Relevance of HBx for Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Pathogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Relevance of HBV for Global Health
1.2. Viral Characteristics of HBV
1.3. Pathogenesis
2. Hallmarks of HBV-Induced Chronic Liver Disease Pathogenesis
2.1. General Factors Associated with Disease Progression
2.2. Clinical Significance of HBx
3. Properties and Challenges of the HBx Protein in Context of HBV-Associated HCC
3.1. Characteristics of the HBx Protein
3.2. Technical Limitations and Challenges in HBx-Associated HCC Research
4. HBx-Induced Signaling Pathways and Phenotypic Changes as a Driving Force of Virus-Induced Pathogenesis
4.1. Nuclear Localized HBx in Context of Cancer Promoting Signaling Pathways
4.2. Cytosolic HBx-Mediated Signaling Pathway Regulation and Pathological Effects for the Liver
4.3. Impact of HBx-Dependent Interaction with Mitochondria and Endoplasmic Reticulum
5. HBx towards a Cure of HBV-Related HCCs
5.1. Therapeutic Opportunities for HBV Treatment
5.2. siRNA Constitutes a Promising Therapy Approach against HBx
5.3. HBx-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies and Therapeutic Vaccines for Treatment of Chronic HBV
5.4. HBx as Potential Therapeutic Target for Small Molecule Inhibitors
6. Final Remarks and Further Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vos, T.; Lim, S.S.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasi, M.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunbul, M. Hepatitis B virus genotypes: Global distribution and clinical importance. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 5427–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrscher, C.; Roingeard, P.; Blanchard, E. Hepatitis B Virus Entry into Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Ploss, A. Hepatitis B virus cccDNA is formed through distinct repair processes of each strand. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukuda, S.; Watashi, K. Hepatitis B virus biology and life cycle. Antivir. Res. 2020, 182, 104925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, T.; Budzinska, M.A.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Shackel, N.A.; Urban, S. Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration Occurs Early in the Viral Life Cycle in an In Vitro Infection Model via Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide-Dependent Uptake of Enveloped Virus Particles. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02007-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Hildt, E. Intracellular Trafficking of HBV Particles. Cells 2020, 9, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dane, D.S.; Cameron, C.H.; Briggs, M. Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia-antigen-associated hepatitis. Lancet 1970, 1, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Glitscher, M.; Tonnemacher, S.; Schollmeier, A.; Raupach, J.; Zahn, T.; Eberle, R.; Krijnse-Locker, J.; Basic, M.; Hildt, E. Presence of Intact Hepatitis B Virions in Exosomes. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 15, 237–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hong, X.; Xi, J.; Menne, S.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.C.-Y. Cryo-EM structures of human hepatitis B and woodchuck hepatitis virus small spherical subviral particles. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabo4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, C.-T.; Fontana, R.J.; Polson, J.; Hussain, M.; Shakil, A.O.; Han, S.-H.; Davern, T.J.; Lee, W.M.; Lok, A.S.-F. Clinical outcome and virological characteristics of hepatitis B-related acute liver failure in the United States. J. Viral Hepat. 2005, 12, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemello, L.; Pontisso, P.; Fattovich, G.; Schiavon, E.; Alberti, A.; Realdi, G. Hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg) in serum of patients with chronic hepatitis B detected by a modified radioimmunoassay. J. Med. Virol. 1985, 17, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.-N.; Tsai, H.-W.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Ho, C.-H.; Wu, I.-C.; Chang, T.-T. Clinical significance of serum HBsAg levels and association with liver histology in HBeAg positive chronic hepatitis B. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 57, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Tian, T.; Meng, L.; Song, C.; Yu, C.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Dai, J.; Hu, Z. HBV mutations in EnhII/BCP/PC region contribute to the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 3086–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnhenn, L.; Jiang, B.; Kubesch, A.; Vermehren, J.; Knop, V.; Susser, S.; Dietz, J.; Carra, G.; Finkelmeier, F.; Grammatikos, G.; et al. Impact of HBV genotype and mutations on HBV DNA and qHBsAg levels in patients with HBeAg-negative chronic HBV infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 1523–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smalls, D.J.; Kiger, R.E.; Norris, L.B.; Bennett, C.L.; Love, B.L. Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation: Risk Factors and Current Management Strategies. Pharmacotherapy 2019, 39, 1190–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanning, G.C.; Zoulim, F.; Hou, J.; Bertoletti, A. Therapeutic strategies for hepatitis B virus infection: Towards a cure. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk-Fong Lok, A. Hepatitis B Treatment: What We Know Now and What Remains to Be Researched. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, L.-Y.; Wong, D.K.-H.; Pollicino, T.; Raimondo, G.; Hollinger, F.B.; Yuen, M.-F. Occult hepatitis B infection and hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology, virology, hepatocarcinogenesis and clinical significance. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassemer, M.; Finkernagel, M.; Peiffer, K.-H.; Glebe, D.; Akhras, S.; Reuter, A.; Scheiblauer, H.; Sommer, L.; Chudy, M.; Nübling, C.M.; et al. Comparative characterization of hepatitis B virus surface antigen derived from different hepatitis B virus genotypes. Virology 2017, 502, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, T.; Isenberg, D. The endocrinologic associations of the autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1987, 17, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-H.; Chen, P.-J.; Yeh, S.-H. Gender disparity in chronic hepatitis B: Mechanisms of sex hormones. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybicka, M.; Woziwodzka, A.; Romanowski, T.; Sznarkowska, A.; Stalke, P.; Dręczewski, M.; Bielawski, K.P. Host genetic background affects the course of infection and treatment response in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Clin. Virol. 2019, 120, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Zou, G.; Li, J.; Lu, M. Host Genetic Determinants of Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Chen, C.; Yan, D.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Yan, D.; Cui, D.; Yang, S. Exhausted phenotype of circulating CD8+ T cell subsets in hepatitis B virus carriers. BMC Immunol. 2022, 23, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copeland, N.K.; Eller, M.A.; Kim, D.; Creegan, M.; Esber, A.; Eller, L.A.; Semwogerere, M.; Kibuuka, H.; Kiweewa, F.; Crowell, T.A.; et al. Brief Report: Increased Inflammation and Liver Disease in HIV/HBV-Coinfected Individuals. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2021, 88, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouamé, G.M.; Gabillard, D.; Moh, R.; Badje, A.; Ntakpé, J.B.; Emième, A.; Maylin, S.; Toni, T.d.; Ménan, H.; Zoulim, F.; et al. Higher risk of mortality in HIV-HBV co-infected patients from sub-Saharan Africa is observed at lower CD4+ cell counts. Antivir. Ther. 2021, 26, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puoti, M.; Torti, C.; Bruno, R.; Filice, G.; Carosi, G. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B in co-infected patients. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, S65–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barili, V.; Vecchi, A.; Rossi, M.; Montali, I.; Tiezzi, C.; Penna, A.; Laccabue, D.; Missale, G.; Fisicaro, P.; Boni, C. Unraveling the Multifaceted Nature of CD8 T Cell Exhaustion Provides the Molecular Basis for Therapeutic T Cell Reconstitution in Chronic Hepatitis B and C. Cells 2021, 10, 2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Ji, D.; Wang, Y.; Wu, V.; Karlberg, J.; Lau, G. Hepatitis B reactivation in hepatitis B and C coinfected patients treated with antiviral agents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 2017, 66, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeffe, E.B. Hepatitis A and B superimposed on chronic liver disease: Vaccine-preventable diseases. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2006, 117, 227–237; Discussion 237–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nasir, M.; Wu, G.Y. HEV and HBV Dual Infection: A Review. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2020, 8, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagnelli, C.; Sagnelli, E.; Russo, A.; Pisaturo, M.; Occhiello, L.; Coppola, N. HBV/HDV Co-Infection: Epidemiological and Clinical Changes, Recent Knowledge and Future Challenges. Life 2021, 11, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-I.; Yeh, S.-H.; Chen, P.-J.; Iloeje, U.H.; Jen, C.-L.; Su, J.; Wang, L.-Y.; Lu, S.-N.; You, S.-L.; Chen, D.-S.; et al. Associations between hepatitis B virus genotype and mutants and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2008, 100, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Park, D.; Cafiero, T.R.; Bram, Y.; Chandar, V.; Tseng, A.; Gertje, H.P.; Crossland, N.A.; Su, L.; Schwartz, R.E.; et al. Molecular clones of genetically distinct hepatitis B virus genotypes reveal distinct host and drug treatment responses. JHEP Rep. 2022, 4, 100535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Iijima, S.; Kani, S.; Sugiyama, M.; Murakami, S.; Matsuura, K.; Kusakabe, A.; Shinkai, N.; et al. Mechanism of the dependence of hepatitis B virus genotype G on co-infection with other genotypes for viral replication. J. Viral Hepat. 2013, 20, e27–e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-J.; Yang, H.-I.; Iloeje, U.H. Hepatitis B virus DNA levels and outcomes in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2009, 49, S72–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laras, A.; Koskinas, J.; Dimou, E.; Kostamena, A.; Hadziyannis, S.J. Intrahepatic levels and replicative activity of covalently closed circular hepatitis B virus DNA in chronically infected patients. Hepatology 2006, 44, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giersch, K.; Allweiss, L.; Volz, T.; Dandri, M.; Lütgehetmann, M. Serum HBV pgRNA as a clinical marker for cccDNA activity. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 460–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chi, X.; Wu, R.; Xu, H.; Gao, X.; Yu, L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, M.; Tan, Y.; Niu, J.; et al. Serum HBV RNA correlated with intrahepatic cccDNA more strongly than other HBV markers during peg-interferon treatment. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magri, A.; Harris, J.M.; D’Arienzo, V.; Minisini, R.; Jühling, F.; Wing, P.A.C.; Rapetti, R.; Leutner, M.; Testoni, B.; Baumert, T.F.; et al. Inflammatory Gene Expression Associates with Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA- but Not Integrant-Derived Transcripts in HBeAg Negative Disease. Viruses 2022, 14, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooddell, C.I.; Yuen, M.-F.; Chan, H.L.-Y.; Gish, R.G.; Locarnini, S.A.; Chavez, D.; Ferrari, C.; Given, B.D.; Hamilton, J.; Kanner, S.B.; et al. RNAi-based treatment of chronically infected patients and chimpanzees reveals that integrated hepatitis B virus DNA is a source of HBsAg. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaan0241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wei, W.; Hou, F.; Xu, H.; Cui, X. The integration model of hepatitis B virus genome in hepatocellular carcinoma cells based on high-throughput long-read sequencing. Genomics 2022, 114, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, M.; Tanaka, H.; Shiraishi, Y.; Unida, T.; Imamura, M.; Fujimoto, A.; Fujita, M.; Sasaki-Oku, A.; Maejima, K.; Nakano, K.; et al. Characterization of HBV integration patterns and timing in liver cancer and HBV-infected livers. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 25075–25088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.-H.; Liu, X.; Yan, H.-X.; Li, W.-Y.; Zeng, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, S.-P.; Zhuang, X.-H.; Lin, C.; et al. Genomic and oncogenic preference of HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budzinska, M.A.; Shackel, N.A.; Urban, S.; Tu, T. Sequence analysis of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA during HBeAg-seroconversion. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagiozian-Angelova, V.; Alagiozian, D.; Antonov, K.; Krustev, Z. Clinical significance of serum HBeAg and HBV-DNA-specific values of virus replication in chronic hepatitis-B virus infection. Folia Med. 1998, 40, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyama, S.; Sagara, K.; Takano, J.; Iwaoka, D.; Deguchi, T.; Mizuno, K.; Ohtomo, N. Incidence and clinical significance of HBe antigen and antibody in HBsAg-positive various liver diseases. Gastroenterol. Jpn. 1979, 14, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiffer, K.-H.; Spengler, C.; Basic, M.; Jiang, B.; Kuhnhenn, L.; Obermann, W.; Zahn, T.; Glitscher, M.; Loglio, A.; Facchetti, F.; et al. Quadruple mutation GCAC1809-1812TTCT acts as a biomarker in healthy European HBV carriers. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e135833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, D.T.Y.; Ganova-Raeva, L.; Wang, J.; Mogul, D.; Chung, R.T.; Lisker-Melman, M.; Chang, K.-M.; Shaikh, O.S.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Wahed, A.S.; et al. Precore and Basal Core Promoter Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Variants Are Present From a Young Age and Differ Across HBV Genotypes. Hepatology 2021, 73, 1637–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.C.K.; Joshi, S.S.; Mahoney, D.J.; Mason, A.L.; van Marle, G.; Osiowy, C.; Coffin, C.S. Differences in HBV Replication, APOBEC3 Family Expression, and Inflammatory Cytokine Levels Between Wild-Type HBV and Pre-core (G1896A) or Basal Core Promoter (A1762T/G1764A) Mutants. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramvis, A.; Kostaki, E.-G.; Hatzakis, A.; Paraskevis, D. Immunomodulatory Function of HBeAg Related to Short-Sighted Evolution, Transmissibility, and Clinical Manifestation of Hepatitis B Virus. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Luo, J.; Zhu, D.; Zhou, W.; Yang, X.; Feng, X.; Lu, M.; Zheng, X.; Dittmer, U.; Yang, D.; et al. HBeAg Is Indispensable for Inducing Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cell Activation by Hepatitis B Virus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 797915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneveld, M.J.; Hansen, B.E.; Brouwer, W.P.; Chan, H.L.-Y.; Piratvisuth, T.; Jia, J.-D.; Zeuzem, S.; Chien, R.-N.; de Knegt, R.J.; Wat, C.; et al. Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Levels Can Be Used to Rule Out Cirrhosis in Hepatitis B e Antigen-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B: Results From the SONIC-B Study. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 225, 1967–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rydell, G.E.; Prakash, K.; Norder, H.; Lindh, M. Hepatitis B surface antigen on subviral particles reduces the neutralizing effect of anti-HBs antibodies on hepatitis B viral particles in vitro. Virology 2017, 509, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildt, E.; Munz, B.; Saher, G.; Reifenberg, K.; Hofschneider, P.H. The PreS2 activator MHBs(t) of hepatitis B virus activates c-raf-1/Erk2 signaling in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, N.; Li, B.; Liu, S.; Cheng, J.; Fu, X.; Zhang, J. Interaction of LHBs with C53 promotes hepatocyte mitotic entry: A novel mechanism for HBV-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Xu, J.; Zhou, L.; Yun, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Sun, L.; Wen, Y.; Gu, J. Hepatitis B virus large surface antigen promotes liver carcinogenesis by activating the Src/PI3K/Akt pathway. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7547–7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Ye, S.; Lin, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, Z.; Liu, W.; Chen, W.; Lin, X.; Lin, X. Small hepatitis B virus surface antigen promotes malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced FGF19/JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Cancer Lett. 2021, 499, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisari, F.V.; Pinkert, C.A.; Milich, D.R.; Filippi, P.; McLachlan, A.; Palmiter, R.D.; Brinster, R.L. A transgenic mouse model of the chronic hepatitis B surface antigen carrier state. Science 1985, 230, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, H.E.; Zhang, Z.S.; Galun, E.; von Weizsäcker, F.; Garner, B.; Liang, T.J.; Wands, J.R. Hepatitis B virus X protein is not central to the viral life cycle in vitro. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 1223–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirakata, Y.; Kawada, M.; Fujiki, Y.; Sano, H.; Oda, M.; Yaginuma, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Koike, K. The X gene of hepatitis B virus induced growth stimulation and tumorigenic transformation of mouse NIH3T3 cells. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1989, 80, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Cheng, S.-T.; Qin, Y.-P.; He, X.; Li, F.; Wu, D.-Q.; Ren, F.; Yu, H.-B.; Liu, J.; et al. Rapamycin inhibits hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA transcription by enhancing the ubiquitination of HBx. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 850087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belloni, L.; Pollicino, T.; de Nicola, F.; Guerrieri, F.; Raffa, G.; Fanciulli, M.; Raimondo, G.; Levrero, M. Nuclear HBx binds the HBV minichromosome and modifies the epigenetic regulation of cccDNA function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19975–19979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, C.K.; Cheng, C.Y.S.; Tsoi, S.Y.J.; Huang, F.-Y.; Liu, F.; Fung, J.; Seto, W.-K.; Lai, K.K.-Y.; Lai, C.-L.; Yuen, M.-F.; et al. HBV X protein mutations affect HBV transcription and association of histone-modifying enzymes with covalently closed circular DNA. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Lin, Y.; et al. Identification of Estradiol Benzoate as an Inhibitor of HBx Using Inducible Stably Transfected HepG2 Cells Expressing HiBiT Tagged HBx. Molecules 2022, 27, 5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Jung, H.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Yi, N.-J.; Suh, K.-S.; Jang, J.-J.; Lee, K.-B. Nuclear Expression of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Is Associated with Recurrence of Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinomas: Role of Viral Protein in Tumor Recurrence. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2016, 50, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhai, W.; Lin, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H. Prognostic analysis in chronic hepatitis B patients: A retrospective study of 216 cases about Scheuer scores, in situ expression of viral antigens and tissue hepatitis B virus DNA levels. Liver Int. 2006, 26, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.-Y.; Lin, C.-Y.; Huang, L.-M.; Wang, Y.-H.; Wang, J.-C.; Hsu, C.-T.; Yang, S.-S.; Wu, C.-C. Detection of the hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) antigen and anti-HBx antibodies in cases of human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5598–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitvitski-Trépo, L.; Kay, A.; Pichoud, C.; Chevallier, P.; de Dinechin, S.; Shamoon, B.M.; Mandart, E.; Trépo, C.; Galibert, F. Early and frequent detection of HBxAg and/or anti-HBx in hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 1990, 12, 1278–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qahtani, A.A.; Al-Anazi, M.R.; Nazir, N.; Ghai, R.; Abdo, A.A.; Sanai, F.M.; Al-Hamoudi, W.K.; Alswat, K.A.; Al-Ashgar, H.I.; Khan, M.Q.; et al. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) X gene mutations and their association with liver disease progression in HBV-infected patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 105115–105125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, M.; Vijayaraghavan, S.; Sarangan, G.; Barani, R.; Abraham, P.; Srikanth, P. Hepatitis B virus X protein: The X factor in chronic hepatitis B virus disease progression. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 37, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, W.A.; Yano, Y.; Yamani, L.N.; Lusida, M.I.; Soetjipto; Liang, Y.; Mardian, Y.; Wasityastuti, W.; Hayashi, Y. Association Between HBx Variations and Development of Severe Liver Disease Among Indonesian Patients. Kobe J. Med. Sci. 2019, 65, E28–E35. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, Q.; Deng, Q.; Li, J.; Xia, N.; Wang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Tong, S. Lost Small Envelope Protein Expression from Naturally Occurring PreS1 Deletion Mutants of Hepatitis B Virus is Often Accompanied by Increased HBx and Core Protein Expression as Well as Genome Replication. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0066021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, Z.I.; Azam, S.A.; Khan, W.H.; Afroz, M.; Farooqui, S.R.; Amir, F.; Azmi, M.I.; Anwer, A.; Khan, S.; Mehmankhah, M.; et al. An in vitro Study on the Role of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein C-Terminal Truncation in Liver Disease Development. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 633341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Yuan, D.; Li, Q.; Zhang, N.; Kong, D.; Yu, T.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, R.; Kong, F.; et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein increases LASP1 SUMOylation to stabilize HER2 and facilitate hepatocarcinogenesis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 226, 996–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Shi, W.; Luan, F.; Xu, S.; Yang, F.; Sun, W.; Liu, J.; Ma, C. Hepatitis B virus X protein upregulates transcriptional activation of human telomerase reverse transcriptase. Virus Genes 2010, 40, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhuang, H.; Li, J.; Wang, J. HBx 128–133 Deletion Affecting HBV Mother-to-Child Transmission Weakens HBV Replication via Reducing HBx Level and CP/ENII Transcriptional Activity. Viruses 2022, 14, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Sarkar, D.P. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein: Structure-Function Relationships and Role in Viral Pathogenesis. In Transcription Factors; Starke, K., Gossen, M., Kaufmann, J., Triezenberg, S.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 377–407. ISBN 978-3-642-62361-5. [Google Scholar]
