Deferiprone and Iron–Maltol: Forty Years since Their Discovery and Insights into Their Drug Design, Development, Clinical Use and Future Prospects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diseases of Iron Metabolism Imbalance and Their Treatment
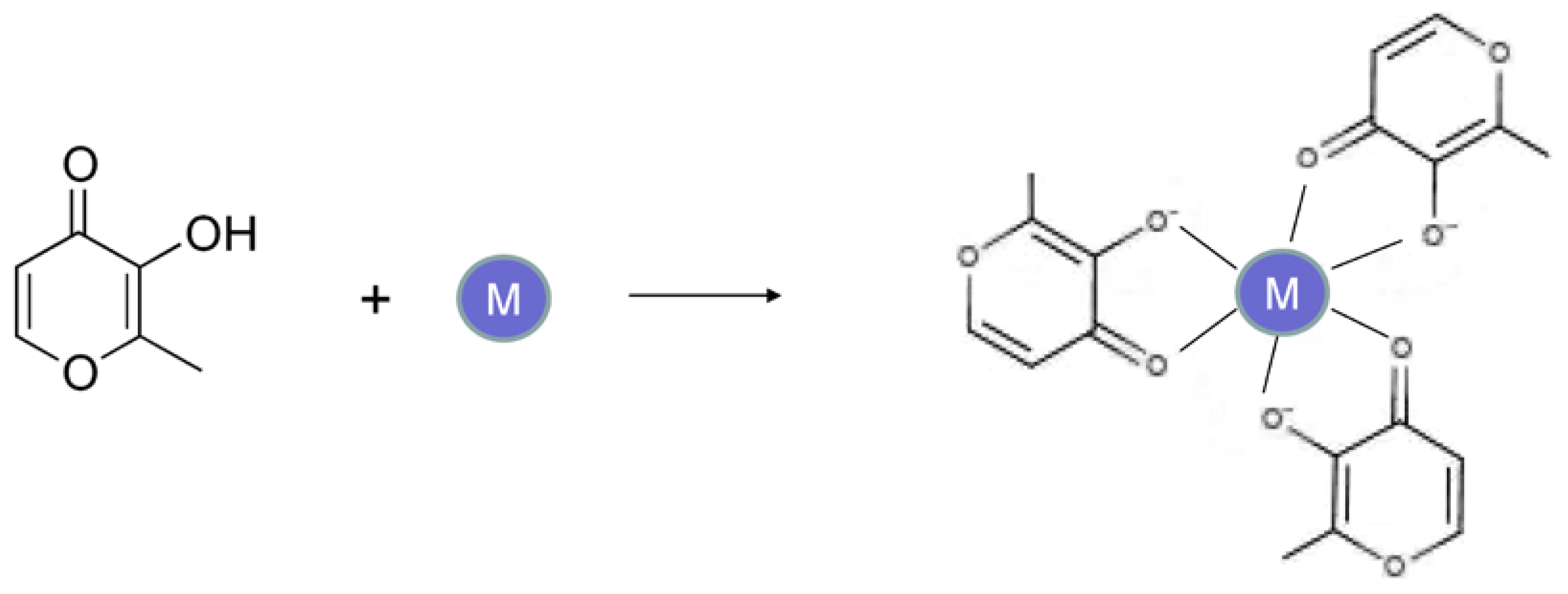
3. The Design and Development of Deferiprone and the Maltol–Iron Complex
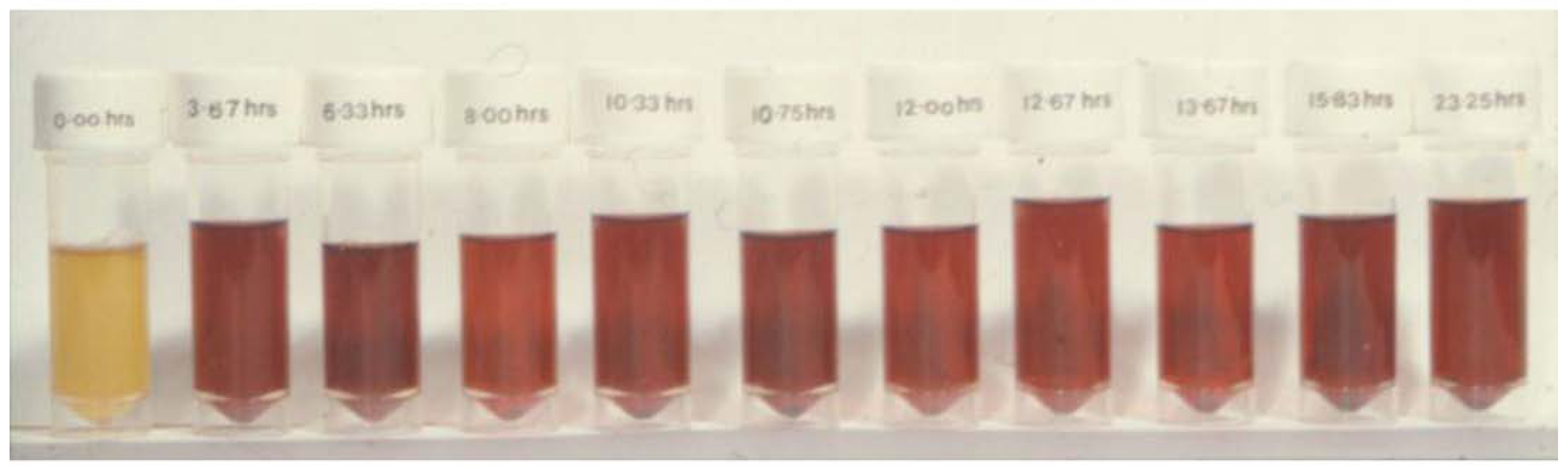
3.1. The Pre-Clinical and Clinical Development of Deferiprone
3.2. The Pre-Clinical and Clinical Development of the Maltol–Iron Complex
4. New Clinical Applications of Deferiprone and the Maltol–Iron Complex
4.1. The Use of Deferiprone in Transfusional Iron Overload and Other Diseases
4.2. The Use of Maltol–Metal Complexes in Diseases Other Than Iron Deficiency Anemia
5. Future Prospects in the Use of Deferiprone and the Maltol–Iron Complex
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| COVID-19 | coronavirus disease 2019 |
| DF | deferoxamine |
| DFRA | deferasirox |
| EDTA | ethylenediaminetriacetic acid |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration (USA) |
| HIF | Hypoxia-inducible factor |
| ICOC | International Committee on Chelation |
| IDA | iron deficiency anemia |
| L1 | deferiprone |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| NDRG | 1N-MYC downstream-regulated gene-1 |
| NBIA | neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation |
| PKAN | Pantothenate-kinase-associated neurodegeneration |
| STEAP4 | six transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate, family member 4 protein |
References
- Katsarou, A.; Pantopoulos, K. Basics and principles of cellular and systemic iron homeostasis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2020, 75, 100866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozzelino, R.; Arosio, P. Iron Homeostasis in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, E130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairo, G.; Bernuzzi, F.; Recalcati, S. A precious metal: Iron, an essential nutrient for all cells. Genes Nutr. 2006, 1, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, A.S. Zinc: An overview. Nutrition 1995, 11, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, J.E. Zinc proteins: Enzymes, storage proteins, transcription factors, and replication proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1992, 61, 897–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.S. Zinc deficiency. BMJ 2003, 326, 409–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, K.G.; Harbach, R.H.; Guida, W.C.; Dou, Q.P. Copper storage diseases: Menkes, Wilson’s, and Cancer. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 2652–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomme, P.T.; McCann, K.B.; Bertolini, J. Transferrin: Structure, function and potential therapeutic actions. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantopoulos, K. TfR2 links iron metabolism and erythropoiesis. Blood 2015, 125, 1055–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makey, D.G.; Seal, U.S. The detection of four molecular forms of human transferrin during the iron binding process. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Protein Struct. 1976, 453, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargent, P.J.; Farnaud, S.; Evans, R.W. Structure/Function Overview of Proteins Involved in Iron Storage and Transport. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 2683–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arosio, P.; Elia, L.; Poli, M. Ferritin, cellular iron storage and regulation. IUBMB Life 2017, 69, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theil, E.C. Ferritin: The Protein Nanocage and Iron Biomineral in Health and in Disease. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 12223–12233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iancu, T.C. Ferritin and hemosiderin in pathological tissues. Electron Microsc. Rev. 1992, 5, 209–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehlenbacher, M.; Poli, M.; Arosio, P.; Santambrogio, P.; Levi, S.; Chasteen, N.D.; Bou-Abdallah, F. Iron Oxidation and Core Formation in Recombinant Heteropolymeric Human Ferritins. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 3900–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H. Storage Iron Turnover from a New Perspective. Acta Haematol. 2019, 141, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, H. Transferrin and transferrin receptors update. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, D.R. Molecular Mechanisms of Iron Uptake by Cells and the Use of Iron Chelators for the Treatment of Cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 2711–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghe, C.N.; Kolnagou, A.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Potential clinical applications of chelating drugs in diseases targeting transferrin-bound iron and other metals. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2013, 22, 591–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Kontoghiorghe, C.N. Iron and Chelation in Biochemistry and Medicine: New Approaches to Controlling Iron Metabolism and Treating Related Diseases. Cells 2020, 9, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, N.C. Disorders of Iron Metabolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1986–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, E.; Cogswell, M.; Egli, I.; Wojdyla, D.; De Benoist, B. Worldwide prevalence of anaemia, WHO Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System, 1993–2005. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasricha, S.-R.; Tye-Din, J.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; Swinkels, D.W. Iron deficiency. Lancet 2021, 397, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardy, A.-L.; Pouteau, E.; Marquez, D.; Yilmaz, C.; Scholey, A. Vitamins and Minerals for Energy, Fatigue and Cognition: A Narrative Review of the Biochemical and Clinical Evidence. Nutrients 2020, 12, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustarah, F.; Mohiuddin, S.S. Dietary Iron; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, J. Treating Iron Deficiency Anemia. Indian J. Pediatr. 2019, 86, 1085–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Węgier, L.P.; Kubiak, M.; Liebert, A.; Clavel, T.; Montagne, A.; Stennevin, A.; Roye, S.; Boudribila, A. Ferrous sulfate oral solution in young children with iron deficiency anemia: An open-label trial of efficacy, safety, and acceptability. Pediatr. Int. 2020, 62, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, C.; Olivares, M.; Brito, A.; Hamilton-West, C.; Pizarro, F. Is a 40% Absorption of Iron from a Ferrous ascorbate Reference Dose Appropriate to Assess Iron Absorption Independent of Iron Status? Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 155, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.; Geevarghese, P.; Khaire, P.; Joshi, T.; Suryawanshi, A.; Mundada, S.; Pawar, S.; Farookh, A. Comparison of Therapeutic Efficacy of Ferrous Ascorbate and Iron Polymaltose Complex in Iron Deficiency Anemia in Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Indian J. Pediatr. 2019, 86, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liabeuf, S.; Gras, V.; Moragny, J.; Laroche, M.-L.; Andréjak, M. Ulceration of the oral mucosa following direct contact with ferrous sulfate in elderly patients: A case report and a review of the French National Pharmacovigilance Database. Clin. Interv. Aging 2014, 9, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkien, Z.; Stecher, L.; Mander, A.P.; Pereira, D.I.; Powell, J.J. Ferrous sulfate supplementation causes significant gastro-intestinal side-effects in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, N.R.; Hasinoff, B.B. Iron supplements: A common cause of drug interactions. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1991, 31, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.; Kolnagou, A.; Demetriou, T.; Neocleous, M.; Kontoghiorghe, C. New Era in the Treatment of Iron Deficiency Anaemia Using Trimaltol Iron and Other Lipophilic Iron Chelator Complexes: Historical Perspectives of Discovery and Future Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manz, D.H.; Blanchette, N.L.; Paul, B.T.; Torti, F.M.; Torti, S.V. Iron and cancer: Recent insights. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1368, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, P.; Nicolini, A.; Manca, M.L.; Rossi, G.; Anselmi, L.; Conte, M.; Carpi, A.; Bonino, F. Treatment of mild non-chemotherapy-induced iron deficiency anemia in cancer patients: Comparison between oral ferrous bisglycinate chelate and ferrous sulfate. Biomed. Pharm. 2012, 66, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punj, S.; Ghafourian, K.; Ardehali, H. Iron deficiency and supplementation in heart failure and chronic kidney disease. Mol. Asp. Med. 2020, 75, 100873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kshirsagar, A.V.; Li, X. Long-Term Risks of Intravenous Iron in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2019, 26, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataatmadja, M.S.; Francis, R. Recurrent severe hypophosphatemia following intravenous iron administration. Clin. Case Rep. 2020, 8, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rund, D. Intravenous iron: Do we adequately understand the short- and long-term risks in clinical practice? Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 193, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerbach, M.; Gafter-Gvili, A.; Macdougall, I.C. Intravenous iron: A framework for changing the management of iron deficiency. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e342–e350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantadakis, E.; Chatzimichael, E.; Zikidou, P. Iron Deficiency Anemia in Children Residing in High and Low-Income Countries: Risk Factors, Prevention, Diagnosis and Therapy. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 12, e2020041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, K.; Kumar, T.; Doda, A.; Bhutani, R.; Yadav, S.; Kaushal, P.; Kapoor, R.; Sharma, S. Prevalence of anaemia and its association with dietary habits among pregnant women in the urban area of Haryana. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2020, 9, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. Community control of hereditary anaemias: Memorandum from a WHO meeting. Bull. World Health Organ. 1983, 61, 63–80. [Google Scholar]
- Weatherall, D.J.; Clegg, J.B. Inherited haemoglobin disorders: An increasing global health problem. Bull. World Health Organ. 2001, 79, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Modell, B.; Berdoukas, V. The Clinical Approach to Thalassaemia; Grune and Stratton: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 165–169. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, J.C.; Edwards, C.Q. (Eds.) Hemochromatosis: Genetics, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Feder, J.N.; Gnirke, A.; Thomas, W.; Tsuchihashi, Z.; Ruddy, D.A.; Basava, A.; Dormishian, F.; Domingo, R., Jr.; Ellis, M.C.; Fullan, A.; et al. A novel MHC class I–like gene is mutated in patients with hereditary haemochromatosis. Nat. Genet. 1996, 13, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrangelo, A. Hereditary Hemochromatosis—A New Look at an Old Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2383–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, S.; Kowdley, K.V. Targeted screening for hereditary haemochromatosis in high-risk groups. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, I.C. Burden of genetic disorders in india. Indian J. Pediatr. 2000, 67, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolnagou, A.; Kontoghiorghe, C.N.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Transition of Thalassaemia and Friedreich ataxia from fatal to chronic diseases. World J. Methodol. 2014, 4, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Eracleous, E.; Economides, C.; Kolnagou, A. Advances in Iron Overload Therapies. Prospects for Effective Use of Deferiprone (L1), Deferoxamine, the New Experimental Chelators ICL670, GT56-252, L1NAll and their Combinations. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 2663–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telfer, P.T.; Warburton, F.; Christou, S.; Hadjigavriel, M.; Sitarou, M.; Kolnagou, A.; Angastiniotis, M. Improved survival in thalassemia major patients on switching from desferrioxamine to combined chelation therapy with desferrioxamine and deferiprone. Haematologica 2009, 94, 1777–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, M.A.; Galanello, R.; Dessi, C.; Smith, G.C.; Westwood, M.A.; Agus, A.; Pibiri, M.; Nair, S.V.; Walker, J.M.; Pennell, D.J. Combined chelation therapy in thalassemia major for the treatment of severe myocardial siderosis with left ventricular dysfunction. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2008, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepe, A.; Meloni, A.; Pistoia, L.; Cuccia, L.; Gamberini, M.R.; Lisi, R.; D’Ascola, D.G.; Rosso, R.; Allò, M.; Spasiano, A.; et al. MRI multicentre prospective survey in thalassaemia major patients treated with defer-asirox versus deferiprone and desferrioxamine. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 183, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-H.; Chen, X.; Wu, C.-C.; Wu, K.-H.; Song, T.-S.; Weng, T.-F.; Hsieh, Y.-W.; Peng, C.-T. Therapeutic mechanism of combined oral chelation therapy to maximize efficacy of iron removal in transfusion-dependent thalassemia major-a pilot study. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2019, 12, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eghbali, A.; Shokri, P.; Afzal, R.R.; Bagheri, B. A 1-year randomized trial of deferasirox alone versus deferasirox and deferoxamine combination for the treatment of iron overload in thalassemia major. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2019, 58, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Neocleous, K.; Kolnagou, A. Benefits and risks of deferiprone in iron overload in thalassaemia and other conditions: Comparison of epidemiological and therapeutic aspects with deferoxamine. Drug Saf. 2003, 26, 553–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontoghiorghe, C.N.; Andreou, N.; Constantinou, K.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. World health dilemmas: Orphan and rare diseases, orphan drugs and orphan patients. World J. Methodol. 2014, 4, 163–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. The Design of Orally Active Iron Chelators for the Treatment of Thalassaemia. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Essex, Colchester, UK, 1982; pp. 1–243. Available online: https://www.pri.ac.cy/files/KGJ_thesis_1982.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Design, Properties, and Effective Use of the Oral Chelator L1 and Other Alpha-Ketohydroxypyridines in the Treatment of Transfusional Iron Overload in Thalassemia. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1990, 612, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.; Pattichis, K.; Neocleous, K.; Kolnagou, A. The Design and Development of Deferiprone (L1) and Other Iron Chelators for Clinical Use: Targeting Methods and Application Prospects. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 2161–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Kleanthous, M.; Kontoghiorghe, C.N. The History of Deferiprone (L1) and the Paradigm of the Complete Treatment of Iron Overload in Thalassaemia. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 12, e2020011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Wilson, M.T. Structural and kinetic studies on eisenia foetida erythrocruorin. In Invertebrate Oxygen Binding Proteins, Structure, Active Site and Function; Lamy, J., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1981; pp. 385–391. [Google Scholar]
