Peripheral and Central Iron Measures in Alcohol Use Disorder and Aging: A Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Higher Serum Ferritin Level and Concentration in Individuals with AUD Than Controls
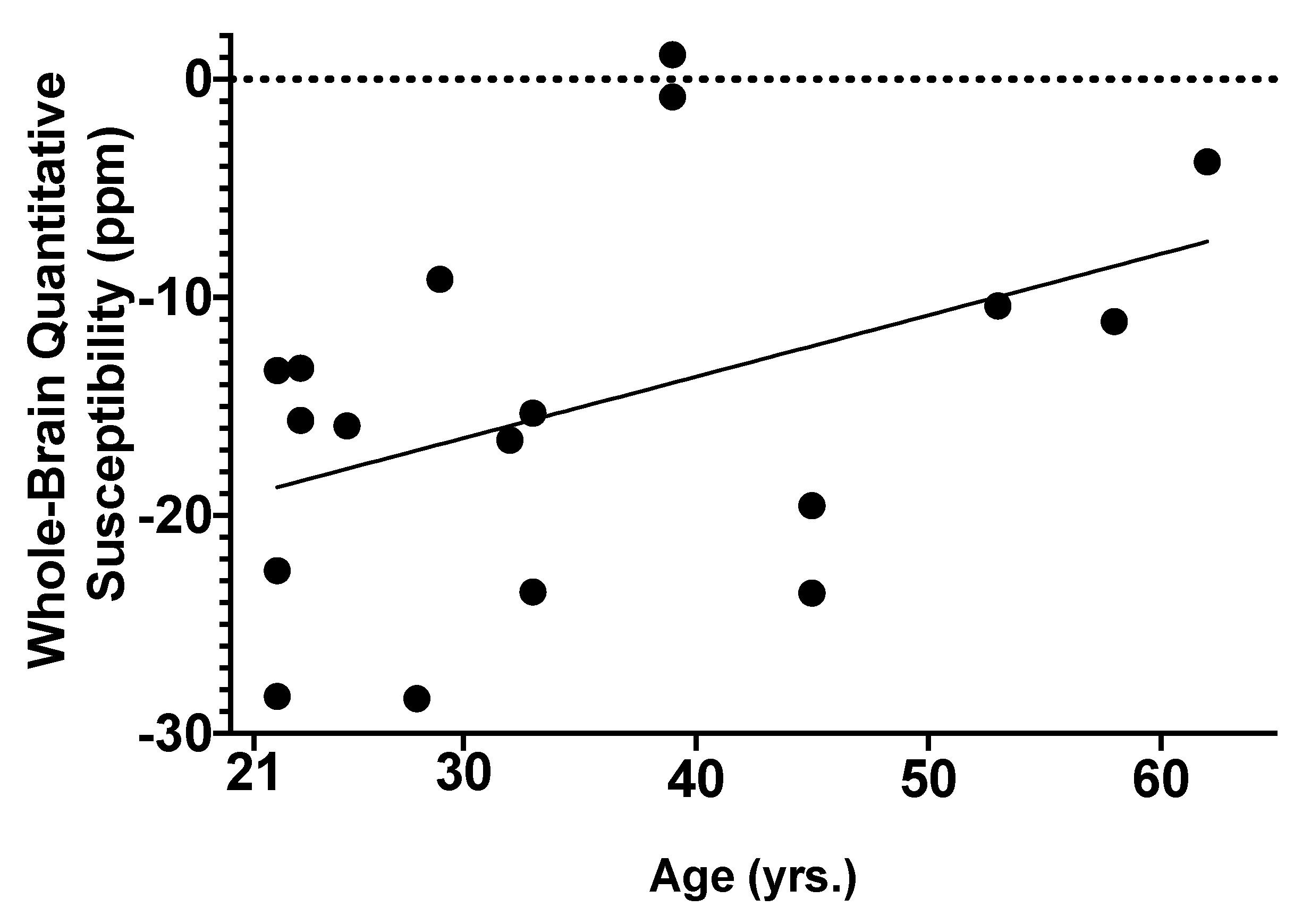
2.2. Associations of AUD and Age with Global Brain Iron Susceptibility
2.3. Whole-Brain Voxel-Wise QSM Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Participants
4.1.1. NIH Sample
4.1.2. Penn Sample
4.2. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM)
4.3. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mills, E.; Dong, X.P.; Wang, F.; Xu, H. Mechanisms of brain iron transport: Insight into neurodegeneration and CNS disorders. Future Med. Chem. 2010, 2, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moos, T.; Rosengren Nielsen, T.; Skjørringe, T.; Morgan, E.H. Iron trafficking inside the brain. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 1730–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M. Oxygen free radicals and iron in relation to biology and medicine: Some problems and concepts. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1986, 246, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masaldan, S.; Belaidi, A.A.; Ayton, S.; Bush, A.I. Cellular Senescence and Iron Dyshomeostasis in Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, G.; Berk, M.; Carvalho, A.F.; Maes, M.; Walker, A.J.; Puri, B.K. Why should neuroscientists worry about iron? The emerging role of ferroptosis in the pathophysiology of neuroprogressive diseases. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 341, 154–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhás, M.; Sun, H.; Brown, M.R.G.; MacKay, M.B.; Mann, K.F.; Sommer, W.H.; Wilman, A.H.; Dursun, S.M.; Greenshaw, A.J. Deep grey matter iron accumulation in alcohol use disorder. NeuroImage 2017, 148, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, D.S.; McPherson, K.L.; Manza, P.; Schwandt, M.L.; Shen, P.H.; Goldman, D.; Diazgranados, N.; Wang, G.J.; Wiers, C.E.; Volkow, N.D. Elevated transferrin saturation in individuals with alcohol use disorder: Association with HFE polymorphism and alcohol withdrawal severity. Addict. Biol. 2022, 27, e13144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moirand, R.; Lescoat, G.; Delamaire, D.; Lauvin, L.; Campion, J.P.; Deugnier, Y.; Brissot, P. Increase in glycosylated and nonglycosylated serum ferritin in chronic alcoholism and their evolution during alcohol withdrawal. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1991, 15, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, W.; Tong, K.A.; Yeom, K.W.; Kuzminski, S. Susceptibility-weighted imaging and quantitative susceptibility mapping in the brain. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 42, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langkammer, C.; Schweser, F.; Krebs, N.; Deistung, A.; Goessler, W.; Scheurer, E.; Sommer, K.; Reishofer, G.; Yen, K.; Fazekas, F.; et al. Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) as a means to measure brain iron? A post mortem validation study. NeuroImage 2012, 62, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Rochefort, L.; Liu, T.; Kressler, B.; Liu, J.; Spincemaille, P.; Lebon, V.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y. Quantitative susceptibility map reconstruction from MR phase data using bayesian regularization: Validation and application to brain imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 63, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Araiz, A.; Porcu, F.; Pérez-Hernández, M.; García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Aracil-Fernández, M.A.; Gutierrez-López, M.D.; Guerri, C.; Manzanares, J.; O’Shea, E.; Colado, M.I. Disruption of blood-brain barrier integrity in postmortem alcoholic brain: Preclinical evidence of TLR4 involvement from a binge-like drinking model. Addict. Biol. 2017, 22, 1103–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, H.; Tan, G.C.; Ibrahim, S.F.; Shaikh, M.F.; Mohamed, I.N.; Mohamed, R.M.P.; Hamid, A.A.; Ugusman, A.; Kumar, J. Alcohol Use Disorder, Neurodegeneration, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease: Interplay Between Oxidative Stress, Neuroimmune Response and Excitotoxicity. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartzokis, G.; Tishler, T.A.; Shin, I.S.; Lu, P.H.; Cummings, J.L. Brain ferritin iron as a risk factor for age at onset in neurodegenerative diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1012, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, R.J.; Zucca, F.A.; Duyn, J.H.; Crichton, R.R.; Zecca, L. The role of iron in brain ageing and neurodegenerative disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cogswell, P.M.; Wiste, H.J.; Senjem, M.L.; Gunter, J.L.; Weigand, S.D.; Schwarz, C.G.; Arani, A.; Therneau, T.M.; Lowe, V.J.; Knopman, D.S.; et al. Associations of quantitative susceptibility mapping with Alzheimer’s disease clinical and imaging markers. NeuroImage 2021, 224, 117433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariou, V.; Bauer, C.E.; Seago, E.R.; Panayiotou, G.; Hall, E.D.; Butterfield, D.A.; Gold, B.T. Healthy dietary intake moderates the effects of age on brain iron concentration and working memory performance. Neurobiol. Aging 2021, 106, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallgren, B.; Sourander, P. The effect of age on the non-haemin iron in the human brain. J. Neurochem. 1958, 3, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgic, B.; Pfefferbaum, A.; Rohlfing, T.; Sullivan, E.V.; Adalsteinsson, E. MRI estimates of brain iron concentration in normal aging using quantitative susceptibility mapping. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 2625–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Betts, M.J.; Acosta-Cabronero, J.; Cardenas-Blanco, A.; Nestor, P.J.; Düzel, E. High-resolution characterisation of the aging brain using simultaneous quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) and R2* measurements at 7T. NeuroImage 2016, 138, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Shen, B.; Shen, W.Q.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Y.F.; Fei, J.J. Dysfunction of the Glymphatic System Might Be Related to Iron Deposition in the Normal Aging Brain. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 559603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topiwala, A.; Wang, C.; Ebmeier, K.P.; Burgess, S.; Bell, S.; Levey, D.F.; Zhou, H.; McCracken, C.; Roca-Fernández, A.; Petersen, S.E.; et al. Associations between moderate alcohol consumption, brain iron, and cognition in UK Biobank participants: Observational and mendelian randomization analyses. PLoS Med. 2022, 19, e1004039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fede, S.J.; Abrahao, K.P.; Cortes, C.R.; Grodin, E.N.; Schwandt, M.L.; George, D.T.; Diazgranados, N.; Ramchandani, V.A.; Lovinger, D.M.; Momenan, R. Alcohol effects on globus pallidus connectivity: Role of impulsivity and binge drinking. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0224906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, S.H.; Hong, H.G.; Jeon, S.-M. Personality and alcohol use: The role of impulsivity. Addict. Behav. 2012, 37, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Casal, M.N.; Pasricha, S.R.; Martinez, R.X.; Lopez-Perez, L.; Peña-Rosas, J.P. Serum or plasma ferritin concentration as an index of iron deficiency and overload. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 5, Cd011817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dignass, A.; Farrag, K.; Stein, J. Limitations of Serum Ferritin in Diagnosing Iron Deficiency in Inflammatory Conditions. Int. J. Chronic Dis. 2018, 2018, 9394060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Casal, M.N.; Pasricha, S.R.; Martinez, R.X.; Lopez-Perez, L.; Peña-Rosas, J.P. Are Current Serum and Plasma Ferritin Cut-offs for Iron Deficiency and Overload Accurate and Reflecting Iron Status? A Systematic Review. Arch. Med. Res. 2018, 49, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.; Jensen, L.N.; Krabbe, K. Hereditary haemochromatosis: A case of iron accumulation in the basal ganglia associated with a parkinsonian syndrome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1995, 59, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ersche, K.D.; Acosta-Cabronero, J.; Jones, P.S.; Ziauddeen, H.; van Swelm, R.P.; Laarakkers, C.M.; Raha-Chowdhury, R.; Williams, G.B. Disrupted iron regulation in the brain and periphery in cocaine addiction. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, D.; Ding, J.; Liu, J.Y.; He, Y.F.; Dai, Z.; Chen, C.Z.; Cheng, W.Z.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X. Decreased serum hepcidin concentration correlates with brain iron deposition in patients with HBV-related cirrhosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, W.; Monnot, A.D. Regulation of brain iron and copper homeostasis by brain barrier systems: Implication in neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 133, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, Z.M.; Shen, X. Brain iron transport and neurodegeneration. Trends Mol. Med. 2001, 7, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sethi, S.K.; Zhang, C.; Miao, Y.; Yerramsetty, K.K.; Palutla, V.K.; Gharabaghi, S.; Wang, C.; He, N.; Cheng, J.; et al. Iron Content in Deep Gray Matter as a Function of Age Using Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping: A Multicenter Study. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 607705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecca, L.; Youdim, M.B.H.; Riederer, P.; Connor, J.R.; Crichton, R.R. Iron, brain ageing and neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banker, L.; Tadi, P. Neuroanatomy, Precentral Gyrus. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tennant, V.R.; Harrison, T.M.; Adams, J.N.; La Joie, R.; Winer, J.R.; Jagust, W.J. Fusiform Gyrus Phospho-Tau is Associated with Failure of Proper Name Retrieval in Aging. Ann. Neurol. 2021, 90, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadery, C.; Pirpamer, L.; Hofer, E.; Langkammer, C.; Petrovic, K.; Loitfelder, M.; Schwingenschuh, P.; Seiler, S.; Duering, M.; Jouvent, E.; et al. R2* mapping for brain iron: Associations with cognition in normal aging. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penke, L.; Valdés Hernandéz, M.C.; Maniega, S.M.; Gow, A.J.; Murray, C.; Starr, J.M.; Bastin, M.E.; Deary, I.J.; Wardlaw, J.M. Brain iron deposits are associated with general cognitive ability and cognitive aging. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 510–517.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta-Cabronero, J.; Betts, M.J.; Cardenas-Blanco, A.; Yang, S.; Nestor, P.J. In Vivo MRI Mapping of Brain Iron Deposition across the Adult Lifespan. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5™, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013; p. xliv, 947. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, P.; Santos, A.; Pinto, N.R.; Mendes, R.; Magalhães, T.; Almeida, A. Iron levels in the human brain: A post-mortem study of anatomical region differences and age-related changes. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2014, 28, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubić Kezele, T.; Ćurko-Cofek, B. Age-Related Changes and Sex-Related Differences in Brain Iron Metabolism. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latour, C.; Kautz, L.; Besson-Fournier, C.; Island, M.L.; Canonne-Hergaux, F.; Loréal, O.; Ganz, T.; Coppin, H.; Roth, M.P. Testosterone perturbs systemic iron balance through activation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in the liver and repression of hepcidin. Hepatology 2014, 59, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tishler, T.A.; Raven, E.P.; Lu, P.H.; Altshuler, L.L.; Bartzokis, G. Premenopausal hysterectomy is associated with increased brain ferritin iron. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barton, J.C.; Edwards, C.Q.; Acton, R.T. HFE gene: Structure, function, mutations, and associated iron abnormalities. Gene 2015, 574, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalpouzos, G.; Mangialasche, F.; Falahati, F.; Laukka, E.J.; Papenberg, G. Contributions of HFE polymorphisms to brain and blood iron load, and their links to cognitive and motor function in healthy adults. Neuropsychopharmacol. Rep. 2021, 41, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brissot, P.; Pietrangelo, A.; Adams, P.C.; de Graaff, B.; McLaren, C.E.; Loréal, O. Haemochromatosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 18016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ellor, S.; Sun, J.M.; Liu, C.; Kurtzburg, J.; Song, A.W. DTI Tract-Based Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping: An Initial Feasibility Study to Investigate the Potential Role of Myelination in Brain Connectivity Change in Cerebral Palsy Patients During Autologous Cord Blood Cell Therapy Using a Rotationally-Invariant Quantitative Measure. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 53, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeynes, K.D.; Gibson, E.L. The importance of nutrition in aiding recovery from substance use disorders: A review. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017, 179, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spence, H.; McNeil, C.J.; Waiter, G.D. The impact of brain iron accumulation on cognition: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, G.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Rivero, M.; Pérez-Brocal, V.; Garre-Olmo, J.; Puig, J.; Daunis, I.E.P.; Biarnés, C.; Gich, J.; Fernández-Aranda, F.; et al. The Gut Metagenome Changes in Parallel to Waist Circumference, Brain Iron Deposition, and Cognitive Function. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 2962–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, J.T.; Sykora, K.; Schneiderman, J.; Naranjo, C.A.; Sellers, E.M. Assessment of alcohol withdrawal: The revised clinical institute withdrawal assessment for alcohol scale (CIWA-Ar). Br. J. Addict. 1989, 84, 1353–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobell, L.C.; Sobell, M.B. Timeline follow-back: A technique for assessing self-reported alcohol consumption. In Measuring Alcohol Consumption: Psychosocial and Biochemical Methods; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 1992; pp. 41–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, H.A.; Sheu, W.J. Reliability of alcohol use indices. The Lifetime Drinking History and the MAST. J. Stud. Alcohol 1982, 43, 1157–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, J.B.; Aasland, O.G.; Babor, T.F.; de la Fuente, J.R.; Grant, M. Development of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT): WHO Collaborative Project on Early Detection of Persons with Harmful Alcohol Consumption-II. Addiction 1993, 88, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heatherton, T.F.; Kozlowski, L.T.; Frecker, R.C.; Fagerström, K.O. The Fagerström Test for Nicotine Dependence: A revision of the Fagerström Tolerance Questionnaire. Br. J. Addict. 