- Twu, J.S.; Schloemer, R.H. Transcriptional trans-activating function of hepatitis B virus. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 3448–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollersheim, M.; Debelka, U.; Hofschneider, P.H. A transactivating function encoded in the hepatitis B virus X gene is conserved in the integrated state. Oncogene 1988, 3, 545–552. [Google Scholar]
- Slagle, B.L.; Andrisani, O.M.; Bouchard, M.J.; Lee, C.G.L.; Ou, J.-H.J.; Siddiqui, A. Technical standards for hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) research. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.-Y.; Kim, Y.-J. C-terminal region of HBx is crucial for mitochondrial DNA damage. Cancer Lett. 2013, 331, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Xu, F.; Xiao, Q.; Tan, G. Hepatitis B virus X protein and its host partners. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1345–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Yan, L.; Xu, B.; Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Han, N.; Tang, H.; Huang, F. Screening of the HBx transactivation domain interacting proteins and the function of interactor Pin1 in HBV replication. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Cha, E.-J.; Lim, J.-E.; Kwon, S.-H.; Kim, D.-H.; Cho, H.; Han, K.-H. Structural characterization of an intrinsically unfolded mini-HBX protein from hepatitis B virus. Mol. Cells 2012, 34, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, D.; Xing, W.; Beran, R.K.; Chemuru, S.; Rohrs, H.; Niedziela-Majka, A.; Marchand, B.; Mehra, U.; Zábranský, A.; Doležal, M.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Function Requires Zinc Binding. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00250-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Robert, E.I.; van Breugel, P.C.; Strubin, M.; Zheng, N. A promiscuous alpha-helical motif anchors viral hijackers and substrate receptors to the CUL4-DDB1 ubiquitin ligase machinery. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Liu, M.; Wu, J.; Shi, Y. Structural and biochemical analysis of Bcl-2 interaction with the hepatitis B virus protein HBx. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2074–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, E.; de Moura, P.R.; Gonçalves, K.D.A.; Kobarg, J. Expression and spectroscopic analysis of a mutant hepatitis B virus onco-protein HBx without cysteine residues. J. Virol. Methods 2005, 126, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Mal, T.K.; Jayasuryan, N.; Chauhan, V.S. Assignment of disulphide bonds in the X protein (HBx) of hepatitis B virus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 212, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, S.; Hildt, E.; Eckerskorn, C.; Sirma, H.; Kekulé, A.; Hofschneider, P.H. Isolation and molecular characterization of hepatitis B virus X-protein from a baculovirus expression system. Hepatology 1997, 26, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivière, L.; Ducroux, A.; Buendia, M.A. The oncogenic role of hepatitis B virus. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2014, 193, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Hemert, F.J.; van de Klundert, M.A.A.; Lukashov, V.V.; Kootstra, N.A.; Berkhout, B.; Zaaijer, H.L. Protein X of hepatitis B virus: Origin and structure similarity with the central domain of DNA glycosylase. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.-Y.; Chen, H.-Y.; Cao, J.-L.; Xiong, H.-L.; Mo, X.-B.; Li, T.-L.; Kang, X.-Z.; Zhao, J.-H.; Yin, B.; Zhao, X.; et al. Structural and functional analyses of hepatitis B virus X protein BH3-like domain and Bcl-xL interaction. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.W.; Riegler, J.; Wu, J.; Yen, T.S. Novel short transcripts of hepatitis B virus X gene derived from intragenic promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 22593–22598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altinel, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Wei, Y.; Neuveut, C.; Gupta, I.; Suzuki, A.M.; Dos Santos, A.; Moreau, P.; Xia, T.; Kojima, S.; et al. Single-Nucleotide Resolution Mapping of Hepatitis B Virus Promoters in Infected Human Livers and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 10811–10822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, C.; Montecinos, J.; Jiménez, G.; Riquelme, C.; Garrido, D.; Hernández, S.; Loyola, A.; Villanueva, R.A. Phosphorylation of Phylogenetically Conserved Amino Acid Residues Confines HBx within Different Cell Compartments of Human Hepatocarcinoma Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, S.; Álvarez-Astudillo, F.; Garrido, D.; Prieto, C.; Loyola, A.; Villanueva, R.A. Canonical and Divergent N-Terminal HBx Isoform Proteins Unveiled: Characteristics and Roles during HBV Replication. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henkler, F.; Hoare, J.; Waseem, N.; Goldin, R.D.; McGarvey, M.J.; Koshy, R.; King, I.A. Intracellular localization of the hepatitis B virus HBx protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, M.-Y.; Ryu, D.-K.; Jung, H.-S.; Chang, H.-E.; Ryu, W.-S. Stimulation of hepatitis B virus genome replication by HBx is linked to both nuclear and cytoplasmic HBx expression. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Sun, T.; Park, S.; Shen, G.; Liu, J. The role of hepatitis B virus X protein is related to its differential intracellular localization. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2011, 43, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.G.; Salvay, D.M.; Forgues, M.; Valerie, K.; Farnsworth, J.; Markin, R.S.; Wang, X.W. Distinctive gene expression profiles associated with Hepatitis B virus x protein. Oncogene 2001, 20, 3674–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Shou, S.; Guo, H.; Gao, Z.; Liu, N.; Yang, Y.; Wang, F.; Deng, Q.; Liu, J.; Xie, Y. Establishment and characterization of a new cell culture system for hepatitis B virus replication and infection. Virol. Sin. 2022, 37, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Mo, H.; Svarovskaia, E.; Mateo, R. A primary human hepatocyte/hepatic stellate cell co-culture system for improved in vitro HBV replication. Virology 2021, 559, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gripon, P.; Rumin, S.; Urban, S.; Le Seyec, J.; Glaise, D.; Cannie, I.; Guyomard, C.; Lucas, J.; Trepo, C.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C. Infection of a human hepatoma cell line by hepatitis B virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15655–15660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. eLife 2012, 1, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Lempp, F.A.; Mehrle, S.; Nkongolo, S.; Kaufman, C.; Fälth, M.; Stindt, J.; Königer, C.; Nassal, M.; Kubitz, R.; et al. Hepatitis B and D viruses exploit sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide for species-specific entry into hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1070–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, M.; Watashi, K.; Tsukuda, S.; Aly, H.H.; Fukasawa, M.; Fujimoto, A.; Suzuki, R.; Aizaki, H.; Ito, T.; Koiwai, O.; et al. Evaluation and identification of hepatitis B virus entry inhibitors using HepG2 cells overexpressing a membrane transporter NTCP. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhao, K.; Yao, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Pei, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Productive HBV infection of well-differentiated, hNTCP-expressing human hepatoma-derived (Huh7) cells. Virol. Sin. 2017, 32, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lempp, F.A.; Qu, B.; Wang, Y.-X.; Urban, S. Hepatitis B Virus Infection of a Mouse Hepatic Cell Line Reconstituted with Human Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 4827–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kornyeyev, D.; May, L.; Han, D.; Aeschbacher, T.; Chang, S.; Martin, R.; Mo, H.; Feierbach, B. Establishment and Characterization of an HBV Viral Spread and Infectious System following Long-Term Passage of an HBV Clinical Isolate in the Primary Human Hepatocyte and Fibroblast Coculture System. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0084922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, C.; Sirajee, R.; Steenbergen, R.; Joyce, M.A.; Addison, W.R.; Tyrrell, D.L. In Vitro Infection with Hepatitis B Virus Using Differentiated Human Serum Culture of Huh7.5-NTCP Cells without Requiring Dimethyl Sulfoxide. Viruses 2021, 13, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michailidis, E.; Pabon, J.; Xiang, K.; Park, P.; Ramanan, V.; Hoffmann, H.-H.; Schneider, W.M.; Bhatia, S.N.; de Jong, Y.P.; Shlomai, A.; et al. A robust cell culture system supporting the complete life cycle of hepatitis B virus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akahori, Y.; Kato, H.; Fujita, T.; Moriishi, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Watashi, K.; Imamura, M.; Chayama, K.; Wakita, T.; Hijikata, M. Establishment of a novel hepatitis B virus culture system using immortalized human hepatocytes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otoguro, T.; Tanaka, T.; Kasai, H.; Kobayashi, N.; Yamashita, A.; Fukuhara, T.; Ryo, A.; Fukai, M.; Taketomi, A.; Matsuura, Y.; et al. Establishment of a Cell Culture Model Permissive for Infection by Hepatitis B and C Viruses. Hepatol. Commun. 2021, 5, 634–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, F.; Mitani, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Takayama, K.; Tachibana, M.; Watashi, K.; Wakita, T.; Iijima, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Mizuguchi, H. Human induced-pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells as an in vitro model of human hepatitis B virus infection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.-Z.; Zheng, Y.-W.; Miyakawa, K.; Murata, S.; Zhang, R.-R.; Sekine, K.; Ueno, Y.; Takebe, T.; Wakita, T.; Ryo, A.; et al. Recapitulation of hepatitis B virus-host interactions in liver organoids from human induced pluripotent stem cells. EbioMedicine 2018, 35, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Crignis, E.; Hossain, T.; Romal, S.; Carofiglio, F.; Moulos, P.; Khalid, M.M.; Rao, S.; Bazrafshan, A.; Verstegen, M.M.; Pourfarzad, F.; et al. Application of human liver organoids as a patient-derived primary model for HBV infection and related hepatocellular carcinoma. eLife 2021, 10, e60747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wose Kinge, C.N.; Bhoola, N.H.; Kramvis, A. In Vitro Systems for Studying Different Genotypes/Sub-Genotypes of Hepatitis B Virus: Strengths and Limitations. Viruses 2020, 12, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Chen, P.-J.; Watashi, K.; Wakita, T. Cell and Animal Models for Studying Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Drug Development. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 338–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, M.; Ghildyal, R.; Yuan, Z. Animal Models for the Study of Hepatitis B Virus Pathobiology and Immunity: Past, Present, and Future. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 715450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menne, S.; Cote, P.J. The woodchuck as an animal model for pathogenesis and therapy of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 104–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keasler, V.V.; Hodgson, A.J.; Madden, C.R.; Slagle, B.L. Enhancement of hepatitis B virus replication by the regulatory X protein in vitro and in vivo. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 2656–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.-T.; Hu, J.-L.; Ren, J.-H.; Yu, H.-B.; Zhong, S.; Wai Wong, V.K.; Kwan Law, B.Y.; Chen, W.-X.; Xu, H.-M.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; et al. Dicoumarol, an NQO1 inhibitor, blocks cccDNA transcription by promoting degradation of HBx. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafner, A.; Brandenburg, B.; Hildt, E. Reconstitution of gene expression from a regulatory-protein-deficient hepatitis B virus genome by cell-permeable HBx protein. EMBO Rep. 2003, 4, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasudhan, E.; Blake, N.; Lu, Z.; Meng, J.; Rong, R. Hepatitis B Viral Protein HBx and the Molecular Mechanisms Modulating the Hallmarks of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review. Cells 2022, 11, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Koh, S.S.Y.; Lee, C.G.L. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein and Hepatocarcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elpek, G.O. Molecular pathways in viral hepatitis-associated liver carcinogenesis: An update. World J. Clin. Cases 2021, 9, 4890–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrieri, F.; Belloni, L.; D’Andrea, D.; Pediconi, N.; Le Pera, L.; Testoni, B.; Scisciani, C.; Floriot, O.; Zoulim, F.; Tramontano, A.; et al. Genome-wide identification of direct HBx genomic targets. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisel, M.B.; Guerrieri, F.; Levrero, M. Host Epigenetic Alterations and Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Yang, W.; Song, J.; Wu, Y.; Ni, B. Hepatitis B virus X protein-induced aberrant epigenetic modifications contributing to human hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 2810–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, V.; Srinathan, S.; Pasini, E.; Angeli, M.; Chen, E.; Baciu, C.; Bhat, M. Epigenetic basis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A network-based integrative meta-analysis. World J. Hepatol. 2018, 10, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.Y.; Sohn, B.H.; Yu, E.; Suh, D.J.; Chung, Y.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Surzycki, S.J.; Lee, Y.I. Aberrant epigenetic modifications in hepatocarcinogenesis induced by hepatitis B virus X protein. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1476–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-M.; Lee, Y.; Bae, J.-B.; Choi, J.K.; Tayama, C.; Hata, K.; Yun, Y.; Seong, J.-K.; Kim, Y.-J. HBx induces hypomethylation of distal intragenic CpG islands required for active expression of developmental regulators. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9555–9560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-Z.; Zhu, R.; Fan, J.; Pan, Q.; Li, H.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, H.-G. Hepatitis B virus X protein induces hypermethylation of p16(INK4A) promoter via DNA methyltransferases in the early stage of HBV-associated hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Viral Hepat. 2010, 17, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, G.; Bu, F.; Lu, B.; Liang, A.; Cao, L.; Tong, X.; Lu, X.; Wu, M.; Guo, Y. Epigenetic silence of ankyrin-repeat-containing, SH3-domain-containing, and proline-rich-region- containing protein 1 (ASPP1) and ASPP2 genes promotes tumor growth in hepatitis B virus-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2010, 51, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.-L.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, N.; Xu, X.; Deng, Q.; Teng, X.-M.; Wang, K.-S.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Han, Z.-G. Epigenetic modification induced by hepatitis B virus X protein via interaction with de novo DNA methyltransferase DNMT3A. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rongrui, L.; Na, H.; Zongfang, L.; Fanpu, J.; Shiwen, J. Epigenetic mechanism involved in the HBV/HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, J.; Mo, J.; Liu, D.; Cao, D.; Wang, H.; He, Y.; Wang, H. Global DNA 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine and 5-Formylcytosine Contents Are Decreased in the Early Stage of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2019, 69, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jeong, H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, S.S.; Jang, K.L. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Stimulates Virus Replication Via DNA Methylation of the C-1619 in Covalently Closed Circular DNA. Mol. Cells 2019, 42, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-W.; Siddiqui, A. Hepatitis B virus X protein recruits methyltransferases to affect cotranscriptional N6-methyladenosine modification of viral/host RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2019455118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.-W.; Siddiqui, A. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Expression Is Tightly Regulated by N6-Methyladenosine Modification of Its mRNA. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0165521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freese, K.; Seitz, T.; Dietrich, P.; Lee, S.M.L.; Thasler, W.E.; Bosserhoff, A.; Hellerbrand, C. Histone Deacetylase Expressions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Functional Effects of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors on Liver Cancer Cells In Vitro. Cancers 2019, 11, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guccione, E.; Richard, S. The regulation, functions and clinical relevance of arginine methylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 642–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cougot, D.; Wu, Y.; Cairo, S.; Caramel, J.; Renard, C.-A.; Lévy, L.; Buendia, M.A.; Neuveut, C. The hepatitis B virus X protein functionally interacts with CREB-binding protein/p300 in the regulation of CREB-mediated transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 4277–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shon, J.K.; Shon, B.H.; Park, I.Y.; Lee, S.U.; Fa, L.; Chang, K.Y.; Shin, J.H.; Lee, Y.I. Hepatitis B virus-X protein recruits histone deacetylase 1 to repress insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 transcription. Virus Res. 2009, 139, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Jia, Z.; Tian, Y.; Yang, P.; Sun, H.; Wang, C.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, D.; et al. HBx Protein Contributes to Liver Carcinogenesis by H3K4me3 Modification Through Stabilizing WD Repeat Domain 5 Protein. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1678–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Tsuge, M.; Tsushima, K.; Suehiro, Y.; Fujino, H.; Ono, A.; Yamauchi, M.; Makokha, G.N.; Nakahara, T.; Murakami, E.; et al. Signal Activation of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocarcinogenesis by Up-regulation of SUV39h1. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 2061–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricoli, L.; Niture, S.; Chimeh, U.; Ressom, H.; Kumar, D. Role of microRNAs in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma and drug resistance. Front. Biosci. 2019, 24, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, P.; Xu, Y. Downregulated long non-coding RNA DREH promotes cell proliferation in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 2025–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, M.J.; Yun, J.; Kim, S.G. Role of non-coding RNAs in liver disease progression to hepatocellular carcinoma. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2019, 42, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartorius, K.; Swadling, L.; An, P.; Makarova, J.; Winkler, C.; Chuturgoon, A.; Kramvis, A. The Multiple Roles of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein (HBx) Dysregulated MicroRNA in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HBV-HCC) and Immune Pathways. Viruses 2020, 12, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandiera, S.; Pfeffer, S.; Baumert, T.F.; Zeisel, M.B. miR-122--a key factor and therapeutic target in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, M.; Yang, J.; Cho, W.C.; Zheng, Y. microRNA-21: A key modulator in oncogenic viral infections. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, D.; Chiodo, L.; Alfano, V.; Floriot, O.; Cottone, G.; Paturel, A.; Pallocca, M.; Plissonnier, M.-L.; Jeddari, S.; Belloni, L.; et al. Hepatitis B protein HBx binds the DLEU2 lncRNA to sustain cccDNA and host cancer-related gene transcription. Gut 2020, 69, 2016–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, W.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, H.; Hao, D.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.; He, C.; Xiao, Z. A Novel lncRNA IHS Promotes Tumor Proliferation and Metastasis in HCC by Regulating the ERK- and AKT/GSK-3β-Signaling Pathways. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfister, S.X.; Ashworth, A. Marked for death: Targeting epigenetic changes in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 241–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivière, L.; Quioc-Salomon, B.; Fallot, G.; Halgand, B.; Féray, C.; Buendia, M.-A.; Neuveut, C. Hepatitis B virus replicating in hepatocellular carcinoma encodes HBx variants with preserved ability to antagonize restriction by Smc5/6. Antivir. Res. 2019, 172, 104618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiba, K.; Otsuka, M.; Funato, K.; Miyakawa, Y.; Tanaka, E.; Seimiya, T.; Yamagami, M.; Tsutsumi, T.; Okushin, K.; Miyakawa, K.; et al. HBx-induced degradation of Smc5/6 complex impairs homologous recombination-mediated repair of damaged DNA. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, T.; Goto, T.; Hirotsu, Y.; Moriyama, M.; Omata, M. Molecular Mechanisms Driving Progression of Liver Cirrhosis towards Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B and C Infections: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, S.; Mahmoudvand, S.; Taherkhani, R.; Farshadpour, F.; Jalalian, F.A. Complexity on modulation of NF-κB pathways by hepatitis B and C: A double-edged sword in hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 14734–14742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weil, R.; Sirma, H.; Giannini, C.; Kremsdorf, D.; Bessia, C.; Dargemont, C.; Bréchot, C.; Israël, A. Direct association and nuclear import of the hepatitis B virus X protein with the NF-kappaB inhibitor IkappaBalpha. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 6345–6354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Anazi, M.R.; Nazir, N.; Colak, D.; Al-Ahdal, M.N.; Al-Qahtani, A.A. Deletion and Functional Analysis of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein: Evidence for an Effect on Cell Cycle Regulators. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 1987–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gearhart, T.L.; Bouchard, M.J. The hepatitis B virus X protein modulates hepatocyte proliferation pathways to stimulate viral replication. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2675–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Ma, J.; Xi, Y.; Yang, L.; Su, C.; Shao, B.; Huang, A.; Xiang, R.; et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx)-induced abnormalities of nucleic acid metabolism revealed by (1)H-NMR-based metabonomics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, Q.; Gong, L.; Xu, H.; Liu, B.; Fang, X.; Yu, D.; Li, L.; Wei, T.; Wang, Y.; et al. C-terminal truncated HBx initiates hepatocarcinogenesis by downregulating TXNIP and reprogramming glucose metabolism. Oncogene 2021, 40, 1147–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J. Oncoprotein LAMTOR5 Activates GLUT1 Via Upregulating NF-κB in Liver Cancer. Open Med. 2019, 14, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, D.; Li, Z.; Zhao, J.; Cai, S.; Cao, G. The Mechanism of Hepatitis B Virus X Gene in Promoting Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cancer Sci. Clin. Ther. 2022, 6, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.