MKP-1 Deficiency Exacerbates Skin Fibrosis in a Mouse Model of Scleroderma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Bleomycin-Induced Dermal Fibrosis Is Enhanced in MKP-1-Deficient Mice
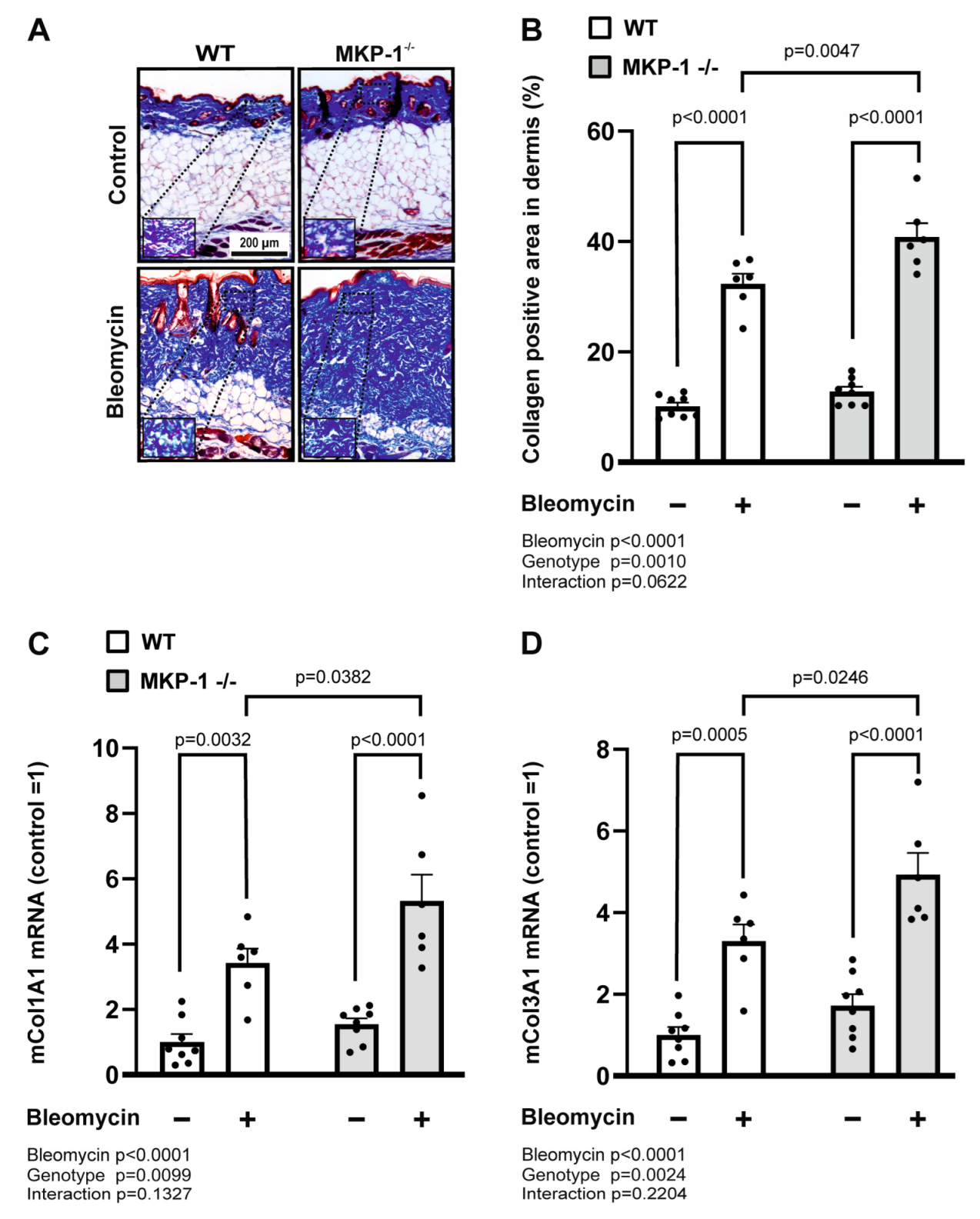
2.2. Collagen Deposition and Expression Is Increased in Bleomycin-Treated Skin from MKP-1-Deficient Mice
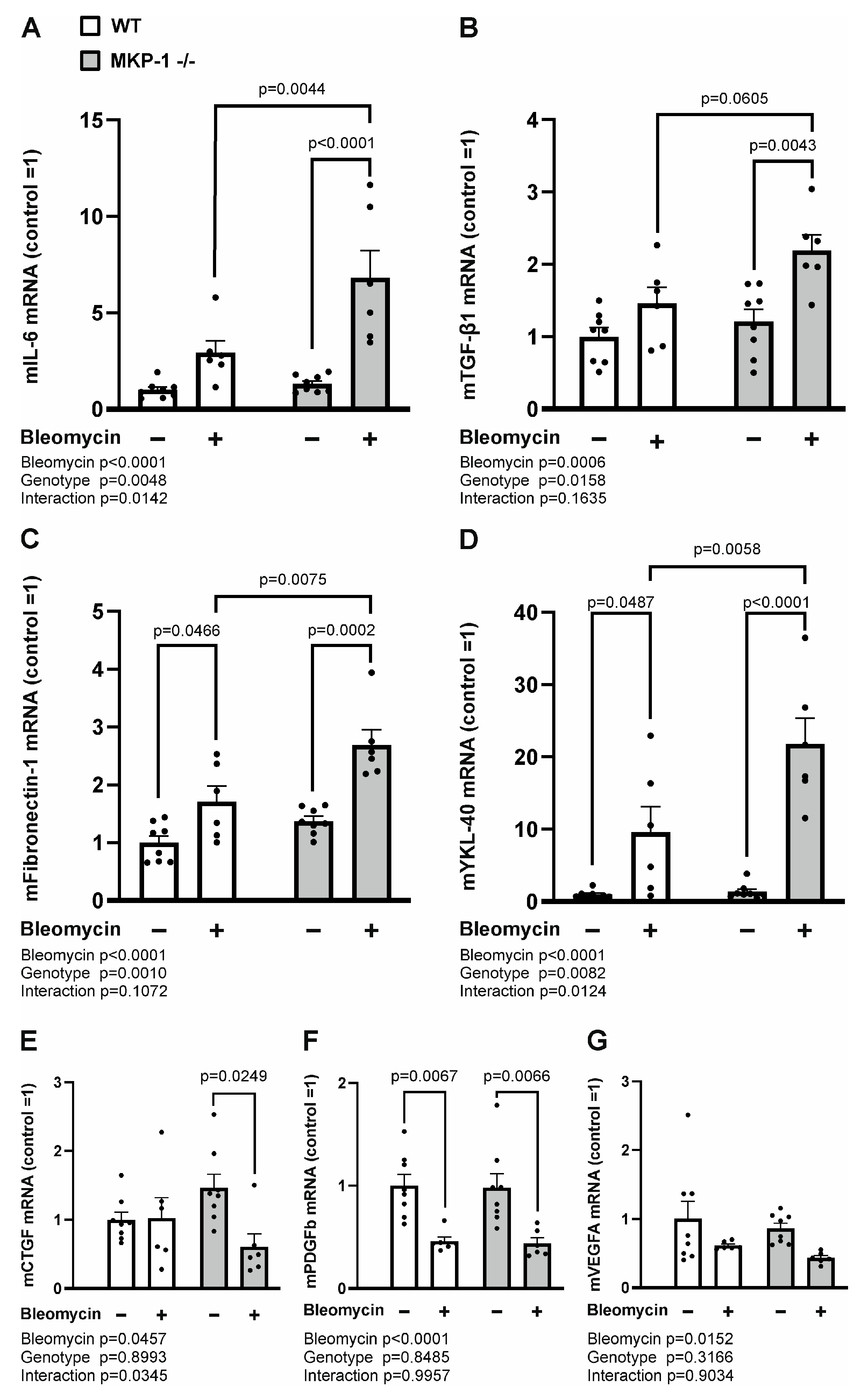
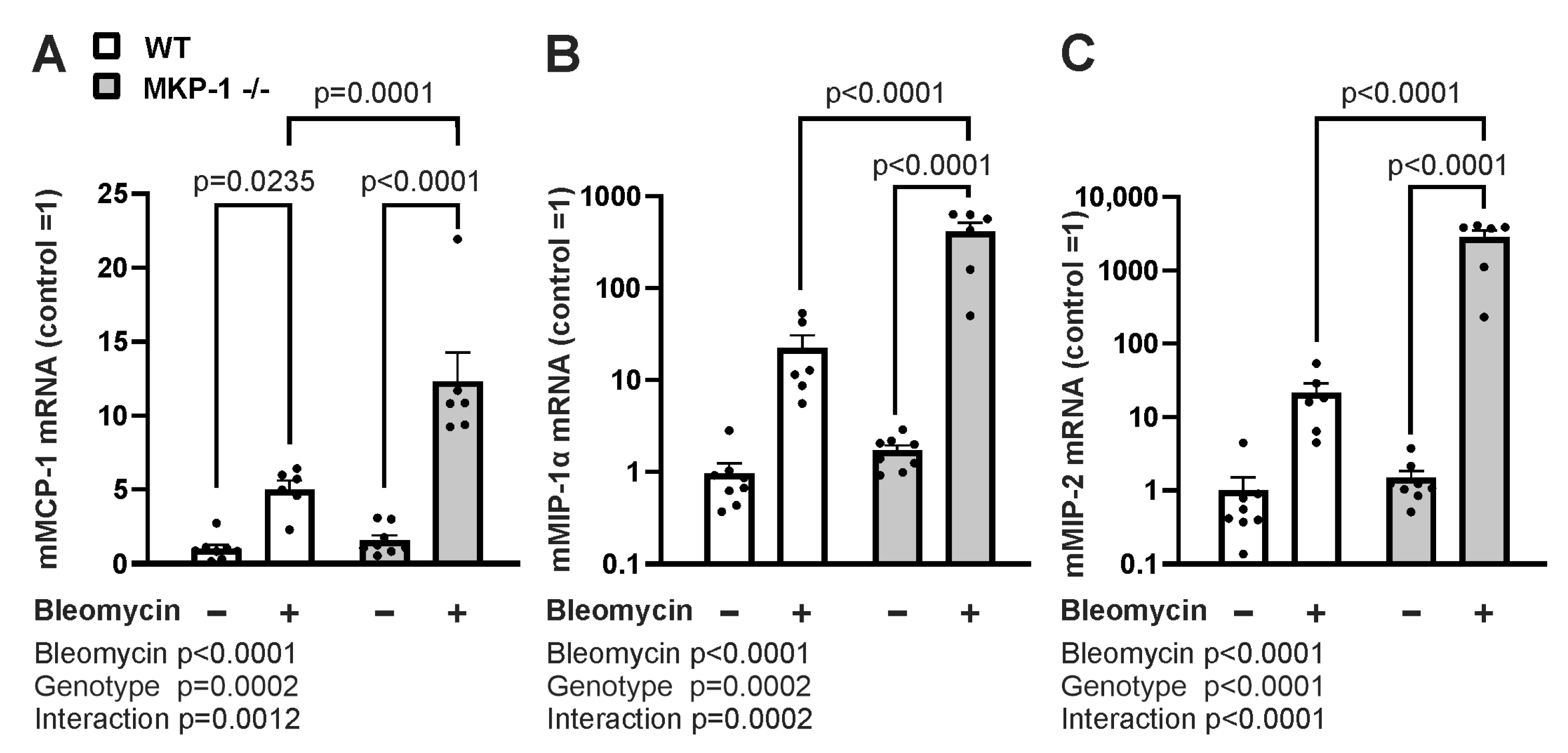
2.3. Expression of Profibrotic Factors and Chemokines Is Enhanced in Bleomycin-Treated Skin from MKP-1-deficient Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Bleomycin Treatment
4.3. Histological Analysis
4.4. RNA Extraction and Quantitative RT-PCR
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D. Systemic Sclerosis. Lancet 2017, 390, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkmann, E.R.; Varga, J. Emerging Targets of Disease-Modifying Therapy for Systemic Sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeRoy, E.C. Increased Collagen Synthesis by Scleroderma Skin Fibroblasts in Vitro: A Possible Defect in the Regulation or Activation of the Scleroderma Fibroblast. J. Clin. Investig. 1974, 54, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckes, B.; Mauch, C.; Hüppe, G.; Krieg, T. Differential Regulation of Transcription and Transcript Stability of Pro-Alpha 1(I) Collagen and Fibronectin in Activated Fibroblasts Derived from Patients with Systemic Scleroderma. Biochem. J. 1996, 315, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihtyanova, S.I.; Sari, A.; Harvey, J.C.; Leslie, A.; Derrett-Smith, E.C.; Fonseca, C.; Ong, V.H.; Denton, C.P. Using Autoantibodies and Cutaneous Subset to Develop Outcome-Based Disease Classification in Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.; Xu, S.; Nihtyanova, S.; Derrett-Smith, E.; Abraham, D.; Denton, C.P.; Ong, V.H. Clinical and Pathological Significance of Interleukin 6 Overexpression in Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.Y.; Baron, M.; Recklies, A.D.; Roughley, P.J.; Mort, J.S. Cells from the Skin of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis Secrete Chitinase 3-like Protein 1. BBA Clin. 2014, 1, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Tredget, E.E. The Role of Chemokines in Fibrotic Wound Healing. Adv. Wound Care 2015, 4, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, N.C.; Rieder, F.; Wynn, T.A. Fibrosis: From Mechanisms to Medicines. Nature 2020, 587, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, S.G.; Samavati, L.; Liu, Y. MAP Kinase Phosphatase-1, a Gatekeeper of the Acute Innate Immune Response. Life Sci. 2020, 241, 117157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, R.; Moilanen, E. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase 1 as an Inflammatory Factor and Drug Target. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 114, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Barry, S.P.; Roth, R.J.; Wu, J.J.; Jones, E.A.; Bennett, A.M.; Flavell, R.A. Dynamic Regulation of Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines by MAPK Phosphatase 1 (MKP-1) in Innate Immune Responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2274–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Reynolds, J.M.; Chang, S.H.; Martin-Orozco, N.; Chung, Y.; Nurieva, R.I.; Dong, C. MKP-1 Is Necessary for T Cell Activation and Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 30815–30824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, R.; Turpeinen, T.; Taimi, V.; Nieminen, R.; Goulas, A.; Moilanen, E. Attenuation of the Acute Inflammatory Response by Dual Specificity Phosphatase 1 by Inhibition of P38 MAP Kinase. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 2059–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuure, L.; Hämäläinen, M.; Whittle, B.J.; Moilanen, E. Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthase-1 Expression in Inflammatory Conditions Is Downregulated by Dexamethasone: Seminal Role of the Regulatory Phosphatase MKP-1. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salojin, K.V.; Owusu, I.B.; Millerchip, K.A.; Potter, M.; Platt, K.A.; Oravecz, T. Essential Role of MAPK Phosphatase-1 in the Negative Control of Innate Immune Responses. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 1899–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Xiao, S.; Li, H.; Zheng, T.; Huang, J.; Hu, R.; Zhang, B.; Liu, X.; Huang, G. MAPK Phosphatase-1 Deficiency Exacerbates the Severity of Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasiform Skin Disease. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Wang, Y.; Shi, L.Z.; Kanneganti, T.-D.; Chi, H. Signaling by the Phosphatase MKP-1 in Dendritic Cells Imprints Distinct Effector and Regulatory T Cell Fates. Immunity 2011, 35, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korhonen, R.; Huotari, N.; Hömmö, T.; Leppänen, T.; Moilanen, E. The Expression of Interleukin-12 Is Increased by MAP Kinase Phosphatase-1 through a Mechanism Related to Interferon Regulatory Factor 1. Mol. Immunol. 2012, 51, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangoni, R.G.; Varga, J.; Tourtellotte, W.G. Animal Models of Scleroderma: Recent Progress. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2016, 28, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Takagawa, S.; Katayama, I.; Yamazaki, K.; Hamazaki, Y.; Shinkai, H.; Nishioka, K. Animal Model of Sclerotic Skin. I: Local Injections of Bleomycin Induce Sclerotic Skin Mimicking Scleroderma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 112, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumoitier, N.; Chaigne, B.; Régent, A.; Lofek, S.; Mhibik, M.; Dorfmüller, P.; Terrier, B.; London, J.; Bérezné, A.; Tamas, N.; et al. Scleroderma Peripheral B Lymphocytes Secrete Interleukin-6 and Transforming Growth Factor β and Activate Fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, O.; Ishikawa, H. Macrophage Infiltration in the Skin of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 1992, 19, 1202–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Feghali, C.A.; Bost, K.L.; Boulware, D.W.; Levy, L.S. Mechanisms of Pathogenesis in Scleroderma. I. Overproduction of Interleukin 6 by Fibroblasts Cultured from Affected Skin Sites of Patients with Scleroderma. J. Rheumatol. 1992, 19, 1207–1211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Väänänen, T.; Koskinen, A.; Paukkeri, E.-L.; Hämäläinen, M.; Moilanen, T.; Moilanen, E.; Vuolteenaho, K. YKL-40 as a Novel Factor Associated with Inflammation and Catabolic Mechanisms in Osteoarthritic Joints. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 215140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Väänänen, T.; Lehtimäki, L.; Vuolteenaho, K.; Hämäläinen, M.; Oksa, P.; Vierikko, T.; Järvenpää, R.; Uitti, J.; Kankaanranta, H.; Moilanen, E. Glycoprotein YKL-40 Levels in Plasma Are Associated with Fibrotic Changes on HRCT in Asbestos-Exposed Subjects. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 1797512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Väänänen, T.; Kallio, J.; Vuolteenaho, K.; Ojala, A.; Luukkaala, T.; Hämäläinen, M.; Tammela, T.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.-L.; Moilanen, E. High YKL-40 Is Associated with Poor Survival in Patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Novel Independent Prognostic Marker. Scand. J. Urol. 2017, 51, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Su, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; You, Q. Chitinase-3 like-Protein-1 Function and Its Role in Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Montagna, G.; D’Angelo, S.; Valentini, G. Cross-Sectional Evaluation of YKL-40 Serum Concentrations in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Relationship with Clinical and Serological Aspects of Disease. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 2147–2151. [Google Scholar]