1991, 86, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachary, R.A.; Paulson, M.J.; Gorsuch, R.L. Estimating WAIS IQ from the Shipley Institute of Living Scale using continuously adjusted age norms. J. Clin. Psychol. 1985, 41, 820–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, T. Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM): Decoding MRI data for a tissue magnetic biomarker. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Spincemaille, P.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. MEDI+0: Morphology enabled dipole inversion with automatic uniform cerebrospinal fluid zero reference for quantitative susceptibility mapping. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 2795–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | AUD (n = 10) | HC (n = 8) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 37.30 (15.72) | 32.50 (8.30) | p = 0.42 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.51 (4.99) | 22.69 (2.59) | p = 0.025 |
| Education, years | 15.00 (2.11) | 16.75 (1.49) | p = 0.065 |
| Shipley Standard IQ score | 109.10 (13.71) | 117.63 (12.09) | p = 0.19 |
| Sex | p = 0.39 | ||
| Female | 3 | 4 | |
| Male | 7 | 4 | |
| Self-reported race | p = 0.91 | ||
| Black/African American | 4 | 3 | |
| White | 6 | 5 | |
| Smoking status | p = 0.090 | ||
| Smoker | 3 | 0 | |
| Non-smoker | 7 | 8 | |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.79 (0.21) | 4.70 (0.27) | p = 0.44 |
| Drinks per week | 25.12 (8.65) | 0.52 (0.70) | p < 0.001 |
| Age of first drink, years | 14.60 (2.63) | 18.00 (2.58) | p = 0.019 |
| Total lifetime drinks (g) (14 g per drink) | 190,596.00 (332,232.50) | 8,557.50 (10,546.07) | p < 0.001 |
| AUDIT score | 14.80 (6.11) | 1.75 (1.04) | p < 0.001 |
| Global Brain Susceptibility (Penn) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | B | SE B | β |
| AUD | −3.55 | 4.58 | −0.212 |
| Age (years) | 0.411 | 0.146 | 0.618 ** |
| BMI | −0.627 | 0.442 | −0.344 |
| Sex | −8.375 | 3.789 | −0.491 * |
| Ferritin (μg/L) | 0.047 | 0.035 | 0.357 |
| R2 | 0.354 | ||
| F | 2.861 ^ | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adams, A.R.; Li, X.; Byanyima, J.I.; Vesslee, S.A.; Nguyen, T.D.; Wang, Y.; Moon, B.; Pond, T.; Kranzler, H.R.; Witschey, W.R.; et al. Peripheral and Central Iron Measures in Alcohol Use Disorder and Aging: A Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054461
Adams AR, Li X, Byanyima JI, Vesslee SA, Nguyen TD, Wang Y, Moon B, Pond T, Kranzler HR, Witschey WR, et al. Peripheral and Central Iron Measures in Alcohol Use Disorder and Aging: A Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping Pilot Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(5):4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054461
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdams, Aiden R., Xinyi Li, Juliana I. Byanyima, Sianneh A. Vesslee, Thanh D. Nguyen, Yi Wang, Brianna Moon, Timothy Pond, Henry R. Kranzler, Walter R. Witschey, and et al. 2023. "Peripheral and Central Iron Measures in Alcohol Use Disorder and Aging: A Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping Pilot Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 5: 4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054461
APA StyleAdams, A. R., Li, X., Byanyima, J. I., Vesslee, S. A., Nguyen, T. D., Wang, Y., Moon, B., Pond, T., Kranzler, H. R., Witschey, W. R., Shi, Z., & Wiers, C. E. (2023). Peripheral and Central Iron Measures in Alcohol Use Disorder and Aging: A Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping Pilot Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(5), 4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054461