- Kontoghiorghe, C.N.; Kolnagou, A.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Phytochelators Intended for Clinical Use in Iron Overload, Other Diseases of Iron Imbalance and Free Radical Pathology. Molecules 2015, 20, 20841–20872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, L.N.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Comparative iron binding studies of bis and tris (3-hydroxy-2-methylpyrid-4-ones) and desferrioxamine. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1991, 188, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Marcus, R.; Huehns, E. Desferrioxamine Suppositories. Lancet 1983, 322, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. New Orally Active Iron Chelators. Lancet 1985, 325, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Sheppard, L.; Hoffbrand, A.V.; Charalambous, J.; Tikerpae, J.; Pippard, M.J. Iron chelation studies using desferrioxamine and the potential oral chelator, 1,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxypyrid-4-one, in normal and iron loaded rats. J. Clin. Pathol. 1987, 40, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Dose response studies using desferrioxamine and orally active chelators in a mouse model. Scand. J. Haematol. 1986, 37, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Orally active alpha-ketohydroxypyridine iron chelators: Studies in mice. Mol. Pharmacol. 1986, 30, 670–673. [Google Scholar]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Hoffbrand, A.V. Orally active α-ketohydroxy pyridine iron chelators intended for clinical use: In Vivo studies in rabbits. Br. J. Haematol. 1986, 62, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Orally Active Alpha-Ketohydroxypyridine Iron Chelators: Effects on Iron and Other Metal Mobilisations. Acta Haematol. 1987, 78, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyparaki, M.; Porter, J.B.; Hirani, S.; Streater, M.; Hider, R.C.; Huehns, E.R. In Vivo Evaluation of Hydroxypyridone Iron Chelators in a Mouse Model. Acta Haematol. 1987, 78, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huehns, E.R.; Porter, J.B.; Hider, R.C. Selection of Hydroxypyridin-4-Ones for the Treatment of Iron Overload Using In Vitro and In Vivo Models. Hemoglobin 1988, 12, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.B.; Morgan, J.; Hoyes, K.P.; Burke, L.C.; Huehns, E.R.; Hider, R.C. Relative oral efficacy and acute toxicity of hydroxy-pyridin-4-one iron chelators in mice. Blood 1990, 76, 2389–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Barr, J.; Nortey, P.; Sheppard, L. Selection of a new generation of orally active α-ketohydroxypyridine iron chelators intended for use in the treatment of iron overload. Am. J. Hematol. 1993, 42, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Sheppard, L. Simple synthesis of the potent iron chelators 1-alkyl-3-hydroxy-2-methylpyrid-4-ones. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1987, 136, L11–L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. (Ed.) Oral chelation in the treatment of thalassaemia and other diseases. Drugs Today 1992, 28, 1–187. [Google Scholar]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Sheppard, L.; Aldouri, M.A.; Hoffbrand, A.V. 1,2-Dimethyl-3-Hydroxypyrid-4-One, an Orally Active Chelator for Treatment of Iron Overload. Lancet 1987, 329, 1294–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Aldouri, M.A.; Hoffbrand, A.V.; Barr, J.; Wonke, B.; Kourouclaris, T.; Sheppard, L. Effective chelation of iron in beta thalassaemia with the oral chelator 1,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxypyrid-4-one. BMJ 1987, 295, 1509–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Iron chelating drugs. BMJ 1988, 296, 1672–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Oral iron chelation is here. BMJ 1991, 303, 1279–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.B.; Singh, S.; Hoyes, K.P.; Epemolu, O.; Abeysinghe, R.D.; Hider, R.C. Lessons from Preclinical and Clinical Studies with 1,2-Diethyl-3-Hydroxypyridin-4-One, CP94 and Related Compounds. In Progress in Iron Research; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; Volume 356, pp. 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.B.; Abeysinghe, R.D.; Hoyes, K.P.; Barra, C.; Huehns, E.R.; Brooks, P.N.; Blackwell, M.P.; Araneta, M.; Brittenham, G.; Singh, S.; et al. Contrasting interspecies efficacy and toxicology of 1, 2-diethy 1–3 -hydroxypyridin-4-one, CP94, relates to differing metabolism of the iron chelating site. Br. J. Haematol. 1993, 85, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epemolu, R.O.; Ackerman, R.; Porter, J.B.; Hider, R.C.; Damani, L.A.; Singh, S. HPLC determination of 1,2-diethyl-3-hydroxypyridin-4-one (CP94), its iron complex [Fe(III) (CP94)3] and glucuronide conjugate [CP94-GLUC] in serum and urine of thalassaemic patients. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1994, 12, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfannkuch, F.; Bentley, P.; Schnebli, H.P. Future of oral iron chelator deferiprone (L1). Lancet 1993, 341, 1480. [Google Scholar]
- Berdoukas, V.; Bentley, P.; Frost, H.; Schnebli, H.P. Toxicity of oral iron chelator L1. Lancet 1993, 341, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershko, C. Development of oral iron chelator L1. Lancet 1993, 341, 1088–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Misinformation about deferiprone (L1). Lancet 1993, 342, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Agarwal, M.B.; Grady, R.W.; Kolnagou, A.; Marx, J.J. Deferiprone for thalassaemia. Lancet 2000, 356, 428–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pippard, M.J.; Weatherall, D.J. Deferiprone for thalassaemia. Lancet 2000, 356, 1444–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Agarwal, M.B.; Tondury, P.; Marx, J.J. Deferiprone or fatal iron toxic effects? Lancet 2001, 357, 882–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffbrand, A.V.; Bartlett, A.N.; Veys, P.A.; O’Connor, N.T.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Agranulocytosis and Thrombocytopenia in Patient with Blackfan-Diamond Anaemia during Oral Chelator Trial. Lancet 1989, 334, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, M.B.; Gupte, S.S.; Viswanathan, C.; Vasandani, D.; Ramanathan, J.; Desai, N.; Puniyani, R.R.; Chhablani, A.T. Long-term assessment of efficacy and safety of L1, an oral iron chelator, in transfusion dependent thalassaemia: Indian trial. Br. J. Haematol. 1992, 82, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Present status and future prospects of oral iron chelation therapy in thalassaemia and other diseases. Indian J. Pediatr. 1993, 60, 485–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.R.; Galanello, R.; Piga, A.; De Sanctis, V.; Tricta, F. Safety and effectiveness of long-term therapy with the oral iron chelator deferiprone. Blood 2003, 102, 1583–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The History of Deferiprone. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZcvSLyIgYd8 (accessed on 1 October 2019).
