Conundrum for Psoriasis and Thyroid Involvement
Abstract
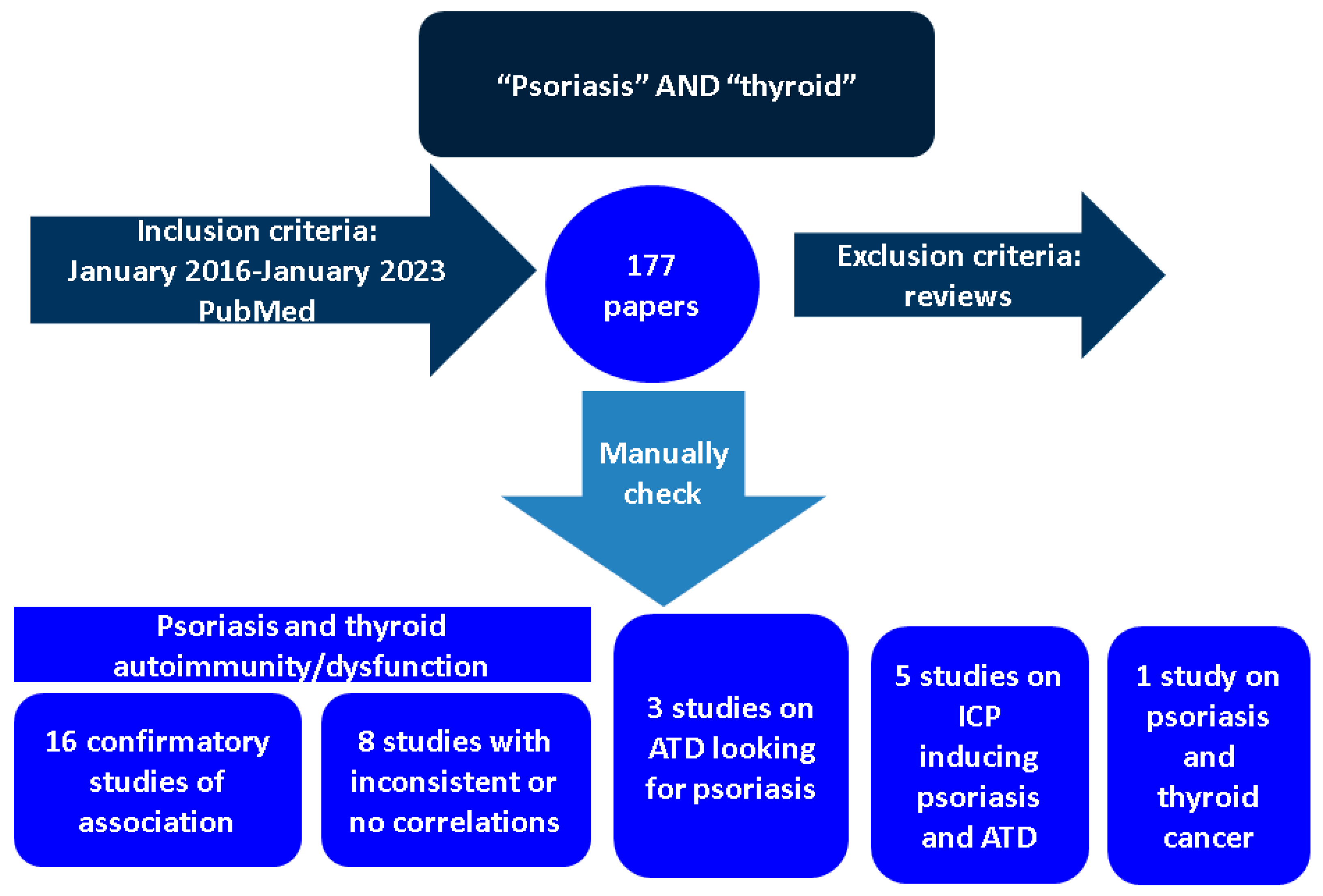
:1. Introduction
Aim
2. Methods
2.1. Thyroid Involvement (Hormonal Imbalance and Positive Autoimmunity) in Individuals with Psoriasis
2.1.1. Confirmatory Data of Association
2.1.2. Studies with Inconsistent Correlations between Psoriasis and Thyroid Anomalies
2.2. Pathogenic Elements Involving Psoriasis and Thyroid Comorbidities
2.2.1. Traditional Pathogenic Frame
2.2.2. Recent Pathogenic Landscape
2.3. Identifying Psoriasis in Patients with Previous Positive Thyroid Autoimmunity
3. Discussions
3.1. Thyroid Cancer in Patients with Psoriasis
3.2. Psoriasis and Thyroiditis among Immune Side Effect of Anti-Cancer Drugs
3.3. Subacute Thyroiditis in Patients Treated for Psoriasis
3.4. Pediatric Population
3.5. Interventional Considerations
3.6. From Today to Tomorrow
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATD | autoimmune thyroid diseases |
| APS | autoimmune poly-glandular syndrome |
| aHR | adjusted Hazard Ratio |
| aOR | adjusted Odds Ratio |
| CRP | C reactive protein |
| CI | confidence interval |
| DPP4is | dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors |
| EP | erythrodermic psoriasis |
| EGF | Epidermal Growth Factor |
| fT3 | free triiodothyronine |
| fT4 | free thyroxine |
| GD | Graves’ disease |
| GPP | generalized pustular psoriasis |
| HLA | Human Leukocytes Antigen |
| HT | Hashimoto’s thyroiditis |
| IFN | interferon |
| IL | interleukin |
| IGF | Insulin like Growth Factor |
| MHC | major histocompatibility complex |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| PsA | psoriatic arthritis |
| PsC | cutaneous psoriasis |
| PP | pustular psoriasis |
| PV | psoriasis vulgaris |
| PASI | Psoriasis Area and Severity Index |
| SNP | Single Nucleotide Polymorphism |
| TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor |
| TPOAb | antithyroperoxidase antibodies |
| TgAb | antithyroglobulin antibodies |
| TSH | Thyroid Stimulating Hormone |
| TRAb | TSH Receptor antibodies |
| T3 | triiodothyronine |
| T4 | thyroxine |
| TNFAIP3 | Tumor Necrosis Factor α-induced protein 3 |
References
- Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/204417/9789241565189_eng.pdf.psoriasis?sequence=1 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Elmets, C.A.; Korman, N.J.; Prater, E.F.; Wong, E.B.; Rupani, R.N.; Kivelevitch, D.; Armstrong, A.W.; Connor, C.; Cordoro, K.M.; Davis, D.M.R.; et al. Joint AAD-NPF Guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with topical therapy and alternative medicine modalities for psoriasis severity measures. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 84, 432–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rielly, D.D.; Jani, M.; Rahman, P.; Elder, J.T. The Genetics of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 2019, 95, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raychaudhuri, S.K.; Maverakis, E.; Raychaudhuri, S.P. Diagnosis and classification of psoriasis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruffilli, I.; Ragusa, F.; Benvenga, S.; Vita, R.; Antonelli, A.; Fallahi, P.; Ferrari, S.M. Psoriasis, Psoriatic Arthritis, and Thyroid Autoimmunity. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Read, C. Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment of Psoriasis: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldenstein-Schainberg, C.; Favarato, M.H.; Ranza, R. Current and relevant concepts in psoriatic arthritis. Rev. Bras. Reumatol. 2012, 52, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, L.C.; Aslam, T.; Al Balushi, F.; Burden, A.D.; Burden-Teh, E.; Caperon, A.R.; Cerio, R.; Chattopadhyay, C.; Chinoy, H.; Goodfield, M.J.; et al. Comparison of three screening tools to detect psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis (CONTEST study). Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 168, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestle, F.O.; Kaplan, D.H.; Barker, J. Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrowski, Y.; Schauber, J. Cathelicidin LL-37: A defense molecule with a potential role in psoriasis pathogenesis. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwan, W.; Nestle, F.O. Pathogenesis and treatment of psoriasis: Exploiting pathophysiological pathways for precision medicine. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33 (Suppl. S93), S2–S6. [Google Scholar]
- Blauvelt, A. T-helper 17 cells in psoriatic plaques and additional genetic links between IL-23 and psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1064–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lowes, M.A.; Russell, C.B.; Martin, D.A.; Towne, J.E.; Krueger, J.G. The IL-23/T17 pathogenic axis in psoriasis is amplified by keratinocyte responses. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boehncke, W.H.; Schön, M.P. Psoriasis. Lancet 2015, 386, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santus, P.; Rizzi, M.; Radovanovic, D.; Airoldi, A.; Cristiano, A.; Conic, R.; Petrou, S.; Pigatto, P.D.M.; Bragazzi, N.; Colombo, D.; et al. Psoriasis and Respiratory Comorbidities: The Added Value of Fraction of Exhaled Nitric Oxide as a New Method to Detect, Evaluate, and Monitor Psoriatic Systemic Involvement and Therapeutic Efficacy. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 3140682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, H.; Takeshita, J.; Mehta, N.N.; Kimmel, S.E.; Ogdie, A.; Margolis, D.J.; Shin, D.B.; Attor, R.; Troxel, A.B.; Gelfand, J.M. Psoriasis severity and the prevalence of major medical comorbidity: A population-based study. JAMA Dermatol. 2013, 149, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vashist, S.; Mahajan, V.K.; Mehta, K.S.; Chauhan, P.S.; Yadav, R.S.; Sharma, S.B.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, A.; Chowdhary, B.; Kumar, P. Association of Psoriasis with Autoimmune Disorders: Results of a Pilot Study. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2020, 11, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.J.; Nguyen, T.U.; Poon, K.Y.; Herrinton, L.J. The association of psoriasis with autoimmune diseases. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 67, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malerba, M.; Damiani, G.; Radaeli, A.; Ragnoli, B.; Olivini, A.; Calzavara-Pinton, P.G. Narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy in psoriasis reduces proinflammatory cytokine levels and improves vitiligo and neutrophilic asthma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 1544–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.N.; Armstrong, A.W. Psoriasis and autoimmune disorders: A review of the literature. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 67, 1076–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandru, F.; Carsote, M.; Albu, S.E.; Dumitrascu, M.C.; Valea, A. Vitiligo and chronic autoimmune thyroiditis. J. Med. Life 2021, 14, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Li, C.W.; Hammerstad, S.S.; Stefan, M.; Tomer, Y. Immunogenetics of autoimmune thyroid diseases: A comprehensive review. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 64, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antonelli, A.; Ferrari, S.M.; Corrado, A.; Di Domenicantonio, A.; Fallahi, P. Autoimmune thyroid disorders. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogusławska, J.; Godlewska, M.; Gajda, E.; Piekiełko-Witkowska, A. Cellular and molecular basis of thyroid autoimmunity. Eur. Thyroid J. 2022, 11, e210024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aversa, T.; Corica, D.; Zirilli, G.; Pajno, G.B.; Salzano, G.; De Luca, F.; Wasniewska, M. Phenotypic Expression of Autoimmunity in Children With Autoimmune Thyroid Disorders. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, L.R.; Neves, C.; Melo, M.; Soares, P. Selenium and Selenoproteins in Immune Mediated Thyroid Disorders. Diagnostics 2018, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dwivedi, S.N.; Kalaria, T.; Buch, H. Thyroid autoantibodies. J. Clin. Pathol. 2023, 76, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vastarella, M.; Megna, M.; Lupoli, G.A.; Napolitano, M.; Gallo, L.; Balato, A.; Tasso, M.; Costa, L.; Fabbrocini, G.; Peluso, R. Is there any association between psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and thyroid autoimmunity? Australas. J. Dermatol. 2021, 62, e207–e211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, V.; Cook, R.J.; Edwin, J.; Shen, H.; Pellett, F.J.; Shanmugarajah, S.; Rosen, C.F.; Gladman, D.D. Soluble biomarkers differentiate patients with psoriatic arthritis from those with psoriasis without arthritis. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiniakou, E.; Costenbader, K.H.; Kriegel, M.A. Sex-specific environmental influences on the development of autoimmune diseases. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 149, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fallahi, P.; Ferrari, S.M.; Ruffilli, I.; Elia, G.; Miccoli, M.; Sedie, A.D.; Riente, L.; Antonelli, A. Increased incidence of autoimmune thyroid disorders in patients with psoriatic arthritis: A longitudinal follow-up study. Immunol. Res. 2017, 65, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofman, A.; Brusselle, G.G.O.; Murad, S.D.; van Duijn, C.M.; Franco, O.H.; Goedegebure, A.; Ikram, M.A.; Klaver, C.C.; Nijsten, T.E.; Peeters, R.P.; et al. The Rotterdam Study: 2016 objectives and design update. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 30, 661–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.R.; Bano, A.; Wakkee, M.; Korevaar, T.I.M.; Franco, O.H.; Nijsten, T.E.C.; Peeters, R.P.; Chaker, L. The association of autoimmune thyroid disease (AITD) with psoriatic disease: A prospective cohort study, systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 177, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, J.; Ma, C.; Wang, R.; Lin, L.; Gao, L.; Chen, S.; Lu, X. Relationship between Different Psoriasis Types and Thyroid Dysfunction: A Retrospective Analysis. Scanning 2021, 2021, 1834556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misiak-Galazka, M.; Wolska, H.; Galazka, A.; Kwiek, B.; Rudnicka, L. General Characteristics and Comorbidities in Patients with Palmoplantar Pustulosis. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. 2018, 26, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trattner, H.; Blüml, S.; Steiner, I.; Plut, U.; Radakovic, S.; Tanew, A. Quality of life and comorbidities in palmoplantar pustulosis—A cross-sectional study on 102 patients. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 1681–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namiki, K.; Kamata, M.; Shimizu, T.; Chijiwa, C.; Uchida, H.; Okinaga, S.; Harafuji, M.; Nagata, M.; Fukaya, S.; Hayashi, K.; et al. Thyroid dysfunction in patients with psoriasis: Higher prevalence of thyroid dysfunction in patients with generalized pustular psoriasis. J. Dermatol. 2020, 47, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Gao, Y.; Liu, N.; Li, Y.; Chen, F.; Yu, N.; Ding, Y.; Yi, X. Higher prevalence of thyroid dysfunction in patients with erythrodermic psoriasis. J. Dermatol. 2020, 47, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Dong, Y.; Lu, L.; Zhang, N. C-reactive protein and thyroid-stimulating hormone levels as risk factors for hypothyroidism in patients with subacute thyroiditis. Endocr. Connect. 2021, 10, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Wang, J.; Lin, Y.S.; Tung, T.H.; Chi, C.C. Increased risk for incident thyroid diseases in people with psoriatic disease: A cohort study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Thatiparthi, A.; Martin, A.; Wu, J.J. Association between psoriasis and thyroid dysfunction among US adults in the 2009-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 86, 897–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiguradze, T.; Bruins, F.M.; Guido, N.; Bhattacharya, T.; Rademaker, A.; Florek, A.G.; Posligua, A.; Amin, S.; Laumann, A.E.; West, D.P.; et al. Evidence for the association of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis with psoriasis: A cross-sectional retrospective study. Int. J. Dermatol. 