Pan-Cancer Analysis Reveals Functional Similarity of Three lncRNAs across Multiple Tumors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
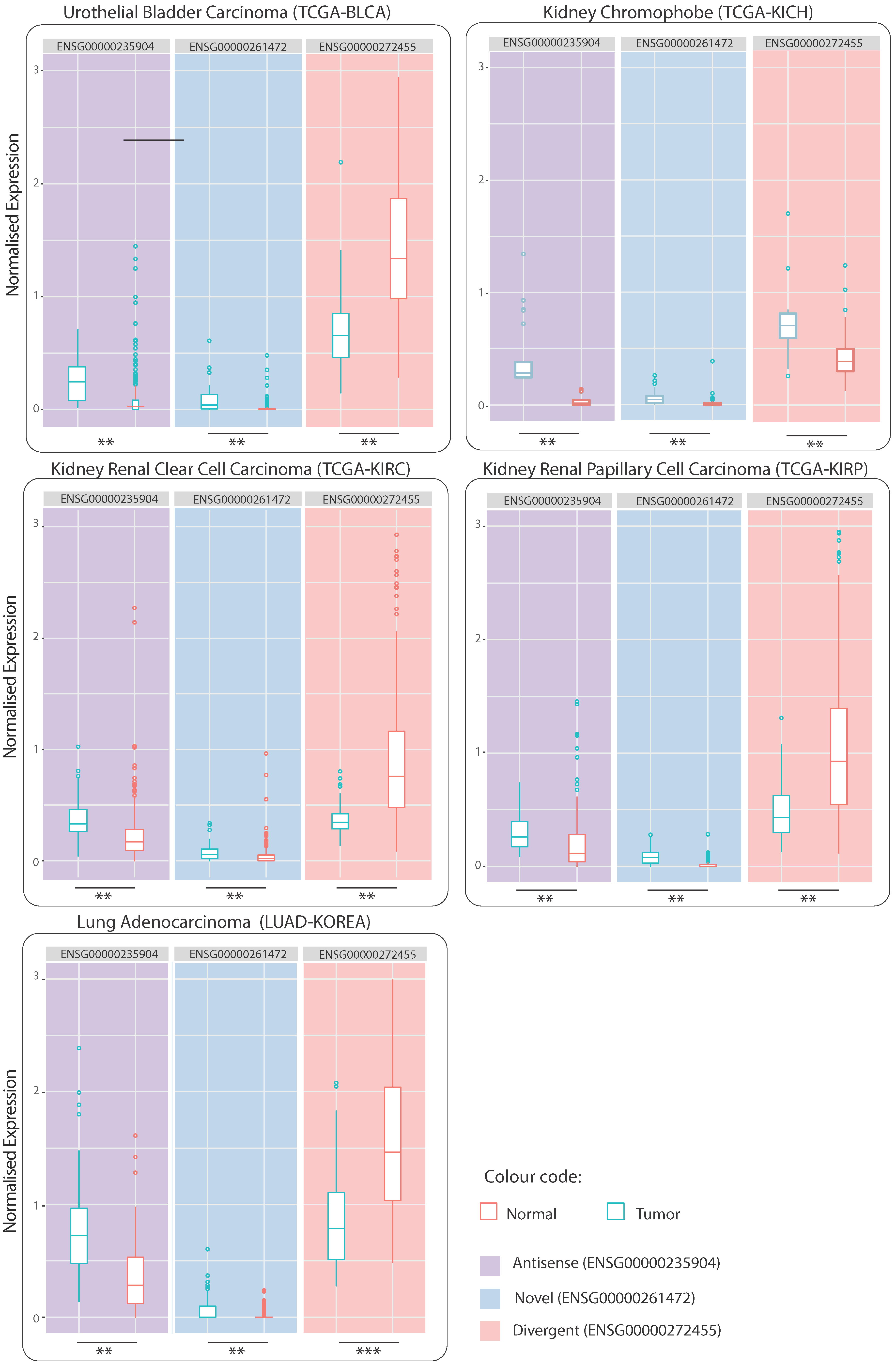
2.1. Common Dysregulated lncRNAs
2.2. Gene Ontologies (GO) for Inference of Functional Similarity
Similarity Networks
3. Discussion
3.1. Dysregulation of lncRNAs among Cancers
3.2. Three Consistently Dysregulated lncRNAs
3.2.1. ENSG00000235904, RBMS3-AS3 “Antisense”
3.2.2. ENSG00000261472 “Novel”
3.2.3. ENSG00000272455, MRPL20-DT “Divergent”
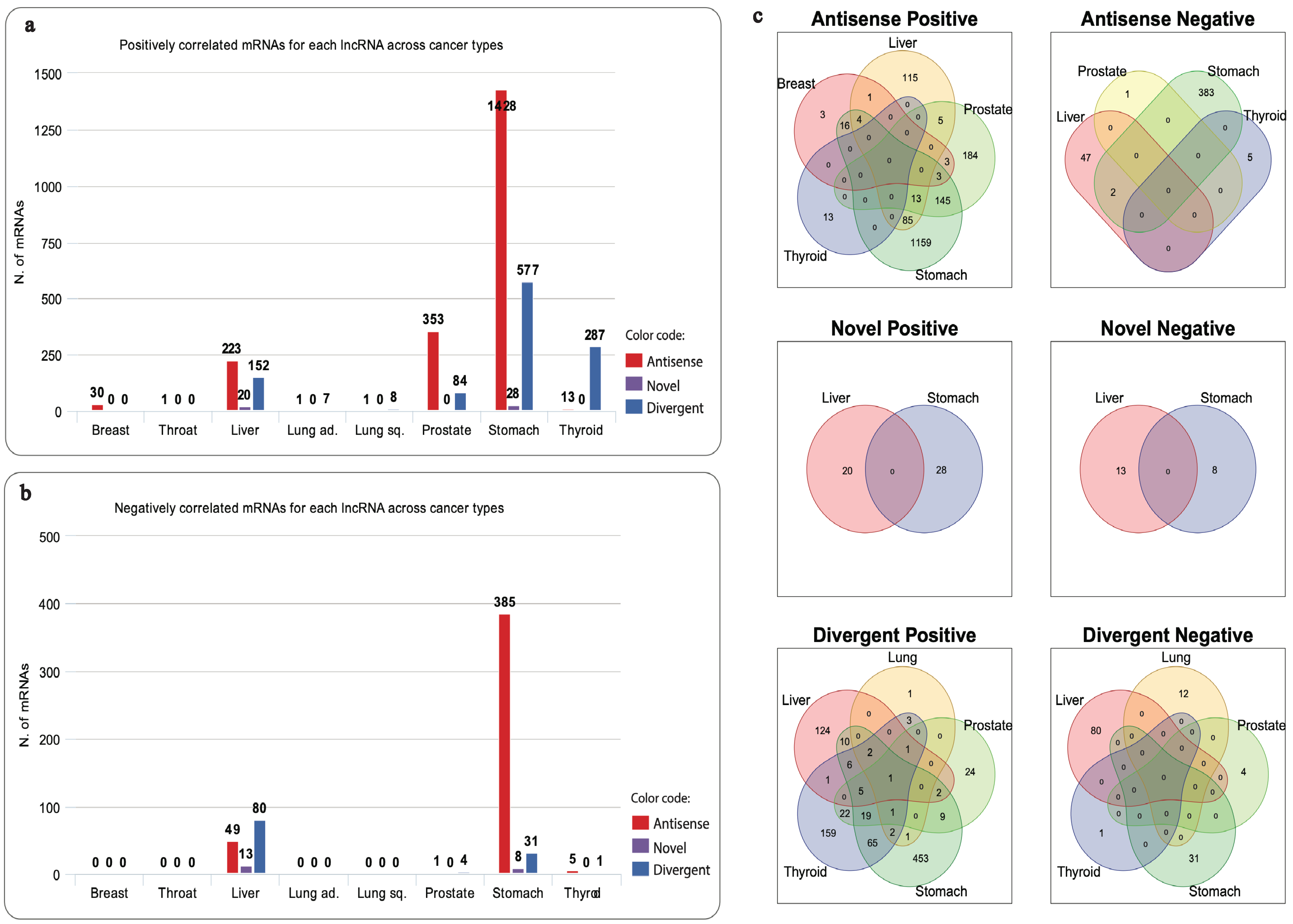
3.3. Specificity of Correlated mRNAs
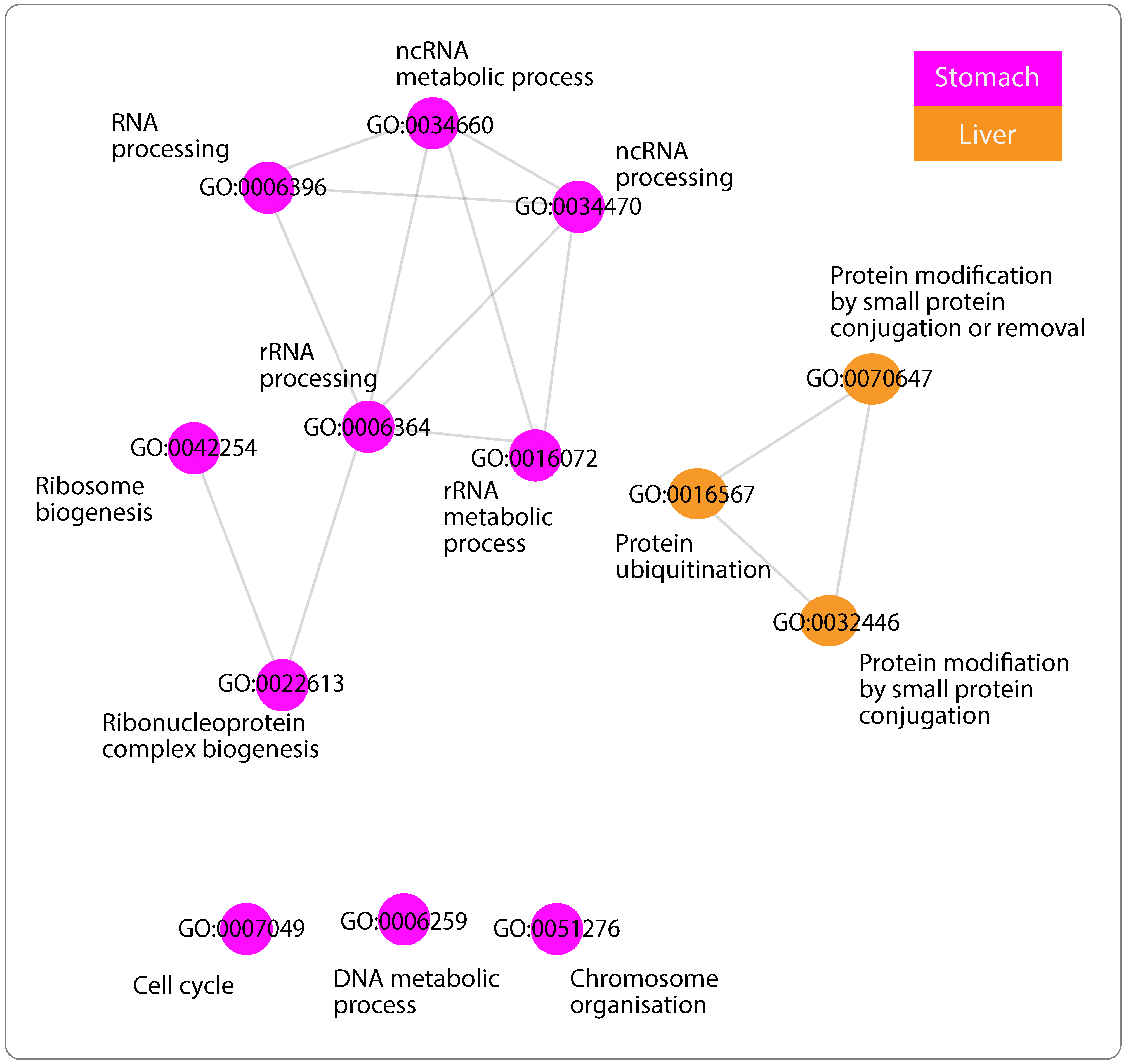
3.4. Enriched GO Terms
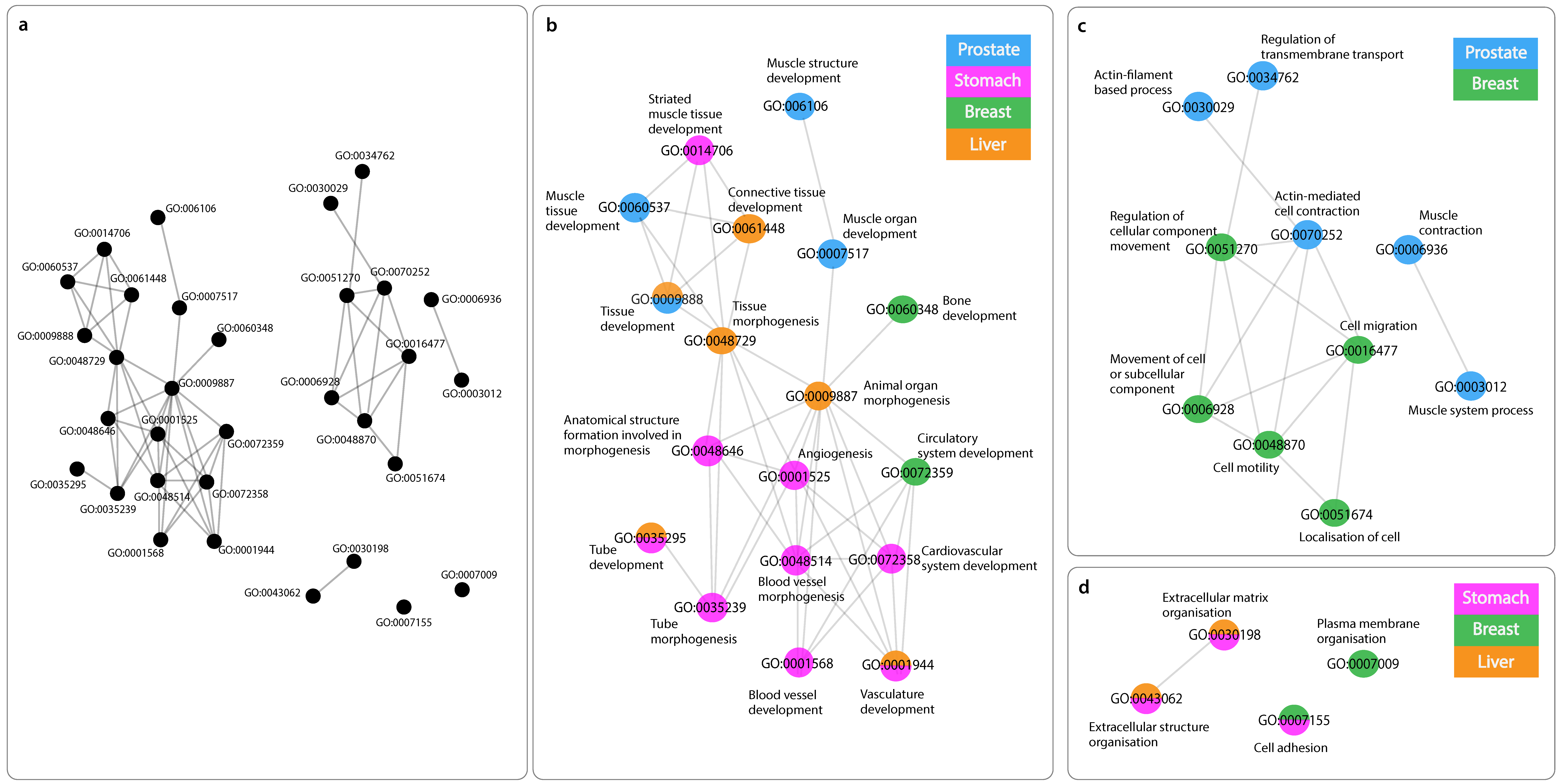
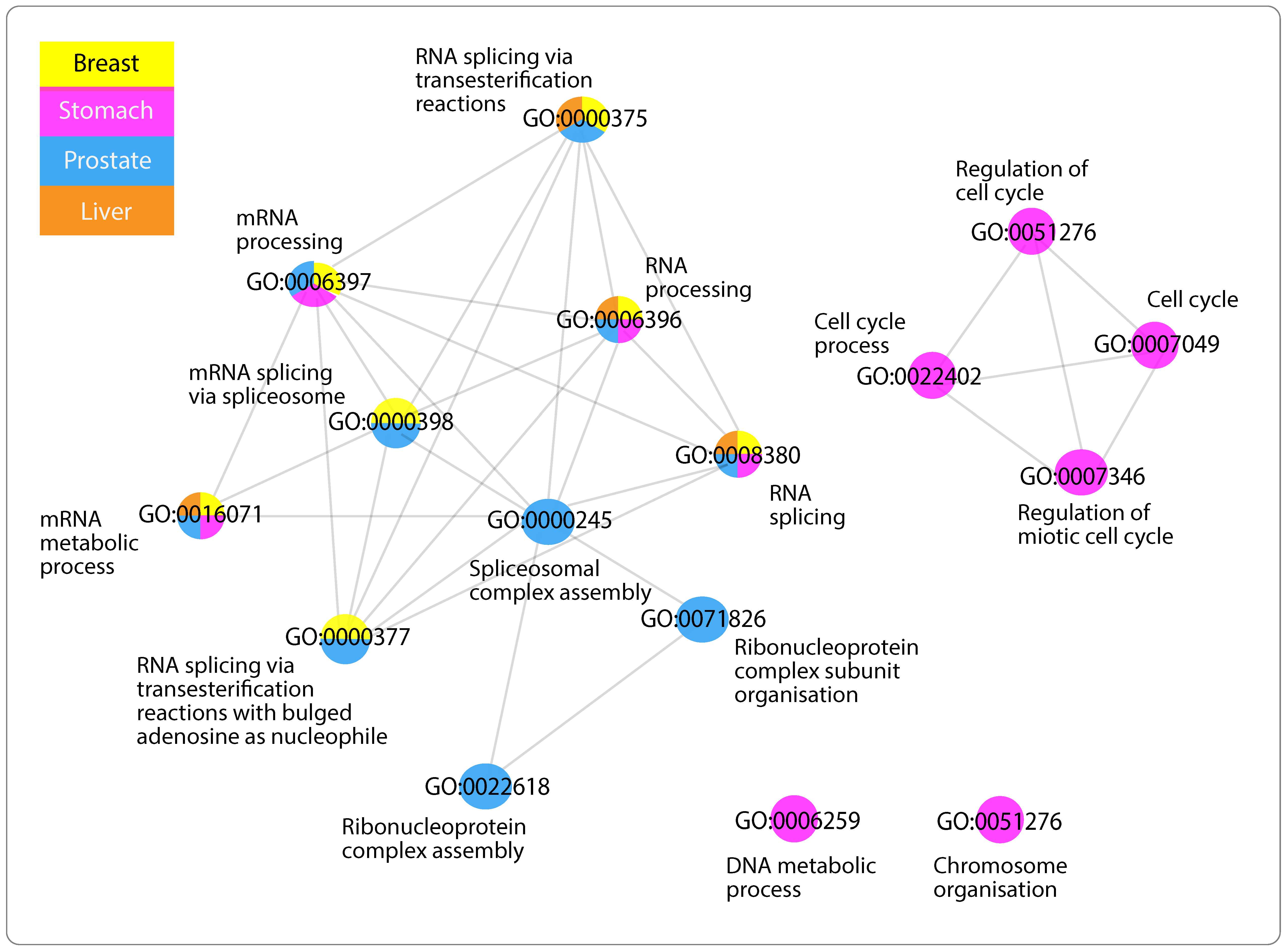
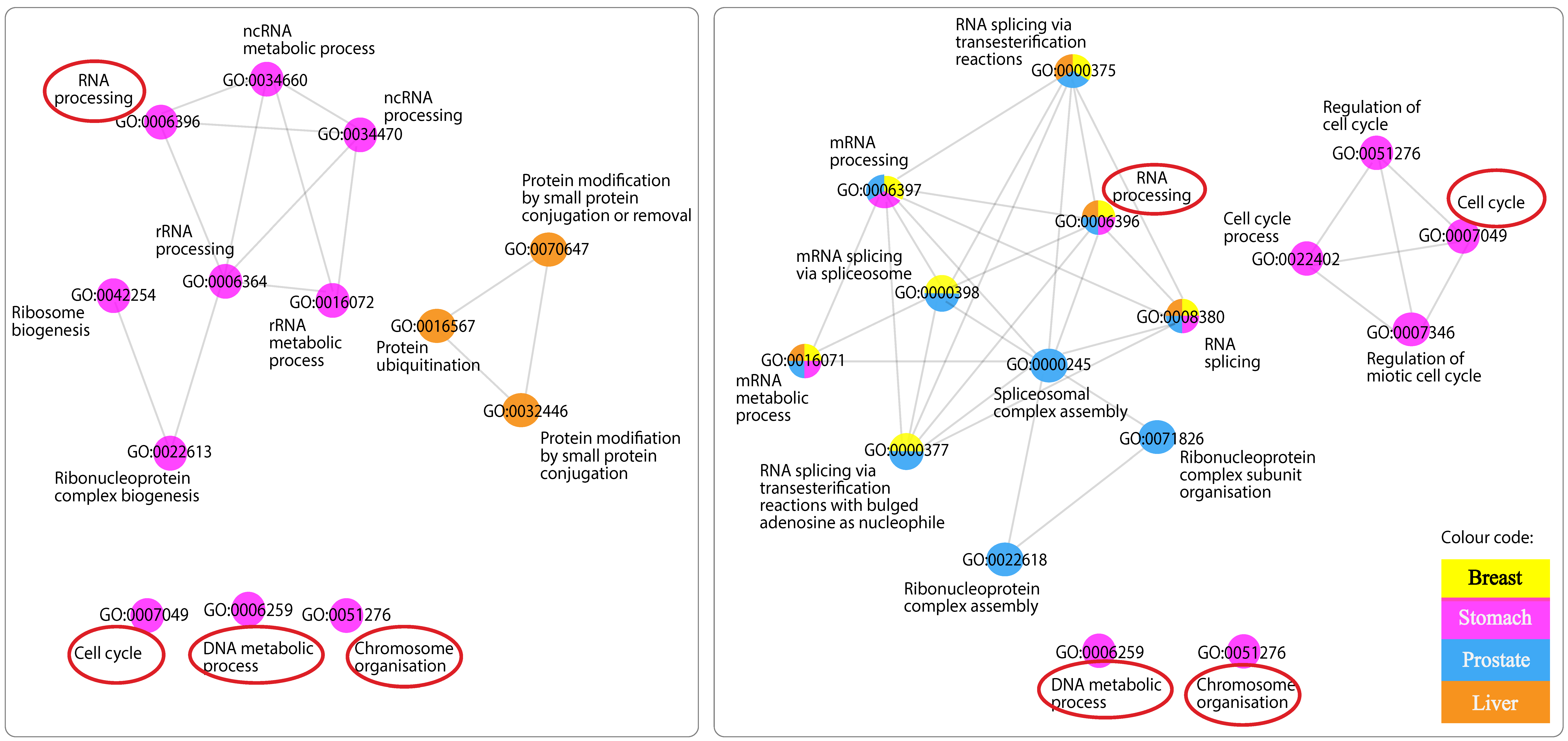
3.5. Networks of Functionally Similar GO Terms
3.5.1. GO Terms of Positively Related mRNAs with “Antisense”
3.5.2. GO Terms of Negatively Related mRNAs with “Antisense”
3.5.3. GO Terms of Positively Related mRNAs with “Divergent”
3.5.4. GO Terms Shared across Networks
3.6. Evaluation of lncRNA DE on Independent Datasets
3.7. Future Direction
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Source
4.2. Differential Exprssion Analysis and Commonality Exploration
4.2.1. mRNA Correlation Analysis
4.2.2. Functional Enrichment Analysis
4.2.3. GO Similarity Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteller, M. Cancer epigenomics: DNA methylomes and histone-modification maps. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.S.; Jones, P.A. Cancer genetics and epigenetics: Two sides of the same coin? Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, R.; Hanahan, D. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar]
- Stratton, M.R.; Campbell, P.J.; Futreal, P.A. The cancer genome. Nature 2009, 458, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pleasance, E.D.; Cheetham, R.K.; Stephens, P.J.; McBride, D.J.; Humphray, S.J.; Greenman, C.D.; Varela, I.; Lin, M.-L.; Ordóñez, G.R.; Bignell, G.R. A comprehensive catalogue of somatic mutations from a human cancer genome. Nature 2010, 463, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, T.J.; Mardis, E.R.; Ding, L.; Fulton, B.; McLellan, M.D.; Chen, K.; Dooling, D.; Dunford-Shore, B.H.; McGrath, S.; Hickenbotham, M. DNA sequencing of a cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukaemia genome. Nature 2008, 456, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutter, C.; Zenklusen, J.C. The Cancer Genome Atlas: Creating Lasting Value beyond Its Data. Cell 2018, 173, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Jin, Z.; Yang, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ji, Y. TCGA-assembler 2: Software pipeline for retrieval and processing of TCGA/CPTAC data. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1615–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, J.S.; Garnett, M.J.; Adams, D.J.; Francies, H.E.; Golub, T.R.; Hahn, W.C.; Iorio, F.; McFarland, J.M.; Parts, L.; Vazquez, F. Cancer research needs a better map. Nature 2021, 589, 514–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, K.; Czerwińska, P.; Wiznerowicz, M. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA): An immeasurable source of knowledge. Contemp. Oncol. 2015, 19, A68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaprico, A.; Silva, T.C.; Olsen, C.; Garofano, L.; Cava, C.; Garolini, D.; Sabedot, T.S.; Malta, T.M.; Pagnotta, S.M.; Castiglioni, I. TCGAbiolinks: An R/Bioconductor package for integrative analysis of TCGA data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriello, G.; Miller, M.L.; Aksoy, B.A.; Senbabaoglu, Y.; Schultz, N.; Sander, C. Emerging landscape of oncogenic signatures across human cancers. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, J.N.; Collisson, E.A.; Mills, G.B.; Shaw, K.R.M.; Ozenberger, B.A.; Ellrott, K.; Shmulevich, I.; Sander, C.; Stuart, J.M. The cancer genome atlas pan-cancer analysis project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The ICGC/TCGA Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes Consortium. Pan-cancer analysis of whole genomes. Nature 2020, 578, 82. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, B.D.; Parsons, C.; Walker, L.; Zhang, W.C.; Slack, F.J. Targeting noncoding RNAs in disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, A.M.; Chang, H.Y. Long noncoding RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampetaki, A.; Albrecht, A.; Steinhofel, K. Long non-coding RNA structure and function: Is there a link? Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulitsky, I. Evolution to the rescue: Using comparative genomics to understand long non-coding RNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinn, J.L.; Chang, H.Y. Genome regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penny, G.D.; Kay, G.F.; Sheardown, S.A.; Rastan, S.; Brockdorff, N. Requirement for Xist in X chromosome inactivation. Nature 1996, 379, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plath, K.; Mlynarczyk-Evans, S.; Nusinow, D.A.; Panning, B. Xist RNA and the mechanism of X chromosome inactivation. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2002, 36, 233–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, S.; Coller, J. RNA in unexpected places: Long non-coding RNA functions in diverse cellular contexts. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.-C.; Manor, O.; Wan, Y.; Mosammaparast, N.; Wang, J.K.; Lan, F.; Shi, Y.; Segal, E.; Chang, H.Y. Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science 2010, 329, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prensner, J.R.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. The emergence of lncRNAs in cancer biology. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatica, A.; Bozzoni, I. Long non-coding RNAs: New players in cell differentiation and development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasiadou, E.; Jacob, L.S.; Slack, F.J. Non-coding RNA networks in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, B.C.; Molloy, P.L.; Graham, L.D. CRNDE: A long non-coding RNA involved in cancer, neurobiology, and development. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.A.; Shah, N.; Wang, K.C.; Kim, J.; Horlings, H.M.; Wong, D.J.; Tsai, M.-C.; Hung, T.; Argani, P.; Rinn, J.L. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature 2010, 464, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huarte, M.; Guttman, M.; Feldser, D.; Garber, M.; Koziol, M.J.; Kenzelmann-Broz, D.; Khalil, A.M.; Zuk, O.; Amit, I.; Rabani, M. A large intergenic noncoding RNA induced by p53 mediates global gene repression in the p53 response. Cell 2010, 142, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlevaro-Fita, J.; Lanzós, A.; Feuerbach, L.; Hong, C.; Mas-Ponte, D.; Pedersen, J.S.; Johnson, R. Cancer LncRNA Census reveals evidence for deep functional conservation of long noncoding RNAs in tumorigenesis. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrama, D.; Reisfeld, R.A.; Becker, J.C. Antibody targeted drugs as cancer therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansoori, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Davudian, S.; Shirjang, S.; Baradaran, B. The different mechanisms of cancer drug resistance: A brief review. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 7, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukowski, K.; Kciuk, M.; Kontek, R. Mechanisms of multidrug resistance in cancer chemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Liu, R.; Yu, Y.; Liang, L.; Yu, S.; Xu, X.; Liu, T. Identification and validation of cetuximab resistance associated long noncoding RNA biomarkers in metastatic colorectal cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, W.; Chang, Z.; Liang, H.; Zhao, W.; Qi, L.; Guo, Z. Differential expression analysis at the individual level reveals a lncRNA prognostic signature for lung adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Han, L.; Roebuck, P.; Diao, L.; Liu, L.; Yuan, Y.; Weinstein, J.N.; Liang, H. TANRIC: An Interactive Open Platform to Explore the Function of lncRNAs in CancerThe Atlas of Noncoding RNAs in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3728–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aran, D.; Sirota, M.; Butte, A.J. Systematic pan-cancer analysis of tumour purity. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbani, R.; Ng, P.K.S.; Werner, H.M.; Shahmoradgoli, M.; Zhang, F.; Ju, Z.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.-Y.; Yoshihara, K.; Li, J. A pan-cancer proteomic perspective on The Cancer Genome Atlas. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanski, C.R.; White, N.M.; Dang, H.X.; Silva-Fisher, J.M.; Rauck, C.E.; Cicka, D.; Maher, C.A. Pan-cancer transcriptome analysis reveals long noncoding RNAs with conserved function. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 628–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Hu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Hu, X.; Yuan, J.; Zhao, S.D.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Shan, W.; He, Q. Comprehensive genomic characterization of long non-coding RNAs across human cancers. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutschner, T.; Diederichs, S. The hallmarks of cancer: A long non-coding RNA point of view. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 703–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutschner, T.; Hämmerle, M.; Eißmann, M.; Hsu, J.; Kim, Y.; Hung, G.; Revenko, A.; Arun, G.; Stentrup, M.; Groß, M. The noncoding RNA MALAT1 is a critical regulator of the metastasis phenotype of lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Piao, H.-L.; Kim, B.-J.; Yao, F.; Han, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Siverly, A.N.; Lawhon, S.E.; Ton, B.N. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 suppresses breast cancer metastasis. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Ou, C.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, S.; Li, G.; Wang, G.; Song, J.; Li, Z. YAP1-induced MALAT1 promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis by sponging miR-126-5p in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2019, 38, 2627–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas-Ponte, D.; Carlevaro-Fita, J.; Palumbo, E.; Pulido, T.H.; Guigo, R.; Johnson, R. LncATLAS database for subcellular localization of long noncoding RNAs. Rna 2017, 23, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Maquat, L.E. lncRNAs transactivate STAU1-mediated mRNA decay by duplexing with 3′ UTRs via Alu elements. Nature 2011, 470, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretz, M. TINCR, staufen1, and cellular differentiation. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 1597–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Srikantan, S.; Yang, X.; Martindale, J.L.; De, S.; Huarte, M.; Zhan, M.; Becker, K.G.; Gorospe, M. LincRNA-p21 suppresses target mRNA translation. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xue, Y.; Han, Y.; Lin, L.; Wu, C.; Xu, S.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Q.; Cao, X. The STAT3-binding long noncoding RNA lnc-DC controls human dendritic cell differentiation. Science 2014, 344, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Sun, L.; Liu, Q.; Gong, C.; Yao, Y.; Lv, X.; Lin, L.; Yao, H.; Su, F.; Li, D. A cytoplasmic NF-κB interacting long noncoding RNA blocks IκB phosphorylation and suppresses breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wan, J.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, S.; Ji, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhai, S.; Cui, R. Identification of competitive endogenous RNAs network in breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 2392–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, P.; Chen, D. Long noncoding RNA RBMS3-AS3 acts as a microRNA-4534 sponge to inhibit the progression of prostate cancer by upregulating VASH1. Gene Ther. 2020, 27, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.; Liu, B. Comprehensive analysis of a long noncoding RNA-associated competing endogenous RNA network in colorectal cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 2453–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, X.; Mao, X.; Lou, Y.; Mu, Y.; Xue, D.; Zhou, H. Construction and analysis of lncRNA-associated ceRNA network identified potential prognostic biomarker in gastric cancer. Transl. Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonsdale, J.; Thomas, J.; Salvatore, M.; Phillips, R.; Lo, E.; Shad, S.; Hasz, R.; Walters, G.; Garcia, F.; Young, N. The genotype-tissue expression (GTEx) project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnubalaji, R.; Shaath, H.; Elkord, E.; Alajez, N.M. Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) transcriptional landscape in breast cancer identifies LINC01614 as non-favorable prognostic biomarker regulated by TGFβ and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) signaling. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imada, E.L.; Sanchez, D.F.; Collado-Torres, L.; Wilks, C.; Matam, T.; Dinalankara, W.; Stupnikov, A.; Lobo-Pereira, F.; Yip, C.-W.; Yasuzawa, K. Recounting the FANTOM CAGE-associated transcriptome. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Zhang, G.; Huang, Y.; Sun, L.; Shi, G.; Ye, D. A 5-lncRNA Signature Associated with Smoking Predicts the Overall Survival of Patients with Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Dis. Markers 2021, 2021, 8839747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Lu, J.; Chen, H.; Ding, N.; Wang, G.; Xu, J.; Li, X. Identifying and functionally characterizing tissue-specific and ubiquitously expressed human lncRNAs. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 7120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlicker, A.; Domingues, F.S.; Rahnenführer, J.; Lengauer, T. A new measure for functional similarity of gene products based on Gene Ontology. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnik, P. Using information content to evaluate semantic similarity in a taxonomy. arXiv 1995, arXiv:cmp-lg/9511007. [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 2000, 407, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuelten, C.H.; Parent, C.A.; Montell, D.J. Cell motility in cancer invasion and metastasis: Insights from simple model organisms. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 296–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, D.; Kurisu, S.; Takenawa, T. Regulation of cancer cell motility through actin reorganization. Cancer Sci. 2005, 96, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.F.; Sahai, E. The actin cytoskeleton in cancer cell motility. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2009, 26, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Weaver, V.M.; Werb, Z. The extracellular matrix: A dynamic niche in cancer progression. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multhaupt, H.A.; Leitinger, B.; Gullberg, D.; Couchman, J.R. Extracellular matrix component signaling in cancer. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 97, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turi, Z.; Lacey, M.; Mistrik, M.; Moudry, P. Impaired ribosome biogenesis: Mechanisms and relevance to cancer and aging. Aging 2019, 11, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narla, A.; Ebert, B.L. Ribosomopathies: Human disorders of ribosome dysfunction. Blood 2010, 115, 3196–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, C.; Grummt, I. Ribosome biogenesis and cell growth: mTOR coordinates transcription by all three classes of nuclear RNA polymerases. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6384–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, V.; Carson, B.B.; Feenstra, J.M.; Dass, R.A.; Sekyrova, P.; Hoshino, A.; Petersen, J.; Guo, Y.; Parks, M.M.; Kurylo, C.M. Ribosome biogenesis during cell cycle arrest fuels EMT in development and disease. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, J.; Thomas, G.; Volarević, S. Ribosome biogenesis in cancer: New players and therapeutic avenues. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeller, D.; Hecker, C.-M.; Dikic, I. Ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins in cancer pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Sun, S.-C. Ubiquitin signaling in immune responses. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 457–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; McClusky, W.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M. Cytoplasmic functions of lncRNAs. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2018, 9, e1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, S.; Cai, C.-Y.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Guo, H.-Q.; Cui, Q.; Wei, L.; Huang, J.-J.; Ashby, C.R., Jr.; Chen, Z.-S. Targeting the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway to overcome anti-cancer drug resistance. Drug Resist. Updates 2020, 48, 100663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-D.; Lee, N.H. Aberrant RNA splicing in cancer and drug resistance. Cancers 2018, 10, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oltean, S.; Bates, D.O. Hallmarks of alternative splicing in cancer. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5311–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Barrios, N.; Legascue, M.F.; Benhamed, M.; Ariel, F.; Crespi, M. Splicing regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 2169–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamizar, O.; Chambers, C.B.; Riberdy, J.M.; Persons, D.A.; Wilber, A. Long noncoding RNA Saf and splicing factor 45 increase soluble Fas and resistance to apoptosis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 13810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.-S.; Ju, Y.S.; Lee, W.-C.; Shin, J.-Y.; Lee, J.K.; Bleazard, T.; Lee, J.; Jung, Y.J.; Kim, J.-O.; Shin, J.-Y. The transcriptional landscape and mutational profile of lung adenocarcinoma. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 2109–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, F.; Wang, H.; Teschendorff, A.; Xie, F.; He, Y. Pan-cancer characterization of long non-coding RNA and DNA methylation mediated transcriptional dysregulation. Ebiomedicine 2021, 68, 103399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beroukhim, R.; Mermel, C.H.; Porter, D.; Wei, G.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Donovan, J.; Barretina, J.; Boehm, J.S.; Dobson, J.; Urashima, M. The landscape of somatic copy-number alteration across human cancers. Nature 2010, 463, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.; Barber, G.P.; Casper, J.; Clawson, H.; Diekhans, M.; Gonzalez, J.N.; Hinrichs, A.S.; Lee, B.T.; Nassar, L.R.; Powell, C.C. UCSC Genome Browser enters 20th year. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D756–D761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaccard, P. Étude comparative de la distribution florale dans une portion des Alpes et des Jura. Bull. Soc. Vaud. Sci. Nat. 1901, 37, 547–579. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, S. Guilt-by-association goes global. Nature 2000, 403, 601–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consortium, G.O. The gene ontology resource: 20 years and still GOing strong. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D330–D338. [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Duncan, D.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, B. WEB-based gene set analysis toolkit (WebGestalt): Update 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W77–W83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Kirov, S.; Snoddy, J. WebGestalt: An integrated system for exploring gene sets in various biological contexts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W741–W748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, W.T.; Skopek, T.R. Statistical test for the comparison of samples from mutational spectra. J. Mol. Biol. 1987, 194, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcon, S.; Gentleman, R. Hypergeometric testing used for gene set enrichment analysis. In Bioconductor Case Studies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 207–220. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Rajapakse, J.C. Gene ontology enrichment improves performances of functional similarity of genes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Khan, I.K.; Ding, Z.; Yerneni, S.; Kihara, D. NaviGO: Interactive tool for visualization and functional similarity and coherence analysis with gene ontology. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khazaal, A.; Zandavi, S.M.; Smolnikov, A.; Fatima, S.; Vafaee, F. Pan-Cancer Analysis Reveals Functional Similarity of Three lncRNAs across Multiple Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4796. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054796
Khazaal A, Zandavi SM, Smolnikov A, Fatima S, Vafaee F. Pan-Cancer Analysis Reveals Functional Similarity of Three lncRNAs across Multiple Tumors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(5):4796. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054796
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhazaal, Abir, Seid Miad Zandavi, Andrei Smolnikov, Shadma Fatima, and Fatemeh Vafaee. 2023. "Pan-Cancer Analysis Reveals Functional Similarity of Three lncRNAs across Multiple Tumors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 5: 4796. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054796
APA StyleKhazaal, A., Zandavi, S. M., Smolnikov, A., Fatima, S., & Vafaee, F. (2023). Pan-Cancer Analysis Reveals Functional Similarity of Three lncRNAs across Multiple Tumors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(5), 4796. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054796






