Properties of a Single Amino Acid Residue in the Third Transmembrane Domain Determine the Kinetics of Ambient Light-Sensitive Channelrhodopsin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
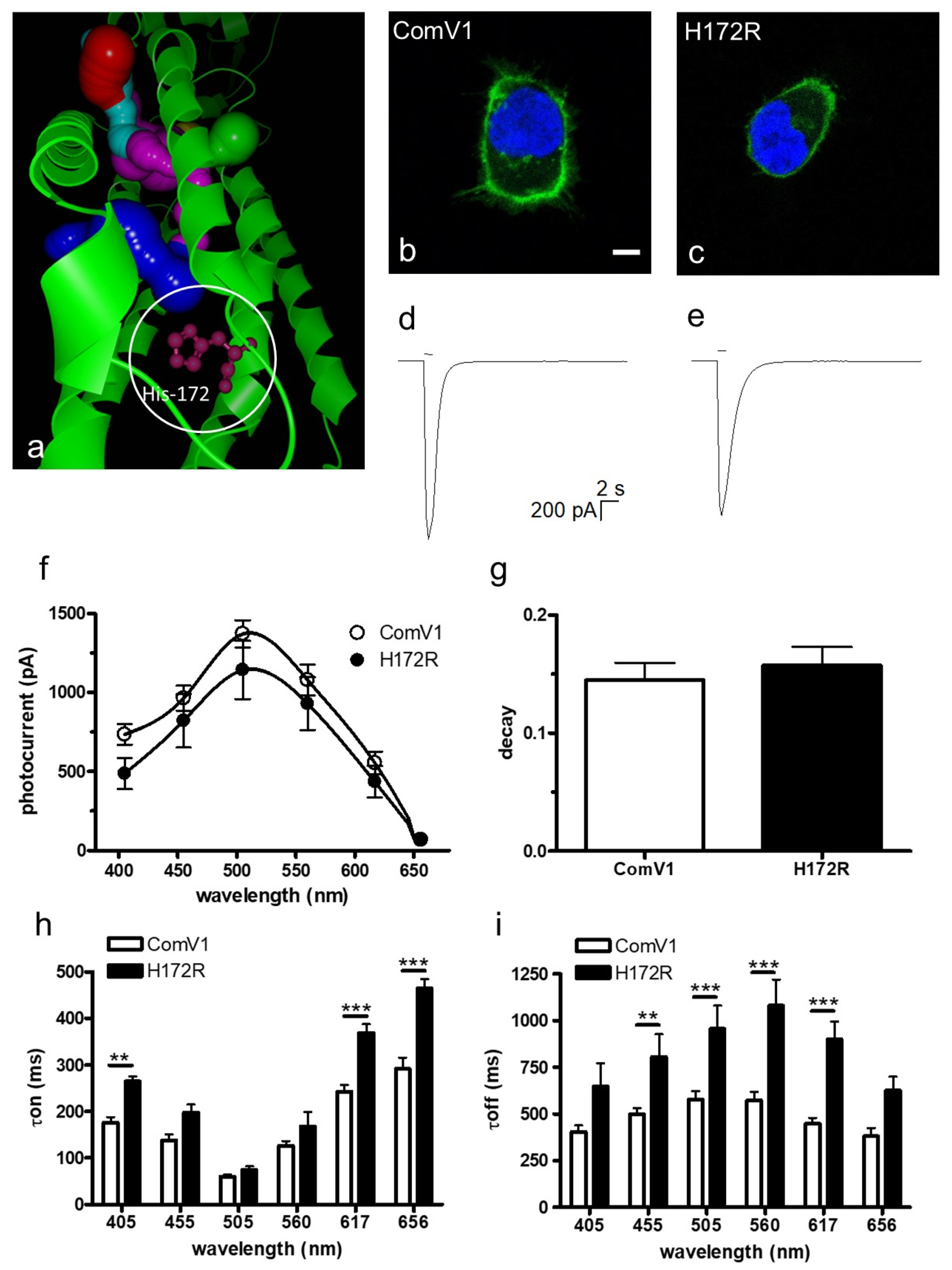
2.1. Photocurrent and Channel Kinetics of the H172R Mutant
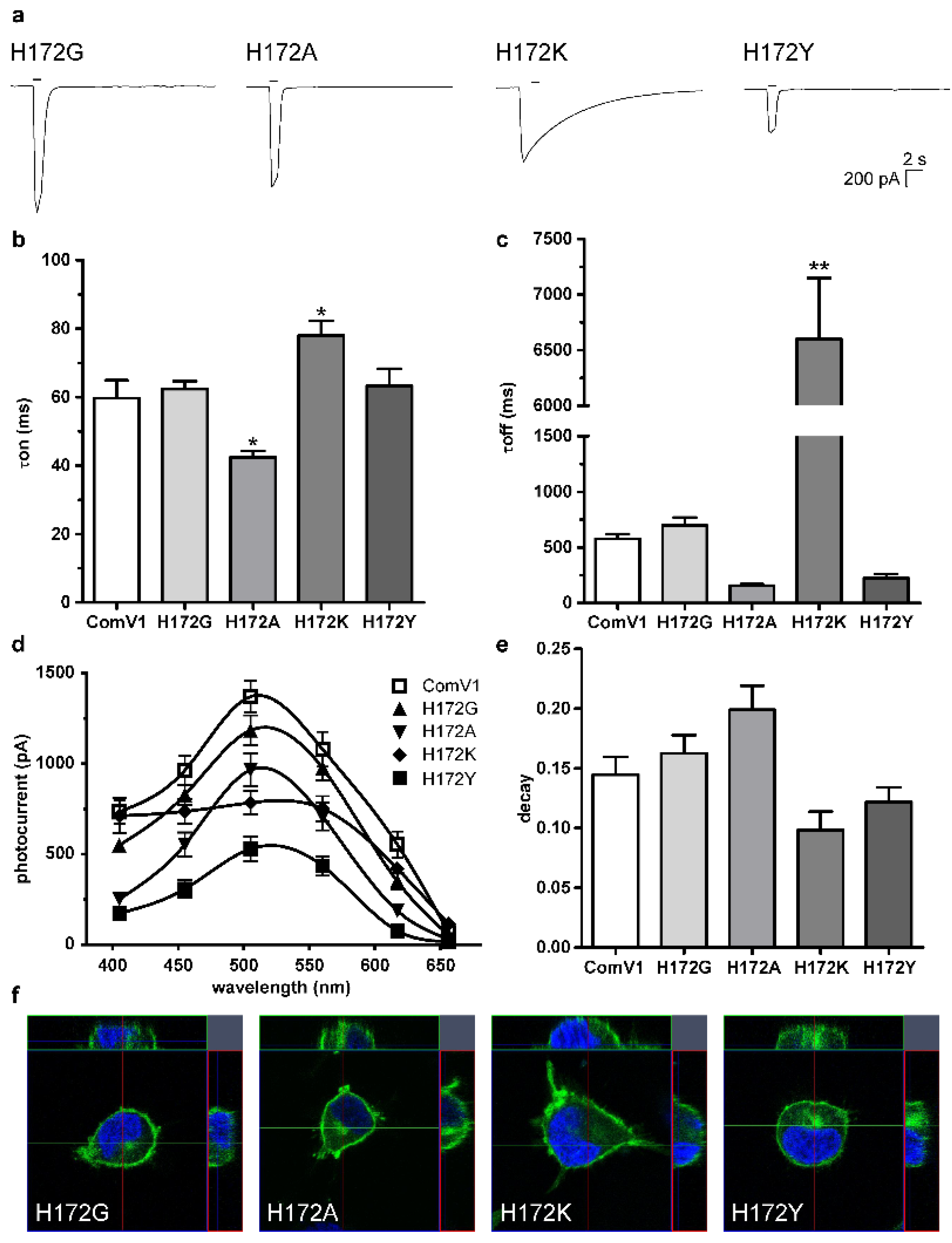
2.2. Photocurrent and Channel Kinetics of the H172 Mutant
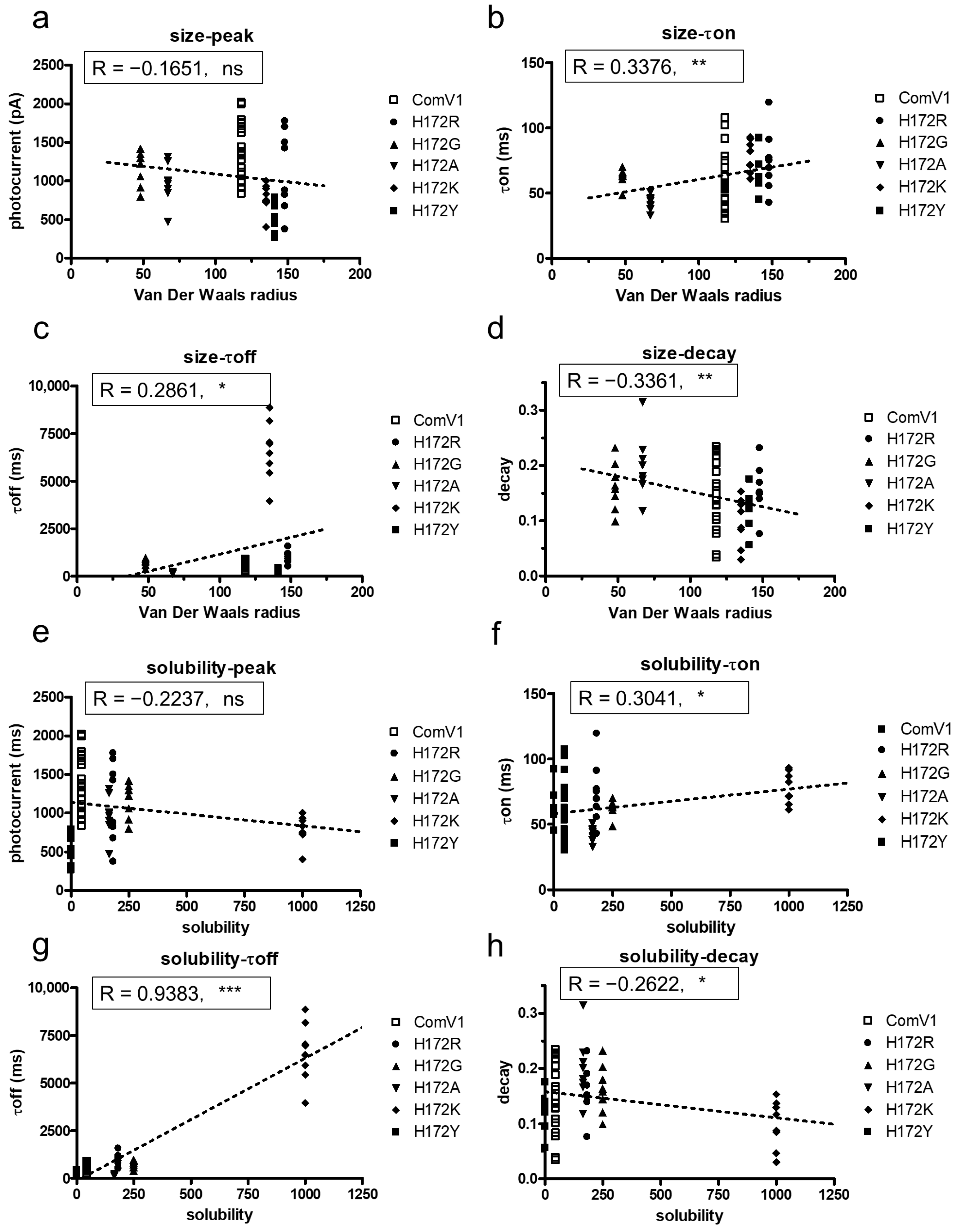
2.3. Analysis of the Correlation between Amino Acid Properties and Channel Function
2.4. Structural Analysis with Molecular Dynamic Simulation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. HEK293 Cell Preparation
4.2. Gene Transfection into HEK293 Cells
4.3. Expression Profile of Each Gene Transfected into Cells
4.4. Patch Clamp Recordings
4.5. Statistics Analysis
4.6. Molecular Dynamic Simulation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hartong, D.T.; Berson, E.L.; Dryja, T.P. Retinitis pigmentosa. Lancet 2006, 368, 1795–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, A.; Cui, J.; Ma, Y.P.; Olshevskaya, E.; Pu, M.; Dizhoor, A.M.; Pan, Z. Ectopic expression of a microbial-type rhodopsin restores visual responses in mice with photoreceptor degeneration. Neuron 2006, 50, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomita, H.; Sugano, E.; Isago, H.; Tamai, M. Channelrhodopsins provide a breakthrough insight into strategies for curing blindness. J. Genet. 2009, 88, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, H.; Sugano, E.; Yawo, H.; Ishizuka, T.; Isago, H.; Narikawa, S.; Kügler, S.; Tamai, M. Restoration of visual response in aged dystrophic RCS rats using AAV-mediated channelopsin-2 gene transfer. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 3821–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, H.; Sugano, E.; Isago, H.; Hiroi, T.; Wang, Z.; Ohta, E.; Tamai, M. Channelrhodopsin-2 gene transduced into retinal ganglion cells restores functional vision in genetically blind rats. Exp. Eye Res. 2010, 90, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, H.; Sugano, E.; Fukazawa, Y.; Isago, H.; Sugiyama, Y.; Hiroi, T.; Ishizuka, T.; Mushiake, H.; Kato, M.; Hirabayashi, M.; et al. Visual properties of transgenic rats harboring the channelrhodopsin-2 gene regulated by the thy-1.2 promoter. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanova, E.; Hwang, G.S.; Pan, Z.H.; Troilo, D. Evaluation of AAV-mediated expression of Chop2-GFP in the marmoset retina. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 5288–5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sugano, E.; Isago, H.; Wang, Z.; Murayama, N.; Tamai, M.; Tomita, H. Immune responses to adeno-associated virus type 2 encoding channelrhodopsin-2 in a genetically blind rat model for gene therapy. Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sugano, E.; Tabata, K.; Takahashi, M.; Nishiyama, F.; Shimizu, H.; Sato, M.; Tamai, M.; Tomita, H. Local and systemic responses following intravitreous injection of AAV2-encoded modified Volvox channelrhodopsin-1 in a genetically blind rat model. Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffiol, A.; Caplette, R.; Jaillard, C.; Brazhnikova, E.; Desrosiers, M.; Dubus, E.; Duhamel, L.; Macé, E.; Marre, O.; Benoit, P.; et al. A new promoter allows optogenetic vision restoration with enhanced sensitivity in macaque retina. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 2546–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabata, K.; Sugano, E.; Hatakeyama, A.; Watanabe, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Ozaki, T.; Fukuda, T.; Tomita, H. Phototoxicities caused by continuous light exposure were not induced in retinal ganglion cells transduced by an optogenetic gene. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahel, J.A.; Boulanger-Scemama, E.; Pagot, C.; Arleo, A.; Galluppi, F.; Martel, J.N.; Esposti, S.D.; Delaux, A.; de Saint Aubert, J.B.; de Montleau, C.; et al. Partial recovery of visual function in a blind patient after optogenetic therapy. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagel, G.; Ollig, D.; Fuhrmann, M.; Kateriya, S.; Musti, A.M.; Bamberg, E.; Hegemann, P. Channelrhodopsin-1: A light-gated proton channel in green algae. Science 2002, 296, 2395–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sineshchekov, O.A.; Jung, K.H.; Spudich, J.L. Two rhodopsins mediate phototaxis to low- and high-intensity light in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8689–8694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagel, G.; Szellas, T.; Huhn, W.; Kateriya, S.; Adeishvili, N.; Berthold, P.; Ollig, D.; Hegemann, P.; Bamberg, E. Channelrhodopsin-2, a directly light-gated cation-selective membrane channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13940–13945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, T.; Yamasaki, K.; Fujita, S.; Oda, K.; Iseki, M.; Yoshida, K.; Watanabe, M.; Daiyasu, H.; Toh, H.; Asamizu, E.; et al. Archaeal-type rhodopsins in Chlamydomonas: Model structure and intracellular localization. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 301, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Prigge, M.; Beyrière, F.; Tsunoda, S.P.; Mattis, J.; Yizhar, O.; Hegemann, P.; Deisseroth, K. Red-shifted optogenetic excitation: A tool for fast neural control derived from Volvox carteri. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 631–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klapoetke, N.C.; Murata, Y.; Kim, S.S.; Pulver, S.R.; Birdsey-Benson, A.; Cho, Y.K.; Morimoto, T.K.; Chuong, A.S.; Carpenter, E.J.; Tian, Z.; et al. Independent optical excitation of distinct neural populations. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Govorunova, E.G.; Sineshchekov, O.A.; Janz, R.; Liu, X.; Spudich, J.L. Neuroscience. Natural light-gated anion channels: A family of microbial rhodopsins for advanced optogenetics. Science 2015, 349, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Sugiyama, Y.; Hikima, T.; Sugano, E.; Tomita, H.; Takahashi, T.; Ishizuka, T.; Yawo, H. Molecular determinants differentiating photocurrent properties of two channelrhodopsins from chlamydomonas. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 5685–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomita, H.; Sugano, E.; Murayama, N.; Ozaki, T.; Nishiyama, F.; Tabata, K.; Takahashi, M.; Saito, T.; Tamai, M. Restoration of the majority of the visual spectrum by using modified Volvox channelrhodopsin-1. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 1434–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.Y.; Knutsen, P.M.; Muller, A.; Kleinfeld, D.; Tsien, R.Y. ReaChR: A red-shifted variant of channelrhodopsin enables deep transcranial optogenetic excitation. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berndt, A.; Schoenenberger, P.; Mattis, J.; Tye, K.M.; Deisseroth, K.; Hegemann, P.; Oertner, T.G. High-efficiency channelrhodopsins for fast neuronal stimulation at low light levels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7595–7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, Z.H.; Ganjawala, T.H.; Lu, Q.; Ivanova, E.; Zhang, Z. ChR2 mutants at L132 and T159 with improved operational light sensitivity for vision restoration. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganjawala, T.H.; Lu, Q.; Fenner, M.D.; Abrams, G.W.; Pan, Z.H. Improved CoChR variants restore visual acuity and contrast sensitivity in a mouse model of blindness under ambient light conditions. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattis, J.; Tye, K.M.; Ferenczi, E.A.; Ramakrishnan, C.; O’Shea, D.J.; Prakash, R.; Gunaydin, L.A.; Hyun, M.; Fenno, L.E.; Gradinaru, V.; et al. Principles for applying optogenetic tools derived from direct comparative analysis of microbial opsins. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, Y.; Sugano, E.; Tabata, K.; Hatakeyama, A.; Sakajiri, T.; Fukuda, T.; Ozaki, T.; Suzuki, T.; Sayama, T.; Tomita, H. Development of an optogenetic gene sensitive to daylight and its implications in vision restoration. Npj Regen. Med. 2021, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.Y.; Lin, M.Z.; Steinbach, P.; Tsien, R.Y. Characterization of engineered channelrhodopsin variants with improved properties and kinetics. Biophys. J. 2009, 96, 1803–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vierock, J.; Grimm, C.; Nitzan, N.; Hegemann, P. Molecular determinants of proton selectivity and gating in the red-light activated channelrhodopsin Chrimson. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.K.; Park, D.; Yang, A.; Chen, F.; Chuong, A.S.; Klapoetke, N.C.; Boyden, E.S. Multidimensional screening yields channelrhodopsin variants having improved photocurrent and order-of-magnitude reductions in calcium and proton currents. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 3806–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, C.; Kamiya, M.; Takemoto, M.; Ishitani, R.; Nureki, O.; Yoshida, N.; Hayashi, S. An atomistic model of a precursor state of light-induced channel opening of channelrhodopsin. Biophys. J. 2018, 115, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oda, K.; Nomura, T.; Nakane, T.; Yamashita, K.; Inoue, K.; Ito, S.; Vierock, J.; Hirata, K.; Maturana, A.D.; Katayama, K.; et al. Time-resolved serial femtosecond crystallography reveals early structural changes in channelrhodopsin. eLife 2021, 10, e62389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lórenz-Fonfría, V.A.; Bamann, C.; Resler, T.; Schlesinger, R.; Bamberg, E.; Heberle, J. Temporal evolution of helix hydration in a light-gated ion channel correlates with ion conductance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5796–E5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kato, H.E.; Kamiya, M.; Sugo, S.; Ito, J.; Taniguchi, R.; Orito, A.; Hirata, K.; Inutsuka, A.; Yamanaka, A.; Maturana, A.D.; et al. Atomistic design of microbial opsin-based blue-shifted optogenetics tools. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takemoto, M.; Kato, H.E.; Koyama, M.; Ito, J.; Kamiya, M.; Hayashi, S.; Maturana, A.D.; Deisseroth, K.; Ishitani, R.; Nureki, O. Molecular dynamics of channelrhodopsin at the early stages of channel opening. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Alexov, E. DelPhiPKa web server: Predicting pKa of proteins, RNAs and DNAs. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 614–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunovic, M.P.; Shen, W.; Lin, J.Y.; Protti, D.A.; Lisowski, L.; Gillies, M.C. Optogenetic approaches to vision restoration. Exp. Eye Res. 2019, 178, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.O.L. Retinal waves and visual system development. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1999, 22, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, Y.; Sugano, E.; Tabata, K.; Ozaki, T.; Saito, T.; Tamai, M.; Tomita, H. Kinetic profiles of photocurrents in cells expressing two types of channelrhodopsin genes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, J.; Takaki, S.; Araki, K.; Tashiro, F.; Tominaga, A.; Takatsu, K.; Yamamura, K. Expression vector system based on the chicken beta-actin promoter directs efficient production of interleukin-5. Gene 1989, 79, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.B.; Glover, C.P.J.; Cosgrave, A.S.; Bienemann, A.; Uney, J.B. Optimizing regulatable gene expression using adenoviral vectors. Exp. Physiol. 2005, 90, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
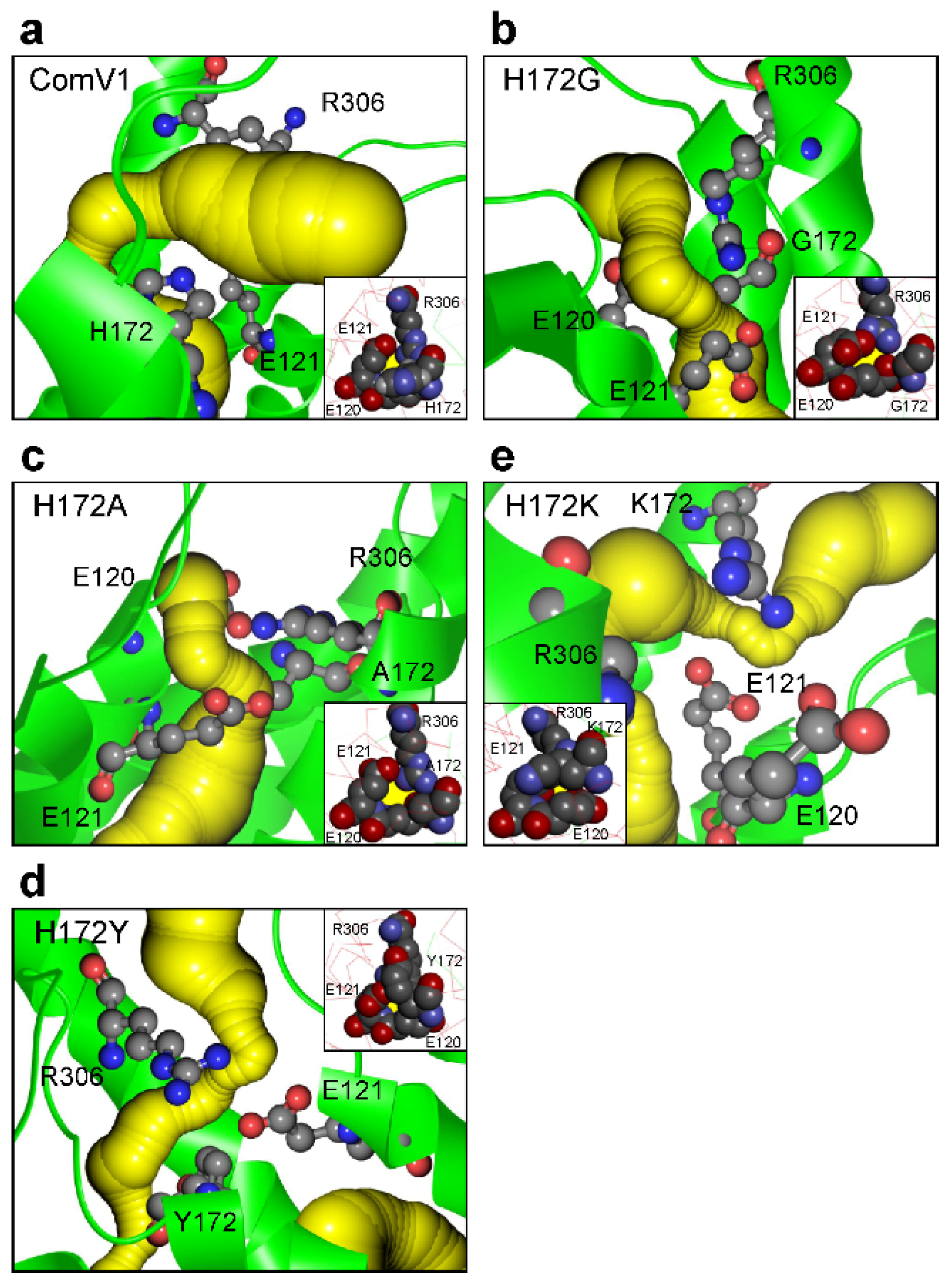
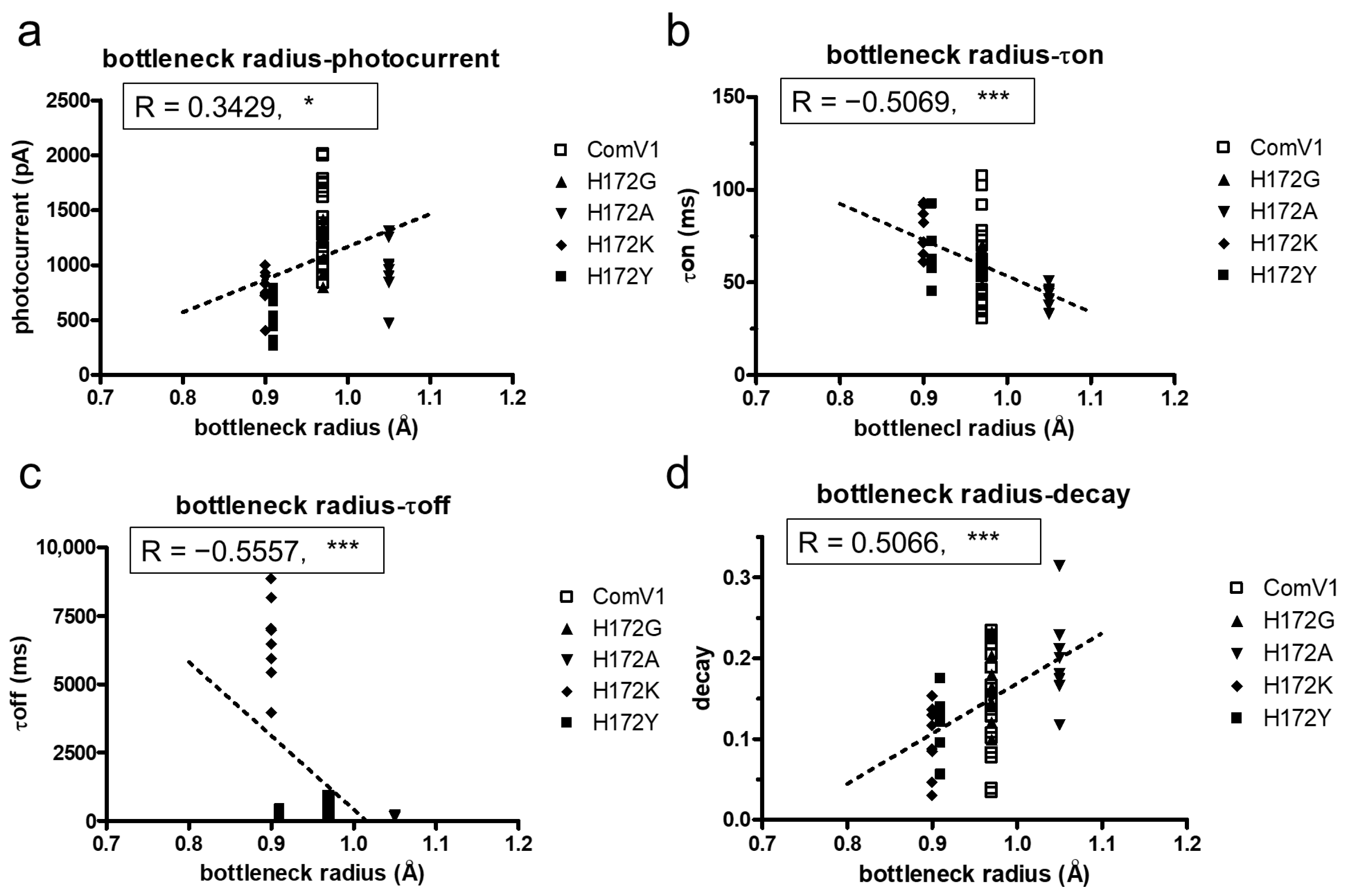
| Bottleneck Radius (Å) | Amino Acids Residue Forming Bottleneck | |
|---|---|---|
| ComV1 | 0.97 | E121, H172, R306 |
| H172G | 0.97 | E120, E121, (G172), R306 |
| H172A | 1.05 | E120, E121, A172, R306 |
| H172K | 0.90 | E120, E121, K172 |