2017, 56, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valduga, J.A.G.; Rebeiko, L.B.; Skare, T.L. Prevalence of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis in psoriasis patients. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2021, 67, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wu, R.; Li, S.; Su, Y.; Zhang, P. Prevalence of autoimmune thyroid disease in patients with psoriasis: A meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e055538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorakopoulou, E.; Yiu, Z.Z.; Bundy, C.; Chularojanamontri, L.; Gittins, M.; Jamieson, L.A.; Motta, L.; Warren, R.B.; Griffiths, C.E. Early- and late-onset psoriasis: A cross-sectional clinical and immunocytochemical investigation. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 175, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yumnam, D.; Kansal, N.K.; Kant, R. Association of Psoriasis With Thyroid Disorders: A Hospital-Based, Cross-Sectional Study. Cureus 2022, 14, e22987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alidrisi, H.A.; Al Hamdi, K.; Mansour, A.A. Is There Any Association Between Psoriasis and Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis? Cureus 2019, 19, e4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, P.R.; Isaksen, J.L.; Jemec, G.B.; Ellervik, C.; Kanters, K.J. Thyroid function in psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 206–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bergholdt, H.K.M.; Bathum, L.; Kvetny, J.; Rasmussen, D.B.R.; Moldow, B.; Hoeg, T.; Jemec, G.B.E.; Berner-Nielsen, H.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Ellervik, C. Study design, participation and characteristics of the Danish General Suburban Population Study. Dan. Med. J. 2013, 60, A4693. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.C.; Yew, Y.W. Psoriasis and thyroid profile: Analysis of the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey database. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2016, 82, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robati, R.M.; Toossi, P.; Rahmati-Roodsari, M.; Khalilazar, S.; Abolhasani, E.; Namazi, N.; Younespour, S. Association of psoriasis severity with serum prolactin, thyroid hormones, and cortisol before and after treatment. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 921819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilatou, E.; Papadavid, E.; Papastamatakis, P.; Alexakos, D.; Koumaki, D.; Katsimbri, P.; Hadjidakis, D.; Dimitriadis, G.; Rigopoulos, D. No association of psoriasis with autoimmune thyroiditis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tas, B.; Kabeloglu, V.; Soysal, A.; Atakli, D. Sleep Quality in Psoriasis Patients and its Relations with Possible Affecting Factors. Med. Bull. Sisli Eftal Hosp. 2020, 54, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rana, A.; Mahajan, V.K.; Chauhan, P.S.; Mehta, K.S.; Sharma, S.B.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, R. The Association of Thyroid Dysfunction with Chronic Plaque Psoriasis: A Hospital-Based Retrospective Descriptive Observational Study. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2020, 11, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktem, A.; Uysal, P.I.; Akdoğan, N.; Tokmak, A.; Yalcin, B. Clinical characteristics and associations of palmoplantar pustulosis: An observational study. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2020, 95, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olazagasti, J.M.; Ma, J.E.; Wetter, D.A. Clinical Features, Etiologic Factors, Associated Disorders, and Treatment of Palmoplantar Pustulosis: The Mayo Clinic Experience, 1996–2013. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, D.; Schweizer, U. Thyroid Hormone Transport and Transporters. Vitam. Horm. 2018, 106, 19–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancino, G.; Miro, C.; Di Cicco, E.; Dentice, M. Thyroid hormone action in epidermal development and homeostasis and its implications in the pathophysiology of the skin. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini, D.; Sibilio, A.; Dentice, M.; Missero, C. An Intimate Relationship between Thyroid Hormone and Skin: Regulation of Gene Expression. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roman, I.I.; Constantin, A.M.; Marina, M.E.; Orasan, R.I. The role of hormones in the pathogenesis of psoriasis vulgaris. Clujul Med. 2016, 89, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utaş, S.; Köse, K.; Yazici, C.; Akdaş, A.; Keleştimur, F. Antioxidant potential of propylthiouracil in patients with psoriasis. Clin. Biochem. 2002, 35, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safer, J.D. Thyroid hormone action on skin. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2012, 19, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Contreras-Jurado, C.; García-Serrano, L.; Gómez-Ferrería, M.; Costa, C.; Paramio, J.M.; Aranda, A. The thyroid hormone receptors as modulators of skin proliferation and inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 24079–24088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antonelli, A.; Ferrari, S.M.; Giuggioli, D.; Ferrannini, E.; Ferri, C.; Fallahi, P. Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand (CXCL)10 in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabgah, A.G.; Fattahi, E.; Shahneh, F.Z. Interleukin-17 in human inflammatory diseases. Postepy Dermatol. Alergol. 2014, 31, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumitru, N.; Ghemigian, A.; Carsote, M.; Albu, S.E.; Terzea, D.; Valea, A. Thyroid nodules after initial evaluation by primary health care practitioners: An ultrasound pictorial essay. Arch. Balk. Med. Union 2016, 51, 434–438. [Google Scholar]