- Töndury, P.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Ridolfi-Lüthy, A.; Hirt, A.; Hoffbrand, A.V.; Lottenbach, A.M.; Sonderegger, T.; Wagner, H.P.; Toundury, P.; Ridolfi-Luuthy, A. L1 (1,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxypyrid-4-one) for oral iron chelation in patients with beta-thalassaemia major. Br. J. Haematol. 1990, 76, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, N.F.; Koren, G.; Louis, P.S.; Freedman, M.H.; McClelland, R.A.; Templeton, D.M. Studies of the oral chelator 1,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxypyrid-4-one in thalassemia patients. Semin. Hematol. 1990, 27, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit, R. Long-term treatment of patients with transfusion hemosiderosis using oral iron chelator 1,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxypyrid-4-one (L1). Ned. Tijdschr. Geneeskd. 1991, 135, 2133–2136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carnelli, V.; Terzoli, S.; Fossati, G.; Careddu, G.; Perri, M.; Pedrotti, L.; Mirra, N. New therapeutic trends in thalassemia: Oral chelating agents. Pediatr. Med. Chir. 1992, 14, 273–275. [Google Scholar]
- Cermák, J.; Brabec, V. Treatment of iron overload states with oral administration of the chelator agent, L1 (Deferiprone). Vnitr. Lek. 1994, 40, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kersten, M.J.; Lange, R.; Smeets, M.E.P.; Vreugdenhil, G.; Roozendaal, K.J.; Lameijer, W.; Goudsmit, R. Long-term treatment of transfusional iron overload with the oral iron chelator deferiprone (L1): A Dutch multicenter trial. Ann. Hematol. 1996, 73, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.M. Royal Society of Chemistry-sixth international symposium on applied bioinorganic chemistry. IDrugs Investig. Drugs J. 2001, 4, 1005–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Rombos, Y.; Tzanetea, R.; Konstantopoulos, K.; Simitzis, S.; Zervas, C.; Kyriaki, P.; Kavouklis, M.; Aessopos, A.; Sakellaropoulos, N.; Karagiorga, M.; et al. Chelation therapy in patients with thalassemia using the orally active iron chelator deferiprone (L1). Haematologica 2000, 85, 115–117. [Google Scholar]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. The Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Chelation held in the USA: Advances on new and old chelation therapies. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2013, 23, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savulescu, J. Thalassaemia major: The murky story of deferiprone. BMJ 2004, 328, 358–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet-Brown, E.; Olivieri, N.F.; Giardina, P.J.; Grady, R.W.; Neufeld, E.J.; Séchaud, R.; Krebs-Brown, A.J.; Anderson, J.R.; Alberti, D.; Sizer, K.C.; et al. Effectiveness and safety of ICL670 in iron-loaded patients with thalassaemia: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation trial. Lancet 2003, 361, 1597–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufeld, E.J. Oral chelators deferasirox and deferiprone for transfusional iron overload in thalassemia major: New data, new questions. Blood 2006, 107, 3436–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. New chelation therapies and emerging chelating drugs for the treatment of iron overload. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2006, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viprakasit, V.; Nuchprayoon, I.; Chuansumrit, A.; Torcharus, K.; Pongtanakul, B.; Laothamatas, J.; Srichairatanakool, S.; Pooliam, J.; Supajitkasem, S.; Suriyaphol, P.; et al. Deferiprone (GPO-L-ONE®) monotherapy reduces iron overload in transfusion-dependent thalassemias: 1-year results from a multicenter prospective, single arm, open label, dose escalating phase III pediatric study (GPO-L-ONE.; A001) from Thailand. Am. J. Hematol. 2013, 88, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. The aim of iron chelation therapy in thalassaemia. Eur. J. Haematol. 2017, 99, 465–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, A.; Kattamis, A.; Felisi, M.; Reggiardo, G.; El-Beshlawy, A.; Bejaoui, M.; Sherief, L.; Christou, S.; Cosmi, C.; Della Pasqua, O.; et al. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of deferiprone compared with deferasirox in paediatric patients with transfusion-dependent haemoglobinopathies (DEEP-2): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, non-inferiority, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e469–e478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.Y.; Lee, V.; Lau, C.W.; Yau, J.; Chan, D.; Chan, E.Y.T.; Cheung, W.W.W.; Ha, S.Y.; Kho, B.; Lee, C.Y.; et al. A synopsis of current care of thalassaemia major patients in Hong Kong. Hong Kong Med. J. 2011, 17, 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- Maggio, A.; Filosa, A.; Vitrano, A.; Aloj, G.; Kattamis, A.; Ceci, A.; Fucharoen, S.; Cianciulli, P.; Grady, R.W.; Prossomariti, L.; et al. Iron chelation therapy in thalassemia major: A systematic review with meta-analyses of 1520 patients included on randomized clinical trials. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2011, 47, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.R.; Galanello, R.; Piga, A.; Dipalma, A.; Vullo, C.; Tricta, F. Safety profile of the oral iron chelator deferiprone: A mul-ticentre study. Br. J. Haematol. 2000, 108, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, A.; Vitrano, A.; Lucania, G.; Capra, M.; Cuccia, L.; Gagliardotto, F.; Pitrolo, L.; Prossomariti, L.; Filosa, A.; Caruso, V.; et al. Long-term use of deferiprone significantly enhances left-ventricular ejection function in thalassemia major patients. Am. J. Hematol. 2012, 87, 732–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolnagou, A.; Kleanthous, M.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Reduction of body iron stores to normal range levels in thalassaemia by using a deferiprone/deferoxamine combination and their maintenance thereafter by deferiprone monotherapy. Eur. J. Haematol. 2010, 85, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Kontoghiorghe, C.N. Efficacy and safety of iron-chelation therapy with deferoxamine, deferiprone, and deferasirox for the treatment of iron-loaded patients with non-transfusion-dependent thalassemia syndromes. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolnagou, A.; Kleanthous, M.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Benefits and Risks in Polypathology and Polypharmacotherapy Chal-lenges in the Era of the Transition of Thalassaemia from a Fatal to a Chronic or Curable Disease. Front. Biosci. 2022, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolnagou, A.; Kontoghiorghe, C.N.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Prevention of Iron Overload and Long Term Maintenance of Normal Iron Stores in Thalassaemia Major Patients using Deferiprone or Deferiprone Deferoxamine Combination. Drug Res. 2017, 67, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolnagou, A.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Chelation protocols for the elimination and prevention of iron overload in thalassaemia. Front. Biosci. 2018, 23, 1082–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Chelators affecting iron absorption in mice. Arzneimittelforschung 1990, 40, 1332–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Barrand, M.A.; Callingham, B.A.; Hider, R.C. Effects of the pyrones, maltol and ethyl maltol, on iron absorption from the rat small intestine. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1987, 39, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrand, M.A.; Callingham, B.A.; Dobbin, P.; Hider, R.C. Dissociation of a ferric maltol complex and its subsequent metabolism during absorption across the small intestine of the rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1991, 102, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, K.H.; Barta, C.A.; Orvig, C. Metal complexes of maltol and close analogues in medicinal inorganic chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, R.S.J.; Reffitt, D.M.; Doig, L.A.; Meenan, J.; Ellis, R.D.; Thompson, R.P.H.; Powell, J.J. Ferric trimaltol corrects iron deficiency anaemia in patients intolerant of iron. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1998, 12, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reffitt, D.M.; Burden, T.J.; Seed, P.T.; Wood, J.; Thompson, R.P.; Powell, J.J. Assessment of iron absorption from ferric trimaltol. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2000, 37, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, A.; Pagan, K.A.; Farland, M.Z. Ferric Maltol: A New Oral Iron Formulation for the Treatment of Iron Deficiency in Adults. Ann. Pharmacother. 