- Väänänen, T.; Vuolteenaho, K.; Kautiainen, H.; Nieminen, R.; Möttönen, T.; Hannonen, P.; Korpela, M.; Kauppi, M.J.; Laiho, K.; Kaipiainen-Seppänen, O.; et al. Glycoprotein YKL-40: A Potential Biomarker of Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis during Intensive Treatment with CsDMARDs and Infliximab. Evidence from the Randomised Controlled NEO-RACo Trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashiyama, M.; Tomita, K.; Sugihara, N.; Nakashima, H.; Furuhashi, H.; Nishikawa, M.; Inaba, K.; Wada, A.; Horiuchi, K.; Hanawa, Y.; et al. Chitinase 3-like 1 Deficiency Ameliorates Liver Fibrosis by Promoting Hepatic Macrophage Apoptosis. Hepatol. Res. J. Jpn. Soc. Hepatol. 2019, 49, 1316–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapouri-Moghaddam, A.; Mohammadian, S.; Vazini, H.; Taghadosi, M.; Esmaeili, S.-A.; Mardani, F.; Seifi, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Afshari, J.T.; Sahebkar, A. Macrophage Plasticity, Polarization, and Function in Health and Disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6425–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codullo, V.; Baldwin, H.M.; Singh, M.D.; Fraser, A.R.; Wilson, C.; Gilmour, A.; Hueber, A.J.; Bonino, C.; McInnes, I.B.; Montecucco, C.; et al. An Investigation of the Inflammatory Cytokine and Chemokine Network in Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, M.; Sato, S.; Takehara, K. Augmented Production of Chemokines (Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-1 (MCP-1), Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-1alpha (MIP-1alpha) and MIP-1beta) in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: MCP-1 and MIP-1alpha May Be Involved in the Development of Pulmonary Fibros. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1999, 117, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.E.; Strieter, R.M.; Zhang, K.; Phan, S.H.; Standiford, T.J.; Lukacs, N.W.; Kunkel, S.L. A Role for C-C Chemokines in Fibrotic Lung Disease. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1995, 57, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Takehara, K.; Sato, S. Longitudinal Analysis of Serum Cytokine Concentrations in Systemic Sclerosis: Association of Interleukin 12 Elevation with Spontaneous Regression of Skin Sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 275–284. [Google Scholar]
- Corral Magaña, O.; Escalas Taberner, J.; Escudero Góngora, M.M.; Giacaman Contreras, A. Morphea in a Patient with Psoriasis on Treatment with Ustekinumab: Comorbidity or Adverse Effect. Actas DermoSifiliogr. 