- Antonelli, A.; Fallahi, P.; Delle Sedie, A.; Ferrari, S.M.; Maccheroni, M.; Bombardieri, S.; Riente, L.; Ferrannini, E. High values of Th1 (CXCL10) and Th2 (CCL2) chemokines in patients with psoriatic arthtritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2009, 27, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Papewalis, C.; Domberg, J.; Scherbaum, W.A.; Schott, M. Chemokines and autoimmune thyroid diseases. Horm. Metab. Res. 2008, 40, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júnior, D.S.T. Environmental and individual factors associated with protection and predisposition to autoimmune diseases. Int J. Health Sci. 2020, 14, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ordoñez-Cañizares, M.C.; Mena-Vázquez, N.; Redondo-Rodriguez, R.; Manrique-Arija, S.; Jimenez-Núñez, F.G.; Ureña-Garnica, I.; Fernández-Nebro, A. Frequency of Polyautoimmunity in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 28, e38–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, M.T.; Subramanian, A.; Adderley, N.J.; Zemedikun, D.T.; Gkoutos, G.V.; Nirantharakumar, K. Allergic diseases and long-term risk of autoimmune disorders: Longitudinal cohort study and cluster analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1900476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manvi, S.; Mahajan, V.K.; Mehta, K.S.; Yadav, R.S.; Bhushan, S.; Chauhan, P.S. Psoriasis and Co-morbidities: Is Hyperhomocystienemia the Common Link? J. Assoc. Physicians India 2019, 67, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fogel, R.; Comerford, M.; Chilukuri, P.; Orman, E.; Chalasani, N.; Lammert, C. Extrahepatic Autoimmune Diseases are Prevalent in Autoimmune Hepatitis Patients and Their First-Degree Relatives: Survey Study. Interact. J. Med. Res. 2018, 7, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldini, E.; Odorisio, T.; Tuccilli, C.; Persechino, S.; Sorrenti, S.; Catania, A.; Pironi, D.; Carbotta, G.; Giacomelli, L.; Arcieri, S.; et al. Thyroid diseases and skin autoimmunity. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2018, 19, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Mao, X.; Song, R.; Mu, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.A. Psoriasis Susceptibility 1 Candidate 1 (PSORS1C1) Polymorphism is Associated with Autoimmune Thyroid Disease in a Chinese Han Population. Immunol. Investig. 2022, 51, 1222–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hautala, T.; Vähäsalo, P.; Kuismin, O.; Keskitalo, S.; Rajamäki, K.; Väänänen, A.; Simojoki, M.; Säily, M.; Pelkonen, I.; Tokola, H.; et al. A Family With A20 Haploinsufficiency Presenting With Novel Clinical Manifestations and Challenges for Treatment. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 27, e583–e587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solvin, Å.Ø.; Chawla, K.; Olsen, L.C.; Hegre, S.A.; Danielsen, K.; Jenssen, M.; Furberg, A.S.; Saunes, M.; Hveem, K.; Saetrom, P.; et al. MicroRNA profiling of psoriatic skin identifies 11 miRNAs associated with disease severity. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 31, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, A.; Miśkiewicz, J.; Strzelec, K.; Wcisło-Dziadecka, D.; Strzalka-Mrozik, B. Apoptosis in Autoimmunological Diseases, with Particular Consideration of Molecular Aspects of Psoriasis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e922035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, S.; Korkmaz, H. Effect of alterations in apoptotic pathway on development of metabolic syndrome in patients with psoriasis vulgaris. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 176, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laron, Z.; Shulman, L.; Hampe, C.; Blumenfeld, O. Hypothesis: Viral infections of pregnant women may be early triggers of childhood type 1 diabetes and other autoimmune disease. J. Autoimmun. 2023, 135, 102977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Ruperto, L.; Busca-Arenzana, C.; Díez-Vidal, A.; Robles-Marhuenda, Á.; Díaz-Almirón, M.; Micán, R.E.; Montejano, R.; Valencia, E.; Montes, M.; Martin-Carbonero, L.; et al. Prevalence and Temporal Trends of Autoimmune Diseases in People Living with HIV. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, Y.F.; Chuang, P.H.; Jen, I.A.; Chen, M.; Lan, Y.C.; Liu, Y.L.; Lee, Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, Y.A. Incidence of autoimmune diseases in a nationwide HIV/AIDS patient cohort in Taiwan, 2000–2012. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mormile, I.; Punziano, A.; Riolo, C.A.; Granata, F.; Williams, M.; de Paulis, A.; Spadaro, G.; Rossi, F.W. Common Variable Immunodeficiency and Autoimmune Diseases: A Retrospective Study of 95 Adult Patients in a Single Tertiary Care Center. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 652487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raglianti, V.; Rossi, G.M.; Vaglio, A. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: An update for nephrologists. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efe, C.; Torgutalp, M.; Henriksson, I.; Alalkim, F.; Lytvyak, E.; Trivedi, H.; Eren, F.; Fischer, J.; Chayanupatkul, M.; Coppo, C.; et al. Extrahepatic autoimmune diseases in primary biliary cholangitis: Prevalence and significance for clinical presentation and disease outcome. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Cao, Z.M.; Zhang, L.L.; Dai, X.C.; Liu, Z.J.; Zeng, Y.X.; Li, X.Y.; Wu, Q.J.; Lv, W.L. Helicobacter Pylori and Autoimmune Diseases: Involving Multiple Systems. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 833424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.H.; Chang, Y.S.; Lin, T.M.; Hu, L.F.; Hou, T.Y.; Hsu, H.C.; Shen, Y.C.; Kuo, P.I.; Chen, W.S.; Lin, Y.C.; et al. Proton Pump Inhibitors Increase the Risk of Autoimmune Diseases: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 736036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kridin, K.; Amber, K.; Khamaisi, M.; Comaneshter, D.; Batat, E.; Cohen, A.D. Is there an association between dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and autoimmune disease? A population-based study. Immunol. Res. 2018, 66, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichrath, J.