2021, 55, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallmach, A.; Büning, C. Ferric maltol (ST10): A novel oral iron supplement for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2015, 16, 2859–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murawska, N.; Fabisiak, A.; Fichna, J. Anemia of Chronic Disease and Iron Deficiency Anemia in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergola, P.E.; Fishbane, S.; Ganz, T. Novel Oral Iron Therapies for Iron Deficiency Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2019, 26, 272–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokemeyer, B.; Krummenerl, A.; Maaser, C.; Howaldt, S.; Mroß, M.; Mallard, N. Randomized Open-Label Phase 1 Study of the Pharmacokinetics of Ferric Maltol in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients with Iron Deficiency. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 42, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasche, C.; Ahmad, T.; Tulassay, Z.; Baumgart, D.C.; Bokemeyer, B.; Büning, C.; Howaldt, S.; Stallmach, A. AEGIS Study Group. Ferric maltol is effective in correcting iron deficiency anemia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: Results from a phase-3 clinical trial program. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, C.; Ahmad, T.; Tulassay, Z.; Baumgart, D.C.; Bokemeyer, B.; Howaldt, S.; Stallmach, A.; Büning, C.; the AEGIS Study Group. Ferric maltol therapy for iron deficiency anaemia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: Long-term extension data from a Phase 3 study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 44, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsey, S.M.; Hider, R.; Bloor, J.R.C.; Blake, D.R.; Gutteridge, C.N.; Newland, A.C. Absorption of low and therapeutic doses of ferric maltol, a novel ferric iron compound, in iron deficient subjects using a single dose iron absorption test. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 1991, 16, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, K.M.; Fuge, J.; Brod, T.; Kamp, J.C.; Schmitto, J.; Kempf, T.; Bauersachs, J.; Hoeper, M.M. Oral iron supplementation with ferric maltol in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2000616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopyt, N.P.; AEGIS-CKD Study Group. Efficacy and safety of oral ferric maltol (FM) in treating iron-deficiency anemia (IDA) in patients with CKD: Randomized controlled trial [FR-OR120]. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 70–71. [Google Scholar]
- Mause, S.F.; Berger, M.; Lim, H.Y.; Vogt, F.; Brandenburg, V.; Stöhr, R. Intravenous iron supplementation in heart failure patients induces temporary endothelial dysfunction with release of endothelial microvesicles. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1092704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, A.F.; Morga, A.; Thomas, C.; Krucien, N.; Tervonen, T.; Jiletcovici, A.; Marsh, K. Preferences for Anaemia Treatment Attributes among Patients with Non-Dialysis-Dependent Chronic Kidney Disease. Adv. Ther. 2023, 40, 641–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, C.; Tsuchiya, K.; Kanemitsu, M.; Maeda, K. Low-Dose Oral Iron Replacement Therapy Is Effective for Many Japanese Hemodialysis Patients: A Retrospective Observational Study. Nutrients 2022, 15, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Luo, Q.; Huang, C.; Shi, L.; Jahangir, A.; Pan, T.; Wei, X.; He, J.; Liu, W.; Shi, R.; et al. Ferric citrate-induced colonic mucosal damage associated with oxidative stress, inflammation responses, apoptosis, and the changes of gut microbial composition. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 249, 114364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghe, C.N.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. New developments and controversies in iron metabolism and iron chelation therapy. World J. Methodol. 2016, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.C. Patent rulings raise hope for cheap cancer drugs in India. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, e441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luangasanatip, N.; Chaiyakunapruk, N.; Upakdee, N.; Wong, P. Iron-chelating therapies in a transfusion-dependent thalassaemia population in Thailand: A cost-effectiveness study. Clin. Drug Investig. 2011, 31, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, N.F.; Matsui, D.; Liu, P.P.; Blendis, L.; Cameron, R.; A McClelland, R.A.; Templeton, D.M.; Koren, G. Oral iron chelation with 1,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxypyrid-4-one (L1) in iron loaded thalassemia patients. Bone Marrow Transpl. 1993, 12, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, N.P.; Rodrat, S.; Piromkraipak, P.; Yamanont, P.; Paiboonsukwong, K.; Fucharoen, S. Iron chelation therapy with de-feriprone improves oxidative status and red blood cell quality and reduces redox-active iron in β-thalassemia/hemoglobin E patients. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-H.; Shaw, C.-F.; Wu, K.-H.; Hsieh, K.-H.; Su, Y.-N.; Lu, P.-J. Treatment with Deferiprone for Iron Overload Alleviates Bone Marrow Failure in a Fanconi Anemia Patient. Hemoglobin 2009, 33, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermak, J.; Jonasova, A.; Vondrakova, J.; Cervinek, L.; Belohlavkova, P.; Neuwirtova, R. A comparative study of deferasirox and deferiprone in the treatment of iron overload in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk. Res. 2013, 37, 1612–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauchenová, L.; Křížová, B.; Kubánek, M.; Fraňková, S.; Melenovský, V.; Tintěra, J.; Kautznerová, D.; Malušková, J.; Jirsa, M.; Kautzner, J. Successful Treatment of Iron-Overload Cardiomyopathy in Hereditary Hemochromatosis with Deferoxamine and Deferiprone. Can. J. Cardiol. 2016, 32, 1574.e1–1574.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Spyrou, A.; Kolnagou, A. Iron chelation therapy in hereditary hemochromatosis and thalassemia intermedia: Regulatory and non regulatory mechanisms of increased iron absorption. Hemoglobin 2010, 34, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabio, G.; Minonzio, F.; Delbini, P.; Bianchi, A.; Cappellini, M.D. Reversal of cardiac complications by deferiprone and deferoxamine combination therapy in a patient affected by a severe type of juvenile hemochromatosis (JH). Blood 2007, 109, 362–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elalfy, M.S.; Hamdy, M.; El-Beshlawy, A.; Ebeid, F.S.E.; Badr, M.; Kanter, J.; Inusa, B.P.; Adly, A.A.M.; Williams, S.; Kilinc, Y.; et al. Deferiprone for transfusional iron overload in sickle cell disease and other anemias: Open-label study of up to 3 years. Blood Adv. 2022, 7, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Barr, J.; Baillod, R.A. Studies of aluminium mobilization in renal dialysis patients using the oral chelator 1,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxypyrid-4-one. Arzneimittelforschung 1994, 44, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Comparative efficacy and toxicity of desferrioxamine, deferiprone and other iron and aluminium chelating drugs. Toxicol. Lett. 1995, 80, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vroegindeweij, L.H.P.; Boon, A.J.W.; Wilson, J.H.P.; Langendonk, J.G. Effects of iron chelation therapy on the clinical course of aceruloplasminemia: An analysis of aggregated case reports. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddaert, N.; Le Quan Sang, K.H.; Rötig, A.; Leroy-Willig, A.; Gallet, S.; Brunelle, F.; Sidi, D.; Thalabard, J.C.; Munnich, A.; Cabantchik, Z.I. Selective iron chelation in Friedreich ataxia: Biologic and clinical implications. Blood 2007, 110, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbruzzese, G.; Cossu, G.; Balocco, M.; Marchese, R.; Murgia, D.; Melis, M.; Galanello, R.; Barella, S.; Matta, G.; Ruffinengo, U.; et al. A pilot trial of deferiprone for neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Haematologica 2011, 96, 1708–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Bastida, A.; Ward, R.J.; Newbould, R.; Piccini, P.; Sharp, D.; Kabba, C.; Patel, M.C.; Spino, M.; Connelly, J.; Tricta, F.; et al. Brain iron chelation by deferiprone in a phase 2 randomised double-blinded placebo controlled clinical trial in Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, P.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Characterization of the Neuroprotective Potential of Derivatives of the Iron Chelating Drug Deferiprone. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, N.; Baiardi, G.; Pinto, V.M.; Quintino, S.; Gianesin, B.; Sasso, R.; Diociasi, A.; Mattioli, F.; Marchese, R.; Abbruzzese, G.; et al. Long-Term Neuroradiological and Clinical Evaluation of NBIA Patients Treated with a Deferiprone Based Iron-Chelation Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapurkar, M.M.; Hegde, U.; Bhattacharya, A.; Alam, M.G.; Shah, S.V. Effect of deferiprone, an oral iron chelator, in diabetic and non-diabetic glomerular disease. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2013, 23, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, D.; Ghosh, K.; Pathare, A.V.; Karnad, D. Deferiprone (L1) as an adjuvant therapy for Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Indian J. Med. Res. 2002, 115, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, D.; Spino, M.; Tricta, F.; Connelly, J.; Cracchiolo, B.M.; Hanauske, A.R.; D’Alliessi Gandolfi, D.; Mathews, M.B.; Karn, J.; Holland, B.; et al. Drug-Based Lead Discovery: The Novel Ablative An-tiretroviral Profile of Deferiprone in HIV-1-Infected Cells and in HIV-Infected Treatment-Naive Subjects of a Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Exploratory Trial. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vreugdenhil, G.; Swaak, A.J.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Van Eijk, H.G. Efficacy and Safety of Oral Iron Chelator L1 in Anaemic Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Lancet 1989, 334, 1398–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpa, J.; Sanz-Gallego, I.; Rodríguez-de-Rivera, F.J.; Domínguez-Melcón, F.J.; Prefasi, D.; Oliva-Navarro, J.; Moreno-Yangüela, M. Triple therapy with deferiprone, idebenone and riboflavin in Friedreich’s ataxia-open-label trial. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2014, 129, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devos, D.; Labreuche, J.; Rascol, O.; Corvol, J.-C.; Duhamel, A.; Delannoy, P.G.; Poewe, W.; Compta, Y.; Pavese, N.; Růžička, E.; et al. Trial of Deferiprone in Parkinson’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2045–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Bartlett, A.N.; Hoffbrand, A.V.; Goddard, J.G.; Sheppard, L.; Barr, J.; Nortey, P. Long-term trial with the oral iron chelator 1,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxypyrid-4-one (L1) I. Iron Chelation and Metabolic Studies. Br. J. Haematol. 1990, 76, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Goddard, J.G.; Bartlett, A.N.; Sheppard, L. Pharmacokinetic studies in humans with the oral iron chelator 1,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxypyrid-4-one. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1990, 48, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Kontoghiorghe, C.N. Prospects for the introduction of targeted antioxidant drugs for the prevention and treatment of diseases related to free radical pathology. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2019, 28, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghe, C.N.; Kolnagou, A.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Antioxidant targeting by deferiprone in diseases related to oxidative damage. Front. Biosci. 2014, 19, 862–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. New Iron Metabolic Pathways and Chelation Targeting Strategies Affecting the Treatment of All Types and Stages of Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitambar, C.R.; Al-Gizawiy, M.M.; Alhajala, H.S.; Pechman, K.R.; Wereley, J.P.; Wujek, R.; Clark, P.A.; Kuo, J.S.; Antholine, W.E.; Schmainda, K.M. Gallium Maltolate Disrupts Tumor Iron Metabolism and Retards the Growth of Glioblastoma by Inhibiting Mitochondrial Function and Ribonucleotide Reductase. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1240–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, L.R.; Van Der Hoeven, J.J.; Boer, R.O. Hepatocellular carcinoma detection by gallium scan and subsequent treatment by gallium maltolate: Rationale and case study. Anti Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, T.W.; Lessmann, G.M.; Saleh, J.; Liu, X.; Chitambar, C.R.; Hwang, S.T. Gallium Maltolate Inhibits Human Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma Tumor Development in Mice. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merli, D.; Profumo, A.; Bloise, N.; Risi, G.; Momentè, S.; Cucca, L.; Visai, L. Indium/Gallium Maltolate Effects on Human Breast Carcinoma Cells: In Vitro Investigation on Cytotoxicity and Synergism with Mitoxantrone. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 4631–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, C.E.; Bordin, A.; Lawhon, S.D.; Libal, M.C.; Bernstein, L.R.; Cohen, N.D. Antimicrobial activity of gallium maltolate against Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant S. aureus and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius: An in vitro study. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 155, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecteau, M.-E.; Aceto, H.W.; Bernstein, L.R.; Sweeney, R.W. Comparison of the antimicrobial activities of gallium nitrate and gallium maltolate against Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in vitro. Vet. J. 2014, 202, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, S.; Visaggio, D.; Pirolo, M.; Frangipani, E.; Bernstein, L.; Visca, P. Antimicrobial Activity of Gallium Compounds on ESKAPE Pathogens. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, K.R.; Sampieri, F.; Chirino, M.; Hamilton, D.L.; Blyth, R.I.R.; Sham, T.-K.; Dowling, P.M.; Thompson, J. Synchrotron X-ray Fluorescence Microscopy of Gallium in Bladder Tissue following Gallium Maltolate Administration during Urinary Tract Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5197–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, E.D. Iron depletion: A defense against intracellular infection and neoplasm. Life Sci. 1992, 50, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Weinberg, E.D. Iron: Mammalian defense systems, mechanisms of disease, and chelation therapy approaches. Blood Rev. 1995, 9, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Kolnagou, A.; Skiada, A.; Petrikkos, G. The Role of Iron and Chelators on Infections in Iron Overload and Non Iron Loaded Conditions: Prospects for the Design of New Antimicrobial Therapies. Hemoglobin 2010, 34, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Advances on Chelation and Chelator Metal Complexes in Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Efstathiou, A.; Ioannou-Loucaides, S.; Kolnagou, A. Chelators Controlling Metal Metabolism and Toxicity Pathways: Applications in Cancer Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment. Hemoglobin 2008, 32, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitambar, C.R. The therapeutic potential of iron-targeting gallium compounds in human disease: From basic research to clinical application. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 115, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlot, A.M.; Kalinowski, D.S.; Kovacevic, Z.; Jansson, P.J.; Sahni, S.; Huang, M.L.; Lok, H.; Richardson, D.R.; Lane, D.J.R. Exploiting Cancer Metal Metabolism using Anti-Cancer Metal-Binding Agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 302–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, E.; Nakano, K.; Nakayachi, T.; Morshed, S.R.; Hashimoto, K.; Kikuchi, H.; Nishikawa, H.; Kawase, M.; Sakagami, H. Cytotoxic activity of deferiprone, maltol and related hydroxyketones against human tumor cell lines. Anticancer Res. 2004, 24, 755–762. [Google Scholar]
- Chitambar, C.R. Gallium and its competing roles with iron in biological systems. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2016, 1863, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Xue, X.; Li, H.; Niu, Q. Role of mGluR 1 in synaptic plasticity impairment induced by maltol aluminium in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 78, 103406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, E.; Yasuda, I.; Yamada, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Ohyashiki, T. Involvement of NO generation in aluminum-induced cell death. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 1390–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowicz-Piasecka, M.; Skupień, A.; Mikiciuk-Olasik, E.; Sikora, J. Biocompatibility Studies of Gadolinium Complexes with Iminodiacetic Acid Derivatives. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 189, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parghane, R.V.; Basu, S. Bilateral Orbital Soft-Tissue Metastases from Renal Neuroendocrine Tumor: Successful Theranostic Application of 68Ga/177Lu-DOTATATE with Improvement of Vision. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2019, 47, 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imberti, C.; Adumeau, P.; Blower, J.E.; Al Salemee, F.; Torres, J.B.; Lewis, J.S.; Zeglis, B.M.; Terry, S.Y.A.; Blower, P.J. Manipu-lating the In Vivo Behaviour of 68Ga with Tris (Hydroxypyridinone) Chelators: Pretargeting and Blood Clearance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, R.J.; Mealey, K.; Cohen, N.D.; Harrington, J.R.; Chaffin, M.K.; Taylor, R.J.; Bernstein, L.R. Pharmacokinetics of gallium maltolate after intragastric administration in neonatal foals. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2007, 68, 1041–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monk, C.S.; Sweeney, R.W.; Bernstein, L.R.; Fecteau, M.E. Serum and tissue concentrations of gallium after oral ad-ministration of gallium nitrate and gallium maltolate to neonatal calves. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2016, 77, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollina, G.F.; Pepe, M.; Dean, A.; Di Marco, V.; Marton, D. Reduction in absorption of gallium maltolate in adult horses following oral administration with food: Chemistry and pharmacokinetics. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 36, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampieri, F.; Alcorn, J.; Allen, A.L.; Clark, C.R.; Vannucci, F.A.; Pusterla, N.; Mapes, S.; Ball, K.R.; Dowling, P.M.; Thompson, J.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of gallium maltolate in Lawsonia intracellularis-infected and uninfected rabbits. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 37, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaur, K.; Vázquez-Salgado, A.M.; Duran-Camacho, G.; Dominguez-Martinez, I.; Benjamín-Rivera, J.A.; Fernández-Vega, L.; Carmona Sarabia, L.; Cruz García, A.; Pérez-Deliz, F.; Méndez Román, J.A.; et al. Iron and Copper Intracellular Chelation as an Anticancer Drug Strategy. Inorganics 2018, 6, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannargudi, M.B.; Deb, S. Clinical Pharmacology and Clinical Trials of Ribonucleotide Reductase Inhibitors: Is It a Viable Cancer Therapy? J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 1499–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelander, L.; Gräslund, A. Mechanism of inhibition of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase by the iron chelate of 1-formylisoquinoline thiosemicarbazone. Destruction of the tyrosine free radical of the enzyme in an oxygen-requiring reaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 4063–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeshaguru, K.; Lally, J.M.; Piga, A.; Hoffbrand, A.V.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Cytotoxic Mechanisms of Iron Chelators. Drugs Today 1992, 28, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Lui, G.Y.; Kovacevic, Z.; Richardson, V.; Merlot, A.M.; Kalinowski, D.S.; Richardson, D.R. Targeting cancer by binding iron: Dissecting cellular signaling pathways. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 18748–18779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatt, J.; Taylor, S.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Comparison of antineuroblastoma activity of desferrioxamine with that of oral iron chelators. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 2925–2927. [Google Scholar]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Iron Mobilization from Transferrin and Non-Transferrin-Bound-Iron by Deferiprone. Implications in the Treatment of Thalassemia, Anemia of Chronic Disease, Cancer and Other Conditions. Hemoglobin 2006, 30, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, E.D. The development of awareness of the carcinogenic hazard of inhaled iron. Oncol. Res. 1999, 11, 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.Y.; Dixon, S.J. Mechanisms of ferroptosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 2195–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y. Autophagy, ferroptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis in tumor immuno-therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 196. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, G.; Zhuang, L.; Gan, B. Targeting ferroptosis as a vulnerability in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Le Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, G.; Jiang, X.; Mo, Y.; Wu, P.; Deng, X.; Li, L.; Zuo, S.; et al. Regulatory pathways and drugs associated with ferroptosis in tumors. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, L.; Gao, W.; Tang, T.-L.; Yan, M. Interaction between macrophages and ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Xu, B.; Hu, N.; Guo, Z.; Bao, W.; Shao, B.; Yang, W. Targeting the Macrophage-Ferroptosis Crosstalk: A Novel Insight into Tumor Immunotherapy. Front. Biosci. 2022, 27, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, M.; Wu, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jin, Q.; Fan, J.; Xu, X.; Gu, R.; Hao, H.; Zhang, A.; et al. Clinical Potential of Hypoxia Inducible Factors Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors in Treating Nonanemic Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 837249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, K.-H.; Chung, L.-C.; Wang, S.-W.; Feng, T.-H.; Chang, P.-L.; Juang, H.-H. Hypoxia upregulates the gene expression of mitochondrial aconitase in prostate carcinoma cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 51, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.K.; Desouki, M.M.; Franklin, R.B.; Costello, L.C. Mitochondrial aconitase and citrate metabolism in malignant and nonmalignant human prostate tissues. Mol. Cancer 2006, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, S.; Zaganjor, E.; Haigis, M.C. Mitochondria and Cancer. Cell 2016, 166, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfanou, I.-M.; Argyros, O.; Papapetropoulos, A.; Tseleni-Balafouta, S.; Vougas, K.; Tamvakopoulos, C. Discovery and Pharmacological Evaluation of STEAP4 as a Novel Target for HER2 Overexpressing Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 608201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekmarev, J.; Azad, M.G.; Richardson, D.R. The Oncogenic Signaling Disruptor, NDRG1: Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Activity. Cells 2021, 10, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Tchou-Wong, K.M.; Costa, M. Egr-1 mediates hypoxia-inducible transcription of the NDRG1 gene through an overlapping Egr-1/Sp1 binding site in the promoter. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9125–9133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, R.V.; Veeraperumal, S.; Serganova, I.S.; Kruchevsky, N.; Varshavsky, J.; Blasberg, R.G.; Ackerstaff, E.; Koutcher, J.A. Inhibition of prostate cancer proliferation by Deferiprone. NMR Biomed. 2017, 30, e3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, M.; Tóth, F.; Brindisi, M.; Sotgia, F.; Lisanti, M.P. Deferiprone (DFP) Targets Cancer Stem cell (CSC) Propagation by Inhibiting Mitochondrial Metabolism and Inducing ROS Production. Cells 2020, 9, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donfrancesco, A.; Deb, G.; Domicini, C.; Angioni, A.; Caniglia, M.; De Sio, L.; Fidani, P.; Amici, A.; Helson, L. Deferoxamine, cyclophosphamide, etoposide, carboplatin and thotepa (DCECaT): A new cytoreductive chelation-chemotherapy regimen in patients with advanced neuroblastoma. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 1992, 15, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, S.; Ross, K.N.; Lander, E.S.; Golub, T.R. A molecular signature of metastasis in primary solid tumours. Nature Genet. 2003, 33, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Piga, A.; Hoffbrand, A. Cytotoxic effects of the lipophilic iron chelator omadine. FEBS Lett. 1986, 204, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Gadde, R.; Fan, Y.; Kulkarni, N.; Shevale, N.; Bao, K.; Choi, H.S.; Betharia, S.; Kim, J. Reversal of genetic brain iron accumulation by N,N′-bis(2-mercaptoethyl)isophthalamide, a lipophilic metal chelator, in mice. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 96, 1951–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Piga, A.; Hoffbrand, A.V. Cytotoxic and DNA-inhibitory effects of iron chelators on human leukaemic cell lines. Hematol. Oncol. 1986, 4, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Deferiprone: A Forty-Year-Old Multi-Targeting Drug with Possible Activity against COVID-19 and Diseases of Similar Symptomatology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Lobbous, M.; Nabors, L.B.; Markert, J.M.; Kim, J. Undesired impact of iron supplement on MRI assessment of post-treatment glioblastoma. CNS Oncol. 2022, 11, CNS90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talboom, K.; Borstlap, W.A.A.; Roodbeen, S.X.; Bruns, E.R.J.; Buskens, C.J.; Hompes, R.; Tytgat, K.M.A.J.; Tuynman, J.B.; Consten, E.C.J.; Heuff, G.; et al. FIT collaborative group. Ferric carboxymaltose infusion versus oral iron supplementation for preoperative iron deficiency anaemia in patients with colorectal cancer (FIT): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Haematol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. How to manage iron toxicity in post-allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation? Expert Rev. Hematol. 2020, 13, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Advances in oral iron chelation in man. Int. J. Hematol. 1992, 55, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Kolnagou, A. Effective new treatments of iron overload in thalassaemia using the ICOC combination therapy protocol of deferiprone (L1) and deferoxamine and of new chelating drugs. Haematologica 2006, 91, ELT04. [Google Scholar]