-R.; Zheng, D.-H.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Xie, W.-H.; Huang, Y.-H.; Chen, Z.-X.; Wang, X.-Z.; Li, D. Effect of HBx on inflammation and mitochondrial oxidative stress in mouse hepatocytes. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 2861–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.-Y. Relevance of reactive oxygen species in liver disease observed in transgenic mice expressing the hepatitis B virus X protein. Lab. Anim. Res. 2020, 36, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.-H.; Ding, J.; Xie, X.-X.; Yang, X.-H.; Wu, X.-F.; Chen, Z.-X.; Guo, Q.-L.; Gao, W.-Y.; Wang, X.-Z.; Li, D. Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes liver cell pyroptosis under oxidative stress through NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 69, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saurav, S.; Tanwar, J.; Ahuja, K.; Motiani, R.K. Dysregulation of host cell calcium signaling during viral infections: Emerging paradigm with high clinical relevance. Mol. Asp. Med. 2021, 81, 101004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casciano, J.C.; Bouchard, M.J. Hepatitis B virus X protein modulates cytosolic Ca2+ signaling in primary human hepatocytes. Virus Res. 2018, 246, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.-H.; Liu, Z.-J.; Yi, J.-H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.-N. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Upregulates Intracellular Calcium Signaling by Binding C-terminal of Orail Protein. Curr. Med. Sci. 2018, 38, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casciano, J.C.; Duchemin, N.J.; Lamontagne, R.J.; Steel, L.F.; Bouchard, M.J. Hepatitis B virus modulates store-operated calcium entry to enhance viral replication in primary hepatocytes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.G.; Akter, S.; Ohsaki, E.; Ueda, K. Impact of the Interaction of Hepatitis B Virus with Mitochondria and Associated Proteins. Viruses 2020, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, K.-W.; Siddiqui, A. Characterization of the mitochondrial association of hepatitis B virus X protein, HBx. Mitochondrion 2002, 1, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.K.; Ho, S.F.; Tsui, K.W.; Fung, K.P.; Waye, M.Y.M. Identification of functionally important amino acid residues in the mitochondria targeting sequence of hepatitis B virus X protein. Virology 2008, 381, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clippinger, A.J.; Bouchard, M.J. Hepatitis B virus HBx protein localizes to mitochondria in primary rat hepatocytes and modulates mitochondrial membrane potential. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 6798–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.-Y.; Fang, X.-F.; Zou, L.-Y.; Huang, Y.-H.; Chen, Z.-X.; Li, D.; Zhou, L.-Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.-Z. The co-localization of HBx and COXIII upregulates COX-2 promoting HepG2 cell growth. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.-Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.W.; Sohn, S.; Kim, K.; Cho, H. Hepatitis B virus x protein induces perinuclear mitochondrial clustering in microtubule- and Dynein-dependent manners. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1714–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-J.; Khan, M.; Quan, J.; Till, A.; Subramani, S.; Siddiqui, A. Hepatitis B virus disrupts mitochondrial dynamics: Induces fission and mitophagy to attenuate apoptosis. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani, Z.; Huh, K.W.; Lasher, R.; Siddiqui, A. Hepatitis B virus X protein colocalizes to mitochondria with a human voltage-dependent anion channel, HVDAC3, and alters its transmembrane potential. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 2840–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-Y.; Li, D.; Chen, Z.-X.; Huang, Y.-H.; Gao, W.-Y.; Zheng, B.-Y.; Wang, X.-Z. Hepatitis B Virus X protein elevates Parkin-mediated mitophagy through Lon Peptidase in starvation. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 368, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, W.; Song, D.; Yan, Y.; Yang, M.; Sun, Y. A Potential Role for Mitochondrial DNA in the Activation of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Liver Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 5835910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waris, G.; Huh, K.W.; Siddiqui, A. Mitochondrially associated hepatitis B virus X protein constitutively activates transcription factors STAT-3 and NF-kappa B via oxidative stress. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 7721–7730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Xun, Z.; Lin, J.; Fu, Y.; Wu, W.; Fu, X.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Ou, Q. Association between mitochondrial DNA content and baseline serum levels of HBsAg in chronic hepatitis B infection. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 1958–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, D.S.; Nayak, V.; Srinivasamoorthy, G.; Khudyakov, Y. Entropy of mitochondrial DNA circulating in blood is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Med. Genom. 2019, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Li, D.Y.; Guo, X.; Cao, H.Y.; Chen, Y.B.; Zhou, F.; Ge, N.J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, S.S.; Zhao, Z.; et al. NGS-based profiling reveals a critical contributing role of somatic D-loop mtDNA mutations in HBV-related hepatocarcinogenesis. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.-Y.; Zheng, B.-Y.; Fang, X.-F.; Li, D.; Huang, Y.-H.; Chen, Z.-X.; Zhou, L.-Y.; Wang, X.-Z. HBx co-localizes with COXIII in HL-7702 cells to upregulate mitochondrial function and ROS generation. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2461–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.-S.; Park, Y.-J.; Lee, H.-S.; Oanh, N.T.K.; Cho, M.-Y.; Heo, J.; Lee, E.-S.; Cho, H.; Park, Y.-Y.; Cho, H. Mitochondria ubiquitin ligase, MARCH5 resolves hepatitis B virus X protein aggregates in the liver pathogenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Choi, M.; Kim, J.K.; Ahn, J.K. Hepatitis B virus X protein induces apoptosis by enhancing translocation of Bax to mitochondria. IUBMB Life 2008, 60, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, S.; Shirakata, Y.; Kaneniwa, N.; Koike, K. Association of hepatitis B virus X protein with mitochondria causes mitochondrial aggregation at the nuclear periphery, leading to cell death. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6965–6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.-Y.; Wong, D.K.-H.; Seto, W.-K.; Mak, L.-Y.; Cheung, T.-T.; Yuen, M.-F. Tumor suppressive role of mitochondrial sirtuin 4 in induction of G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shen, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Yuan, Z. Residues Asn118 and Glu119 of hepatitis B virus X protein are critical for HBx-mediated inhibition of RIG-I-MAVS signaling. Virology 2020, 539, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Qin, S.; Yang, X.; Kong, D.; Pan, X.; You, H.; Zheng, K.; Tang, R. Calcium signaling in hepatitis B virus infection and its potential as a therapeutic target. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitelson, M.A.; Arzumanyan, A.; Spector, I.; Medhat, A. Hepatitis B x (HBx) as a Component of a Functional Cure for Chronic Hepatitis B. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassal, M. HBV cccDNA: Viral persistence reservoir and key obstacle for a cure of chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2015, 64, 1972–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tian, Z. HBV-Induced Immune Imbalance in the Development of HCC. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, A.S.J.; Kwok, R.; Ahmed, T. Alpha-interferon treatment in hepatitis B. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Pan, C.; Yu, W.; Dang, S.; Li, J.; Wu, S.; Jiang, N.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, F.; et al. Comparison of the long-term efficacy of tenofovir and entecavir in nucleos(t)ide analogue-naïve HBeAg-positive patients with chronic hepatitis B: A large, multicentre, randomized controlled trials. Medicine 2019, 98, e13983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidrich, B.; Manns, M.P.; Wedemeyer, H. Treatment options for hepatitis delta virus infection. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2013, 15, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, J.; Akahane, T.; Nakayama, H.; Kimura, O.; Kobayashi, T.; Kisara, N.; Sato, T.; Morosawa, T.; Izuma, M.; Kakazu, E.; et al. Comparison of hepatitis B virus genotypes B and C among chronically hepatitis B virus-infected patients who received nucleos(t)ide analogs: A multicenter retrospective study. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 1263–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemori, T.; Sugimoto-Ishige, A.; Nishitsuji, H.; Futamura, Y.; Harada, M.; Kimura-Someya, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Honma, T.; Tanaka, M.; Yaguchi, M.; et al. Establishment of a Monoclonal Antibody against Human NTCP That Blocks Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0168621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, B.; Choi, J.; Kang, J.-A.; Park, S.-G.; Seo, J.; Kim, T.-Y. Development of a mass spectrometric screening assay for hepatitis B virus entry inhibitors. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 178, 112959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, J.; Ma, J.; Hu, Z.; Wu, S.; Hwang, N.; Kulp, J.; Du, Y.; Guo, J.-T.; Chang, J. Discovery of Novel Hepatitis B Virus Nucleocapsid Assembly Inhibitors. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, T.; Urban, S. Virus entry and its inhibition to prevent and treat hepatitis B and hepatitis D virus infections. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 30, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucifora, J.; Arzberger, S.; Durantel, D.; Belloni, L.; Strubin, M.; Levrero, M.; Zoulim, F.; Hantz, O.; Protzer, U. Hepatitis B virus X protein is essential to initiate and maintain virus replication after infection. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slagle, B.L.; Bouchard, M.J. Hepatitis B Virus X and Regulation of Viral Gene Expression. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a021402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-W.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Lee, S.-K.; Han, J.-W.; Sung, P.-S.; Bae, S.-H.; Choi, J.-Y.; Yoon, S.-K.; Han, D.-J.; et al. Distinct Patterns of HBV Integration and TERT Alterations between in Tumor and Non-Tumor Tissue in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muroyama, R.; Nakagawa, R.; Matsubara, Y.; Hirata, Y.; Omata, M.; Shirasawa, H.; Kato, N. Fusion HBx from HBV integrant affects hepatocarcinogenesis through deregulation of ER stress response. Virus Res. 2022, 315, 198787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Hou, Z.; Yin, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J. 5’-triphosphate siRNA targeting HBx elicits a potent anti-HBV immune response in pAAV-HBV transfected mice. Antivir. Res. 2019, 161, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Cao, H.; Chen, X.-W.; Zhou, M.-J.; Liu, Z.-H.; Ding, Z.-H. Downregulation of HBx mRNA in HepG2.2.15 cells by small interfering RNA. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 19, 1114–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Y.; Ren, X.-H.; Han, D.; Guan, Y.-Y.; Liu, P.-L.; Cheng, S.-X.; Liu, H. Codelivery of HBx-siRNA and Plasmid Encoding IL-12 for Inhibition of Hepatitis B Virus and Reactivation of Antiviral Immunity. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allweiss, L.; Giersch, K.; Pirosu, A.; Volz, T.; Muench, R.C.; Beran, R.K.; Urban, S.; Javanbakht, H.; Fletcher, S.P.; Lütgehetmann, M.; et al. Therapeutic shutdown of HBV transcripts promotes reappearance of the SMC5/6 complex and silencing of the viral genome in vivo. Gut 2022, 71, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Pan, S.; Gu, C.; Wei, L.; Kang, N.; Xie, Y.; Liu, J. Characterization and engineering of broadly reactive monoclonal antibody against hepatitis B virus X protein that blocks its interaction with DDB1. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-F.; Xiong, H.-L.; Cao, J.-L.; Wang, S.-J.; Guo, X.-R.; Lin, B.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.-H.; Wang, Y.-B.; Zhang, T.-Y.; et al. A cell-penetrating whole molecule antibody targeting intracellular HBx suppresses hepatitis B virus via TRIM21-dependent pathway. Theranostics 2018, 8, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horng, J.-H.; Lin, W.-H.; Wu, C.-R.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Wu, L.-L.; Chen, D.-S.; Chen, P.-J. HBV X protein-based therapeutic vaccine accelerates viral antigen clearance by mobilizing monocyte infiltration into the liver in HBV carrier mice. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, D.T.; Dou, Y.; de Wilde, J.W.; Woltman, A.M.; Buschow, S.I. Designing the next-generation therapeutic vaccines to cure chronic hepatitis B: Focus on antigen presentation, vaccine properties and effect measures. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2021, 10, e1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medhat, A.; Arzumanyan, A.; Feitelson, M.A. Hepatitis B x antigen (HBx) is an important therapeutic target in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 2421–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, F.; Tong, X.; Hoffmann, D.; Zuo, J.; Lu, M. Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Using Small Molecule Modulators of Nucleocapsid Assembly: Recent Advances and Perspectives. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiba, K.; Otsuka, M.; Ohno, M.; Yamagami, M.; Kishikawa, T.; Suzuki, T.; Ishibashi, R.; Seimiya, T.; Tanaka, E.; Koike, K. Inhibition of HBV Transcription From cccDNA With Nitazoxanide by Targeting the HBx-DDB1 Interaction. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 7, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartorius, K.; An, P.; Winkler, C.; Chuturgoon, A.; Li, X.; Makarova, J.; Kramvis, A. The Epigenetic Modulation of Cancer and Immune Pathways in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Influence of HBx and miRNA Dysregulation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 661204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
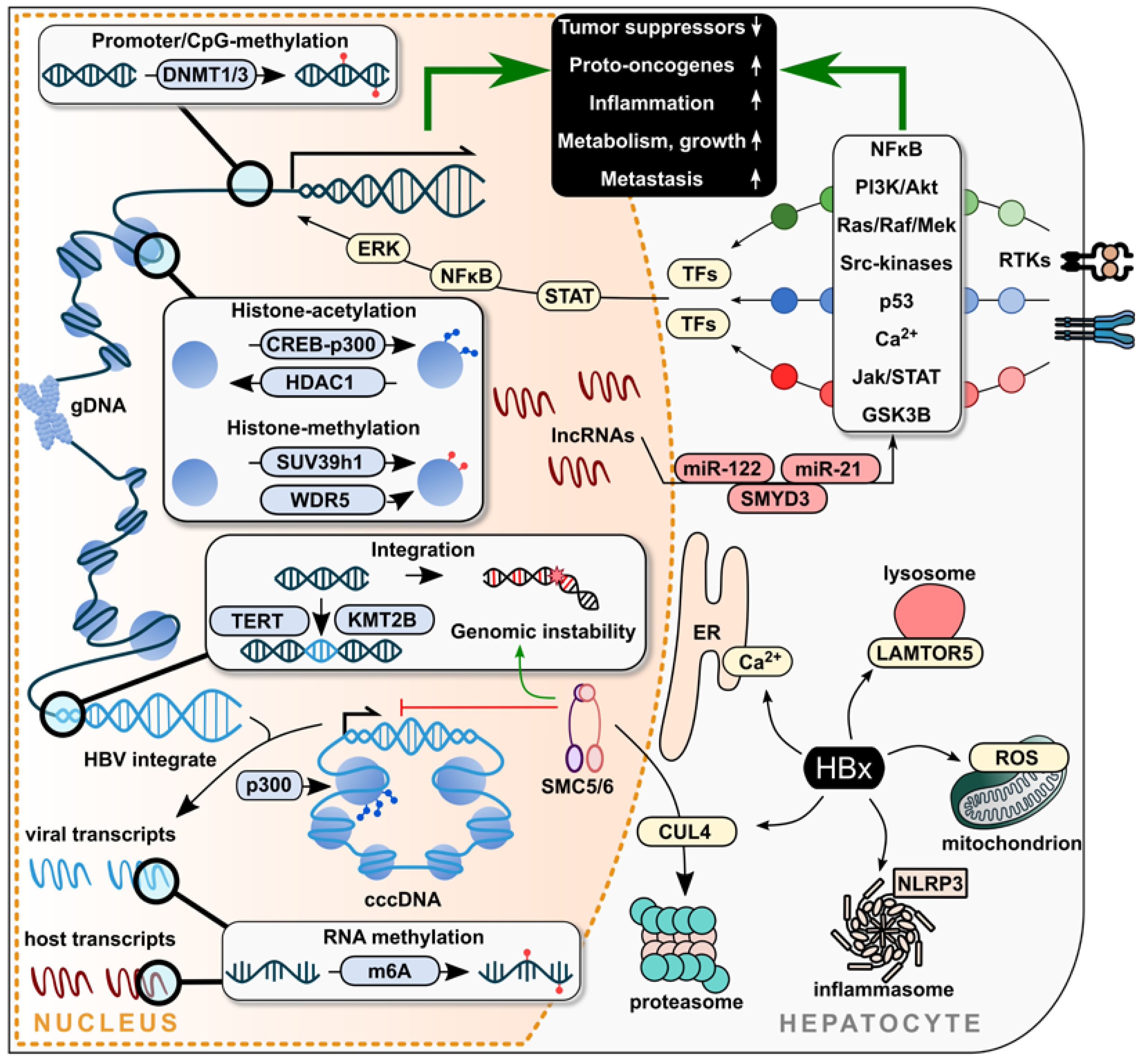
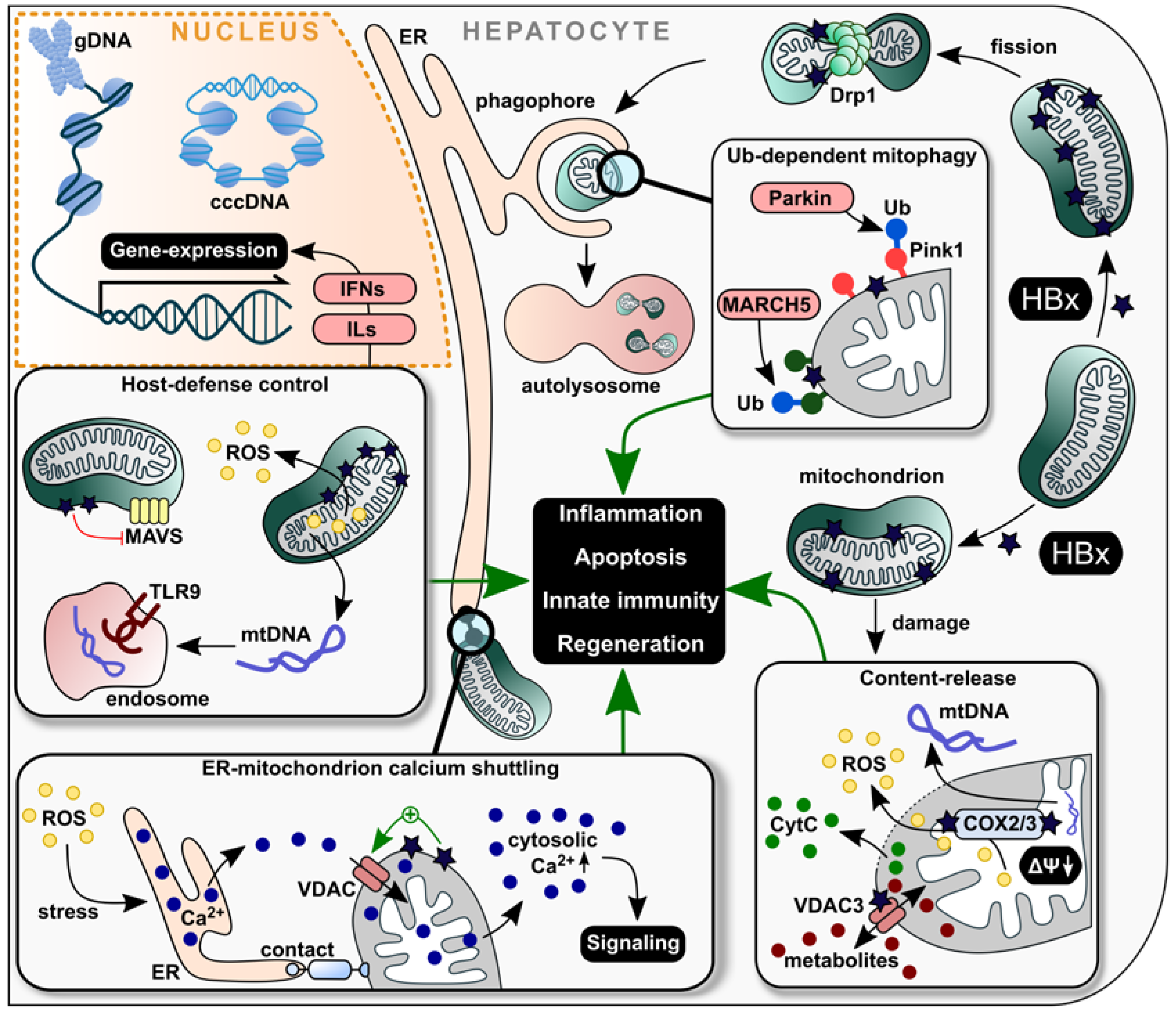
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schollmeier, A.; Glitscher, M.; Hildt, E. Relevance of HBx for Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054964
Schollmeier A, Glitscher M, Hildt E. Relevance of HBx for Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Pathogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(5):4964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054964
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchollmeier, Anja, Mirco Glitscher, and Eberhard Hildt. 2023. "Relevance of HBx for Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Pathogenesis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 5: 4964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054964
APA StyleSchollmeier, A., Glitscher, M., & Hildt, E. (2023). Relevance of HBx for Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Pathogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(5), 4964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054964