2017, 108, 487–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steuer, A.B.; Peterson, E.; Lo Sicco, K.; Franks, A.G. Morphea in a Patient Undergoing Treatment with Ustekinumab. JAAD Case Rep. 2019, 5, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieminen, R.; Korhonen, R.; Moilanen, T.; Clark, A.R.; Moilanen, E. Aurothiomalate Inhibits Cyclooxygenase 2, Matrix Metalloproteinase 3, and Interleukin-6 Expression in Chondrocytes by Increasing MAPK Phosphatase 1 Expression and Decreasing P38 Phosphorylation: MAPK Phosphatase 1 as a Novel Target for Antirheumatic Drugs. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, R.; Hömmö, T.; Keränen, T.; Laavola, M.; Hämäläinen, M.; Vuolteenaho, K.; Lehtimäki, L.; Kankaanranta, H.; Moilanen, E. Attenuation of TNF Production and Experimentally Induced Inflammation by PDE4 Inhibitor Rolipram Is Mediated by MAPK Phosphatase-1. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 1525–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.S.; Prabhala, P.; Oliver, B.G.; Ammit, A.J. Inhibitors of Phosphodiesterase 4, but Not Phosphodiesterase 3, Increase Β2-Agonist-Induced Expression of Antiinflammatory Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase 1 in Airway Smooth Muscle Cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 52, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keränen, T.; Hömmö, T.; Hämäläinen, M.; Moilanen, E.; Korhonen, R. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Β2-Receptor Agonists Salbutamol and Terbutaline Are Mediated by MKP-1. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassel, O.; Sancono, A.; Krätzschmar, J.; Kreft, B.; Stassen, M.; Cato, A.C. Glucocorticoids Inhibit MAP Kinase via Increased Expression and Decreased Degradation of MKP-1. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 7108–7116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuure, L.; Hämäläinen, M.; Nummenmaa, E.; Moilanen, T.; Moilanen, E. Downregulation of Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthase-1 (MPGES-1) Expression in Chondrocytes Is Regulated by MAP Kinase Phosphatase-1 (MKP-1). Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 71, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keränen, T.; Moilanen, E.; Korhonen, R. Suppression of Cytokine Production by Glucocorticoids Is Mediated by MKP-1 in Human Lung Epithelial Cells. Inflamm. Res. J. Eur. Histamine Res. Soc. 2017, 66, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal-Bielecka, O.; Fransen, J.; Avouac, J.; Becker, M.; Kulak, A.; Allanore, Y.; Distler, O.; Clements, P.; Cutolo, M.; Czirjak, L.; et al. Update of EULAR Recommendations for the Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pemmari, A.; Leppänen, T.; Hämäläinen, M.; Moilanen, T.; Vuolteenaho, K.; Moilanen, E. Widespread Regulation of Gene Expression by Glucocorticoids in Chondrocytes from Patients with Osteoarthritis as Determined by RNA-Seq. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilz, R.B.; Casteel, D.E. Regulation of Gene Expression by Cyclic GMP. Circ. Res. 2003, 93, 1034–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, N.; Tomcik, M.; Zerr, P.; Lang, V.; Dees, C.; Avouac, J.; Palumbo, K.; Horn, A.; Akhmetshina, A.; Beyer, C.; et al. Jun N-terminal Kinase as a Potential Molecular Target for Prevention and Treatment of Dermal Fibrosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihn, H.; Yamane, K.; Tamaki, K. Increased Phosphorylation and Activation of Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase p38 in scleroderma fibroblasts. J. Invest. Derm. 2005, 125, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoryev, D.N.; Dalal, J.; Becker, M.L.; Ye, S.Q. Combined Meta-analysis of Systemic Effects of Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation and Systemic Sclerosis. BMC Hematol. 2014, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorfman, K.; Carrasco, D.; Gruda, M.; Ryan, C.; Lira, S.A.; Bravo, R. Disruption of the Erp/Mkp-1 Gene Does Not Affect Mouse Development: Normal MAP Kinase Activity in ERP/MKP-1-Deficient Fibroblasts. Oncogene 1996, 13, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.J.; Vetteth, S.; Periyasamy, S.M.; Kanj, M.; Fedorova, L.; Khouri, S.; Kahaleh, M.B.; Xie, Z.; Malhotra, D.; Kolodkin, N.I.; et al. Central Role for the Cardiotonic Steroid Marinobufagenin in the Pathogenesis of Experimental Uremic Cardiomyopathy. Hypertension 2006, 47, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scotece, M.; Hämäläinen, M.; Leppänen, T.; Vuolteenaho, K.; Moilanen, E. MKP-1 Deficiency Exacerbates Skin Fibrosis in a Mouse Model of Scleroderma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054668
Scotece M, Hämäläinen M, Leppänen T, Vuolteenaho K, Moilanen E. MKP-1 Deficiency Exacerbates Skin Fibrosis in a Mouse Model of Scleroderma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(5):4668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054668
Chicago/Turabian StyleScotece, Morena, Mari Hämäläinen, Tiina Leppänen, Katriina Vuolteenaho, and Eeva Moilanen. 2023. "MKP-1 Deficiency Exacerbates Skin Fibrosis in a Mouse Model of Scleroderma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 5: 4668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054668
APA StyleScotece, M., Hämäläinen, M., Leppänen, T., Vuolteenaho, K., & Moilanen, E. (2023). MKP-1 Deficiency Exacerbates Skin Fibrosis in a Mouse Model of Scleroderma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(5), 4668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054668