- Kolnagou, A.; Economides, C.; Eracleous, E.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Long Term Comparative Studies in Thalassemia Patients Treated with Deferoxamine or a Deferoxamine/Deferiprone Combination. Identification of Effective Chelation Therapy Protocols. Hemoglobin 2008, 32, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Kolnagou, A.; Kontoghiorghe, C.N.; Mourouzidis, L.; Timoshnikov, V.A.; Polyakov, N.E. Trying to Solve the Puzzle of the Interaction of Ascorbic Acid and Iron: Redox, Chelation and Therapeutic Implications. Medicines 2020, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshnikov, V.A.; Kobzeva, T.V.; Polyakov, N.E.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Redox Interactions of Vitamin C and Iron: Inhibition of the Pro-Oxidant Activity by Deferiprone. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshnikov, V.A.; Selyutina, O.Y.; Polyakov, N.E.; Didichenko, V.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Mechanistic Insights of Chelator Complexes with Essential Transition Metals: Antioxidant/Pro-Oxidant Activity and Applications in Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinou, E.; Pashalidis, I.; Kolnagou, A.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Interactions of Hydroxycarbamide (Hydroxyurea) with Iron and Copper: Implications on Toxicity and Therapeutic Strategies. Hemoglobin 2011, 35, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voest, E.E.; Vreugdenhil, G.; Marx, J.J.M. Iron-Chelating Agents in Non-Iron Overload Conditions. Ann. Intern. Med. 1994, 120, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, K.E.; Weeks, K.; Carter, D.A. Lactoferrin Is Broadly Active against Yeasts and Highly Synergistic with Amphotericin B. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e02284-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, L.; Cutone, A.; Lepanto, M.S.; Paesano, R.; Valenti, P. Lactoferrin: A Natural Glycoprotein Involved in Iron and Inflammatory Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Chávez, S.A.; Arévalo-Gallegos, S.; Rascón-Cruz, Q. Lactoferrin: Structure, function and applications. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 33, 301.e1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, X.; Zhao, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, P.; Zang, D.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Long, H.; Yang, L.; Huang, H.; et al. Platinum pyrithione induces apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukemia cells resistant to imatinib via DUB inhibition-dependent caspase activation and Bcr-Abl downregulation. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Ni Liu, N.; Liao, Y.; Liu, N.; Cai, J.; Xia, X.; Guo, Z.; Li, Y.; Wen, Q.; Yin, Q.; et al. Platinum-containing compound platinum pyrithione suppresses ovarian tumor proliferation through proteasome inhibition. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthyala, R.; Shin, W.S.; Xie, J.; Sham, Y.Y. Discovery of 1-hydroxypyridine-2-thiones as selective histone deacetylase inhibitors and their potential application for treating leukemia. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 4320–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naves, M.A.; Graminha, A.E.; Vegas, L.C.; Luna-Dulcey, L.; Honorato, J.; Menezes, A.C.S.; Batista, A.A.; Cominetti, M.R. Transport of the Ruthenium Complex [Ru(GA)(dppe)2]PF6 into Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells Is Facilitated by Transferrin Receptors. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 1167–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Jin, H.; Zhuo, H.; Huang, H. Enhanced antitumor efficacy of cisplatin for treating ovarian cancer in vitro and in vivo via transferrin binding. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 45597–45611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Kolnagou, A. Molecular factors and mechanisms affecting iron and other metal excretion or absorption in health and disease. The role of natural and synthetic chelators. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 2695–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppner, D.G.; Hallaway, P.E.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Eaton, J.W. Antimalarial properties of orally active iron chelators. Blood 1988, 72, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldari, S.; Di Rocco, G.; Toietta, G. Current Biomedical Use of Copper Chelation Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barve, A.; Kumbhar, A.; Bhat, M.; Joshi, B.; Butcher, R.; Sonawane, U.; Joshi, R. Mixed-ligand copper (II) maltolate complexes: Synthesis, characterization, DNA binding and cleavage, and cytotoxicity. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 9120–9132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehtab, S.; Goncalves, G.; Roy, S.; Tomaz, A.I.; Santos-Silva, T.; Santos, M.F.A.; Romao, M.J.; Jakusch, T.; Kiss, T.; Pessoa, J.C. Interaction of vanadium(IV) with human serum apo-transferrin. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2013, 121, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levina, A.; Lay, P.A. Transferrin Cycle and Clinical Roles of Citrate and Ascorbate in Improved Iron Metabolism. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.G.P. The Role of Iron and Siderophores in Infection, and the Development of Siderophore Antibiotics. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, S529–S537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.R.; Bogdan, A.R.; Miyazawa, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Tsuji, Y. Siderophores in Iron Metabolism: From Mechanism to Therapy Potential. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 1077–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, Y.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Ueda, E.; Kondo, M.; Takahashi, S.; Matsukura, T.; Sakurai, H.; Hiroi, T.; Imaoka, S.; Funae, Y. Blood glucose lowering and toxicological effects of zinc (II) complexes with maltol, threonine, and picolinic acid. Res. Commun. Mol. Pathol. Pharmacol. 2002, 112, 91–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, A.S.; Edwards, J.J.E.; Fu, Y.; Spellberg, B. Deferiprone iron chelation as a novel therapy for experimental mucormycosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 1070–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, S.; Ikeda, M.; Nakamura, M.; Katoh, A.; Yan, X.; Xie, Y.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. The Effects of Bicarbonate and its Combination with Chelating Agents Used for the Removal of Depleted Uranium in Rats. Hemoglobin 2008, 32, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, S.; Ikeda, M.; Anzai, K.; Suzuki, M.; Katoh, A.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Radiation Protection by Deferiprone in Animal Models. Hemoglobin 2006, 30, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eybl, V.; Svihovcova, P.; Koutensky, J.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Interaction of L1, L1NAll and deferoxamine with gallium in vivo. Drugs Today 1992, 28, 173–175. [Google Scholar]
- Badawy, S.M.; Kattamis, A.; Ezzat, H.; Deschamps, B.; Sicard, E.; Fradette, C.; Zhao, F.; Tricta, F.; Tsang, Y.C.; Sheth, S.; et al. The safety and acceptability of twice-daily deferiprone for transfusional iron overload: A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 197, e12–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Deferiprone and Iron–Maltol: Forty Years since Their Discovery and Insights into Their Drug Design, Development, Clinical Use and Future Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4970. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054970
Kontoghiorghes GJ. Deferiprone and Iron–Maltol: Forty Years since Their Discovery and Insights into Their Drug Design, Development, Clinical Use and Future Prospects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(5):4970. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054970
Chicago/Turabian StyleKontoghiorghes, George J. 2023. "Deferiprone and Iron–Maltol: Forty Years since Their Discovery and Insights into Their Drug Design, Development, Clinical Use and Future Prospects" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 5: 4970. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054970
APA StyleKontoghiorghes, G. J. (2023). Deferiprone and Iron–Maltol: Forty Years since Their Discovery and Insights into Their Drug Design, Development, Clinical Use and Future Prospects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(5), 4970. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054970





