therapy. Molecules 2020, 25, 5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The conjugation efficiency of compound B, bearing the longer alkyl side-chain, was slightly higher than that of A. This was ascribed to the reduction of steric encumbence around the nitrogen atoms. Nevertheless, such trend was reverted for samples CoPol3-A and CoPol3-B. Unfortunately, it was not possible to find a rationale for this anomaly.
- Villani, S.; Adami, R.; Reverchon, E.; Ferretti, A.M.; Ponti, A.; Lepretti, M.; Caputo, I.; Izzo, L. pH-sensitive polymersomes: Controlling swelling via copolymer structure and chemical composition. J. Drug. Targ. 2017, 25, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagami, R.; Sortino, G.; Caruso, E.; Malacarne, M.C.; Banfi, S.; Patane, S.; Monsu Scolaro, L.; Mazzaglia, A. Tailored-BODIPY/amphiphilic cyclodextrin nanoassemblies with PDT effectiveness. Langmuir 2018, 34, 8639–8651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Entry | Sample ID | χDMAEMAfeed | χDMAEMA a | Tg b (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CoPol1 | 0.50 | 0.51 | 72 |
| 2 | CoPol2 | 0.33 | 0.43 | 65 |
| 3 | CoPol3 | 0.25 | 0.29 | 90 |
| Entry | Sample ID | BODIPY | χDMAEMA (%) | %BODIPY (mgBODIPY/mgcopolymer) | molBODIPY/gcopolymer | Tg (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CoPol1-A | A | 51 | 1.02 | 1.40 × 10−5 | 75 |
| 2 | CoPol1-B | B | 1.25 | 1.59 × 10−5 | 80 | |
| 3 | CoPol2-A | A | 43 | 0.70 | 9.57 × 10−6 | 83 |
| 4 | CoPol2-B | B | 0.75 | 9.40 × 10−6 | 84 | |
| 5 | CoPol3-A | A | 29 | 1.23 | 1.58 × 10−5 | 100 |
| 6 | CoPol3-B | B | 0.51 | 6.34 × 10−6 | 93 |
| Entry | Sample ID | MCoPol (μg) | nBODIPY (μmol) | MG1655 Zone of Inhibition (mm) | Average (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Replicates | |||||||
| I | II | III | |||||
| 1 | CoPol1-A | 712 | 0.01 | 15.0 | 13.4 | 18.9 | 15.77 ± 2.83 |
| 2 | CoPol1-B | 630 | 0.01 | 11.9 | 13.1 | 15.3 | 13.43 ± 1.72 |
| 3 | CoPol2-A | 1040 | 0.01 | 16.5 | 15.8 | 15.4 | 15.90 ± 0.56 |
| 4 | CoPol2-B | 1060 | 0.01 | 16.0 | 16.8 | 16.8 | 16.53 ± 0.46 |
| 5 | CoPol3-A | 630 | 0.01 | 15.6 | 14.0 | 11.7 | 13.77 ± 1.96 |
| 6 | CoPol3-B | 1570 | 0.01 | 13.2 | 15.7 | 13.7 | 14.20 ± 1.32 |
| Entry | Sample ID | MCoPol (μg) | nBODIPY (μmol) | MSSA Zone of Inhibition (mm) | Average (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Replicates | |||||||
| I | II | III | |||||
| 1 | CoPol1-A | 712 | 0.01 | 25.7 | 19.5 | 30.0 | 25.07 ± 5.28 |
| 2 | CoPol1-B | 630 | 0.01 | 21.8 | 26.8 | 26.4 | 25.00 ± 2.78 |
| 3 | CoPol2-A | 1040 | 0.01 | 32.9 | 22.9 | 30.3 | 28.60 ± 5.14 |
| 4 | CoPol2-B | 1060 | 0.01 | 40.2 | 26.7 | 31.6 | 32.83 ± 6.83 |
| 5 | CoPol3-A | 630 | 0.01 | 27.1 | 23.4 | 19.0 | 23.17 ± 4.06 |
| 6 | CoPol3-B | 1570 | 0.01 | 24.5 | 23.4 | 22.0 | 23.30 ± 1.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santoro, O.; Malacarne, M.C.; Sarcone, F.; Scapinello, L.; Pragliola, S.; Caruso, E.; Orlandi, V.T.; Izzo, L. Inherently Antimicrobial P(MMA-ran-DMAEMA) Copolymers Sensitive to Photodynamic Therapy: A Double Bactericidal Effect for Active Wound Dressing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054340
Santoro O, Malacarne MC, Sarcone F, Scapinello L, Pragliola S, Caruso E, Orlandi VT, Izzo L. Inherently Antimicrobial P(MMA-ran-DMAEMA) Copolymers Sensitive to Photodynamic Therapy: A Double Bactericidal Effect for Active Wound Dressing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(5):4340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054340
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantoro, Orlando, Miryam Chiara Malacarne, Francesco Sarcone, Luca Scapinello, Stefania Pragliola, Enrico Caruso, Viviana Teresa Orlandi, and Lorella Izzo. 2023. "Inherently Antimicrobial P(MMA-ran-DMAEMA) Copolymers Sensitive to Photodynamic Therapy: A Double Bactericidal Effect for Active Wound Dressing" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 5: 4340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054340
APA StyleSantoro, O., Malacarne, M. C., Sarcone, F., Scapinello, L., Pragliola, S., Caruso, E., Orlandi, V. T., & Izzo, L. (2023). Inherently Antimicrobial P(MMA-ran-DMAEMA) Copolymers Sensitive to Photodynamic Therapy: A Double Bactericidal Effect for Active Wound Dressing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(5), 4340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054340