| H172Y | 0.91 | E120, E121, Y172 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hatakeyama, A.; Sugano, E.; Sayama, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Tabata, K.; Endo, Y.; Sakajiri, T.; Fukuda, T.; Ozaki, T.; et al. Properties of a Single Amino Acid Residue in the Third Transmembrane Domain Determine the Kinetics of Ambient Light-Sensitive Channelrhodopsin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24055054
Hatakeyama A, Sugano E, Sayama T, Watanabe Y, Suzuki T, Tabata K, Endo Y, Sakajiri T, Fukuda T, Ozaki T, et al. Properties of a Single Amino Acid Residue in the Third Transmembrane Domain Determine the Kinetics of Ambient Light-Sensitive Channelrhodopsin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(5):5054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24055054
Chicago/Turabian StyleHatakeyama, Akito, Eriko Sugano, Tatsuki Sayama, Yoshito Watanabe, Tomoya Suzuki, Kitako Tabata, Yuka Endo, Tetsuya Sakajiri, Tomokazu Fukuda, Taku Ozaki, and et al. 2023. "Properties of a Single Amino Acid Residue in the Third Transmembrane Domain Determine the Kinetics of Ambient Light-Sensitive Channelrhodopsin" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 5: 5054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24055054
APA StyleHatakeyama, A., Sugano, E., Sayama, T., Watanabe, Y., Suzuki, T., Tabata, K., Endo, Y., Sakajiri, T., Fukuda, T., Ozaki, T., & Tomita, H. (2023). Properties of a Single Amino Acid Residue in the Third Transmembrane Domain Determine the Kinetics of Ambient Light-Sensitive Channelrhodopsin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(5), 5054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24055054