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Vogt, T.; Holick, M.F. Targeting the vitamin D endocrine system (VDES) for the management of inflammatory and malignant skin diseases: An historical view and outlook. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2016, 17, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweta, K.; Freeda, M.M.; Lenin, M. The Putative Role of Thyroid Hormones and Vitamin D on Severity and Quality of Life in Psoriasis. Int. J. Appl. Basic Med. Res. 2020, 10, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osher, E.; Macaulay, V.M. Therapeutic Targeting of the IGF Axis. Cells 2019, 8, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garmendia, J.V.; García, A.H.; De Sanctis, C.V.; Hajdúch, M.; De Sanctis, J.B. Autoimmunity and Immunodeficiency in Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Prolonged COVID-19. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 45, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallek, M.; Adorjan, K.; Behrends, U.; Ertl, G.; Suttorp, N.; Lehmann, C. Long COVID Working Group of the Scientific Advisory Board within the German Medical Association. Post-COVID Syndrome. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votto, M.; Castagnoli, R.; Marseglia, G.L.; Licari, A.; Brambilla, I. COVID-19 and autoimmune diseases: Is there a connection? Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 23, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, N.K.; Bansal, S.K. Autoimmune Thyroid Disease and Psoriasis Vulgaris after COVID-19 in a Male Teenager. Case Rep. Pediatr. 2021, 2021, 7584729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishina, I.A.; Zakharova, M.Y.; Kurbatskaia, I.N.; Mamedov, A.E.; Belogurov, A.A., Jr.; Gabibov, A.G. MHC Class II Presentation in Autoimmunity. Cells 2023, 12, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandalova, T.; Sala, B.M.; Achour, A. Structural aspects of chemical modifications in the MHC-restricted immunopeptidome; Implications for immune recognition. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 861609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmungil, H.; İlgen, U.; Direskeneli, R.H. Autoimmunity in psoriatic arthritis: Pathophysiological and clinical aspects. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 51, 1601–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, M.Y.; Belyanina, T.A.; Sokolov, A.V.; Kiselev, I.S.; Mamedov, A.E. The Contribution of Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II Genes to an Association with Autoimmune Diseases. Acta Nat. 2019, 11, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Tian, E.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Z.; Peng, Q. Gut microbiota and its roles in the pathogenesis and therapy of endocrine system diseases. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 268, 127291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhaș, M.C.; Gavrilaș, L.I.; Candrea, R.; Cătinean, A.; Mocan, A.; Miere, D.; Tătaru, A. Gut Microbiota in Psoriasis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thye, A.Y.; Bah, Y.R.; Law, J.W.; Tan, L.T.; He, Y.W.; Wong, S.H.; Thurairajasingam, S.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H.; Letchumanan, V. Gut-Skin Axis: Unravelling the Connection between the Gut Microbiome and Psoriasis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kierasińska, M.; Donskow-Łysoniewska, K. Both the microbiome and the macrobiome can influence immune responsiveness in psoriasis. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 46, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tizu, M.; Mărunțelu, I.; Cristea, B.M.; Nistor, C.; Ishkitiev, N.; Mihaylova, Z.; Tsikandelova, R.; Miteva, M.; Caruntu, A.; Sabliov, C.; et al. PLGA Nanoparticles Uptake in Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth and Oral Keratinocyte Stem Cells. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenneman, A.C.; Bruinstroop, E.; Nieuwdorp, M.; van der Spek, A.H.; Boelen, A. A Comprehensive Review of Thyroid Hormone Metabolism in the Gut and Its Clinical Implications. Thyroid 2023, 33, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargiel, P.; Szczuko, M.; Stachowska, L.; Prowans, P.; Czapla, N.; Markowska, M.; Petriczko, J.; Kledzik, J.; Jędrzejczyk-Kledzik, A.; Palma, J.; et al. Microbiome Metabolites and Thyroid Dysfunction. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, N. The genetics of pediatric cutaneous autoimmunity: The sister diseases vitiligo and alopecia areata. Clin. Dermatol. 2022, 40, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayir, A.; Engin, R.I.; Turan, M.I.; Pala, E. Psoriasis vulgaris and autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I: A case report. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 27, 791–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poojary, S.A.; Lodha, N.; Gupta, N. Psoriasis in autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I: A possible complication or a non-endocrine minor component? Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2015, 81, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, B.; Saur, S.; Rall, K.; Pecher, A.C.; Hübner, S.; Henes, J.; Henes, M. Prevalence of autoimmune disease in women with premature ovarian failure. Eur. J. Contracept. Reprod. Health Care 2020, 25, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørklund, G.; Pivin, M.; Hangan, T.; Yurkovskaya, O.; Pivina, L. Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1: Clinical manifestations, pathogenetic features, and management approach. Autoimmun. Rev. 2022, 21, 103135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perniola, R.; Fierabracci, A.; Falorni, A. Autoimmune Addison’s Disease as Part of the Autoimmune Polyglandular Syndrome Type 1: Historical Overview and Current Evidence. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 606860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezzio, C.; Della Corte, C.; Vernero, M.; Di Luna, I.; Manes, G.; Saibeni, S. Inflammatory bowel disease and immune-mediated inflammatory diseases: Looking at the less frequent associations. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2022, 15, 17562848221115312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanWagner, L.B.; Rinella, M.E. Extrahepatic Manifestations of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Curr. Hepatol. Rep. 2016, 15, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akiyama, M.; Ueno, T.; Kanzaki, A.; Kuwana, M.; Nagao, M.; Saeki, H. Association of psoriasis with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, Sjögren’s syndrome and dermatomyositis. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 711–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichna, M.; Małecki, P.P.; Gębarski, B.; Gębarska, H.; Ruchała, M. Aggregation of autoimmunity in extended families of people with autoimmune Addison disease. Intern. Med. J. 2022, 52, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, P.; Ferrari, S.M.; Ruffilli, I.; Elia, G.; Biricotti, M.; Vita, R.; Benvenga, S.; Antonelli, A. The association of other autoimmune diseases in patients with autoimmune thyroiditis: Review of the literature and report of a large series of patients. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 1125–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelada, M.; Avari, P.; Farag, S.; Akishar, R.; Jain, R.; Aziz, A.; Feeney, C.; Bravis, V.; Meeran, K.; Lee, V. Association of Other Autoimmune Diseases With Thyroid Eye Disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 644200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takir, M.; Özlü, E.; Köstek, O.; Türkoğlu, Z.; Mutlu, H.H.; Uzunçakmak, T.K.; Akdeniz, N.; Karadağ, A.S. Skin findings in autoimmune and nonautoimmune thyroid disease with respect to thyroid functional status and healthy controls. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 47, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusiñol, L.; Camiña-Conforto, G.; Puig, L. Biologic treatment of psoriasis in oncologic patients. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2022, 22, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Yoo, D.M.; Chung, J.; Choi, H.G. Thyroid Cancer and Psoriasis: A Nested Case-Control Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borson-Chazot, F.; Borget, I.; Mathonnet, M.; Leenhardt, L. SFE-AFCE-SFMN 2022 consensus on the management of thyroid nodules: Epidemiology and challenges in the management of thyroid nodules. Ann. Endocrinol. 2022, 83, 378–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoula, E.; Iakovou, I.; Giovanella, L.; Vrachimis, A. Updated clinical management guidance during the COVID-19 pandemic: Thyroid nodules and cancer. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2022, 186, G1–G7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apalla, Z.; Rapoport, B.; Sibaud, V. Dermatologic immune-related adverse events: The toxicity spectrum and recommendations for management. Int. J. Women’s Dermatol. 2021, 7 Pt A, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, V.; Fernández, M.A.; Collazo-Lorduy, A.; Franco, F.; Núñez, B.; Provencio, M. Use of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with solid tumors and pre-existing autoimmune or inflammatory disease: Real-world data. Lung Cancer Manag. 2021, 10, LMT51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danlos, F.X.; Voisin, A.L.; Dyevre, V.; Michot, J.M.; Routier, E.; Taillade, L.; Champiat, S.; Aspeslagh, S.; Haroche, J.; Albiges, L.; et al. Safety and efficacy of anti-programmed death 1 antibodies in patients with cancer and pre-existing autoimmune or inflammatory disease. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 91, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.J.; Weppler, A.; Bhave, P.; Allayous, C.; Patrinely, J.R., Jr.; Ott, P.; Sandhu, S.; Haydon, A.; Lebbe, C.; Johnson, D.B.; et al. Combination anti-PD1 and ipilimumab therapy in patients with advanced melanoma and pre-existing autoimmune disorders. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, F.; Zeng, X. Rheumatic immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors compared with placebo in oncologic patients: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2021, 12, 2040622320976996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Mazón, I.; Sánchez-Bilbao, L.; Martín-Varillas, J.L.; García-Castaño, A.; Delgado-Ruiz, M.; Bernat Piña, I.; Hernández, J.L.; Castañeda, S.; Llorca, J.; González-Gay, M.A.; et al. Immune-related adverse events in patients with solid-organ tumours treated with immunotherapy: A 3-year study of 102 cases from a single centre. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elosua-González, M.; Pampín-Franco, A.; Mazzucchelli-Esteban, R.; Mielgo-Rubio, X.; Rodriguez-Vásquez, X.; García-Zamora, E.; López-Estebaranz, J.L. A case of de novo palmoplantar psoriasis with psoriatic arthritis and autoimmune hypothyroidism after receiving nivolumab therapy. Dermatol. Online J. 2017, 23, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B.; Sullivan, R.J.; Ott, P.A.; Carlino, M.S.; Khushalani, N.I.; Ye, F.; Guminski, A.; Puzanov, I.; Lawrence, D.P.; Buchbinder, E.I.; et al. Ipilimumab Therapy in Patients With Advanced Melanoma and Preexisting Autoimmune Disorders. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furtak, A.; Wedrychowicz, A.; Starzyk, J. Anti-tumour necrosis factor α therapy—Does it increase the risk of thyroid disease or protect against its development? Pediatr. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2020, 26, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez Quintero, B.; Yazbeck, C.; Sweeney, L.B. Thyroiditis: Evaluation and Treatment. Am. Fam. Physician 2021, 104, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.G.; An, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Yoon, M.S.; Lee, H.J. A Case of Interstitial Lung Disease and Autoimmune Thyroiditis Associated with Ustekinumab. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2019, 99, 331–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.A.; Chuang, W.C.; Hong, C.H. Subacute thyroiditis in a patient with psoriasis treated with a tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor. Int. J. Dermatol. 2018, 57, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabi, B.; Ayob, S. Thyrotoxicosis Associated with Ustekinumab Treatment for Psoriasis. Case Rep. Dermatol. Med. 2020, 2020, 8868553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, J.; Fujikawa, K.; Akagi, M.; Nakaji, K.; Yasui, J.; Hanatani, Y.; Hara, T.; Mizokami, A.; Kawakami, A. Subacute thyroiditis in a patient with psoriatic arthritis switched from secukinumab to adalimumab: A case report and literature review. Mod. Rheumatol. Case Rep. 2021, 5, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senlis, M.; Ottaviani, S.; Gardette, A.; Palazzo, E.; Coustet, B.; Dieudé, P. Subacute thyroiditis in psoriatic arthritis treated by adalimumab. Jt. Bone Spine 2017, 84, 745–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, R.; Opris, A.; Costantino, F.; Hayem, G.; Breban, M. Cytomegalovirus subacute thyroiditis in a patient treated by infliximab for psoriatic arthritis. Jt. Bone Spine 2016, 83, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capo, A.; Amerio, P. Polyglandular autoimmune syndrome type III with a prevalence of cutaneous features. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 42, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Skowronek, I.; Michalczyk, A.; Piekarski, R.; Wysocka-Łukasik, B.; Banecka, B. Type III Polyglandular Autoimmune Syndromes in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2013, 20, 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Van Straalen, J.W.; de Roock, S.; Giancane, G.; Alexeeva, E.; Koskova, E.; Mesa-Del-Castillo Bermejo, P.; Zulian, F.; Civino, A.; Montin, D.; Wulffraat, N.M.; et al. Prevalence of familial autoimmune diseases in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Results from the international Pharmachild registry. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2022, 20, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tronconi, E.; Miniaci, A.; Pession, A. The autoimmune burden in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2017, 43, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarandi, E.; Kruger Krasagakis, S.; Tsoukalas, D.; Rudofsky, G.; Tsatsakis, A. A Clinical Trial for the Identification of Metabolic Biomarkers in Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis and in Psoriasis: Study Protocol. Pathophysiology 2021, 28, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, J.; Cook, N.R.; Alexander, E.K.; Friedman, S.; Walter, J.; Bubes, V.; Kotler, G.; Lee, I.M.; Manson, J.E.; Costenbader, K.H. Vitamin D and marine omega 3 fatty acid supplementation and incident autoimmune disease: VITAL randomized controlled trial. BMJ 2022, 376, e066452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passali, M.; Josefsen, K.; Frederiksen, J.L.; Antvorskov, J.C. Current Evidence on the Efficacy of Gluten-Free Diets in Multiple Sclerosis, Psoriasis, Type 1 Diabetes and Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifico, A.; Conic, R.R.Z.; Cristaudo, A.; Garbarino, S.; Ardigò, M.; Morrone, A.; Iacovelli, P.; di Gregorio, S.; Pigatto, P.D.M.; Grada, A.; et al. Diet-Related Phototoxic Reactions in Psoriatic Patients Undergoing Phototherapy: Results from a Multicenter Prospective Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, P.D.; Harkin, G.; Hussey, M.; Christopher, B.; Kiat, C.; Chin, J.L.; Trimble, V.; McNamara, D.; MacMathuna, P.; Egan, B.; et al. Prevalence of coexisting autoimmune thyroidal diseases in coeliac disease is decreasing. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2020, 8, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conti, L.; Lahner, E.; Galli, G.; Esposito, G.; Carabotti, M.; Annibale, B. Risk Factors Associated with the Occurrence of Autoimmune Diseases in Adult Coeliac Patients. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 3049286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bibbò, S.; Pes, G.M.; Usai-Satta, P.; Salis, R.; Soro, S.; Quarta Colosso, B.M.; Dore, M.P. Chronic autoimmune disorders are increased in coeliac disease: A case-control study. Medicine 2017, 96, e8562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegiel, M.; Antosz, A.; Gieburowska, J.; Szeliga, K.; Hankus, M.; Grzybowska-Chlebowczyk, U.; Wiecek, S.; Malecka-Tendera, E.; Gawlik, A. Autoimmunity Predisposition in Girls with Turner Syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanakatti Shankar, R. Immunological Profile and Autoimmunity in Turner Syndrome. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2020, 93, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Authors/ Year of Publication Reference | Type of Study | Studied Population | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Khan 2016 [33] | Prospective cohort study (Rotterdam studyMeta-analysis) (4 studies) Systematic review (7 studies) | Rotterdam study: | TPOAb positivity 1077 (13.1%) Association between psoriasis and:
|
| N = 8.214 | |||
| mean age: 62.3 ± 8.4 y | |||
| Theodorakopoulou 2016 [45] | Cross-sectional study | Patients with psoriasis: | Autoimmune thyroiditis N1 < N2: OR = 5.05; 95% CI 1.62–15.7 |
| N1 = 278 early onset (<40 y) | |||
| N2 = 62 late onset (>40 y) | |||
| Kiguradze 2017 [42] | Cross-sectional study | N1 = 9654 individuals with psoriasis | Association between psoriasis and HT: OR = 2.49; 95% CI 1.79–3.48, p < 0.0001 |
| N2 = 1745 patients with HT | |||
| Trattner 2017 [36] | Cross-sectional study | N = 102 patients with palmoplantar pustulosis | |
| Fallahi 2017 [31] | Prospective study | N1 = 97 PsA | PsA more frequent vs. controls:
|
| mean age: 56 ± 12 y | |||
| N2 = 97 controls | |||
| mean age: 57 ± 11 y | |||
| Misiak-Galazka 2018 [35] | Prospective study | N1 = patients with palmoplantar pustulosis | Thyroid disease: 31.75% vs. 13.51%; p = 0.0421 |
| N2 = 34 PV | |||
| Namiki 2019 [37] | Retrospective study | N1 = 51 PV | Highest prevalence of thyroid dysfunction in GPP group (45% GPP vs. 13% PsA, respective 8% PV) |
| mean age: 52.86 ± 21.0 y | |||
| N2 = 23 PsA | |||
| mean age: 46.7 ± 15.86 y | |||
| N3 = 11 GPP | |||
| mean age: 63.73 ± 11.63 y | |||
| Wang 2019 [40] | Retrospective population-based cohort study | N1 = 149,576 PV | PV patients at risk of developing:
|
| mean age: 45.11 ± 20.09 y | |||
| N2 = 162,842 control group | |||
| mean age: 44.95 ± 19.91 y | |||
| Vashist 2020 [17] | Pilot study | N = 80 patients with psoriasis |
|
| age between 13 and 75 y | |||
| Zheng 2020 [38] | Retrospective study | N1 = 74 PV | Highest prevalence of TD in EP (59.57%) followed by GPP (42.11%), PsA (19.05%), PV (18.99%) |
| mean age: 56.12 ± 14.05 y N2 = 42 PsA | |||
| mean age: 53.79 ± 11.43 y | |||
| N3 = 38 GPP | |||
| mean age: 46.16 ± 17.69 y | |||
| N4 = 47 EP | |||
| mean age: 57.51 ± 15.20 y | |||
| N5 = 80 control group | |||
| mean age 56.78 ± 15.48 y | |||
| Vastarella 2021 [28] | Prospective study | N = 208 | PsA vs. PsC:
|
| N1 = 108 PsA | |||
| mean age: 39.9 ± 10.8 y | |||
| N2 = 100 PsC | |||
| mean age: 50.1 ± 11.7 y | |||
| Du 2021 [34] | Retrospective study | N1 = 300 PV |
|
| mean age: 47.8 ± 15.5 y | |||
| N2 = 60 PP | |||
| mean age: 46.6 ± 18.6 y | |||
| N3 = 54 EP | |||
| mean age: 51.8 ± 15.8 y | |||
| N4 = 54 PsA | |||
| mean age: 47.4 ± 13.1 y | |||
| N5 = 200 controls | |||
| Liu 2022 [41] | Population based cohort study | N = 15.091 | |
| Valdulga 2022 [43] | Cross-sectional observational study | N1 = 60 patients with psoriasis | HT prevalence: 21.6 vs. 6.6% (p = 0.002)| |
| N2 = 60 controls | |||
| Zhang 2022 [44] | Meta-analysis (11 studies) | N1= 253.313 PV | PV has:
|
| N2= 1.376.533 controls | |||
| Yumnam 2022 [46] | Hospital-Based, Cross-Sectional Study | N = 111 patients with psoriasis | Thyroid dysfunction associated with a severe form of psoriasis versus mild psoriasis (61.9% vs. 38.1%) |
| Authors/ Year of Publication Reference | Type of Study | Studied Population | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lai 2016 [50] | Population-based study | N = 5560 responders from 2011–2012 U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey database | No correlation between psoriasis and thyroid involvement |
| Olazagasti 2017 [56] | Retrospective study | N = 215 patients with palmoplantar pustulosis |
|
| Vassilatou 2017 [52] | Case-control study | N1 = 114 patients with psoriasis | Psoriasis group versus controls:
|
| N2 = 286 controls | |||
| Aldrisi 2019 [47] | Case-control study | N1 = 56 PV group | PV versus controls:
|
| mean age: 43.05 ± 16.72 y | |||
| N2 = 54 control group | |||
| mean age: 41.28 ± 14.78 y | |||
| Hansen 2019 [48] | Cross-sectional study | N1 = 1127 PV | PV versus controls:
|
| mean age: 56.9 ± 12.2 y | |||
| N2 = 5635 controls | |||
| mean age: 56.9 ± 13.5 y | |||
| Tas 2020 [53] | Cross-sectional study | N = 74 patients with psoriasis | Weak correlation between Psoriasis Quality of Life Index and thyroid diseases (r = 0.248, p < 0.05). |
| Rana 2020 [54] | Cross-sectional study | N = 290 patients with plaque psoriasis |
|
| Oktem 2020 [55] | Cross-sectional | N = 48 patients with palmoplantar pustulosis |
|
| Authors/ Year of Publication Reference | Type of Study | Studied Population | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fallahi 2016 [117] | Prospective study | N1 = 3.069 AT | Higher prevalence of PsA in AT patients (p < 0.0180), nor for PsC group (p = 0.6237) |
| mean age: 54 ± 16 y | |||
| N2 = 1.023 controls | |||
| mean age: 53 ± 15 y | |||
| Takir 2017 [119] | Cross-sectional, controlled study | N1 = 173 with autoimmune thyroid disorders | Higher prevalence of psoriasis in N1 vs. N2 (p = 0.001) |
| N2 = 127 with non-autoimmune conditions | |||
| N3 = 100 controls | |||
| Kelada 2021 [118] | Retrospective study | N = 267 patients with thyroid eye disease | 13.9% of studied population had non-thyroid autoimmunity: 3% psoriasis |
| median age: 46 years |
| Authors/ Year of Publication Reference | Type of Study | Studied Population | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kim 2022 [121] | Nested case-control study | N1 = 6822 subjects with thyroid cancer | TC versus controls: |
| N2 = 27,288 controls | previous history of psoriasis: OR = 1.02; 95% CI 0.85–1.22 |
| Study Year Reference | Studied Population | Anti-Cancer Drug | Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Johnson 2016 [131] | N = 30 patients with melanoma and preexisting autoimmune disorders | ipilimumab |
|
| Elosua-González 2017 [130] | N = 1 patient with lung cancer | nivolumab (anti-PD1) | The patient developed de novo:
|
| Brown 2021 [127] | N = 55 patients with melanoma and preexisting autoimmune disorders | ipilimumab and anti-PD1 | flare of autoimmune diseases:
|
| Zhang 2021 [128] | N = 5560 oncologic patients (meta-analysis) | immune checkpoint inhibitors |
|
| Gonzalez-Mazón 2021 [129] | N = 102 oncologic patients (3-year, single-center experience) | immune checkpoint inhibitors |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cira, C.-I.; Carsote, M.; Nistor, C.; Petca, A.; Petca, R.-C.; Sandru, F. Conundrum for Psoriasis and Thyroid Involvement. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054894
Cira C-I, Carsote M, Nistor C, Petca A, Petca R-C, Sandru F. Conundrum for Psoriasis and Thyroid Involvement. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(5):4894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054894
Chicago/Turabian StyleCira, Cristina-Ilinca, Mara Carsote, Claudiu Nistor, Aida Petca, Razvan-Cosmin Petca, and Florica Sandru. 2023. "Conundrum for Psoriasis and Thyroid Involvement" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 5: 4894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054894
APA StyleCira, C.-I., Carsote, M., Nistor, C., Petca, A., Petca, R.-C., & Sandru, F. (2023). Conundrum for Psoriasis and Thyroid Involvement. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(5), 4894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054894










